Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Activity in Stems and Leaves of Paeonia Intersubgeneric Hybrids
-
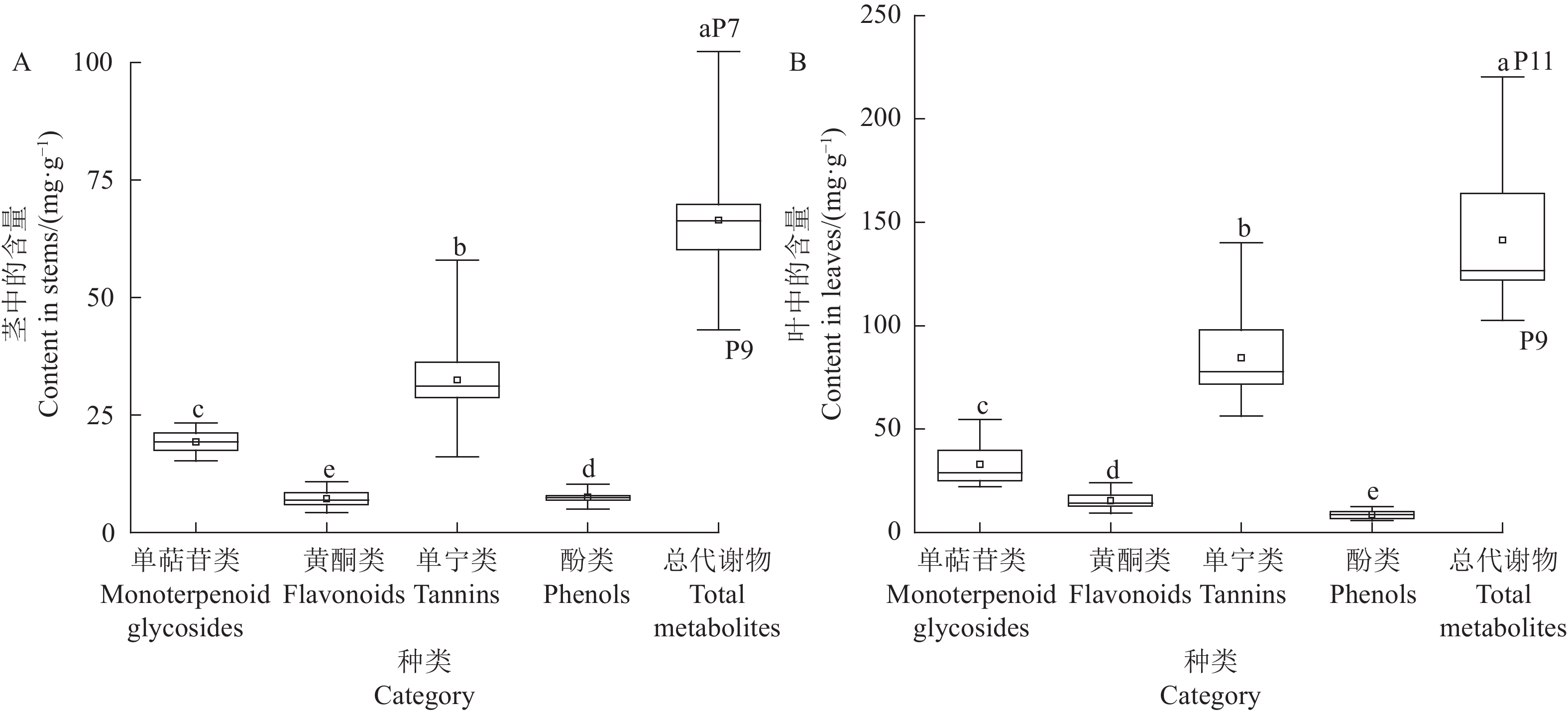
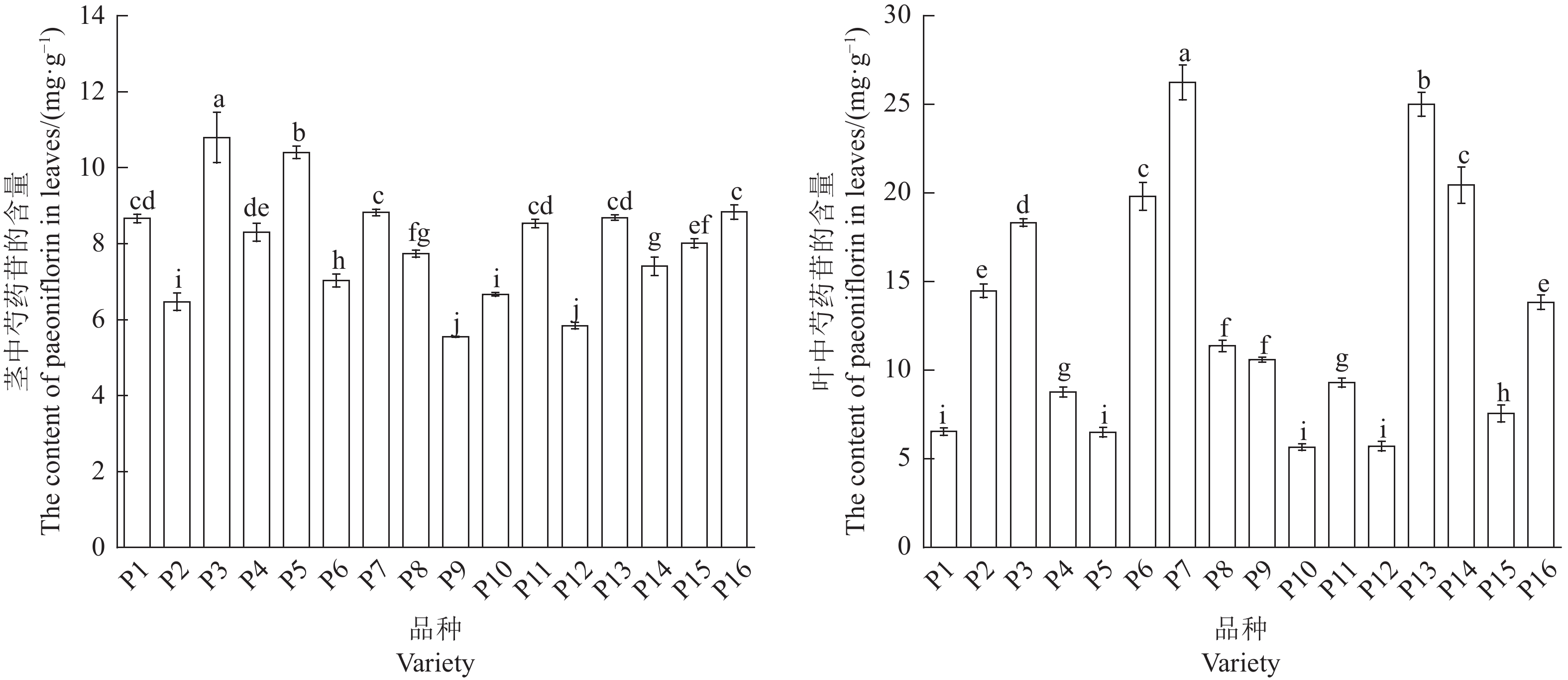
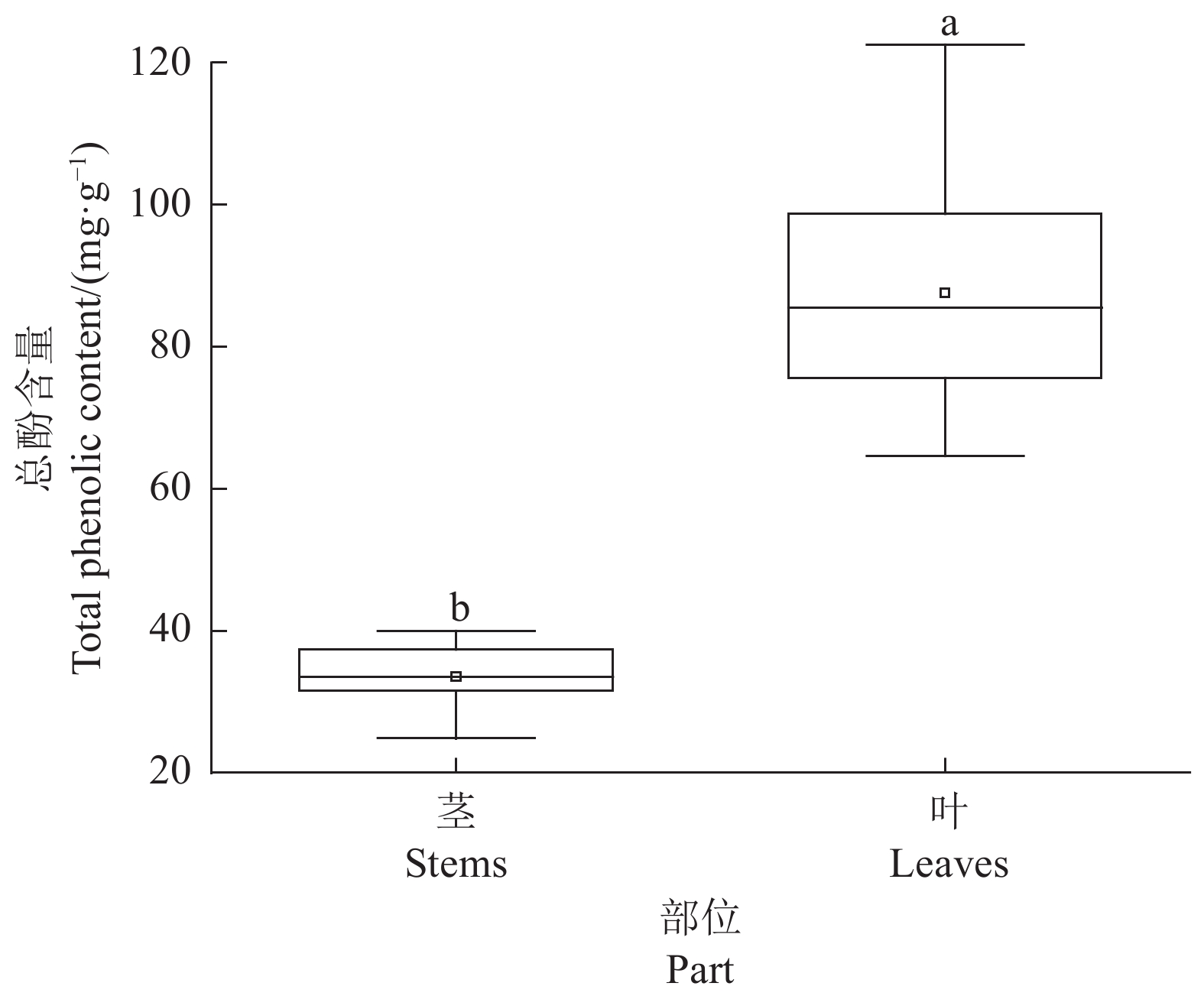
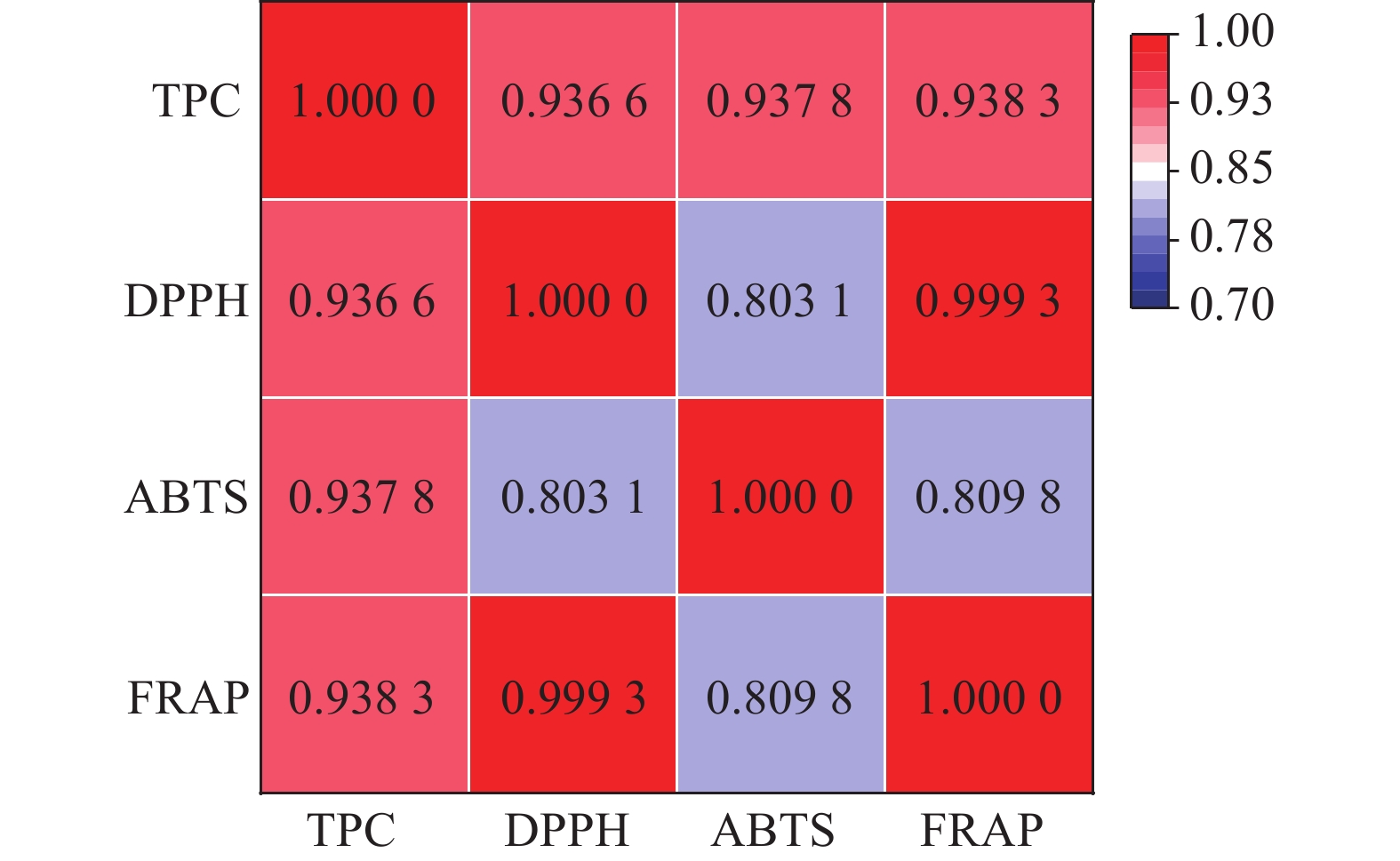
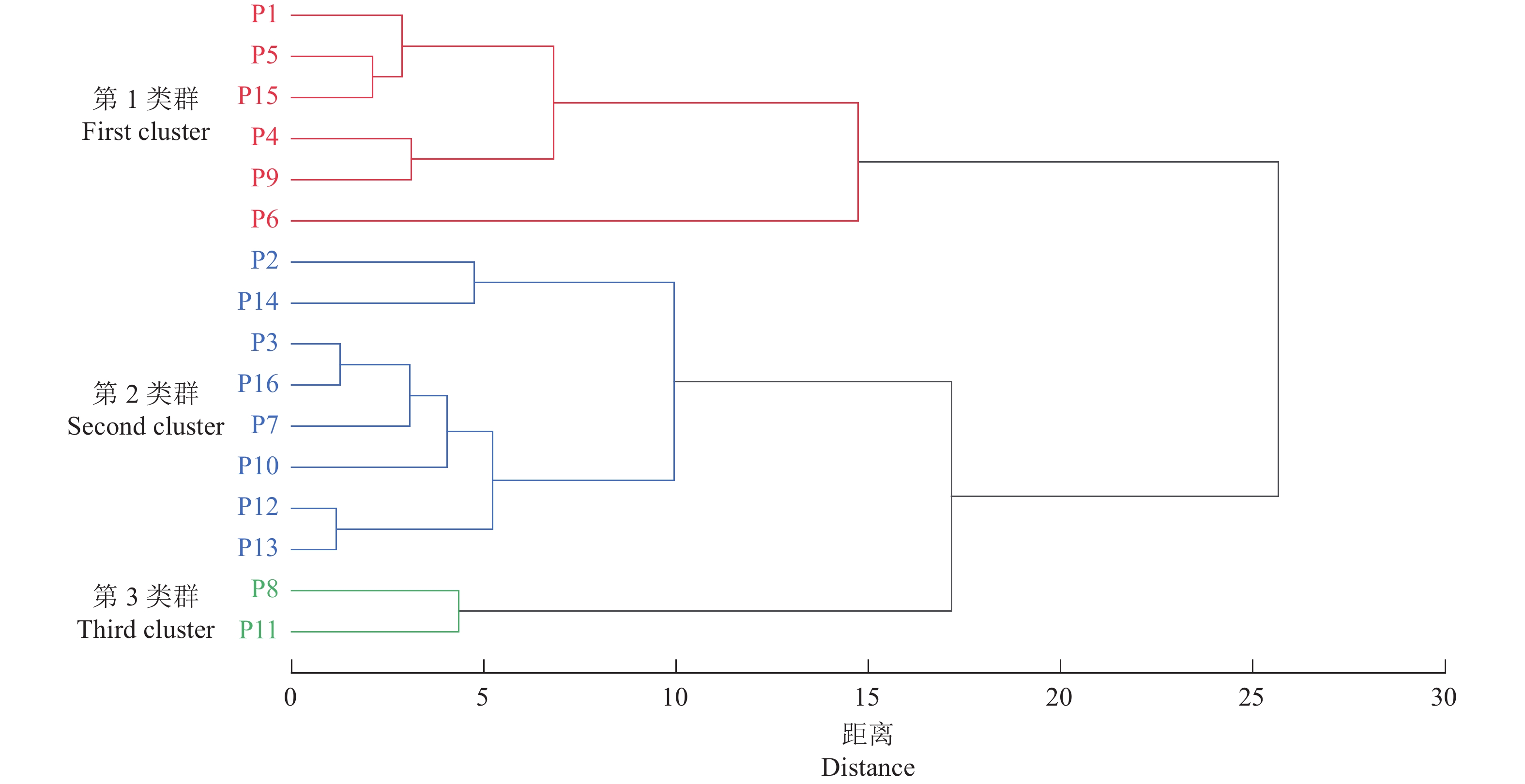
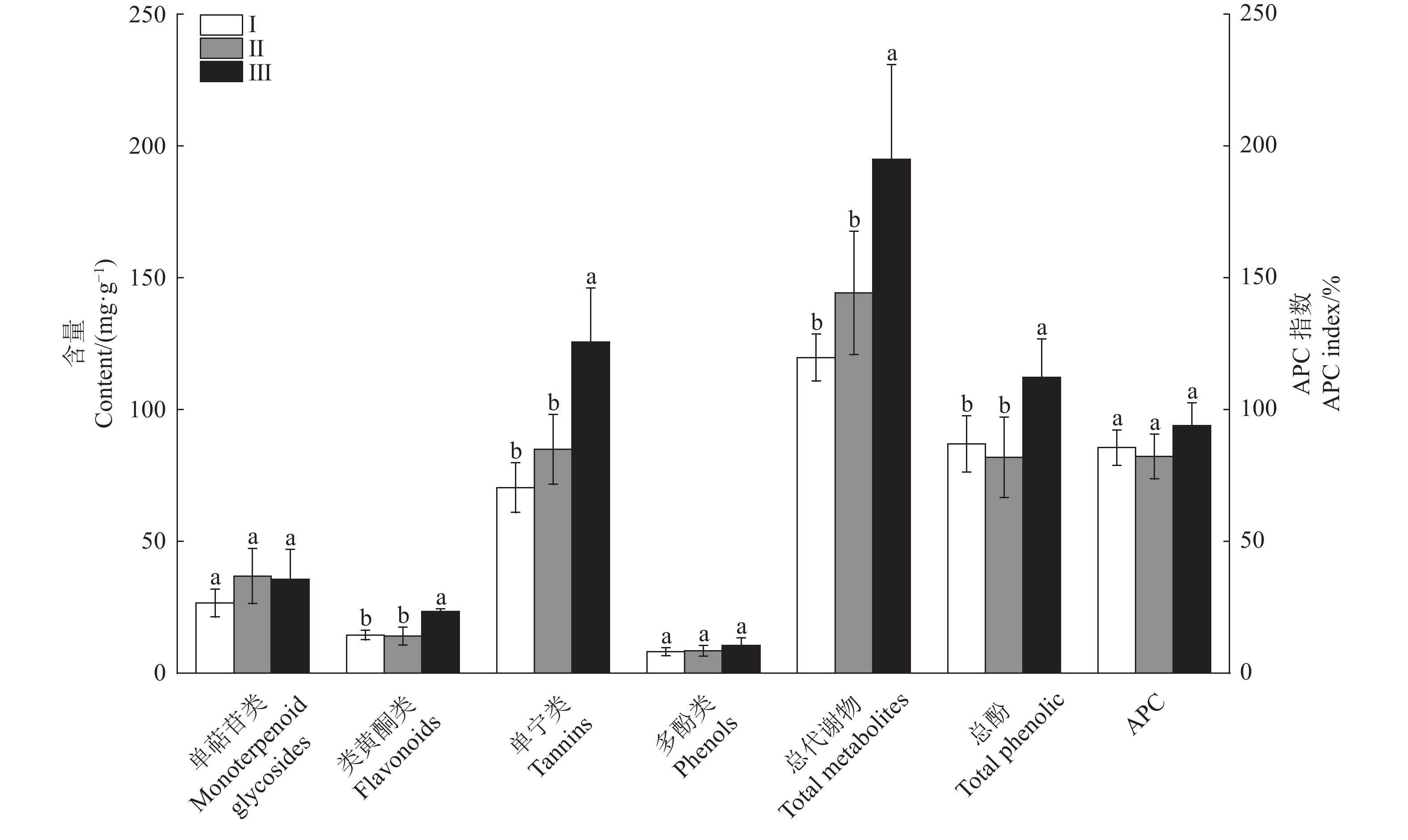
摘要:目的 探究芍药属亚属间杂种(伊藤杂种)的茎叶药用价值。方法 利用高效液相色谱-二极管阵列检测(HPLC-DAD)与高效液相色谱-四级杆-飞行时间串联质谱技术(HPLC-Q-TOF-MS)对16个伊藤杂种茎、叶的次生代谢物进行定性、定量分析,并对其总酚含量和体外抗氧化活性进行测定。结果 在16个伊藤杂种茎叶中共检测到19种次生代谢物,分别属于单萜苷类(5种)、黄酮类(6种)、单宁类(4种)、酚类(4种)。16个伊藤杂种茎叶中的代谢物成分基本相同;除酚类外,叶中其他3类代谢物和总代谢物含量均显著高于茎。16个伊藤杂种叶的抗氧化能力均显著高于茎;5个品种叶中的芍药苷含量高于药典规定的最低标准(18 mg·g−1)。聚类分析结果显示,16个品种被聚为3类,其中第3类群包含2个品种,特点为叶中除单萜苷类含量中等外,各项指标均最高。结论 伊藤杂种的茎叶具有潜在的药用价值,筛选出2个具有药用植物潜力的伊藤杂种Unique和Lollipop。Abstract:Objective Pharmaceutical property of the stems and leaves of Paeonia intersubgeneric hybrids (PIHs) was evaluated.Method Secondary metabolites in 16 PIHs were extracted from the stems and leaves and analyzed by the high-performance liquid chromatography with a diode array detector (HPLC-DAD) and the high-performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-fight mass spectrometry (HPLC-Q-TOF-MS). Total phenolic content and in vitro antioxidant activity of the extract were measured.Results (1) Nineteen metabolites were identified from the extracts that included 5 monoterpene glycosides, 6 flavonoids, 4 tannins, and 4 phenols. (2) The compositions of all tested hybrids were essentially identical. (3) Except for phenols, the content of individual group or total amount of compounds in the 3 groups were significantly higher in the leaves than in the stems. (4) The in vitro antioxidant activity was tested significantly greater in the leaves than in the stems as well. (5) The contents of paeoniflorin in the leaves of 5 varieties were above the minimum 18 mg·g−1 as stipulated by the pharmacopoeia. (6) A cluster analysis grouped the 16 cultivars into 3 categories with one that contained two varieties, which scored the highest on all indicators except being moderate on monoterpene glycosides.Conclusion The stems and leaves of “Unique” and “Lollipop” in the 16 tested PIHs appeared to have pharmaceutical values.
-
Keywords:
- Paeonia /
- intersubgeneric hybrids /
- functional ingredient /
- antioxidant activity /
- paeoniflorin
-
当前,相场法已成为模拟凝固组织、界面形貌的重要方法[1]。相场法[2] 的理论基础是金兹堡-朗道相变理论,系统的模拟二元系统的相变微观结构,研究了等温结晶过程中界面厚度对冰晶生长的扩散、有序化势以及热力学驱动力的综合作用,这是一种通过该理论的微分方程来反映的一种计算方法。近年来,国内外研究者利用相场法模拟凝固微观组织经历了从二维→三维[3-4]、 二元合金→多元合金[5]、单晶粒→多晶粒[6-8]、自由枝晶→定向凝固[9-10]、单相场→多相场[11]、无流场→包含流场[12-16]逐步深入的发展历程,从而对凝固过程进行真实的模拟[17]。一般情况下,凝固体微观组织的形成取决于溶质扩散、界面曲率与热扩散[1, 18]。迄今关于利用相场法模拟在果汁冷冻浓缩过程中的冰晶生长情况的相关研究较少,目前仍处于初步摸索的阶段[19-20],亟待进行深入研究。
如今,研究果汁冷冻浓缩尚未构建冰晶生长特征的数学物理模型[21-22],还是主要以实验为基础,冰晶夹带的影响因素主要有溶液浓度、降温速率、结晶时间等[23-25],另外,还包括处于非平衡态热力学条件下的动力学规律[18, 26]。根据目前已有研究结果表明,研究者何立群等[27] 提出:异相成核后,研究呈现分形生长的冰晶形态结构和冰晶的演变过程,并基于分形的相关理论,对水分子的结晶能力与降温的速率、溶液的浓度之间的关系进行分析。陈梅英等[19-20, 28-29]首次把相场模型引入食品领域,对冷冻浓缩过程冰晶生长机制进行初步探索,理论分析了冷冻浓缩过冷时间、过冷度等对冰晶生长的影响。
按理界面厚度应取其真实值,但在相场法模拟中需要一个能计算的界面厚度。本研究基于Kim S G等提出的KKS相场模型[26],结合Allen[30]提出的弥散型界面厚度的定义,探寻能反映真实情况且提高计算效率的界面厚度取值,将果汁的多元成分视为水和溶质二元系统,对二元系统冷冻浓缩等温结晶过程进行相场法模拟,分析冰晶生长过程中界面厚度与冰晶形貌和溶质分布之间的关系。
1. 建立冰晶生长的相场模型
1.1 相场法的控制方程
冰晶生长相场模型以自由能减小原理为基础,基于kim S G等[26]提出的KKS相场模型,并结合近似稀溶液时的基础方程,从而建立了果汁在冷冻浓缩过程中,冰晶生长的相场模拟模型。相场和溶质场方程采用自由能密度形式的相场法分别推导出。自由能密度的定义是:利用固相与液相的自由能密度,分别乘以各自的分数,之后再加上剩余自由能的和,可将其表示为:
f(c,ϕ)=h(ϕ)fS(cS)+[1−h(ϕ)]fL(cL)+Wg(ϕ) (1) 式(1)中: f为自由能密度,J·m-2;fS 表示固相,J·m-2;fL表示液相,J·m-2;且其固相分数为 h(ø),h(ø)=ø3(6ø2-15ø+10),液相分数为1-h(ø);c为溶质浓度;ø为相场变量,ø=-1或0时为液相,ø=1时为固相,在液-固的界面上,ø值在-1~1或0~1的范围内发生连续的变化;Wg(ø)表示剩余自由能,其中,W是相场参数,g(ø)是剩余自由能函数,g(ø)=ø2(1-ø)2。可将相场方程表示为:
∂t∂tϕt=M[ε2∇2ϕ−f(ϕ)] (2) 式(2)中:M为相场迁移率参数[式(9)]; f(ø)是自由能密度对相场ø的一阶导数;ε为与界面能有关的相场参数。当利用稀溶液来近似时,则表达式为:
f(ϕ)=RTVmh′(ϕ)ln(1−ceS)(1−cL)(1−ceL)(1−cS)+Wg′(ϕ) (3) 式(3)中: R表示气体常数,R的值为8.31 J·kmol-1;T表示温度,K;Vm表示摩尔体积,L·mol-1;ce表示平衡浓度;下标L和S分别表示液相和固相; h′(ø)为h(ø)的导函数,h′(ø)=30ø2(1-ø)2; g′(ø)为 g(ø)的导函数,g′(ø)=2ø(1-ø)(1-2ø)。
1.2 溶质场扩散方程
采用自由能密度的形式,可以将溶质场的扩散方程,改写表示为:
∂c∂t=∇(D(ϕ)fcc∇fc)+D(ϕ)fcc∇⋅∇f (4) 式(4)中:D(ø) 表示溶质扩散率;fc 表示自由能对浓度的一阶导数;fcc表示自由能对浓度的二阶导数。界面区域的溶质浓度c,是指固、液相的摩尔分数之和,在固相和液相达到平衡时,在界面区域中,任意一点的固相和液相的化学势相等,即:
c=h(ϕ)cS[1−h(ϕ)]cL (5) μS[cS(x,t)]=μL[cL(x,t)] (6) 式(6)中μL和μS分别为液相和固相的化学势。
1.3 加入扰动
计算时,在界面处施加微小的扰动也会影响真实的枝晶形貌,在相场方程中加入人为的随机扰动:
f(∂ϕ∂t)=∂ϕ∂t+16g(ϕ)χˉw (7) 式中χ在-1到1之间随机取值,ˉw是与时间相关的相扰动强度因子,16g(ø)用以控制在固液界面中出现扰动,最大扰动可能出现在ø=0.5处,若远离界面则扰动迅速减小。
2. 确定相场参数及模拟计算
2.1 参数的确定
相场参数ε和W与界面厚度及界面能都有关系,相场迁移率参数M则与界面动力学系数有关,它们可以表示为:
ε=√6λ2.2σ,W=6.6σλ (8) M−1=ε2σ⋅RTVm⋅1−keμk me (9) 式(8)和(9)中:σ表示固液两相的界面能,J·m-2;R表示气体常数;T表示温度;Vm表示摩尔体积;ke表示平衡常数;μk表示动力系数;me表示液相线斜率;ε表示与界面能有关的参数,λ表示界面厚度,μm。
2.2 物性参数的取值
从已有的研究[31-34]得知,冰晶结构在一般情况下,均表现为密排的六方结构。模拟冰晶结构各向异性模数k的取值为6。当控制其他相关的物性参数取值不发生改变时,只改变界面厚度λ,观察及分析界面厚度对冰晶形貌的影响。选用质量分数为9.6%的糖水溶液视为水和溶质二元系统,将其作为研究对象。在进行计算时,所使用的物性参数,具体如表 1所示。
2.3 数值计算
(1) 边界条件与初始条件。当计算界面区域的边界时,相场与溶质场的边界条件都取绝热边界条件。r表示初始晶核半径,则
{x2+y2≤r2,ϕ=1,T=Tm−ΔTx2+y2>r2,ϕ=0,T=Tm−ΔT (10) 式(10)中: x是模拟中的横坐标;y是模拟中的纵坐标;T表示有量纲温度,Tm表示模拟的初始温度,ΔT表示过冷度。
(2) 数值计算方法。相场方程利用显示有限差分求解,时间步长Δt受到溶质场计算的限制,即Δt <(Δx)2/4DL,DL 表示液相中的溶质扩散系数,取值为:Δt=1.5×10-9s。晶体轴生长主轴与直角坐标系的x轴和y轴相对应。模拟计算网格数为1400×1400,空间步长为5×10-8m,初始晶核为半径r=10个网格数的球。
3. 模拟结果与分析
在相变过程中,固体与液体之间存在明显分界面。将固液界面厚度扩大至可计算的尺度,在不同的界面厚度下利用相场法进行模拟,研究界面厚度这个因素对冰晶形貌与其冰晶溶质分布的影响情况,这样就能获得稳定的界面推进速度。
3.1 界面厚度对冰晶形貌的影响
图 1所示为不同界面厚度下的冰晶生长形貌。当λ=1.5dx时,晶粒形貌呈现等轴枝晶形貌,且二次分支不明显;随着界面厚度的增加,当λ=3dx时随着界面厚度的增加,晶粒开始出现分支,二次分支更加发达;当λ=4dx时枝晶的主干变细,二次枝晶生长发达,枝晶整体形貌呈六边形生长。当λ=4.5dx及λ=5dx时,界面厚度进一步增大,主轴枝晶变得更细,部分主轴枝晶消失,枝晶整体形貌呈球形。这是因为扰动对枝晶的影响存在一定的范围。在扰动的影响范围内,当界面厚度较小的时候,受到扰动的影响较小,二次枝晶不明显;随着界面厚度的增大,扰动的影响随之增大,晶体的界面前沿不稳定,二次枝晶开始产生,并随着界面厚度的增加愈加发达。当界面厚度增大到一定程度时,能有效地限制扰动的对晶粒的影响减弱,二次枝晶减少最终晶粒没有二次枝晶的产生,如图 1-d、e。这种现象分别与于艳梅[36]、王智平[37]等模拟的结果相吻合。
![]() 图 1 界面厚度λ对冰晶形貌的影响注:(a)λ=1.5dx;(b)λ=3dx;(c)λ=4dx;(d)λ=4.5dx;(e)λ=5dx。图 2同。Figure 1. Influence of interfacial thickness on ice crystal pattern
图 1 界面厚度λ对冰晶形貌的影响注:(a)λ=1.5dx;(b)λ=3dx;(c)λ=4dx;(d)λ=4.5dx;(e)λ=5dx。图 2同。Figure 1. Influence of interfacial thickness on ice crystal pattern3.2 界面厚度对冰晶溶质分布的影响
图 2 显示了不同界面厚度条件下的溶质分布情况,图 1和图 2对比可知相场和溶质场相吻合。从述两幅图中可以发现,枝晶的固相中夹带着部分的溶质,凝固界面的溶质浓度比周围环境低,且枝晶前沿富集了大量的溶质。这是溶质扩散的过程。一方面水分子和溶质分子都在不断运动中,水分子之间容易形成氢键而结晶,同时溶质分子与水分子相互作用,造成了夹带;另外一方面,在结晶过程中,水结成冰是一个膨胀的过程,因为冰晶生长的速率大于溶质扩散的速率,所以在溶质来不及充分扩散之前,冰晶内的浓缩溶质会被迅速挤向尖端,从而在枝晶前端富集,形成一股流行尖端的溶质流。由图 2可以发现,随着界面厚度的逐渐增大,枝晶的生长速率逐渐加快,而枝晶尖端半径则逐渐减小。同时,从方程(9)可以看出,随着界面厚度取值的增大,界面的迁移速率减小,溶质的扩散较为充分,溶质梯度较少,枝晶生长凝固时间越短,所以生长速度越快。所以,方程(9)的理论结果与相场模拟结果吻合。
由图 1和图 2可知,当界面厚度取值过大时,枝晶生长形貌变异。所以采用相场法模拟冰晶的生长时,界面厚度取值应在3dx左右,这样不仅可以得到较可靠的冰晶生长形貌,又可以提高计算机的模拟效率。
4. 讨论与结论
将果汁视作水和溶质的二元系统,利用相场法模拟二元系统冷冻浓缩过程中的冰晶生长情况,探讨界面厚度对冰晶形貌的影响。界面厚度对晶粒的形貌有正负影响,当界面厚度尺度达到一定取值时,其数值误差随之被放大,从而在界面处形成误差噪音,误差噪音在界面上形成明显的扰动,使计算得到的冰晶形态发生变化。在扰动干扰的范围内,随着界面厚度的增大,二次枝晶越来越发达,枝晶尖端也尖锐;在扰动干扰范围外,晶粒不产生二次枝晶,同时主轴枝晶变细,部分主轴枝晶消失。由于误差噪音的性质难以描述,故利用相场法模拟冰晶生长时,界面厚度大小应有适当的取值,从而达到有效控制误差噪音。
相场和溶质场相吻合,溶质分布情况随着界面厚度发生变化。随着界面厚度取值越大,界面的迁移速率越小,导致溶质的扩散速度与冰晶的生长速度相差较小,溶质扩散有相对足够的时间,避免大量溶质聚集在固-液界面前沿,削弱了界面前沿出现溶质截留现象。因此溶质的扩散较为充分,溶度梯度较少,枝晶生长凝固时间越短,所以生长速度越快。
晶粒生长速率和枝晶尖端半径受界面厚度取值的影响,界面厚度取值越大,晶粒生长速率越快,而枝晶尖端半径减小。刚开始,晶粒生长速度呈指数上升,且随着界面厚度取值的增大而迅速上升。这是由于开始结晶的时候伴随着能量起伏波动,从而影响初始速度,界面厚度较小的时候,扰动对其的影响较少,在扰动干扰的范围内,随着界面厚度的增大,二次枝晶越来越发达,枝晶尖端半径减小。因此界面厚度的取值应在3 dx左右,较能真实反映晶粒的生长形貌;界面厚度取值不恰当,将使冰晶形貌发生变异,也会受到误差噪音的影响。
在果汁冷冻浓缩过程中,忽略冰晶结晶时释放的潜热,本研究采用相场法对冰晶生长进行等温模拟,但模拟的结果很大程度上受到参数取值的影响。今后将继续在探讨热扩散率、初始晶核半径等其他他相关参数取值方面努力,以取得更优的模拟结果。
-
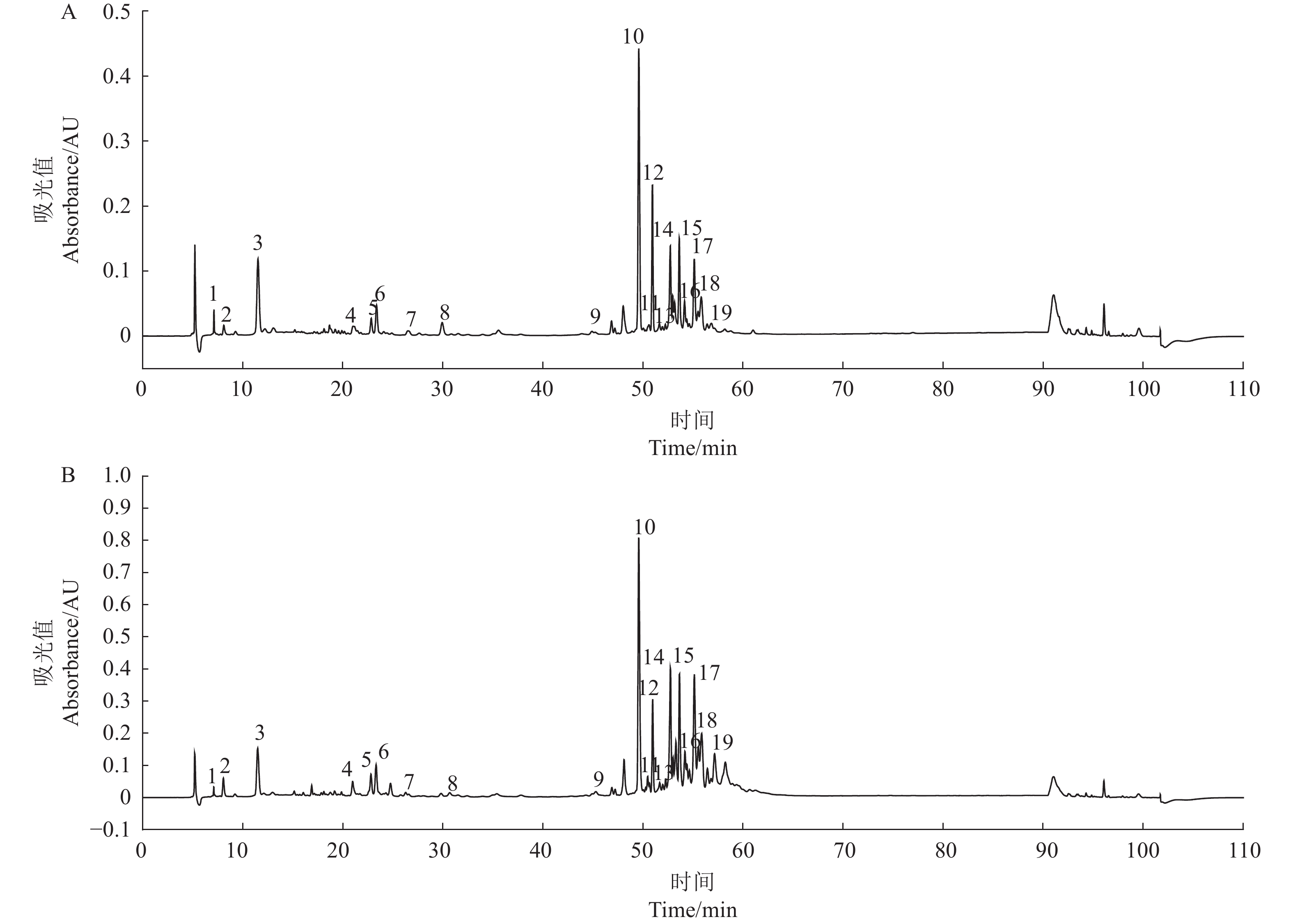
图 1 代表性伊藤杂种茎叶成分HPLC图谱 (254 nm)
1:去苯甲酰芍药苷;2:没食子酰己糖;3:没食子酸;4:氧化芍药苷;5:没食子酸甲酯;6:二没食子酸;7:木犀草素二己糖苷;8:芍药苷;9:四没食子酰己糖;10:槲皮素;11:木犀草素己糖苷;12:1,2,3,4,6-五没食子酰葡萄糖;13:没食子酸二甲酯;14:没食子酰芍药苷;15:芹菜素二己糖苷;16:芹菜素己糖苷;17:六没食子酰己糖;18:木犀草素己糖醛酸苷;19:苯甲酰氧化芍药苷。(A) 伊藤杂种 Garden Treasure 的茎 (B) 伊藤杂种Garden Treasure 的叶。
Figure 1. HPLC 254 nm chromatograms of typical compounds in stems
1: Debenzoyl-paeonifforin; 2: Galloyl-hexose; 3: Gallic acid; 4: Oxypaeonifforin; 5: Methyl gallate; 6: Digallic acid; 7: Luteolin-dihexoside; 8: Paeonifforin; 9: Tetra-galloyl-hexose; 10: Quercetin; 11: Luteolin-hexoside; 12: Penta-galloyl-glucose; 13: Methyl digallate; 14: Galloyl-paeonifforin; 15: Apigenin-dihexoside; 16: Apigenin-hexoside; 17: Hexa-galloyl-hexose; 18: Luteolin-hexuronide; 19: Benzoyl-oxypaeonifforin. (A) and leaves (B) of PIH “Garden Treasure”.
表 1 16个伊藤杂种品种名录
Table 1 Sixteen PIHs
编号 Code 品种名 Cultivar 编号 No. 品种名 Cultivar P1 Scarlet Heaven P9 First Arrival P2 Sonoma Sun P10 Callie's Memory P3 Visions of Sugar Plums P11 Lollipop P4 Lemon Dream P12 Bartzella P5 Yankee Doudle Dandy P13 Prairie Charm P6 Hillary P14 Border Charm P7 Kopper Kettle P15 Garden Treasure P8 Unique P16 Oriental Gold 表 2 HPLC梯度洗脱条件
Table 2 HPLC gradient program
时间
Time/min流动相A
Eluent A/%流动相B
Eluent B/%流速
Flow rate/(mL·min−1)0 5 95 0.6 4 5 95 0.6 12 14 86 0.6 35 14 86 0.6 46 26 74 0.6 60 26 74 0.6 85 40 60 0.6 86 95 5 0.6 96 95 5 0.6 97 5 95 0.6 110 5 95 0.6 表 3 伊藤杂种茎叶成分标准品的线性响应
Table 3 Linear relationship between composition and standards of compounds in stems and leaves of PIHs
成分
Compound回归方程
Regression equation拟合度
Regression (R2)芍药苷 Paeoniflorin y = 3988892.99x−209564.63 0.9993 氧化芍药苷 Oxypaeoniflorin y = 61595437.91x−763226.02 0.9993 没食子酰芍药苷 Galloyl-paeoniflorin y = 17881895.64x−169740.93 0.9994 苯甲酰氧化芍药苷 Benzoyl-oxypaeoniflorin y = 43785733.20x−594224.40 0.9997 槲皮素 Quercetin y = 105165792.29x−1704829.32 0.9999 没食子酸 Gallic acid y = 71520130.70x−1356976.83 0.9995 没食子酸甲酯 Methyl gallate y = 50561017.43x + 287227.39 0.9998 1,2,3,4,6-五没食子酰葡萄糖 1,2,3,4,6-Penta-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose y = 22509909.82x−838629.67 0.9992 表 4 伊藤杂种茎叶总酚与抗氧化活性标准品的线性响应
Table 4 Linear relationship between in vitro antioxidant activity of standard and total phenolic in stems and leaves of PIHs
指标
Index回归方程
Regression equation拟合度
Regression (R2)总酚
Total phenolic contenty = 2.0065x−0.0046 0.9991 DPPH自由基清除能力
DPPH assayy = 6.5516x + 0.0497 0.9948 ABTS自由基清除能力
FRAP assayy = 2.5199x + 0.0137 0.9969 FRAP铁离子还原能力
ABTS assayy = 4.4112x + 0.2067 0.9983 表 5 伊藤杂种茎叶次生代谢物鉴定
Table 5 Secondary metabolites identified in extracts of stems and leaves of PIHs
编号
No.成分
Compound分子式
Molecular
Formula保留
时间
TR/
min紫外
吸收峰
UV λmax/
nm观测精确
分子量
Observed exact
mass/Da理论精确
分子量
Theoretically
exact mass/Da分子量准
确度
Mass accuracy其他离子碎片
Other fragmentions of
[M−H]−
at low energy/(m/z)1 去苯甲酰芍药苷
Debenzoyl paeonifforinC16H23O10 7.682 237.9 375.1293 375.1297 −1.0663 165 2 没食子酰己糖
Galloyl-hexoseC13H15O10 8.548 278.1 331.0680 331.0665 4.5308 169 3 没食子酸
Gallic acidC7H6O5 11.909 271.0 169.0159 169.0143 9.4667 125 4 氧化芍药苷
OxypaeonifforinC23H27O12 20.973 257.3 495.1501 495.1493 1.6157 137 5 没食子酸甲酯
Methyl gallateC8H8O5 22.297 271.5 183.0314 183.0299 8.1954 124 6 二没食子酸
Digallic acidC14H10O9 22.552 257.3 321.0263 321.0244 5.9186 169, 125 7 木犀草素二己糖苷
Luteolin dihexosideC27H30O16 26.168 230.1 609.1455 609.1456 −0.1642 446, 285 8 芍药苷
PaeonifforinC23H28O11 30.394 238.3 479.1548 479.1614 −13.7741 165, 121 9 四没食子酰己糖
Tetra-galloyl-hexoseC34H28O22 45.240 277.4 787.1006 787.1008 −0.2541 617, 169 10 槲皮素
QuercetinC15H10O7 49.745 253.2, 366.8 301.0006 301.0019 −4.3189 145 11 木犀草素己糖苷
Luteolin-hexosideC21H20O11 50.203 253.7 447.0934 447.0957 −5.1443 285 12 1,2,3,4,6-五没食子酰葡萄糖
Penta-galloyl-glucoseC41H32O26 50.408 278.6 939.1198 939.1126 7.6668 769, 617 13 没食子酸二甲酯
Methyl digallateC15H12O9 51.833 272.7 335.0423 335.0409 4.1786 183, 124 14 没食子酰芍药苷
Galloyl-paeonifforinC30H32O15 52.800 272.7 631.1658 631.1663 −0.7922 313, 169 15 芹菜素二己糖苷
Apigenin-dihexosideC27H30O14 53.004 267.9 577.1552 577.1598 −7.9701 269 16 芹菜素己糖苷
Apigenin-hexosideC21H20O10 54.226 267.9 431.1020 431.1015 1.1598 269 17 六没食子酰己糖
Hexa-galloyl-hexoseC48H36O30 54.841 278.1 1091.1247 1091.1245 0.1833 939, 769 18 木犀草素己糖醛酸苷
Luteolin-hexuronideC21H18O12 55.448 277.4 461.1125 461.1116 1.9518 285 19 苯甲酰氧化芍药苷
Benzoyl-oxypaeonifforinC30H32O13 57.342 276.3 599.1111 599.1106 0.8346 447, 313 表 6 16个伊藤杂种茎叶抗氧化活性
Table 6 Antioxidant activities of stems and leaves of 16 PIHs
编号
CodeDPPH自由基清除能力
DPPH assay/(mg·g−1)ABTS自由基清除能力
ABTS assay/(mg·g−1)FRAP铁离子还原能力
FRAP assay/(mg·g−1)茎
Stem叶
Leaf茎
Stem叶
Leaf茎
Stem叶
LeafP1 9.63±0.08 ab 38.11±0.28 a 30.13±2.01 b 61.19±6.39 bc 4.90±0.10 ab 16.80±0.32 cdefgh P2 9.60±0.05 ab 38.37±0.29 a 19.00±3.12 e 81.30±0.35 a 4.53±0.05 b 16.76±0.40 defgh P3 9.62±0.08 ab 37.37±1.17 a 18.72±2.78 e 50.27±4.43 de 4.70±0.09 ab 16.89±0.40 bcdefg P4 9.64±0.04 ab 38.22±0.12 a 18.57±2.06 e 46.85±4.52 ef 4.69±0.21 ab 17.22±0.20 abcd P5 9.63±0.07 ab 38.30±0.17 a 26.51±1.54 bc 57.04±3.89 bcd 4.78±0.09 ab 17.39±0.10 abc P6 9.63±0.03 ab 38.18±0.16 a 18.00±2.61 e 54.41±2.25 cd 4.56±0.17 b 17.18±0.10 abcde P7 9.63±0.05 ab 38.25±0.15 a 45.84±0.66 a 62.20±8.59 b 5.07±0.08 a 17.50±0.30 ab P8 9.60±0.03 ab 38.34±0.11 a 17.49±2.57 e 55.44±3.26 bcd 4.59±0.13 ab 16.98±0.58 abcdef P9 9.57±0.07 ab 34.44±0.51 c 6.23±0.81 g 31.35±4.00 i 4.43±0.08 b 15.94±0.28 i P10 9.49±0.25 b 37.81±0.36 a 10.12±2.64 f 42.71±2.16 fg 4.73±0.06 ab 16.56±0.11 efgh P11 9.60±0.04 ab 38.36±0.12 a 17.08±2.56 e 83.59±3.64 a 4.72±0.03 ab 17.57±0.30 a P12 9.59±0.03 ab 35.82±0.60 b 18.24±1.03 e 32.92±3.63 hi 4.59±0.04 ab 16.28±0.42 ghi P13 9.61±0.05 ab 37.15±0.97 a 18.05±0.99 e 30.30±4.31 i 4.85±0.11 ab 16.37±0.39 fghi P14 9.63±0.06 ab 37.19±0.80 a 19.99±3.11 de 38.73±1.93 gh 4.69±0.02 ab 16.25±0.09 hi P15 9.66±0.03 a 38.24±0.16 a 23.36±0.78 cd 60.93±2.09 bc 4.72±0.04 ab 17.39±0.33 abc P16 9.62±0.03 ab 35.53±1.45 b 16.88±3.58 e 31.58±1.91 i 4.72±0.89 ab 15.86±0.47 i 范围 Range 9.49~9.66 34.44~38.37 6.23~45.84 30.30-83.59 4.43~5.07 15.86~17.57 平均值 Average 9.61±0.08 37.48±1.28 20.26±8.77 51.30±16.58 4.71±0.25 16.81±0.61 同列数据无字母或含相同字母者表示差异不显著(P>0.05),字母完全不同者表示差异显著(P <0.05)。
Data with no or same letter indicate no significant difference at P>0.05; those with different letters indicate significant difference at P<0.05.表 7 16个伊藤杂种茎的APC指数
Table 7 APC indices of stems of 16 PIHs
编号
CodeAPC综合指数
APC index/%排名
Rank编号
CodeAPC综合指数
APC index/%排名
RankingP1 87.35 2 P9 66.75 16 P2 76.72 9 P10 71.19 15 P3 77.77 7 P11 76.60 10 P4 77.62 8 P12 76.59 11 P5 84.01 3 P13 78.25 6 P6 76.36 13 P14 78.64 5 P7 99.91 1 P15 81.38 4 P8 76.06 14 P16 76.54 12 表 8 16个伊藤杂种叶的APC指数
Table 8 APC indices of leaves of 16 PIHs
编号
CodeAPC综合指数
APC index/%排名
Rank编号
CodeAPC综合指数
APC index/%排名
RankingP1 89.39 5 P9 72.66 16 P2 97.55 2 P10 81.31 11 P3 84.56 9 P11 99.99 1 P4 84.55 10 P12 75.12 14 P5 89.00 6 P13 75.41 13 P6 87.46 8 P14 78.58 12 P7 91.22 3 P15 90.51 4 P8 87.64 7 P16 73.56 15 -
[1] HONG D Y. Peonies of the world: Taxonomy and phytogeography [M]. United Kingdom: Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, United Kingdom, 2010.
[2] HONG D Y. Peonies of the world: Polymorphism and diversity [M]. United Kingdom: Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, 2011.
[3] YANG Y, SUN M, LI S S, et al. Germplasm resources and genetic breeding of Paeonia: A systematic review [J]. Horticulture Research, 2020, 7: 107. DOI: 10.1038/s41438-020-0332-2
[4] 康晓飞, 郭先锋, 许世磊, 等. 三个观赏芍药品种芍药苷含量的动态变化研究 [J]. 北方园艺, 2011(5):85−87. KANG X F, GUO X F, XU S L, et al. Study on the dynamic change of paeoniflorin content from three herbaceous peony cultivars [J]. Northern Horticulture, 2011(5): 85−87.(in Chinese)
[5] Stern F C. Genus Paeonia [J]. Research Horticulture Society., 1943, 68: 124−131.
[6] JI L J, TEIXEIRA DA SILVA J A, ZHANG J J, et al. Development and application of 15 novel polymorphic microsatellite markers for sect. Paeonia (Paeonia L. ) [J]. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 2014, 54: 257−266. DOI: 10.1016/j.bse.2014.02.009
[7] 秦魁杰. 芍药[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2004: 43-44. [8] The Gardener's Peony: Herbaceous and Tree Peonies[M]. Portland: Timber Press, 2005
[9] ZHOU S L, XU C, LIU J, et al. Out of the Pan-Himalaya: Evolutionary history of the Paeoniaceae revealed by phylogenomics [J]. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 2021, 59(6): 1170−1182. DOI: 10.1111/jse.12688
[10] 郝青, 刘政安, 舒庆艳, 等. 中国首例芍药牡丹远缘杂交种的发现及鉴定 [J]. 园艺学报, 2008, 35(6):853−858. HAO Q, LIU Z A SHU Q Y, et al. Identification of intersectional hybrid between section moutan and section Paeonia found in China for the first time [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2008, 35(6): 853−858.(in Chinese)
[11] 孙菊芳, 成仿云. 芍药与牡丹组间杂种引种栽培初报 [J]. 中国园林, 2007, 23(5):51−54. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6664.2007.05.012 SUN J F, CHENG F Y. Preliminary report on the introduction of intersectional hybrids between tree and herbaceous peonies [J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 2007, 23(5): 51−54.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6664.2007.05.012
[12] 马翔龙, 吴敬需, 刘少华. 伊藤牡丹发展现状与展望 [J]. 中国花卉园艺, 2018(16):28−31. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8496.2018.16.013 MA X L, WU J X, LIU S H. Development status and prospect of Ito peony [J]. China Flowers & Horticulture, 2018(16): 28−31.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8496.2018.16.013
[13] 庄倩, 朱松岩, 杜晓琪, 等. 芍药属组间杂种引进东北地区栽培试验 [J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2011, 39(4):21−23. ZHUANG Q, ZHU S Y, DU X Q, et al. Introduction of interspecific hybrids of Paeonia to northeast China [J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2011, 39(4): 21−23.(in Chinese)
[14] 吴敬需, 刘少华, 隋承权. 国外引进的牡丹芍药组间杂种品种[J]. 中国花卉园艺, 2022(5): 54-60. WU J X, LIU S H, SUI C Q. Inter-group hybrid varieties of Paeonia suffruticosa introduced from abroad[J]. China Flowers & Horticulture, 2022(5): 54-60.(in Chinese)
[15] HE C N, PENG Y, ZHANG Y C, et al. Phytochemical and biological studies of Paeoniaceae [J]. Chemistry & Biodiversity, 2010, 7(4): 805−838.
[16] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典-一部: 2020年版[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020: 154. [17] PARKER S, MAY B, ZHANG C, et al. A pharmacological review of bioactive constituents of Paeonia lactiflora Pallas and Paeonia veitchii lynch [J]. Phytotherapy Research:PTR, 2016, 30(9): 1445−1473. DOI: 10.1002/ptr.5653
[18] MANAYI A, OMIDPANAH S, BARRECA D, et al. Neuroprotective effects of paeoniflorin in neurodegenerative diseases of the central nervous system [J]. Phytochemistry Reviews, 2017, 16(6): 1173−1181. DOI: 10.1007/s11101-017-9527-z
[19] WANG Z Q, HE C N, PENG Y, et al. Origins, phytochemistry, pharmacology, analytical methods and safety of cortex moutan (Paeonia suffruticosa andrew): A systematic review [J]. Molecules, 2017, 22(6): 946. DOI: 10.3390/molecules22060946
[20] SHAHIDI F, ZHONG Y. Measurement of antioxidant activity [J]. Journal of Functional Foods, 2015, 18: 757−781. DOI: 10.1016/j.jff.2015.01.047
[21] WANG L J, SU S, WU J, et al. Variation of anthocyanins and flavonols in Vaccinium uliginosum berry in Lesser Khingan Mountains and its antioxidant activity [J]. Food Chemistry, 2014, 160: 357−364. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.03.081
[22] WANG L J, WU J, WANG H X, et al. Composition of phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity in the leaves of blueberry cultivars [J]. Journal of Functional Foods, 2015, 16: 295−304. DOI: 10.1016/j.jff.2015.04.027
[23] SEERAM N P, AVIRAM M, ZHANG Y J, et al. Comparison of antioxidant potency of commonly consumed polyphenol-rich beverages in the United States [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2008, 56(4): 1415−1422. DOI: 10.1021/jf073035s
[24] ZHANG X X, ZUO J Q, WANG Y T, et al. Paeoniflorin in Paeoniaceae: Distribution, influencing factors, and biosynthesis [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 980854. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.980854
[25] SUN M, WANG Y Z, YANG Y, et al. Analysis of chemical components in the roots of eight intersubgeneric hybrids of Paeonia [J]. Chemistry & Biodiversity, 2021, 18(2): e2000848.
[26] 徐佳新, 许浚, 曹勇, 等. 中药白芍现代研究进展及其质量标志物的预测分析 [J]. 中国中药杂志, 2021, 46(21):5486−5495. XU J X, XU J, CAO Y, et al. Modern research progress of traditional Chinese medicine Paeoniae Radix Alba and prediction of its Q-markers [J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2021, 46(21): 5486−5495.(in Chinese)
[27] 张育贵, 张淑娟, 边甜甜, 等. 芍药苷药理作用研究新进展 [J]. 中草药, 2019, 50(15):3735−3740. ZHANG Y G, ZHANG S J, BIAN T T, et al. New progress in pharmacological action of paeoniflorin [J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2019, 50(15): 3735−3740.(in Chinese)
[28] ZHANG L L, WEI W. Anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory effects of paeoniflorin and total glucosides of paeony [J]. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 2020, 207: 107452.
[29] OH G S, PAE H O, OH H, et al. In vitro anti-proliferative effect of 1, 2, 3, 4, 6-penta-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucose on human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line, SK-HEP-1 cells [J]. Cancer Letters, 2001, 174(1): 17−24. DOI: 10.1016/S0304-3835(01)00680-2
[30] HE C N, PENG B, DAN Y, et al. Chemical taxonomy of tree peony species from China based on root cortex metabolic fingerprinting [J]. Phytochemistry, 2014, 107: 69−79. DOI: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2014.08.021
[31] 高玉鹏, 郭久荣, 刘斌峰. 热应激环境蛋鸡免疫力变化机理研究Ⅱ 免疫力、氧自由基代谢、耐热力间的关系 [J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2001, 29(5):33−36. GAO Y P, GUO J R, LIU B F. The study of layers on the immune feature and relation with HSST Ⅱ Relationship among immunity, oxygen radixal metabolites, HSST [J]. Journal of Northwest Sci-Tech University of Agriculture and Forestry, 2001, 29(5): 33−36.(in Chinese)
[32] LI S, LI S K, GAN R Y, et al. Antioxidant capacities and total phenolic contents of infusions from 223 medicinal plants [J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2013, 51: 289−298. DOI: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.09.017
[33] TONG N N, ZHOU X Y, PENG L P, et al. A comprehensive study of three species of Paeonia stem and leaf phytochemicals, and their antioxidant activities [J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2021, 273: 113985. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.113985
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 杨燕,李娜,袁训锋. 界面各向异性对速冻保鲜过程中冰晶生长行为的影响. 食品与发酵科技. 2021(04): 86-90 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 杨燕,李娜,袁训锋. 速冻保鲜过程中冰晶生长形态研究. 食品与发酵科技. 2020(05): 55-59 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨燕,袁训锋. 强各向异性冰晶生长对速冻食品品质的影响. 食品与发酵科技. 2019(04): 59-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 杨燕,景伟强,袁训锋. 过冷度影响冰晶生长的相场法研究. 低温与超导. 2018(09): 67-71+76 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 杨燕,袁训锋,乔希民,范娜. 食品速冻保鲜过程冰晶生长的相场模拟. 食品与机械. 2018(12): 108-114 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: