Transcriptome Analysis on Effect of Glutamic and Aspartic Acids on Growth of Sparassis latifolia
-
摘要:目的 通过转录组测序分析添加不同氮源培养后广叶绣球菌基因差异表达情况,旨在探究氨基酸调节基质降解的分子机理,为其高效生产提供理论依据。方法 以硫酸铵、鱼粉蛋白胨、天冬氨酸和谷氨酸为氮源,测定菌丝生长速度并利用转录组测序技术对不同氮源诱导下广叶绣球菌进行基因差异表达分析。结果 天冬氨酸和谷氨酸相对于硫酸铵、鱼粉蛋白胨可显著促进菌丝生长(P<0.01);GO功能富集分析显示差异基因主要富集在氧化还原酶活性、铁离子跨膜转运蛋白活性和铁离子的还原和转运同化等;KEGG通路富集分析显示,富集度较高的通路主要有色氨酸代谢、花生四烯酸代谢和氮代谢等。差异基因中溶血素蛋白ostreolysin A6、GroES类似蛋白和6-甲基水杨酸脱羧酶等基因在天冬氨酸或谷氨酸诱导下表达量变化倍数较大(P<0.01)。结论 天冬氨酸和谷氨酸可能通过促进绣球菌氧化还原酶活性及铁离子代谢过程,提高其基质利用能力。研究结果为进一步研究广叶绣球菌木质纤维素降解机制及栽培生理提供理论依据。Abstract:Objective Effects of differential expression genes (DEGs) of Sparassis latifolia cultured with varied nitrogen sources on substrate degradation were analyzed for efficient cultivation of the mushroom.Method Cultured on substrates of varied nitrogen sources, such as ammonium sulfate (As), fish peptone (Pep), aspartic acid (Asp), and glutamic acid (Glu), S. latifolia mycelium growth was observed. Transcriptomes of DEGs were determined.Result Of the various nitrogen sources, Asp and Glu significantly promoted the mycelial growth (P<0.01). According to a GO enrichment analysis, the DEGs in the mushrooms were mainly related to the activities of oxidoreductase, iron ion transmembrane transport, and iron assimilation by reduction and transport. And the KEGG showed their involvement in the metabolisms of tryptophan, arachidonic acid, and nitrogen. The expressions of the ostreolysin A6, GroES-like protein, and 6-methylsalicylic acid decarboxylase genes were significantly altered by the presence of Asp and Glu (P<0.01).Conclusion The use of Asp and Glu as a nitrogen source promoted the substrate utilization through the heightened oxidoreductase activity and iron metabolism in S. latifolia. Hence, the addition would facilitate an efficient mushroom cultivation.
-
Keywords:
- Sparassis latifolia /
- transcriptome /
- amino acid /
- glutamic acid /
- aspartic acid
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】广叶绣球菌(Sparassis latifolia)作为一种具有极高营养和药用价值的珍稀食用菌[1-3],已在福建、江苏、浙江和陕西等地实现了工厂化栽培。目前,绣球菌的研究主要集中于生物学特性、葡聚糖及其活性等方面[1-2, 4-5]。然而,国内的工厂化生产模式中,从接种至采摘需要 90 d左右,而其生物学效率仅为65%左右。此外,胞外酶活性与基质降解速率的变化具有一定的相关性,在一定程度上可以反映食用菌的生长速度和生物转化率[6]。因此,通过进一步解析特定营养因子对胞外酶活性和基质降解速率的影响,或能提高绣球菌生物学效率,缩短工厂化栽培周期。【前人研究进展】食用菌栽培添加剂在生产上可提高产量,以氨基酸为主要成分的食用菌添加剂在香菇(Lentinula edodes)、草菇(Volvariella volvacea)、双孢蘑菇(Agaricus bisporus)等食用菌提高产量、缩短栽培周期方面具有一定的效果[7-9]。不同氨基酸氨对真菌胞外酶活性的影响存在差异,例如DL-蛋氨酸、DL-色氨酸、甘氨酸和DL-缬氨酸可促进黑蛋巢菌(Cyathus bulleri)漆酶的产生,但L-半胱氨酸则完全抑制漆酶的产生[10]。DL-正亮氨酸、L-亮氨酸、DL-异亮氨酸、L-赖氨酸单盐酸盐和 DL-β-苯丙氨酸可以提高链霉菌(Streptomyces sp.)木聚糖酶和果胶酶的产量约3倍,且复合使用DL-正亮氨酸, L-亮氨酸, DL-异亮氨酸可以提升酶的产量约6倍[11]。半胱氨酸对烟曲霉(Aspergillus fumigatus)内切葡聚糖酶、外切葡聚糖酶、β-葡萄糖苷酶和木聚糖酶的产生具有促进作用,而蛋氨酸对胞外酶的产生则具有一定的抑制作用[12]。此外,在以半胱氨酸为单一氮源的处理中,烟曲霉的分泌蛋白中可检测出大量的过氧化氢酶,而在以蛋氨酸和硫酸铵为单一氮源的处理中则未检测出过氧化氢酶[12]。过氧化氢酶与羟基自由基的产生有关,可能通过芬顿反应参与了木质素的及纤维素解聚。【本研究切入点】在广叶绣球菌生长发育过程中,氮源是必不可少的,特别是氮源的种类和比例对绣球菌菌丝生长和子实体生长发育至关重要。[5, 13]。氨基酸作为重要的氮源因子,可以刺激多种真菌胞外酶的产生,但相关机制尚不清楚。厘清氨基酸如何通过调节酶活变化和基质降解速率来促进菌丝生长,能够为绣球菌营养添加提供参考。【拟解决的关键问题】以PDB为基础培养基,分别添加无机氮源硫酸铵(As)、有机复合氮源鱼粉蛋白胨(Pep)、谷氨酸(Glu)和天冬氨酸(Asp),通过转录组测序分析氨基酸对广叶绣球菌基质降解相关基因表达的影响,旨在探究氨基酸调节广叶绣球菌降解机制的分子机理,为其高效生产提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 菌株和试验材料
广叶绣球菌闽绣1号由福建省农业科学院食用菌研究所保藏。马铃薯葡萄糖肉汤培养基(potato dextrose broth,PDB)购自美国BD公司,鱼粉蛋白胨购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司,谷氨酸和天冬氨酸购自北京索莱宝科技有限公司。
PDA培养基:PDB粉末24 g·L−1,琼脂15 g·L−1,121 ℃高压灭菌20 min。液体种子培养基:PDB粉末24 g·L−1,121 ℃高压灭菌20 min。氮源平板试验培养基:PDB粉末24 g·L−1,琼脂15 g·L−1,121 ℃高压灭菌20 min,温度降至50 ℃后分别加入经0.22 μm滤膜过滤除菌的硫酸铵、谷氨酸、天冬氨酸、鱼粉蛋白胨,终质量浓度为1 g·L−1。氮源诱导培养基:氮源平板试验培养基配方中不添加琼脂。
1.2 菌丝生长测定
将活化后的广叶绣球菌菌块接种于不同氮源培养基中[13],25 ℃黑暗培养25 d,利用十字交叉法测定菌丝生长速度,每个试验设4次重复。
1.3 不同氮源液体培养
将经PDA活化的绣球菌菌块接种于100 mL液体种子培养基,25 ℃,150 r·min−1振荡培养9 d,过滤去除培养基收集菌丝体,加入100 mL无菌水,匀浆后取5 mL加入100 mL氮源诱导培养基,25 ℃,150 r·min−1振荡培养6 d后收集菌丝体,液氮速冻后保藏于−80 ℃超低温冰箱。每个处理组重复3次。
1.4 转录组测序
使用TRIzol总RNA提取试剂盒提取不同氮源培养条件下的绣球菌总RNA。总RNA经纯化、质检合格后构建文库上机测序。使用FastQC(http://www.bioinformatics. babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/)对测序原始数据进行过滤,获得高质量测序数据。通过StringTie[14]软件对所有的clean reads进行转录本拼接与合并。与S. latifolia参考基因组[15]比对后,利用edgeR[16]软件计算不同氮源试验处理样品中转录本丰度与差异比较。以log2FC的绝对值≥1且P < 0.05为标准筛选差异表达基因。分别采用Goatools和KOBAS[17]软件对天冬氨酸/硫酸铵(Asp/As)、谷氨酸/硫酸铵(Glu/As)、天冬氨酸/鱼粉蛋白胨(Asp/Pep)、谷氨酸/鱼粉蛋白胨(Glu/Pep)和天冬氨酸/谷氨酸(Asp/Glu)比较组差异表达基因分别进行GO和KEGG富集分析,P<0.05时为显著富集。
1.5 数据分析
用Excel和TBtools[18]进行数据整理和热图的绘制,菌丝生长速度统计分析采用SPSS 19进行。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同氮源对菌丝生长的影响
不同类型氮源对绣球菌菌丝生长的影响见图1。以天冬氨酸(Asp)和谷氨酸(Glu)为氮源时菌丝平均生长速度较快,分别可达0.31 cm·d−1和0.30 cm·d−1,以硫酸铵(As)为氮源时菌丝生长速度为0.24 cm·d−1,以鱼粉蛋白胨(Pep)为氮源时菌丝生长速度为0.26 cm·d−1。以氨基酸Asp和Glu为氮源时,相对于As和Pep,菌丝生长速度差异极显著(P<0.01)。且以Asp和Glu为氮源培养时,绣球菌菌丝较浓密,呈絮状。
2.2 不同氮源差异表达基因的鉴定
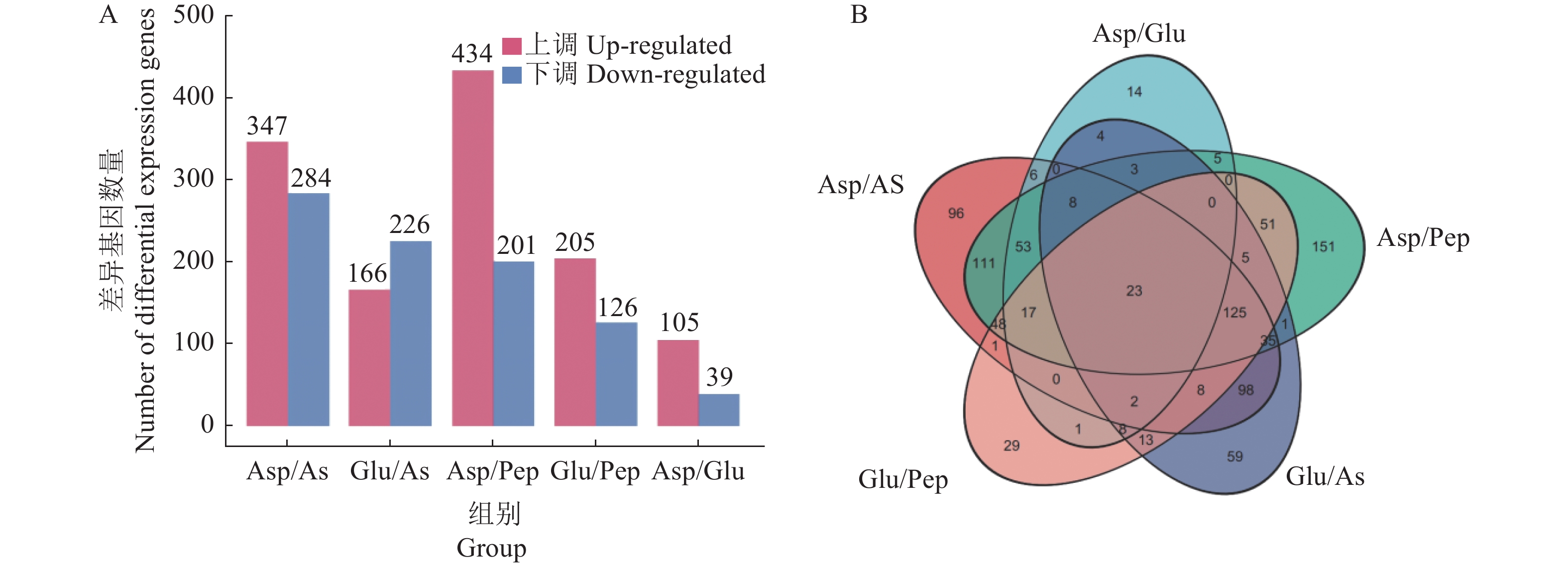
以|log2FC|≥1为变化阈值,且P<0.05为标准,获得不同氮源比较组间的差异表达基因(differential expression genes, DEGs)。从图2-A看出,比较组Asp/As获得DEGs 631个,Glu/As获得DEGs 392个,Asp/Pep获得DEGs 635个,Glu/Pep获得DEGs 331,Asp/Glu获得DEGs 144个。从图2-B得知,不同比较组间共有的DEGs有23个。
2.3 不同氮源比较组差异表达基因的功能分析
通过对不同氮源比较组间DEGs的GO功能富集(图3-A)可以看出:Asp和Glu与硫酸铵、蛋白胨相比差异基因主要富集在氧化还原酶活性(oxidoreductase activity)、高亲和力亚铁离子跨膜转运蛋白活性(high-affinity ferrous iron transmembrane transporter activity)、铁离子跨膜转运蛋白活性(iron ion transmembrane transporter activity)和铁离子的还原和转运同化(iron assimilation by reduction and transport)等。差异基因的KEGG通路富集分析结果(图3-B)显示:Asp和Glu与硫酸铵、蛋白胨相比差异基因富集度较高的通路主要有色氨酸代谢(tryptophan metabolism)、花生四烯酸代谢(arachidonic acid metabolism)、氮代谢(nitrogen metabolism)、甘油酯代谢(glycerolipid metabolism)、脂肪酸降解(fatty acid degradation)等。
2.4 不同组间变化倍数显著差异基因分析
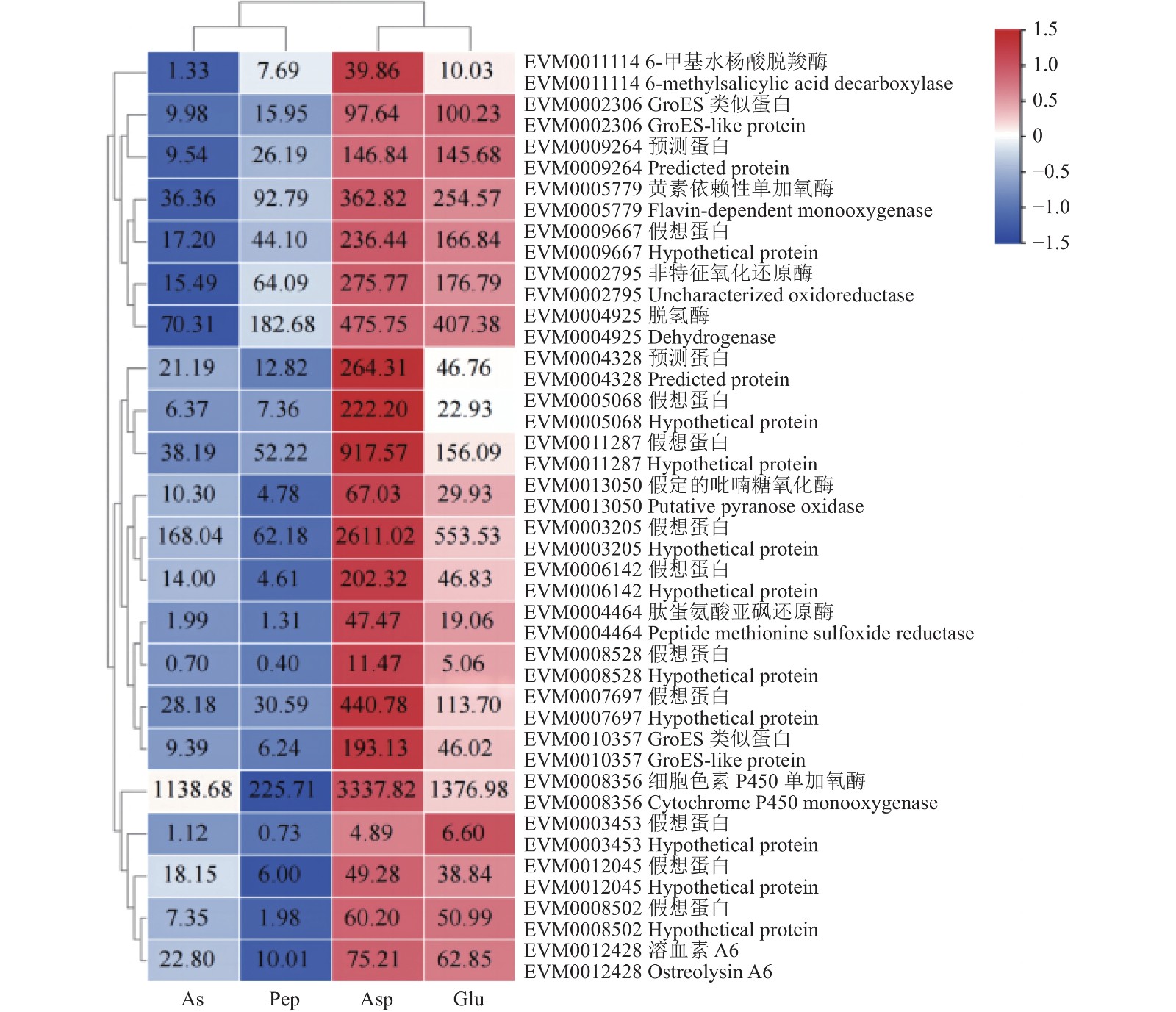
根据不同比较组间DEGs的变化倍数,分别筛选Asp/As、Glu/As、Asp/Pep和Glu/Pep比较组内上调前10的DEGs,共获得22个DEGs,基因相对表达量FPKM(fragments per kilobase of exon model per million mapped fragments)值如图4所示。相对于As和Pep,变化显著的基因主要编码细胞色素P450单加氧酶(Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase)、溶血素蛋白ostreolysin A6、吡喃糖氧化酶(pyranose oxidase)、肽蛋氨酸亚砜还原酶(peptide methionine sulfoxide reductase)、GroES类似蛋白(GroES-like protein)、6-甲基水杨酸脱羧酶(6-methylsalicylic acid decarboxylase)、黄素依赖性单加氧酶(flavin-dependent monooxygenase)、脱氢酶orsE(dehydrogenase orsE)以及部分未能获得注释的假想蛋白。
2.5 不同比较组基质降解差异显著基因分析
不同比较组间所有的DEGs共注释到95个氧化还原酶基因,聚类分析可区分为2个分支(图5)。其中一个分支含60个基因,在Asp或Glu组中表达量相对较高,另外一个分支含35个基因在Pep或As组中表达量相对较高。氧化还原酶中单加氧酶数量最多(18个),其次为短链脱氢酶(15个)。在Asp/As、Glu/As、Asp/Pep和Glu/Pep比较组中上调倍数较大的有:EVM0004464肽甲硫氨酸亚砜还原酶(peptide methionine sulfoxide reductase)分别上调23.81倍、9.56倍、36.24倍和14.54倍(P<0.01),EVM0011114 6-甲基水杨酸脱羧酶(6-methylsalicylic acid decarboxylase)分别上调13.75倍、9.70倍、5.36倍和3.78倍(P<0.01),EVM0013050吡喃糖氧化酶(putative pyranose oxidase)分别上调24.02倍、4.09倍、17.57倍 和2.99倍(P<0.01)。
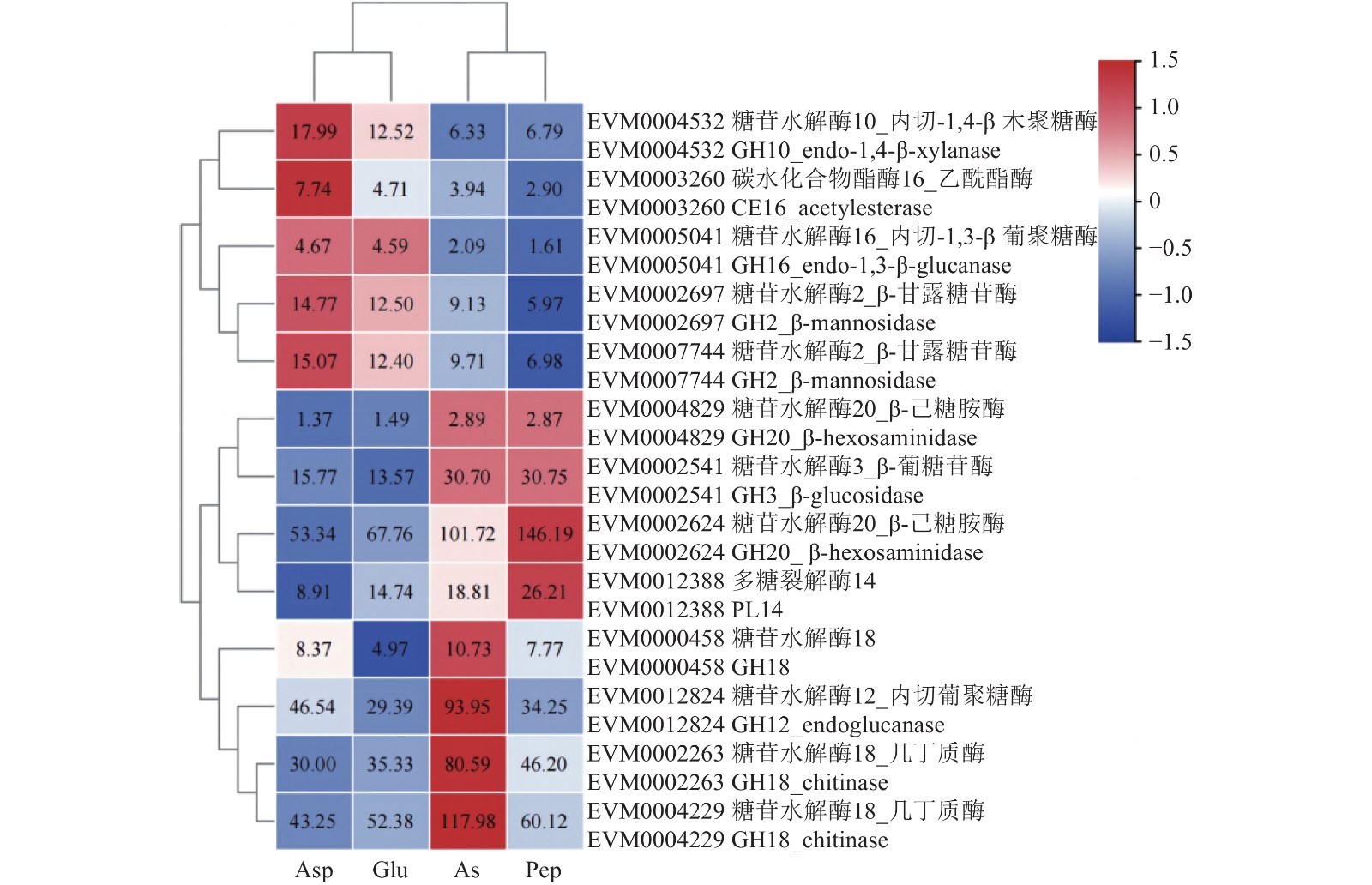
通过dbCAN [19]在线注释工具对不比较组间所有差异基因进行注释,其中与纤维素和半纤维素降解相关的糖苷水解酶(glycoside hydrolases,GHs)11个,碳水化合物酯酶(carbohydrate esterases,CEs)1个,多糖裂解酶(polysaccharide lyases,PLs)1个(图6)。主要包括2个β-己糖胺酶(β-hexosaminidase)、2个几丁质酶(chitinase)及2个β-甘露糖苷酶(β-mannosidase)等。大多数纤维素和半纤维素降解相关酶基因在Asp和 Glu组中相对于As和Pep表达量下调,而内切-1,4-β-木聚糖酶(endo-1,4-β-xylanase)基因在Asp/As和Asp/Pep比较组中表达量显著上调(P<0.01),内切-1,3-β-葡聚糖酶(endo-1,3-β-glucanase)在Asp和 Glu中相对于As和Pep表达量均显著上调(P<0.01),2个β-甘露糖苷酶基因在Asp/Pep比较组中均显著上调(P<0.01)。
差异基因中与铁离子转运和还原相关的基因共鉴定出8个(图7),包括2个质膜铁离子渗透酶(plasma membrane iron permease)、2个铁离子还原酶(iron reductase)、2个铁转运多铜氧化酶(iron transport multicopper oxidase fio1)、1个锌/铁离子渗透酶(zinc/iron permease)和1个铁离子摄取簇蛋白(hypothetical iron uptake cluster protein)。其中,EVM0004041(incomplete iron reductase)在As中表达量相对较高,其余铁离子代谢相关基因在Asp和Glu组中表达量相对较高。
3. 讨论
外源额外添加营养物质,可以为生物体生长发育提供适宜及必需的营养因子,促进其生长发育或次级代谢产物合成。如特异性添加糖类[20-21]、氨基酸[12, 22]、矿质元素[23]、芳香族化合物[24]、有机酸[25-26]等,可促进食用菌菌丝生长或胞外酶活性。因此针对一些生长周期较长、基质转化率较低的食用真菌,可通过添加适宜的生长促进物质,提高木质纤维素降解酶活性,促进栽培基质的高效利用。
本研究通过比较Asp、Glu与无机氮源硫酸铵、有机复合氮源鱼粉蛋白胨对绣球菌菌丝生长的影响,结果表明 Asp、Glu不仅可促进菌丝生长,且菌丝更浓密。在生长培养基中添加谷氨酸和天冬酰胺可提高里氏木霉菌(Trichoderma reesei)的纤维素酶和β-木聚糖酶活性[27],谷氨酸对拟层孔菌(Fomitopsis sp.)羧甲基纤维素酶活性促进作用较天冬酰胺和天冬氨酸效果更好[28]。天冬酰胺也可以促进地曲霉(Aspergillus terreus)的纤维素酶合成[29]并提高金针菇(Flammulina velutipes)β-葡萄糖苷酶的产量[30]。因此,Asp和Glu促进绣球菌生长可能由于相关胞外酶活性的提升,促进了菌丝生长。
为进一步分析Asp和Glu对绣球菌生长促进作用的机制,试验通过转录组测序分析4种不同氮源诱导下菌丝体基因表达差异。DEGs中与纤维素和半纤维素利用相关的基因较少,内切-1,4-β-木聚糖酶、内切-1,3-β-葡聚糖酶和β-甘露糖苷酶在Asp或Glu处理组中表达量上调,但上调倍数较小(2~3倍)。而氧化还原酶中上调基因数量较多,其中肽甲硫氨酸亚砜还原酶、6-甲基水杨酸脱羧酶和吡喃糖氧化酶等在Asp或Glu处理组中上调倍数相对较大(3~36倍),同时与铁离子转运(plasma membrane iron permease、iron transport multicopper oxidase fio1和hypothetical iron uptake cluster protein)、还原(iron reductase)相关的差异表达基因在Asp或Glu处理组中大都表达量上调。氧化还原反应及铁离子代谢与木腐真菌基质降解过程中的芬顿反应相关,氧化还原反应参与了H2O2的产生,铁离子与H2O2反应产生羟基自由基,羟基自由基在木质素修饰及纤维素解聚方面起关键作用[31-32]。GO功能富集结果也表明氧化还原酶活性和铁离子跨膜转运活性富集度较高。因此推测Asp和Glu对绣球菌芬顿反应具有一定的促进作用。
不同比较组中差异变化上调倍数排名靠前的基因中除了功能未知的假想蛋白和氧化还原酶基因,溶血素蛋白ostreolysin A6和GroES类蛋白基因受Asp和Glu诱导上调显著。溶血素基因在糙皮侧耳(Pleurotus ostreatus)原基形成和子实体阶段特异性表达,可抑制菌丝生长和诱导原基形成[33-34],溶血素A6基因是子实体形成的触发基因[35]。蛋白质组和qPCR结果也显示绣球菌溶血素基因在幼菇阶段表达量最高,与菌丝阶段相比分别上调23倍和280倍,也可能参与了子实体的形成过程[36]。GroES作为蛋白质折叠过程中的辅分子伴侣,协助GroEL完成蛋白质的折叠[37]。由于绣球菌基因组功能注释还不完善,基因功能的研究更是鲜见报道,因此ostreolysin A6、GroES以及功能未知的假想蛋白基因在其生长发育过程中的作用还需更加深入的研究。
4. 结论
本研究结果初步表明Asp和Glu可促进广叶绣球菌菌丝的生长。Asp和Glu可能通过促进绣球菌氧化还原酶活性及铁离子代谢过程,提高其基质利用能力。多种氨基酸的复合使用是否能够发挥更好的促进作用还需进一步研究。同时,结合蛋白质组技术分析氨基酸对绣球菌降解木质纤维素的影响,可为木质纤维素降解机制、栽培生理及代谢研究更好的奠定基础。
-
-
[1] KIMURA T. Natural products and biological activity of the pharmacologically active cauliflower mushroom Sparassis crispa [J]. BioMed Research International, 2013, 2013: 982317.
[2] SHARMA N, TAPWAL A, VERMA R, et al. Medicinal, nutritional, and nutraceutical potential of Sparassis crispa s. lat. : A review [J]. IMA Fungus, 2022, 13(1): 8. DOI: 10.1186/s43008-022-00095-1
[3] WEI X, CHENG F E, LIU J Y, et al. Sparassis latifolia polysaccharides inhibit colon cancer in mice by modulating gut microbiota and metabolism [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2023, 232: 123299. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123299
[4] 肖冬来, 马璐, 杨驰, 等. 不同碳源条件下广叶绣球菌转录组分析 [J]. 微生物学通报, 2019, 46(7):1654−1661. XIAO D L, MA L, YANG C, et al. Transcriptome analysis of Sparassis latifolia cultivated with different carbon sources [J]. Microbiology China, 2019, 46(7): 1654−1661.(in Chinese)
[5] 马璐, 杨驰, 肖冬来, 等. 基质碳氮比对广叶绣球菌生长发育的影响 [J]. 菌物学报, 2021, 40(12):3196−3213. MA L, YANG C, XIAO D L, et al. Effects of different substrate carbon to nitrogen ratio(C/N) on the growth and development of Sparassis latifolia [J]. Mycosystema, 2021, 40(12): 3196−3213.(in Chinese)
[6] 安琪, 吴雪君, 吴冰, 等. 不同碳源和氮源对金针菇降解木质纤维素酶活性的影响 [J]. 菌物学报, 2015, 34(4):761−771. AN Q, WU X J, WU B, et al. Effects of carbon and nitrogen sources on lignocellulose decomposition enzyme activities in Flammulina velutipes [J]. Mycosystema, 2015, 34(4): 761−771.(in Chinese)
[7] 刘秀明, 陈强, 邬向丽, 等. 国内外食用菌增产添加物研究进展 [J]. 食用菌学报, 2018, 25(1):120−125. LIU X M, CHEN Q, WU X L, et al. Usage of mineral and amino acid additives in edible mushroom cultivation [J]. Acta Edulis Fungi, 2018, 25(1): 120−125.(in Chinese)
[8] NAIM L, ALSANAD M A, SHABAN N, et al. Production and composition of Pleurotus ostreatus cultivated on Lithovit(®)-Amino25 supplemented spent substrate [J]. AMB Express, 2020, 10(1): 188. DOI: 10.1186/s13568-020-01124-1
[9] CARRASCO J, ZIED D C, PARDO J E, et al. Supplementation in mushroom crops and its impact on yield and quality [J]. AMB Express, 2018, 8(1): 146. DOI: 10.1186/s13568-018-0678-0
[10] DHAWAN S, KUHAD R C. Effect of amino acids and vitamins on laccase production by the bird’s nest fungus Cyathus bulleri [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2002, 84(1): 35−38. DOI: 10.1016/S0960-8524(02)00026-3
[11] BEG Q K, BHUSHAN B, KAPOOR M, et al. Production and characterization of thermostable xylanase and pectinase from Streptomyces sp. QG-11-3 [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2000, 24(6): 396−402. DOI: 10.1038/sj.jim.7000010
[12] MIAO J X, WANG M M, MA L, et al. Effects of amino acids on the lignocellulose degradation by Aspergillus fumigatus Z5: Insights into performance, transcriptional, and proteomic profiles [J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2019, 12: 4. DOI: 10.1186/s13068-018-1350-2
[13] 林衍铨, 马璐, 应正河, 等. 碳源和氮源对绣球菌菌丝生长的影响 [J]. 食用菌学报, 2011, 18(3):22−26. LIN Y Q, MA L, YING Z H, et al. Effect of carbon and nitrogen source on the growth of Sparassis crispa Mycelium [J]. Acta Edulis Fungi, 2011, 18(3): 22−26.(in Chinese)
[14] PERTEA M, PERTEA G M, ANTONESCU C M, et al. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads [J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2015, 33(3): 290−295. DOI: 10.1038/nbt.3122
[15] YANG C, MA L, XIAO D L, et al. Chromosome-scale assembly of the Sparassis latifolia genome obtained using long-read and Hi-C sequencing [J]. G3, 2021, 11(8): jkab173. DOI: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab173
[16] ROBINSON M D, MCCARTHY D J, SMYTH G K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data [J]. Bioinformatics, 2010, 26(1): 139−140. DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616
[17] XIE C, MAO X Z, HUANG J J, et al. KOBAS 2.0: A web server for annotation and identification of enriched pathways and diseases [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2011, 39(S2): W316−W322. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr483
[18] CHEN C J, CHEN H, ZHANG Y, et al. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data [J]. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(8): 1194−1202. DOI: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
[19] ZHANG H, YOHE T, HUANG L, et al. dbCAN2: A meta server for automated carbohydrate-active enzyme annotation [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 46(W1): W95−W101. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gky418
[20] 杨焕玲, 查磊, 赵旭, 等. 培养基中添加海藻糖对大球盖菇、斑玉蕈菌丝生长的影响 [J]. 微生物学通报, 2019, 46(5):1108−1114. YANG H L, ZHA L, ZHAO X, et al. Effect of adding trehalose to culture medium on the growth of Stropharia rugosoannulata and Hypsizigus marmoreus [J]. Microbiology China, 2019, 46(5): 1108−1114.(in Chinese)
[21] 韩美玲, 边禄森, 姜宏浩, 等. 不同碳氮源对糙皮侧耳木质纤维素酶活性的影响 [J]. 菌物学报, 2020, 39(8):1538−1550. HAN M L, BIAN L S, JIANG H H, et al. Effects of different carbon and nitrogen sources on lignocellulolytic enzyme activities of Pleurotus ostreatus [J]. Mycosystema, 2020, 39(8): 1538−1550.(in Chinese)
[22] SHENG Y Q, ZHANG Y, MA H Z, et al. Enhancing prehydrolysates fermentability by adding nucleophilic amino acids and proteins in biomass pretreatment [J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2020, 8(21): 7892−7900.
[23] VRSANSKA M, VOBERKOVA S, LANGER V, et al. Induction of laccase, lignin peroxidase and manganese peroxidase activities in white-rot fungi using copper complexes [J]. Molecules, 2016, 21(11): 1553. DOI: 10.3390/molecules21111553
[24] 张津京, 陈明杰, 冯志勇, 等. 芳香族化合物对斑玉蕈菌丝生物量、漆酶活性及其转录水平的影响 [J]. 菌物学报, 2016, 35(9):1130−1138. ZHANG J J, CHEN M J, FENG Z Y, et al. Effects of aromatic compounds on biomass, laccase activities and transcript levels of Hypsizygus marmoreus [J]. Mycosystema, 2016, 35(9): 1130−1138.(in Chinese)
[25] 张津京, 汪虹, 陈明杰, 等. 曲酸对斑玉蕈子实体形成过程中木质纤维素酶的影响研究 [J]. 菌物学报, 2018, 37(12):1680−1687. ZHANG J J, WANG H, CHEN M J, et al. Effects of kojic acid on lignocellulase at fruiting body formation process of Hypsizygus marmoreus [J]. Mycosystema, 2018, 37(12): 1680−1687.(in Chinese)
[26] 王言, 余昌霞, 曹晖, 等. 三种有机酸对刺芹侧耳和金针菇菌丝生长的影响 [J]. 食用菌学报, 2015, 22(3):38−42. WANG Y, YU C X, CAO H, et al. Effect of oxalic, citric and tartaric acids on Pleurotus eryngii and Flammulina velutipes mycelial biomass production and DNA content [J]. Acta Edulis Fungi, 2015, 22(3): 38−42.(in Chinese)
[27] CRISTICA M, CIORNEA E, MANOLIU A. Influence of some aminoacids on the activity of cellulolytic and xylanolytic enzymes in the fungus Trichoderma reesei qm-9414 [J]. Agronomy Series of Scientific Research/Lucrari Stiintifice Seria Agronomie, 2012, 55(2): 317−320.
[28] DESWAL D, KHASA Y P, KUHAD R C. Optimization of cellulase production by a brown rot fungus Fomitopsis sp. RCK2010 under solid state fermentation [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(10): 6065−6072. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2011.03.032
[29] VYAS A, VYAS D, VYAS K. Production and optimization of cellulases on pretreated groundnut shell by Aspergillus terreus AV49 [J]. Journal of Scientific and Industrial Research, 2005, 64(4): 281−286.
[30] MALLERMAN J, PAPINUTTI L, LEVIN L. Characterization of β-glucosidase produced by the white rot fungus Flammulina velutipes [J]. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 25(1): 57−65. DOI: 10.4014/jmb.1401.01045
[31] ARANTES V, MILAGRES A M F, FILLEY T R, et al. Lignocellulosic polysaccharides and lignin degradation by wood decay fungi: The relevance of nonenzymatic Fenton-based reactions [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2011, 38(4): 541−555.
[32] SHAH F, MALI T, LUNDELL T K. Polyporales brown rot species Fomitopsis pinicola: Enzyme activity profiles, oxalic acid production, and Fe(3+)-reducing metabolite secretion [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2018, 84(8): e02662−17.
[33] BERNE S, POHLEVEN J, VIDIC I, et al. Ostreolysin enhances fruiting initiation in the oyster mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus) [J]. Mycological Research, 2007, 111(12): 1431−1436. DOI: 10.1016/j.mycres.2007.09.005
[34] VIDIC I, BERNE S, DROBNE D, et al. Temporal and spatial expression of ostreolysin during development of the oyster mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus) [J]. Mycological Research, 2005, 109(3): 377−382. DOI: 10.1017/S0953756204002187
[35] BARH A, SHARMA K, BHATT P, et al. Identification of key regulatory pathways of basidiocarp formation in Pleurotus spp. using modeling, simulation and system biology studies [J]. Journal of Fungi, 2022, 8(10): 1073. DOI: 10.3390/jof8101073
[36] 肖冬来, 马璐, 应正河, 等. 广叶绣球菌溶血素基因的序列分析及表达动态 [J]. 食用菌学报, 2016, 23(4):7−13. XIAO D L, MA L, YING Z H, et al. Sequence characterization and differential expression of a hemolysin gene and the encoded protein from Sparassis latifolia [J]. Acta Edulis Fungi, 2016, 23(4): 7−13.(in Chinese)
[37] HAYER-HARTL M, BRACHER A, HARTL F U. The GroEL-GroES chaperonin machine: A nano-cage for protein folding [J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 2016, 41(1): 62−76. DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.07.009
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 王沛然,张家林,高祥斌,涂佳才. 水肥耦合对‘聊红’椿幼苗生长特性的影响. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(02): 153-161 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王沛然,张家林,高祥斌,涂佳才. 水肥耦合对‘聊红’椿幼苗根系形态特征的影响. 山东农业科学. 2024(05): 87-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 尹明华,郭依瑶,李启诺,罗泽全,林文龙,熊姿雯. 信前胡烟草花叶病毒lncRNA测序鉴定、原核蛋白表达及其序列分析. 中国农学通报. 2024(21): 106-113 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载: