Cloning, Expression, and Polymorphism of Homologous Brassica napus P5CR
-
摘要:目的 克隆油菜菌核病抗性相关基因,进一步为油菜抗病分子标记开发以及通过分子标记辅助育种途径选育抗菌核病油菜新品种提供理论基础。方法 以高抗、高感菌核病油菜为研究材料,对甘蓝型油菜A03、C03染色体上的P5CR(Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase,吡咯林-5-羧酸还原酶)同源基因进行特异PCR扩增,克隆和测序及表达分析。利用DNAMAN软件对测序结果进行序列比对,寻找抗、感材料中的差异SNP位点,并分析这些位点与油菜菌核病抗性的关系。利用qPCR技术分析A03及C03染色体上P5CR同源基因在抗、感菌核病油菜材料中接种核盘菌前及接种后6 h、12 h、24 h、48 h的表达。结果 C03染色体上的P5CR同源基因全长1457 bp,该基因在抗、感菌核病油菜材料中共有7个SNP位点,其中3个SNP位点可能与抗病性相关;A03染色体上的P5CR同源基因全长1526 bp,在抗、感菌核病油菜材料中该基因共有15个SNP位点,其中2个SNP位点可能与抗病性相关。A03及C03染色体上的P5CR基因在抗病材料接种后24 h表达量显著升高。结论 油菜P5CR基因上存在多个可能与菌核病抗性相关的位点且在抗病材料接种后表达升高,表明P5CR可能参与油菜对菌核病的抗性反应。本研究为进一步揭示甘蓝型油菜菌核病抗病机理及油菜抗菌核病分子标记开发奠定基础。Abstract:Objective The gene related to Sclerotinia-resistance in Brassica napus was cloned and studied to provide information for the development of disease-resistant rapeseed cultivars by means of molecular marker-assisted breeding.Method Using the rapeseed plants known to be either highly resistant or highly susceptible to sclerotinia stem rot, the homologous P5CR (pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase) on A03 and C03 chromosomes were amplified, cloned, sequenced, and expression analyzed. DNAMAN software was used to compare the sequencing results to locate the relevant SNP sites. Expressions of P5CR before and 6 h, 12 h, 24 h, and 48 h after inoculation into rapeseed plants were detected by qPCR.Result The P5CR on C03 chromosome was 1457 bp in length with 7 SNP loci, of which, 3 might be related to the disease resistance. The gene on A03 chromosome was 1526 bp in length with 15 SNP sites, of which, two might be associated with the disease resistance. The expressions of P5CR on A03 and C03 chromosomes significantly increased 24 h after inoculation.Conclusion Multiple loci in the P5CR of B. napus could be associated with the plant resistance to sclerotinia stem rot. The significant increase on the gene expression after inoculation suggested a close relationship between P5CR and the disease resistance. Further investigation is needed to unveil the underline mechanism.
-
Keywords:
- P5CR /
- sclerotinia stem rot /
- Brassica napus /
- disease resistance
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】油菜作为重要的油料作物,是我国乃至世界范围内食用油供给的主要来源。油菜除了油用,还可作为蔬菜、饲料、观赏作物及蜜源,具有重要的经济价值。我国油菜种植面积及分布居油料作物之首[1]。因此,油菜安全生产对国民经济意义重大。由真菌-核盘菌引起的菌核病给油菜生产带来严重威胁,引起油菜产量及品质大幅度降低[2,3]。我国长江中下游地区气候湿润,加之近些年油菜种植密度增加,加重了该病害的发生[4]。克隆油菜抗菌核病基因,研究油菜抗菌核病分子机理,对通过分子设计育种途径选育性状优良的抗病油菜新品种意义重大[5]。【前人研究进展】吡咯林-5-羧酸还原酶(Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase,P5CR )是真核生物中重要的一种管家蛋白,催化脯氨酸生物合成的最后一步反应,负责在细胞质中将脯氨酸、精氨酸、鸟氨酸和谷氨酸中间代谢产物吡咯啉-5-羧酸(Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate,P5C)还原成为脯氨酸,在氨基酸代谢的调节中发挥重要作用。实验室前期通过大豆菌核病全基因组关联分析得出P5CR基因与菌核病抗性强关联[6] ,推测该基因可能与油菜菌核病抗性有关。Senthil-Kuma等研究表明鸟氨酸氨基转移酶(δOAT)和脯氨酸脱氢酶(ProDH1和ProDH2)通过调控P5C代谢诱导的超敏反应进而参与非寄主抗性[7]。周婉莹等对甘蓝型油菜A10、C09上的P5CR同源基因进行克隆及多态性分析,结果得出,A10染色体中的P5CR同源基因上的多态性位点与菌核病抗性没有显著关联,C09染色体上P5CR同源基因在感病材料中存在一段A10染色体上P5CR同源基因片段的插入,导致前者ORF改变,进而可能造成该基因抗病性丧失。推测C09染色体中的P5CR同源基因与油菜对菌核病的抗性相关[8]。【本研究切入点】目前,关于P5CR基因与油菜抗菌核病关系研究报道较少。甘蓝型油菜A03、C03染色体上的P5CR同源基因与油菜菌核病抗性关系及抗性相关多态性位点尚不清楚。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究以对菌核病具有较好抗性的中油821、沪16油菜以及感病油菜川秦6R及南12R为研究材料,设计特异引物,对甘蓝型油菜C03、A03染色体上的P5CR同源基因进行PCR扩增、克隆测序及表达研究,分析P5CR基因中的SNP位点及其与油菜菌核病抗性的相关性,为油菜菌核病抗性基因克隆、油菜抗菌核病机制揭示及通过分子标记辅助育种选育抗病油菜新品种提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料
本研究选用高抗、高感菌核病油菜为试验材料(表1),抗病材料记为R,感病材料记为S。油菜材料于2021年种植于汉中勉县黄沙镇试验田(106°7′91.26″E,33°13′77.72″N)。大肠杆菌DH5α(TaKaRa,中国大连)由本实验室保存。核盘菌(Sclerotinia sclerotiorum)由汉中市农业技术推广与培训中心惠赠。TransStart fast Pfu fly DNA polymerse (全式金公司,北京)、植物总RNA提取试剂盒(庄萌生物,北京)、EvoM-MLV反转录试剂盒II(艾科瑞生物,湖南)、CTAB、琼脂糖、异丙醇、无水乙醇、Goldview核酸染料购自西安沃尔森公司。
表 1 油菜样品的编号、品种名称和表现型Table 1. Codes, variety names, and phenotypes of B. napus samples编号
Number样本
Sample抗性
ResistanceY4 川秦6R Chuanqin 6R S Y7 南12R Nan 12R S Y8 中油821 Zhongyou 821 R Y12 沪16 Hu 16 R 1.2 油菜基因组DNA提取及检测
采集供试油菜材料幼嫩叶片。采取改良CTAB法[9]提取油菜基因组DNA。通过1%的琼脂糖凝胶检测基因组DNA完整性。
1.3 引物设计、PCR扩增及克隆测序
从拟南芥基因组数据库(https://www.arabidopsis.org/)中下载拟南芥P5CR基因(AT5G14800)蛋白序列,通过NCBI 数据库(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/)中的Blast软件,在甘蓝型油菜数据库中进行同源基因比对(比对指标为序列覆盖度达90%以上,同源性大于80%,e-value小于1e-5)。针对甘蓝型油菜C03及A03染色体上P5CR同源基因设计特异引物(表2)。引物由西安沃尔森科技有限公司合成。
表 2 甘蓝型油菜C03及A03染色体上P5CR同源基因引物序列信息Table 2. Primer sequence of P5CR on chromosomes C03 and A03 of B. napus引物名称
Primer name序列(5′-3′)
Sequence(5′-3′)产物大小
Product length/bpP5CRC03F2 GCCTTGGTAAGCGAATGG 1879 P5CRC03R2 TCGTACCCTGTGACGATTCA P5CRA03F1 TGTGTTGGGCCTTTGTAAAACAAT 1977 P5CRA03R1 TGCAATTTGGTCGTACCCTTTAAC qP5CR A03 F1 GGAAGTGGACCAGCATACG 197 qP5CR A03 R1 GCTATTGTAGTCCCGCCA qP5CR C03 F1 TCGGAACAGCGGCAAGTGA 257 qP5CR C03R1 CTTCCCTGTCTTGCTCACCAT Ubc21F2 TCCCGAACCGTATCCTCTGC 156 Ubc21R2 GGTTACCTGAGTCGCAGTTGAG PCR反应体系共25 μL,其中TransStart fast Pfu fly DNA polymerse 0.5 µL, 5×TransStrat Fast Pfu Fly buffer 5 µL,2.5 mmol·L−1 dNTP 2 µL,50 ng·μL−1 DNA模板0.5 μL,ddH2O 17 μL。PCR预变性采取94 ℃ 4 min,接着94 ℃变性1 min,然后58 ℃退火30 s,最后72 ℃延伸2 min,循环35次,72 ℃延伸7 min后4 ℃保存。PCR产物经1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳分离后胶回收目标产物,并与PMD19-T载体(TaKaRa)连接,转化大肠杆菌DH5α,将转化体系涂布于LB固体培养基上(含IPTG 200 mg·L−1,X-Gal 20 mg·L−1) 37 ℃倒置培养过夜,进行菌落PCR鉴定,将阳性克隆送测序。
1.4 序列分析
高抗、高感菌核病油菜材料P5CR同源基因测序结果通过DNASTAR Lasergene中的Megalign软件进行序列比对,分析抗、感材料之间的多态性位点。同时,从NCBI网站中甘蓝型油菜数据库中下载甘蓝型油菜C03及A03染色体上P5CR基因的参考序列,与测序结果进行多重序列比对。利用DNAMAN软件将P5CR基因翻译成蛋白序列,并对抗、感油菜材料中P5CR基因编码蛋白序列进行比对分析。
1.5 核盘菌培养、接种及样品采集
将核盘菌菌核置于马铃薯葡萄糖琼脂(PDA)培养基上22 ℃暗培养4 d。接着,将边缘的菌丝转移至新的PDA培养基上生长。2 d后,菌丝体直径约为6 mm,用于接种试验。于油菜初花期,采集抗菌核病油菜材料中油821及感病材料南12R相同部位相同大小的叶片,通过叶片离体接种法对其进行核盘菌接种[10]。分别采集接种前(即接种0 h)及接种后6 h、12 h、24 h及48 h抗、感菌核病油菜叶片,迅速放入液氮中速冻后保存于−80 ℃冰箱,每个样品取3个重复。
1.6 RNA提取及反转录
总RNA提取采用植物总RNA试剂盒提取(提取步骤参照试剂盒说明书),通过琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测RNA完整性,采用Nanodrop核酸蛋白检测仪测定RNA浓度。采取Evo M-MLV反转录试剂盒II进行反转录。用ddH2O将合成的cDNA稀释10倍,冷冻保存备用。
1.7 qPCR检测P5CR基因表达
根据A03及C03上P5CR同源基因序列分别设计特异引物,通过定量PCR分析A03及C03染色体上P5CR基因在抗、感菌核病油菜材料接种前及接种后6 h、12 h、24 h、48 h的表达量。本研究中的内参基因为Ubc21。P5CR基因及内参引物序列信息见表2。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 甘蓝型油菜A03及C03染色体上P5CR同源基因的扩增
将拟南芥P5CR基因在甘蓝型油菜基因组数据库中比对,共得到4个P5CR同源基因,分别位于A10、C09、C03及A03染色体上(基因序列号分别为106372121、106416421、106417090、106431715)。课题组前期已对A10、C09染色体上P5CR同源基因进行了克隆[8],本研究对A03及C03染色体上P5CR基因进行克隆及序列分析。
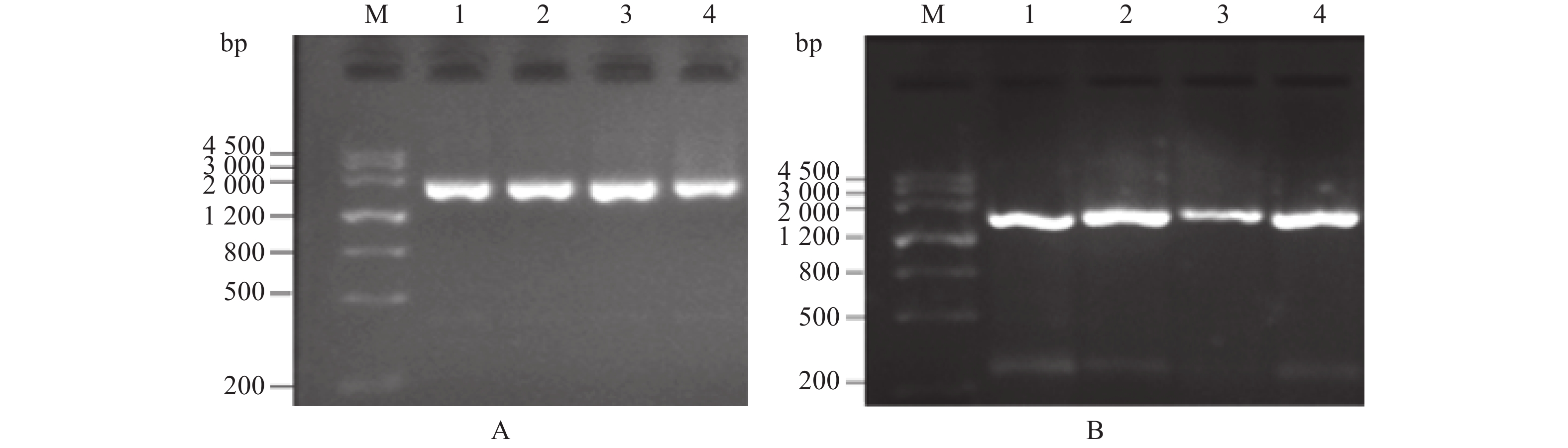
在抗、感菌核病油菜材料中,利用引物P5CRA03F1/P5CRA03R1对A03染色体上的P5CR同源基因进行扩增,得到一条2000 bp左右的特异性条带,与预期条带大小(1977 bp)相符(图1A)。接着,对PCR产物进行胶回收、克隆及测序。
![]() 图 1 甘蓝型油菜A03及C03染色体上P5CR同源基因扩增产物电泳图A、B分别为A03及C03染色体上P5CR基因扩增电泳结果。Marker各条带分子量见图左侧标注。M,Marker III;1,川秦6R;2,南12R:3,中油821;4,沪16。Figure 1. Electrophoretic map of amplified products of P5CR on chromosome A03 and C03 of B. napusA & B: Amplified electrophoretic diagram of P5CRs on chromosome A03 and C03, respectively. Molecular weight of band of marker shown on left. M: Marker III; 1: Chuanqin 6R; 2: Nan 12R; 3: Zhongyou 821; 4: Hu 16.
图 1 甘蓝型油菜A03及C03染色体上P5CR同源基因扩增产物电泳图A、B分别为A03及C03染色体上P5CR基因扩增电泳结果。Marker各条带分子量见图左侧标注。M,Marker III;1,川秦6R;2,南12R:3,中油821;4,沪16。Figure 1. Electrophoretic map of amplified products of P5CR on chromosome A03 and C03 of B. napusA & B: Amplified electrophoretic diagram of P5CRs on chromosome A03 and C03, respectively. Molecular weight of band of marker shown on left. M: Marker III; 1: Chuanqin 6R; 2: Nan 12R; 3: Zhongyou 821; 4: Hu 16.利用引物P5CRC03F2/P5CRC03R2对抗、感菌核病油菜材料C03染色体上P5CR同源基因进行扩增,扩增产物为大小介于1200~2000 bp的特异性条带(图1B),与本研究预期扩增产物大小(1889 bp)相符。对PCR产物进行胶回收、克隆测序。
2.2 抗、感菌核病油菜P5CR基因多态性分析
抗、感菌核病油菜材料A03染色体上P5CR基因扩增产物经克隆测序、序列分析得出,该基因全长1526 bp,有6个内含子,7个外显子。该基因在抗、感菌核病油菜材料中共存在15个多态性位点,分别位于A03染色体上P5CR同源基因的21、34、70、130、153、234、235、580、631、736、766、803、841、1546及1574位。其中,234位在感病油菜材料中为C、在抗病油菜材料中为A,235位在感病油菜中为C,与参考基因序列一致,在抗病油菜中突变为T。推测这2个多态性位点与油菜菌核病抗性相关(图2)。
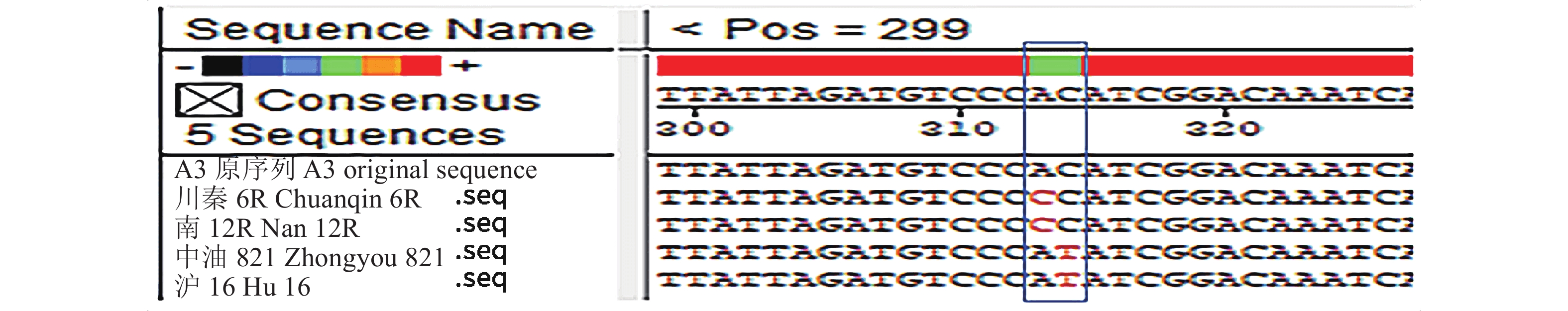
抗、感菌核病油菜材料C03染色体上P5CR基因扩增产物经克隆测序、序列分析得出,该基因全长1457 bp,有6个内含子,7个外显子。抗、感材料中该基因共存在7个多态性位点,分别位于该基因的564、579、636、671、673、676、679位。其中3个多态性位点与材料的抗、感性状相关(图3),即抗病材料中该基因564、636及679位由C突变为T,推测这三个位点与油菜抗病性相关。
A03染色体上P5CR基因编码蛋白序列分析得出,该基因编码蛋白质含276个氨基酸。在抗、感菌核病油菜中存在多态性的位点234及235均位于该基因第一个内含子中,不引起编码氨基酸序列改变。抗、感菌核病油菜材料C03染色体上P5CR基因编码蛋白序列分析得出,该基因编码蛋白质含144个氨基酸。分析抗、感材料中可能与油菜菌核病抗性相关的位点得出,抗性材料的P5CR基因564位SNP为同义突变,不引起编码氨基酸改变,其余两个SNP位点(636及679位)位于内含子中,不编码蛋白质。
2.3 qPCR分析抗、感菌核病油菜中P5CR基因表达
为进一步分析P5CR基因是否参与油菜对菌核病的抗性,通过qPCR分析A03及C03染色体上P5CR基因在抗、感菌核病油菜材料中接种核盘菌前及接种后不同时间的表达。结果显示,A03上的P5CR基因在接种前后的抗、感菌核病油菜材料中表达模式不同。抗病油菜材料中,A03上的P5CR基因在接种前后变化明显,在接种后24 h该基因的表达量最高,达到未接种时的2倍多。感病材料中,A03上的P5CR基因在接种前后表达量差异不大(图4A)。C03染色体上的P5CR基因在接种前后抗、感菌核病油菜材料中同样存在不同的表达模式,其在抗病材料中接种后24 h表达量最高,为未接种时的3倍多。感病材料中,C03染色体上的P5CR基因在接种后6 h、12 h表达量相对于未接种时略有所提高(图4B)。综上,A03及C03染色体上的P5CR基因在抗病材料接种后24 h表达量显著升高,说明该基因可能参与了油菜对菌核病的抗性。感病材料中,C03染色体上的P5CR基因虽然在接种后6 h、12 h表达量相对于未接种时略有所提高,但整体变化不大,导致其对菌核病未能表现出较好的抗性。
![]() 图 4 qPCR分析A03及C03染色体上P5CR基因在抗、感菌核病油菜材料中的表达结果A、B分别为A03、C03染色体上P5CR基因的qPCR结果图。对同一时间不同材料中P5CR基因的表达量进行差异性分析(*表示P < 0.05,**表示P < 0.01)。Figure 4. Expressions of P5CRs on A03 and C03 chromosomes in sclerotia-resistant and susceptible rapeseed materials detected by qPCRA & B: qPCR data on P5CRs on A03 and C03 chromosomes, respectively. Expressions of P5CR gene in different materials at the same time (* indicates P < 0.05, ** indicates P < 0.01).
图 4 qPCR分析A03及C03染色体上P5CR基因在抗、感菌核病油菜材料中的表达结果A、B分别为A03、C03染色体上P5CR基因的qPCR结果图。对同一时间不同材料中P5CR基因的表达量进行差异性分析(*表示P < 0.05,**表示P < 0.01)。Figure 4. Expressions of P5CRs on A03 and C03 chromosomes in sclerotia-resistant and susceptible rapeseed materials detected by qPCRA & B: qPCR data on P5CRs on A03 and C03 chromosomes, respectively. Expressions of P5CR gene in different materials at the same time (* indicates P < 0.05, ** indicates P < 0.01).3. 讨论
油菜是世界范围内广泛种植的油料作物。油菜菌核病是世界范围内尤其是温带地区普遍发生的一种严重的油菜病害。我国的东南沿海地区及长江流域,该病的田间发病率较高,导致油菜产量降低10%~30%,甚至高达80%,给油菜生产造成很大损失[11]。近年来,由于油菜机械化高密度种植,该病有不断加重的趋势。克隆油菜抗菌核病基因,开发抗病基因分子标记,通过分子标记辅助育种方式选育抗病油菜新品种是防治油菜菌核病最根本有效的途径。
P5CR是脯氨酸生物合成途径的关键酶。脯氨酸作为一种抗渗透胁迫调节剂,在植物渗透调节中发挥重要作用。研究表明,脯氨酸的积累是植物对各种胁迫(包括盐和渗透胁迫)的普遍反应,脯氨酸累积量与植物的胁迫耐受能力呈正相关[12,13]。首个P5CR基因在大豆中被克隆到,该基因全长1.2 kb,编码蛋白为单体蛋白[14]。之后相继在拟南芥、水稻、黑麦草、木薯等植物中分离到P5CR基因[15-18]。付莉莉等(2016)克隆了木薯中P5CR基因,对该基因在干旱胁迫下的表达分析表明,P5CR基因表达受胁迫调控。P5CR基因还响应低温、盐和ABA等胁迫条件[19]。在低温胁迫条件下,AtP5CR的表达量显著提高[20]。拟南芥中,P5CR基因表达受盐胁迫调控[21]。Cao等(2015)克隆了黑麦草(Lolium perenne L.)P5CR基因,其全长1047 bp,受盐、PEG、低温和ABA处理诱导[15]。
目前,关于P5CR基因与植物抗病性的研究报道较少。甘蓝型油菜基因组中共有4个P5CR同源基因,课题组前期克隆了C09、A10上P5CR同源基因。本研究对C03、A03染色体上的P5CR同源基因进行克隆测序及多态性分析,研究得出甘蓝型油菜C03染色体上P5CR同源基因全长1457 bp,抗、感油菜材料中,C03染色体上P5CR同源基因共存在7个多态性位点,其中3个多态性位点(564、636及679位)推测与油菜抗病性相关。A03染色体上的P5CR同源基因全长1526 bp,其在抗、感菌核病油菜材料中共存在15个多态性位点,其中,234、235位2个多态性位点推测与油菜菌核病抗性相关。进一步,P5CR基因编码蛋白质预测分析显示,抗性材料中C03染色体上P5CR基因564位SNP为同义突变,不引起编码氨基酸改变,其余两个SNP位点(636及679位)位于内含子中。A03上与菌核病抗性相关的两个位点234、235位均位于内含子中。通过qPCR分析A03、C03染色体上P5CR在抗、感油菜接种前及接种后不同时间的表达量。结果显示,在抗病材料中,A03及C03染色体上的P5CR基因在接种后24 h表达量均明显提高,说明A03、C03染色体上的P5CR基因均可能与油菜菌核病抗性相关。结合基因测序及定量PCR结果,本研究得出P5CR基因可能是通过基因表达水平的变化参与油菜抗菌核病反应。下一步,研究将扩大样本量,筛选出更多的高抗、高感菌核病油菜材料,对P5CR基因进行克隆及测序,从而进一步验证抗、感菌核病油菜材料中P5CR基因上的多态性位点与油菜菌核病抗性相关性。同时,研究将通过转基因、RNA干扰等实验对P5CR基因进行功能验证。
本研究为揭示油菜抗菌核病分子机理、油菜抗菌核病分子标记开发及油菜抗病新品种选育奠定基础。
-
图 1 甘蓝型油菜A03及C03染色体上P5CR同源基因扩增产物电泳图
A、B分别为A03及C03染色体上P5CR基因扩增电泳结果。Marker各条带分子量见图左侧标注。M,Marker III;1,川秦6R;2,南12R:3,中油821;4,沪16。
Figure 1. Electrophoretic map of amplified products of P5CR on chromosome A03 and C03 of B. napus
A & B: Amplified electrophoretic diagram of P5CRs on chromosome A03 and C03, respectively. Molecular weight of band of marker shown on left. M: Marker III; 1: Chuanqin 6R; 2: Nan 12R; 3: Zhongyou 821; 4: Hu 16.
图 4 qPCR分析A03及C03染色体上P5CR基因在抗、感菌核病油菜材料中的表达结果
A、B分别为A03、C03染色体上P5CR基因的qPCR结果图。对同一时间不同材料中P5CR基因的表达量进行差异性分析(*表示P < 0.05,**表示P < 0.01)。
Figure 4. Expressions of P5CRs on A03 and C03 chromosomes in sclerotia-resistant and susceptible rapeseed materials detected by qPCR
A & B: qPCR data on P5CRs on A03 and C03 chromosomes, respectively. Expressions of P5CR gene in different materials at the same time (* indicates P < 0.05, ** indicates P < 0.01).
表 1 油菜样品的编号、品种名称和表现型
Table 1 Codes, variety names, and phenotypes of B. napus samples
编号
Number样本
Sample抗性
ResistanceY4 川秦6R Chuanqin 6R S Y7 南12R Nan 12R S Y8 中油821 Zhongyou 821 R Y12 沪16 Hu 16 R 表 2 甘蓝型油菜C03及A03染色体上P5CR同源基因引物序列信息
Table 2 Primer sequence of P5CR on chromosomes C03 and A03 of B. napus
引物名称
Primer name序列(5′-3′)
Sequence(5′-3′)产物大小
Product length/bpP5CRC03F2 GCCTTGGTAAGCGAATGG 1879 P5CRC03R2 TCGTACCCTGTGACGATTCA P5CRA03F1 TGTGTTGGGCCTTTGTAAAACAAT 1977 P5CRA03R1 TGCAATTTGGTCGTACCCTTTAAC qP5CR A03 F1 GGAAGTGGACCAGCATACG 197 qP5CR A03 R1 GCTATTGTAGTCCCGCCA qP5CR C03 F1 TCGGAACAGCGGCAAGTGA 257 qP5CR C03R1 CTTCCCTGTCTTGCTCACCAT Ubc21F2 TCCCGAACCGTATCCTCTGC 156 Ubc21R2 GGTTACCTGAGTCGCAGTTGAG -
[1] 周颖. 中国冬油菜籽供给反应模型及实证分析[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2017. ZHOU Y. Study on the supply response model of Chinese winter rapeseed and its empirical analysis[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese)
[2] WEN L, TAN T L, SHU J B, et al. Using proteomic analysis to find the proteins involved in resistance against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in adult Brassica napus [J]. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 2013, 137(3): 505−523. DOI: 10.1007/s10658-013-0262-z
[3] WANG Z R, WAN L L, ZHANG X H, et al. Interaction between Brassica napus polygalacturonase inhibition proteins and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum polygalacturonase: Implications for rapeseed resistance to fungal infection [J]. Planta, 2021, 253(2): 34. DOI: 10.1007/s00425-020-03556-2
[4] 雷蕾, 梁龙兵, 秦信蓉, 等. 抗菌核病甘蓝型油菜种质的筛选与鉴定 [J]. 种子, 2020, 39(3):29−33. LEI L, LIANG L B, QIN X R, et al. Screening and identification of Sclerotinia-resistant germplasm of Brassica napus L [J]. Seed, 2020, 39(3): 29−33.(in Chinese)
[5] WU J, CAI G Q, TU J Y, et al. Identification of QTLs for resistance to Sclerotinia stem rot and BnaC. IGMT5. a as a candidate gene of the major resistant QTL SRC6 in Brassica napus [J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(7): e67740. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067740
[6] 张羽, FRANCOIS BELZILE. 大豆抗菌核病的全基因组关联研究 [J]. 华北农学报, 2020, 35(1):205−213. DOI: 10.7668/hbnxb.20190364 ZHANG Y, BELZILE F. Genome-wide association study for Sclerotinia sclerotiorum resistance of soybean [J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2020, 35(1): 205−213.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7668/hbnxb.20190364
[7] SENTHIL-KUMAR M, MYSORE K S. Ornithine-delta-aminotransferase and proline dehydrogenase genes play a role in non-host disease resistance by regulating pyrroline-5-carboxylate metabolism-induced hypersensitive response [J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2012, 35(7): 1329−1343.
[8] 周婉莹, 张晓娟, 孙晓敏, 等. 油菜P5CR基因克隆及其多态性分析 [J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2020, 39(12):5678−5683. DOI: 10.13417/j.gab.039.005678 ZHOU W Y, ZHANG X J, SUN X M, et al. Cloning and polymorphism analysis of P5CR in rapeseed(B. napus) [J]. Genomics and Applied Biology, 2020, 39(12): 5678−5683.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13417/j.gab.039.005678
[9] 蓝碧秀, 王凛, 吴子恺, 等. 利用改良CTAB法快速小量提取微胚乳玉米基因组DNA [J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2015, 34(1):190−194. DOI: 10.13417/j.gab.034.000190 LAN B X, WANG L, WU Z K, et al. Rapid miniprep extraction of genomic DNA from micro-endosperm maize with modified CTAB method [J]. Genomics and Applied Biology, 2015, 34(1): 190−194.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13417/j.gab.034.000190
[10] MEI J, QIAN L, DISI J O, et al. Identification of resistant sources against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in Brassica species with emphasis on B. oleracea [J]. Euphytica, 2011, 177(3): 393−399. DOI: 10.1007/s10681-010-0274-0
[11] DING L N, LI M, GUO X J, et al. Arabidopsis GDSL1 overexpression enhances rapeseed Sclerotinia sclerotiorum resistance and the functional identification of its homolog in Brassica napus [J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 18(5): 1255−1270. DOI: 10.1111/pbi.13289
[12] LEBRETON S, CABASSA-HOURTON C, SAVOURÉ A, et al. Appropriate activity assays are crucial for the specific determination of proline dehydrogenase and pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase activities [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 602939. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2020.602939
[13] FUNCK D, WINTER G, BAUMGARTEN L, et al. Requirement of proline synthesis during Arabidopsis reproductive development [J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2012, 12: 191. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-191
[14] DELAUNEY A J, VERMA D P. A soybean gene encoding delta 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase was isolated by functional complementation in Escherichia coli and is found to be osmoregulated [J]. Molecular & General Genetics:MGG, 1990, 221(3): 299−305.
[15] CAO L, WEI S Q, HAN L, et al. Gene cloning and expression of the pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase gene of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) [J]. Horticultural Plant Journal, 2015, 1(2): 113−120.
[16] SRIPINYOWANICH S, KLOMSAKUL P, BOONBURAPONG B, et al. Exogenous ABA induces salt tolerance in indica rice (Oryza sativa L.): The role of OsP5CS1 and OsP5CR gene expression during salt stress [J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2013, 86: 94−105. DOI: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2010.01.009
[17] 王丽媛, 丁国华, 黎莉. 脯氨酸代谢的研究进展 [J]. 哈尔滨师范大学自然科学学报, 2010, 26(2):84−89. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5617.2010.02.024 WANG L Y, DING G H, LI L. Progress in synthesis and metabolism of proline [J]. Natural Science Journal of Harbin Normal University, 2010, 26(2): 84−89.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5617.2010.02.024
[18] MOLINARI H B C, MARUR C J, DAROS E, et al. Evaluation of the stress-inducible production of proline in transgenic sugarcane (Saccharum spp.): Osmotic adjustment, chlorophyll fluorescence and oxidative stress [J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2007, 130(2): 218−229. DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2007.00909.x
[19] 付莉莉, 韩冰莹, 谭德冠, 等. 木薯MeP5CS和MeP5CR基因克隆及其干旱胁迫下的表达分析 [J]. 湖北农业科学, 2016, 55(15):4024−4028. FU L L, HAN B Y, TAN D G, et al. Gene cloning of me P5CS and me P5CR in cassava and their expression analysis under drought stress [J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 55(15): 4024−4028.(in Chinese)
[20] XUE Y, PENG R H, XIONG A S, et al. Yeast heat-shock protein gene HSP26 enhances freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis [J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2009, 166(8): 844−850. DOI: 10.1016/j.jplph.2008.11.013
[21] DE RONDE J A, CRESS W A, KRÜGER G H J, et al. Photosynthetic response of transgenic soybean plants, containing an Arabidopsis P5CR gene, during heat and drought stress [J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2004, 161(11): 1211−1224. DOI: 10.1016/j.jplph.2004.01.014
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 熊雪,李鹏,向准,黄静. 一株我国特有低温草菇菌株液体菌种发酵条件优化. 广东农业科学. 2024(10): 42-52 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: