Critical Sterility-inducing Temperature of Rice Affected by tms5 Mutation Site
-
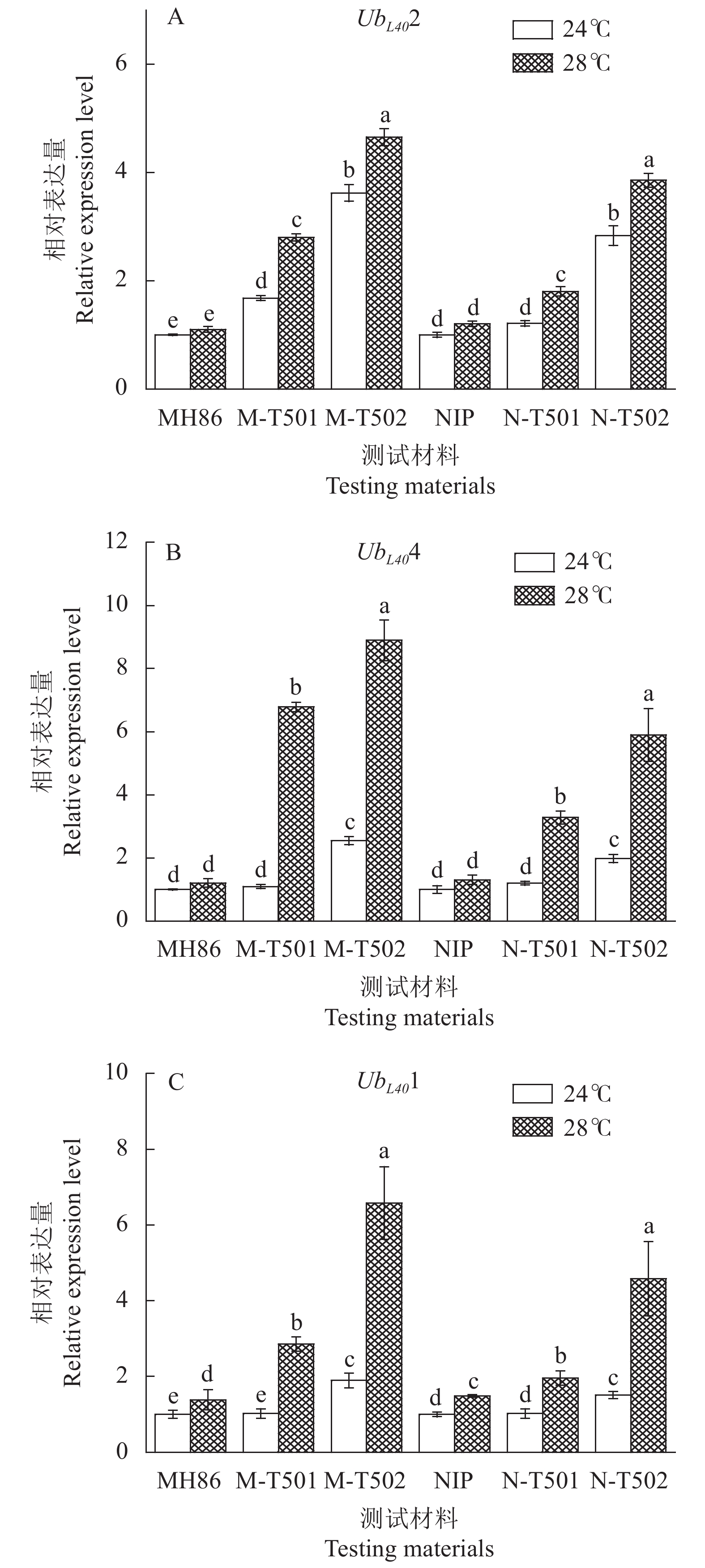
摘要:目的 研究不同水稻tms5突变位点对雄性不育起点温度的影响,探讨不育起点温度遗传调控途径。方法 在水稻TMS5的6个外显子上设计11个CRISPR/Cas9基因编辑靶点,依次命名为T501 — T511,构建相应载体转化粳稻品种日本晴和籼稻品种明恢86,获得各靶点的tms5移码突变体。田间自然高温及人工气候箱(设日平均22 、24和28 ℃ 3种温度)条件下分析tms5突变体的花粉碘染及自交结实率,鉴定不育起点温度。结果 粳稻日本晴tms5突变体的不育起点温度高于28 ℃,籼稻明恢86的不同tms5突变体不育起点温度为22~28 ℃。此外,同一遗传背景下,通过T501靶点编辑产生的tms5-1移码突变体不育起点温度均显著高于T502靶点的tm5-2突变体,其他位点上的tms5突变体育性特征与tm5-2突变体并无差异。基因表达量分析表明,tms5-1突变体幼穗UbL40 基因表达量显著低于tm5-2突变体的表达量。结论 水稻tms5突变体不育起点温度不仅受遗传背景的影响,tms5基因突变位点不同也会影响不育起点温度,特别是T501位点与其余位点突变体间不育起点温度差异显著,为研究水稻tms5两系不育起点温度的分子机理及遗传调控网络提供了新思路。
-
关键词:
- 水稻 /
- CRISPR/Cas9 /
- TMS5 /
- 温敏核不育 /
- 不育起点温度
Abstract:Objective Effects of tms5 mutation site and related genetic regulatory factors in rice on the critical sterility-inducing temperature (CSIT) of the plant were investigated.Method Eleven CRISPR/Cas9 sequentially numbered T501 through T511 were designed to target 6 exons of tms5 to create mutants of Nipponbare (NIP, Oryza sativa ssp. Geng) and Minghui 86 (MH86, O. sativa ssp. Xian). Pollen male fertility and seed setting rate of the mutants were monitored under long day and high temperature field conditions in early August in Fuzhou (NHT) or at 22, 24, and 28 ℃ in phytotrons to identify the CSIT.Result The CSIT of the NIP mutants were higher than 28 ℃, while that of the MH86 mutants between 22 ℃ and 28°C. The tms5-1 T501 mutant had a significantly higher CSIT than the genetically identical tms5-2 counterparts T502, but the other 9 tm5 and the tm5-2 mutants did not differ on it. Expressions of the 3 UbL40 in young panicles were lower in the tms5-1 than the tm5-2 mutants of either rice varieties.Conclusion It appeared that the CSIT of tms5 mutants was affected by the genetic factors as well as the mutation site as the tms5-1 mutant T501 was shown significantly differed from the others. -
-
图 1 CRISPR/Cas9系统介导的TMS5基因特异性突变
A:TMS5基因结构的示意图,黑色矩形代表TMS5的6个外显子,图中短竖线所指位置为各靶点在TMS5基因上的位置。B:CRISPR/Cas9介导的TMS5突变实例,每个靶点只列出了一种突变类型, T505、T508、T510靶点列出的是杂合型突变,T511靶点是双突变,其余位点列出的均为纯合型突变;图上三角形处为缺失或插入突变发生的位置。
Figure 1. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing of tms5
A.Schematic tms5 structure; black rectangles represent 6 exons of tms5; short vertical line refers to position of each target. B. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated tms5 mutants; only one mutation type is listed for each target; T505, T508, and T510 are listed as heterozygous mutations; T511 as biallelic mutation; and remainders as homozygous mutations; triangles point at deletion and insertion sites.
图 2 T1代tms5突变体在田间高温下的花粉育性
①A和B:明恢86(A)及日本晴(B)遗传背景的tms5突变体T1代材料花粉育性;两种背景的tms5突变体(依次为T501至T511靶点突变)育性敏感期处于福州8月初的自然长日高温条件;MH86为明恢86,NIP为日本晴;M-#和N-#分别代表明恢86和日本晴遗传背景的突变体。C:明恢86和日本晴两种遗传背景的野生型、tms5-1突变体及tms5-2突变体穗部开花特征。D: M-T501-#1同一穗上出现可育与不育的颖花。②标尺长度:80 µm(A、B), 0.5 cm(C、D)。
Figure 2. Pollen fertility of T1 tms5 mutants under NHT
①Aand B: Pollen fertility of tms5 mutants in MH86 (A) and NIP (B) induced at 11 targets from T501 to T511; NHT was in early August in Fuzhou; M-# and N-# are mutant plants of MH86 and NIP, respectively. C: Flowering characteristics of WT, tms5-1, and tms5-2 mutants of NIP and MH86 backgrounds. D: Both fertile and sterile spikelets were set on same panicle of M-T501-#1. ②Scale bars represent 80 μm for A and B, 0.5 cm for C and D.
图 3 T2代tms5突变体在不同温度条件下的花粉育性
① 22℃ 、24 ℃、28 ℃、NHT分别表示明恢86及日本晴遗传背景的tms5-1及tms5-2突变体在人工气候箱22 ℃、24 ℃、28 ℃及福州8月初自然高温条件下(NHT)的花粉育性。MH86为明恢86,NIP为日本晴,M-#和N-#分别代表明恢86和日本晴遗传背景的突变体。②标尺长度:80 µm。
Figure 3. Pollen fertility of T2 tms5 mutants under varied temperatures
① Pollen fertility of tms5-1 and tms5-2 mutants of MH86 and NIP backgrounds cultivated at 22 ℃, 24 ℃ or 28 ℃ in phytotrons, or under NHT, respectively; M-# and N-# represent mutant plants of MH86 and NIP backgrounds, respectively. ② Scale bars are 80 μm in length.
表 1 本试验所用sgRNA序列
Table 1 sgRNA applied
靶位点
Target序列(5′- 3′)
Sequence试验目的
PurposeT501S CAGGAACAGCGGCAAGTCATCGC sgRNA构建/
sgRNA ConstructionT501A AACGCGATGACTTGCCGCTGTTC T502S CAGCCACCGCGCCGCCACCGGGT sgRNA构建/
sgRNA ConstructionT502A AACACCCGGTGGCGGCGCGGTGG T503S CAGCACCGTCGAGGGCTACCCCG sgRNA构建/
sgRNA ConstructionT503A AACCGGGGTAGCCCTCGACGGTG T504S CAGCCCATGTACGTCGCCACCCG sgRNA构建/
sgRNA ConstructionT504A AACCGGGTGGCGACGTACATGGG T505S CAGAACCTCGTCCCCCTCGAGAT sgRNA构建/
sgRNA ConstructionT505A AACATCTCGAGGGGGACGAGGTT T506S CAGGTAGGGGTATGTGATATACA sgRNA构建/
sgRNA ConstructionT506A AACTGTATATCACATACCCCTAC T507S CAGATCAAGCAGCTGAAGCTGTC sgRNA构建/
sgRNA ConstructionT507A AACGACAGCTTCAGCTGCTTGAT T508S CAGTGCTTTTACCGGAGATACGA sgRNA构建/
sgRNA ConstructionT508A AACTCGTATCTCCGGTAAAAGCA T509S CAGTGGGCACACCCATCTGTTTG sgRNA构建/
sgRNA ConstructionT509A AACCAAACAGATGGGTGTGCCCA T510S CAGTTCTGCTCGTTATACCGCAG sgRNA构建/
sgRNA ConstructionT510A AACCTGCGGTATAACGAGCAGAA T511S CAGAAGTAGAGTTCATGCATTGA sgRNA构建/
sgRNA ConstructionT511A AACTCAATGCATGAACTCTACTT 表 2 供试引物
Table 2 Primers selected
引物名
Primer name序列
Sequence (5′-3′)试验目的
PurposeHptF AGGTCAGGCTCTCGCTAAAC 转基因阳性株检测/
Identify transgenic plantsHpt-R ACGTAAGGGATGACGCACAAT TMS5F CCATCGTGCTTCGTGCCA TMS5基因扩增、测序
PCR and Sanger sequence for TMS5TMS5R GAGTTCTTGGTACATGAGTGC UBL401F CTACCCCAAGGGGATCGAG Real-Time PCR UBL401R GCAAGGCGGTCGATTGAACT UBL402F TCGCTCAGGGTCCTCGCCTA Real-Time PCR UBL402R CTAGATTCGGCATCCAGTAG UBL404F TACACCATCCAGGAGCCCA Real-Time PCR UBL404R GGTAGCTGGGCATACGAAG ActinF CGTCTGCGATAATGGAACTG Real-Time PCR ActinR TCTGGGTCATCTTCTCACGA 表 3 各载体转化T0代植株突变分析
Table 3 Mutation of T0 transgenic plants
载体
Construct靶点位置
Target site品种
Variety转基因植株数
Numbers of transgenic plants含突变植株数
Numbers of mutation plants突变率
Mutation rates/%TMS501 TMS5第一外显子
First exon of TMS5Nipponbare 21 15 71.4 MH86 18 16 88.9 TMS502 Nipponbare 22 21 95.5 MH86 11 11 100.0 TMS503 Nipponbare 29 11 37.9 MH86 9 6 33.3 TMS504 Nipponbare 21 11 52.4 MH86 15 7 46.7 TMS505 Nipponbare 21 6 28.6 MH86 21 7 33.3 TMS506 TMS5第二外显子
2nd exon of TMS5Nipponbare 19 13 68.4 MH86 24 21 87.5 TMS507 Nipponbare 10 2 20.0 MH86 11 1 9.1 TMS508 TMS5第三外显子
3rd exon of TMS5Nipponbare 10 1 10.0 MH86 18 2 11.1 TMS509 TMS5第四外显子
4th exon of TMS5Nipponbare 21 14 66.6 MH86 18 13 72.2 TMS510 TMS5第五外显子
5th exon of TMS5Nipponbare 10 1 10.0 MH86 15 2 13.3 TMS511 TMS5第六外显子
6th exon of TMS5Nipponbare 14 12 85.7 MH86 11 9 81.8 表 4 T1代tms5材料结实率
Table 4 Seed setting rates of T1 generation of tms5 mutants
背景
Background材料
Lines突变序列
§ Mutation sequences平均结实率
†Average seed setting rates/%明恢86
MH86MH86 87.5±4.3 a M-T501-#1 T501gaacagcggcaagtcatAcgccgg 6.9±9.6 b M-T501-#2 T501gaacagcggcaagtcatTcgccgg 4.0±5.6 b M-T501-#3 T501gaacagcggcaagtcatCcgccgg 5.4±6.9 b M-T502-#1 T502ccaccgcgcc-------ggtc 0 c M-T502-#2 T502ccaccgcgccgccaccgCggtcgg 0 c M-T502-#3 T502ccaccgcgccgccaccgTggtcgg 0 c M-T511-#1 T511gtagagttcatgcat-gaaggaa 0 c M-T511-#2 T511gtagagttcatgcatTtgaaggaa 0 c M-T511-#3 T511gtagagttcatgcatAtgaaggaa 0 c Nipponbare 89.5±2.0 a 日本晴
NipponbareN-T501-#1 T501gc-----------------gacc 48.9±22.1 c N-T501-#2 T501gaacagcggcaagtca--gccgg 54.2±15.8 b N-T501-#3 T501gaacagcggcaagtcatTcgccgg 44.1±12.2 c N-T502-#1 T502ccaccgcgccg------Cggtcggc 10.1±10.2 d N-T502-#2 T502ccaccgcgccgccaccgAggtcggc 8.8±10.1 d N-T502-#3 T502ccaccgcgccgccaccgTggtcgg 9.4±9.6 d N-T511-#1 T511gtagagttcatgca--gaaggaa 9.6±8.4 d N-T511-#2 T511gtagagttcatgcatCtgaaggaa 10.6±10.0 d N-T511-#3 T511gtagagttcatgcatAtgaaggaa 10.4±8.9 d ①§靶点位置的大写字母和短划线分别表示插入与缺失突变类型。 ②†结实率为10穗结实率的平均值±标准差。③同列数据后不同小写字母表示依据LSD多重比较,同一遗传背景材料间的差异达显著水平(P<0.05),下同。
①§ Capital letters and dashes at target sites indicate type of insertion and deletion mutations, respectively. ②† Average seed setting rates are mean ± standard deviation calculated from 10 panicles. ③ Data with different lowercase letters on same column indicate significant difference according to LSD multiple comparison (P<0.05), Same for below.表 5 T2代tms5 突变体花粉育性及自交结实率
Table 5 Pollen fertility and seed setting rates of T2 tms5 mutants
植株编号
Plant ID花粉黑染率
Stained pollens rate/%自交结实率
Seed setting rate/%22 ℃ 24 ℃ 28 ℃ 自然条件
Natural condition22 ℃ 24 ℃ 28 ℃ 自然条件
Natural conditionMH86 86.7±7.8 a 87.1±6.9 a 87.2±5.8 a 88.3±7.1 a 83.4±8.7 a 83.1±6.4 a 85.2±7.2 a 85.9±6.5 a M-T501-#1 87.5±10.3 a 61.6±13.5 c 0 b 20.5±11.5 c 67.8±20.3 b 30.7±12.3 c 0 b 8.5±10.6 c M-T501-#2 80.1±12.0 b 62.7±10.4 c 0 b 28.2±16.3 b 65.3±16.5 bc 40.2±20.5 b 0 b 21.3±16.3 b M-T501-#3 83.3±8.7 ab 71.2±20.2 b 0 b 25.6±15.6 bc 62.2±8.5 c 41.4±17.4 b 0 b 18.7±21.5 b M-T502-#1 12.1±10.6cd 0 d 0 b 0 d 1.5±0.3 d 0 d 0 b 0 d M-T502-#2 9.3±5.8d 0 d 0 b 0 d 1.8±0.6 d 0 d 0 b 0 d M-T502-#3 13.9±10.1 c 0 d 0 b 0 d 1.9±1.3 d 0 d 0 b 0 d Nipponbare 92.5±5.9a 90.6±7.3 a 91.1±6.3 a 92.5±6.5 a 87.6±8.2 a 88.1±9.3 a 87.8±6.6 a 90.5±2.3 a N-T501-#1 84.2±5.7 b 78.2±20.4 b 35.1±11.3 c 67.4±6.9 c 84.1±8.3 a 66.4±10.6 b 13.1±7.2 c 45.2±33.1 c N-T501-#2 86.2±19.5 b 80.2±12.9 b 37.1±8.8 bc 75.7±15.2 b 83.2±7.8 a 68.5±10.3 b 14.8±5.1 bc 52.1±35.8b N-T501-#3 82.3±21.2 b 80.1±18.1 b 40.1±10.5 b 69.1±9.6 c 83.1±10.9 a 50.5±12.2 c 18.6±9.5 b 50.7±28.3 bc N-T502-#1 82.2±6.8 b 70.0±20.2 c 6.1±2.5 d 25.2±19.0 e 72.3±9.2 bc 35.3±28.1 d 3.5±1.6 c 14.1±11.2 d N-T502-#2 85.5±6.3 b 72.2±18.5 c 7.6±6.6 d 31.1±16.9d 75.8±12.3 b 33.4±16.9 d 7.5±8.1 c 18.6±10.3 d N-T502-#3 84.1±9.2 b 70.5±16.7 c 9.2±8.1 d 26.3±27.7 e 69.6±9.2 c 25.4±20.3 e 4.2±2.5 c 17.6±16.3 d 花粉黑染率及自交结实率均为5株的平均值,自然条件指福州8月份的长日高温条件。
Data are means on 5 plants; NHT was defined as long day and high temperature in August in Fuzhou. -
[1] 牟同敏. 中国两系法杂交水稻研究进展和展望 [J]. 科学通报, 2016, 61(35):3761−3769. DOI: 10.1360/N972016-01045 MOU T M. The research progress and prospects of two-line hybrid rice in China [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016, 61(35): 3761−3769.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.1360/N972016-01045
[2] 范优荣, 曹晓风, 张启发. 光温敏雄性不育水稻的研究进展[J]. 科学通报, 2016, 61(35): 3822−3832. FAN Y R, CAO X F, ZHANG Q F. Progress on photoperiod thermo-sensitive genic male sterile rice[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016, 61(35): 3822−3832. (in Chinese)
[3] 陶爱林, 曾汉来, 章元明, 等. 光温敏雄性不育水稻不育临界温度性状的遗传分析 [J]. 遗传学报, 2003, 30(1):40−48. TAO A L, ZENG H L, ZHANG Y M, et al. Genetic analysis of the low critical sterility temperature point in photoperiod-thermo sensitive genic male sterile rice [J]. Acta Genetica Sinica, 2003, 30(1): 40−48.(in Chinese)
[4] 武小金, 尹华奇. 温敏核不育基因置于不同遗传背景下的育性表现变异 [J]. 杂交水稻, 1997, 12(1):26−29. WU X J, YIN H Q. Variation of Fertility Expression of the TGMS Gene in Different Genetic Backgrounds [J]. Hybrid Rice, 1997, 12(1): 26−29.(in Chinese)
[5] DENG Q Y, YUAN L P. Fertility Stability of P(T)GMS Lines in Rice and Its Identification Techniques [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science., 1998, 12(4): 200−206.
[6] FAN Y R, YANG J Y, MATHIONI S M, et al. PMS1T, producing phased small-interfering RNAs, regulates photoperiod-sensitive male sterility in rice [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(52): 15144−15149.
[7] DING J H, LU Q, OUYANG Y D, et al. A long noncoding RNA regulates photoperiod-sensitive male sterility, an essential component of hybrid rice [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(7): 2654−2659.
[8] ZHOU H, LIU Q J, LI J, et al. Photoperiod- and thermo-sensitive genic male sterility in rice are caused by a point mutation in a novel noncoding RNA that produces a small RNA [J]. Cell Research, 2012, 22(4): 649−660. DOI: 10.1038/cr.2012.28
[9] ZHOU H, ZHOU M, YANG Y Z, et al. RNaseZS1 processes UbL40mRNAs and controls thermosensitive genic male sterility in rice [J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 4884. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms5884
[10] YU J P, HAN J J, KIM Y J, et al. Two rice receptor-like kinases maintain male fertility under changing temperatures [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(46): 12327−12332.
[11] ZHANG H, XU C X, HE Y, et al. Mutation in CSA creates a new photoperiod-sensitive genic male sterile line applicable for hybrid rice seed production [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(1): 76−81.
[12] WU L Y, JING X H, ZHANG B L, et al. A natural allele of OsMS1 responds to temperature changes and confers thermosensitive genic male sterility [J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 2055. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-29648-z
[13] QIN P, DENG L C, CHEN W L, et al. A fragment substitution in promoter of MS92/PTC1 causes male sterility in rice [J]. Rice Science, 2020, 27(5): 396−404. DOI: 10.1016/j.rsci.2020.03.004
[14] TAN Y N, SUN X W, FANG B H, et al. The Cds. 71 on TMS5 may act as a mutation hotspot to originate a TGMS trait in indica rice cultivars [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020, 11: 1189. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2020.01189
[15] ZHOU H, HE M, LI J, et al. Development of commercial thermo-sensitive genic male sterile rice accelerates hybrid rice breeding using the CRISPR/Cas9-mediated TMS5 editing system [J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 37395. DOI: 10.1038/srep37395
[16] 陈日荣, 周延彪, 王黛君, 等. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术编辑水稻温敏不育基因TMS5 [J]. 作物学报, 2020, 46(8):1157−1165. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2020.92059 CHEN R R, ZHOU Y B, WANG D J, et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated editing of the thermo-sensitive genic male-sterile gene TMS5 in rice [J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2020, 46(8): 1157−1165.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2020.92059
[17] BARMAN H N, SHENG Z H, FIAZ S, et al. Generation of a new thermo-sensitive genic male sterile rice line by targeted mutagenesis of TMS5 gene through CRISPR/Cas9 system [J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 109. DOI: 10.1186/s12870-019-1715-0
[18] 吴明基, 林艳, 刘华清, 等. 利用CRISPR/Cas-9技术创制水稻温敏核不育系 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2018, 33(10):1011−1015. WU M J, LIN Y, LIU H Q, et al. Development of thermo-sensitive male sterile rice with CRISPR/Cas9 technology [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 33(10): 1011−1015.(in Chinese)
[19] 黄忠明, 周延彪, 唐晓丹, 等. 基于CRISPR/Cas9技术的水稻温敏不育基因tms5突变体的构建 [J]. 作物学报, 2018, 44(6):844−851. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2018.00844 HUANG Z M, ZHOU Y B, TANG X D, et al. Construction of tms5 mutants in rice based on CRISPR/Cas9 technology [J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2018, 44(6): 844−851.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2018.00844
[20] 杜茜, 费云燕, 王芳权, 等. 敲除TMS5基因获得温敏不育粳稻新材料 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2019, 33(5):429−435. DU X, FEI Y Y, WANG F Q, et al. Thermo-sensitive male sterile line created by editing TMS5 gene in Japonica rice [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2019, 33(5): 429−435.(in Chinese)
[21] FANG Y Y, YANG J L, GUO X Y, et al. CRISPR/Cas9-induced mutagenesis of TMS5 confers thermosensitive genic male sterility by influencing protein expression in rice (Oryza sativa L. ) [J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(15): 8354. DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158354
[22] 梁敏敏, 张华丽, 陈俊宇, 等. 利用CRISPR/Cas9 技术创制抗稻瘟病香型早籼温敏核不育系 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 2022, 36(3):248−258. LIANG M M, ZHANG H L, CHEN J Y, et al. Developing fragrant early indica TGMS line with blast resistance by using CRISPR/Cas9 technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2022, 36(3): 248−258.(in Chinese)
[23] 苏军, 胡昌泉, 翟红利, 等. 农杆菌介导籼稻明恢86高效稳定转化体系的建立 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2003, 18(4):209−213. SU J, HU C Q, ZHAI H L, et al. Establishment of a highly efficient and stable tranforming system mediated by Agrobacterium tumefacien in indica rice [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2003, 18(4): 209−213.(in Chinese)
[24] 王慧娜, 初志战, 马兴亮, 等. 高通量PCR模板植物基因组DNA制备方法 [J]. 作物学报, 2013, 39(7):1200−1205. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2013.01200 WANG H N, CHU Z Z, MA X L, et al. A high through-put protocol of plant genomic DNA preparation for PCR [J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2013, 39(7): 1200−1205.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2013.01200
[25] HE Y Q, YANG J, XU C G, et al. Genetic bases of instability of male sterility and fertility reversibility in photoperiod-sensitive genic male-sterile rice [J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 1999, 99(3): 683−693.
[26] 武小金, 尹华奇. 温敏核不育基因置于不同遗传背景下育性表现变异的遗传初探 [J]. 中国水稻科学, 1996, 10(1):1−6. WU X J, YIN H Q. Preliminary genetic study on the variation of fertility expression of TGMS gene in different genetic backgrounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 1996, 10(1): 1−6.(in Chinese)
[27] ROSSI A, KONTARAKIS Z, GERRI C, et al. Genetic compensation induced by deleterious mutations but not gene knockdowns [J]. Nature, 2015, 524(7564): 230−233. DOI: 10.1038/nature14580
[28] MA Z P, ZHU P P, SHI H, et al. PTC-bearing mRNA elicits a genetic compensation response via Upf3a and COMPASS components [J]. Nature, 2019, 568(7751): 259−263. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1057-y
[29] EL-BROLOSY M A, KONTARAKIS Z, ROSSI A, et al. Genetic compensation triggered by mutant mRNA degradation [J]. Nature, 2019, 568(7751): 193−197. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1064-z
[30] RODRIGUEZ-LEAL D, XU C, KWON C T, et al. Evolution of buffering in a genetic circuit controlling plant stem cell proliferation [J]. Nature Genetics, 2019, 51(5): 786−792. DOI: 10.1038/s41588-019-0389-8
[31] 马志鹏, 陈军. 无义突变与“遗传补偿效应” [J]. 遗传, 2019, 41(5):359−364. DOI: 10.16288/j.yczz.19-101 MA Z P, CHEN J. Nonsense mutations and genetic compensation response [J]. Hereditas, 2019, 41(5): 359−364.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.16288/j.yczz.19-101





 下载:
下载: