Condition Optimization for Leucaena leucocephala Seedling Growth in Factory
-
摘要:目的 探明银合欢幼苗在植物工厂中水培的最优生长条件,为生产优质的银合欢苗奠定基础。方法 分析不同光照时长(12、16、20、24 h·d−1)、光照强度(100、200、300、400 μmol·m−2·s−1)、营养液盐度(7‰、15‰、20‰、25‰)、氮浓度(7.5、15、30、60 mmol·L−1)和磷浓度(0.5、1、2、4 mmol·L−1)下银合欢幼苗的形态和生理指标,优化银合欢幼苗的生长条件。结果 单因素试验结果表明,随着光照时长、光照强度、氮浓度或磷浓度的增加,银合欢幼苗的形态指标呈现先增后降的趋势。幼苗定植35 d后,在光照时长20 h·d−1下幼苗鲜重(5.61±0.11) g·株−1,比12、24 h·d−1分别增加60.0%和14.6%;光强200 μmol·m−2·s−1下鲜重(6.55±0.10) g·株−1,比100、400 μmol·m−2·s−1分别增加21.5%和62.1%;氮浓度15 mmol·L−1下鲜重(4.32±0.10) g·株−1,比7.5、60 mmol·L−1分别增加6.1%和108.6%;磷浓度1 mmol·L−1下鲜重(5.65±0.21) g·株−1,比0.5、4 mmol·L−1分别增加40.9%和64.7%。银合欢幼苗的叶绿素含量、叶绿素荧光参数和抗氧化酶活性也表现出相似的规律。相比之下,随着营养液盐度的增加,银合欢幼苗的形态指标、叶绿素含量、叶绿素荧光参数和抗氧化酶活性均呈现下降趋势。在盐度7‰时鲜重、干重、株高、根长和总叶绿素含量均达到最大值,分别为(8.95±0.05) g·株−1、(2.16±0.16) g·株−1、(31.17±1.67) cm、(60.67±0.93) cm、(1.72±0.06) mg·g−1。7‰盐度下幼苗的叶绿素荧光参数和抗氧化酶活性指标也较好。结论 银合欢幼苗在光照时长20 h·d−1、光强200 μmol·m−2·s−1、盐度7‰、氮浓度15 mmol·L−1、磷浓度1 mmol·L−1 的条件下,其形态指标、叶绿素含量、抗氧化酶活性及叶绿素荧光参数等指标较优,最适合银合欢幼苗生长。Abstract:Objective Optimal conditions for the growth of Leucaena leucocephala seedlings in an indoor facility were studied.Methods Selected morphological and physiological indices of L. leucocephala seedlings were monitored for the optimization in a chamber under varied light exposures (i.e., 12, 16, 20, and 24 h·d−1) with the intensity of 100, 200, 300, or 400 μmol·m−2·s−1 in a nutrient solution of a salinity of 7‰, 15‰, 20‰, or 25‰, a N concentration of 7.5, 15, 30, or 60 mmol·L−1, and a P concentration of 0.5, 1, 2, or 4 mmol·L−1.Results The single factor experiment showed the seedling morphological indices increased at first and then decreased with increasing light exposure, light intensity, N or P concentration. After 35 d of cultivation, the average fresh weight of an individual seedling exposed to 20 h·d−1 of light reached (5.61±0.11) g, which was 60.0% higher than that exposed to 12 h·d−1 or 14.6% higher than that exposed to 24 h·d−1. The intensity of light at 200 μmol·m−2·s−1 resulted in a (6.55±0.10) g·plant−1 of fresh seedling, which was 21.5% or 62.1% higher than at 100 μmol·m−2·s−1 or 400 μmol·m−2·s−1, respectively. The nutrient solution containing 15 mmol·L−1 N yielded a fresh seedling weight of (4.32±0.10) g·plant−1, which was 6.1% and 108.6% higher than those at 7.5 and 60 mmol·L−1, respectively, in concentration. Whereas P at 1 mmol·L−1, the fresh seedling weight was (5.65±0.21) g·plant−1, which was 40.9% and 64.7% higher than P at 0.5 mmol·L−1 and 4 mmol·L−1, respectively. And the seedlings exhibited similar patterns under those conditions on chlorophyll content, chlorophyll fluorescence parameters, and antioxidant enzyme activities. On the other hand, the seedlings growing under an increasing salinity displayed decreasing trends on the morphological indices, chlorophyll content, chlorophyll fluorescence parameters, and antioxidant enzyme activities. At 7‰ salinity, the greatest fresh seedling weight of (8.95±0.05) g·plant−1, dry weight of (2.16±0.16) g·plant−1, plant height of (31.17±1.67) cm, root length of (60.67±0.93) cm, and total chlorophyll content of (1.72±0.06) mg·g−1 were recorded. In contrast, the chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and antioxidant enzyme activities were improved.Conclusion Under 20 h·d−1 of 200 μmol·m−2·s−1 light exposure, the growth of L. leucocephala seedlings in a nutrient solution of 7‰ salinity that contained 15 mmol·L−1 N and 1 mmol·L−1 P rendered the morphological indices, antioxidant enzyme activities, and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters superior to the other tested conditions in a nursery.
-
Keywords:
- L. leucocephala /
- plant factory /
- light /
- salinity /
- nitrogen and phosphorus
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】毛竹(Phyllostachys edulis)是我国南方重要的森林资源,又名楠竹,是竹类中分布最广、面积最大、价值最高的优良竹种[1]。自然生长的毛竹林头年大量发笋长竹,第二年生鞭换叶,交替进行,每两年为一周期,如此周而复始,形成了毛竹林生长的大小年周期循环[2]。大小年毛竹林,往往只靠大年出笋成竹,小年不出笋或者很少出笋,两者隔年交替,严重影响毛竹单产的进一步提高[3]。植物是一个超级有机体,在植物表面和内部富集了数量庞大且种类繁多的微生物,植物与微生物共同进化、相互作用[4]。在长期的进化过程中,植物对微生物群落进行选择形成了植物特定的微生物群落,即微生物组[5]。微生物组在植物的生长发育、抗病、抗逆中扮演着重要的角色,而研究毛竹林大小年和微生物组的关联性对了解毛竹周年生长特性具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】植物不同生长发育阶段,微生物群落结构会发生变化,不同的微环境条件塑造了不同的微生物群落[6]。对马铃薯、甜菜和萝卜等作物研究表明,根际微生物可以通过改变土壤结构、pH以及营养物质的转化等,在植物生长、营养吸收、产量和抗病性中发挥关键作用[7-8]。【本研究切入点】国内外针对毛竹林大小年的研究多集中在大小年毛竹林本体上,认为毛竹林大小年属于生理现象,由毛竹自身营养物质积累消耗的节律变化及其内源激素在立竹个体生长中的节律变化[9],并同时受外部环境的影响而形成的,缺少毛竹林、土壤和微生物三者之间关系的研究,有关大小年毛竹林周期循环与微生物组之间变化规律的研究鲜见报道。毛竹林大小年的形成机制是否与毛竹微生物组有关联;大小年毛竹林生长与根际细菌和内生细菌群落结构变化之间是否存在驱动机制等值得探讨。【拟解决的关键问题】本文以大小年毛竹林中I、II、IV度毛竹的竹鞭、鞭根、根际土壤和林间土壤为研究对象,通过Illumina高通量测序技术研究大、小年毛竹根际细菌和内生细菌群落的结构和多样性特征,为进一步研究毛竹林大小年和微生物组的关联性提供理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 样本采集
采样地点设在福建省三明市永安市西洋镇三畲村毛竹林基地(东经117°46′,北纬25°89′),土壤类型为黄壤。在典型的大小年毛竹林地,于2020年5月(小年)、2021年5月(大年)分别采集I度(1年生)、II度(2~3年生)、IV度(6~7年生)各5株毛竹的竹鞭、鞭根、根际土壤及林间土壤共20个样本,样本编码规则见表1。选取根际土壤时,沿毛竹竹鞭挖开,顺竹鞭选取附着在鞭根上粒径小于1cm土壤作为根际土壤,并采集毛竹林间土壤作为对照。同一种样本采集后立即混合作为混合样放入无菌袋中,24 h 内放入−20 ℃保存。
表 1 样本编码规则Table 1. Sample codes毛竹类型P. edulis type 样本编码 Sample encoding 竹鞭Rhizome 鞭根Rhizome root 根际土壤Rhizosphere soil 林间土壤Forest soil 大年毛竹IOn-year P. edulis I ON.1.A5 ON.1.B5 ON.1.C5 ON.CK.C5 大年毛竹IIOn-year P. edulis II ON.2.A5 ON.2.B5 ON.2.C5 大年毛竹IVOn-year P. edulis IV ON.4.A5 ON.4.B5 ON.4.C5 小年毛竹IOff-year P. edulis I OF.1.A5 OF.1.B5 OF.1.C5 OF.CK.C5 小年毛竹IIOff-year P. edulis II OF.2.A5 OF.2.B5 OF.2.C5 小年毛竹IVOff-year P. edulis IV OF.4.A5 OF.4.B5 OF.4.C5 1.2 基因组DNA提取和16S rRNA高通量测序
用每份样本袋内的混合样提取DNA进行测序(其中组织样本经表面消毒并验证无菌),采用天根DNA提取试剂盒提取样本的基因组DNA,采用上游引物799F(5′-AACMGGATTAGATACCCKG-3′)和1193R (5′-ACGTCATCCCCACCTTCC-3′)对各样本16S rRNA基因 V5~V7可变区进行扩增。PCR体系:5 μL 10×Buffer;5 μL dNTPs(2 mmol·L−1); 1 μL DNA聚合酶;引物各1.5 μL;50 ngDNA模板;双蒸水补足50 μL。反应条件:94 ℃ 10 min;94 ℃ 30 s,56 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃ 30 s,35 个循环;72 ℃ 10 min稳定延伸。质检合格的文库利用Illumina NovaSeq测序平台,利用双末端测序(Paired-End)的方法,构建小片段文库进行测序(北京诺禾致源科技股份有限公司)。
1.3 数据分析
测序得到的原始数据处理后得到有效数据,在97%相似水平下进行 OTUs聚类和物种信息分析[10]。利用R语言工具制作样本稀释曲线[11];利用R语言工具统计后作出Venn图;采用mothur[12]软件计算Alpha多样性指数,并采用Wilxocon秩和检验进行Alpha多样性的组间差异分析,利用R语言进行NMDS统计分析和作图;利用R语言PCoA统计分析和作图;利用Qiime计算Beta多样性距离矩阵,然后用R语言作图画样本层次聚类树;基于数据库中OTU的tree和OTU上的基因信息进行PICRUSt分析,预测菌群代谢功能[13]。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 测序结果分析
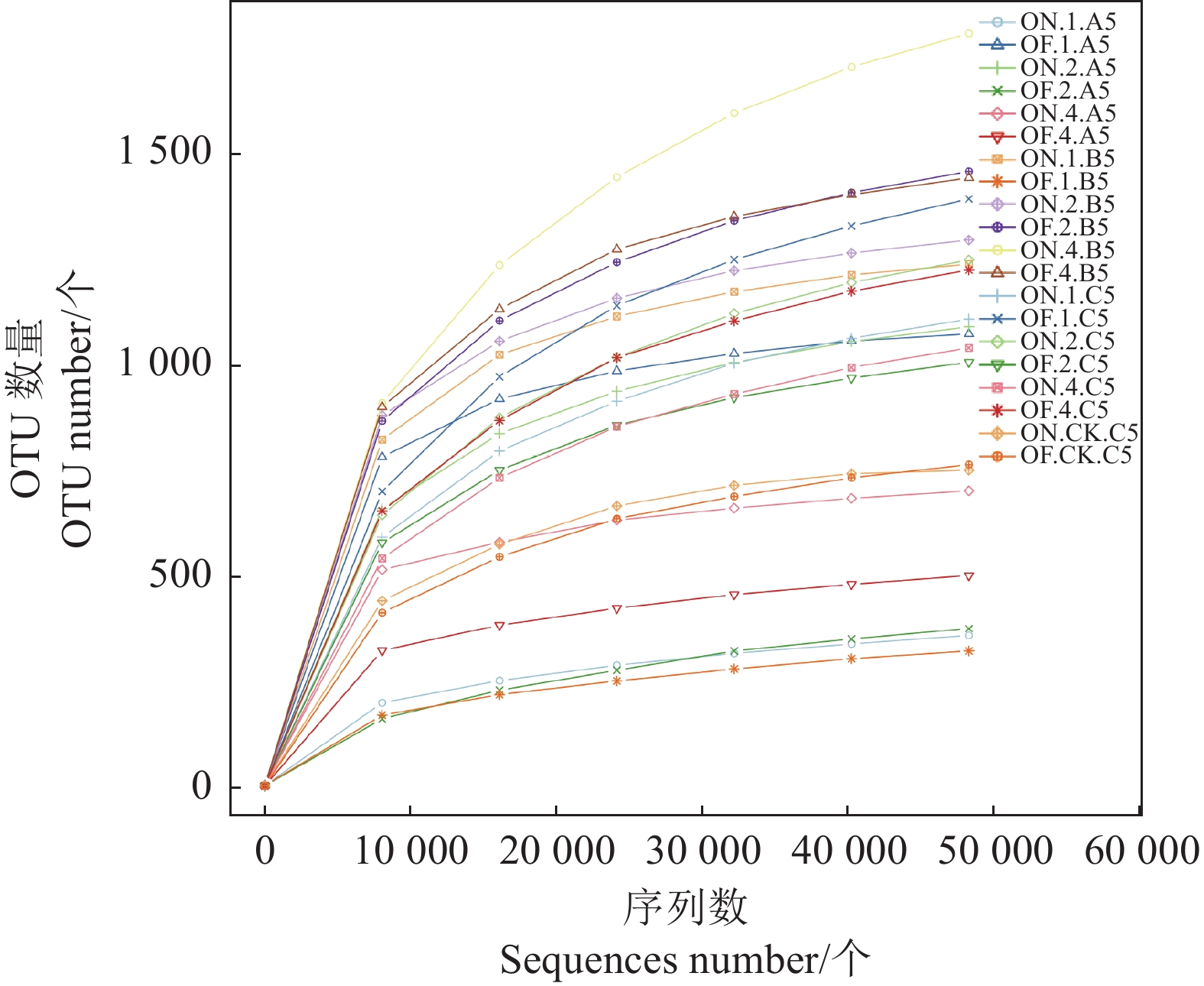
各组样本细菌16S rRNA基因高通量测序后共得到5037118条有效序列,样本测序深度为99.42%~99.92%。质控后的序列依据97%的序列相似性聚类获得细菌OTU数5802个。图1显示各组稀释曲线随着测序量的增大逐渐平缓,观测物种数趋于稳定,表明测序深度足以可靠描述毛竹和土壤样本相关的细菌微生物组。通过构建稀释曲线,表明竹鞭样本OTUs在400~1 000个饱和,鞭根样本 OTUs在1 200~1 400个饱和,根际土壤样本OTUs在1 000~1 400个 达到饱和,林间土壤样本 OTUs在750个左右达到饱和。
大小年毛竹各样本共鉴定出细菌31门、49纲、108目、212科、472属。从图2-a可以看出,I、II、IV度大、小年竹鞭样本ON.1.A5、OF.1.A5、ON.2.A5、OF.2.A5、ON.4.A5、OF.4.A5共有OTU有108个,特有OTU分别为61、424、440、42、215、67个。从图2-b可以看出,I、II、IV度大、小年鞭根样本ON.1.B5、OF.1.B5、ON.2.B5、OF.2.B5、ON.4.B5、OF.4.B5共有OTU170个,特有OTU分别为212、9、272、396、652、536个。从图2-c可以看出,I、II、IV度大、小年根际土壤样本及林间土壤样本ON.1.C5、OF.1.C5、ON.2.C5、OF.2.C5、ON.4.C5、OF.4.C5、ON.CK.C5、OF.CK.C5有269共有OTU为269个,特有OTU分别为176、382、287、133、162、312、192、104个。从各样本OTU数目可以看出,毛竹鞭根特有OTU数目随着毛竹生长而增加;毛竹小年根际土壤特有OTU数目均多于小年林间土壤样本。
2.2 细菌群落组成分析
为进一步研究大、小年毛竹根际细菌和内生细菌群落中特定分类群的变化,笔者比较了不同水平上根际细菌和内生细菌的相对丰度。
在门水平上,从图3可以看出,竹鞭和鞭根样本中优势菌门为变形菌门,而土壤样本的优势菌门为酸杆菌门。I度、II度样本在门水平的细菌群落组成上,大年和小年毛竹竹鞭样本间差异较小,而IV度毛竹的大年和小年竹鞭样本之间表现出一定差异。I度大年竹鞭在放线菌门的丰度为38.04%,大于I度小年竹鞭的22.25%;II度大年竹鞭在放线菌门和拟杆菌门的丰度为20.33%和6.46%,大于II度小年竹鞭的12.42%和1.07%;IV度大年竹鞭在放线菌门和酸杆菌门的丰度为21.54%和17.44%,大于IV度小年竹鞭的12.86%和2.57%,而IV度小年竹鞭在蓝藻菌门有较高占比为15.26%,远大于IV度大年竹鞭的0.09%。在酸杆菌门和变形菌门的丰度上,大年鞭根样本大于小年样本;而在厚壁菌门和拟杆菌门的丰度上,大年鞭根样本小于小年样本。II度毛竹大小年鞭根样本则在酸杆菌门的占比上表现出较明显的差异;林间土壤和各组根际土壤比较也有一定差异,林间土壤样本的绿弯菌门的丰度较根际土样本高。
在纲水平上,从图4可以看出,I、II、IV度的大、小年毛竹竹鞭样本之间,大年毛竹竹鞭样本在γ-变形菌纲的丰度低于小年毛竹竹鞭样本,在α-变形菌纲的丰度高于小年毛竹竹鞭样本;而IV度的大年毛竹竹鞭样本在酸杆菌纲表现出了较其他组样本更高的丰度。大小年毛竹鞭根样本之间比较,I、II、IV度的大年毛竹鞭根样本在α-变形菌纲的丰度都高于小年毛竹鞭根样本;I度、IV度大年和小年样本在纲水平的细菌群落组成的差异相似,大年样本在酸杆菌纲的丰度大于小年样本,在γ-变形菌纲和拟杆菌纲的丰度小于小年样本;而II度毛竹鞭根样本大年和小年的差异表现在酸杆菌纲。I、II、IV度的大年和小年毛竹鞭根土壤样本之间比较,在纲水平的细菌群落组成上差异不大;而林间土壤样本在α-变形菌纲的丰度略低于各组根际土壤样本。
在目水平上,从图5可以看出,I、II、IV度的大、小年毛竹竹鞭样本在目水平的细菌群落组成上,呈现的规律性较弱,可以看出大年毛竹竹鞭样本在根瘤菌目的占比都高于小年的毛竹竹鞭样本,在弗兰克氏菌目的丰富度普遍高于小年的毛竹竹鞭样本。在I、II、IV度的大小年毛竹鞭根样本中呈现的规律与毛竹竹鞭样本相同,大年的毛竹鞭根样本在根瘤菌目的丰度都高于小年的毛竹鞭根样本,在弗兰克氏菌目的丰度普遍高于小年的毛竹鞭根样本。I、II、IV度的大小年毛竹鞭根土壤样本在目水平的细菌群落组成上差异不大,而林间土壤样本和各组根际土壤样本相比,在根瘤菌目的占比较小。
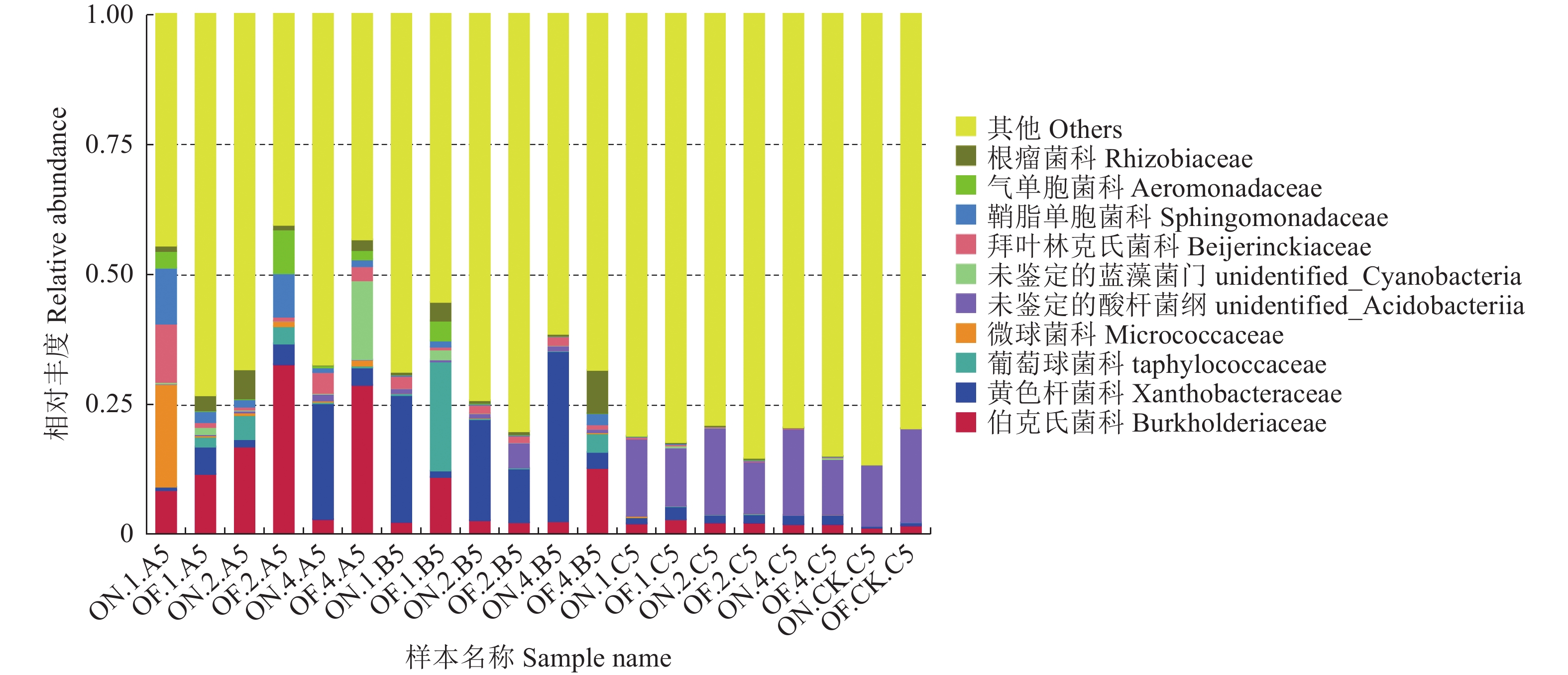
在科水平上,从图6可以看出,I、II、IV度大、小年毛竹竹鞭样本在科水平的细菌群落组成上表现出一定差异,大年的毛竹竹鞭样本在伯克氏菌科的丰富度都小于小年的毛竹竹鞭样本;I度大年毛竹竹鞭样本与其他组样本有一定差异,在微球菌科、拜叶林克氏菌科和鞘脂单胞菌科上占比较大。在毛竹鞭根样本科水平的细菌群落组成上,大年样本在黄色杆菌科的丰度都大于小年样本,I度、IV度大年毛竹鞭根样本在伯克氏菌科和葡萄球菌科的丰度小于小年样本。各组大小年毛竹鞭根土壤样本之间比较,在科水平的细菌群落组成上差异不大。
在属水平上,大小年毛竹竹鞭、鞭根和根际土壤样本细菌主要包括葡萄球菌属Staphylococcus、考克氏菌属Kocuria、慢生根瘤菌属Bradyrhizobium、甲基杆菌属Methylobacterium、鞘氨醇单胞菌属Sphingomonas、罗尔斯通菌属Ralstonia、气单胞菌属Aeromonas。从图7可以看出,大年毛竹鞭根样本在慢生根瘤菌属的丰度大于小年毛竹鞭根样本。各组大小年毛竹根际土壤样本之间比较,在属水平的细菌群落组成上差异不大。
2.3 细菌群落Alpha多样性分析
大小年毛竹的竹鞭、鞭根和土壤样本基于OTU数的Alpha多样性指数如表2所示,II度和IV度的毛竹竹鞭大年样本的细菌多样性大于小年样本,而I度毛竹竹鞭的大年样本的细菌多样性小于小年样本。毛竹鞭根样本的细菌多样性没有呈现明显规律,但总体上是大年的I度和IV度毛竹鞭根样本的细菌多样性大于小年的样本,而大年II度鞭根样本的细菌多样性小于小年样本。I度和IV度的根际土大年样本的细菌多样性小于小年样本,而II度的根际土大年样本的细菌多样性大于小年样本。毛竹根际细菌的多样性和丰度均要高于林间土壤样本。
表 2 各组样本的Alpha 多样性指数Table 2. Alpha diversity index of samples样本Sample 观测物种数/个Observed Species/piece 丰度指数ACE 香农指数Shannon 谱系多样性指数PD whole Tree 文库覆盖率Coverage/ % ON.1.A5 364 487.039 5.814 72.574 99.8 OF.1.A5 1078 1121.452 7.854 395.731 99.8 ON.2.A5 1095 1222.288 7.202 176.932 99.6 OF.2.A5 381 533.381 5.436 76.422 99.7 ON.4.A5 707 792.52 7.308 112.857 99.8 OF.4.A5 507 606.924 6.04 66.159 99.8 ON.1.B5 1243 1312.372 7.763 99.038 99.7 OF.1.B5 327 443.358 5.564 38.95 99.8 ON.2.B5 1300 1399.941 7.863 113.514 99.7 OF.2.B5 1462 1635.752 7.565 145.073 99.5 ON.4.B5 1790 2110.068 7.489 158.795 99.1 OF.4.B5 1447 1561.34 7.769 334.921 99.6 ON.1.C5 1113 1277.2 5.884 94.135 99.5 OF.1.C5 1397 1626.968 5.974 155.08 99.3 ON.2.C5 1253 1460.243 5.924 194.704 99.4 OF.2.C5 1011 1129.53 5.889 115.281 99.6 ON.4.C5 1045 1227.566 5.473 95.286 99.5 OF.4.C5 1229 1409.537 5.54 109.603 99.5 ON.CK.C5 756 756 5.776 95.302 100 OF.CK.C5 769 877.076 5.082 67.327 99.7 2.4 细菌群落Beta多样性分析
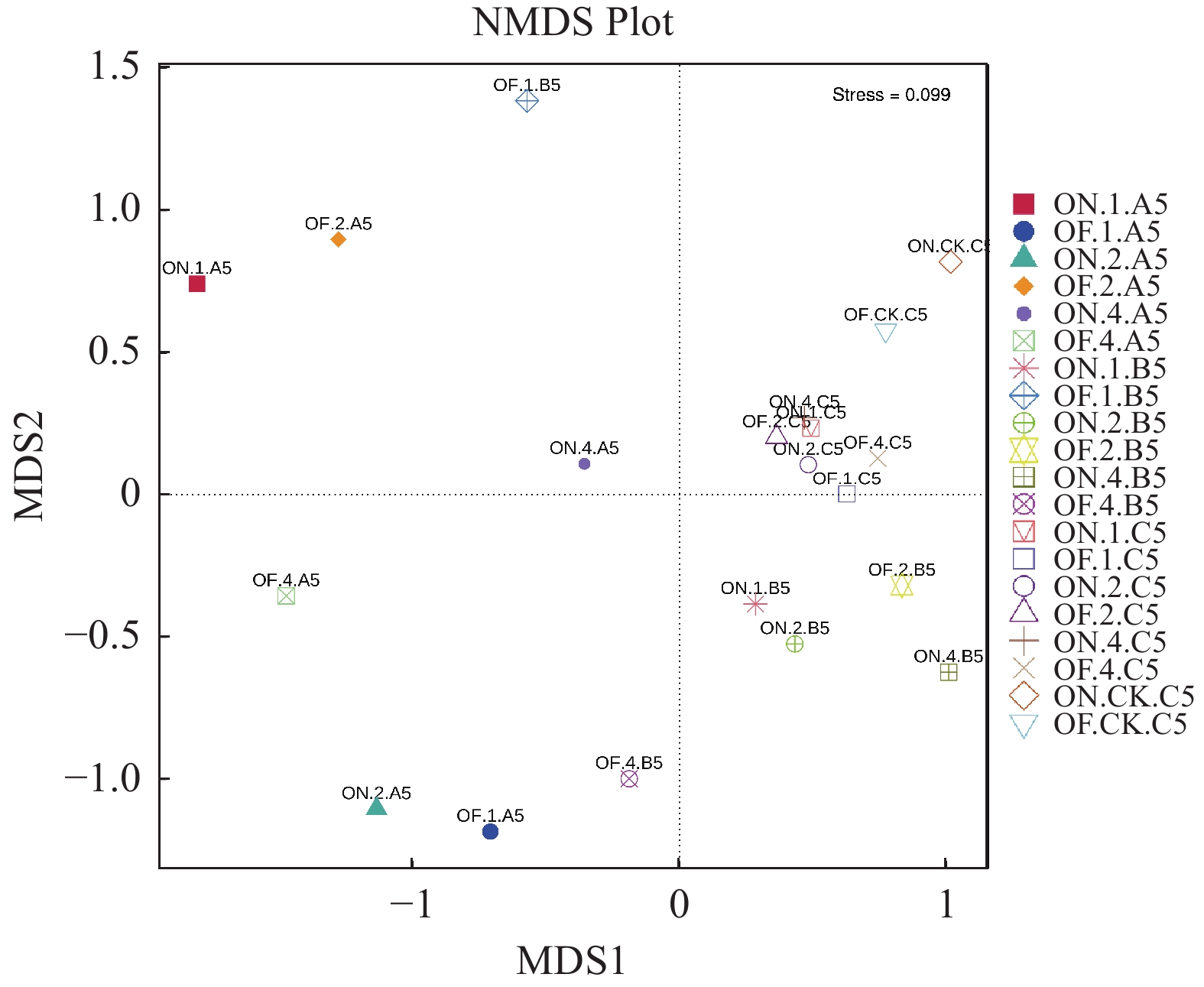
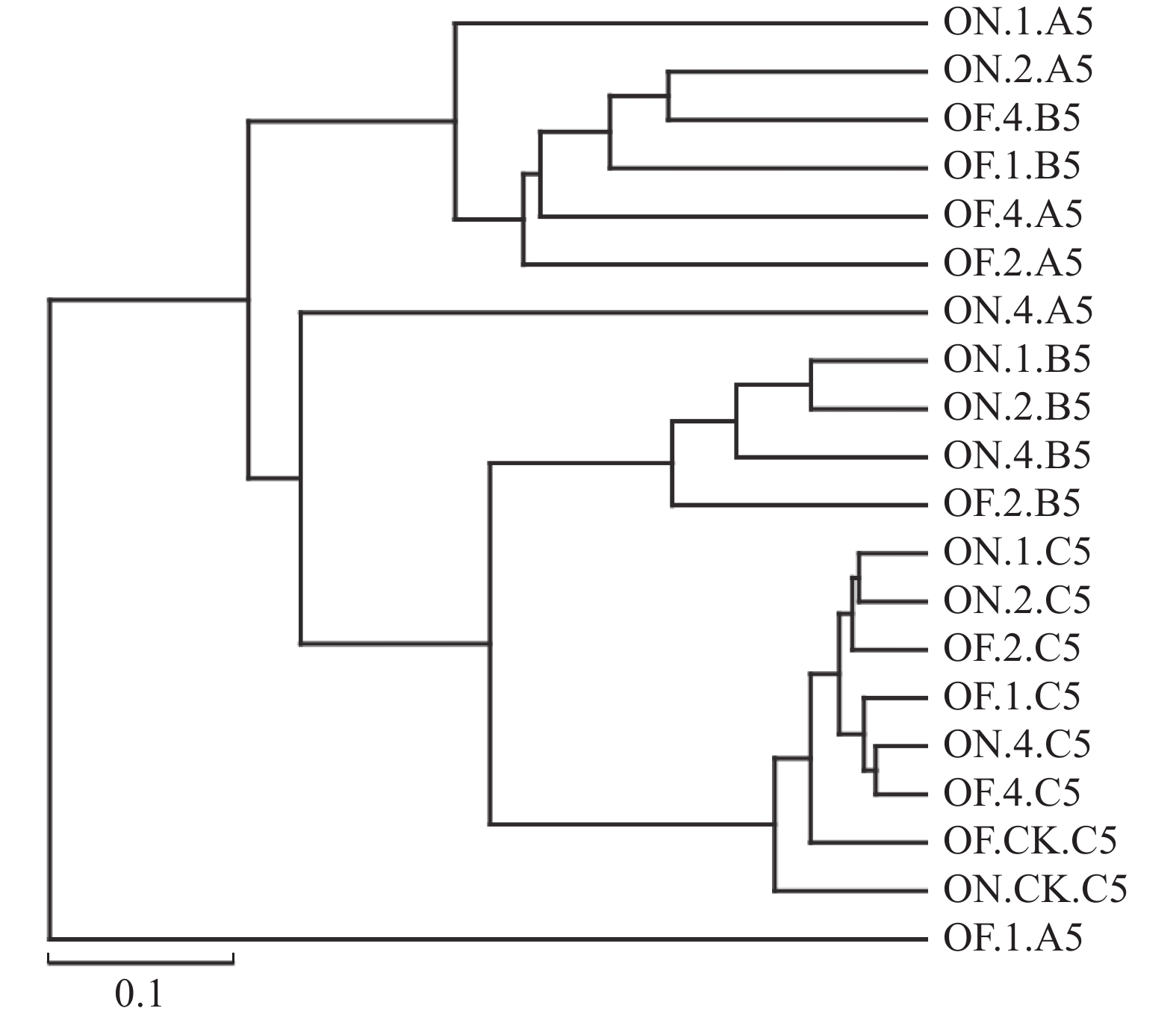
对各组样本进行NMDS分析(图8)并同时构建样本聚类树(图9)。可以看出,大小年毛竹的竹鞭样本之间距离较远,说明存在差异,即不同竹龄的大、小年毛竹竹鞭的细菌群落组成结构存在差异。大小年毛竹的鞭根样本间趋向于聚集但并不紧密,说明样本间有一定差距但差距较小。大小年毛竹的根际土壤样本紧密聚集,说明各样本群落组成较为相似,而与林间土壤样本存在一定距离,说明毛竹根部对土壤的细菌群落组成有一定选择作用。从图9可以看出,样本聚类树显示大年毛竹竹鞭和鞭根样本与小年毛竹竹鞭和鞭根样本之间呈现不同程度的区分。大小年毛竹的根际土壤样本之间区分不明显,而根际土壤样本与林间土壤样本有一定区分。
3. 讨论与结论
3.1 毛竹竹鞭、鞭根和根际土壤中细菌群落的差异
OTU数量与分布显示,毛竹鞭根内生细菌的特有OTU数目随着毛竹生长而增加,鞭根内生细菌共有的OTU数目明显多于竹鞭共有的OTU数目,毛竹根际土壤特有OTU数目要普遍多于林间土壤,小年I度根鞭土壤的特有OTU 最多,小年林间土壤的特有OTU数目最少,说明不同竹龄的毛竹对细菌的影响不同,鞭根的生长产生一定的有机质,为细菌创造了有利的生存环境,使细菌富集[14-16]。
Alpha多样性指数显示,毛竹根际细菌的多样性与丰富度都要高于林间土壤,说明毛竹鞭根根际为土壤细菌创造了有利的生存环境。Beta多样性分析显示,根际土壤样本与林间土壤样本有一定区分,这与禾本科的根际微生物研究结果一致[17-19]。大小年毛竹的根际土壤样本聚集紧密,而与林间土壤样本存在一定距离,表明随着毛竹的生长,毛竹根部分泌物逐步沉积造成根际土壤有机质成分与林间土的不同改变了某些细菌的生境,从而改变细菌的定殖能力,使根际土壤逐渐产生了高丰度的,以及特有化的微生物种群[8,20]。但大小年毛竹的根际土壤样本之间的多样性区分不明显,在细菌群落组成上差异也不大,说明根际土的细菌群落组成对毛竹大小年的形成无影响。
3.2 大小年毛竹竹鞭和鞭根内生细菌群落的优势菌群及作用
在门水平上,大年竹鞭样本在放线菌门的丰富度都要高于小年竹鞭样本,Henning等[21]研究表明,放线菌门在碳循环中起重要作用,其与有机质降解和利用相关,从而推测大年毛竹竹鞭在碳元素相关营养物质的消耗上可能要多于小年毛竹竹鞭。在纲和目水平上,大年竹鞭和鞭根样本与小年样本比较,主要优势菌群为弗兰克氏菌目和α-变形菌纲下属的根瘤菌目;多项研究证明,根瘤菌目具有固氮功能,参与生态系统中氮的修复[22-23], 变形菌的丰度也与植株的营养条件成正比,它能在细菌群落的建立中起关键作用[24-25]。同时弗兰克氏菌是一类能够与木本植物共生结瘤固氮的放线菌[26],其可修复植株在逆境下对氮元素的吸收[27]。这两类菌群可能有利于大年毛竹根际土中氮元素的循环。而在科水平上,小年毛竹竹鞭和鞭根样本细菌在伯克氏菌科的丰富度都要高于大年毛竹竹鞭和鞭根样本。伯克氏菌被认为是一种植物促生菌,其在生物固氮和促进植物生长方面发挥重要作用[28-29]。所以本研究推测大年毛竹和小年毛竹的竹鞭和鞭根在养分吸收方面相关联的主要菌群不同。
3.3 大小年毛竹竹鞭和鞭根内生细菌群落组成的差异
从本研究的数据分析可以看出,大年和小年毛竹的竹鞭和鞭根样本细菌群落组成存在差异,且I度、II度和IV度毛竹在差异上也有所不同。细菌定殖虽是一个动态过程,但健康的毛竹能在不同时期能选择合适的细菌占据毛竹组织的定殖生态位[30-31],因此造成不同时期细菌群落组成差异。但本研究具有一定的局限性,有关大年和小年毛竹的竹鞭和鞭根样本细菌群落差异与大小年之间是否存在耦合机理,是否受竹龄影响等的具体规律还有待进一步研究。
综上,本研究对I度、II度、IV度大小年毛竹的竹鞭、鞭根和根际细菌群落组成进行了分析,比较了不同水平上细菌群落的相对丰度,找到一定差异规律,分析了差异菌群的相关作用,并推测大、小年毛竹的竹鞭和鞭根在养分吸收方面的主要菌群不同。本研究有助于研究毛竹林大年和小年的竹鞭和鞭根细菌群落及根际细菌的差异特征,为进一步研究毛竹林大小年和细菌群落的关联性提供理论基础。但毛竹相关细菌群落和养分吸收之间的具体关系,以及与毛竹竹龄相互影响的规律尚不明晰,有待进一步研究。
-
表 1 银合欢在不同光照时长下的表观生长指标和生理指标
Table 1 Growth and physiological indices of Leucaena leucocephala under different light duration
参数 Parameters 光照时长 Duration of light/(h·d−1) 12 16 20 24 鲜重 Fresh weight/(g·株−1) 3.54±0.22 d 4.14±0.06 c 5.66±0.11 a 4.94±0.13 b 干重 Dry weight/(g·株−1) 0.57±0.05 c 0.81±0.03 b 1.13±0.06 a 0.92±0.08 b 株高 Shoot height/(cm·株−1) 17.00±0.58 a 13.33±0.60 b 11.17±0.44 c 10.43±0.09 c 根长 Root length/(cm·株−1) 23.00±1.00 c 38.50±0.29 a 30.50±0.50 b 24.50±0.76 c 总叶绿素 Total chlorophyll/ (mg·g−1) 0.94±0.08 b 1.09±0.14 ab 1.30±0.06 a 1.26±0.09 a 叶绿素a Chlorophyll a/(mg·g−1) 0.76±0.07 b 0.89±0.08 ab 1.04±0.08 a 1.01±0.07 a 叶绿素b Chlorophyll b/(mg·g−1) 0.18±0.01 a 0.19±0.07 a 0.26±0.01 a 0.25±0.01 a 超氧化物歧化酶 SOD/(U·g−1) 564.7±1.6 c 572.9±3.5 c 582.7±1.4 b 590.2±1.6 a 过氧化物酶 POD/(U·g−1) 242.5±6.6 c 600.1±30.5 b 680.3±20.8 b 823.7±39.8 a 丙二醛 MDA/(nmol·g−1) 12.63±0.69 b 12.49±1.36 b 12.44±0.93 b 16.69±1.34 a 非光化学淬灭系数 NPQ 0.21±0.05 b 0.20±0.02 b 0.21±0.03 b 0.50±0.03 a 光化学效率 Fv/Fm 0.68±0.01 c 0.75±0.01 a 0.71±0.01 b 0.61±0.01 d 光化学淬灭系数 qP 0.78±0.02 b 0.88±0.02 a 0.88±0.01 a 0.79±0.03 b 电子传递速率 ETR 37.40±0.68 ab 41.10±0.43 a 39.62±1.19 a 33.97±2.22 b 同行不同小写字母代表不同处理之间显著差异(P <0.05),下同。Datas with different lowercase letters on the same row represent significant differences between treatments (P < 0.05). Same for below. 表 2 银合欢在不同光照强度下的表观生长指标和生理指标
Table 2 Growth and physiological indices of L. leucocephala under different light intensities
参数 Parameters 光照强度 Light intensity/(μmol·m−2·s−1) 100 200 300 400 鲜重 Fresh weight/(g·株−1) 5.39±0.22 b 6.55±0.10 a 6.41±0.07 a 4.04±0.15 c 干重 Dry weight/(g·株−1) 1.16±0.08 bc 1.52±0.12 a 1.26±0.05 b 0.94±0.04 c 株高 Shoot height/(cm·株−1) 14.27±0.14 a 14.07±0.22 a 12.77±0.40 b 12.90±0.47 b 根长 Root length/(cm·株−1) 35.33±2.77 a 36.93±1.88 a 34.67±2.09 a 34.17±0.44 a 总叶绿素 Total chlorophyll/ (mg·g−1) 1.38±0.08 b 1.80±0.10 a 1.28±0.06 b 1.25±0.05 b 叶绿素a Chlorophyll a/ (mg·g−1) 1.12±0.06 b 1.44±0.08 a 1.03±0.03 b 0.97±0.07 b 叶绿素b Chlorophyll b/ (mg·g−1) 0.26±0.02 a 0.36±0.02 a 0.25±0.07 a 0.28±0.04 a 超氧化物歧化酶 SOD/(U·g−1) 562.6±6.9 a 559.5±3.1 a 560.4±4.9 a 569.4±2.2 a 过氧化物酶 POD/(U·g−1) 482.6±13.3 c 761.9±25.5 b 815.4±22.6 b 960.7±28.8 a 丙二醛 MDA/(nmol·g−1) 22.98±0.86 a 21.97±1.26 a 21.69±1.16 a 22.40±1.92 a 非光化学淬灭系数 NPQ 0.34±0.02 c 0.38±0.02 bc 0.42±0.01 ab 0.48±0.01 a 光化学效率 Fv/Fm 0.79±0.01 a 0.75±0.01 b 0.70±0.01 c 0.68±0.01 d 光化学淬灭系数 qP 0.87±0.01 a 0.80±0.01 b 0.79±0.02 b 0.51±0.01 c 电子传递速率 ETR 67.13±3.61 bc 76.51±3.13 ab 84.35±1.73 a 60.46±2.99 c 表 3 银合欢在不同盐度下的表观生长指标和生理指标
Table 3 Growth and physiological indices of L. leucocephala at different salinities
参数 Parameters 盐度 Salinity/‰ 7 15 20 25 鲜重 Fresh weight/(g·株−1) 8.95±0.05 a 7.94±0.14 b 4.44±0.38 c 2.33±0.15 d 干重 Dry weight/(g·株−1) 2.16±0.16 a 1.58±0.03 b 0.90±0.02 c 0.32±0.01 d 株高 Shoot height/(cm·株−1) 31.17±1.67 a 24.83±0.44 b 19.00±0.50 c 12.17±0.33 d 根长 Root length/(cm·株−1) 60.67±0.93 a 47.67±1.36 b 26.40±0.90 c 19.17±1.48 d 总叶绿素 Total chlorophyll/(mg·g−1) 1.72±0.06 a 1.64±0.11 ab 1.44±0.06 b 1.09±0.01 c 叶绿素a Chlorophyll a/(mg·g−1) 1.35±0.05 a 1.29±0.03 a 1.16±0.05 b 0.88±0.01 c 叶绿素b Chlorophyll b/(mg·g−1) 0.38±0.01 a 0.35±0.10 a 0.29±0.01 a 0.21±0.01 a 超氧化物歧化酶 SOD/(U·g−1) 584.3±4.0 a 578.8±9.3 a 576.0±8.7 a 565.1±7.4 a 过氧化物酶 POD/(U·g−1) 476.9±12.0 b 567.1±14.1 a 483.2±7.9 b 469.1±9.4 b 丙二醛 MDA/(nmol·g−1) 11.51±0.41 b 14.33±1.71 b 19.94±1.48 a 20.49±1.60 a 非光化学淬灭系数 NPQ 0.19±0.04 b 0.27±0.06 b 0.87±0.07 a 1.07±0.14 a 光化学效率 Fv/Fm 0.79±0.01 a 0.77±0.01 a 0.77±0.01 a 0.72±0.01 b 光化学淬灭系数 qP 0.87±0.04 a 0.80±0.01 a 0.80±0.03 a 0.79±0.02 a 电子传递速率 ETR 44.61±2.20 a 41.43±0.16 a 35.47±2.04 b 32.66±2.06 b 表 4 银合欢在不同氮浓度下的表观生长指标和生理指标
Table 4 Growth and physiological indices of L. leucocephala at different nitrogen concentrations
参数 Parameters 氮浓度 Nitrogen concentration/(mmol·L−1) 7.5 15 30 60 鲜重 Fresh weight/(g·株−1) 4.07±0.08 a 4.32±0.10 a 3.38±0.13 b 2.07±0.13 c 干重 Dry weight/(g·株−1) 0.66±0.01 b 0.84±0.05 a 0.56±0.05 b 0.38±0.02 c 株高 Shoot height/(cm·株−1) 15.13±0.23 b 21.73±0.89 a 15.83±0.17 b 10.67±0.84 c 根长 Root length/(cm·株−1) 27.17±1.09 a 27.67±0.44 a 27.00±4.31 a 24.73±0.62 a 总叶绿素 Total chlorophyll/(mg·g−1) 1.23±0.01 b 1.33±0.08 ab 1.46±0.03 a 1.28±0.03 b 叶绿素a Chlorophyll a/(mg·g−1) 0.99±0.01 b 1.07±0.07 ab 1.17±0.02 a 1.04±0.03 b 叶绿素b Chlorophyll b/(mg·g−1) 0.24±0.01 b 0.26±0.01 b 0.29±0.01 a 0.24±0.01 b 超氧化物歧化酶 SOD/(U·g−1) 534.8±4.3 a 555.0±3.8 a 534.2±7.4 a 530.2±13.4 a 过氧化物酶 POD/(U·g−1) 529.3±4.9 b 487.7±12.6 bc 468.9±3.9 c 591.2±25.8 a 丙二醛 MDA/(nmol·g−1) 14.21±1.31 a 13.92±1.01 a 16.19±1.31 a 16.12±0.09 a 非光化学淬灭系数 NPQ 0.52±0.03 a 0.38±0.02 b 0.51±0.02 a 0.51±0.04 a 光化学效率 Fv/Fm 0.70±0.01 b 0.76±0.01 a 0.69±0.01 b 0.68±0.01 c 光化学淬灭系数 qP 0.91±0.01 a 0.92±0.01 a 0.70±0.02 c 0.77±0.02 b 电子传递速率 ETR 38.30±0.71 c 60.67±0.29 a 39.60±0.30 c 42.71±1.28 b 表 5 银合欢在不同磷浓度下的表观生长指标和生理指标
Table 5 Growth and physiological indices of L. leucocephala at different phosphorus concentrations
参数Parameters 磷浓度 Phosphorus concentration/(mmol·L−1) 0.5 1 2 4 鲜重 Fresh weight/(g·株−1) 4.01±0.24 b 5.65±0.21 a 4.04±0.16 b 3.43±0.22 b 干重 Dry weight/(g·株−1) 0.71±0.05 b 0.98±0.05 a 0.69±0.05 bc 0.54±0.05 c 株高 Shoot height/(cm·株−1) 13.33±0.84 b 15.63±0.58 a 15.27±0.39 ab 11.07±0.58 c 根长 Root length/(cm·株−1) 36.20±0.35 a 37.57±1.10 a 32.50±0.58 b 32.47±1.50 b 总叶绿素 Total chlorophyll/(mg·g−1) 1.53±0.07 b 1.87±0.11 a 1.58±0.07 b 1.56±0.05 b 叶绿素a Chlorophyll a/(mg·g−1) 1.23±0.05 b 1.44±0.05 a 1.25±0.04 b 1.23±0.04 b 叶绿素b Chlorophyll b/(mg·g−1) 0.29±0.04 a 0.42±0.08 a 0.33±0.05 a 0.34±0.01 a 超氧化物歧化酶 SOD/(U·g−1) 554.0±8.22 a 571.2±8.80 a 573.8±6.22 a 567.6±6.35 a 过氧化物酶POD/(U·g−1) 661.0±6.9 b 807.2±16.5 a 828.2±34.8 a 604.6±12.0 b 丙二醛 MDA/(nmol·g−1) 17.96±0.6 a 18.68±0.4 a 18.70±1.6 a 19.17±0.2 a 非光化学淬灭系数 NPQ 0.56±0.05 b 0.38±0.02 c 0.56±0.04 b 1.25±0.08 a 光化学效率 Fv/Fm 0.76±0.01 a 0.77±0.01 a 0.70±0.01 b 0.46±0.01 c 光化学淬灭系数 qP 0.71±0.03 b 0.84±0.01 a 0.62±0.02 c 0.76±0.01 b 电子传递速率 ETR 39.91±2.69 b 54.09±0.60 a 37.11±2.43 b 24.20±0.62 c -
[1] 赵英, 陈小斌, 蒋昌顺. 我国银合欢研究进展 [J]. 热带农业科学, 2006, 26(4):55−58,63. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2196.2006.04.019 ZHAO Y, CHEN X B, JIANG C S. Advances on studies of Leucaena Bentham in China [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 2006, 26(4): 55−58,63.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2196.2006.04.019
[2] GRAAMANS L, BAEZA E, VAN DEN DOBBELSTEEN A, et al. Plant factories versus greenhouses: Comparison of resource use efficiency [J]. Agricultural Systems, 2018, 160: 31−43. DOI: 10.1016/j.agsy.2017.11.003
[3] 崔羽, 严思维, 吴建召, 等. 不同林龄银合欢生长季土壤呼吸影响因素分析 [J]. 武夷学院学报, 2018, 37(9):31−38. CUI Y, YAN S W, WU J Z, et al. Analyzing the factors that affect soil respiration during the growing season in Leucaena leucocephala (Lam.) de wit [J]. Journal of Wuyi University, 2018, 37(9): 31−38.(in Chinese)
[4] 徐文栋, 李春兰. 密闭式植物工厂内大黄育苗技术研究 [J]. 南方农机, 2022, 53(12):25−27,31. XU W D, LI C L. Study on seedling raising technology of Dahuang in closed plant factory [J]. South Agricultural Machinery, 2022, 53(12): 25−27,31.(in Chinese)
[5] 黄思杰. 植物工厂条件下不同基质对番茄产量和品质的影响[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2013. HUANG S J. Effects of different substrates on yield and quality of tomato cultivated in plant factory[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2013. (in Chinese)
[6] 苗妍秀, 曲梅, 李伟, 等. 植物工厂中不同供液方式对辣椒育苗的影响 [J]. 长江蔬菜, 2012(6):33−36. DOI: 10.3865/j.issn.1001-3547.2012.06.010 MIAO Y X, QU M, LI W, et al. Effects of different irrigation systems on pepper seedling in plant factory [J]. Journal of Changjiang Vegetables, 2012(6): 33−36.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3865/j.issn.1001-3547.2012.06.010
[7] 陈永快, 王涛, 兰婕, 等. 植物工厂内LED光调控在作物栽培中的研究进展 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(23):40−46. CHEN Y K, WANG T, LAN J, et al. Research progress of LED light regulation in plant factories in crop cultivation [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(23): 40−46.(in Chinese)
[8] 刘文科, 吴启保, 查凌雁. LED连续光照的植物生理作用及植物工厂应用策略 [J]. 照明工程学报, 2020, 31(5):5−8,21. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-440X.2020.05.002 LIU W K, WU Q B, ZHA L Y. Application strategies and physiological mechanisms of LED continuous light for plant factory with artificial light [J]. China Illuminating Engineering Journal, 2020, 31(5): 5−8,21.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-440X.2020.05.002
[9] 季延海. 韭菜营养液栽培的关键技术[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2014. JI Y H. The key technology of nutrient solutions cultivation of Chinese chives[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese)
[10] 刘青. 营养液配方对盆栽水芹生长和品质的影响[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2020. LIU Q. Effect of nutrient solution formula on growth and quality of the potted water dropwort (Oenanthe javanica (Roxb) Wall. )[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2020. (in Chinese)
[11] 乔源. 氮磷钾供应对水培芹菜产量、品质及元素利用效率影响的研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2016. QIAO Y. Effects of NPK on yield, quality and element utilization efficiency of hydroponic celery[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2016. (in Chinese)
[12] 李莉萍, 应东山, 王琴飞, 等. 银合欢种子研究进展 [J]. 热带农业科学, 2014, 34(2):21−26. LI L P, YING D S, WANG Q F, et al. Research progress of Leucaena seeds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Agriculture, 2014, 34(2): 21−26.(in Chinese)
[13] 蔡克强, 黄维南. 银合欢幼苗根瘤固氮特性研究 [J]. 植物生理学通讯, 1986(3):35−37. CAI K Q, HUANG W N. Nitrogen fixation characteristics of nodules of Acacia seedlings [J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 1986(3): 35−37.(in Chinese)
[14] 杨韡韡. 矿山废弃地生态修复技术与效应研究——以河南省鲁山县某铁矿区为例[D]. 郑州: 华北水利水电学院, 2012. YANG W W. Ecological restoration technology and effect research of abandoned mines ——Take an iron mining area in Lushan Countyof Henan Province for example[D]. Zhengzhou: North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power, 2012. (in Chinese)
[15] 过聪, 关伟, 曾祥国, 等. 不同营养液配方对水培白蝴蝶合果芋的影响 [J]. 湖北农业科学, 2020, 59(23):87−93. GUO C, GUAN W, ZENG X G, et al. Influence of different nutrient solution formulations on hydroponic Syngonium podoopphyllum cv. White Butterfly [J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 59(23): 87−93.(in Chinese)
[16] LU T, YU H J, LI Q, et al. Improving plant growth and alleviating photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative stress from low-light stress with exogenous GR24 in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L. ) seedlings [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 10: 490. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00490
[17] VENISSE J S, PAULIN J P, RISSET M N. Mechanisms underlying disease and resistance in host plants of fire blight [J]. Acta Hortic, 2002, 590(72): 467−468.
[18] LACAN D, BACCOU J C. High levels of antioxidant enzymes correlate with delayed senescence in nonnetted muskmelon fruits [J]. Planta, 1998, 204(3): 377−382. DOI: 10.1007/s004250050269
[19] 王学奎. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 2版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006. [20] 刘杰, 胡笑涛, 王文娥, 等. 光强和光周期对水培生菜光合及叶绿素荧光特性的影响 [J]. 西南农业学报, 2019, 32(8):1784−1790. LIU J, HU X T, WANG W E, et al. Effects of light intensity and photoperiod on photosynthetic characteristics and chlorophyll fluorescence of hydroponic lettuce [J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 32(8): 1784−1790.(in Chinese)
[21] 闫晓花, 郁继华. LED补光对温室黄瓜幼苗抗衰老及抗氧化酶系统的影响 [J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(2):392−398. YAN X H, YU J H. Effects of supplemental LED light on photosynthetic pigment contents and antioxidant enzyme activities of cucumber seedling leaves [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2016, 36(2): 392−398.(in Chinese)
[22] HALLIDAY K J, MARTÍNEZ-GARCÍA J F, JOSSE E M. Integration of light and auxin signaling [J]. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 2009, 1(6): a001586.
[23] 张悦. 不同光质、光照强度及光周期对苦苣生长特性及营养品质的影响[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2021. ZHANG Y. Effects of different light quality, light intensity and photoperiod on growth characteristics and nutritional quality of chicory[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2021. (in Chinese)
[24] ALAM M, KHAN M A, IMTIAZ M, et al. Indole-3-Acetic Acid Rescues Plant Growth and Yield of Salinity Stressed Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.) [J]. Gesunde Pflanzen, 2020, 72: 87−95. DOI: 10.1007/s10343-019-00489-z
[25] MADANI S M, PIRI S, SEDAGHATHOOR S. The response of three mandarin cultivars grafted on sour orange rootstock to salinity stress [J]. International Journal of Fruit Science, 2022, 22(1): 264−274. DOI: 10.1080/15538362.2022.2036669
[26] BHUTTA T S, ZAFAR-UL-HYE M, SHAABAN M, et al. Influence of plant growth promoting rhizobacterial inoculation on wheat productivity under soil salinity stress [J]. Phyton, 2019, 88(2): 119. DOI: 10.32604/phyton.2019.06570
[27] GERAMI M, MAJIDIAN P, GHORBANPOUR A, et al. Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni responses to salt stress and chitosan elicitor [J]. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants:an International Journal of Functional Plant Biology, 2020, 26(5): 965−974. DOI: 10.1007/s12298-020-00788-0
[28] SAYYAD-AMIN P, JAHANSOOZ M R, BORZOUEI A, et al. Changes in photosynthetic pigments and chlorophyll-a fluorescence attributes of sweet-forage and grain sorghum cultivars under salt stress [J]. Journal of Biological Physics, 2016, 42(4): 601−620. DOI: 10.1007/s10867-016-9428-1
[29] JAYAWARDENA D M, HECKATHORN S A, BOLDT J K. Effects of Elevated Carbon Dioxide and Chronic Warming on Nitrogen (N)-Uptake Rate, -Assimilation, and -Concentration of Wheat [J]. Plants (Basel)., 2020, 9(12): 1689.
[30] CECHIN I, DE FÁTIMA F T. Effect of nitrogen supply on growth and photosynthesis of sunflower plants grown in the greenhouse [J]. Plant Science, 2004, 166(5): 1379−1385. DOI: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.01.020
[31] CHEN J, LIU S D, ZHANG S P, et al. Nitrogen modulates cotton root morphology by affecting abscisic acid (ABA) and salicylic acid (SA) content [J]. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 2021, 67(12): 1722−1738. DOI: 10.1080/03650340.2020.1807518
[32] FORNARI E Z, GAVIRAGHI L, BASSO C J, et al. Relationship between photosynthetic pigments and corn production under nitrogen sources [J]. Pesquisa Agropecuária Tropical, 2020, 50: 1−9.
[33] CHEN G, WANG L, FABRICE M R, et al. Physiological and nutritional responses of pear seedlings to nitrate concentrations [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018: 1679.
[34] CRUZ J L, MOSQUIM P R, PELACANI C R, et al. Photosynthesis impairment in cassava leaves in response to nitrogen deficiency [J]. Plant and Soil, 2003, 257(2): 417−423. DOI: 10.1023/A:1027353305250
[35] ZANGANI E, AFSAHI K, SHEKARI F. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Addition to Soil Improves Seed Yield, Foliar Stomatal Conductance, and the Photosynthetic Response of Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) [J]. Agriculture., 2021, 11(6): 483. DOI: 10.3390/agriculture11060483
[36] TU P F, DENG L S, LI J, et al. Effect of phosphorus on N, P, K, Mg accumulation and plant growth of different citrus rootstocks [J]. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 2018, 16(1): 819−836. DOI: 10.15666/aeer/1601_819836
[37] JOHNSON N C. Responses of Salsola kali and Panicum virgatum to mycorrhizal fungi, phosphorus and soil organic matter: implications for reclamation [J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 1998, 35: 86−94. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2664.1998.00277.x
[38] SOBCZAK A, KOWALCZYK K, GAJC-WOLSKA J, et al. Growth, yield and quality of sweet pepper fruits fertilized with polyphosphates in hydroponic cultivation with LED lighting [J]. Agronomy, 2020, 10(10): 1560. DOI: 10.3390/agronomy10101560
[39] CETNER M D, KALAJI H M, BORUCKI W. Phosphorus deficiency affects the I-step of chlorophyll a fluorescence induction curve of radish [J]. Photosynthetica, 2020, 58(2): 671−681.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 张清,项春铸,田佳怡,江明君,房翠莲,李全,曹婷婷,宋新章. 毛竹篼根和鞭根解磷细菌对磷添加的响应. 应用生态学报. 2025(01): 284-292 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘志中. 促生菌作用下的毛竹根系分泌物对土壤微生物的影响研究. 佳木斯大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(10): 172-175 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)
计量
- 文章访问数: 479
- HTML全文浏览量: 172
- PDF下载量: 15
- 被引次数: 2




 下载:
下载: