Effects of Cinnamomum bodinieri Addition in Culture Substrate on Growth and Physiochemical Characteristics of Antrodia cinnamomea
-
摘要:目的 明确添加猴樟Cinnamomum bodinieri基质对牛樟芝Antrodia cinnamomea生长及生理生化特性的影响,并筛选出适宜的猴樟茎、叶浓度。方法 比较分析在牛樟芝基础培养基中添加质量浓度分别为0.125 、0.25、0.5、1 、2 、4、8 、16、32 、64 g·L−1的猴樟嫩枝、嫩叶、枝叶混合物时,牛樟芝的生长特性、生物量、SOD活性和总三萜(TT)含量的差异。结果 在PDA培养基中添加质量浓度分别为0.5~4 g·L−1、2~8 g·L−1、1~4 g·L−1、4~16 g·L−1的猴樟嫩枝基质,牛樟芝相应表现出生长特性较优、生物量、SOD活性和TT含量较高的优势,并显著高于对照水平;在PDA培养基中添加猴樟嫩叶基质质量浓度为1~2 g·L−1时,其生长特性较优,SOD活性较高,当添加量为2~4 g·L−1时,其生物量和TT含量较高;在PDA培养基中添加猴樟枝叶混合物基质质量浓度分别为2~4 g·L−1、1~4 g·L−1、0.125~1 g·L−1、4~8 g·L−1时,其相应表现为生长特性较优、生物量、SOD活性和TT含量较高的优势。结论 研究结果表明,总体来说,在PDA培养基中添加猴樟基质均能促进牛樟芝菌丝体、生物量、SOD活性和总三萜含量的提高,其中猴樟嫩叶基质2 g·L−1对菌丝体和生物量的提高最显著、猴樟嫩枝1 g·L−1或嫩叶基质2 g·L−1对菌丝体SOD活性的促进效果最显著;猴樟嫩枝基质8 g·L−1,对菌丝体总三萜含量的促进效果最显著,达到23.73 mg·g−1,较对照组提高了81.77%。该结果是樟属植物对牛樟芝培养的补充,为牛樟芝的规模化生产和开发利用提供了理论依据。Abstract:Objective Effects and optimal amounts of branches and/or leaves of Cinnamomum bodinieri added in culture substrate on the growth and physiochemical characteristics of Antrodia cinnamomea were determined.Method The growth characteristics, biomass, SOD activity and total triterpenes (TT) content of A. cinnamomea were compared and analyzed when the young branches, leaves, both branches and leaves of C. bodinieri was added with mass concentration of 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64 g·L−1 in PDA medium.Result When various concentrations of C. bodinieri young branches 0.5–4 g·L−1, 2–8 g·L−1, 1–4 g·L−1and 4–16 g·L−1 were added to the PDA medium, the growth, biomass, SOD activity, and TT content of A. cinnamomea were significantly higher than those of control without the addition. With 1–2 g·L−1 added leaves in the substrate, A. cinnamomea grew well with an increased SOD activity; while at 2–4 g·L−1, raised biomass and TT content. By adding both branches and leaves at 2–4 g·L−1, 1–4 g·L−1, 0.125–1 g·L−1 and 4–8 g·L−1, the mushroom growth could be improved with increases on biomass, SOD activity, and TT content.Conclusion The results showed that, in general, the mycelium, biomass, SOD activity and total triterpene content of A.cinnammomea were increased by adding C. bodinieri in PDA mediu. Among them, 2 g·L−1 C. bodinieri young leaves significantly increased mycelium and biomassm. C.bodinieri young branches 1 g·L−1or leaves 2 g·L−1, the promotion effect of SOD activity in mycelium was the most significant. The 8 g·L−1 branches of C. bodinieri had the most significant promoting effect on the total triterpenoid content of mycelium, reaching 23.73 mg·g−1, which was increased by 81.77% compared with the control group. This result is a supplement to the culture of A. cinnammomea , and provided a theoretical basis for the large-scale production, development and utilization of A. cinnammomea.
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】牛樟芝(Antrodia cinnamomea)是一种珍稀食药两用真菌,隶属多孔菌科(Polyporaceae)、薄孔菌属(Antrodia)[1]。牛樟芝子实体的颜色一般为橘黄色且没有菌柄、没有固定的形状。牛樟芝有两种不同形态的菌丝体:营养菌丝和骨架菌丝[2]。牛樟芝的菌丝体及子实体均含有大量对人体有益的生物活性成分,包括三萜类化合物、多糖、脱氧腺苷、超氧化物歧化酶、马来酸和琥珀酸衍生物等[3-6],且其子实体中的三萜类化合物含量远高于灵芝[7],极具食用价值。此外,牛樟芝能预防和治疗多种疾病,如保肝、抗氧化、消炎、抗肿瘤、免疫调节等作用,尤其对肝癌、肺癌、乳腺癌、胰腺癌等有特效[8-13],对人类的健康大有增益,因此被称为“森林红宝石”[14-15]。牛樟芝经济价值高,市场前景广阔,已开发了许多价格昂贵且备受欢迎的胶囊、粉剂、颗粒类型的牛樟芝保健产品[16-17]。但是,由于牛樟芝专性腐生于台湾特有保育树种——牛樟(Cinnamomum kanehirai)中空腐朽的心材内壁或枯死倒伏木阴暗潮湿的表面[18],导致牛樟芝供不应求,有价无市。牛樟生长缓慢,数量稀少,牛樟芝专性腐生的生物学特性等因素成为遏制牛樟芝产业发展的主要因素。为了解决这一难题,课题组前期采用多种云南乡土樟属树种为基质进行了牛樟芝的接种培养,发现猴樟(Cinnamomum bodinieri)可以作为牛樟芝培养的适宜替代菌材,有望培养出活性成分多、含量高的牛樟芝。【前人研究进展】在实现牛樟芝活体培养的基础上,科研人员进行了大量的科研工作,李晶等[19]发现以不同菌草作为培养基质时,香茅草浸出液不仅能够促进菌丝体的生长还能促进三萜含量的积累;张知晓等[20]通过添加外源茉莉酸甲酯的同时添加氯化钙可以显著增加牛樟芝的生物量和总三萜含量;谢春芹等[21]优化牛樟芝液体培养基,菌丝体生长良好且鲜重达到每100 mL中14.58 g;赵能等[22-23]研究使用不同碳氮源优化培养基,果糖含量在4%以内,菌丝体生长的各指标与果糖浓度呈正相关。【本研究切入点】云南发展牛樟芝具备得天独厚的生物资源和自然条件优势。云南樟科植物极为丰富,其中樟属植物有27种,居全国各省区之首,云南是樟属尤其是樟组的起源中心[24-25],探寻、选育牛樟芝的替代菌材具有极大的可行性。猴樟同为樟属植物,为中国特有种,香味浓郁,所富含化学成分与牛樟有很大的相似性。而有关猴樟对牛樟芝生长及生理生化特性的影响的研究有待深入探讨。【拟解决的关键问题】通过在牛樟芝基础培养基中添加不同浓度的猴樟嫩枝、嫩叶、枝叶混合物基质,筛选出最适的猴樟枝、叶浓度,旨在为牛樟芝的人工培养条件优化及规模化生产推广提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
1.1.1 供试菌株和植物材料
牛樟芝菌株(AC001)由福建省林业科技试验中心惠赠,现保藏于西南林业大学云南省森林灾害预警与控制重点实验室。猴樟(Cinnamomum bodinieri Levl.)基质选择云南珍樟生物科技有限公司的普洱市倚象镇樟树培育示范基地栽种的猴樟1年生实生苗,引种至西南林业大学温室大棚培育管理,待苗龄达4年生时,选取其当年生枝、叶作为培养基质添加物。
1.1.2 试剂药品
磷酸二氢钠、磷酸二氢钾、硫酸镁(天津市风船化学试剂科技有限公司);葡萄糖(天津市北辰方正试剂厂);酵母粉[盛世中方(北京)生物科技有限公司];核黄素、氮蓝四唑、甲硫氨酸、VB1(Biotopped公司);琼脂(Biosharp公司);香草醛(天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司);乙二胺四乙酸二钠、冰醋酸(西陇科学股份有限公司);高氯酸(成都市科隆化学品有限公司);磷酸氢二钠(天津市大茂化学试剂厂);乙酸乙酯(天津市恒兴化学试剂制造有限公司)。
1.1.3 培养基
基础培养基(PDA):马铃薯200 g·L−1(煮汁)、葡萄糖20 g·L−1、硫酸镁0.5 g·L−1、酵母粉5 g·L−1、磷酸二氢钾1 g·L−1、VB1 0.1 g·L−1、琼脂16 g·L−1,pH自然。以PDA培养基为对照,并添加不同浓度的猴樟嫩枝、嫩叶基质,灭菌冷却后定容备用。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 猴樟基质配制
在西南林业大学云南省森林灾害预警与控制重点实验室,将4年生猴樟当年新鲜嫩枝、嫩叶分别称取100 g,以自来水作为溶剂,分别按照质量体积比m (100 g)∶V (50 mL)=2∶1的比例制成匀浆基质备用。在基础培养基上分别将枝、叶、枝叶混合物[质量比m (枝32 g)∶m (叶32 g)=1∶1]基质加入500 mL锥形瓶中并定容至250 mL,分别配制成0.125 、0.25、0.5、1 、2 、4、8 、16、32 、64 g·L−1共10种添加浓度的培养基,混匀后封口,高压蒸汽121 ℃灭菌30 min。待培养基冷却至75 ℃,在超净工作台内分装至各平皿中,冷却凝固后供接种用。
1.2.2 牛樟芝培养
用打孔器在已经完成活化的平板上均匀打孔,分别将每块牛樟芝菌种接种到各处理的不同培养基中央,在28 ℃下恒温暗培养30 d[23],期间每隔5 d观察记录其生长指标,主要包括菌落直径、颜色、菌丝密度、菌落长势、生长速度、生长指数。
1.2.3 牛樟芝生物量测定
刮取在培养基上形成的菌丝层,测量菌丝的重量。将菌丝体在60 ℃下干燥到恒重后称量。
1.2.4 总三萜含量(TT)的测定
在不同培养基条件下经过30 d的培养,采用香草醛-冰醋酸显色反应分光光度法测定牛樟芝菌丝体的总三萜(TT)含量[26]。
1.2.5 牛樟芝超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性测定
采用氮蓝四唑光化还原法测定牛樟芝菌丝体的SOD活性。称取0.5 g牛樟芝菌丝体样品,加入预冷的2 mL磷酸缓冲液、适量碳酸钙和二氧化硅研磨后立即置于冰上,向匀浆中加入适量磷酸缓冲液进一步研磨,于10 mL容量瓶中定容,吸取2 mL于离心管中离心(4 ℃、10000 r ·min−1、15 min),上清液即为SOD提取液。在各个对照管中加入相应试剂,每组3次重复。遮光对照管置于暗处,其他各管置于光照箱内(4000 lx,20 min),反应结束,避光终止反应,以遮光对照管为空白,于560 nm测定吸光值,计算SOD活性。
1.2.6 数据分析
采用SPSS 26软件进行数据整理分析,各组数据以平均值±标准差的形式表示,采用ANOVA和多重比较法进行方差分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 添加猴樟基质对牛樟芝生长特性的影响
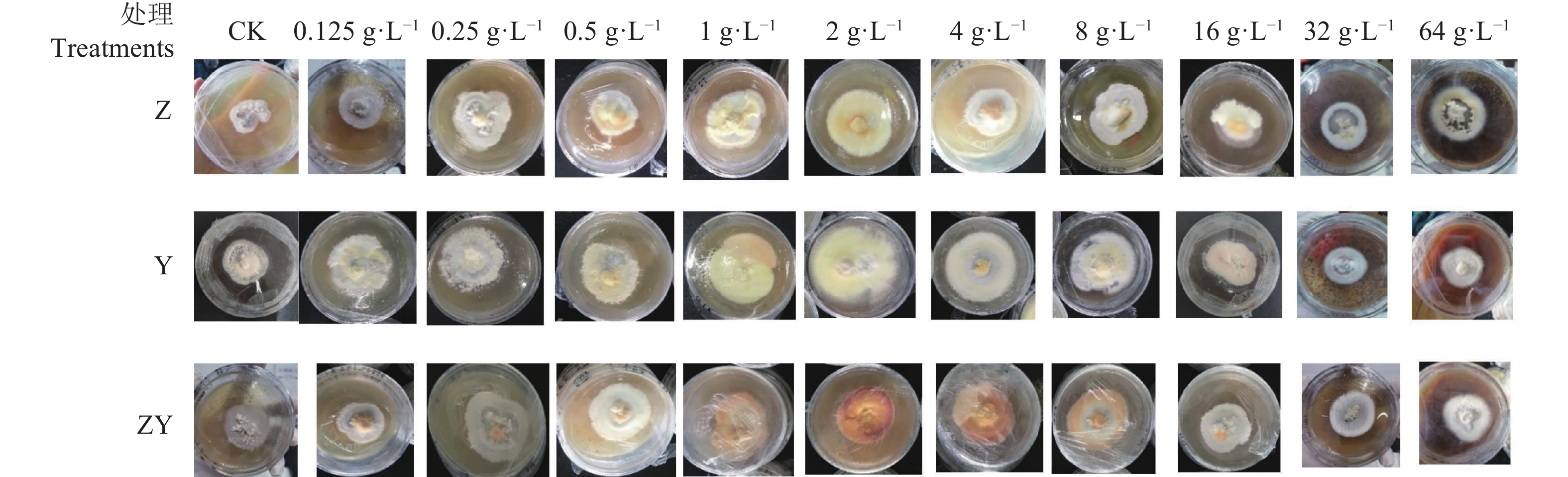
以PDA培养基上生长的牛樟芝菌丝体作为对照,分析猴樟基质枝、叶、枝叶混合添加物0.125、0.25、0.5、1、2、4、8、16、32 、64 g·L−1 质量浓度对牛樟芝生长特性的影响。结果发现,经过30 d的培养,在猴樟基质培养基上培养的牛樟芝菌丝体直径明显大于PDA培养基,且不同浓度的促进效果不同,中低浓度处理能够显著促进菌丝体的生长,但随着基质添加浓度的增加,其促进效果逐渐减弱。此外,在猴樟枝、叶基质添加物上生长的牛樟芝菌落颜色较淡,而在枝叶混合基质上生长的菌落颜色更加鲜艳,其中2 g·L−1添加量下的菌落颜色最优。在猴樟枝基质添加质量浓度32 、64 g·L−1上生长的牛樟芝菌落中心接种区出现轻微程度的老化,而在叶、枝叶混合基质上生长的牛樟芝菌落中心接种区未出现老化现象(图1)。
2.1.1 添加猴樟嫩枝基质对牛樟芝生长特性的影响
添加猴樟嫩枝基质对牛樟芝生长特性的影响结果如表1所示。不同浓度猴樟嫩枝基质添加处理与对照(PDA-0)培养条件下的牛樟芝生长特性具有显著差异(P<0.05)。基于菌落直径、菌落长势、菌落生长速度和生长指数等生长指标来看,与PDA-0相比,在中低浓度各处理中随着浓度升高,牛樟芝的生长特性表现出明显的提高,Z-0.5~Z-4处理显著促进了牛樟芝菌丝体的生长,其中Z-2处理(嫩枝2 g·L−1)的促进效果最好。然而,高浓度处理(Z-16~Z-64)条件下牛樟芝的生长指标均有不同程度的降低。
表 1 添加猴樟嫩枝基质对牛樟芝生长特性的影响Table 1. Effect of C. bodinieri branches addition in culture substrate on growth of A. cinnamomea处理
Treatments菌落直径
Colony diameter/mm菌落颜色
Colony color菌丝密度
Colony density菌落长势
Growth tendency生长速度
Growth speed/(mm·d−1)生长指数
Growth indexPDA-0 34.08±9.82 f ☆ ++ 1.5 1.14±0.33 e 1.71±0.50 f Z-0.125 47.20±6.50 d ☆ ++ 1.5 1.58±0.22 d 2.37±0.33 e Z-0.25 51.93±8.20 cd ☆☆ +++ 2.5 1.73±0.27 cd 4.33±0.68 d Z-0.5 58.60±8.56 ab ☆☆☆ +++ 3 1.95±0.29 bc 5.85±0.87 ab Z-1 59.88±10.58 ab ☆☆☆ +++ 3 1.90±0.35 bc 5.70±1.05 ab Z-2 62.36±10.33 a ☆☆☆ +++ 3 2.00±0.34 ab 6.24±1.02 a Z-4 55.30±7.69 bc ☆☆ +++ 2.5 1.84±0.26 bc 4.60±0.65 bc Z-8 51.92±7.00 cd ☆☆ +++ 2.5 1.73±0.23 cd 4.33±0.58 d Z-16 49.71±9.65 d ☆☆ +++ 2.5 1.99±0.32 b 4.98±0.8 b Z-32 39.93±5.23 e ☆☆ ++ 2 2.00±0.17 b 4.00±0.34 d Z-64 38.50±5.16 ef ☆☆ ++ 2 2.28±0.17 a 4.56±0.34 cd ① “+”越多,密度越高;“☆”越多,颜色越深;菌落长势评级数值越高,长势越好。菌落长势的评级标准= (菌丝密度×菌落颜色)/2[22] 。② 表中不同小写字母表示在0.05水平差异显著;③ Z:猴樟嫩枝;Y:猴樟嫩叶;ZY:猴樟嫩枝叶混合;基质代号后的数值为添加量 (g·L−1)。下同。
① More "+" indicates greater density; more "☆", darker color; and higher colony growth rating, better colony growth. Rating standard of colony growth = (mycelium density × colony color) /2[22].② Data with different lowercase letters on same column indicate significant differences at 0.05 level. ③ Z: C. bodinieri branches; Y: C. bodinieri leaves; ZY: C. bodinieri both branches and leaves. Numbers in the treatment name were addition amount of C.bodinieri branches(g·L-1). Same for below.2.1.2 添加猴樟嫩叶基质对牛樟芝生长特性的影响
添加猴樟嫩叶基质对牛樟芝生长特性的影响结果如表2所示。不同浓度猴樟嫩叶基质添加处理与对照(PDA-0)培养条件下的牛樟芝生长特性具有显著差异(P<0.05)。基于菌落直径、菌落长势、菌落生长速度和生长指数等生长指标来看,与PDA-0相比,在中低浓度各处理中随着浓度升高,牛樟芝的生长特性表现出明显的提高,Y-1~Y-4处理显著促进了牛樟芝菌丝体的生长,其中Y-1处理(嫩叶1 g·L−1)的促进效果最好。然而,高浓度处理(Y-8~Y-64)条件下牛樟芝的生长指标均有不同程度的降低。
表 2 添加猴樟嫩叶基质对牛樟芝生长特性的影响Table 2. Effect of C. bodinieri leaves addition in culture substrate on growth of A. cinnamomea处理
Treatments菌落直径
Colony diameter/mm菌落颜色
Colony color菌丝密度
Colony density菌落长势
Growth tendency菌落生长速度
Growth speed/(mm·d−1)生长指数
Growth IndexPDA-0 34.08±9.82 e ☆ ++ 1.5 1.14±0.33 b 1.71±0.59 g Y-0.125 53.75±0.75 cd ☆☆ ++ 2 1.79±0.02 ab 3.58±0.04 f Y-0.25 54.17±6.18 cd ☆☆ ++ 2 2.14±0.54 ab 4.28±1.08 de Y-0.5 58.70±9.08 c ☆☆ ++ 2 1.96±0.30 ab 3.92±0.60 ef Y-1 71.19±6.96 b ☆☆☆ +++++ 4 2.37±0.23 a 9.49±0.92 a Y-2 86.60±4.28 a ☆☆☆ ++++ 3.5 2.65±0.14 a 9.28±0.49 a Y-4 69.44±8.49 b ☆☆ +++ 2.5 2.11±0.28 ab 5.28±0.70c Y-8 56.50±6.35 c ☆☆ +++ 2.5 2.55±0.21 a 6.38±0.53 b Y-16 52.25±7.49 cd ☆☆ +++ 2.5 2.41±0.25 ab 6.03±0.63 b Y-32 42.42±8.82 de ☆☆ ++ 2 2.41±0.29 ab 4.82±0.48 cd Y-64 35.50±8.89 e ☆☆ ++ 2 2.52±0.30 ab 5.04±0.60 c 2.1.3 添加猴樟枝叶混合物基质对牛樟芝生长特性的影响
添加猴樟嫩枝叶混合基质对牛樟芝生长特性的影响结果如表3所示。不同浓度猴樟嫩枝叶混合基质添加处理与对照(PDA-0)培养条件下的牛樟芝生长特性具有显著差异(P<0.05)。基于菌落直径、菌落长势、菌落生长速度和生长指数等生长指标来看,与(PDA-0)相比,在中低浓度各处理中随着浓度升高,牛樟芝的生长特性表现出明显的提高,ZY-0.5~ZY-4处理显著促进了牛樟芝菌丝体的生长,其中ZY-2处理(嫩枝叶混合2 g·L−1)的促进效果最好。然而,高浓度处理(ZY-8~ZY-64)条件下牛樟芝的生长指标均有不同程度的降低。
表 3 添加猴樟枝叶混合物基质对牛樟芝生长特性的影响Table 3. Effect of adding mixture of C. bodinieri branches and leaves in culture substrate on growth of A. cinnamomea处理
Treatments菌落直径
Colony diameter/mm菌落颜色
Colony color菌丝密度
Colony density菌落长势
Growth tendency菌落生长速度
Growth speed/(mm·d−1)生长指数
Growth indexPDA-0 34.08±4.82 d ☆ ++ 1.5 1.14±0.33 c 1.71±0.50 e ZY-0.125 47.86±5.67 abcd ☆☆ ++ 2 1.93±0.36 ab 4.83±0.90 bc ZY-0.25 52.42±6.30 abc ☆☆ ++ 2 1.75±0.21 ab 4.37±0.53 cd ZY-0.5 55.57±1.95 abc ☆☆ +++ 2.5 1.69±0.07 b 5.06±0.21 b ZY-1 57.21±3.75 ab ☆☆☆ ++ 2.5 1.91±0.12 ab 4.78±0.30 bcd ZY-2 61.06±7.80 a ☆☆☆☆☆ ++++ 4.5 2.04±0.26 ab 6.12±0.78 a ZY-4 61.94±5.10 a ☆☆☆☆ ++++ 4 2.06±0.17 a 6.19±0.51 a ZY-8 54.63±8.84 abc ☆☆☆ +++ 3 1.82±0.29 ab 4.55±0.73 cd ZY-16 48.17±7.94 abcd ☆☆ +++ 2.5 1.94±0.29 ab 4.85±073 bc ZY-32 43.10±5.62 bcd ☆☆ ++ 2 2.44±0.19 ab 4.88±0.38 bc ZY-64 42.25±10.08 cd ☆☆ ++ 2 2.08±0.34 a 4.16±0.68 d 2.1.4 添加猴樟基质对牛樟芝生物量的影响
添加猴樟基质对牛樟芝生物量的影响结果如表4所示。不同浓度猴樟嫩枝基质添加处理与对照(PDA-0)培养条件下的牛樟芝生物量具有显著差异(P<0.05)。与PDA-0相比,在中低浓度各处理中随着浓度升高,牛樟芝菌丝体生物量表现出明显的提高,Z-2~Z-8处理显著提高了牛樟芝菌丝体生物量,其中Z-2处理(嫩枝2 g·L−1)的促进效果最好。然而,高浓度处理(Z-16~Z-64)条件下牛樟芝菌丝体生物量均有不同程度的降低。不同浓度猴樟嫩叶基质添加处理与对照(PDA-0)培养条件下的牛樟芝生物量具有显著差异(P<0.05)。与PDA-0相比,在中低浓度各处理中随着浓度升高,牛樟芝菌丝体生物量表现出明显的提高,Y-2~Y-8处理显著提高了牛樟芝菌丝体生物量,其中Y-2处理(嫩叶2 g·L−1)的促进效果最好。然而,高浓度处理(Y-16~Y-64)条件下牛樟芝菌丝体生物量均有不同程度的降低。不同浓度猴樟嫩枝叶混合基质添加处理与对照(PDA-0)培养条件下的牛樟芝生物量具有显著差异(P<0.05)。与PDA-0相比,在中低浓度各处理中随着浓度升高,牛樟芝菌丝体生物量表现出明显的提高,ZY-0.5~ZY-32处理显著提高了牛樟芝菌丝体生物量,其中ZY-1处理(枝叶混合1 g·L−1)的促进效果最好。然而,高浓度处理条件下牛樟芝菌丝体生物量均有不同程度的降低。
表 4 添加猴樟基质对牛樟芝生物量的影响Table 4. Effect of C. bodinieri addition in culture substrate on biomass of A. cinnamomea处理
Treatments干重
Dry weight/g处理
Treatments干重
Dry weight/g处理
Treatments干重
Dry weight/gPDA-0 0.06±0.01 d PDA-0 0.06±0.01 d PDA-0 0.06±0.01 e Z-0.125 0.07±0.02 cd Y-0.125 0.07±0.02 d ZY-0.125 0.09±0.01 de Z-0.25 0.09±0.01 bcd Y-0.25 0.07±0.03 d ZY-0.25 0.11±0.02 bcde Z-0.5 0.11±0.02 bcd Y-0.5 0.09±0.03 cd ZY-0.5 0.16±0.05 abcd Z-1 0.12±0.03 bcd Y-1 0.14±0.02 bcd ZY-1 0.20±0.02 a Z-2 0.19±0.03 a Y-2 0.24±0.07 a ZY-2 0.19±0.05 ab Z-4 0.15±0.06 ab Y-4 0.20±0.05 ab ZY-4 0.17±0.04 abc Z-8 0.13±0.03 abc Y-8 0.18±0.04 abc ZY-8 0.16±0.04 abcd Z-16 0.12±0.02 bcd Y-16 0.13±0.06 bcd ZY-16 0.16±0.04 abcd Z-32 0.09±0.02 bcd Y-32 0.11±0.05 bcd ZY-32 0.14±0.03 abcd Z-64 0.09±0.02 bcd Y-64 0.10±0.02 bcd ZY-64 0.10±0.02 cde 2.2 添加猴樟基质对牛樟芝超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性的影响
2.2.1 添加猴樟嫩枝基质对牛樟芝SOD活性的影响
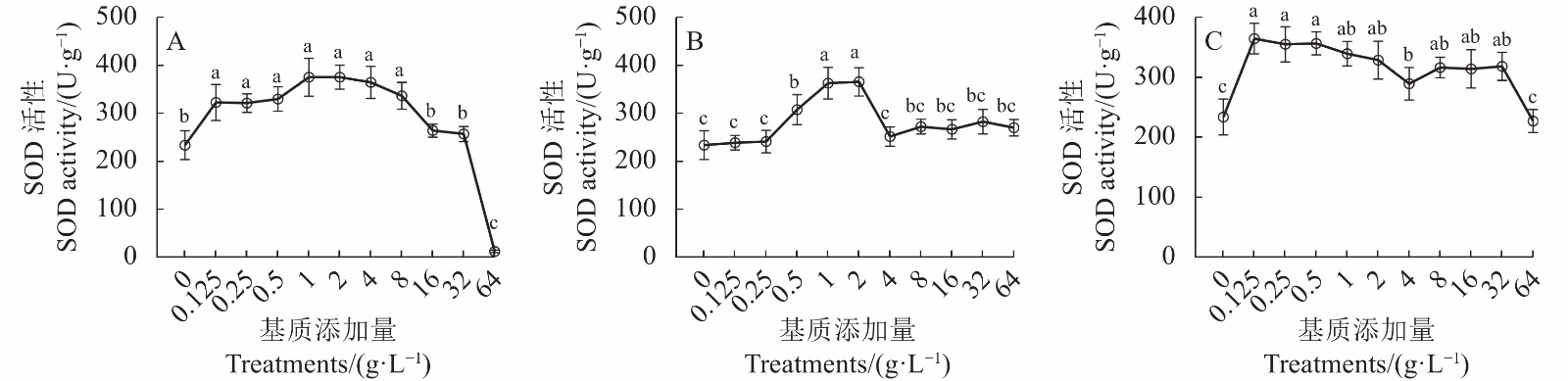
添加猴樟嫩枝基质对牛樟芝生长特性的影响结果如图2-A所示。不同浓度猴樟嫩枝基质添加处理与对照(PDA-0)培养条件下的牛樟芝SOD活性具有显著差异(P<0.05)。与PDA-0相比,在中低浓度各处理中随着浓度升高,牛樟芝中SOD活性表现出明显的提高,Z-0.125~Z-8处理显著提高了牛樟芝菌丝体中SOD的活性,其中Z-1、Z-2处理(嫩枝1 g·L−1、2 g·L−1)的促进效果最好。然而,高浓度处理(Z-16~Z-64)条件下牛樟芝中SOD的活性均有不同程度的降低,64 g·L−1时处于抑制状态。
![]() 图 2 添加猴樟基质对牛樟芝SOD活性的影响A:猴樟嫩枝基质;B:猴樟嫩叶基质;C:猴樟枝叶混合基质。小写字母表示在0.05水平差异显著,下同。Figure 2. Effect of C. bodinieri addition in culture substrate on SOD activity of A. cinnamomeaA: C. bodinieri branches; B: C. bodinieri leaves; C: both branches and leaves of C. bodinieri. Data with different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at 0.05 level. Same for Fig.3.
图 2 添加猴樟基质对牛樟芝SOD活性的影响A:猴樟嫩枝基质;B:猴樟嫩叶基质;C:猴樟枝叶混合基质。小写字母表示在0.05水平差异显著,下同。Figure 2. Effect of C. bodinieri addition in culture substrate on SOD activity of A. cinnamomeaA: C. bodinieri branches; B: C. bodinieri leaves; C: both branches and leaves of C. bodinieri. Data with different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at 0.05 level. Same for Fig.3.2.2.2 添加猴樟嫩叶基质对牛樟芝SOD活性的影响
猴樟嫩叶基质添加对牛樟芝SOD活性的影响结果如图2 -B所示。不同浓度猴樟嫩叶基质添加处理与对照(PDA-0)培养条件下的牛樟芝SOD活性具有显著差异(P<0.05)。与PDA-0相比,在中低浓度各处理中随着浓度升高,牛樟芝中SOD的活性表现出明显的提高,Y-0.5~Y-2处理显著促进了牛樟芝中SOD活性的提高,其中Y-2处理(嫩叶2 g·L−1)的促进效果最优。然而,高浓度处理(Y-4~Y-64)条件下牛樟芝中SOD的活性均有不同程度的降低。
2.2.3 添加猴樟嫩枝叶混合基质对牛樟芝SOD活性的影响
添加猴樟嫩枝叶混合基质对牛樟芝中SOD的活性影响结果见图2-C所示。不同浓度猴樟嫩枝叶混合基质添加处理与对照(PDA-0)培养条件下的牛樟芝SOD活性具有显著差异(P<0.05)。与PDA-0相比,在中低浓度各处理中随着浓度升高,牛樟芝中SOD的活性表现出明显的提高,ZY-0.125~ZY-0.5处理显著提高了牛樟芝中SOD的活性,其中ZY-0.125处理(嫩枝叶混合匀浆0.125 g·L−1)的促进效果最好。然而,高浓度处理(ZY-1~ZY-64)条件下牛樟芝中SOD的活性均有不同程度的降低。
2.3 添加猴樟基质对牛樟芝菌丝体中总三萜含量(TT)的影响
2.3.1 添加猴樟嫩枝基质对牛樟芝总三萜(TT)含量的影响
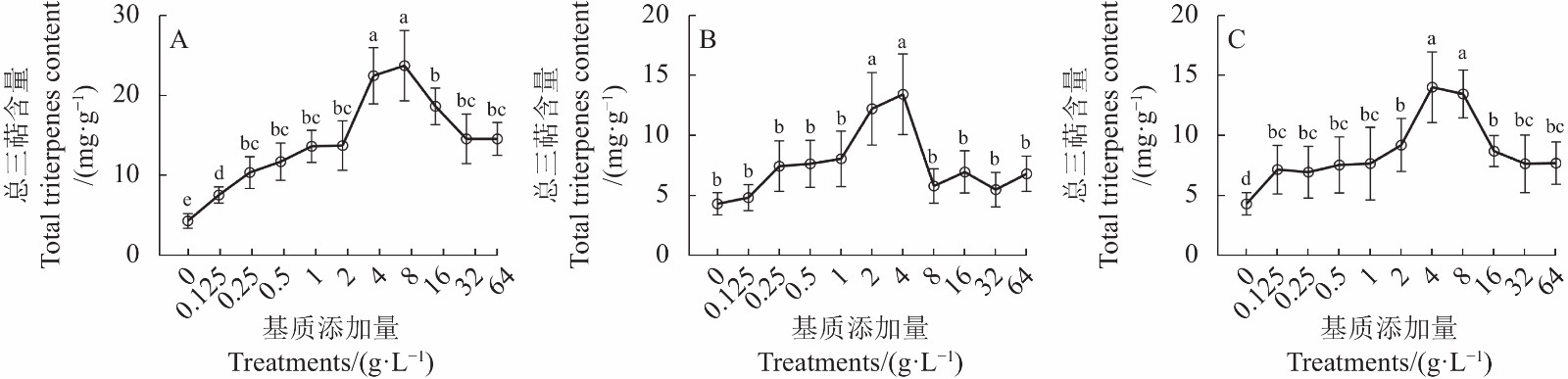
猴樟嫩枝基质添加对牛樟芝总三萜(TT)含量的影响结果如图3-A所示。不同浓度猴樟嫩枝基质添加处理与对照(PDA-0)培养条件下的牛樟芝总三萜(TT)含量具有显著差异(P<0.05)。与PDA-0相比,在中低浓度各处理中随着浓度升高,牛樟芝总三萜(TT)含量表现出明显的提高,Z-4、Z-8处理显著提高了牛樟芝总三萜(TT)含量,其中Z-8处理(嫩枝8 g·L−1)的促进效果最好。然而,高浓度处理(Z16~Z64)条件下牛樟芝总三萜(TT)含量出现了不同程度的降低。
2.3.2 添加猴樟嫩叶基质对牛樟芝总三萜(TT)含量的影响
添加猴樟嫩叶基质对牛樟芝总三萜(TT)含量的影响结果如图3-B所示。不同浓度猴樟嫩叶基质添加处理与对照(PDA-0)培养条件下的牛樟芝总三萜(TT)含量具有显著差异(P<0.05)。与PDA-0相比,在中低浓度各处理中随着浓度升高,牛樟芝总三萜(TT)含量表现出明显的提高,Y-2~Y-4处理显著提高了牛樟芝总三萜(TT)含量,其中Y-4处理(嫩叶4 g·L−1)的促进效果最好。然而,高浓度处理(Y-8~Y-64)条件下牛樟芝总三萜(TT)含量均有不同程度的降低。
2.3.3 添加猴樟嫩枝叶混合基质对牛樟芝总三萜(TT)含量的影响
添加猴樟嫩枝叶混合基质对牛樟芝总三萜(TT)含量的影响结果见图3-C所示。不同浓度猴樟嫩枝叶混合基质添加处理与对照(PDA-0)培养条件下的牛樟芝总三萜(TT)含量具有显著差异(P<0.05)。与PDA-0相比,在中低浓度各处理中随着浓度升高,牛樟芝总三萜(TT)含量表现出明显的提高,ZY-2~ZY-8处理显著提高了牛樟芝总三萜(TT)含量,其中ZY-4处理(嫩枝叶混合匀浆4 g·L−1)的促进效果最好。然而,高浓度处理(ZY-16~ZY-64)条件下牛樟芝总三萜(TT)含量均有不同程度的降低。
3. 讨论与结论
3.1 讨论
牛樟芝作为珍稀的食药用真菌,由于其对宿主植物的要求很高,使得牛樟芝在市场上一直供不应求,逐渐兴起的牛樟芝人工培养可以在一定程度上缓解产量问题,也能够推动牛樟芝的科学研究。本研究以皿式培养法对牛樟芝进行培养,探究了猴樟枝、叶、枝叶混合基质对牛樟芝菌丝体生长及生理生化特性的影响。研究发现有很多因素可以影响牛樟芝菌丝体的生长活力,其中接种原料、活化时间、取样位置十分关键[22]。因此本研究选择了牛樟芝接种原料生长活力较好的活化方法,研究结果表明猴樟对牛樟芝菌丝体生长、提高菌丝体产量和内含活性成分的含量有促进作用。
本研究中,向PDA培养基中添加猴樟基质枝2 g·L−1、叶1 g·L−1、枝叶混合2 g·L−1时,菌丝体致密,显著促进牛樟芝菌丝体的生长,菌落中心接种区在高浓度时出现菌落老化现象。孟红岩等[27]研究发现牛樟、香樟和樟树木屑热水提取物20、40、60 g·L−1均能促进牛樟芝菌丝体直径的扩大,但是促进作用呈现中低浓度促进、高浓度抑制的趋势,牛樟芝菌落中心接种区在3种樟属植物的培养基中均出现不同程度的菌落老化现象,且随着基质浓度的增大,老化程度加重,牛樟芝菌落中心接种区在香樟木屑热水提取物60 g·L−1培养基上已完全老化;当向PDA培养基中添加猴樟基质枝2 g·L−1、叶2 g·L−1、枝叶混合1 g·L−1时,显著促进牛樟芝菌丝体生物量的积累。陆震鸣[28]研究结果也表明香樟的水提物能显著促进牛樟芝菌丝体的生长;当向PDA培养基中添加猴樟基质枝2 g·L−1、叶2 g·L−1、枝叶混合0.125 g·L−1时,能显著提高牛樟芝菌丝体中SOD活性,增强抗氧化活性。汪雯翰等[29-30]研究表明,采用固体发酵法获得的菌丝体氯仿萃取物具有显著清除超氧阴离子自由基的抗氧化活性。在本研究中,当向PDA培养基中添加猴樟嫩枝8 g·L−1时,牛樟芝总三萜含量较对照组提高了81.77%,添加嫩叶4 g·L−1时较对照组提高了67.82%,添加枝叶混合4 g·L−1时较对照组提高了70.59%,表现出显著促进牛樟芝菌丝体总三萜含量的效果。刁浩[31]研究结果表明,香樟枝、叶水提物对总三萜含量随着处理浓度的增加呈现出先促进后抑制的作用。
3.2 结论
本研究结果表明,在PDA培养基中添加猴樟嫩叶基质2 g·L−1,对菌丝体的生长特性和生物量的促进效果最显著;在PDA培养基中添加猴樟嫩枝1 g·L−1或嫩叶基质2 g·L−1,对菌丝体SOD活性的促进效果最显著;在PDA培养基中添加猴樟嫩枝基质8 g·L−1,对菌丝体总三萜含量的促进效果最显著,达23.73 mg·g−1,较对照组提高了81.77%。因此,若以收获大批量牛樟芝菌丝体为目的,应当选择猴樟叶基质2 g·L−1;若在规模化生产时,则需要综合考虑菌落的扩散直径、生物量、SOD活性、总三萜含量等因素,添加猴樟枝基质4 g·L−1为宜。
-
图 2 添加猴樟基质对牛樟芝SOD活性的影响
A:猴樟嫩枝基质;B:猴樟嫩叶基质;C:猴樟枝叶混合基质。小写字母表示在0.05水平差异显著,下同。
Figure 2. Effect of C. bodinieri addition in culture substrate on SOD activity of A. cinnamomea
A: C. bodinieri branches; B: C. bodinieri leaves; C: both branches and leaves of C. bodinieri. Data with different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at 0.05 level. Same for Fig.3.
表 1 添加猴樟嫩枝基质对牛樟芝生长特性的影响
Table 1 Effect of C. bodinieri branches addition in culture substrate on growth of A. cinnamomea
处理
Treatments菌落直径
Colony diameter/mm菌落颜色
Colony color菌丝密度
Colony density菌落长势
Growth tendency生长速度
Growth speed/(mm·d−1)生长指数
Growth indexPDA-0 34.08±9.82 f ☆ ++ 1.5 1.14±0.33 e 1.71±0.50 f Z-0.125 47.20±6.50 d ☆ ++ 1.5 1.58±0.22 d 2.37±0.33 e Z-0.25 51.93±8.20 cd ☆☆ +++ 2.5 1.73±0.27 cd 4.33±0.68 d Z-0.5 58.60±8.56 ab ☆☆☆ +++ 3 1.95±0.29 bc 5.85±0.87 ab Z-1 59.88±10.58 ab ☆☆☆ +++ 3 1.90±0.35 bc 5.70±1.05 ab Z-2 62.36±10.33 a ☆☆☆ +++ 3 2.00±0.34 ab 6.24±1.02 a Z-4 55.30±7.69 bc ☆☆ +++ 2.5 1.84±0.26 bc 4.60±0.65 bc Z-8 51.92±7.00 cd ☆☆ +++ 2.5 1.73±0.23 cd 4.33±0.58 d Z-16 49.71±9.65 d ☆☆ +++ 2.5 1.99±0.32 b 4.98±0.8 b Z-32 39.93±5.23 e ☆☆ ++ 2 2.00±0.17 b 4.00±0.34 d Z-64 38.50±5.16 ef ☆☆ ++ 2 2.28±0.17 a 4.56±0.34 cd ① “+”越多,密度越高;“☆”越多,颜色越深;菌落长势评级数值越高,长势越好。菌落长势的评级标准= (菌丝密度×菌落颜色)/2[22] 。② 表中不同小写字母表示在0.05水平差异显著;③ Z:猴樟嫩枝;Y:猴樟嫩叶;ZY:猴樟嫩枝叶混合;基质代号后的数值为添加量 (g·L−1)。下同。
① More "+" indicates greater density; more "☆", darker color; and higher colony growth rating, better colony growth. Rating standard of colony growth = (mycelium density × colony color) /2[22].② Data with different lowercase letters on same column indicate significant differences at 0.05 level. ③ Z: C. bodinieri branches; Y: C. bodinieri leaves; ZY: C. bodinieri both branches and leaves. Numbers in the treatment name were addition amount of C.bodinieri branches(g·L-1). Same for below.表 2 添加猴樟嫩叶基质对牛樟芝生长特性的影响
Table 2 Effect of C. bodinieri leaves addition in culture substrate on growth of A. cinnamomea
处理
Treatments菌落直径
Colony diameter/mm菌落颜色
Colony color菌丝密度
Colony density菌落长势
Growth tendency菌落生长速度
Growth speed/(mm·d−1)生长指数
Growth IndexPDA-0 34.08±9.82 e ☆ ++ 1.5 1.14±0.33 b 1.71±0.59 g Y-0.125 53.75±0.75 cd ☆☆ ++ 2 1.79±0.02 ab 3.58±0.04 f Y-0.25 54.17±6.18 cd ☆☆ ++ 2 2.14±0.54 ab 4.28±1.08 de Y-0.5 58.70±9.08 c ☆☆ ++ 2 1.96±0.30 ab 3.92±0.60 ef Y-1 71.19±6.96 b ☆☆☆ +++++ 4 2.37±0.23 a 9.49±0.92 a Y-2 86.60±4.28 a ☆☆☆ ++++ 3.5 2.65±0.14 a 9.28±0.49 a Y-4 69.44±8.49 b ☆☆ +++ 2.5 2.11±0.28 ab 5.28±0.70c Y-8 56.50±6.35 c ☆☆ +++ 2.5 2.55±0.21 a 6.38±0.53 b Y-16 52.25±7.49 cd ☆☆ +++ 2.5 2.41±0.25 ab 6.03±0.63 b Y-32 42.42±8.82 de ☆☆ ++ 2 2.41±0.29 ab 4.82±0.48 cd Y-64 35.50±8.89 e ☆☆ ++ 2 2.52±0.30 ab 5.04±0.60 c 表 3 添加猴樟枝叶混合物基质对牛樟芝生长特性的影响
Table 3 Effect of adding mixture of C. bodinieri branches and leaves in culture substrate on growth of A. cinnamomea
处理
Treatments菌落直径
Colony diameter/mm菌落颜色
Colony color菌丝密度
Colony density菌落长势
Growth tendency菌落生长速度
Growth speed/(mm·d−1)生长指数
Growth indexPDA-0 34.08±4.82 d ☆ ++ 1.5 1.14±0.33 c 1.71±0.50 e ZY-0.125 47.86±5.67 abcd ☆☆ ++ 2 1.93±0.36 ab 4.83±0.90 bc ZY-0.25 52.42±6.30 abc ☆☆ ++ 2 1.75±0.21 ab 4.37±0.53 cd ZY-0.5 55.57±1.95 abc ☆☆ +++ 2.5 1.69±0.07 b 5.06±0.21 b ZY-1 57.21±3.75 ab ☆☆☆ ++ 2.5 1.91±0.12 ab 4.78±0.30 bcd ZY-2 61.06±7.80 a ☆☆☆☆☆ ++++ 4.5 2.04±0.26 ab 6.12±0.78 a ZY-4 61.94±5.10 a ☆☆☆☆ ++++ 4 2.06±0.17 a 6.19±0.51 a ZY-8 54.63±8.84 abc ☆☆☆ +++ 3 1.82±0.29 ab 4.55±0.73 cd ZY-16 48.17±7.94 abcd ☆☆ +++ 2.5 1.94±0.29 ab 4.85±073 bc ZY-32 43.10±5.62 bcd ☆☆ ++ 2 2.44±0.19 ab 4.88±0.38 bc ZY-64 42.25±10.08 cd ☆☆ ++ 2 2.08±0.34 a 4.16±0.68 d 表 4 添加猴樟基质对牛樟芝生物量的影响
Table 4 Effect of C. bodinieri addition in culture substrate on biomass of A. cinnamomea
处理
Treatments干重
Dry weight/g处理
Treatments干重
Dry weight/g处理
Treatments干重
Dry weight/gPDA-0 0.06±0.01 d PDA-0 0.06±0.01 d PDA-0 0.06±0.01 e Z-0.125 0.07±0.02 cd Y-0.125 0.07±0.02 d ZY-0.125 0.09±0.01 de Z-0.25 0.09±0.01 bcd Y-0.25 0.07±0.03 d ZY-0.25 0.11±0.02 bcde Z-0.5 0.11±0.02 bcd Y-0.5 0.09±0.03 cd ZY-0.5 0.16±0.05 abcd Z-1 0.12±0.03 bcd Y-1 0.14±0.02 bcd ZY-1 0.20±0.02 a Z-2 0.19±0.03 a Y-2 0.24±0.07 a ZY-2 0.19±0.05 ab Z-4 0.15±0.06 ab Y-4 0.20±0.05 ab ZY-4 0.17±0.04 abc Z-8 0.13±0.03 abc Y-8 0.18±0.04 abc ZY-8 0.16±0.04 abcd Z-16 0.12±0.02 bcd Y-16 0.13±0.06 bcd ZY-16 0.16±0.04 abcd Z-32 0.09±0.02 bcd Y-32 0.11±0.05 bcd ZY-32 0.14±0.03 abcd Z-64 0.09±0.02 bcd Y-64 0.10±0.02 bcd ZY-64 0.10±0.02 cde -
[1] 吴雨. 皿培式牛樟芝化学成分及质量控制和活性研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2018. WU Y. Study on chemical composition and quality control and activities of the Petri-dish cultured Antrodia camphorate[D]. Xiamen : Xiamen University, 2018.
[2] 冯路瑶. 牛樟芝人工培养工艺及三萜类成分产生规律的研究[D]. 烟台: 鲁东大学, 2017. FENG L Y. Studies on artificial culture and the total triterpenes producing in Antrodia camphorata[D]. Yantai: Ludong University, 2017.
[3] CHERNG I H, CHIANG H C, CHENG M C, et al. Three new triterpenoids from Antrodia cinnamomea [J]. Journal of Natural Products, 1995, 58(3): 365−371. DOI: 10.1021/np50117a004
[4] CHENG I H, WU D P, Chiang H C. Triterpenoids from Antrodia cinnamomea [J]. Phytochemistry, 1996, 41(1): 263−267. DOI: 10.1016/0031-9422(95)00541-2
[5] NAKAMURA N, HIRAKAWA A, GAO J J, et al. Five new maleic and succinic acid derivatives from the mycelium of Antrodia camphorata and their cytotoxic effects on LLC tumor cell line [J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2004, 67(1): 46−48. DOI: 10.1021/np030293k
[6] MENG L M, PAI M H, LIU J J, et al. Polysaccharides from extracts of Antrodia camphorata mycelia and fruiting bodies modulate inflammatory mediator expression in mice with polymicrobial Sepsis [J]. Nutrition (Burbank, Los Angeles County, Calif ), 2012, 28(9): 942−949. DOI: 10.1016/j.nut.2012.01.006
[7] 张远腾, 李晓波. 牛樟芝化学成分及其药理作用研究进展 [J]. 中草药, 2016, 47(6):1034−1042. ZHANG Y T, LI X B. Research progress on active components of Antrodia cinnamomea and their pharmacological effects [J]. Acupuncture Research, 2016, 47(6): 1034−1042.(in Chinese)
[8] SONG T Y, YEN G C. Antioxidant properties of Antrodia cinnamomea in submerged cultures [J]. J Agri Food Chem, 2002, 50(11): 3322−3327. DOI: 10.1021/jf011671z
[9] HUANG T T, WU S P, CHONG K Y, et al. The medicinal fungus Antrodia cinnamomea suppresses inflammation by inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome [J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2014, 155(1): 154−164. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.04.053
[10] HSU Y L, KUO P L, CHO C Y, et al. Antrodia cinnamomea fruiting bodies extract suppresses the invasive potential of human liver cancer cell line PLC/PRF/5 through inhibition of nuclear factor kappaB pathway [J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2007, 45(7): 1249−1257. DOI: 10.1016/j.fct.2007.01.005
[11] HSIAO G, SHEN M Y, LIN K H, et al. Antioxidative and hepatoprotective effects of Antrodia camphorata extract [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2003, 51(11): 3302−3308. DOI: 10.1021/jf021159t
[12] KUO M C, CHANG C Y, CHENG T L, et al. Immunomodulatory effect of Antrodia camphorata mycelia and culture filtrate [J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2008, 120(2): 196−203. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2008.08.011
[13] 李晶, 林雄杰, 王泽辉, 等. 牛樟芝鲨烯环氧酶基因的克隆、生物信息学及表达分析 [J]. 中草药, 2018(10):2440−2446. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2018.10.028 LI J, LIN X J, WANG Z H, et al. Cloning, bioinformatics, and expression analysis of squalene epoxidase in Antrodia cinnamomea [J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2018(10): 2440−2446.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2018.10.028
[14] CHIU K Y, WU C C, CHIA C H, et al. Inhibition of growth, migration and invasion of human bladder cancer cells by antrocin, a sesquiterpene lactone isolated from Antrodia cinnamomea, and its molecular mechanisms [J]. Cancer Letters, 2016, 373(2): 174−184. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.11.046
[15] LU M C, EL-SHAZLY M, WU T Y, et al. Recent research and development of Antrodia cinnamomea [J]. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 2013, 139(2): 124−156.
[16] 张东柱. 台湾特有珍贵药用真菌牛樟芝 [J]. 食药用菌, 2011(1):33−34. ZHANG D Z. Taiwan unique precious medicinal fungus Antrodia cinnamomea [J]. Edible and Medicinal Mushrooms, 2011(1): 33−34.(in Chinese)
[17] 李菁, 胡佳, 陈绪涛, 等. 珍稀药用真菌牛樟芝的研究与利用进展 [J]. 食药用菌, 2022(2):103−108. LI J, HU J, CHEN X T, et al. Advances in the research and utilization of rare medicinal mushroom Antrodia camphorata [J]. Edible and Medicinal Mushrooms, 2022(2): 103−108.(in Chinese)
[18] CHANG T T, CHOU W N. Antrodia cinnamomea sp. nov. on Cinnamomum kanehirai in Taiwan [J]. Mycol Res, 1995, 99(6): 756−758. DOI: 10.1016/S0953-7562(09)80541-8
[19] 李晶, 夏舒宁, 张黛, 等. 不同菌草对皿培牛樟芝菌丝体的影响 [J]. 北方园艺, 2022(8):108−115. LI J, XIA S N, ZHANG D, et al. Effects of different Juncao on solid cultured mycelium of Antrodia camphorata [J]. Northern Horticulture, 2022(8): 108−115.(in Chinese)
[20] 张知晓, 季梅, 刘凌, 等. 外源茉莉酸甲酯对牛樟芝产总三萜及多糖含量的影响 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2019(19):133−133,134. ZHANG Z X, JI M, LIU L, et al. Impact of exogenous methyl jasmonate on total triterpenoids and polysaccharide contents of Antrodia camphorate [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2019(19): 133−133,134.(in Chinese)
[21] 谢春芹, 许俊齐, 曹正, 等. 牛樟芝液体培养基优化及饮品加工工艺研究 [J]. 食品研究与开发, 2018(17):64−69. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2018.17.012 XIE C Q, XU J Q, CAO Z, et al. The research of optimization of liquid medium and technology of drink processing of Antrodia camphorata [J]. Food Research and Development, 2018(17): 64−69.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2018.17.012
[22] 赵能, 原晓龙, 陈剑, 等. 不同碳氮源对牛樟芝菌丝体生长的影响 [J]. 西部林业科学, 2016(4):7−12. DOI: 10.16473/j.cnki.xblykx1972.2016.04.002 ZHAO N, YUAN X L, CHEN J, et al. Effect of different carbon and nitrogen sources on mycelia growth of Antrodia cinnamomea [J]. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 2016(4): 7−12.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.16473/j.cnki.xblykx1972.2016.04.002
[23] 周夏, 王超. 牛樟芝高产总三萜固体培养基的优化 [J]. 食品科技, 2021(5):38−44. DOI: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2021.05.007 ZHOU X, WANG C. Optimization of solid medium for triterpenoids-enriched Antrodia camphorata [J]. Food Science and Technology, 2021(5): 38−44.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2021.05.007
[24] 李捷. 云南樟科植物区系地理 [J]. 云南植物研究, 1992(4):353−361. LI J. The floristic geography of lauraceous plants in Yunnan [J]. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 1992(4): 353−361.(in Chinese)
[25] 杨永, 刘冰. 中国樟科物种编目: 问题和展望 [J]. 生物多样性, 2015(2):232−236. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2015027 YANG Y, LIU B. Species catalogue of Lauraceae in China: Problems and perspectives [J]. Biodiversity Science, 2015(2): 232−236.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.17520/biods.2015027
[26] 张倩倩, 黄青. 基于香草醛-高氯酸显色反应测定灵芝三萜的方法探讨与修正 [J]. 菌物学报, 2018, 37(12):1792−1801. ZHANG Q Q, HUANG Q. Revised method for determining Ganoderma Lingzhi terpenoids by UV-Vis spectrophotometry based on colorimetric vanillin perchloric acid reaction [J]. Mycosystema, 2018, 37(12): 1792−1801.(in Chinese)
[27] 孟红岩, 郭莺, 林文珍, 等. 3种樟属植物对皿式培养牛樟芝菌丝生长的影响 [J]. 西南农业学报, 2018(10):2173−2178. MENG H Y, GUO Y, LIN W Z, et al. Effects of three Cinnamomum plants on hyphae growth of plate cultured Antrodia camphorata [J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018(10): 2173−2178.(in Chinese)
[28] 陆震鸣. 樟芝深层液态发酵及其三萜类化合物的研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2009. LU Z M. Study on Submerged Culture of Antrodia camphorcta and its Triterpenoids[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2009. (in Chinese)
[29] 汪雯翰, 孙太萍, 杨海芮, 等. 樟芝子实体和菌丝体萃取物的抑菌及抗氧化活性 [J]. 食用菌学报, 2016(2):79−83. DOI: 10.16488/j.cnki.1005-9873.2016.02.016 WANG W H, SUN T P, YANG H R, et al. Antibacterial and anti-oxidant properties of extracts derived from fruit bodies and mycelia of Taiwanofungus camphoratus [J]. Acta Edulis Fungi, 2016(2): 79−83.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.16488/j.cnki.1005-9873.2016.02.016
[30] YANG F C, YANG Y H, LU H C. Enhanced antioxidant and antitumor activities of Antrodia cinnamomea, cultured with cereal substrates in solid state fermentation[J] Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 78: 108-113.
[31] 刁浩. 外源添加物对牛樟芝液体发酵的影响[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2019. DIAO H. Effects of exogenous additives on liquid fermentation of antrodia cinnamomea[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2019.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 袁文华,胡涛,孙克诚,胡丹丹,周静静,王梓旭. 牛樟芝培养物对产蛋高峰后期蛋鸡生产性能、蛋品质及血清抗氧化指标的影响. 饲料工业. 2024(05): 38-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张红玲,余娜,武自强,张颖,郑元. 诱导子添加对牛樟芝生长特性的影响. 热带农业科学. 2024(12): 40-46 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: