Cloning and Expression of VcILR1 in Blueberry
-
摘要:目的 克隆蓝莓(Vaccinium spp)生长素酰胺水解酶基因VcILR1,分析该基因在蓝莓花、叶、茎、果和根中的表达模式和经过赤霉素处理的青果和成熟果两个时期的表达情况,为进一步探究该基因功能和蓝莓胚珠败育的机制提供依据。方法 以蓝莓果实的cDNA为模板克隆得到VcILR1基因,利用ProtParam等工具对VcILR1进行生物信息学分析,利用qRT-PCR方法对VcILR1基因在蓝莓不同组织及赤霉素处理的青果和成熟果中的表达量进行分析。结果 成功克隆到蓝莓VcILR1基因,该基因含976 bp的开放阅读框(ORF),编码325个氨基酸,有两个保守结构域,分别是Peptidase_M20和M20_dimer;编码蛋白的分子质量35364.20 kDa,理论等电点5.67,不稳定系数43.57,脂肪系数88.55,亲水性平均值−0.054,属于不稳定亲水性蛋白。系统进化树分析表明蓝莓VcILR1基因与山茶科植物的茶树(Camellia sinensis)生长素酰胺水解酶(IAA-Leucine Resistant 1-like,ILL)基因亲缘关系较近。qRT-PCR分析结果显示,VcILR1在蓝莓花、叶、茎、果和根中均有表达,在叶片中表达量最高,具有组织特异性;赤霉素处理能上调果实中VcILR1的表达。结论 赤霉素处理后蓝莓青果和成熟果中VcILR1的表达量均显著增高,推测赤霉素处理能够促进蓝莓果实中生长素含量的提高,从而抑制胚珠发育,导致果实无籽。Abstract:Objective VcILR1 of blueberry was cloned to analyze the expressions in various plant organs as well as after being treated by gibberellin to decipher its function and association with ovule abortion.Method Using the cDNA of blueberry as the template, VcILR1 was cloned by RT-PCR. Bioinformatics on the amino acid sequence was performed utilizing ProtParam and other relevant tools. Expressions of the gene in the flowers, leaves, stems, fruits, and roots of the plant as well as those in green and ripe fruits after being treated by gibberellin were determined.Result VcILR1 was successfully cloned and found to contain 976 bp ORF encoding 325 amino acids with two conserved structural domains, peptidase_M20 and M20_dimer, a molecular mass of 35364.20 kDa, a theoretical isoelectric point of 5.67, an instability coefficient of 43.57, and a lipid coefficient of 88.55. It was an unstable protein with a hydrophilic mean value of −0.054. A phylogenetic tree analysis showed the gene to closely relate to Camellia sinensis IAA-Leucine Resistant 1-like (ILL) gene. The qRT-PCR analysis revealed that the gene was expressed tissue-specific with the highest in the leaves, and that the gibberellin treatment up-regulated the expression in the fruits.Conclusion The expressions of VcILR1 in the blueberries significantly increased after being treated by gibberellin. It suggested that the plant hormone could stimulate IAA generation in the fruits and might also affect the ovule development.
-
Keywords:
- Blueberry /
- VcILR1 gene /
- gene cloning /
- seedless
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】蓝莓(Vaccinium spp.)为杜鹃花科越橘属落叶或常绿多年生灌木状果树,其浆果酸甜可口、果肉细腻,富含维生素、花青素、黄酮、多酚等多种天然抗氧化物,具有明目、延缓衰老等独特功效,在食品加工方向具有广阔的研究和开发前景[1-3]。蓝莓品种丰富[4],主要分为矮丛蓝莓、半高丛蓝莓、高丛蓝莓和兔眼蓝莓4个类型[5],各类型的品种间果实品质差异显著,其中兔眼蓝莓果实与其他品种比较单果质量、硬度和糖酸相对较高,但是种籽含量最高,严重影响了口感[6]。对于种籽含量较高的水果,对其进行去籽加工是一道增加生产成本的工序[7],而无籽果实的研究将会大大改善此类问题。植物通常利用内源激素的分泌与转运调节自身生长发育控制相应器官生长[8],高浓度的生长素会促进珠心细胞降解[9],从而导致胚珠败育形成无籽果实。生长素酰胺水解酶(IAA-Leucine Resistant 1-like Hydrolase,ILL)基因所编码的酶类能够催化生长素氨基酸结合态释放出游离态的生长素[10],在诱导蓝莓胚胎败育从而产生无籽果实方面具有可能性。【前人研究进展】ILL基因最早在拟南芥中发现,其蛋白家族有7个成员,分别为AtILR1、AtIAR3和5个ILR1-like蛋白(AtILL1、AtILL2、AtILL3、AtILL5和AtILL6)[11]。ILL蛋白家族已被鉴别证明参与植物果实发育[12]、花器官生长[13]以及对环境因子的响应[14]等。花生AhILL5被证明通过调节激素水平影响种子的大小和质量[15];番茄SlILL1、SlILL5和SlILL6通过改变生长素含量以及影响PIN基因的表达介导番茄花梗脱落[16];萝卜miR172通过介导RsILL5对萝卜主根增厚产生影响[17];番茄SlIAR3基因的沉默表达可以增强植株对黄萎病的基础防御[18]。ILL家族蛋白能够增加植物体内游离的生长素积累,进而促进植物的营养生长,也可能促进珠心细胞降解造成果实胚珠的败育。【本研究切入点】目前关于ILL家族基因在蓝莓胚胎败育方面的研究还鲜有报道。【拟解决的关键问题】课题组前期研究中发现赤霉素处理可导致蓝莓果实胚胎败育进而出现无籽果实,从赤霉素处理后的蓝莓果实转录组数据分析中筛选出了差异表达的生长素酰胺酶(IAA-leucine resistant 1, ILR1 )基因VcILR1[19]。本研究克隆了蓝莓生长素酰胺酶基因VcILR1,并对其进行生物信息学分析及时空表达分析,探究其功能,为进一步探究蓝莓胚胎败育的分子机制提供理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
试验所使用的材料为蓝莓品种Baldwin,植株无病虫害和机械损伤,栽植于南京市溧水区江苏省中科院植物研究所蓝莓试验基地(119°03′E,31°35′N),于生长期取花、叶片、茎、果和根,用液氮速冻带回实验室于−80 ℃超低温冰箱保存备用。花后10 d使用质量浓度为100 mg·L−1的赤霉素(GA3)浸蘸果穗5 s,之后收集青果(花后60 d)和成熟果(花后100 d),用液氮速冻带回实验室于−80 ℃超低温冰箱保存,用于目的基因的相对表达量分析。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 RNA的提取和cDNA的合成
使用TaKaRa RNA提取试剂盒提取蓝莓花、果、茎、叶和根的RNA。使用5×Prime Script RT Master Mis试剂与提取的RNA,按照体积比1∶4配制20 μL体系合成cDNA。
1.2.2 VcILR1基因的克隆
根据蓝莓Baldwin的转录组测序数据(SRA数据库登录号:PRJNA831576),利用Bioxm2.7软件设计引物(表1)。cDNA扩增反应体系:Prime star Max Premix (2×)20 μL、cDNA模板1.5 μL、上下游引物各1.2 μL、ddH2O 21.1 μL。扩增反应程序:预变性98 ℃ 3 min;变性98 ℃ 10 s,退火55 ℃ 5 s,延伸72 ℃ 15 s,循环35次;终延伸72 ℃ 3 min,8 ℃保持。制备1%琼脂糖凝胶对PCR产物进行电泳鉴定,条带大小验证正确后再进行回收纯化,之后进行TA克隆,转化大肠杆菌,进行菌液验证,选取阳性克隆进行测序。
表 1 VcILR1基因扩增引物信息Table 1. VcILR1 primer information引物名称Primer name 引物序列(5′-3′)primer sequence(5′-3′) VcILR1-F ATGGATGCTTTGCCCATTCAGGA VcILR1-R AGAATAAGAAATGGGGTTTCTTCC qRT-VcILR1-F GAGGAACAAGGCCAAGGTGCAA qRT-VcILR1-R CCTGGCCTTGCTGCAACAGT Actin-F AGGCTAACCGTGAGAAGATGAC Actin-R AGAGTCCAGCACGATTCCAG 1.2.3 生物信息学分析
采用在线工具ProtParam(https://web.expasy.org/protparam/)分析VcILR1基因编码蛋白质的分子量、理论等电点、氨基酸组成成分、脂肪系数等理化性质;利用WoLF-PSORT II 在线软件(https://www.genscript.com/wolf-psort.html?src=leftbar)预测VcILR1蛋白的亚细胞定位;利用DeepTMHMM在线软件(https://dtu.biolib.com/DeepTMHMM)预测VcILR1蛋白跨膜结构;利用 SignalP 6.0 Server 在线软件(https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?SignalP)预测信号肽;利用NetPhos 3.1 Server在线软件(https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?NetPhos-3.1)分析蛋白磷酸化位点;利用 ExPasy-ProtScale (https://web.expasy.org/protscale/)分析VcILR1蛋白亲水/疏水性;利用SOPM在线软件(https://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=npsa_sopma.html)预测VcILR1蛋白的二级结构,利用 Swiss-Model在线软件预测VcILR1蛋白的三级结构。
1.2.4 基因表达模式分析
利用Primer Premier 6设计特异引物qRT-VcILR1-F、qRT-VcILR1-R(表1)进行荧光定量PCR分析,选取内参基因Actin对蓝莓花、叶片、茎、果实和根样本进行qRT-PCR检测。
1.3 数据分析
利用SPSS 26对荧光定量结果进行差异显著性分析,用Origin 2021作表达分析图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 蓝莓VcILR1基因的克隆
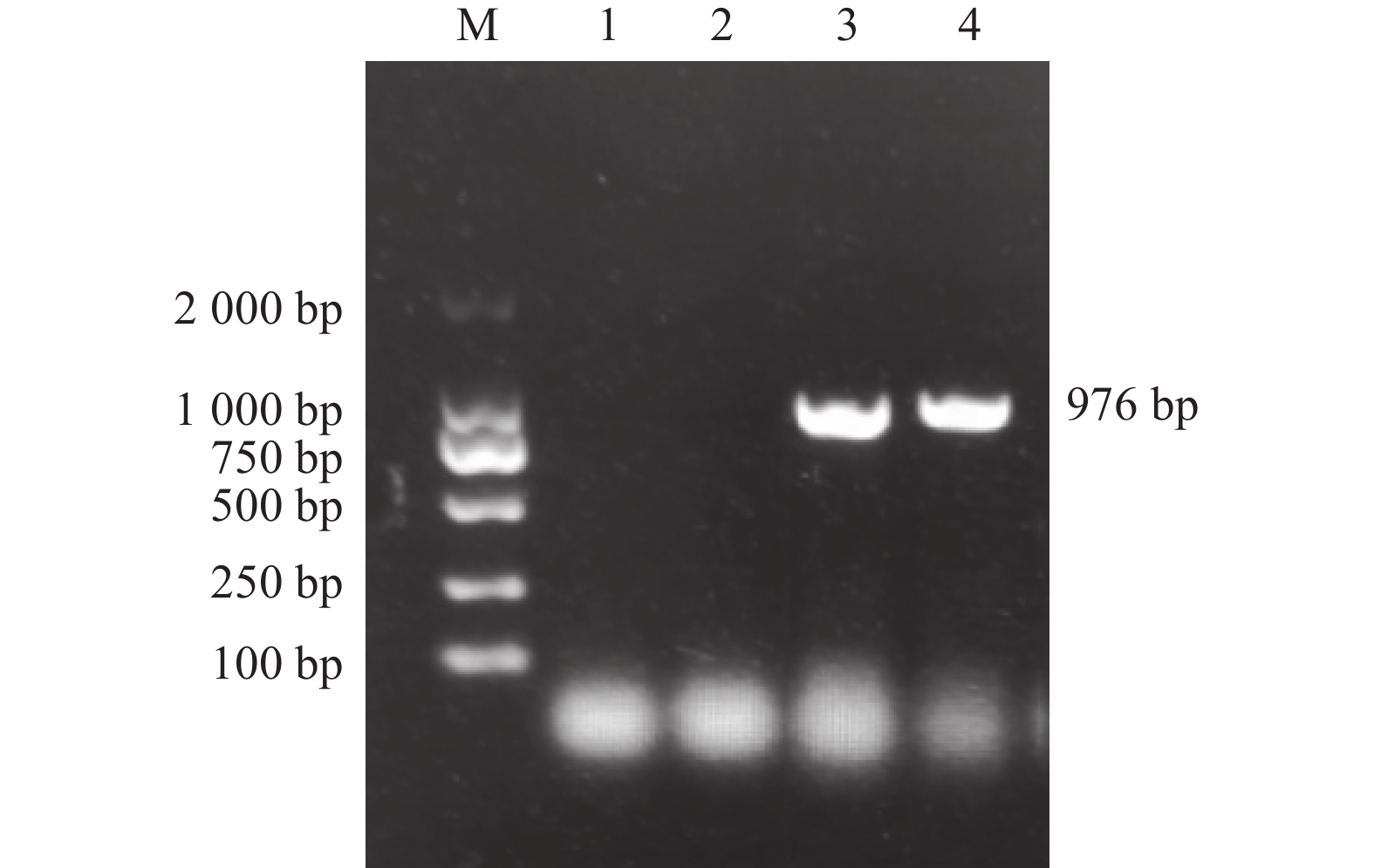
以蓝莓Baldwin果实的cDNA为模板进行PCR扩增,得到大小为976 bp的清晰条带(图1),表明蓝莓VcILR1基因克隆成功。
2.2 VcILR1基因的生物信息学分析
2.2.1 理化性质分析
对蓝莓VcILR1基因编码蛋白的理化性质分析结果表明,VcILR1编码蛋白氨的基酸数量为325个,分子质量为35364.20 kDa,分子式为C1577H2460N430O471S12,理论等电点为5.67。VcILR蛋白的氨基酸组成分析显示,该蛋白中的丙氨酸(Ala)含量最高,为10.5%,含量最低的是色氨酸(Trp),仅为0.3%。该结构中负电荷残基(Asp+Glu)数量为38个,而正电荷残基(Arg+Lys)数量为27个。不稳定系数为43.57,推断其属于不稳定蛋白。脂肪系数为88.55,亲水性总平均值(GRAVY)为−0.054,推测该蛋白为亲水性蛋白。
2.2.2 蛋白结构域分析
利用NCBI中的Concserved Domain搜索,结果显示蓝莓吲哚-3-乙酸(IAA)-氨基酸水解酶(IAA-amino acid hydrolase,ILR1)蛋白质特定匹配(Specific hits)在M20_IAA_Hyd(由第1~314个氨基酸编码),其属于Zinc_peptidase_like超家族。蛋白质分类分析显示,ILR1是一种M20家族金属肽酶,可以将吲哚-3-乙酰-N-天冬氨酸水解为吲哚-3-乙酸的植物氨基酰化酶-1,即吲哚-3-乙酸-L-天冬氨酸水解酶(IAA-Asp)(图2)。而IAA-Asp在植物中作为IAA储存形式起作用,ILR1/ILL可将其转化为游离态IAA。
2.2.3 亚细胞定位及跨膜区结构域和信号肽预测
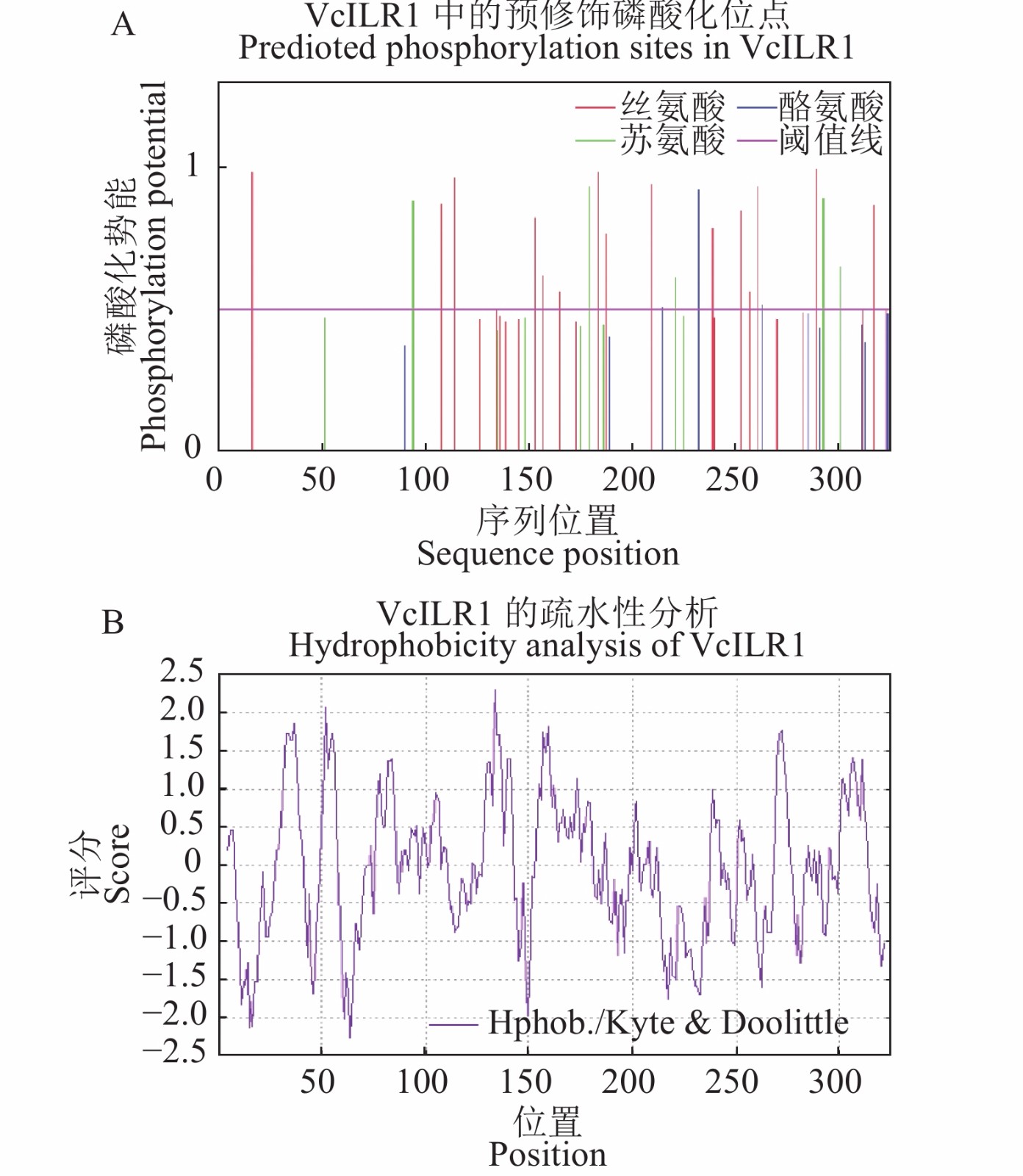
对蓝莓VcILR1蛋白的亚细胞定位分析结果显示,该蛋白定位于细胞骨架(K值为11)、细胞质(K值为3),说明该蛋白最可能定位于细胞骨架;跨膜结构域预测发现VcILR1蛋白无跨膜结构域;信号肽预测发现VcILR1蛋白是非分泌性蛋白,不含信号肽;VcILR1蛋白的磷酸化位点数量为23个,其中丝氨酸(S)15个、苏氨酸(T)5个、酪氨酸(Y)3个(图3A)。VcILR1蛋白的亲水/疏水性分析结果显示(图3B),整条肽链的氨基酸预测值大部分均为负值,判断该蛋白具有亲水性蛋白的特征,该判断与蛋白质的理化性质的推断结果相一致。
2.2.4 VcILR1蛋白的二级、三级结构预测
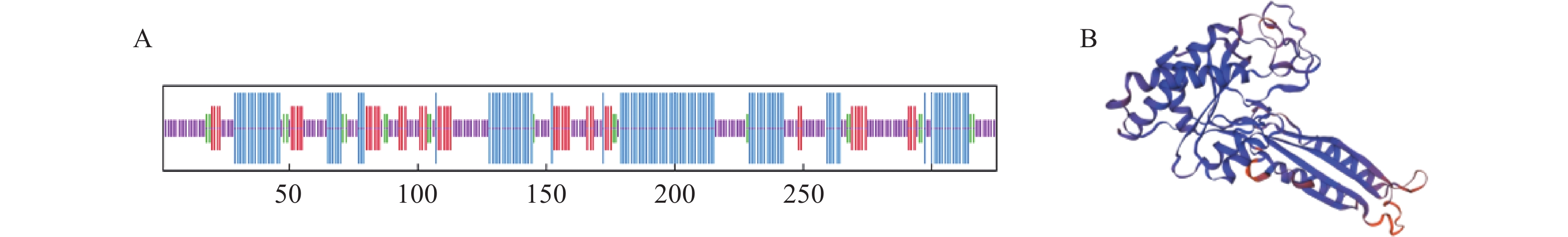
VcILR1蛋白的二级结构预测结果显示,α-螺旋(Hh)占比为37.23%,延伸链(Ee)占比为7.44%,β-转角(Tt)占比为6.15%,无规则卷曲(C)占比为39.47%(图4A)。VcILR1蛋白的三级结构预测结果显示(图4B),该蛋白为α-螺旋、β-转角组成无规则卷曲的三维空间结构,与二维结构预测结果一致。
2.2.5 VcILR1基因系统发育树的构建与分析
利用NCBI中的BLAST工具,对蓝莓VcILR1基因序列进行在线比对,选取16个物种的ILL基因序列进行比对并构建系统发育树,结果(图5)显示蓝莓VcILR1与山茶科(Theaceae)植物ILL亲缘关系较近,与漆树科(Anacardiaceae)植物ILL亲缘关系较远。
2.2.6 VcILR1氨基酸序列同源性比对
由构建的系统发育树分析结果选出与蓝莓VcILR1基因同源性高的3个物种,分别为茶树(Camellia sinensis)、欧亚种葡萄(Vitis vinifera)、河岸葡萄(Vitis riparia)。利用DNAMAN软件对蓝莓和其他植物的ILL家族蛋白进行序列比对,包含ILL蛋白家族保守结构域Peptidase_M20(图6红线区域)和M20_dimer(图6蓝线区域)。使用BioXM 2.7软件对氨基酸序列相似率进行计算,得出蓝莓ILR1蛋白与茶树ILL1蛋白氨基酸相似率为65.92%,与欧亚种葡萄ILL1蛋白和ILL4蛋白相似率分别为63.15%、61.22%,与河岸葡萄ILL4蛋白相似率为65.77%。综上可得,进化过程中蓝莓ILR1基因与茶树ILL1和河岸葡萄ILL4基因具有较高的同源性。
![]() 图 6 蓝莓VcILR1氨基酸序列与其他物种ILL家族蛋白氨基酸序列对比分析以相似性 50%为阈值,蓝色标注:相似性 ≥ 50%;粉色标注:相似性 ≥ 75%;黑色标注:相似性 ≥100%;红线、蓝线:保守结构域。Figure 6. Amino acid sequence alignment of VcILR1 with other ILL family proteinsWith threshold at 50 % similarity, blue indicates≥50%; pink, ≥75%; black, 100%; red and blue lines, conservative domains.
图 6 蓝莓VcILR1氨基酸序列与其他物种ILL家族蛋白氨基酸序列对比分析以相似性 50%为阈值,蓝色标注:相似性 ≥ 50%;粉色标注:相似性 ≥ 75%;黑色标注:相似性 ≥100%;红线、蓝线:保守结构域。Figure 6. Amino acid sequence alignment of VcILR1 with other ILL family proteinsWith threshold at 50 % similarity, blue indicates≥50%; pink, ≥75%; black, 100%; red and blue lines, conservative domains.2.3 VcILR1基因的表达分析
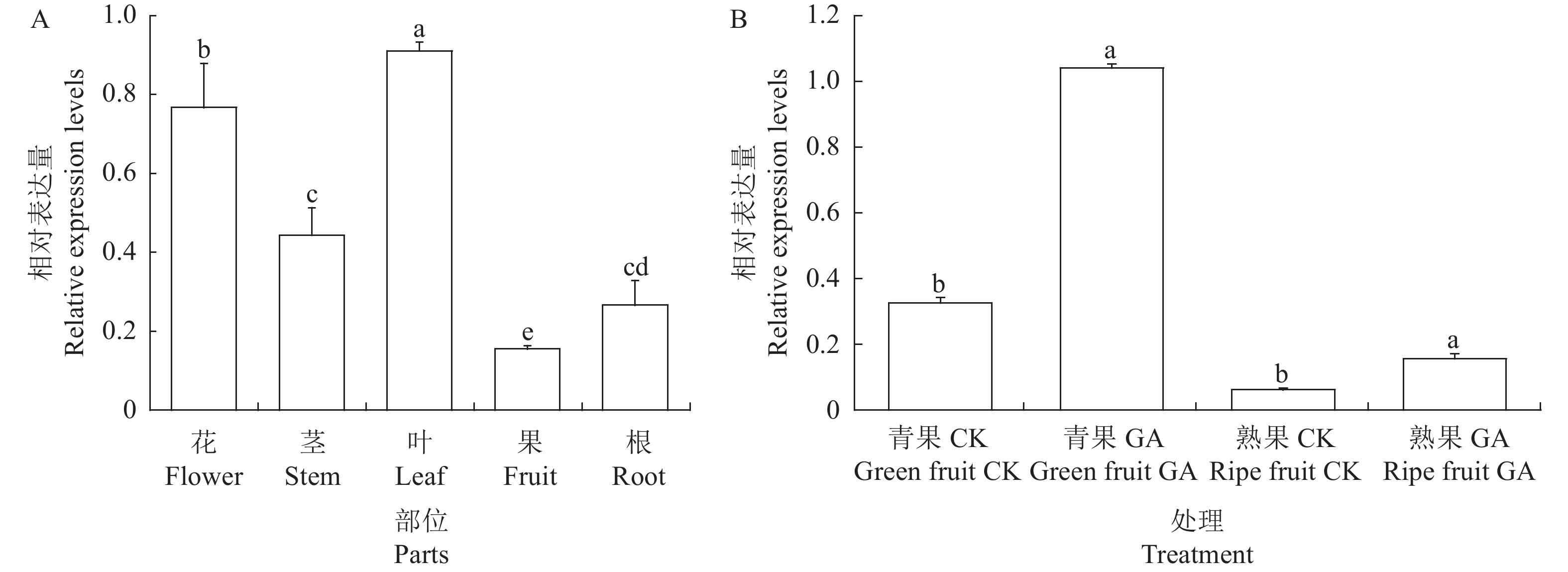
荧光定量PCR分析结果显示,在蓝莓Baldwin品种的花、果、茎、叶和根中均能检测到VcILR1基因的表达(图7-A),且不同部位的表达量存在显著差异。VcILR1在蓝莓叶中的表达量最高,在果实中表达量最低,前者是后者的6倍。由赤霉素处理后蓝莓青果和成熟果中VcILR1的表达量图(图7-B)可知,赤霉素处理的蓝莓青果中VcILR1的表达量较高,相比对照组上升约3.2倍;VcILR1基因在成熟果中的表达量均低于青果,但对照组VcILR1表达量最低,比赤霉素处理组低约39%。由此推测,赤霉素处理可以诱导蓝莓果实中VcILR1基因的表达上调。
![]() 图 7 VcILR1在蓝莓不同部位(A)和赤霉素处理下的相对表达量(B)A:不同的小写字母表示不同部位间差异显著(P<0.05)。B:青果CK——对照组青果期果实;青果GA——赤霉素处理组青果期果实;熟果CK——对照组成熟果实;熟果GA——赤霉素处理组成熟果实。不同小写字母表示同一阶段果实不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。Figure 7. Expressions of VcILR1 in different organs of blueberry plant (A) and of that being treated by gibberellin (B)A: Data with different lowercase letters indicate significant difference between organs (P<0.05); B: Green fruit CK—control green fruit stage; green fruit GA—gibberellin treated group green fruit stage; ripe fruit CK—control ripe fruit; ripe fruit GA—gibberellin treated group ripe fruit. Data with different lowercase letters indicate significant difference between treatments on fruits at the same growth stage (P<0.05).
图 7 VcILR1在蓝莓不同部位(A)和赤霉素处理下的相对表达量(B)A:不同的小写字母表示不同部位间差异显著(P<0.05)。B:青果CK——对照组青果期果实;青果GA——赤霉素处理组青果期果实;熟果CK——对照组成熟果实;熟果GA——赤霉素处理组成熟果实。不同小写字母表示同一阶段果实不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。Figure 7. Expressions of VcILR1 in different organs of blueberry plant (A) and of that being treated by gibberellin (B)A: Data with different lowercase letters indicate significant difference between organs (P<0.05); B: Green fruit CK—control green fruit stage; green fruit GA—gibberellin treated group green fruit stage; ripe fruit CK—control ripe fruit; ripe fruit GA—gibberellin treated group ripe fruit. Data with different lowercase letters indicate significant difference between treatments on fruits at the same growth stage (P<0.05).3. 讨论与结论
蓝莓品种丰富,各品种间种子含量差异较大,其中兔眼蓝莓品种由于籽粒较多,严重影响口感,大大降低其商品价值。研究如何获得少籽/无籽蓝莓果实,是提升多籽品种蓝莓果实品质的重要手段。常用的获得无籽果实的方法是赤霉素处理。赤霉素和生长素作为果实受精后生长所需的主要激素[20],它们之间互作影响着果实授粉和单性结实的坐果问题[21]。基于转录组数据,本研究对蓝莓生长素酰胺水解酶基因VcILR1进行了克隆和表达分析,以期为赤霉素调控蓝莓种子发育的机理提供科学依据。
本研究从蓝莓Baldwin品种中克隆获得了VcILR1基因,生物信息学分析显示该基因编码325个氨基酸,编码蛋白的分子质量为35364.20 kDa,理论电子量为5.677,为亲水性蛋白。跨膜区结构域和信号肽预测结果显示,VcILR1蛋白既无跨膜结构域也不含信号肽,因为信号肽是分泌性蛋白的决定性因子[22],所以推测VcILR1为非分泌性蛋白。系统进化树分析结果显示,VcILR1基因与山茶科植物的茶树(Camellia sinensis)生长素酰胺水解酶(IAA-Leucine Resistant 1-like,ILL)亲缘关系较近,而与漆树科植物的ILL亲缘关系较远。从拟南芥7个ILL家族基因的深入研究得知,AtILR1能够水解生长素-氨基酸螯合物,其符合所有拟南芥生长素酰胺水解酶基因(AtILLs)拥有的M20二聚体结构域所具有的水解生长素螯合物作用的机制。使用SMART对蓝莓VcILR1基因的结构域分析发现,VcILR1中也拥有M20二聚体结构域(M20_dimer),因此蓝莓VcILR1可能也具有水解生长素-氨基酸螯合物的功能。大量研究表明,ILL家族基因在不同组织中的表达具有特异性。蓝莓各部位中VcILR1基因的表达量分析结果显示,花、叶、茎和根中的表达量相对于果实都较高,可能的原因是果实为生殖器官,生长素含量过多会抑制果实和种子的正常发育,这与Weijers等[23]、Adamowski等[24]和Blakeslee等[25]的研究结果基本一致。本研究中,赤霉素处理的蓝莓果实中VcILR1基因的表达量均明显增强,表明VcILR1发挥了ILL家族基因所具有的调控游离态IAA的释放进而调控果实继续发育的功能[26],推测由此可能会造成生长素的累积,从而影响珠心发育,导致胚胎败育,形成无籽果实,但具体机理还有待进一步研究。
-
图 6 蓝莓VcILR1氨基酸序列与其他物种ILL家族蛋白氨基酸序列对比分析
以相似性 50%为阈值,蓝色标注:相似性 ≥ 50%;粉色标注:相似性 ≥ 75%;黑色标注:相似性 ≥100%;红线、蓝线:保守结构域。
Figure 6. Amino acid sequence alignment of VcILR1 with other ILL family proteins
With threshold at 50 % similarity, blue indicates≥50%; pink, ≥75%; black, 100%; red and blue lines, conservative domains.
图 7 VcILR1在蓝莓不同部位(A)和赤霉素处理下的相对表达量(B)
A:不同的小写字母表示不同部位间差异显著(P<0.05)。B:青果CK——对照组青果期果实;青果GA——赤霉素处理组青果期果实;熟果CK——对照组成熟果实;熟果GA——赤霉素处理组成熟果实。不同小写字母表示同一阶段果实不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 7. Expressions of VcILR1 in different organs of blueberry plant (A) and of that being treated by gibberellin (B)
A: Data with different lowercase letters indicate significant difference between organs (P<0.05); B: Green fruit CK—control green fruit stage; green fruit GA—gibberellin treated group green fruit stage; ripe fruit CK—control ripe fruit; ripe fruit GA—gibberellin treated group ripe fruit. Data with different lowercase letters indicate significant difference between treatments on fruits at the same growth stage (P<0.05).
表 1 VcILR1基因扩增引物信息
Table 1 VcILR1 primer information
引物名称Primer name 引物序列(5′-3′)primer sequence(5′-3′) VcILR1-F ATGGATGCTTTGCCCATTCAGGA VcILR1-R AGAATAAGAAATGGGGTTTCTTCC qRT-VcILR1-F GAGGAACAAGGCCAAGGTGCAA qRT-VcILR1-R CCTGGCCTTGCTGCAACAGT Actin-F AGGCTAACCGTGAGAAGATGAC Actin-R AGAGTCCAGCACGATTCCAG -
[1] 温靖, 关小莺, 徐玉娟, 等. 不同蓝莓品种品质特性研究 [J]. 热带作物学报, 2018, 39(9):1846−1855. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2018.09.025 WEN J, GUAN X Y, XU Y J, et al. Quality evaluation of different blueberry cultivars [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2018, 39(9): 1846−1855.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2018.09.025
[2] 许文静, 陈昌琳, 邓莎, 等. 基于主成分分析和聚类分析的蓝莓品质综合评价 [J]. 食品工业科技, 2022, 43(13):311−319. XU W J, CHEN C L, DENG S, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of blueberry quality based on principal component analysis and cluster analysis [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(13): 311−319.(in Chinese)
[3] 周继芬, 兰武, 王军, 等. 蓝莓营养及独特保健功能研究 [J]. 北方园艺, 2020(21):138−145. ZHOU J F, LAN W, WANG J, et al. Nutritional ingredients of blueberry and research on its unique health-care function [J]. Northern Horticulture, 2020(21): 138−145.(in Chinese)
[4] 杨海燕, 吴文龙, 闾连飞, 等. 蓝莓新品种‘寨选7号’ [J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(3):227−228. YANG H Y, WU W L, LV L F, et al. A new cultivar of blueberry’Zhaixuan 7’ [J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2020, 44(3): 227−228.(in Chinese)
[5] 张西臣. 临沂适种果树栽培技术新编[M]. 济南: 山东科学技术出版社, 2013. [6] 王小敏, 赵慧芳, 吴文龙, 等. 蓝莓不同品种果实与种子特性的比较分析 [J]. 北方园艺, 2021(20):47−52. WANG X M, ZHAO H F, WU W L, et al. Comparison and analysis of fruit and seed characteristics of different blueberry cultivars [J]. Northern Horticulture, 2021(20): 47−52.(in Chinese)
[7] 吕真真, 焦中高, 刘慧, 等. 不同制汁方式对石榴酒品质的影响 [J]. 果树学报, 2020, 37(12):1941−1952. DOI: 10.13925/j.cnki.gsxb.20200212 LÜ Z Z, JIAO Z G, LIU H, et al. Effect of different juicing methods on quality of pomegranate wines [J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2020, 37(12): 1941−1952.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13925/j.cnki.gsxb.20200212
[8] 周琪. GA3处理对葡萄果实水分及发育的调控机理研究[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2021. ZHOU Q. Regulation Mechanism of GA3 treatments on Water and Development of Grape(V. vinifera L.)berry[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2021. (in Chinese)
[9] WANG J Z, GUO X L, XIAO Q, et al. Auxin efflux controls orderly nucellar degeneration and expansion of the female gametophyte in Arabidopsis [J]. The New Phytologist, 2021, 230(6): 2261−2274. DOI: 10.1111/nph.17152
[10] 付欣, 李天来, 许涛, 等. 番茄离体花柄脱落过程中生长素酰胺水解酶家族的序列特征及表达分析[EB/OL]. 北京: 中国科技论文在线(2016-12-29). http://www.paper.edu.cn/releasepaper/content/201612-593. FU X, LI T L, XU T, et al. Sequence characteristics and expression analysis of IAA-leucine resistant1-like hydrolase genes on tomato pedicel abscission in vitro. [EB/OL] Beijing: China Science and Technology Papers Online(2016-12-29). http://www.paper.edu.cn/releasepaper/content/201612-593. (in Chinese)
[11] CAMPANELLA J J, SMITH S M, LEIBU D, et al. The auxin conjugate hydrolase family of Medicago truncatula and their expression during the interaction with two symbionts [J]. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2008, 27(1): 26−38. DOI: 10.1007/s00344-007-9027-2
[12] WANG X B, MENG J R, DENG L, et al. Diverse functions of IAA-leucine resistant PpILR1 provide a genic basis for auxin-ethylene crosstalk during peach fruit ripening [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 655758. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.655758
[13] CHEN Y, XU Z H, SHEN Q, et al. Floral organ-specific proteome profiling of the floral ornamental orchid (Cymbidium goeringii) reveals candidate proteins related to floral organ development [J]. Botanical Studies, 2021, 62(1): 23. DOI: 10.1186/s40529-021-00330-9
[14] DU H Q, SHI Y H, LI D F, et al. Screening and identification of key genes regulating fall dormancy in alfalfa leaves [J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(12): e0188964. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188964
[15] LI Z F, ZHANG X G, ZHAO K K, et al. Comprehensive transcriptome analyses reveal candidate genes for variation in seed size/weight during peanut (Arachis hypogaea L. ) domestication [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 666483. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.666483
[16] FU X, SHI Z H, JIANG Y, et al. A family of auxin conjugate hydrolases from Solanum lycopersicum and analysis of their roles in flower pedicel abscission [J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 233. DOI: 10.1186/s12870-019-1840-9
[17] YU R G, WANG Y, XU L, et al. Transcriptome profiling of root microRNAs reveals novel insights into taproot thickening in radish (Raphanus sativus L. ) [J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2015, 15: 30. DOI: 10.1186/s12870-015-0427-3
[18] D’IPPOLITO S, VANKOVA R, JOOSTEN M H A J, et al. Knocking down expression of the auxin-amidohydrolase IAR3 alters defense responses in Solanaceae family plants [J]. Plant Science, 2016, 253: 31−39. DOI: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2016.09.008
[19] WANG X M, WU Y Q, HU L C, et al. Elucidation of the mechanism underlying seedless blueberry formation after GA3 treatment based on the phenotype, physiology, metabolism and transcriptome [J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2023, 311: 111781. DOI: 10.1016/j.scienta.2022.111781
[20] DE JONG M, WOLTERS-ARTS M, FERON R, et al. The Solanum lycopersicum auxin response factor 7 (SlARF7) regulates auxin signaling during tomato fruit set and development [J]. The Plant Journal:for Cell and Molecular Biology, 2009, 57(1): 160−170. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03671.x
[21] TANG N, DENG W, HU G J, et al. Transcriptome profiling reveals the regulatory mechanism underlying pollination dependent and parthenocarpic fruit set mainly mediated by auxin and gibberellin [J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(4): e0125355. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125355
[22] 张维洵, 潘小勇, 沈红斌. 基于深度学习与领域规则建模的蛋白质信号肽及其切割位点预测 [J]. 南京理工大学学报, 2020, 44(3):278−287. DOI: 10.14177/j.cnki.32-1397n.2020.44.03.004 ZHANG W X, PAN X Y, SHEN H B. Predicting protein signal peptides and their cleavage sites based on deep learning and domain rule modeling [J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2020, 44(3): 278−287.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.14177/j.cnki.32-1397n.2020.44.03.004
[23] WEIJERS D, NEMHAUSER J, YANG Z B. Auxin: Small molecule, big impact [J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2018, 69(2): 133−136. DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erx463
[24] ADAMOWSKI M, FRIML J. PIN-dependent auxin transport: Action, regulation, and evolution [J]. The Plant Cell, 2015, 27(1): 20−32. DOI: 10.1105/tpc.114.134874
[25] BLAKESLEE J J, PEER W A, MURPHY A S. Auxin transport [J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2005, 8(5): 494−500. DOI: 10.1016/j.pbi.2005.07.014
[26] DAVIES R T, GOETZ D H, LASSWELL J, et al. IAR3 encodes an auxin conjugate hydrolase from Arabidopsis [J]. The Plant Cell, 1999, 11(3): 365−376. DOI: 10.1105/tpc.11.3.365




 下载:
下载: