Prodigiosin-producing Genes in Serratia plymuthica ACCC 02146
-
摘要:目的 鉴定影响普城沙雷氏菌ACCC 02146产灵菌红素能力的基因,构建ACCC 02146的转座子突变体文库,为进一步研究普城沙雷氏菌ACCC 02146灵菌红素合成机制奠定基础。方法 采用平板划线法从菌种保藏中心购买菌株和实验室保藏菌株中获得15株产灵菌红素的菌株。采用16S rRNA基因测序法鉴定各菌株,邻接建树将其分类,并比较不同类别菌株灵菌红素合成基因簇启动子序列差异,观察各菌株产色能力。对16S rDNA序列和灵菌红素合成基因簇启动子序列均有异于其他菌株的普城沙雷氏菌ACCC 02146合成灵菌红素的调控基因展开研究。构建ACCC 02146的转座子突变体文库,筛选出产色能力明显改变的克隆子并鉴定出对应的转座子插入突变基因。结果 该突变体文库中有74个突变体表现出产灵菌红素能力的变化。其中25个突变体转座子插入发生在pigA、pigB、pigC、pigD和pigH 等5个灵菌红素合成簇基因上,49个突变体转座子插入基因为灵菌红素合成基因簇之外的基因。在鉴定到的产色能力改变的突变体中,麦芽糖O-乙酰基转移酶基因突变菌株有6个,二氢乳清酸脱氢酶基因突变菌株有4个,MarR家族转录因子SlyA基因突变体有3个,winged helix家族的双组分转录调控因子RstA基因突变体有3个,H-醌氧化还原酶亚基I基因突变菌株有3个,NADH-醌氧化还原酶G链基因突变菌株有3个,肽基脯氨酰异构酶B基因突变菌株有3个,其他突变基因对应的克隆子数量为1~2个。结论 在沙雷氏菌中,除了灵菌红素合成簇基因调控灵菌红素合成,推测灵菌红素合成簇外编码相关酶、转录调控因子和一些结构蛋白的基因通过直接或间接途径在不同程度上调控了灵菌红素的合成。Abstract:Objective Genes relating to prodigiosin synthesis in Serratia plymuthica ACCC 02146 were identified, and a transposon mutant library on the strain constructed.Methods Fifteen prodigiosin-producing microbes were obtained from a conservation center and a laboratory. After identification by 16S rRNA gene sequencing, they were classified according to the neighbor-joining trees. Promoter sequences of prodigiosin synthesis gene were analyzed, and color producing capacity of the individual strains evaluated. Selected strain was cloned and further studied to establish a library on the transposon mutants.Results Differed from other strains in terms of 16S rDNA and promoter sequences of the prodigiosin biosynthesis gene clusters, S.plymuthica ACCC 02146 was selected to clone the candidate gene for further investigation. A transposon mutant library was constructed subsequently. In the library, of 74 mutants showing significant variations in prodigiosin-producing ability, 25 had the insertions in pigA, pigB, pigC, pigD, and pigH, while 49 in the genes outside the cluster. On color formation, 6 strains with the mutation on maltose o-acetyltransferase gene, 4 on dihydroorotate dehydrogenase gene, 3 on MarR family of transcription factor SlyA genes, 3 on two-component transcriptional regulator RstA of the winged helix family, 3 on NAD(P)H-quinone oxidoreductase subunit I gene, 3 on NADH-quinone oxidoreductase, chain G gene, 3 on peptidylprolyl isomerase B gene, and one to two on other genes were found possibly related to significant alterations on the prodigiosin production as well.Conclusion Aside from the identified specific clusters of prodigiosin synthesis-associated genes, additional factors in the forms of enzymes, transcriptional regulators, and/or structural proteins were now speculated to also directly or indirectly contribute in varying degrees to the prodigiosin synthesis in Serratia sp.
-
Keywords:
- Serratia marcescens /
- prodigiosin /
- transposon /
- mutant library /
- regulatory gene
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】灵菌红素族(Prodigiosins)是一类具有甲氧基吡咯环骨架结构的天然色素[1],是由沙雷氏菌属(Serratia sp.)、放线菌属(Actinomycetes)、假单胞菌属(Pseudomonas)、链霉菌属(Streptomyces)等产生的次级代谢产物,根据其侧链基团结构的不同,可分为灵菌红素(Prodigiosin,PG)、十一烷基灵菌红素(Undecylprodigiosin,UPG)、间环丙菌素(Metacycloprodigiosin,MPG)、环丙烷灵菌红素(Cycloprodigiosin,CPG)和壬烷基灵菌红素(Nonylprodigiosin,NPG)等系列结构类似物[2]。灵菌红素对酸碱性敏感,在碱性条件下易分解,在酸性条件下可较长时间保存[3]。灵菌红素是一种脂溶性色素,难溶于水,易溶于甲醇、乙醇、乙醚、氯仿等有机溶剂[4]。灵菌红素对多种癌细胞具有抑制作用[5,6],还具有免疫抑制[7]、抗细菌[8]、抗真菌[9]、抗疟疾[10]、抗原生动物[11]、染色[12]和除藻[13,14]等多种功能。因此,对灵菌红素的深入研究有重要的应用价值。合成灵菌红素的能力受多种内外因素影响,外在因素包括培养基组分、发酵温度和pH等;内在因素为灵菌红素合成基因簇相关酶的活性和多种基因的调控。相关调控基因的鉴定和调控机制的阐明有助于发现细菌新的次生代谢产物合成调控机制,从而应用基因工程技术提升菌株灵菌红素的产量。【前人研究进展】沙雷氏菌合成菌红素是由两个分叉途径组成,这两个途径合成了两个前体物质2-甲基-3-n-戊基吡咯(2-methyl-3-n-amyl pyrrole,MAP)和4-甲氧基-2-2′-双吡咯-5-甲醛(4-methoxy-2-2′-dipyrrolid-5-formaldehyde,MBC),再由MAP和MBC缩合生成灵菌红素[15]。灵菌红素生物合成由pigA–pigN共14个编码基因共同参与,将这14个编码基因称为pig基因簇。其中,2-辛烯醛作为起始前体用来合成MAP,在pigD、pigB和pigE的催化下氧化脱氢形成MAP;MBC的合成是以L-脯氨酸为起始底物,在基因pigA、pigF、pigG、pigH、pigI、pigJ、pigK、pigL、pigM和pigN的作用下通过一系列酶促反应合成MBC[16]。在沙雷氏菌中,灵菌红素的合成也受到其他转录调控因子的直接或间接调控,包括灵菌红素合成负调控因子MetR[17]、SpnR[18]和SmaR[19],以及正调控因子EepR[20]、RbsR[21]和PigP[22]等。【本研究切入点】但是,有关沙雷氏菌转录调控因子和其他基因参与灵菌红素合成的调控机制还有待深入研究。【拟解决的关键问题】经测序与比对,普城沙雷氏菌ACCC 02146在16S rDNA序列和pig基因簇启动子序列上均与已广泛研究的产灵菌红素沙雷氏菌有较大区别,怀疑该菌株合成灵菌红素的调控机制可能也与已报道菌株有所区别。因此,建立普城沙雷氏菌ACCC 02146的转座子突变体库,鉴定该菌株参与调控灵菌红素合成的基因,为进一步提升沙雷氏菌产灵菌红素能力提供理论参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 供试材料
1.1.1 菌株及培养条件
供试菌株为15株沙雷氏菌,FZSF02、S1、S2和S3菌株来源于本实验室,CICC 23703、CICC 23838、CICC 24478、CICC 10698、CICC 20223和CICC 24369等菌株来源于中国工业菌种保藏中心,CCTCC AB2014323和CCTCC AB2015384来源于中国典型培养物保藏中心,ACCC 02146、ACCC 01294和ACCC 04168来源于中国农业微生物菌种保藏中心。试验所用引物由铂尚生物公司合成(表1)。如无特殊说明,黏质沙雷氏菌在27 ℃培养,使用LB培养基(酵母粉0.5%、胰蛋白胨1%、氯化钠0.5%)或者NA培养基(蛋白胨1%、牛肉膏0.3%、氯化钠0.5%),固体培养基含2%琼脂。卡那霉素工作液质量浓度为100 mg·L−1。
表 1 供试引物Table 1. Primes applied引物 Primes 序列 Sequences(5′-3′) 用途 Purpose 来源 Sources 27F AGAGTTTGATCC TGGCTCAG 16S rDNA 测序 [23] 1492R ACGGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT 16S rDNA 测序 [23] LAD1 ACGATGGACTCCAGAG(G/C/A)N(G/C/A)NNNGGAA 高效热不对称交错PCR [24] LAD3 ACGATGGACTCCAGAG(T/A/C)N(A/G/C)NNNCCAC 高效热不对称交错PCR [24] AC1 ACGATGGACTCCAGAG 高效热不对称交错PCR [24] F389 TCAAGCATTTTATCCGTACTCCTG 高效热不对称交错PCR [24] F536 CGGTTGCATTCGATTCCTGTTTGTA 高效热不对称交错PCR [24] F772 TAGGTTGTATTGATGTTGGACGAG 高效热不对称交错PCR [24] KproF GCAACACTCCGCAATCTATA 菌株ACCC 02146启动子序列 本研究 KproR CTCTATCTCCATGAAAGAGT 菌株ACCC 02146启动子序列 本研究 1.1.2 主要试剂及仪器
高保真DNA聚合酶PrimeSTAR®Max DNA Polymerase(R045A)购自宝日医生物技术(北京)有限公司;转座子突变试剂盒EZ-Tn5™ <KAN-2> TnpTransposome™ Kit(TSM99K2,Epicentre)购自北京全式金生物技术有限公司;琼脂粉购自擎科生物;3-18K超高速冷冻离心机购自德国Sigma公司;SpectraMax 190光吸收酶标仪购自Molecular Devices Corporation;PCR扩增仪购自赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司;细菌DNA提取试剂盒购自北京百泰克生物技术有限公司;电转化仪Gene Pulser Xcell购自Bio-Rad;稳压稳流电泳仪DYY-6B购自北京六一仪器厂;引物合成以及DNA测序服务均由铂尚生物公司提供。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 菌株的鉴定分类
(1)形态学观察。挑取一定量的菌落用平板划线法在NA固体培养基上活化菌株,置于27 ℃的恒温培养箱培养2 d后,肉眼和光学显微镜结合观察比较15株沙雷氏菌菌落形态和颜色。
(2)16S rDNA测序鉴定。在NA平板上活化15株灵菌红素产生菌,27 ℃培养箱培养12 h。挑取单菌落于装有1mL ddH2O的1.5 mL EP管中,吹打均匀,用细菌基因组提取试剂盒提取菌株全基因组,经琼脂糖凝胶电泳验证后作为模板。本研究使用细菌16S rRNA基因通用引物27F及1492R[23] (表1)进行PCR扩增,扩增得到的相应序列用DNAMAN软件拼接,并在BLAST(https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/)比对,MEGA5软件对测序所得序列构建进化树。PCR扩增反应程序:94 ℃ 5 min;然后94 ℃ 30 s;54 ℃ 30 s;72 ℃ 2 min,32个循环;最后72 ℃ 10 min后延伸。产物应用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳鉴定,验证后送擎科生物科技有限公司测序。
1.2.2 灵菌红素产量和菌株生长的测定
从琼脂平板上挑取一环新鲜的单菌落接入装有50 mL LB液体培养基的250 mL三角瓶中,180 r·min -1 、27 ℃恒温振荡培养箱培养12 h作为种子液。
应用比色法测定灵菌红素产量。取1 mL菌体发酵液加入4 mL酸性甲醇[V(浓盐酸)∶V(甲醇)=1.67∶500],剧烈振荡后静置10 min,8000 r·min−1离心5 min,利用酶标仪测定上清液535 nm处吸光值评价灵菌红素产量。通过测定菌株发酵液的OD600值来判断菌株的生长状况。
1.2.3 突变体库的建立
采用MEGA5邻接建树对15株沙雷氏菌进行聚类分析,并经过BLAST比对,发现沙雷氏菌ACCC 02146的灵菌红素合成基因簇启动子不同于其他14株沙雷氏菌,因此选择沙雷氏菌ACCC 02146进行突变体库的建立。37 ℃、180 r·min−1培养至 OD600值约1.0的新鲜菌液冰浴30 min,冰浴结束后转移至50 mL离心管,于4 ℃离心机中5000 r·min−1离心10 min;弃上清后用40 mL预冷的无菌水洗涤后4 ℃离心10 min,再用无菌水重复洗涤离心1次;用40 mL的冰预冷的10%甘油洗涤后,4 ℃离心10 min,重复用10%甘油洗涤离心1次;用0.5 mL 10%甘油悬浮菌体沉淀,以100 μL每管分装至1.5 mL离心管作为电转感受态细胞。
EZ-Tn5™<KAN-2> Tnp Transposome™Kit (TSM99K2)用来构建突变文库。使用0.1 cm电穿孔比色皿(Cat: 1652083, Bio-Rad)在Gene Pulser Xcell™(Bio-Rad)上进行电子脉冲操作,电穿孔参数如下:25 μF,200 Ω,1800 F。电击结束后立即将菌液转入1 mL NB液体培养基中,37 ℃、200 r·min−1振荡培养2 h。将培养液适当稀释后在涂布于含卡那霉素(100 mg·L−1)的NA琼脂平板上,27 ℃倒置培养24 h后挑选产色能力发生改变的单菌落。
1.2.4 鉴定突变体中转座子插入位点
采用高效热不对称交错PCR技术鉴定突变体转座子插入位点[25,26],引物见表1。该方法分为3个步骤。第一步反应:PCR反应总体积为20 μL,含有10 μL STAR Max DNA聚合酶(TAKARA Japan),2 μL引物F389(20 pmol),1 μL(约100 ng)基因组DNA和7 μL ddH2O;第二步反应:将第一步反应产物稀释10倍作为模板,PCR反应总反应体积为25 μL,其中12.5 μL STAR Max DNA聚合酶(TAKARA Japan),2 μL引物F536(20 pmol),0.5 μL引物LAD1(5 pmol),0.5 μL引物LAD3(5 pmol),1 μL模板以及8.5 μL ddH2O;第三步反应:将第二步反应产物稀释50倍作为模板,PCR反应总体积为25 μL,其中12.5 μL STAR Max DNA聚合酶(TAKARA Japan),1 μL引物F772(10 pmol),1 μL引物LAC1(10 pmol),1 μL稀释后的PCR产物作为模板,9.5 μL ddH2O。反应程序如下:第一步反应程序为98 ℃ 10 s;58 ℃或60 ℃ 5 s,72 ℃ 30 s,20个循环。将第一步反应产物稀释10倍,作为第二步反应的模板,第二步反应程序为98 ℃ 10 s,68 ℃ 5 s,72 ℃ 1 min;然后98 ℃ 10 s,25 ℃ 15 s,72 ℃ 1 min;最后98 ℃ 10 s,58 ℃ 5 s,72 ℃ 30 s,45个循环。将第二步反应产物稀释50倍,作为第三步反应的模板,第三步反应程序为98 ℃ 10 s,60 ℃ 5 s,72 ℃ 30 s,98 ℃ 10 s,56 ℃ 5 s,72 ℃ 30 s,98 ℃ 10 s,52 ℃ 5 s,72 ℃ 30 s,12个循环。
PCR产物经1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测后送铂尚福州测序部进行测序,将测序结果在BLAST(https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/)比对以鉴定转座子插入基因及插入位置。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 菌株的分子生物学鉴定及分类
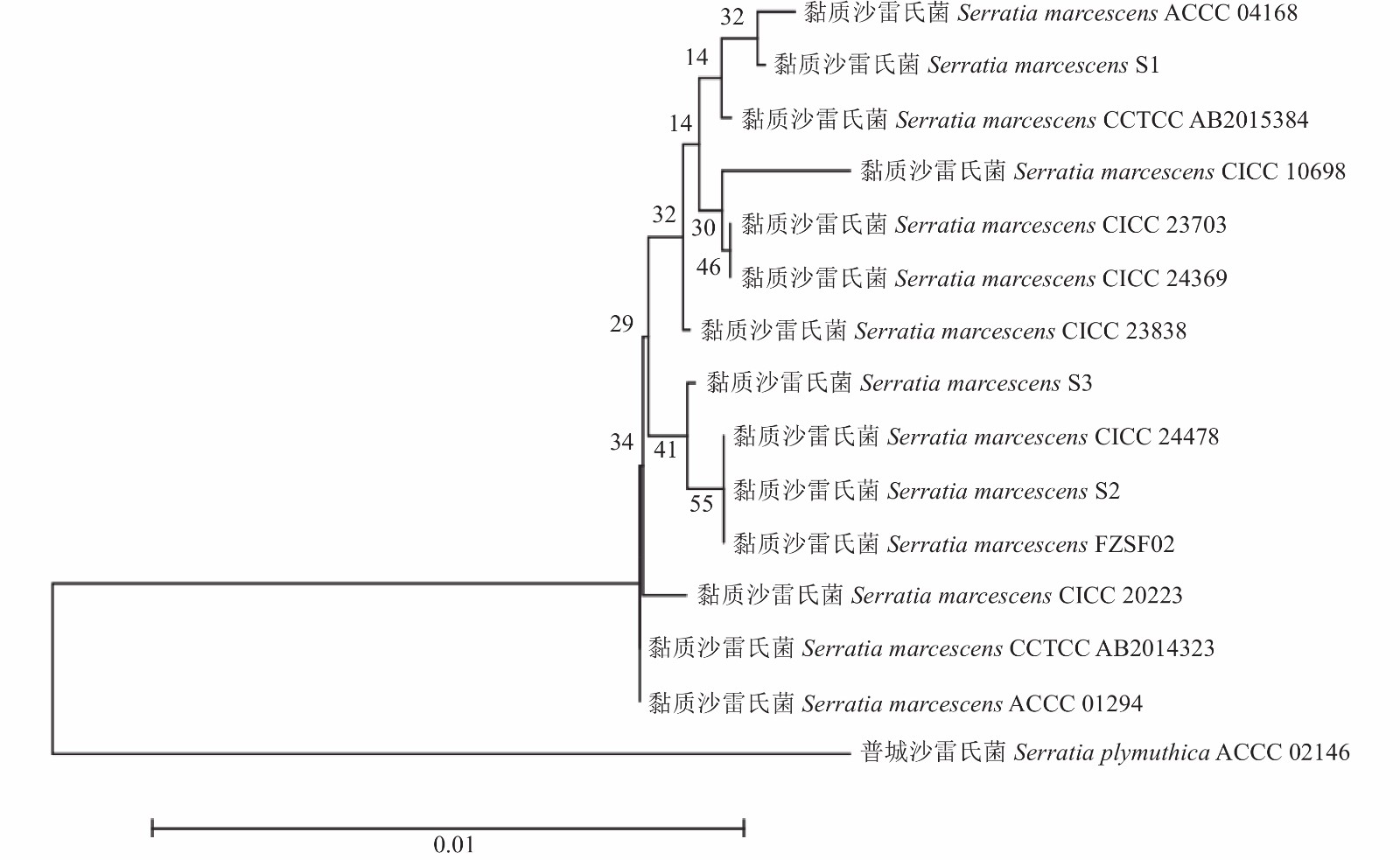
15株具有灵菌红素合成能力的沙雷氏菌属菌株16S rDNA序列经BLAST比对可知,与菌株ACCC 02146序列同源性最高菌株属于普城沙雷氏菌Serratia plymuthica,同源性达99.93%,其他研究菌株同源性最高的菌株都属于黏质沙雷氏菌Serratia marcescens,同源性均高达99%以上。
形态学鉴定各菌株菌落形态特征见表2,结合形态学鉴定及16S rRNA基因序列,鉴定菌株ACCC 02146为普城沙雷氏菌Serratia plymuthica,其他菌株为黏质沙雷氏菌Serratia marcescens。MEGA5软件将所有菌株进行多序列比对,通过邻接法构建系统发育树(图1),所有菌株分为4类:第一类包括菌株ACCC 02146;第二类包括菌株ACCC 04168、S1、CCTCC AB2015384、CICC 10698、CICC 23703、CICC 24369、CICC 23838;第三类包括菌株CICC 24478、S3、S2和FZSF02;第四类包括菌株CICC 20223、CCTCC AB2014323和ACCC 01294。其中菌株ACCC 02146与其他菌株同源性最低。
表 2 菌落形态特征Table 2. Colony morphology菌株编号
Strain No.菌落形态特征
Colony morphology characteristicsFZSF02 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,红色 S1 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,红色 S2 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,红色 S3 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,红色 CICC 23703 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,深红色 CICC 23838 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,红色 CICC 24478 圆形凸起,表面干燥粗糙,红色 CICC 10698 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,橙红色 CICC 20223 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,橙色 CICC 24369 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,深红色 CCTCC AB2014323 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,深红色 CCTCC AB2015384 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,红色 ACCC 02146 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,橙红色 ACCC 01294 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,深红色 ACCC 04168 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,深红色 2.2 各菌株灵菌红素合成能力比较
经不同温度试验发现15株沙雷氏菌产灵菌红素最适温度均为27 ℃。在27 ℃温度条件下,S2菌株产灵菌红素量比已报道的黏质沙雷氏 FZSF02更高[27],且其产灵菌红素能力最强;普城沙雷氏菌ACCC 02146 产灵菌红素能力高于黏质沙雷氏 CCTCC AB2015384、CICC 10698、 CICC 23838、CCTCC AB2014323、CICC 23703、S1和CICC 20223菌株,低于黏质沙雷氏S2、ACCC 01294、ACCC 04168、S3、CICC 24369和CICC 24478菌株,黏质沙雷氏S1和CICC 20223菌株的产灵菌红素能力最差(图2)。
2.3 构建普城沙雷氏菌ACCC 02146的EZ-Tn5突变文库
应用EZ-Tn5转座子构建了转座子突变体库,平板划线法筛选到74个表现出产色能力变化的突变体。其中有25株突变基因位于灵菌红素合成基因簇,剩余49个突变体对应的插入突变基因位于灵菌红素合成基因簇外部,对应基因及其插入位点见表3。挑选31株分别对应31个不同突变基因的菌株进行灵菌红素合成能力和菌株生长能力检测。在27°C LB液体培养基中培养36 h后,测定各突变菌株的灵菌红素产量(535 nm处 OD值)和菌量(600 nm 处OD值)(表3)。
表 3 突变体产灵菌红素能力及其菌量Table 3. Prodigiosin synthesis capabilities and quantity of S.plymuthica mutant基因登录号
Gene accession number突变体(基因长度/插入位点)
Mutant (gene length/insertion site)/bp功能
FunctionOD600 OD600
改变倍数
OD600 fold changeOD535 OD535改变倍数
OD535 fold
changeOD535改变倍数/
OD600改变倍数
OD535 fold change/
OD600 fold change普城沙雷氏菌 ACCC 02146 2.540 1.000 0.213 1.000 1.000 AEG27540.1 B5-10 (2 673/1 075), B9-2 (2 673/
1 274), B6-4 (2 673/1 075), B6-6
(2 673/792), B5-6 (2 673/792),
B2-11 (2 673/1 266), B5-9 (2 673/153)利用磷酸烯醇式丙酮酸酶(PigC) 2.880 1.134↑ 0.005 0.023↓ 0.020 AEG27539.1 B5-1 (2 601/2 116),B8-1 (2 601/2 096), B7-5 (2 601/1 099), B7-6 (2 601/1 099), B7-11 (2 601/1 338), B9-4 (2 601/2 072), B9-5 (2 601/2 071) 假设蛋白(PigD) 2.644 1.041↑ 0.005 0.023↓ 0.022 AEG27535.1 B7-7 (1 971/1 905), B7-1 (1 971/1 905) 甘氨酸C-乙酰转移酶(PigH) 2.600 1.025↑ 0.015 0.070↓ 0.068 AEG27542.1 B5-12 (1 161/195), B5-13 (1 161/794), B6-8 (1 161/35), B7-8 (1 161/35), B9-1 (1 161/35) 异戊酰基-辅酶A脱氢酶(PigA) 2.731 1.075↑ 0.004 0.019↓ 0.02 AEG27541.1 B5-2 (2 031/1 865), B5-11 (2 031/
1 865), B6-7 (2 031/1 865), B7-12
(1 161/35)富马酸还原酶/琥珀酸脱氢酶黄蛋白结构域蛋白(PigB) 2.665 1.049↑ 0.012 0.056↓ 0.053 AEG30298.1 F5-7 (558/202), F5-4 (558/524), F5-10 (558/273), F5-5 (558/518), F5-6 (558/495), F5-9 (558/189) 麦芽糖O-乙酰转移酶 2.618 1.031↑ 0.037 0.174↓ 0.169 AEG29267.1 H8-8 (978/910), H8-9 (978/262), H9-8 (978/217) H-醌氧化还原酶亚基1 2.355 0.927↓ 0.245 1.150↑ 1.241 AEG27501.1 H7-1 (1 011/842), H7-4 (1 011/425), H9-3 (1 011/378), H9-6 (1 011/234) 二氢乳清酸脱氢酶 1.967 0.774↓ 0.589 2.765↑ 3.572 AEG29268.1 H9-8 (2 748/217), H7-5 (2 748/2 682), H7-9 (2 748/2 041) NADH-醌氧化还原酶G链 2.216 0.872↓ 0.243 1.140↑ 1.307 AEG26904.1 B9-3 (495/290), B7-2 (495/290), B7-3 (495/290) 肽基脯氨酰异构酶B 3.827 1.507↑ 0.008 0.038↓ 0.025 AEG26553.1 H8-12 (1 800/1 017), H7-3 (1 800/1 236) 亚硫酸盐还原酶(NADPH)黄蛋白α组分 2.646 1.042↑ 0.269 1.263↑ 1.212 AEG29408.1 H9-5 (1 728/1 484), H7-11 (1 728/1 484) 磷酸烯醇丙酮酸蛋白磷酸转移酶Ptsl 2.660 1.047↑ 0.574 2.695↑ 2.574 AEG29263.1 H8-4 (1 848/189), H9-1 (1 848/853) NADH-醌氧化还原酶亚基L 2.473 0.974↓ 0.231 1.085↑ 1.114 AEG27032.1 H6-5 (390/192) 琥珀酸脱氢酶,细胞色素b556亚基 1.758 0.692↓ 0.230 1.080↑ 1.561 AEG29294.1 H9-10 (1 518/1 085) 氨基磷酸核糖转移酶 2.317 0.912↓ 0.273 1.282↑ 1.406 AEG27629.1 H9-9 (1 047/533) 二氢乳清酸酶 2.164 0.852↓ 0.231 1.085↑ 1.273 AEG27038.1 H8-3 (1 167/336) 琥珀酰辅酶a合成酶(ADP形成)β亚基 2.230 0.878↓ 0.282 1.324↑ 1.508 AEG27031.1 H8-5 (1 293/402), H8-2 (1 293/0) 柠檬酸合成酶I 2.052 0.808↓ 0.333 1.563↑ 1.934 AEG29271.1 H8-7 (1 797/618) NADH-醌氧化还原酶亚基C/D 2.542 1.001↑ 0.293 1.376↑ 1.375 AEG26076.1 H7-7 (1 284/606) 磷酸核糖胺-甘氨酸连接酶 2.579 1.015↑ 0.239 1.122↑ 1.105 AEG30581.1 F4-1 (1 785/73) ATP结合蛋白 2.640 1.040↑ 0.052 0.244↓ 0.235 AEG26238.1 B5-3 (630/624) 假设蛋白ALQ63_03 824 1.416 0.557↓ 0.01 0.047↓ 0.084 AEG29272.1 H7-6 (675/317) H-醌氧化还原酶亚基K 2.342 0.922↓ 0.285 1.338↑ 1.451 AEG27034.1 H7-8 (1 710/1 665), H9-7 (1 710 /1 352) 琥珀酸脱氢酶或富马酸还原酶黄蛋白亚基 1.603 0.631↓ 0.055 0.258↓ 0.409 AEG27939.1 B4-1 (435/109), B6-3 (435/109), B6-5 (435/108) MarR家族转录调控因子SlyA 2.712 1.068↑ 0.006 0.028↓ 0.026 AEG28365.1 F4-4 (849/38), F4-2 (849/36), F4-3 (849/38) winged helix家族双组分转录调控因子RstA 2.71 1.067↑ 0.039 0.183↓ 0.172 AEG30425.1 H8-1 (633/262) cAMP激活的全局转录调控因子CRP,转录调控因子Crp/Fnr家族 2.243 0.883↓ 0.860 4.038↑ 4.573 AEF52 157.1 H7-14 (267/3) FAD装配因子SdhE 2.737 1.078↑ 0.259 1.216↑ 1.128 AEG27490.1 H7-10 (1 110/1 089) 孔蛋白OmpC 1.460 0.575↓ 0.585 2.746↑ 4.776 AEG26866.1 F5-12 (1 188/864) 多药外排RND转运蛋白质周适配器亚单位SdeX 2.910 1.146↑ 0.022 0.103↓ 0.090 AEG29409.1 H3-1 (510/364) 葡萄糖转运蛋白亚基IIA_ 2.234 0.880↓ 0.051 0.239↓ 0.272 下划线标注的为代表性突变体;“↑”代表升高;“↓”代表降低。
Underline indicates mutant; "↑" indicates elevation; "↓" indicates decline.本试验中,有5个灵菌红素合成基因簇基因突变后菌株合成灵菌红素能力改变,有利用磷酸烯醇式丙酮酸酶(pigC)突变体7个、假设蛋白(pigD)突变体7个、甘氨酸C-乙酰基转移酶(pigH)突变体2个、异戊酰基-辅酶A脱氢酶(pigA)突变体5个和富马酸还原酶/琥珀酸脱氢酶黄蛋白结构域蛋白(pigB)突变体5个(表3)。
灵菌红素合成簇外,参与了灵菌红素合成的调控、产灵菌红素能力改变的突变体包括麦芽糖O-乙酰基转移酶基因突变菌株6个,二氢乳清酸脱氢酶基因突变菌株4个,MarR家族转录因子SlyA基因突变体3个,winged helix家族的双组分转录调控因子RstA基因突变体3个,H-醌氧化还原酶亚基I基因突变菌株3个,NADH-醌氧化还原酶G链基因突变菌株3个,肽基脯氨酰异构酶B基因突变菌株3个,其他突变基因对应的克隆子数量为1~2个。
转座子插入到普城沙雷氏菌ACCC 02146中编码NADH-醌氧化还原酶亚基L(AEG29263.1)、磷酸核糖胺-甘氨酸连接酶(AEG26076.1)、H-醌氧化还原酶亚基1(AEG29267.1)、NADH-醌氧化还原酶G链(AEG29268.1)、FAD装配因子SdhE(AEF52157.1)、亚硫酸盐还原酶(NADPH)黄蛋白α组分(AEG26553.1)、琥珀酰辅酶a合成酶(ADP形成)β亚基(AEG27038.1)、H-醌氧化还原酶亚基K(AEG29272.1)、NADH-醌氧化还原酶亚基C/D(AEG29271.1)、氨基磷酸核糖转移酶(AEG29294.1)、柠檬酸合成酶I(AEG27031.1)、磷酸烯醇丙酮酸蛋白磷酸转移酶Ptsl(AEG29408.1)、孔蛋白OmpC(AEG27490.1)、二氢乳清酸脱氢酶(AEG27501.1)、Crp/Fnr家族转录调控因子cAMP激活的全局转录调控因子CRP(AEG30425.1)、琥珀酸脱氢酶细胞色素b556亚基(AEG27032.1)和二氢乳清酸酶(AEG27629.1)的基因中,对应突变体不同程度地增加了灵菌红素的产量,灵菌红素增加倍数见表3。
转座子插入普城沙雷氏菌ACCC 02146中编码琥珀酸脱氢酶或富马酸还原酶黄蛋白亚基(AEG27034.1)、假设蛋白ALQ63_03824(AEG26238.1)和葡萄糖转运蛋白亚基IIA(AEG29409.1)基因后,基因突变导致灵菌红素产量和菌量均下降,这些基因对应的突变体灵菌红素改变倍数和菌量改变倍数分别见表3。
普城沙雷氏菌ACCC 02146中编码利用磷酸烯醇式丙酮酸酶(AEG27540.1)、假设蛋白(AEG27539.1)、甘氨酸C-乙酰基转移酶(AEG27535.1)、异戊酰基-辅酶 A脱氢酶(AEG27542.1)和富马酸还原酶/琥珀酸脱氢酶黄蛋白结构域蛋白(AEG27541.1)肽基脯氨酰异构酶B(AEG26904.1)、ATP结合蛋白(AEG30581.1)、MarR家族转录调控因子SlyA(AEG27939.1)、winged helix家族双组分转录调控因子RstA(AEG28365.1)、多药外排RND转运蛋白质周适配器亚单位SdeX(AEG26866.1)的基因突变后灵菌红素合成能力降低,但是菌体生长能力提高,这些基因对应的突变体灵菌红素改变倍数和菌量改变倍数分别见表3。
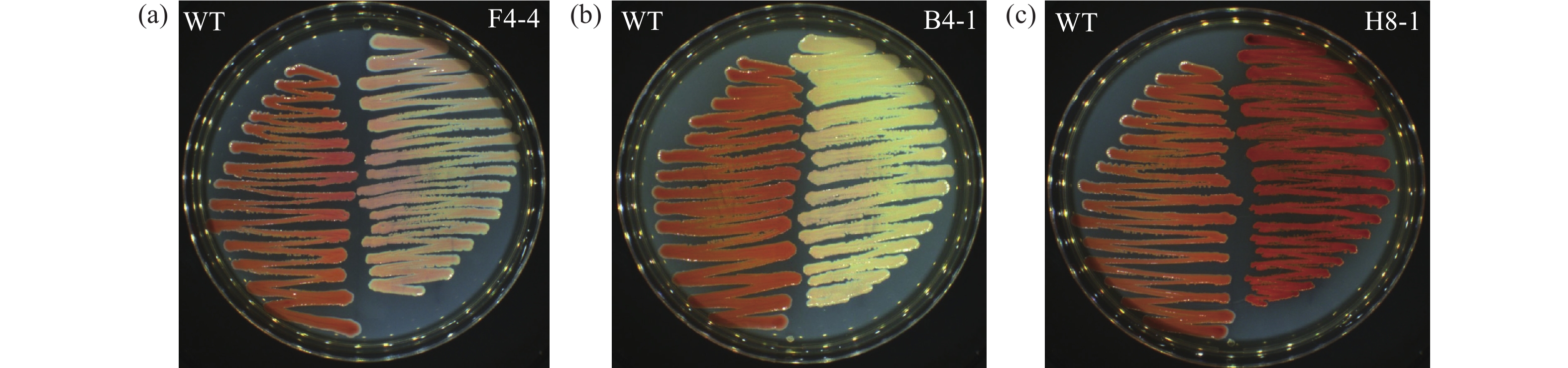
图3是本试验突变体库中出现的3种转录调控因子突变体菌落,其中突变体F4-4显示粉色,产灵菌红素能力下降;突变体B4-1显示白色,产灵菌红素能力基本消失;突变体H8-1显示深红色,产灵菌红素能力明显增加。
3. 讨论
沙雷氏菌中有众多基因调控灵菌红素合成,然而本研究发现的灵菌红素合成中起调控作用的基因尚未完全被报道。
双组分系统(TCS)是一种能够感知环境或生理信号,进而改变基因表达,使细胞适应环境的信号转导系统。通常情况下,传感器激酶感知到信号并自我磷酸化,然后将磷酸基团给反应调控子,磷酸化反应调控子调控靶基因的转录[28]。双组分调控系统在调控灵菌红素合成中起着重要作用,目前在沙雷氏菌中发现的参与调控色素合成的双组分系统有PhoB/PhoR[29]、EepR/EepS [30]、RssB/RssA [31]、PigQ/PigW[32]、CpxR/A[33]、ecrA1/ecrA2[34]、GacA/GacS[35]、BaeS/R[36]和 EnvZ/OmpR[37]。PhoB/PhoR是一种双组分体系,最初被描述为在磷限制下参与无机磷酸盐(Pi)的运输和代谢[38],通过PhoB/PhoR双组分系统会导致沙雷菌39006的次生代谢上调[39],即正向调控灵菌红素合成。EepR/EepS和PigQ/PigW双组分系统是通过效应蛋白直接与pigA上游启动子区结合激活灵菌红素合成基因簇的表达而正向调控灵菌红素合成[30,32];RssB/RssA系统通过RssB与pigA上游启动子直接结合抑制灵菌红素合成基因簇表达从而负调控灵菌红素的合成[31];CpxA的磷酸酶活性在灵菌红素的生物合成调控中起着至关重要的作用,CpxR/A通过负调控来调控灵菌红素的生物合成[33]。ecrA1/ecrA2基因对灵菌红素合成基因簇具有正调控作用[34]。GacA/GacS双组分体系调控沙雷氏菌产生表面活性剂,表面活性剂又对灵菌红素的扩散有重要作用[35]。BaeS/R双组分调控系统中BaeS是一种内膜结合的组氨酸激酶,BaeR是一种细胞质的转录因子,能在BaeS的作用下发生磷酸化,增强与DNA结合的亲和力,BaeS/R的缺失突变会导致沙雷氏菌对卡那霉素抗性的增强[36]。EnvZ/OmpR双组分调控系统通过影响整个基因簇的转录实现正调控灵菌红素的合成[37]。本研究winged helix家族双组分转录调控因子RstA在灵菌红素合成过程中起着重要的作用,Tn5转座子插入普城沙雷氏菌ACCC 02146中RstA的基因后,产灵菌红素能力明显下降,显示该转录调控因子在灵菌红素合成过程中起着正向调控的作用,该基因是本研究新发现的一个尚未报道的灵菌红素合成调控基因。
除双组分调控系统基因外,本研究发现MarR家族转录调控因子SlyA和Crp/Fnr家族转录调控因子cAMP-Crp也在灵菌红素合成过程中起着重要的作用。有报道称SlyA/MarR家族的转录调节因子Rap被认为与耶尔森菌属的全局调控因子RovA(毒性调节因子)有相似之处,是沙雷氏菌39006中次生代谢的激活因子[29],新的SlyA同系物形成了一个高度保守的亚群,在一个不断增长的细菌调节蛋白超家族中,控制着人类、动物和植物病原体的各种生理过程[40],删除转录调控因子slyA基因后,ΔslyA菌株失去了灵菌红素的合成能力,但具有更高的细胞密度[41]。本研究Tn5转座子插入到普城沙雷氏菌ACCC 02146中编码MarR家族转录调控因子SlyA基因中后,普城沙雷氏菌ACCC 02146几乎丧失合成灵菌红素的能力,MarR家族转录调控因子SlyA对沙雷氏菌产灵菌红素能力起着正转录调控的作用。富马酸盐和硝酸盐还原调节因子Fnr是结构相关转录因子扩展超家族的创始成员[42],Fnr 抑制沙雷氏菌ATCC 39006 有氧条件下的灵菌红素生产,起着负转录调控的作用[43]。本研究中Tn5转座子插入普城沙雷氏菌ACCC 02146中编码Crp/Fnr 家族cAMP激活的全局转录调控因子Crp的基因中后,突变体与野生型相比灵菌红素产量明显升高超过4倍,Crp/Fnr家族转录调控因子cAMP-Crp对沙雷氏菌产灵菌红素能力起着负转录调控的作用。
Tn5转座子插入某些编码蛋白基因,突变体显著降低了灵菌红素产量,这些基因包括编码多药外排RND转运蛋白质周适配器亚单位SdeX和琥珀酸脱氢酶或富马酸还原酶黄蛋白亚基的基因。RND蛋白家族是一类以质子驱动力(即质子进入细胞质释放的自由能转化为RND把底物排出细胞所需要的动力)为能量的外排系统,由3部分组成,包括外膜外排蛋白(OMP)、膜融合蛋白(MFP)和内膜外排蛋白(IMP),膜融合蛋白(MFP)具有一个α-螺旋发卡结构、酯域和β-桶状结构,这些结构组装成含β片段的α-螺旋柱状结构,产生一个跨整个周质空间的通道,诱导或稳定了外膜蛋白开放状态,使底物直接排到细胞外[44]。Gristwood等[45]发现黏质沙雷氏菌ATCC 39006中一个TetR家族的调节器PigZ,它通过直接与zrpA-PigZ基因间区域结合,抑制由zrp(PigZ抑制的泵)ADBC编码的RND外排泵的转录,这个假定的RND泵包含两个预测的膜融合蛋白(MFPs):ZrpA和ZrpD。一些编码结构蛋白的基因缺失后,沙雷氏菌显著提升了灵菌红素的产量,这些基因包括编码SdhE、亚硫酸盐还原酶(NADPH)黄蛋白α组分、琥珀酸脱氢酶和富马酸还原酶铁硫蛋白、孔蛋白OmpC和琥珀酸脱氢酶细胞色素b556亚基的基因。琥珀酸脱氢酶是电子传递链和三羧酸循环的重要组成部分,在琥珀酸上作为唯一的碳源生长和琥珀酸脱氢酶的功能都需要SdhE。SdhE最初被确定为一个邻近YgfX的基因,YgfX是一种灵菌红素生产的调控因子,而这些基因中的任何一个或两个的缺失都会导致灵菌红素合成操纵子的转录下降[46];大肠杆菌的亚硫酸盐还原酶具有α8β4亚单位结构,其中α8是一种黄素蛋白(SiR-FP),含有FAD和FMN两个修复基团。它还表现出NADPH黄素氧化还原酶的活性,此活性可能在核糖核苷酸还原酶的激活过程中或在铁素体的还原过程中发挥作用[47],但亚硫酸盐还原酶黄蛋白α组分在沙雷氏菌产灵菌红素过程中所起作用未有报道;有报道称铁硫蛋白特殊的结构负责氧化磷酸化中的氧化应激,它也是易被各种损伤因子攻击的靶点。琥珀酸脱氢酶铁硫蛋白功能在沙雷氏菌产灵菌红素过程中所起作用未有报道。有研究称在沙雷氏菌中缺乏孔蛋白OmpC或OmpF后对银离子的抗性是野生型菌株的3~4倍[48]。黏质沙雷氏菌对广泛抗生素具有天然耐药性,导致这种天然抗生素耐药性的一个因素是外膜通透性降低,部分受OmpF和OmpC孔蛋白控制[49],本研究中转座子插入普城沙雷氏菌ACCC 02146中编码孔蛋白OmpC的基因后,突变菌产灵菌红素能力与野生型相比得到显著提升。
一些编码代谢酶和其他酶的基因也影响着灵菌红素的生物合成。本研究中Tn5转座子插入编码H -醌氧化还原酶亚基1、NADH-醌氧化还原酶G、NADH -醌氧化还原酶亚基L、H-醌氧化还原酶亚基K和NADH -醌氧化还原酶亚基C/D的基因产生突变菌产灵菌红素能力显著提升。醌氧化还原酶1(NQO1)是一种抗氧化酶,能催化几种不同种类的醌类化合物(醌类、醌亚胺类和硝基芳烃类)的双电子还原。醌或醌类代谢物的单电子还原产生半醌,以启动氧化还原循环,负责产生活性氧和氧化应激,NADH-醌氧化还原酶1可将质子泵过线粒体内膜或许多细菌的质膜,络合物I通过氧化NADH催化电子传递的第一步,从而为醌还原为喹啉提供两个电子。络合物I中的电子转移过程与穿过内膜的4个质子的易位相耦合,从而产生电化学质子梯度[50],NADH-醌氧化还原酶是呼吸链中最大、最不为人知的酶复合体[51],转座子Tn5插入醌氧化还原酶1中,将其结构破坏,但是增加了灵菌红素的产量,但它如何影响灵菌红素的合成还不清楚。据报道二氢乳清酸脱氢酶、二氢乳清酸酶中有降低黏质沙雷氏菌合成灵菌红素能力的作用[26],但本研究中有提升普城沙雷氏菌合成灵菌红素能力的作用,二氢乳清酸脱氢酶、二氢乳清酸酶到底如何调控沙雷氏菌产灵菌红素能力还有待研究。
4. 结论
本研究发现15株产灵菌红素沙雷氏菌菌株,根据16S rDNA序列同源性分为4类,ACCC 02146与普城沙雷氏菌同源性最高,处于一个单独的分支上。灵菌红素合成基因簇启动子序列比较也发现ACCC 02146有异与其他菌株。应用Tn5转座子构建了普城沙雷氏菌ACCC 02146的突变文库,获得了74个灵菌红素合成能力发生变化的转座突变体。这些突变体中鉴定到31个参与灵菌红素合成或调控的不同基因,其中5个基因位于灵菌红素合成簇上,其他26个基因位于灵菌红素合成簇外。上述基因簇外的基因分别编码相关酶、转录调控因子和一些结构蛋白,推测这些基因通过直接或间接途径在不同程度上调控了灵菌红素的合成。本研究在基因组水平上鉴定了普城沙雷氏菌ACCC 02146潜在的灵菌红素合成调控基因,这些基因将有助于更好地了解次生代谢物灵菌红素的调控机制,为通过基因工程改造该菌株从而大规模发酵生产灵菌红素提供候选靶标基因。
-
表 1 供试引物
Table 1 Primes applied
引物 Primes 序列 Sequences(5′-3′) 用途 Purpose 来源 Sources 27F AGAGTTTGATCC TGGCTCAG 16S rDNA 测序 [23] 1492R ACGGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT 16S rDNA 测序 [23] LAD1 ACGATGGACTCCAGAG(G/C/A)N(G/C/A)NNNGGAA 高效热不对称交错PCR [24] LAD3 ACGATGGACTCCAGAG(T/A/C)N(A/G/C)NNNCCAC 高效热不对称交错PCR [24] AC1 ACGATGGACTCCAGAG 高效热不对称交错PCR [24] F389 TCAAGCATTTTATCCGTACTCCTG 高效热不对称交错PCR [24] F536 CGGTTGCATTCGATTCCTGTTTGTA 高效热不对称交错PCR [24] F772 TAGGTTGTATTGATGTTGGACGAG 高效热不对称交错PCR [24] KproF GCAACACTCCGCAATCTATA 菌株ACCC 02146启动子序列 本研究 KproR CTCTATCTCCATGAAAGAGT 菌株ACCC 02146启动子序列 本研究 表 2 菌落形态特征
Table 2 Colony morphology
菌株编号
Strain No.菌落形态特征
Colony morphology characteristicsFZSF02 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,红色 S1 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,红色 S2 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,红色 S3 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,红色 CICC 23703 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,深红色 CICC 23838 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,红色 CICC 24478 圆形凸起,表面干燥粗糙,红色 CICC 10698 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,橙红色 CICC 20223 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,橙色 CICC 24369 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,深红色 CCTCC AB2014323 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,深红色 CCTCC AB2015384 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,红色 ACCC 02146 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,橙红色 ACCC 01294 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,深红色 ACCC 04168 圆形凸起,湿润黏稠,深红色 表 3 突变体产灵菌红素能力及其菌量
Table 3 Prodigiosin synthesis capabilities and quantity of S.plymuthica mutant
基因登录号
Gene accession number突变体(基因长度/插入位点)
Mutant (gene length/insertion site)/bp功能
FunctionOD600 OD600
改变倍数
OD600 fold changeOD535 OD535改变倍数
OD535 fold
changeOD535改变倍数/
OD600改变倍数
OD535 fold change/
OD600 fold change普城沙雷氏菌 ACCC 02146 2.540 1.000 0.213 1.000 1.000 AEG27540.1 B5-10 (2 673/1 075), B9-2 (2 673/
1 274), B6-4 (2 673/1 075), B6-6
(2 673/792), B5-6 (2 673/792),
B2-11 (2 673/1 266), B5-9 (2 673/153)利用磷酸烯醇式丙酮酸酶(PigC) 2.880 1.134↑ 0.005 0.023↓ 0.020 AEG27539.1 B5-1 (2 601/2 116),B8-1 (2 601/2 096), B7-5 (2 601/1 099), B7-6 (2 601/1 099), B7-11 (2 601/1 338), B9-4 (2 601/2 072), B9-5 (2 601/2 071) 假设蛋白(PigD) 2.644 1.041↑ 0.005 0.023↓ 0.022 AEG27535.1 B7-7 (1 971/1 905), B7-1 (1 971/1 905) 甘氨酸C-乙酰转移酶(PigH) 2.600 1.025↑ 0.015 0.070↓ 0.068 AEG27542.1 B5-12 (1 161/195), B5-13 (1 161/794), B6-8 (1 161/35), B7-8 (1 161/35), B9-1 (1 161/35) 异戊酰基-辅酶A脱氢酶(PigA) 2.731 1.075↑ 0.004 0.019↓ 0.02 AEG27541.1 B5-2 (2 031/1 865), B5-11 (2 031/
1 865), B6-7 (2 031/1 865), B7-12
(1 161/35)富马酸还原酶/琥珀酸脱氢酶黄蛋白结构域蛋白(PigB) 2.665 1.049↑ 0.012 0.056↓ 0.053 AEG30298.1 F5-7 (558/202), F5-4 (558/524), F5-10 (558/273), F5-5 (558/518), F5-6 (558/495), F5-9 (558/189) 麦芽糖O-乙酰转移酶 2.618 1.031↑ 0.037 0.174↓ 0.169 AEG29267.1 H8-8 (978/910), H8-9 (978/262), H9-8 (978/217) H-醌氧化还原酶亚基1 2.355 0.927↓ 0.245 1.150↑ 1.241 AEG27501.1 H7-1 (1 011/842), H7-4 (1 011/425), H9-3 (1 011/378), H9-6 (1 011/234) 二氢乳清酸脱氢酶 1.967 0.774↓ 0.589 2.765↑ 3.572 AEG29268.1 H9-8 (2 748/217), H7-5 (2 748/2 682), H7-9 (2 748/2 041) NADH-醌氧化还原酶G链 2.216 0.872↓ 0.243 1.140↑ 1.307 AEG26904.1 B9-3 (495/290), B7-2 (495/290), B7-3 (495/290) 肽基脯氨酰异构酶B 3.827 1.507↑ 0.008 0.038↓ 0.025 AEG26553.1 H8-12 (1 800/1 017), H7-3 (1 800/1 236) 亚硫酸盐还原酶(NADPH)黄蛋白α组分 2.646 1.042↑ 0.269 1.263↑ 1.212 AEG29408.1 H9-5 (1 728/1 484), H7-11 (1 728/1 484) 磷酸烯醇丙酮酸蛋白磷酸转移酶Ptsl 2.660 1.047↑ 0.574 2.695↑ 2.574 AEG29263.1 H8-4 (1 848/189), H9-1 (1 848/853) NADH-醌氧化还原酶亚基L 2.473 0.974↓ 0.231 1.085↑ 1.114 AEG27032.1 H6-5 (390/192) 琥珀酸脱氢酶,细胞色素b556亚基 1.758 0.692↓ 0.230 1.080↑ 1.561 AEG29294.1 H9-10 (1 518/1 085) 氨基磷酸核糖转移酶 2.317 0.912↓ 0.273 1.282↑ 1.406 AEG27629.1 H9-9 (1 047/533) 二氢乳清酸酶 2.164 0.852↓ 0.231 1.085↑ 1.273 AEG27038.1 H8-3 (1 167/336) 琥珀酰辅酶a合成酶(ADP形成)β亚基 2.230 0.878↓ 0.282 1.324↑ 1.508 AEG27031.1 H8-5 (1 293/402), H8-2 (1 293/0) 柠檬酸合成酶I 2.052 0.808↓ 0.333 1.563↑ 1.934 AEG29271.1 H8-7 (1 797/618) NADH-醌氧化还原酶亚基C/D 2.542 1.001↑ 0.293 1.376↑ 1.375 AEG26076.1 H7-7 (1 284/606) 磷酸核糖胺-甘氨酸连接酶 2.579 1.015↑ 0.239 1.122↑ 1.105 AEG30581.1 F4-1 (1 785/73) ATP结合蛋白 2.640 1.040↑ 0.052 0.244↓ 0.235 AEG26238.1 B5-3 (630/624) 假设蛋白ALQ63_03 824 1.416 0.557↓ 0.01 0.047↓ 0.084 AEG29272.1 H7-6 (675/317) H-醌氧化还原酶亚基K 2.342 0.922↓ 0.285 1.338↑ 1.451 AEG27034.1 H7-8 (1 710/1 665), H9-7 (1 710 /1 352) 琥珀酸脱氢酶或富马酸还原酶黄蛋白亚基 1.603 0.631↓ 0.055 0.258↓ 0.409 AEG27939.1 B4-1 (435/109), B6-3 (435/109), B6-5 (435/108) MarR家族转录调控因子SlyA 2.712 1.068↑ 0.006 0.028↓ 0.026 AEG28365.1 F4-4 (849/38), F4-2 (849/36), F4-3 (849/38) winged helix家族双组分转录调控因子RstA 2.71 1.067↑ 0.039 0.183↓ 0.172 AEG30425.1 H8-1 (633/262) cAMP激活的全局转录调控因子CRP,转录调控因子Crp/Fnr家族 2.243 0.883↓ 0.860 4.038↑ 4.573 AEF52 157.1 H7-14 (267/3) FAD装配因子SdhE 2.737 1.078↑ 0.259 1.216↑ 1.128 AEG27490.1 H7-10 (1 110/1 089) 孔蛋白OmpC 1.460 0.575↓ 0.585 2.746↑ 4.776 AEG26866.1 F5-12 (1 188/864) 多药外排RND转运蛋白质周适配器亚单位SdeX 2.910 1.146↑ 0.022 0.103↓ 0.090 AEG29409.1 H3-1 (510/364) 葡萄糖转运蛋白亚基IIA_ 2.234 0.880↓ 0.051 0.239↓ 0.272 下划线标注的为代表性突变体;“↑”代表升高;“↓”代表降低。
Underline indicates mutant; "↑" indicates elevation; "↓" indicates decline. -
[1] PANDEY R, CHANDER R, SAINIS K B. A novel prodigiosin-like immunosuppressant from an alkalophilic Micrococcus sp. [J]. International Immunopharmacology, 2003, 3(2): 159−167. DOI: 10.1016/S1567-5769(02)00114-5
[2] 朱雄伟, 徐智鹏, 张楠, 等. 粘质沙雷氏菌代谢产物灵菌红素的鉴定 [J]. 化学与生物工程, 2012, 29(11):80−82. ZHU X W, XU Z P, ZHANG N, et al. Identification of metabolite prodigiosin of Serratia marcescens [J]. Chemistry & Bioengineering, 2012, 29(11): 80−82.(in Chinese)
[3] 袁保红, 杜青平, 蔡创华, 等. 海洋细菌Pseudomonas sp. 色素的提取及稳定性的研究 [J]. 海洋通报, 2005, 24(6):92−96. YUAN B H, DU Q P, CAI C H, et al. Study on the extraction and stability of pigments from a marine bacterium Pseudomonas sp [J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2005, 24(6): 92−96.(in Chinese)
[4] 傅奇. 灵菌红素产生菌的筛选鉴定及其发酵条件优化[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2011. FU Q. Screening and identification of prodigiosin-producing bacteria and optimization of fermentation conditions[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2011. (in Chinese)
[5] JÉRSIA ARAÚJO A, MARINHO FILHO J D B, SOUSA T S, et al. Evidences for the involvement of HER on prodigiosin anticancer effects [J]. Planta Medica, 2012, 78(11): 78−92.
[6] ZHAO C, QIU S Z, HE J, et al. Prodigiosin impairs autophagosome-lysosome fusion that sensitizes colorectal cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil-induced cell death [J]. Cancer Letters, 2020, 481: 15−23. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.03.010
[7] D'ALESSIO R, BARGIOTTI A, CARLINI O, et al. Synthesis and immunosuppressive activity of novel prodigiosin derivatives [J]. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2000, 43(13): 2557−2565. DOI: 10.1021/jm001003p
[8] 王玉洁, 孙诗清, 朱长俊, 等. 天然红色素灵菌红素的抗菌性能及应用 [J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2012, 24(11):1626−1629,1654. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6880.2012.11.027 WANG Y J, SUN S Q, ZHU C J, et al. Antibacterial property and application of natural red pigment prodigiosin [J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2012, 24(11): 1626−1629,1654.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6880.2012.11.027
[9] NAKASHIMA T, YAMAGUCHI K, ODA T, et al. Evaluation of the anti-Trichophyton activity of a prodigiosin analogue produced by γ-proteobacterium, using stratum corneum epidermis of the Yucatan micropig [J]. Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy, 2005, 11(3): 123−128. DOI: 10.1007/s10156-005-0376-0
[10] KANCHARLA P, LI Y X, YELUGURI M, et al. Total synthesis and antimalarial activity of 2-(p-hydroxybenzyl)-prodigiosins, isoheptylprodigiosin, and geometric isomers of tambjamine MYP1 isolated from marine bacteria [J]. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2021, 64(12): 8739−8754. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00748
[11] GENES C, BAQUERO E, ECHEVERRI F, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in Trypanosoma cruzi: The role of Serratia marcescens prodigiosin in the alternative treatment of Chagas disease [J]. Parasites & Vectors, 2011, 4(1): 66.
[12] KRAMAR A, ILIC-TOMIC T, PETKOVIC M, et al. Crude bacterial extracts of two new Streptomyces sp. isolates as bio-colorants for textile dyeing [J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2014, 30(8): 2231−2240. DOI: 10.1007/s11274-014-1644-x
[13] JEONG H, YIM J H, LEE C, et al. Genomic blueprint of Hahella chejuensis, a marine microbe producing an algicidal agent [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2005, 33(22): 7066−7073. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki1016
[14] ZHANG H J, WANG H, ZHENG W, et al. Toxic effects of prodigiosin secreted by Hahella sp. KA22 on harmful Alga Phaeocystis globosa [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017, 8: 999. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00999
[15] WILLIAMS R P, GOLDSCHMIDT M E, GOTT C L. Inhibition by temperature of the terminal step in biosynthesis of prodigiosin [J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 1965, 19(2): 177−181. DOI: 10.1016/0006-291X(65)90500-0
[16] ZHANG F, WEI Q E, TONG H, et al. Crystal structure of MBP-PigG fusion protein and the essential function of PigG in the prodigiosin biosynthetic pathway in Serratia marcescens FS14 [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2017, 99: 394−400. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.02.088
[17] PAN X W, SUN C H, TANG M, et al. LysR-type transcriptional regulator MetR controls prodigiosin production, methionine biosynthesis, cell motility, H2O2 tolerance, heat tolerance, and exopolysaccharide synthesis in Serratia marcescens [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2020, 86(4): e02241−e02219.
[18] WEI Y H, CHEN W C. Enhanced production of prodigiosin-like pigment from Serratia marcescens SMdeltaR by medium improvement and oil-supplementation strategies [J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2005, 99(6): 616−622. DOI: 10.1263/jbb.99.616
[19] KHAYYAT AHDAB N, ABBAS HISHAM A, KHAYAT MAAN T, et al. Secnidazole is a promising imidazole mitigator of Serratia marcescens virulence [J]. Microorganisms, 2021, 9(11): 2333. DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9112333
[20] SHANKS R M Q, STELLA N A, LAHR R M, et al. Suppressor analysis of eepR mutant defects reveals coordinate regulation of secondary metabolites and serralysin biosynthesis by EepR and HexS [J]. Microbiology (Reading, England), 2017, 163(2): 280−288. DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.000422
[21] LEE C M, MONSON R E, ADAMS R M, et al. The LacI-family transcription factor, RbsR, is a pleiotropic regulator of motility, virulence, siderophore and antibiotic production, gas vesicle morphogenesis and flotation in Serratia [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017, 8: 1678. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01678
[22] GRISTWOOD T, MCNEIL M B, CLULOW J S, et al. PigS and PigP regulate prodigiosin biosynthesis in Serratia via differential control of divergent operons, which include predicted transporters of sulfur-containing molecules [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2011, 193(5): 1076−1085. DOI: 10.1128/JB.00352-10
[23] 刘径, 张珂恒, 曾永三. 昆虫病原线虫Oscheius myriophila共生细菌菌株B1的分离与鉴定 [J]. 广东农业科学, 2016, 43(3):111−115. LIU J, ZHANG K H, ZENG Y S. Isolation and identification of a symboiotic bacterial strain (B1) from an entomopathogenic nematode, Oscheius myriophila [J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 43(3): 111−115.(in Chinese)
[24] JIA X B, LIN X J, CHEN J C. Linear and exponential TAIL-PCR: A method for efficient and quick amplification of flanking sequences adjacent to Tn5 transposon insertion sites [J]. AMB Express, 2017, 7(1): 195. DOI: 10.1186/s13568-017-0495-x
[25] LIU Y G, CHEN Y L. High-efficiency thermal asymmetric interlaced PCR for amplification of unknown flanking sequences[J]. BioTechniques, 2007, 43(5): 649−656.
[26] JIA X B, LIU F C, ZHAO K, et al. Identification of essential genes associated with prodigiosin production in Serratia marcescens FZSF02 [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2021, 12: 705853. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.705853
[27] 刘方晨, 贾宪波, 吴良泉, 等. 黏质沙雷氏菌灵菌红素合成基因簇异源表达及其潜在的温度调控机制 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2021, 36(3):337−344. LIU F C, JIA X B, WU L Q, et al. Heterologous expression and temperature regulation of prodigiosin-synthesis gene cluster in Serratia marcecens [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 36(3): 337−344.(in Chinese)
[28] WEATHERSPOON-GRIFFIN N, YANG D Z, KONG W, et al. The CpxR/CpxA two-component regulatory system up-regulates the multidrug resistance cascade to facilitate Escherichia coli resistance to a model antimicrobial peptide [J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2014, 289(47): 32571−32582. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.565762
[29] GRISTWOOD T, FINERAN P C, EVERSON L, et al. The PhoBR two-component system regulates antibiotic biosynthesis in Serratia in response to phosphate [J]. BMC Microbiology, 2009, 9: 112. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-112
[30] STELLA N A, LAHR R M, BROTHERS K M, et al. Serratia marcescens cyclic AMP receptor protein controls transcription of EepR, a novel regulator of antimicrobial secondary metabolites [J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2015, 197(15): 2468−2478. DOI: 10.1128/JB.00136-15
[31] HORNG Y T, CHANG K C, LIU Y N, et al. The RssB/RssA two-component system regulates biosynthesis of the tripyrrole antibiotic, prodigiosin, in Serratia marcescens [J]. International Journal of Medical Microbiology, 2010, 300(5): 304−312. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2010.01.003
[32] FINERAN P C, SLATER H, EVERSON L, et al. Biosynthesis of tripyrrole and beta-lactam secondary metabolites in Serratia: Integration of quorum sensing with multiple new regulatory components in the control of prodigiosin and carbapenem antibiotic production [J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2005, 56(6): 1495−1517. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04660.x
[33] QIU S S, JIA S S, ZHANG F, et al. Two component system CpxR/a regulates the prodigiosin biosynthesis by negative control in Serratia marcescens FS14 [J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2021, 579: 136−140. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.09.050
[34] LI Y Q, CEN P L, CHEN S F, et al. A pair of two-component regulatory genes ecrA1/A2 in S. coelicolor [J]. Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE A, 2004, 5(2): 173−179. DOI: 10.1631/jzus.2004.0173
[35] WILLIAMSON N R, FINERAN P C, OGAWA W, et al. Integrated regulation involving quorum sensing, a two-component system, a GGDEF/EAL domain protein and a post-transcriptional regulator controls swarming and RhlA-dependent surfactant biosynthesis in Serratia [J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2008, 10(5): 1202−1217. DOI: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01536.x
[36] 张亚. 粘质沙雷氏菌BaeS胞外感受器结构域晶体结构及双组份系统BaeS/R功能的研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2016. ZHANG Y. Study on crystal structure of BaeS extracellular receptor domain of Serratia marcescens and BaeS/R function of two-component system[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2016. (in Chinese)
[37] 贾宪波, 刘方晨, 赵恪, 等. 粘质沙雷氏菌FZSF02中转录调控因子OmpR的生物学功能 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2021, 36(12):1491−1498. JIA X B, LIU F C, ZHAO K, et al. Biological functions of transcription factor OmpR in Serratia marcescens FZSF02 [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 36(12): 1491−1498.(in Chinese)
[38] LERY L M S, GOULART C L, FIGUEIREDO F R, et al. A comparative proteomic analysis of Vibrio cholerae O1 wild-type cells versus a phoB mutant showed that the PhoB/PhoR system is required for full growth and rpoS expression under inorganic phosphate abundance [J]. Journal of Proteomics, 2013, 86: 1−15. DOI: 10.1016/j.jprot.2013.04.038
[39] HARRIS A K P, WILLIAMSON N R, SLATER H, et al. The Serratia gene cluster encoding biosynthesis of the red antibiotic, prodigiosin, shows species- and strain-dependent genome context variation[J]. Microbiology (Reading, England), 2004, 150(Pt 11): 3547-3560.
[40] THOMSON N R, COX A, BYCROFT B W, et al. The Rap and Hor proteins of Erwinia, Serratia and Yersinia: A novel subgroup in a growing superfamily of proteins regulating diverse physiological processes in bacterial pathogens [J]. Molecular Microbiology, 1997, 26(3): 531−544. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.5981976.x
[41] XIANG T T, ZHOU W, XU C L, et al. Transcriptomic analysis reveals competitive growth advantage of non-pigmented Serratia marcescens mutants [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2022, 12: 793202. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.793202
[42] GREEN J, SCOTT C, GUEST J R. Functional versatility in the CRP-FNR superfamily of transcription factors: FNR and FLP[M]//Advances in Microbial Physiology. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2001: 1-34.
[43] SUN D, ZHOU X G, LIU C, et al. Fnr negatively regulates prodigiosin synthesis in Serratia sp. ATCC 39006 during aerobic fermentation [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2021, 12: 734854. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.734854
[44] 刘星, 王希东, 刘君. 西瓜食酸菌RND蛋白家族外排转运体cusB基因抗铜功能研究 [J]. 微生物学通报, 2016, 43(1):97−106. LIU X, WANG X D, LIU J. Functional analysis of a RND family effiux transporter component-cusB gene associated with copper resistance in Acidovorax citrulli [J]. Microbiology China, 2016, 43(1): 97−106.(in Chinese)
[45] GRISTWOOD T, FINERAN P C, EVERSON L, et al. PigZ, a TetR/AcrR family repressor, modulates secondary metabolism via the expression of a putative four-component resistance-nodulation-cell-division efflux pump, ZrpADBC, in Serratia sp. ATCC 39006 [J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2008, 69(2): 418−435. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06291.x
[46] MCNEIL M B, CLULOW J S, WILF N M, et al. SdhE is a conserved protein required for flavinylation of succinate dehydrogenase in bacteria [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2012, 287(22): 18418−18428. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.293803
[47] ESCHENBRENNER M, COVÈS J, FONTECAVE M. The flavin reductase activity of the flavoprotein component of sulfite reductase from Escherichia coli [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1995, 270(35): 20550−20555. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.270.35.20550
[48] RADZIG M A, KOKSHAROVA O A, KHMEL’ I A. Antibacterial effects of silver ions on growth of gram-negative bacteria and biofilm formation [J]. Molecular Genetics, Microbiology and Virology, 2009, 24(4): 194−199. DOI: 10.3103/S0891416809040065
[49] BEGIC S, WOROBEC E A. Site-directed mutagenesis studies to probe the role of specific residues in the external loop (L3) of OmpF and OmpC porins in susceptibility of Serratia marcescens to antibiotics [J]. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 2007, 53(6): 710−719. DOI: 10.1139/W07-018
[50] BRANDT U. Energy converting NADH: Quinone oxidoreductase (complex I) [J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 2006, 75: 69−92. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.75.103004.142539
[51] SCHULER F, YANO T, DI BERNARDO S, et al. NADH-quinone oxidoreductase: PSST subunit couples electron transfer from iron–sulfur cluster N2 to quinone [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1999, 96(7): 4149−4153. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.7.4149




 下载:
下载: