Regulating Effect of Exogenous Melatonin on Aluminum Toxicity in Solanum lycopersicum L.
-
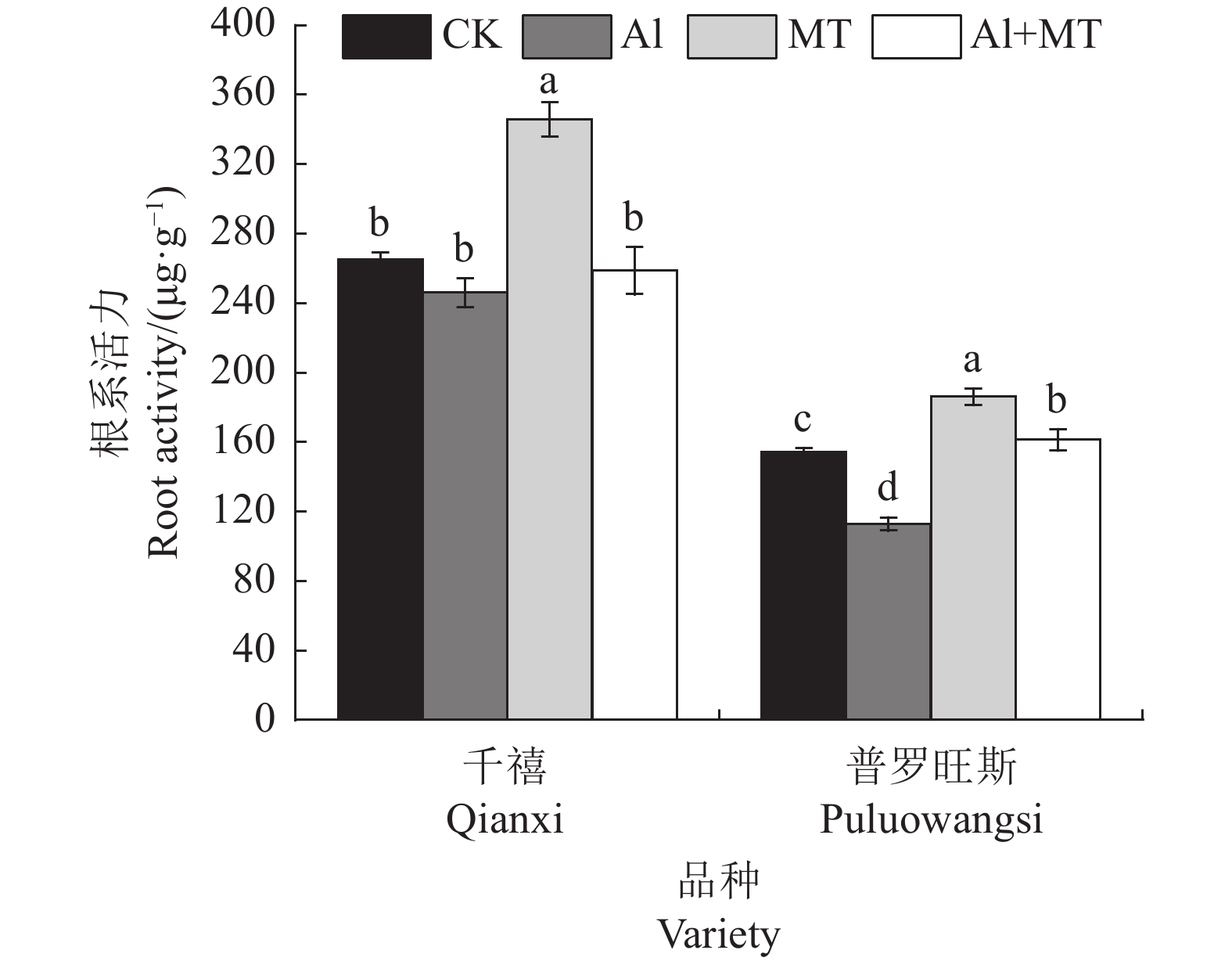
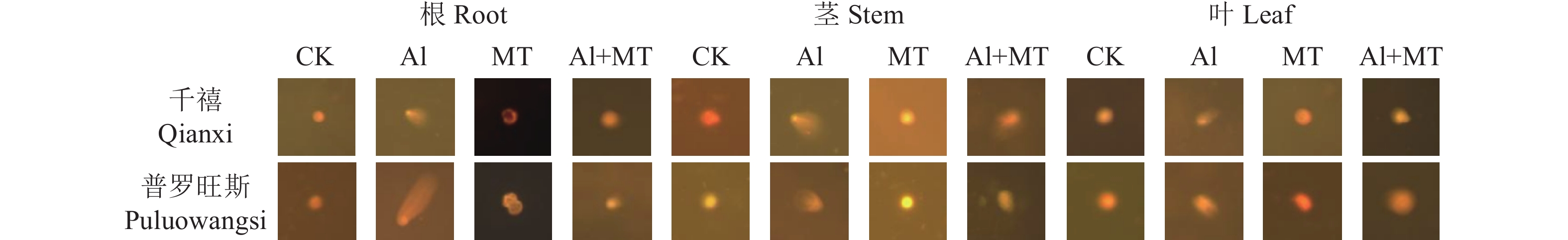
摘要:目的 研究褪黑素对铝胁迫下番茄生理上的调控作用,为缓解土壤酸铝化对番茄生长造成的不利影响提供理论依据。方法 以耐铝品种千禧番茄和铝敏感品种普罗旺斯番茄为供试植物,设置空白组、单铝组、褪黑素(MT)处理组和铝+褪黑素共同施加组,测定各处理组生长周期(10 d、20 d、30 d)过程中番茄叶片抗氧化酶[超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化物酶(POD)和过氧化氢酶(CAT)]活性、丙二醛(MDA)、脯氨酸(Pro)、抗坏血酸(AsA)、谷胱甘肽(GSH)含量、叶绿素含量和叶绿素荧光参数,检测根部铝富集含量和根系活力,并对番茄的根、茎、叶进行DNA损伤检测。结果 铝逆境下两品种番茄生长发育均受到严重抑制,各器官DNA均受损严重,且其根系DNA损伤最为严重。施用褪黑素能够明显缓解番茄的铝毒症状,两品种番茄株高、根长及叶面积等主要生长指标均有所增长;抗氧化酶活性得到显著提高,且随实验周期延长呈现先上升后下降的趋势;GSH和AsA含量最大增幅达91.14%、13.52%;MDA含量降幅最大可达38.39%,脯氨酸含量增幅可达144.81%,调节番茄体内渗透平衡;叶绿素含量明显升高,各项荧光参数得到改善,恢复其光合能力;千禧番茄和普罗旺斯番茄根系活力增幅分别为5.19%和43.03%,两者的根、茎、叶铝富集能力均降低。同时,施加褪黑素也能够有效减缓番茄各器官DNA拖尾现象,修复细胞DNA损伤。结论 施加外源褪黑素能有效激活铝胁迫下番茄的各项生理响应,促进其生长发育,不仅能提高抗氧化酶系统活性,增强光合能力与根系活力,还可以减少植株体内铝含量,降低细胞DNA受损程度,进一步提升其抗铝能力,为探索MT对逆境下植物的调控作用提供新思路。Abstract:Objective Regulating effect of melatonin application on the physiology of a tomato plant under aluminum stress was studied.Method Al-tolerant Millennial tomato and Al-sensitive Provence tomato plants were grown in blank control, Al-added, melatonin-added (MT), or Al-and-melatonin-added (AMT) potting soils. Activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD), and catalase (CAT), contents of malondialdehyde (MDA), proline (Pro), ascorbic acid (AsA), glutathione (GSH), and chlorophyll as well as chlorophyll fluorescence parameters, Al-accumulation, and root activity in the plants were monitored. DNA damage occurred to the roots, stems, and leaves of the plants during the experimentation were recorded. Statistical analysis was performed on all collected data using the one-way ANOVA and Duncan test.Result Under Al-stress, the growth and development of the tomato plants of either variety were severely inhibited, and the DNA in the organs, especially the roots, seriously damaged. Whereas the presence of melatonin in the soil (MT and/or AMT ) significantly alleviated the symptoms of Al-toxicity on the plants. For instance, with the addition, the main growth indicators, such as plant height, root length, and leaf area, were improved; the activity of antioxidant enzymes significantly heightened with an increasing trend initially and followed by a decline as treatment duration prolonged; the contents of GSH and AsA raised by 91.14% and 13.52% respectively; the reduction on MDA maximized at 38.39%; proline, which regulates the osmotic balance in tomato, increased to 144.81% and chlorophyll significantly; the fluorescence parameters improved; the photosynthetic capacity much restored; the root activity of Millennial tomato plant increased by 5.19%, and that of Provence tomato by 43.03%; the Al-accumulation in the roots, stems, and leaves significantly reduced; the DNA tailing in organs slowed; and the repairs on damaged DNA in cells observed.Conclusion Applying exogenous melatonin in soil effectively activated various physiological responses, raised the activity of antioxidant enzymes, enhanced the plant photosynthesis, reduced damage on cellular DNA, and elevated the resistance to Al-toxicity of the tomato plants under the heavy metal stress.
-
Keywords:
- Melatonin /
- Solanum lycopersicum /
- aluminum stress /
- physiological response /
- DNA damage
-
0. 引 言
【研究意义】卷荚相思(Acacia cincinnata)属豆科金(Leguminosae)合欢(Vachellia farnesiana)属植物,在我国南方地区广泛种植。卷荚相思是沿海沙地重要的树种资源之一,具有适生性强、产量高、生长快、性状优良等特性,是优质的家具用材和造纸树种[1]。但在林业生产中,经常会出现种子空壳、质量不高、籽粒不饱满等现象,最终导致卷荚相思种子萌发率不高,因此选择合适的方法提高卷荚相思种子的萌发率非常必要。物理农林业是物理技术和农林业生产有机结合的一种生产方式,将电、磁、光、热等物理学科知识与农林业生产相关领域的前沿技术结合起来,使用特殊技术方法处理植物,在无污染的条件下,达到增产、优质、抗病和高效的目的,并且在工艺上和成本上都易于实现,在农林业中的应用和研究是十分广泛的。目前,电场种子处理技术应用于种植业和养殖业,在农林业生产和环境保护中已发挥巨大的作用[2]。为此探讨电场处理对卷荚相思种子萌发的影响效应,为研究种子萌发提供理论基础。【前人研究进展】相关研究表明,电场与时间两者交互处理不仅可以刺激植物种子萌发、生长、愈伤组织形成以及细胞融合,而且可以提高细胞膜内的电位差,膜内外电位差的改变,影响物质交换的速度[3];电场处理技术在食品加工和贮存[4]、畜牧业[5]、水产养殖业[6]和病虫害防治[7]等方面都获得了重要的成果,取得了显著的经济效益[8]。种子顺利萌发、成苗是植物完成生活史的前提,除受种子自身大小、质量、环境和储存方式等因素影响外,还受制于前期对种子的处理等重要因素[9]。利用适宜的电场处理植物种子可以明显提高种子活力,并且提高种子的发芽率、发芽势和发芽指数,使其出苗整齐和迅速,促进了作物对生长发育所需要养分的吸收,加速植物的生长发育,促进其光合作用,提高植物的产量及质量[10−15]。【本研究切入点】目前电场处理对卷荚相思种子萌发影响和生长的影响研究鲜见报道,电场强度和处理时间对植物种子萌发的影响阈值尚未确定。【拟解决的关键问题】开展不同电场强度和处理时间交互下对卷荚相思种子萌发的影响试验,研究萌发阈值及其对生长指标影响等问题,为卷荚相思种子萌发及可持续经营提供理论参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验区概况
试验地位于福建农林大学(119°13′51.73″E、26°04′55.5″N),属于亚热带季风性气候,全年冬暖夏凉,年平均日照1755.4 h,无霜期达360 d以上。年均温为19.9 ℃,极端最高温42 ℃,最低温度为0 ℃,年空气相对湿度79 %。
1.2 供试材料
试验所用卷荚相思种子于2022年3月采集于福建省漳浦中西国有林场,选取大小一致、颗粒饱满的种子用于萌发试验。
1.3 试验设计
本试验电场由波尔高压电源73030P型电场发生器产生,使用2块平行金属板进行连接且金属板之间保持0.5 cm距离并形成一个连续可调的电场,种子均匀分布在底层金属板上。利用二次通用旋转组合设计[16]进行预试验,设置电场强度分别为0.2、0.4、0.6、0.8、1.0 kV·cm−1和处理时间分别为15、30、45、60 min的电场处理,未经处理为对照(CK),以电压强度和时间为控制因素,共计20个处理,1个对照,每个处理3个重复,每个重复50粒种子。
1.4 试验方法
电场处理种子后第2天进行置床,采用纸上培养法[17]进行种子萌发试验,将处理后的种子用15% 福尔马林消毒30 min并用蒸馏水冲洗数遍。将各培养皿内滤纸润湿后每个培养皿50粒种子,并重复3次。将培养皿放入恒温培养箱中进行发芽试验,设定萌发条件为温度25 ℃,湿度70%,12 h光照和12 h黑暗交替。在每个培养皿中加入2 mL蒸馏水,每天17:00记录种子萌发情况。当种子胚根突破种皮2 mm时,视为种子萌发。
1.5 萌发指标计算
卷荚相思种子在第3天开始萌发并于12 d后结束发芽,发芽结束后分别计算发芽率、发芽势和发芽指数。公式如下[18]:
发芽率(GE)/% = (发芽种子数/供试种子数) ×100;
发芽势(GR)/% = (初期发芽种子数/供试种子数) ×100;
发芽指数 (GI) = ∑(第t天种子发芽数/相应发芽天数)。
1.6 数据分析
采用SPSS 25.0对种子萌发指标进行统计分析,运用Duncan’s法进行多重比较(P<0.05)不同电场和时间交互处理种子萌发特性;种子萌发指标采用平均值±标准误表示。为了验证数据是否满足条件,对其进行KS检验,如若原始数据不满足正态分布,对原始数据进行10作底数的lg(x+1)对数转换,保证数据呈正态分布。采用Origin 2022进行非线性回归分析和聚类分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 电压和时间交互处理对种子萌发特性的影响
2.1.1 不同电场强度和时间交互处理对种子发芽率的影响
在电场强度和时间交互处理下,卷荚相思的种子发芽率在一定程度上存在差异(表1)。从电场强度看,在15~60 min时发芽率随着电场的增高与CK相比呈现先降后升再降的趋势,且在电场强度0.6 kV·cm−1,处理时长为45、60 min时和电场强度0.8 kV·cm−1,处理时长为30 min时卷荚相思种子的发芽率均达较高水平,分别为75.00%、74.67%和74.33%,比CK分别提高13.64%、13.14%和12.62%,且存在显著差异。从处理时间来看,在电场强度为0.6 、0.8 kV·cm−1时,随着处理时间的延长,卷荚相思种子发芽率逐渐提高,呈现先升后降的趋势,且均高于CK,0.6 kV·cm−1时与CK相比分别提高2.5%、8.1%、13.63%和13.14%;0.8 kV·cm−1时与CK相比分别提高1.0%、12.62%、8.1%和6.1%。说明在电场强度0.8 kV·cm−1、处理时间45 min的双因素交互处理下,可以有效提高种子的发芽率。
表 1 不同电场强度与时间交互处理对卷荚相思种子发芽率的影响Table 1. Effect of applied electric field and treatment time on germination rate of A. cincinnata seeds(单位:%) 电场强度
Electric field strength/(kV·cm−1)处理时间 Handling time 0 min 15 min 30 min 45 min 60 min 0.0 66.00±4.00 aA 66.00±4.00 aA 66.00±4.00 aB 66.00±4.00 aC 66.00±4.00 aAB 0.2 66.00±4.00 aA 48.67±2.52 cC 55.00±2.00 bcD 66.00±3.00 aC 60.67±5.77 abB 0.4 66.00±4.00 aA 56.00±2.00 bB 67.33±1.15 aB 70.33±1.53 aAB 70.00±3.46 aA 0.6 66.00±4.00 bA 67.67±2.52 abA 71.33±3.06 abAB 75.00±3.00 aA 74.67±7.57 aA 0.8 66.00±4.00 cA 66.67±2.08 bcA 74.33±3.51 aA 71.33±2.52 abAB 70.00±2.00 abcA 1.0 66.00±4.00 aA 65.33±2.52 aA 60.33±3.51 abC 59.33±2.52 bD 50.00±2.00 cC 同行中不同小写字母代表不同处理时间存在显著差异(P<0.05),同列中不同大写字母代表不同电场强度存在显著差异(P<0.05)。下同。
Data with different lowercase letters on same row represent significant differences under different treatment times (P<0.05); and those with different uppercase letters on same column represent significant differences under different electric field (P<0.05). Same for below.2.1.2 不同电场强度和时间交互处理对种子发芽势的影响
不同电场强度和时间交互处理对卷荚相思种子发芽势有不同程度的影响且存在一定差异(表2)。不同强度的电场可产生不同的生物学效应,发芽势有时升高,有时降低,但整体呈现出促进作用。0.2 kV·cm−1处理下随着时间的延长呈现先下降后上升再下降的趋势,且在15 min时与CK有显著差异(P<0.05);0.4 kV·cm−1处理下随着时间的延长呈现先降后升的趋势,在60 min时发芽势达最高,但是与CK无显著差异(P>0.05);0.6~1.0 kV·cm−1 处理下随着时间的延长呈现先升后降的趋势,且电场强度在0.8 kV·cm−1、处理时间45 min时发芽势达到最高并且与CK相比有显著差异(P<0.05),表2可以看出电场强度在0.6 、0.8 kV·cm−1,处理时间在30~45 min时,对卷荚相思种子的发芽势有一定的促进作用,并且与CK相比显著提高(P<0.05)。说明电场处理对卷荚相思种子具有一定的改善作用,在电场强度0.8 kV·cm−1、处理时间45 min可以促进发芽势的提高。
表 2 不同电场强度与时间交互处理对卷荚相思种子发芽势的影响Table 2. Effect of applied electric field and treatment time on germination potential of A. cincinnata seeds(单位:%) 电场强度
Electric field strength/(kV·cm−1)处理时间 Handling time 0 min 15 min 30 min 45 min 60 min 0.0 39.67±2.08 aA 39.67±2.08 aCD 39.67±2.08 aB 39.67±2.08 aB 39.67±2.08 aB 0.2 39.67±2.08 abA 30.51±1.47 cE 36.24±3.31 abB 40.38±3.19 aB 35.33±1.15 bBC 0.4 39.67±2.08 abA 37.99±1.98 cD 38.38±4.65 cB 42.43±5.00 abB 46.67±4.16 aA 0.6 39.67±2.08 bA 48.02±1.60 aA 49.99±4.52 aA 50.58±1.87 aA 49.00±3.00 aA 0.8 39.67±2.08 cA 47.33±3.88 bAB 50.37±1.46 abA 52.73±1.79 aA 47.33±3.05 bA 1.0 39.67±2.08 abA 42.98±3.61 aBC 41.26±3.85 aB 41.23±5.27 aB 33.19±2.71 bC 2.1.3 不同电场强度和时间交互处理对种子发芽指数的影响
不同电场强度和时间交互处理对卷荚相思种子发芽指数有不同程度的影响并且存在一定的差异(表3)。从不同的电场强度看,0.2 kV·cm−1处理下的发芽指数在45 min时处于最高值,与CK相比提高了13.91%,但并无显著差异(P>0.05);0.4 kV·cm−1处理下的发芽指数呈现先降后升的趋势;0.6~1.0 kV·cm−1处理下的发芽指数均呈现先升后降的趋势,且在电场强度0.8 kV·cm−1、处理时间45 min时处于最高值,与CK相比提高了24.63%,具有显著差异(P<0.05);0.6 kV·cm−1处理下在处理时间15~60 min时与CK均有显著差异(P<0.05),1.0 kV·cm−1处理下在45 、60 min与CK相比降低了11.95%和12.68%,具有显著差异(P<0.05)。在相同处理时间下,随着电场强度的增强对发芽指数均产生不同程度的影响,可以看出0.4~0.6 kV·cm−1电场强度在30~60 min处理时间下对卷荚相思种子发芽指数刺激的作用优于0.2 、1.0 kV·cm−1的电场强度。从表中可以看出在电场和时间两者交互处理下能够促进卷荚相思种子的萌发,在电场强度0.8 kV·cm−1、处理时间45 min可以促进发芽指数的提高,具有优化促进作用。
表 3 不同电场强度与时间交互处理对卷荚相思种子发芽指数的影响Table 3. Effect of applied electric field and treatment time on germination index of A. cincinnata seeds电场强度
Electric field strength/(kV·cm−1)处理时间 Handling time 0 min 15 min 30 min 45 min 60 min 0.0 8.12±0.40 aA 8.12±0.40 aB 8.12±0.40 aBC 8.12±0.40 aCD 8.12±0.40 aBCD 0.2 8.12±0.40 abA 6.21±0.41 cD 7.38±0.63 bC 9.25±1.01 aABC 7.79±0.51 bCD 0.4 8.12±0.40 abA 7.12±0.47 bC 8.74±0.77 aAB 8.63±0.79 aBC 9.15±0.36 aAB 0.6 8.12±0.40 bA 9.24±0.66 abA 9.83±0.71 aA 9.57±0.55 abAB 9.35±1.18 abA 0.8 8.12±0.40 cA 8.91±0.22 bcAB 9.67±0.55 abA 10.12±0.52 aA 8.85±0.47 bcABC 1.0 8.12±0.40 aA 8.16±0.37 aB 7.64±0.70 abBC 7.15±0.23 bD 7.09±0.33 bD 2.1.4 电场和时间双因素交互处理对种子形态指标的影响
电场和时间交互处理对卷荚相思种子形态指标的双因素方差分析结果(表4)表明,电场、时间及两者交互处理对卷荚相思种子的发芽率、发芽势和发芽指数均具有显著影响(P<0.05)。
表 4 电场和时间交互处理对卷荚相思种子形态指标影响的双因素方差分析Table 4. Two-way ANOVA on effects of applied electric field and treatment time on morphological indexes of A. cincinnata seeds参数
Parameter电场强度
Electric field strength处理时间
Handling time电场强度×处理时间
electric field strength×
Handling timeF值
F valueP值
P valueF值
F valueP值
P valueF值
F valueP值
P value发芽率 GE 51.004 0.000 13.908 0.000 8.292 0.000 发芽势 GR 42.144 0.000 4.332 0.010 3.139 0.003 发芽指数 GI 27.919 0.000 7.365 0.000 4.294 0.000 2.2 卷荚相思种子萌发特性模型及分类分析
2.2.1 卷荚相思种子发芽率非线性回归方程的建立
对不同电场强度与处理时间进行非线性回归分析(表5)。发芽率(Y)作为因变量,自变量为电场(X1)和时间(X2),将这2个变量引入方程。通过非线性回归分析,不同电场强度与时间交互处理下的最优回归方程为:Y=7.73+135.23X1+1.24X2−86.16X12−0.00911X22−0.75X1X2,非线性回归方程达到显著水平(P<0.05),对回归方程进行显著性F检验,其F值为45.01806,大于F0.05(5,50)=2.40,表明非线性回归方程与实际情况拟合度高,能反映2项因素与发芽率的综合关系,说明上述模型具有统计学意义。
表 5 不同电场强度与时间交互处理对发芽率非线性回归模型Table 5. Nonlinear regression model between seed germination rate and applied electric field/time方程拟合度
R2调整后R2
Adjusted R2平方和 Square sum df 均方 Mean square F值 F value 回归
regression残差
residual error回归
regression残差
residual error回归
regression残差
residual error0.81 0.79 3251.04548 779.93786 5 54 650.2091 14.44329 45.01806 2.2.2 不同电场强度和时间交互处理下种子萌发特性热图及其聚类分析
为了直观分析5种电场强度在经过不同处理时间的交互作用,卷荚相思萌发期3个指标在相同环境下的变化情况,利用热图对卷荚相思种子萌发期性状的变化量进行可视化处理,通过纵向聚类反映3个指标在同一环境下的相互关系。5种电场强度处理下萌发期3个指标相对值的变化热图及聚类分析结果见图1。
![]() 图 1 不同电场强度与时间交互处理下的聚类分析①热图中红色表示电场对指标有促进作用,且颜色越深,作用越强;② t1-0.2、t2-0.2、t3-0.2、t4-0.2代表0.2 kV·cm−1,t1~t4分别代表处理时间为15、30、45和60 min,以此类推;③GE:发芽率,GR:发芽势,GI:发芽指数。Figure 1. Clustering of applied electric field and treatment time.①Red indicates how electric field promotes indicators--the darker the color, the stronger the effect; ② t1−0.2, t2−0.2, t3−0.2, and t4−0.2 represent treatments under 0.2kV·cm−1; t1-t4 represent treatments of 15, 30, 45, and 60m, respectively. Same for the others; ③GE stands for germination rate; GR stands for germination potential; GI stands for germination index.
图 1 不同电场强度与时间交互处理下的聚类分析①热图中红色表示电场对指标有促进作用,且颜色越深,作用越强;② t1-0.2、t2-0.2、t3-0.2、t4-0.2代表0.2 kV·cm−1,t1~t4分别代表处理时间为15、30、45和60 min,以此类推;③GE:发芽率,GR:发芽势,GI:发芽指数。Figure 1. Clustering of applied electric field and treatment time.①Red indicates how electric field promotes indicators--the darker the color, the stronger the effect; ② t1−0.2, t2−0.2, t3−0.2, and t4−0.2 represent treatments under 0.2kV·cm−1; t1-t4 represent treatments of 15, 30, 45, and 60m, respectively. Same for the others; ③GE stands for germination rate; GR stands for germination potential; GI stands for germination index.由图1可以看出,在不同电场强度和时间交互处理下的4个不同处理时间对发芽率影响不显著;发芽指数显示区域在t2-0.6和t3-0.8时呈现深红色,说明在此时间段下可以显著提高发芽指数;且在t1-0.2时显示区域呈现米白色,说明对发芽指数影响不大。发芽势在t3-0.8处理下显示区域呈现深红色,说明在此时间段下可以提高发芽势。综上,说明不同的电场强度和时间交互处理下对这3个指标的作用效果有所区别。电场处理下,根据卷荚相思种子各指标变化情况可将3个指标分为2类,指标发芽率单独聚为一类,发芽势和发芽指数聚为一类。
3. 讨论与结论
种子萌发期是植物生长发育初期阶段最为敏感的环节,关系到植物种子能否健康生长[19, 20]。发芽率、发芽势和发芽指数由种子最终发芽个数和萌发时间决定,可以反映种子萌发的生活力程度、发芽速率和整齐度[21]。本研究电场处理对卷荚相思种子萌发特性的影响与前人的研究结果基本一致,如武翠卿等[22]研究发现经高压静电场预处理后,谷子(Setaria italica)、荞麦(Fagopyrum esculentum Moench)及高粱(Sorghum bicolor)的千粒质量及产量都有增加,适宜的电场强度可促进谷子株高的增加,场强过低或者过高反而抑制株高的增加。李美清等[23]研究表明高压静电场处理改变了番茄(Solanum lycopersicum)的生长特性,适宜的电场对茎粗、鲜质量、叶绿素含量、根系形态具有促进作用,并提高产量。本研究发现不同电场强度和时间交互处理对卷荚相思种子的发芽率、发芽势和发芽指数具有不同程度的影响。发芽率在电场强度0.6 kV·cm−1、处理时间45 min时处于最佳状态,发芽势在电场强度0.8 kV·cm−1、处理时间45 min时均处于最高值,并且与CK有显著差异,发芽指数在电场强度0.6~0.8 kV·cm−1、处理时间30~45 min时均处于最优状态。说明卷荚相思种子在适宜的电场和时间交互处理对种子萌发有一定的作用,但是达到一定的电场阈值之后明显抑制种子的萌发。低压电场对种子萌发特性并没有促进作用,反而抑制了种子的萌发,这可能是卷荚相思种子表面附着一层保护膜,电场处理没有穿过种子表面的保护层,引起植物种子细胞内外物质的扩散[24]以及种子萌发反应所需要的养分条件。但高压电场对种子萌发特性具有抑制作用,这可能是电场回路里产生的电压太强直接击穿卷荚相思种子保护膜,对种子内部造成了一定的损伤,影响了植物种子体内电子传递和质子流的传递,并影响种子的萌发特性[25]。
植物种子的发芽率受本身特性和外界环境的双重影响,它们共同决定了植物的生长发育[26]。合理的电场强度和处理时间等对植物种子发芽率的提高具有重要作用[27]。前人研究表明,电场和时间两者交互处理下可以调控植物种子的发芽率[28]。在电场处理种子前,需要考虑电场强度的大小对植物种子的生物效应(在一定的场强范围内,才能引起生物效应),但是电场处理的作用时间对生物效应的影响也很重要,在选择最佳电场强度时也要考虑作用时间的长短,当电场强度和时间适宜时可以提升发芽速度并且提高发芽率[29]。本研究通过对不同电场强度和时间交互处理下对卷荚相思种子发芽率进行多元非线性回归分析,构建显著的多元非线性回归方程,得到不同电场强度和时间交互处理下最优非线性回归方程:Y=7.73+135.23X1+1.24X2−86.16X12−0.00911X22−0.75X1X2(R2=0.81,P<0.05)。非线性回归分析表明,卷荚相思种子发芽率与电场强度和处理时间之间存在显著(P<0.05)的相关性,且电场和时间两者交互处理能够影响卷荚相思种子发芽率。
通过聚类分析将发芽率、发芽势和发芽指数3个指标划分为2类,第1类为发芽率,第2类为发芽势和发芽指数组成。从分类结果上看,卷荚相思种子萌发期的发芽指数表现趋势较为显著。发芽指数放大种子活力特征,使活力不同的种子差异更加明显[30]。刘继宏[31]研究发现静电处理种子可以加速种子的新陈代谢,促进种子的萌发,并有效提高种子活力,增强酶活性。有研究发现电场的回路会产生电晕放电,可击穿空气中的NO和O3,与空气中的水发生反应,并使种子内部的生理条件发生变化,有利于种子的萌发[32, 33]。这可能是电场和时间交互处理下激发种子体内的潜力,改变种子膜内外电位差以及物质交换的速度,从而影响种子体内各种酶的活性,最终影响种子的萌发特性。
综上所述,卷荚相思种子发芽率在电场强度0.6 kV·cm−1、处理时间45 min时处于最高状态;发芽势和发芽指数均在电场强度0.8 kV·cm−1、处理时间45 min时处于最高状态。试验表明不同电场强度和时间两者交互处理对卷荚相思种子的萌发起到了促进作用但也产生了阻碍作用,造成不同的作用效果取决于电场强度和处理时间。结果表明适宜的电场强度和时间交互处理能够刺激卷荚相思种子的内部各种贬藏物质由休眠状态转变为活跃状态从而促进种子萌发,改善种子的活力。
-
表 1 外源MT对铝胁迫下番茄生长特性的影响
Table 1 Effect of MT on growth of tomato plants under Al-stress
品种
Varieties处理组
Treatments株高
Plant height/cm叶面积
leaf area/cm2根长
Root length/cm千禧 Qianxi CK 64.25±1.35 b 49.16±2.60 a 9.75±0.76 a Al 59.32±1.44 c 33.09±2.24 b 4.33±2.35 b MT 69.16±2.07 a 60.76±3.14 a 11.59±1.35 a Al+MT 65.92±3.12 b 55.40±1.47 a 10.47±1.32 a 普罗旺斯 Puluowangsi CK 59.37±1.21 b 37.95±1.24 a 12.64±1.84 a Al 51.31±2.74 c 25.88±3.27 b 8.24±2.46 b MT 62.81±2.68 a 41.84±1.55 a 16.05±1.27 a Al+MT 60.44±1.67 ab 39.62±2.47 a 14.18±0.55 a 表内数据为平均值±标准误差,同项同列数据后相同字母表示无显著差异(P > 0.05),下同。
Datas are mean ± standard error; those with same letter on same line indicate no significant difference ( P>0.05). Same for below. 表 2 外源MT对铝胁迫下番茄抗氧化酶的影响
Table 2 Effects of MT on antioxidant enzymes of tomato plants under Al-stress
测量指标
Measured indicators处理
Treatment千禧 Qianxi 普罗旺斯 Puluowangsi 10 d 20 d 30 d 10 d 20 d 30 d SOD/(U·g−1) CK 3902.26±334.93 b 950.64±36.19 c 675.79±15.47 a 4457.17±75.413 a 906.62±17.75 d 583.64±12.05 b AI 6536.58±237.21 a 1288.10±16.24 ab 529.74±5.01 b 5609.25±138.00 a 1139.10±25.28 b 472.19±7.09 c MT 4421.31±299.02 b 1142.93±41.86 bc 694.85±33.19 a 4712.67±180.63 a 1041.19±24.62 c 595.65±29.14 b AI+MT 8008.05±193.70 a 1407.24±34.62 a 629.48±11.85 a 6600.04±281.52 a 1314.23±32.45 a 813.36±28.87 a POD/
(△OD470·min−1·g−1)CK 58.25±2.72 a 75.33±2.21 b 163.72±7.11 c 110.56±12.98 bc 113.50±8.86 b 118.62±10.85 c AI 55.01±14.66 c 95.76±11.25 b 97.96±13.18 d 42.86±8.97 bc 138.95±9.53 ab 95.42±4.70 d MT 64.88±7.39 ab 80.43±11.95 b 192.96±3.54 b 93.16±6.10 bc 124.86±8.80 ab 171.23±6.18 b AI+MT 73.31±3.57 a 184.41±26.62 a 238.29±9.09 a 114.05±7.30 ab 152.73±5.39 a 193.36±10.77 a CAT/
(μmol·min−1·g−1)CK 5.89±1.53 c 18.36±3.04 b 58.60±1.42 b 9.06±0.99 d 18.50±3.72 d 73.77±1.31 b AI 24.54±3.74 b 32.18±2.51 b 53.00±0.98 c 69.52±2.06 c 60.60±0.92 c 52.53±1.32 c MT 12.03±3.40 c 21.47±4.46 b 29.31±1.43 b 63.31±1.43 b 73.77±0.49 b 83.63±1.89 a AI+MT 61.12±1.96 a 77.17±1.21 a 74.67±1.39 a 74.67±1.39 a 89.77±2.03 a 82.17±1.88 a 表 3 外源MT对铝胁迫下番茄内源性抗氧化物的影响
Table 3 Effect of MT on antioxidants in tomato plants under Al-stress
测量指标
Measured indicators处理
Treatment千禧 Qianxi 普罗旺斯 Puluowangsi 10 d 20 d 30 d 10 d 20 d 30 d GSH含量
GSH content/(μmol·g−1)CK 0.44±0.01 d 1.07±0.043 a 1.06±0.05 c 0.66±0.01 d 1.11±0.02 b 1.10±0.02 b AI 1.14±0.01 b 0.86±0.03 a 0.89±0.03 d 1.09±0.02 b 1.06±0.02 c 0.66±0.02 c MT 0.61±0.01 c 1.20±0.02 a 1.69±0.02 a 0.71±0.01 c 1.26±0.01 b 1.30±0.04 a AI+MT 1.20±0.02 a 1.65±0.09 a 1.49±0.05 b 1.13±0.02 a 1.57±0.01 a 1.39±0.02 a AsA含量
AsA content/(mg·g−1)CK 0.03±0.01 d 0.18±0.02 c 0.22±0.03 b 0.14±0.01 d 0.12±0.01 d 0.20±0.02 b AI 0.36±0.01 b 0.39±0.01 b 0.11±0.02 c 0.30±0.05 b 0.28±0.05 b 0.13±0.02 c MT 0.36±0.01 c 0.41±0.02 ab 0.37±0.02 a 0.16±0.03 c 0.16±0.04 c 0.22±0.02 b AI+MT 0.40±0.02 a 0.44±0.02 a 0.36±0.03 a 0.31±0.03 a 0.29±0.03 a 0.26±0.04 a 表 4 外源MT对铝胁迫下番茄脯氨酸和MDA含量的影响
Table 4 Effects of MT on Pro and MDA contents in tomato plants under Al-stress
测量指标
Measured indicators处理
Treatment千禧 Qianxi 普罗旺斯 Puluowangsi 10 d 20 d 30 d 10 d 20 d 30 d MDA含量
MDA content/(nmol·g−1)CK 8.08±0.71 b 6.98±0.40 b 6.19±0.49 c 6.41±0.24 b 6.27±0.72 ab 7.77±0.65 c AI 9.47±0.65 a 8.03±0.47 a 8.01±0.48 a 7.49±0.73 a 7.11±0.70 a 10.17±0.93 a MT 3.43±0.95 ab 4.12±1.15 b 5.83±0.68 c 2.36±0.46 c 5.49±0.52 b 6.95±0.80 c AI+MT 8.75±0.63 c 6.76±0.65 c 6.82±0.62 b 7.20±0.22 a 6.52±0.85 ab 8.72±0.38 b 脯氨酸含量
Proline content/(mg·g−1)CK 4.94±1.33 c 6.39±1.16 c 16.47±1.90 d 2.24±0.97 c 5.10±1.91 b 13.12±1.20 b AI 5.54±1.63 c 9.63±1.43 b 20.23±1.20 c 3.77±0.99 c 8.26±1.82 b 14.43±2.09 b MT 9.64±1.15 b 14.39±1.23 a 34.06±1.06 b 6.48±1.54 b 12.34±2.00 a 25.86±2.03 a AI+MT 12.64±1.20 a 15.34±2.21 a 45.53±2.08 a 13.25±2.86 a 13.89±3.00 a 28.16±3.06 a 表 5 外源MT对铝胁迫下番茄光合特性的影响
Table 5 Effects of MT on photosynthetic characteristics of tomato plants under Al-stress
测量指标
Measured indicators处理
Treatment千禧 Qianxi 普罗旺斯 Puluowangsi 10 d 20 d 30 d 10 d 20 d 30 d SPAD值
SPAD valueCK 28.17±0.37 a 28.60±0.12 b 35.30±0.32 b 31.37±0.62 b 35.87±0.47 b 35.00±0.38 b AI 24.97±0.32 b 25.67±0.26 c 27.30±0.32 c 28.93±0.77 b 29.67±0.23 c 30.27±0.43 c MT 28.23±0.38 a 30.43±0.32 a 37.03±0.08 a 36.10±0.98 a 40.37±0.27 a 38.73±0.68 a AI+MT 27.03±0.46 a 28.93±0.20 b 34.53±0.55 b 31.40±1.36 b 36.27±0.45 b 34.40±0.10 b 初始荧光
FoCK 0.10±0.03 a 0.11±0.04 b 0.11±0.02 c 0.10±0.03 b 0.10±0.07 d 0.11±0.06 c AI 0.09±0.01 a 0.13±0.04 a 0.13±0.07 a 0.12±0.04 a 0.16±0.01 a 0.18±0.05 a MT 0.06±0.03 c 0.07±0.06 d 0.09±0.05 d 0.09±0.06 c 0.11±0.07 c 0.11±0.04 c AI+MT 0.08±0.02 b 0.09±0.05 c 0.11±0.05 b 0.11±0.03 b 0.12±0.04 b 0.14±0.03 b PSII 最大光化学量子产量
Fv /F mCK 0.92±0.03 b 0.93±0.02 a 0.93±0.04 a 0.82±0.03 d 0.81±0.02 b 0.82±0.03 b AI 0.84±0.02 d 0.73±0.03 d 0.69±0.02 c 0.72±0.03 b 0.65±0.03 d 0.61±0.02 d MT 1.04±0.01 a 1.00±0.01 a 0.94±0.02 a 0.94±0.02 a 0.93±0.03 a 0.95±0.03 a AI+MT 0.88±0.01 c 0.78±0.03 c 0.75±0.01 b 0.79±0.01 c 0.71±0.01 c 0.70±0.02 c 表 6 外源MT对铝胁迫下番茄铝富集效能的影响
Table 6 Effect of MT on Al-accumulation of tomato plants under Al-stress
品种 处理 Al含量 Al content/(mg·kg-1) Al富集系数 Al enrichment factor 转运系数
Coefficient of transshipment根
Root茎
Stem叶
Leaf土壤
Soil根
Root茎
Stem叶
Leaf千禧 Qianxi CK 0.13±0.00 c 0.10±0.00 b 0.07±0.01 c 0.83±0.03 bc 0.16±0.01 b 0.12±0.01 b 0.08±0.01 ab 1.29±0.005 a Al 0.22±0.02 a 0.14±0.00 a 0.10±0.02 ab 1.02±0.01 a 0.21±0.02 a 0.14±0.01 a 0.10±0.01 a 1.16±0.003 b MT 0.12±0.02 c 0.07±0.01 b 0.06±0.01 b 0.86±0.02 c 0.15±0.02 b 0.09±0.01 c 0.07±0.02 b 1.09±0.002 c Al+MT 0.18±0.01 b 0.13±0.01 a 0.09±0.01 ab 1.11±0.03 ab 0.17±0.01 b 0.12±0.02 b 0.08±0.01 b 1.20±0.002 b 普罗旺斯 Puluo wangsi CK 0.11±0.01 b 0.09±0.01 b 0.05±0.01 b 0.82±0.06 c 0.13±0.01 a 0.11±0.02 ab 0.06±0.01 b 1.37±0.003 b Al 0.15±0.01 a 0.13±0.01 a 0.09±0.001 a 1.02±0.01 ab 0.15±0.03 a 0.13±0.01 a 0.09±0.01 a 1.47±0.004 a MT 0.10±0.01 b 0.08±0.01 b 0.05±0.006 b 0.85±0.03 bc 0.12±0.01 a 0.10±0.01 b 0.06±0.01 b 1.38±0.002 b Al+MT 0.14±0.01 a 0.12±0.01 a 0.08±0.002 a 1.10±0.01 a 0.14±0.01 a 0.11±0.01 b 0.07±0.01 ab 1.32±0.001 c -
[1] KIMMEL K, FUREY G N, HOBBIE S E, et al. Diversity-dependent soil acidification under nitrogen enrichment constrains biomass productivity [J]. Global Change Biology, 2020, 26(11): 6594−6603. DOI: 10.1111/gcb.15329
[2] RIAZ M, YAN L, WU X W, et al. Boron reduces aluminum-induced growth inhibition, oxidative damage and alterations in the cell wall components in the roots of trifoliate orange [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 153: 107−115. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.02.002
[3] YANG Y, MA L, ZENG H, et al. iTRAQ-based proteomics screen for potential regulators of wheat (Triticum aestivum L. ) root cell wall component response to Al stress [J]. Gene, 2018, 675: 301−311. DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.07.008
[4] 黄凯, 张红宇, 张菡倩, 等. 植物应答铝毒的分子机制研究进展 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2021, 37(3):125−135. HUANG K, ZHANG H Y, ZHANG H Q, et al. Research progress on the molecular mechanism of plants response to aluminum toxicity [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2021, 37(3): 125−135.(in Chinese)
[5] GATSIOS A, NTATSI G, YFANTOPOULOS D, et al. Effects of different organic soil amendments on nitrogen nutrition and yield of organic greenhouse tomato crop [J]. Nitrogen, 2021, 2(3): 347−358. DOI: 10.3390/nitrogen2030024
[6] YANG Q A, PENG Z P, MA W N, et al. Melatonin functions in priming of stomatal immunity in Panax notoginseng and Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Plant Physiology, 2021, 187(4): 2837−2851. DOI: 10.1093/plphys/kiab419
[7] ZAHEDI S M, HOSSEINI M S, FAHADI H N, et al. Exogenous melatonin mitigates salinity-induced damage in olive seedlings by modulating ion homeostasis, antioxidant defense, and phytohormone balance [J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2021, 173(4): 1682−1694. DOI: 10.1111/ppl.13589
[8] SAMI A, SHAH F A, ABDULLAH M, et al. Melatonin mitigates cadmium and aluminium toxicity through modulation of antioxidant potential in Brassica napus L [J]. Plant Biology, 2020, 22(4): 679−690. DOI: 10.1111/plb.13093
[9] POSMYK M M, KURAN H N, MARCINIAK K, et al. Presowing seed treatment with melatonin protects red cabbage seedlings against toxic copper ion concentrations [J]. Journal of Pineal Research, 2008, 45(1): 24−31. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2007.00552.x
[10] 赵海亮, 左璐, 马长恩, 等. 果实膨大期叶面喷施褪黑素对番茄品质的影响 [J]. 北方园艺, 2021(17):15−21. ZHAO H L, ZUO L, MA C E, et al. Effects of foliar spraying melatonin on fruit quality of tomato during fruit expansion [J]. Northern Horticulture, 2021(17): 15−21.(in Chinese)
[11] 许秋怡, 陈兆晖, 季富宴, 等. 褪黑素增强盐害条件下水稻幼苗对稻瘟病的抗病能力 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2018, 46(9):126−128. XU Q Y, CHEN Z H, JI F Y, et al. Melatonin enhancing resistance of rice seedlings to rice blast under salt stress [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 46(9): 126−128.(in Chinese)
[12] ZHAO C F, YANG M, WU X, et al. Physiological and transcriptomic analyses of the effects of exogenous melatonin on drought tolerance in maize (Zea mays L. ) [J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2021, 168: 128−142. DOI: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.09.044
[13] 李阳, 陈静, 刘绍东, 等. 外源褪黑素对盐胁迫下棉花幼苗生长及光合特性的影响 [J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(8):1418−1426. LI Y, CHEN J, LIU S D, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin on growth and photosynthetic characteristics of cotton seedlings under salt stress [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(8): 1418−1426.(in Chinese)
[14] 李方一, 黄璜, 官春云. 作物叶面积测量的研究进展 [J]. 湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 47(3):274−282. LI F Y, HUANG H, GUAN C Y. Review on measurement of crop leaf area [J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University (Natural Sciences), 2021, 47(3): 274−282.(in Chinese)
[15] SHIBAEVA T G, MAMAEV A V, SHERUDILO E G. Evaluation of a SPAD-502 plus chlorophyll meter to estimate chlorophyll content in leaves with interveinal chlorosis [J]. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology, 2020, 67(4): 690−696. DOI: 10.1134/S1021443720040160
[16] 努尔凯麦尔·木拉提, 杨亚杰, 帕尔哈提·阿布都克日木, 等. 小麦叶绿素含量测定方法比较 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2021, 49(9):156−159. NURKHEIMER M, YANG Y J, PARHATI A, et al. Comparative study on determination methods of chlorophyll content in wheat [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 49(9): 156−159.(in Chinese)
[17] LIU Y, ZHANG J M. Lanthanum promotes bahiagrass (Paspalum notatum) roots growth by improving root activity, photosynthesis and respiration [J]. Plants, 2022, 11(3): 382. DOI: 10.3390/plants11030382
[18] 王敏, 宁秋燕, 石元值. 茶树幼苗对不同浓度铝的生理响应差异研究 [J]. 茶叶科学, 2017, 37(4):356−362. WANG M, NING Q Y, SHI Y Z. Study on physiological response of tea plant(Camellia sinensis) seedlings to different aluminum concentrations [J]. Journal of Tea Science, 2017, 37(4): 356−362.(in Chinese)
[19] ARNAO M B, HERNÁNDEZ-RUIZ J. Melatonin: A new plant hormone and/or a plant master regulator? [J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2019, 24(1): 38−48. DOI: 10.1016/j.tplants.2018.10.010
[20] 李格, 孟小庆, 蔡敬, 等. 活性氧在植物非生物胁迫响应中功能的研究进展 [J]. 植物生理学报, 2018, 54(6):951−959. LI G, MENG X Q, CAI J, et al. Advances in the function of reactive oxygen species in plant responses to abiotic stresses [J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2018, 54(6): 951−959.(in Chinese)
[21] JIAO C J, LAN G P, SUN Y H, et al. Dopamine alleviates chilling stress in watermelon seedlings via modulation of proline content, antioxidant enzyme activity, and polyamine metabolism [J]. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2021, 40(1): 277−292. DOI: 10.1007/s00344-020-10096-2
[22] 蒋希瑶, 黄俊杰, 周英杰, 等. 不同浓度外源褪黑素对NaHCO3胁迫下番茄幼苗生长和生理指标的影响 [J]. 北方园艺, 2022(9):1−9. JIANG X Y, HUANG J J, ZHOU Y J, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin on growth and physiological indexes of tomato seedlings under NaHCO3 stress [J]. Northern Horticulture, 2022(9): 1−9.(in Chinese)
[23] 杜昕, 李博, 毛鲁枭, 等. 褪黑素对干旱胁迫下大豆产量及AsA-GSH循环的影响 [J]. 作物杂志, 2022(1):174−178. DU X, LI B, MAO L X, et al. Effects of melatonin on yield and AsA-GSH cycle in soybean under drought stress [J]. Crops, 2022(1): 174−178.(in Chinese)
[24] 陈奋奇, 方鹏, 白明兴, 等. 外源脯氨酸缓解玉米幼苗盐胁迫的效应 [J]. 草业科学, 2022, 39(4):747−755. CHEN F Q, FANG P, BAI M X, et al. Mitigation of salt stress in maize seedlings by exogenous proline application [J]. Pratacultural Science, 2022, 39(4): 747−755.(in Chinese)
[25] GUO M X, ZHANG X T, LIU J J, et al. OsProDH negatively regulates thermotolerance in rice by modulating proline metabolism and reactive oxygen species scavenging [J]. Rice, 2020, 13(1): 61. DOI: 10.1186/s12284-020-00422-3
[26] 吕婷. 褪黑素对小麦铝毒的缓解作用及其机理研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018. LV T. The role of melatonin in alleviating aluminum toxicity in wheat(Triticum aestivum L. )genotypes differing in aluminum tolerance[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018. (in Chinese)
[27] HOU X L, HAN H, CAI L P, et al. Pb stress effects on leaf chlorophyll fluorescence, antioxidative enzyme activities, and organic acid contents of Pogonatherum crinitum seedlings [J]. Flora, 2018, 240: 82−88. DOI: 10.1016/j.flora.2018.01.006
[28] 尹赜鹏, 王珍琪, 齐明芳, 等. 外施褪黑素对盐胁迫下番茄幼苗光合功能的影响 [J]. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(2):467−475. DOI: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.201902.023 YIN Z P, WANG Z Q, QI M F, et al. Effects of melatonin application on photosynthetic function in tomato seedlings under salt stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(2): 467−475.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.201902.023
[29] HOSSEIN P A, ÖZKAN G, BALPINAR N Ö, et al. Estimation of genomic instability and DNA methylation due to aluminum (Al) stress in wheat (Triticum aestivum L. ) using iPBS and CRED-iPBS analyses [J]. Turkish Journal of Botany, 2019, 43(1): 27−37. DOI: 10.3906/bot-1804-23
[30] ACHARY V M M, PARINANDI N L, PANDA B B. Calcium channel blockers protect against aluminium-induced DNA damage and block adaptive response to genotoxic stress in plant cells [J]. Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 2013, 751(2): 130−138. DOI: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2012.12.008
[31] HE S J, HU Y J, WANG H B, et al. Effects of indole-3-acetic acid on arsenic uptake and antioxidative enzymes in Pteris cretica var. nervosa and Pteris ensiformis [J]. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 2017, 19(3): 231−238. DOI: 10.1080/15226514.2016.1207609
[32] NAZIR H, ASGHAR H N, AHMAD Z Z, et al. Judicious use of kinetin to improve growth and yield of rice in nickel contaminated soil [J]. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 2016, 18(7): 651−655. DOI: 10.1080/15226514.2015.1094444




 下载:
下载: