Response Surface Optimization on Enzymatic Extraction Process of Turmeric Starch
-
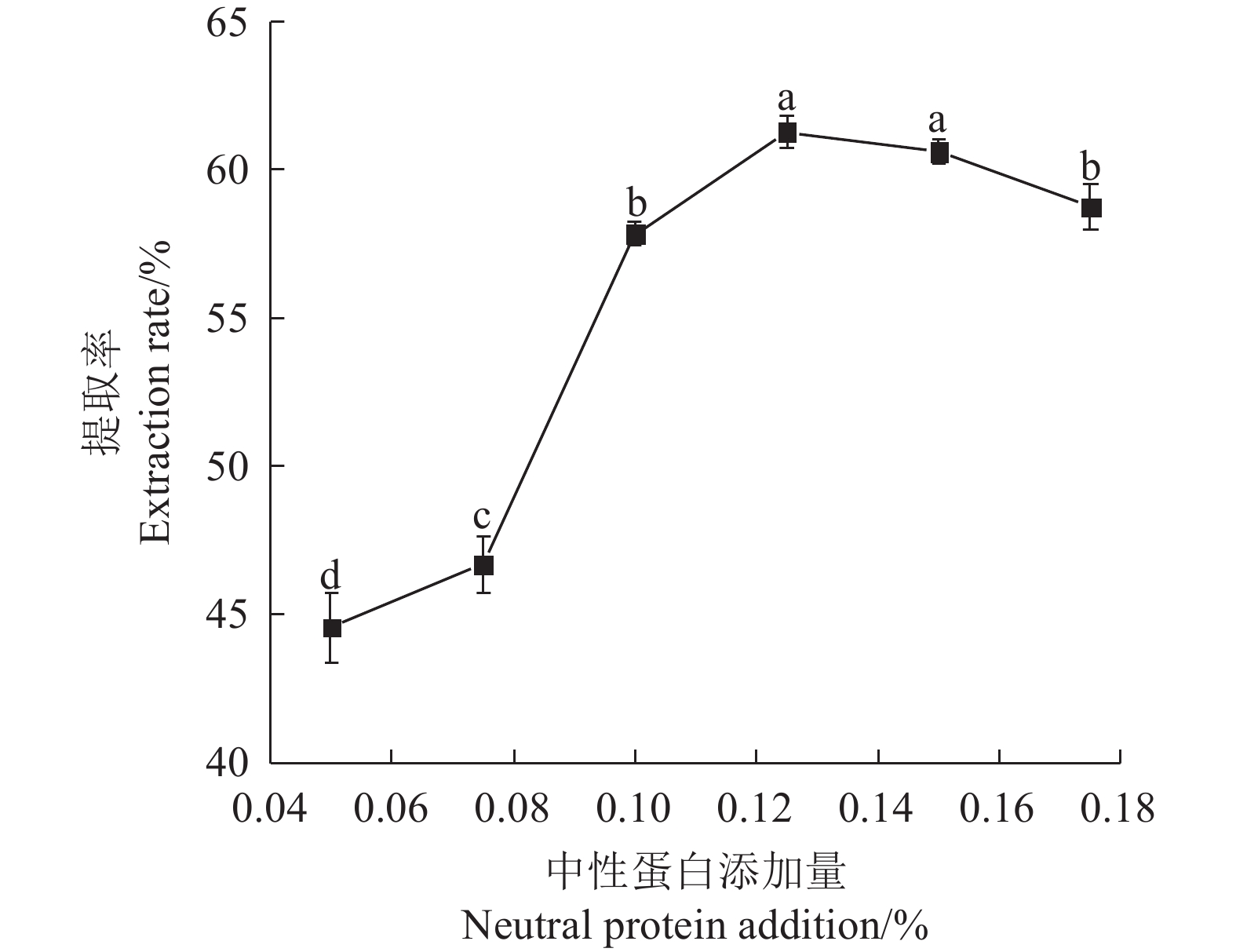
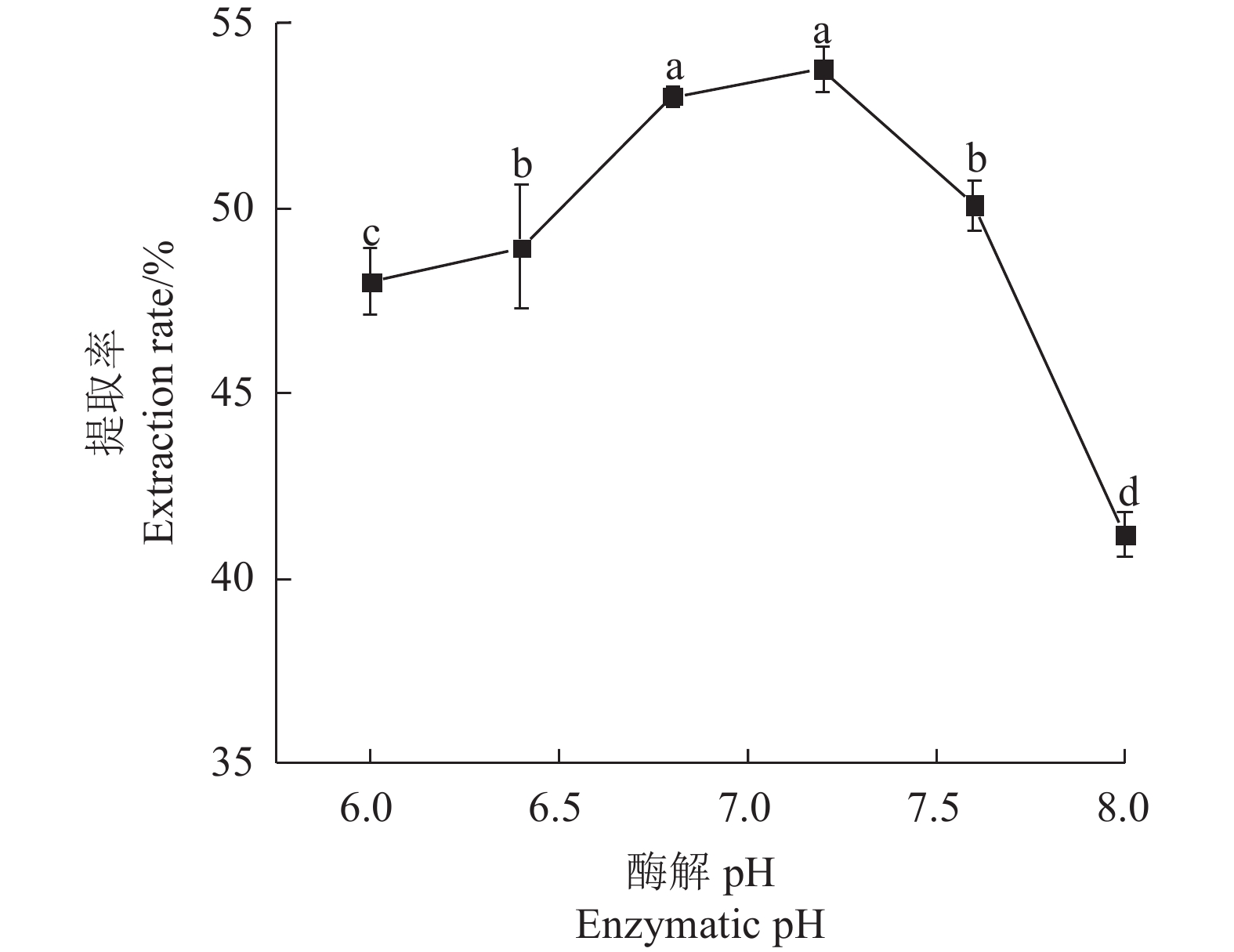
摘要:目的 优化姜黄淀粉酶法提取工艺,提高姜黄淀粉提取率。方法 以新鲜姜黄为原材料,姜黄淀粉提取率为指标,在几种蛋白酶中筛选最佳酶,采用单因素试验进一步确定提取酶解时间、酶解温度、酶解pH和中性蛋白酶添加量等4个因素影响姜黄淀粉提取率的优化范围。在单因素试验基础上,采用Box-Behnken方法,进行4因素3水平响应面优化设计,共进行29组处理,每组处理3次重复,考察酶解时间、酶解温度、酶解pH和中性蛋白酶添加量等4个因素对姜黄淀粉提取率的影响,从而确定姜黄淀粉酶法提取的最佳工艺条件。结果 姜黄淀粉提取最佳工艺参数为:酶解pH6.83、酶解温度51.45 ℃、酶解时间6.20 h、中性蛋白酶添加量0.13%,姜黄淀粉提取率的理论值为62.00%。考虑实际操作的简便,确定姜黄淀粉提取的最佳工艺参数为:酶解时间6 h,酶解温度52 ℃,酶解pH6.8,中性蛋白酶添加量0.13%,在此条件下实际验证值为60.42%,拟合得到的模型与实际吻合良好。结论 通过响应面法优化了姜黄淀粉的酶法提取工艺条件,提高了姜黄淀粉提取量,为姜黄淀粉的工业化生产提供了理论依据。Abstract:Objective Optimization on the enzymatic extraction process of starch from turmeric was improved.Method Using fresh turmeric as raw material, the best enzyme was screened among several proteases according to the starch extraction rate. A single-factor test was conducted to define the range of the time, digestion temperature, pH and the amount of neutral protease for extraction. Based on the single-factor test results, a 4-factor, 3-level Box-Behnken response surface optimization experiment was designed on 29 treatments with 3 replicates each to determine the optimal processing conditions.Results The optimized process applied 0.13% added neutral protease in a solution at pH 6.83 held at 51.45 °C for 6.20 h to achieve 62.00% turmeric starch extraction. For practical application the conditions were modified to be pH 6.8, 52°C, and 6 h to obtain a turmeric extraction rate of 60.42%. The experimental results fitted well with the prediction model. The fitted model was in good agreement with the actual one.Conclusion The enzymatic extraction of turmeric starch was optimized by response surface methodology in preparation for industrialized production.
-
Keywords:
- Turmeric /
- starch /
- extraction /
- response surface methodology /
- neutral protease
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】球虫病是由原生动物寄生虫引起的一种重要的肠道疾病,可导致家畜体重下降、营养不良、失血、脱水和对其他疾病因子的易感性增加,降低动物生产性能,给养殖业带来巨大的经济损失[1-2]。鸡对艾美耳球虫属易感,寄生于盲肠的柔嫩艾美耳球虫感染尤为严重,病理表现为肠道黏膜损伤、盲肠肿胀、出血及排出血便[3-4]。迄今为止,药物防治和活疫苗是两种主要的球虫病控制策略[5],但抗球虫药和接种疫苗会引起鸡只的药物残留、抗药性及虫株变异等风险[6]。因此在分子水平上研究球虫病抗性基因,通过遗传选育、培育抗病品种是解决这一问题的有效途径。【前人研究进展】白介素8(IL-8)是一种趋化性细胞因子,一方面能激活嗜中性粒细胞,诱导中性粒细胞释放溶酶体酶,清除病原菌[7],另一方面参与免疫反应,实现免疫细胞的抵抗功能,促进伤口愈合[8]。Cornelissen等[9]研究表明IL-8能够有效地招募Th1 CD4+、巨噬细胞和单核细胞,进而诱导IFN-γ的产生。Swaggerty等[10]通过连续3个世代选择外周血白细胞促炎性细胞因子白介素6(IL-6)、IL-8和趋化因子CCLi2的高水平表达(非球虫感染)的肉鸡个体进行配种,发现其后代柔嫩艾美耳球虫的抵抗能力极显著高于低表达水平群体。陈仁金等[11]采用混合动物模型将IL-8基因遗传多态性与荷斯坦奶牛7个性状进行关联分析,发现IL8基因连锁突变对荷斯坦牛泌乳性状以及抗病性状有较大的遗传效应,可用于中国荷斯坦牛的分子标记辅助选择。林雨鑫等[12]采用RNA-seq技术对E. tenella感染鸡和非感染对照鸡的盲肠组织进行转录组分析,筛选到许多显著富集的通路和差异表达基因,主要有IL-6、IL-8、IL-12β、IL-15、IL-17和TGFB2等。辛世杰等[8]研究发现,IL-8基因在感染柔嫩艾美耳球虫的京海黄鸡脾脏和盲肠组织中表达量显著升高,表明IL-8基因在鸡球虫感染中发挥一定的作用。【本研究切入点】虽然已有研究发现IL-8参与免疫应答、具有诱导中性粒细胞释放溶酶体酶和清除病原体等作用,但关于IL-8基因5′调控区单核苷酸多态性对球虫抗性指标的影响的研究鲜见报道。【拟解决的关键问题】本试验采用DNA直接测序技术,检测京海黄鸡IL-8基因5′调控区单核苷酸多态性(SNPs),并对5′调控区的SNPs突变前后转录因子进行预测,同时还分析这些SNPs与球虫抗性指标的关联性,旨在筛选与京海黄鸡柔嫩艾美耳球抗性选育有利的突变基因型,为培育球虫病抗性新品种或新品系提供参考依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验动物
选购江苏省海门集团1日龄京海黄鸡共92只,公母各半,饲养于无病原的鸡舍中,所食饲料中不含任何球虫及抗球虫性药物,试验鸡预试期内经粪检无球虫。E. tenella孢子化卵囊为扬州大学兽医学院寄生虫教研室保存虫种,经非球虫免疫健康鸡体内传代一次后收集获得。
1.2 样本处理及采集
30日龄时,每只鸡灌饲1.5万个柔嫩艾美耳球虫孢子化卵囊。记录感染期间0~8 d体增重。在感染后的第8 d翅静脉采血,肝素钠抗凝,立即4 000 r·min−1离心5 min,分离血浆和血细胞后于−20℃冰箱中保存。
1.3 基因组DNA提取及检测
根据文献[8]的方法提取所有试验鸡的全血基因组DNA,用微量紫外可见光分光光度计对基因组DNA进行OD值以及浓度测定,经测定所提取的DNA样品OD260 nm/OD280 nm值在1.8~2.0,质量浓度在500~1 000 μg·μL−1,均符合试验要求。将合格样品稀释至100 ng·μL−1,4℃或−20℃(长期)保存备用。
1.4 引物设计及PCR扩增
根据GenBank中已公布的鸡IL-8基因序列(Gene ID: 396495),使用Primer Premier 5.0对IL-8基因上游−2 000 bp至−1 bp的核苷酸序列共设计4对引物。引物由上海生工生物工程有限公司合成,引物设计详细信息见表1。
表 1 引物序列信息Table 1. Information on primer sequence引物 Primer 引物序列(5′→3′)Primers sequence(5′→3′) 退火温度 Annealing temperature/℃ 长度 Length/bp P1 F: TTCCATTCGCATAAGTCATC 51 638 R: AAAGTTGATTTGGGGATACC P2 F: TGTAATTGGGAATTCAAGGGGGA 58 708 R: CCCATTTGGTGTGTGATAAGATGA P3 F: AGTCCACAGACCACAAAGCA 58 693 R: TCGCAATATAAGTTTCTGATGGCTT P4 F: AAACCAGCAACACAAAGTC 60 574 R: CATCTCAGCAAGTGCCAAG PCR反应体系:10 μL的2×Taq Master Mix,上下游引物各1 μL,DNA模板1 μL,最后加入水补足至20 μL体系。PCR扩增程序:95℃预变性5 min;95℃变性30 s,引物最佳退火温度退火30 s,72℃ 延伸1 min,35个循环;72℃延伸10 min,4℃保存。
1.5 基因测序
PCR产物送至上海生物工程技术服务有限公司进行测序。使用仪器为ABI测序仪(3730xlDNAAnalyzer)。DNA序列拼接后,用MEGA6.06和DNAMAN5.2软件对测序结果进行比对分析,并确定京海黄鸡IL-8基因的SNPs。
1.6 转录因子预测
使用在线软件AliBaba2.1(http://gene-regulation.com/pub/programs/alibaba2/index.html)进行预测IL-8基因5′调控区核苷酸序列突变后可能存在的转录因子结合位点和可能结合的转录因子。
1.7 抗性指标测定
血浆抗氧化指标按试剂盒(购自南京建成生物工程研究所)说明书采用生物素双抗体夹心酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)法测定[13-14],测定指标包括:超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、丙二醛(MDA)、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-PX)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)、一氧化氮(NO)、白介素1-β(IL-1β)、白介素2(IL-2)、白介素6(IL-6)、白介素8(IL-8)、干扰素-γ(IFN-γ)。
1.8 数据统计分析
使用Popgene1.32软件对IL-8基因5′调控区SNPs数据进行群体遗传多样性分析,包括杂合度(H)、有效等位基因数(Ne)和多态信息含量(PIC),统计整理各突变位点的基因型频率、等位基因频率,用χ2检验方法对群体Hardy-Weinberg进行平衡检测。运用SPSS25.0对各抗性指标数据进行关联分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 IL-8基因PCR测序结果
以提取的92只京海黄鸡基因组DNA为模板,依据NCBI数据库中鸡(Gallus gallus)IL-8基因上游−2 000 bp至−1 bp的核苷酸序列设计的引物进行PCR扩增测序及拼接。测序共发现了3个SNPs突变位点(见表2),1号突变位点在−550碱基发生T→C的突变,命名为T-550C。2号突变位点在−398碱基发生G→T的突变,命名为G-398T。3号突变位点在−360碱基发生T→C的突变,命名为T-360C。详细信息见图1。
![]() 图 1 IL-8基因位点位点峰图及序列比对注:A:T-550C位点峰图比对;B:G-398T位点峰图比对;C:T-360C位点峰图比对;D:T-550C位点序列比对图;E:G-398T位点序列比对图;F:T-360C位点序列比对图Figure 1. Peak and sequence alignments of IL-8Note: A: T-550C peak alignment; B: G-398T peak alignment; C: T-360C peak alignment; D: T-550C sequence alignment; E: G-398T sequence alignment; F: T-360C sequence alignment.表 2 IL-8基因5′调控区单核苷酸突变位点信息Table 2. Information on SNPs in 5′ regulation region of IL-8
图 1 IL-8基因位点位点峰图及序列比对注:A:T-550C位点峰图比对;B:G-398T位点峰图比对;C:T-360C位点峰图比对;D:T-550C位点序列比对图;E:G-398T位点序列比对图;F:T-360C位点序列比对图Figure 1. Peak and sequence alignments of IL-8Note: A: T-550C peak alignment; B: G-398T peak alignment; C: T-360C peak alignment; D: T-550C sequence alignment; E: G-398T sequence alignment; F: T-360C sequence alignment.表 2 IL-8基因5′调控区单核苷酸突变位点信息Table 2. Information on SNPs in 5′ regulation region of IL-8序号 Site number 染色体位置 Chromosome position 序列号 Serial number 单核苷酸多态性 SNP 1 51282560 rs740065165 T-550C 2 51282712 rs731947764 G-398T 3 51282750 rs16409254 T-360C 注:A:T-550C位点峰图比对;B:G-398T位点峰图比对;C:T-360C位点峰图比对;D:T-550C位点序列比对图;E:G-398T位点序列比对图;F:T-360C位点序列比对图
Note: A: T-550C peak alignment; B: G-398T peak alignment; C: T-360C peak alignment; D: T-550C sequence alignment; E: G-398T sequence alignment; F: T-360C sequence alignment.2.2 IL-8基因5′调控区SNPs突变引起的转录因子改变预测结果
由表3可见,IL-8基因5′调控区在−550 bp发生了T→C的突变,此处突变导致原有的Oct-1转录因子结合位点消失;在−398 bp发生了G→T的突变,导致此处原先C/EBPalp转录因子的结合位点发生位置改变,且新增了1个Pit-1a转录因子的结合位点;在−360 bp的突变(T→C)导致原有的NF-1转录因子结合位点消失。
表 3 IL-8基因5′调控区SNPs突变前后转录因子变化预测结果Table 3. Predicted transcription factors before and after mutation of IL-8 in 5' regulation region突变位点
Mutation site碱基
Base转录因子
Transcription factor转录因子结合位点碱基序列
Transcription factor binding site base sequence转录因子位置
Transcription factor position−550 bp T Oct-1 GTTGCATTTG −551~−542 bp C −398 bp G C/EBPalp GAAATAAATA −398~−389 bp T Pit-1a TAAATAAATA −398~−389 bp C/EBPalp ACATAAATAA −401~−392 bp −360 bp T NF-1 AGCCAGTTAT −362~−353 bp C 注:图中下划线标注为突变碱基。
Note: The underline in the figure is the mutant base.2.3 IL-8基因5′调控区多态性分析
对IL-8基因5′调控区发现的3个SNPs位点进行多态性及遗传多样性分析(表4),结果表明:3个突变位点均形成了3种基因型,杂合度均在0.436~0.471,PIC值在0.25~0.50,均属于中度多态,遗传差异性较大。卡方检验结果显示,3个突变位点均处于哈代-温伯格平衡状态。其中,除了G-398T突变位点外,原等位基因相对于突变后的等位基因均为优势等位基因,而G-398T突变位点突变后的等位基因为优势等位基因。
表 4 IL-8基因5′调控区多态性Table 4. SNPs in 5′ regulation region of IL-8突变位点
Mutation site基因型
Genotype数量
Number基因型频率
Genotype frequency等位基因
Allelic gene等位基因频率
Allele frequencyχ2值
χ2 valueP值
P value杂合度 H 有效等位
基因数 Ne多态信息含量
PICT-550C TT 40 0.435 T 0.679 1.390 0.500 0.436 1.772 0.341 CC 7 0.076 C 0.321 TC 45 0.489 G-398T GG 13 0.141 G 0.380 0.023 0.990 0.471 1.892 0.360 TT 35 0.381 T 0.720 GT 44 0.478 T-360C TT 40 0.435 T 0.674 0.725 0.699 0.440 1.784 0.343 CC 8 0.087 C 0.326 TC 44 0.478 注:PIC>0.50为高度多态;0.25<PIC<0.50为中度多态;PIC<0.25为低度多态[15]。
Note: PIC>0.50 is highly polymorphic; 0.25<PIC<0.50 is moderately polymorphic; PIC<0.25 means low polymorphism[15].2.4 IL-8基因5′调控区多态性与血浆抗性指标的关联分析
2.4.1 T-550C突变位点各基因型与鸡球虫抗性指标关联分析
T-550C突变位点各基因型与鸡球虫抗性指标关联分析显示(表5),除了SOD、MDA、NO和IL-1β指标外,TC型个体的其他指标均高于其他2种基因型,但差异不显著(P>0.05);TC型的IL-8表达量显著高于TT型(P<0.05),其加性效应值和显性效应值分别为9.10和19.15 ng·L−1;TT型个体的NO含量极显著高于CC型(P<0.01),其加性效应值和显性效应值分别为10.12和7.39 μmol·L−1。
表 5 IL-8基因T-550C突变位点各基因型与鸡球虫抗性指标关联分析Table 5. Correlation between genotypes mutated at T-550C in IL-8 and coccidiosis-resistance indicators指标
Indices基因型 Genotype TT(40) TC(45) CC(7) 超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)/(U·mL−1) 750.63±88.37 720.62±78.91 723.95±67.57 丙二醛(MDA)/(nmol·mL−1) 3.66±0.40 3.74±1.26 4.16±1.03 谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-PX)/(U·mL−1) 151.77±16.94 152.22±17.53 150.83±22.52 过氧化氢酶(CAT)/(U·mL−1) 0.87±0.17 1.01±0.16 0.95±0.19 一氧化氮(NO)/(μmol·L−1) 52.35±5.25 A 49.62±3.79 AB 32.12±3.69 B 白介素1-β(IL-1β)/(ng·L−1) 20.54±2.00 19.75±3.04 20.22±1.19 白介素2(IL-2)/(ng·L−1) 14.78±2.66 15.82±2.04 15.18±2.69 白介素6(IL-6)/(ng·L−1) 69.93±3.55 72.40±8.64 67.81±4.29 白介素8(IL-8)/(ng·L−1) 90.87±7.63 b 119.11±10.42 a 109.06±11.76 ab 干扰素-γ(IFN-γ)/(ng·mL−1) 189.47±15.25 201.21±13.67 195.58±16.06 注:同行数据后不同大写字母表示差异极显著(P<0.01),不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),相同字母或无字母表示差异不显著(P>0.05),表6~7同。
Note: Different uppercase letters on a same row indicate significant differences (P<0.01); different lowercase letters, significant differences (P<0.05); and, same or no letter, no significant differences (P>0.05). Same for Tables 6–7.2.4.2 G-398T突变位点各基因型与鸡球虫抗性指标关联分析
由表6可知,TT型个体SOD活性和GT型个体CAT活性均显著高于GG型(P<0.05),SOD与CAT活性的加性效应值分别为46.77和0.035 U·mL−1,显性效应值分别为10.99和0.175 U·mL−1;TT型个体NO含量均高于其他两种基因型,且与GG型差异极显著(P<0.01),与GT型差异显著(P<0.05),其加性效应值和显性效应值分别为10.86和2.365 μmol·L−1;TT型IL-2表达量显著高于GT型(P<0.05),其加性效应值和显性效应值分别为0.67和2.18 ng·L−1;TT型IL-1β、IL-8表达量均高于GG型个体,但未达到显著水平(P>0.05)。
表 6 IL-8基因G-398T突变位点各基因型与鸡球虫抗性指标关联分析Table 6. Correlation between genotypes mutated at G-398T in IL-8 and coccidiosis-resistance indicators指标
Indices基因型 Genotype GG(13) GT(44) TT(35) 超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)/(U·mL−1) 631.43±50.73 b 667.21±27.41 ab 724.97±87.91 a 丙二醛(MDA)/(nmol·mL−1) 3.66±0.40 3.63±0.39 3.19±0.73 谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-PX)/(U·mL−1) 164.04±21.41 155.20±20.63 158.58±19.50 过氧化氢酶(CAT)/(U·mL−1) 0.84±0.10 b 1.05±0.15 a 0.91±0.18 一氧化氮(NO)/(μmol·L−1) 24.18±4.26 Bab 32.67±9.88 ABb 45.89±11.63 Aa 白介素1-β(IL-1β)/(ng·L−1) 20.45±1.70 22.51±1.30 23.17±1.65 白介素2(IL-2)/(ng·L−1) 15.17±2.54 ab 13.66±1.38 b 16.51±3.10 a 白介素6(IL-6)/(ng·L−1) 65.66±6.05 71.01±7.81 68.40±7.30 白介素8(IL-8)/(ng·L−1) 94.31±9.86 104.24±7.70 105.89±13.30 干扰素-γ(IFN-γ)/(ng·mL−1) 183.25±17.99 179.94±15.83 175.99±17.26 2.4.3 T-360C突变位点各基因型与鸡球虫抗性指标关联分析
由T-360C突变位点各基因型与鸡球虫抗性指标关联分析(表7)可知,除MDA、CAT、IL-1β、IFN-γ指标以外,TT型个体的其他指标均高于其他2种基因型;对于SOD活性,TT型个体与CC型差异极显著(P<0.01),TC型个体与CC型个体差异显著(P<0.05),其加性效应值和显性效应值分别为64.43和10.55 U·mL −1;对于NO含量,TT型和TC型个体均显著高于CC型个体(P<0.05),其加性效应值和显性效应值分别为5.94和4.53 μmol·L−1;对于IL-2、IL-8表达量,TT型个体均显著高于CC型个体(P<0.05),IL-2与IL-8活性的加性效应值分别为1.68和10.02 ng·L−1,显性效应值分别为0.32和1.87 ng·L−1;对于IFN-γ含量,CC型个体显著高于其他2种基因型个体(P<0.05),其加性效应值和显性效应值分别为15.015和9.55 ng·L−1;TT型GSH-PX、IL-6指标均高于其他2种基因型,但差异不显著(P>0.05)。
表 7 IL-8基因T-360C突变位点各基因型与鸡球虫抗性指标关联分析Table 7. Correlation between genotypes mutated at T-360C in IL-8 and coccidiosis-resistance indicators指标 Indices 基因型 Genotype TT(40) TC(44) CC(8) 超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)/(U·mL−1) 781.29±76.94 Aab 706.31±72.85 ABa 652.43±44.92 Bb 丙二醛(MDA)/(nmol·mL−1) 4.01±1.20 3.91±0.49 4.23±0.79 谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-PX)/(U·mL−1) 124.34±11.73 117.17±13.46 116.68±14.53 过氧化氢酶(CAT)/(U·mL−1) 0.77±0.16 0.86±0.30 0.74±0.14 一氧化氮(NO)/(μmol·L−1) 46.91±11.24 a 45.50±9.28 a 35.03±8.11 b 白介素1-β(IL-1β)/(ng·L−1) 20.11±1.03 20.65±1.84 21.55±2.73 白介素2(IL-2)/(ng·L−1) 15.82±2.04 a 13.82±1.84 ab 12.46±1.55 b 白介素6(IL-6)/(ng·L−1) 62.74±10.21 60.80±9.47 57.92±9.38 白介素8(IL-8)/(ng·L−1) 103.19±14.94 a 91.30±13.82 ab 83.15±13.01 b 干扰素-γ(IFN-γ)/(ng·mL−1) 163.28±13.49 b 168.75±15.29 b 193.31±16.32 a 3. 讨论与结论
3.1 IL-8基因5′调控区的多态性检测
5′调控区是基因转录调控的核心区域,该区域突变形成的SNPs可改变原有的转录因子结合位点和转录因子,从而影响与该基因有关性状的表达。因此研究基因5′调控区SNPs及其与相关性状的关联分析是发掘新的分子遗传标记的重要途径之一[4, 15]。宁娟[16]研究表明结构蛋白N和非结构蛋白Nsp2在Marc-145细胞中表达能激活转录因子NF-κB,而活化的NF-κB进入核内与IL-8启动子上的NF-κB位点结合后,能诱导IL-8的表达。Wu等[17]体外试验结果表明,转录激活因子3(ATF3)的抑制可显著提高人支气管上皮细胞中促炎细胞因子IL-6和IL-8的表达。本研究在5′调控区共检测到3个SNP位点:T-550C、G-398T和T-360C。这3个突变位点均形成了3种基因型,杂合度均在0.436~0.471,PIC值在0.25~0.50,均属于中度多态,遗传差异性较大,有利于鸡育种中的群体遗传分化。其中,T-550C和T-360C突变位点均是杂合型所占比例较高,TC为优势基因型,T为优势基因,而G-398T位点突变后的等位基因为优势等位基因,杂合型为优势基因型。卡方检验结果显示,3个突变位点均处于哈代-温伯格平衡状态,这可能是由于群体规模较大,突变位点没有受到选种选配的影响或是在选育过程中达到了新的平衡。生物信息学分析发现:在−550 bp发生了T→C的突变,导致原有的Oct-1转录因子结合位点消失;在−398 bp发生了G→T的突变,导致此处原先C/EBPalp转录因子结合位点发生位置改变,且新增了1个Pit-1a转录因子的结合位点;在−360 bp的突变(T→C)导致原有的NF-1转录因子结合位点消失。本研究发现的这3个突变位点均改变了其原有的转录因子结合位点,转录因子结合位点的改变可能使IL-8基因表达发生变化,进而影响血浆中IL-8的浓度。IL-8参与免疫反应,在炎症和免疫应答中起着重要作用。有研究表明鸡感染球虫后,体内IL-8表达量越高,其抗球虫能力越强[10]。因此推测转录因子结合位点的改变可能会影响鸡抗球虫能力,但具体机制有待进一步研究。
3.2 IL-8基因5′调控区的多态性与鸡球虫抗性指标的关系
目前有关鸡IL-8基因的SNPs与球虫抗性指标关联分析的研究较少。本研究将5′调控区发现的3个SNPs与鸡球虫抗性指标关联分析,结果表明:在T-550C位点突变后形成的3种基因型中,大多数指标均是TC型高于其他2种基因型,且TC型个体IL-8表达量显著高于TT型。对于G-398T突变位点,TT型个体显著或极显著高于GG型的SOD、NO指标,显著高于GT型的IL-2表达量,并且TT型IL-1β、IL-8表达量也都高于GG型个体,因此突变后的TT型个体可能抵抗球虫病能力较强。对于T-360C突变位点,除了对MDA、GSH-Px、CAT、IL-1β、IL-6指标无显著影响外,TT型和TC型个体的SOD活性极显著或显著高于CC型,TT型和TC型个体的NO含量均显著高于CC型个体,TT型个体的IL-2、IL-8表达量均显著高于CC型。IL-8参与免疫应答,能诱导中性粒细胞释放溶酶体酶和清除病原体,在炎症和免疫应答中发挥关键调节作用。本研究在IL-8基因5′调控区检测到的3个SNPs均改变了其原有的转录因子结合位点,进而影响IL-8基因的表达,导致血浆中IL-8的表达量升高,有效地提高鸡体内的免疫水平,增强抵抗E. tenella的能力。
-
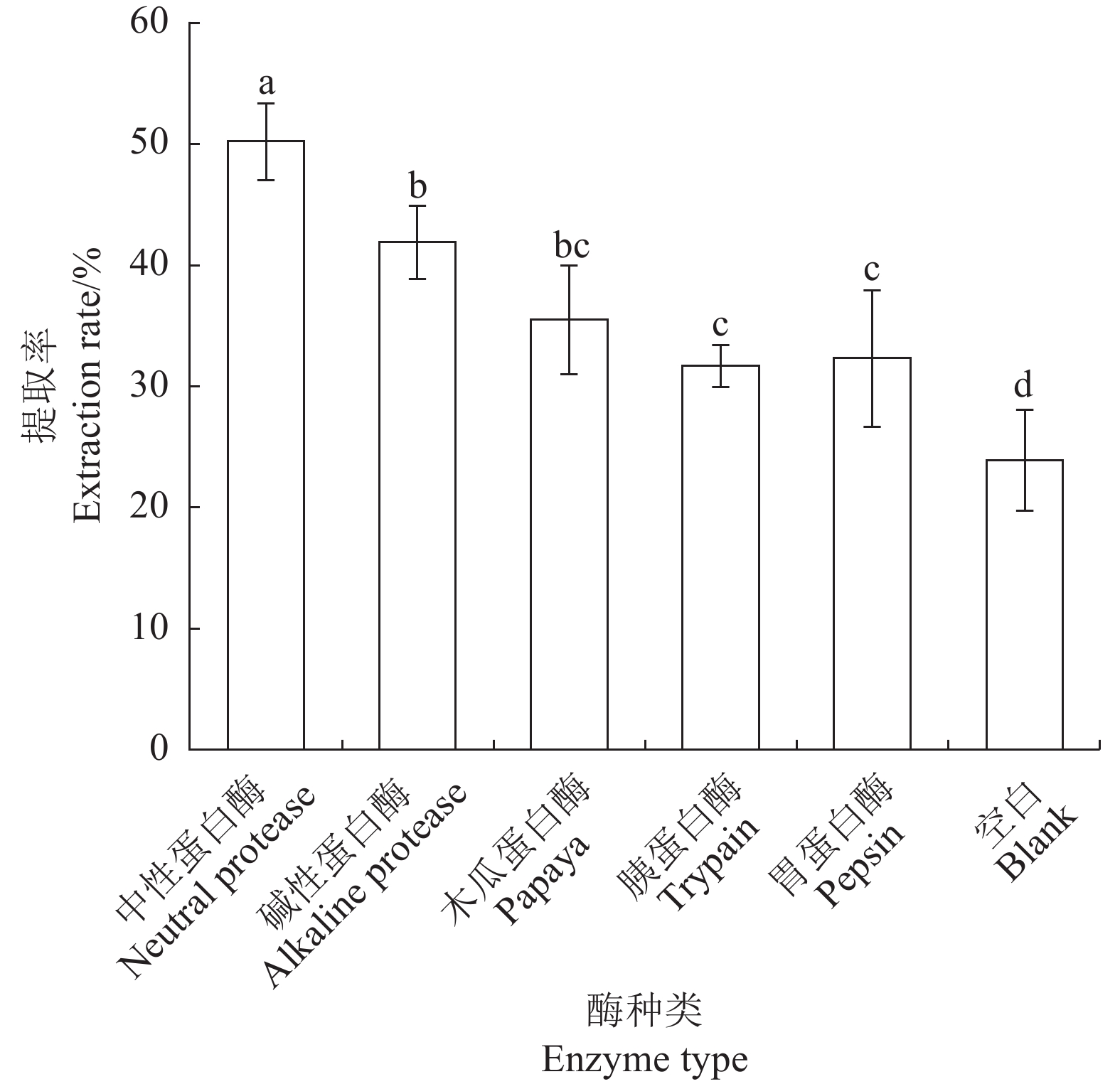
表 1 蛋白酶最适条件
Table 1 Optimum conditions for protease digestion
蛋白酶种类
Protease types最适pH值
Optimum
pH最适温度
Optimum
temperature/
°C蛋白酶添加量
Protease
addition/
(U·mL−1)中性蛋白酶
Neutral protease6.8 60 300 碱性蛋白酶
Alkaline protease11.0 50 300 木瓜蛋白酶
Papain5.7 55 300 胰蛋白酶
Trypsin8.1 37 300 胃蛋白酶
Pepsin3.0 37 300 空白(CK)
Blank(CK)6.8 25 — 表 2 响应面试验的因素和水平
Table 2 Factors and levels of response surface experiments
水平
Level因素
FactorsA:酶解pH
Enzymatic pHB:酶解时间
Enzymatic
digestion
time /hC:酶解温度
Enzymatic
digestion
temperature/°CD:中性蛋白酶添加量
Neutral
protease
addition/%−1 6.4 4 40 0.100 0 6.8 6 50 0.125 1 7.2 8 60 0.150 表 3 响应面试验设计与结果
Table 3 Response surface test design and results
序号
Serial numberA B C D 提取率
Extraction rate/%1 6.4 4 50 0.125 52.14 2 7.2 6 50 0.15 52.67 3 6.8 6 40 0.15 48.39 4 6.8 6 40 0.1 47.65 5 6.8 6 60 0.15 56.44 6 6.8 8 60 0.125 53.62 7 6.8 6 50 0.125 62.18 8 6.8 4 50 0.15 51.44 9 6.8 4 40 0.125 51.34 10 6.8 6 60 0.1 48.66 11 7.2 6 60 0.125 55.23 12 6.8 8 40 0.125 54.69 13 6.8 6 50 0.125 63.24 14 6.4 6 60 0.125 50.74 15 7.2 6 40 0.125 52.46 16 7.2 6 50 0.1 50.69 17 6.8 6 50 0.125 61.57 18 6.8 4 60 0.125 52.07 19 6.4 6 50 0.1 46.78 20 6.4 6 50 0.15 53.48 21 6.8 4 50 0.1 46.64 22 6.8 6 50 0.125 60.24 23 7.2 8 50 0.125 53.3 24 6.4 8 50 0.125 53.19 25 6.4 6 40 0.125 50.09 26 6.8 6 50 0.125 60.89 27 6.8 8 50 0.15 54.18 28 7.2 4 50 0.125 52.94 29 6.8 8 50 0.1 47.84 表 4 回归模型的方差分析
Table 4 Analysis of variance for regression models
方差来源
Source of variance平方和
Sum of squares自由度
Freedom均方
Mean SquareF值
F valueP值
P-value显著性
Significance模型 Model 570.86 14 40.78 21.41 <0.0001 ** A 9.85 1 9.85 5.17 0.0393 * B 8.76 1 8.76 4.60 0.0501 C 12.28 1 12.28 6.45 0.0236 * D 66.93 1 66.93 35.14 <0.0001 ** AB 0.12 1 0.12 0.062 0.8062 AC 1.12 1 1.12 0.59 0.4552 AD 5.57 1 5.57 2.92 0.1093 BC 0.81 1 0.81 0.43 0.5249 BD 0.59 1 0.59 0.31 0.5857 CD 12.39 1 12.39 6.50 0.0231 * A2 124.22 1 124.22 65.21 <0.0001 ** B2 126.50 1 126.50 66.41 <0.0001 ** C2 141.31 1 141.31 74.18 <0.0001 ** D2 294.00 1 294.00 154.34 <0.0001 ** 残差 Residual 26.67 14 1.90 失拟项 Lack of fit 21.29 10 2.13 1.58 0.3487 纯误差 Pure error 5.38 4 1.34 总和 Cor total 597.53 28 相关系数 R2 0.9554 校正相关系数 R2 0.9107 **P<0.01,表示极显著,*P<0.05,表示显著,P>0.05,表示不显著。
** indicates extremely significant at P<0.01, * indicates significant at P<0.05, and no sign indicates not significant at P>0.05. -
[1] 仉瑜, 张洪兵, 郭虹, 等. 姜黄的研究进展及质量标志物(Q-Marker)的预测分析 [J]. 中草药, 2021, 52(15):4700−4710. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2021.15.029 ZHANG Y, ZHANG H B, GUO H, et al. Research progress on Curcumae Longae Rhizoma and predictive analysis of its quality markers [J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2021, 52(15): 4700−4710.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2021.15.029
[2] 庞新华, 何新华, 周全光, 等. 姜黄种质资源的保存及其主要性状评价 [J]. 热带作物学报, 2014, 35(6):1047−1055. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2014.06.002 PANG X H, HE X H, ZHOU Q G, et al. Conservation of Curcuma germplasm resources and evaluation of their main characters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2014, 35(6): 1047−1055.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2014.06.002
[3] 田芳, 柴玉荣, 江亚南, 等. 姜黄素通过下调IκBα磷酸化抑制食管鳞癌细胞的体外增殖 [J]. 基础医学与临床, 2011, 31(7):767−772. TIAN F, CHAI Y R, JIANG Y N, et al. The effect of curcumin through suppression of IκBα phosphorylation on inhibition of proliferation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell lines [J]. Basic & Clinical Medicine, 2011, 31(7): 767−772.(in Chinese)
[4] 周欣, 李章万, 王道平, 等. 姜科姜黄属植物有效成分的研究 [J]. 分析测试学报, 2004, 23(6):53−56. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2004.06.015 ZHOU X, LI Z W, WANG D P, et al. Effective chemical constituents in essential oils from plants of Curcuma genus [J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2004, 23(6): 53−56.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2004.06.015
[5] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典-三部: 2005年版[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005. [6] 汤敏燕, 汪洪武, 孙凌峰. 中药姜黄挥发油化学成分研究 [J]. 江西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2000, 24(3):274−277. DOI: 10.16357/j.cnki.issn1000-5862.2000.03.018 TANG M Y, WANG H W, SUN L F. Studies on the chemical constituents of essential oil from Chinese traditional drug Jianghuang(tubers of Curcuma) [J]. Journal of Jiangxi Normal University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2000, 24(3): 274−277.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.16357/j.cnki.issn1000-5862.2000.03.018
[7] MIYAZAKI T, WADA M, KAWAHARA H, et al. Dynamic load at baseline can predict radiographic disease progression in medial compartment knee osteoarthritis [J]. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 2002, 61(7): 617−622. DOI: 10.1136/ard.61.7.617
[8] LIN X Y, BAI D P, WEI Z X, et al. Curcumin attenuates oxidative stress in RAW264.7 cells by increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes and activating the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway [J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(5): e0216711. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0216711
[9] LIU Y, LIU Y H, HUANG X C, et al. Protective effects and mechanism of curcumin on myocardial injury induced by coronary microembolization [J]. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 2019, 120(4): 5695−5703. DOI: 10.1002/jcb.27854
[10] ASAI A, MIYAZAWA T. Dietary curcuminoids prevent high-fat diet-induced lipid accumulation in rat liver and epididymal adipose tissue [J]. The Journal of Nutrition, 2001, 131(11): 2932−2935. DOI: 10.1093/jn/131.11.2932
[11] 毛新慧. 山药、姜黄等中药淀粉的理化性质及生理活性的研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2017 MAO X H. Study on the physicochemical properties and biological activities of starch from Dioscorea opposita, Curcuma longa and other Chinese materia Medica[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2017. (in Chinese)
[12] DING Y Y, CHENG J J, LIN Q Y, et al. Effects of endogenous proteins and lipids on structural, thermal, rheological, and pasting properties and digestibility of adlay seed (Coix lacryma-jobi L. ) starch [J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 2021, 111: 106254. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106254
[13] 钟雪瑶, 王少曼, 张彦军, 等. 响应面法优化面包果淀粉的酶法提取工艺 [J]. 食品工业科技, 2020, 41(21):139−144. DOI: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020010004 ZHONG X Y, WANG S M, ZHANG Y J, et al. Optimization of enzymatic extraction technology of starch from breadfruit by response surface methodology [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(21): 139−144.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020010004
[14] SANTANA Á L, ZABOT G L, OSORIO-TOBÓN J F, et al. Starch recovery from turmeric wastes using supercritical technology [J]. Journal of Food Engineering, 2017, 214: 266−276. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2017.07.010
[15] 张军, 周佳乐, 王宏亮, 等. 响应面优化超声波提取姜淀粉及其理化性质分析 [J]. 中国食品添加剂, 2022, 33(10):28−37. ZHANG J, ZHOU J L, WANG H L, et al. Ultrasonic extraction of ginger starch by response surface optimization and analysis of physicochemical properties [J]. China Food Additives, 2022, 33(10): 28−37.(in Chinese)
[16] 李敏, 张倩芳, 栗红瑜, 等. 基于不同提取方法对藜麦淀粉性质的比较 [J]. 食品研究与开发, 2022, 43(1):17−24. DOI: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2022.01.003 LI M, ZHANG Q F, LI H Y, et al. Comparison between quinoa starches isolated using different extraction methods [J]. Food Research and Development, 2022, 43(1): 17−24.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2022.01.003
[17] VAN HUNG P, DUYEN T T M, PHI N T L, et al. Fabrication and functional properties of Curcuma starch nanoparticles as affected by different degree of polymerization of debranched Curcuma starch [J]. Starch - Stä rke, 2022, 74(1/2): 2100163.
[18] KUTTIGOUNDER D, LINGAMALLU J R, BHATTACHARYA S. Turmeric Powder and starch: Selected physical, physicochemical, and microstructural properties [J]. Journal of Food Science, 2011, 76(9): C1284−C1291. DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02403.x
[19] VAN HUNG P, VO T N D. Structure, physicochemical characteristics, and functional properties of starches isolated from yellow (Curcuma longa) and black (Curcuma caesia) turmeric rhizomes [J]. Starch - Stä rke, 2017, 69(5/6): 1600285.
[20] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准 食品中淀粉的测定: GB 5009.9—2016[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. [21] 傅新征. 薏苡仁淀粉制备与性质研究及改性应用[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2012. FU X Z. Study on preparation, properties, modification and application of the Coix seed starch[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2012. (in Chinese)
[22] 祝水兰, 周巾英, 刘光宪, 等. 超声波辅助酸酶法提取碎米抗性淀粉工艺的优化 [J]. 南方农业学报, 2019, 50(8):1814−1821. ZHU S L, ZHOU J Y, LIU G X, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted acid enzymatic extraction of resistant starch from broken rice [J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2019, 50(8): 1814−1821.(in Chinese)
[23] 初众, 胡美杰, 徐飞, 等. 响应面法优化酶法提取菠萝蜜种子淀粉工艺 [J]. 食品工业科技, 2016, 37(20):189−193,200. CHU Z, HU M J, XU F, et al. Optimization of enzymatic extraction technology condition of starch from jackfruit seed using response surface methodology [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2016, 37(20): 189−193,200.(in Chinese)
[24] 赵彦巧, 朱志勇, 李建颖, 等. 响应面试验优化中性蛋白酶辅助提取青稞淀粉工艺 [J]. 食品科学, 2016, 37(4):31−36. ZHAO Y Q, ZHU Z Y, LI J Y, et al. Optimization of neutral protease-assisted extraction of highland barley starch [J]. Food Science, 2016, 37(4): 31−36.(in Chinese)
[25] 姜绍通, 殷嘉忆, 王华林, 等. 响应面法优化酶法提取芋头淀粉工艺参数 [J]. 食品科学, 2014, 35(6):24−29. JIANG S T, YIN J Y, WANG H L, et al. Optimization of enzymatic extraction parameters for taro starch [J]. Food Science, 2014, 35(6): 24−29.(in Chinese)
[26] 韩伟, 马婉婉, 骆开荣. 酶法提取技术及其应用进展 [J]. 机电信息, 2010(17):15−18. HAN W, MA W W, LUO K R. Enzymatic extraction technology and its application progress [J]. Mechanical and Electrical Information, 2010(17): 15−18.(in Chinese)
[27] WANG J Q, LAN T, LEI Y S, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic extraction of kiwi starch and evaluation of its structural, physicochemical, and functional characteristics [J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2021, 81: 105866. DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105866
[28] 仪凯, 周瑞宝. 中性蛋白酶水解花生粕的研究 [J]. 中国油脂, 2005, 30(7):71−73. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-7969.2005.07.020 YI K, ZHOU R B. Hydrolysis of peanut meal by neutral protease [J]. China Oils and Fats, 2005, 30(7): 71−73.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-7969.2005.07.020
[29] 李恬心, 聂沫宇, 吴菲, 等. 响应面优化微波辅助提取佛手山药淀粉的工艺 [J]. 食品工业, 2022, 43(1):61−65. LI T X, NIE M Y, WU F, et al. Microwave assisted extraction of starch from Foshou yam by response surface [J]. The Food Industry, 2022, 43(1): 61−65.(in Chinese)
[30] 孔茂竹, 孔露, 余佳熹, 等. 响应面法优化两步浸泡提取玉米淀粉工艺 [J]. 食品科技, 2019, 44(10):269−275. DOI: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2019.10.045 KONG M Z, KONG L, YU J X, et al. Optimization of two-step steeping process for corn starch by response surface methodology [J]. Food Science and Technology, 2019, 44(10): 269−275.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2019.10.045
[31] 杜洋, 史岩, 陈海华. 响应面法优化高粱米淀粉的中性蛋白酶法提取工艺 [J]. 粮食与油脂, 2015, 28(8):12−16. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2015.08.004 DU Y, SHI Y, CHEN H H. Optimization of sorghum starch extracting technology with neutral protease hydrolysis by response surface methodology [J]. Cereals & Oils, 2015, 28(8): 12−16.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2015.08.004
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 符乐毅,陈智雄. 茶梗栽培食用菌研究进展. 现代农业科技. 2024(05): 53-56 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 马婧嘉,李雅茹,雷萍,张文隽,吴亚召. 基于人工神经网络和遗传算法优化用于栽培皱环球盖菇的农业废弃物培养基. 菌物学报. 2024(11): 146-154 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李杨,黄艺鸿,林银娜,王雅婷. 茶梗的综合利用研究进展. 农产品加工. 2023(02): 87-90 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王爱仙,王怡暄,刘福阳,刘金仙,巫仁高. 茶枝屑代料栽培黑木耳配方. 北方园艺. 2021(12): 121-126 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王伟伟,张建勇,陈琳,江和源. 茶梗的综合利用研究进展. 茶叶通讯. 2020(01): 20-24 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 刘金仙,邓家耀,傅仙玉,王爱仙. 茶梗、茶枝屑代料对黑木耳生长及品质的影响. 宜春学院学报. 2020(03): 108-113 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 王丽丽,杨军国,林清霞,项丽慧,陈林. 基于化学组分的铁观音茶梗和叶茶模式识别研究. 茶叶学报. 2019(01): 1-8 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: