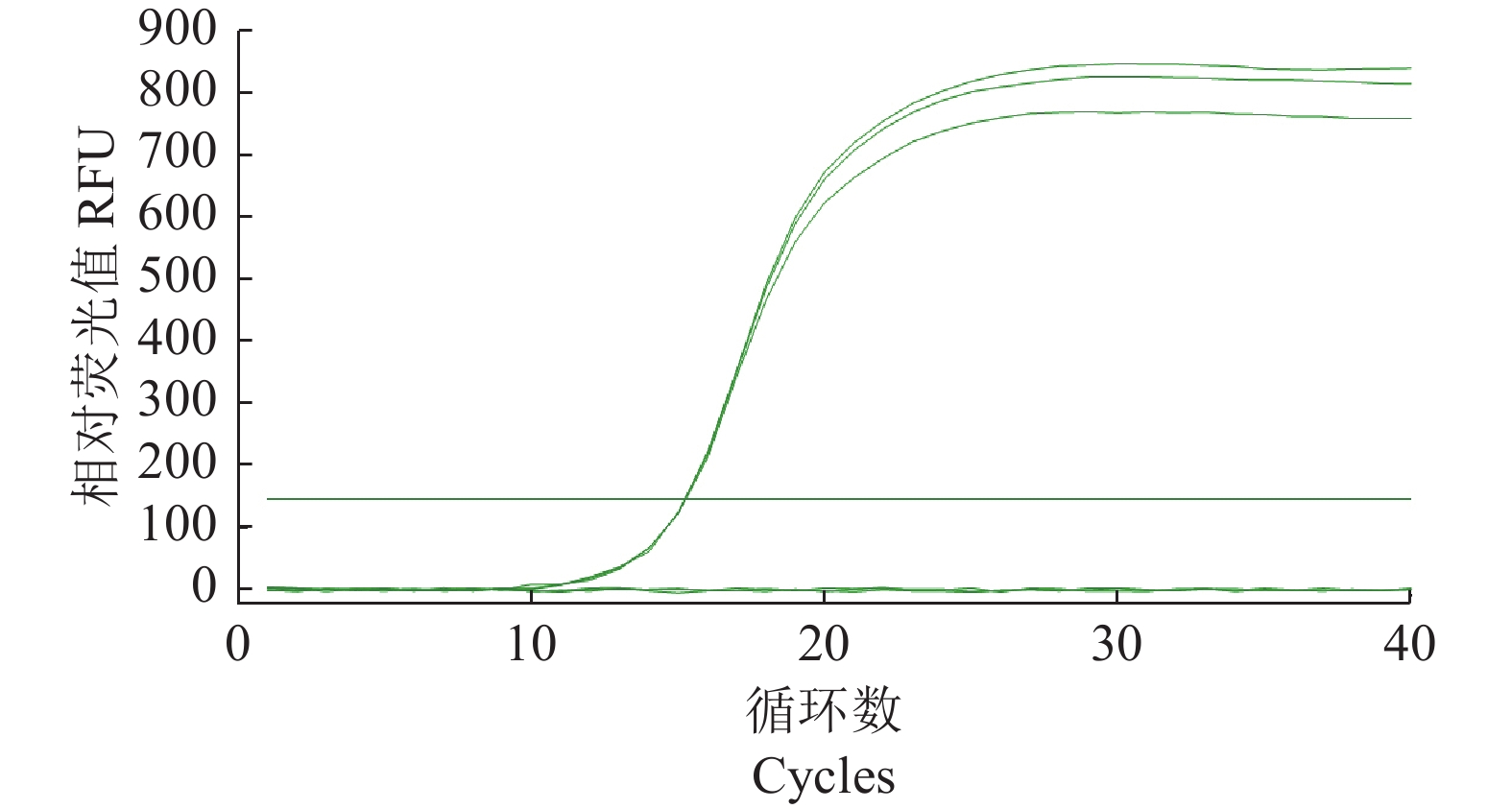
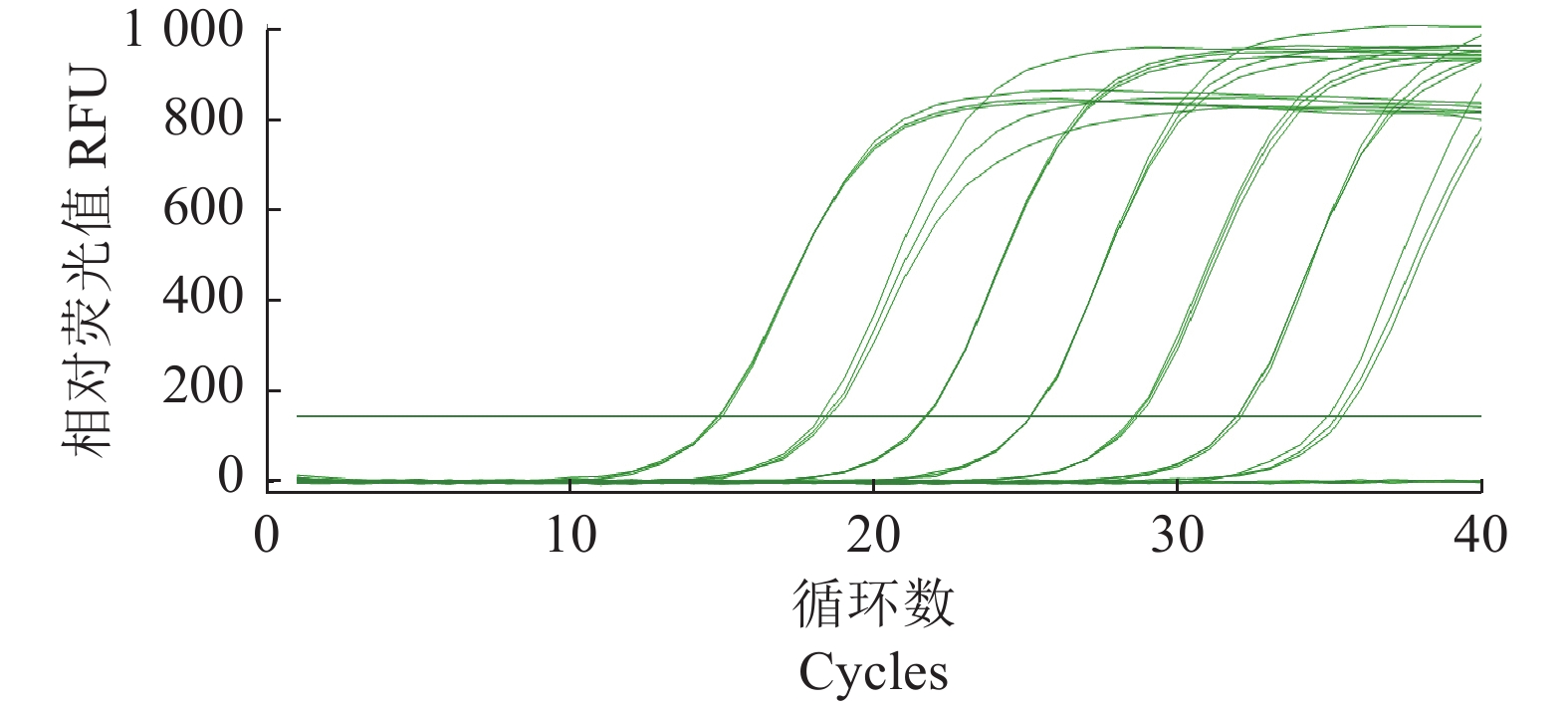
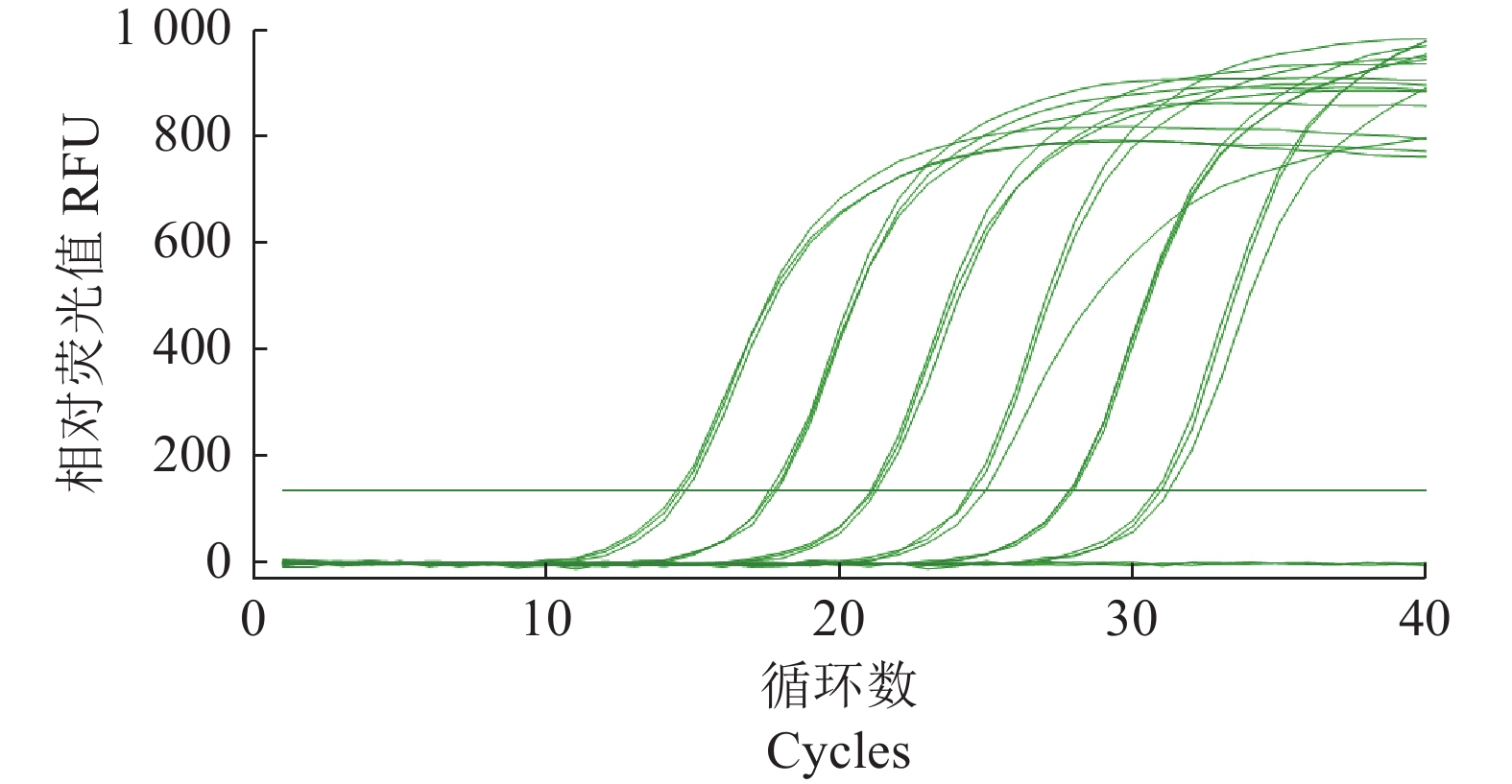
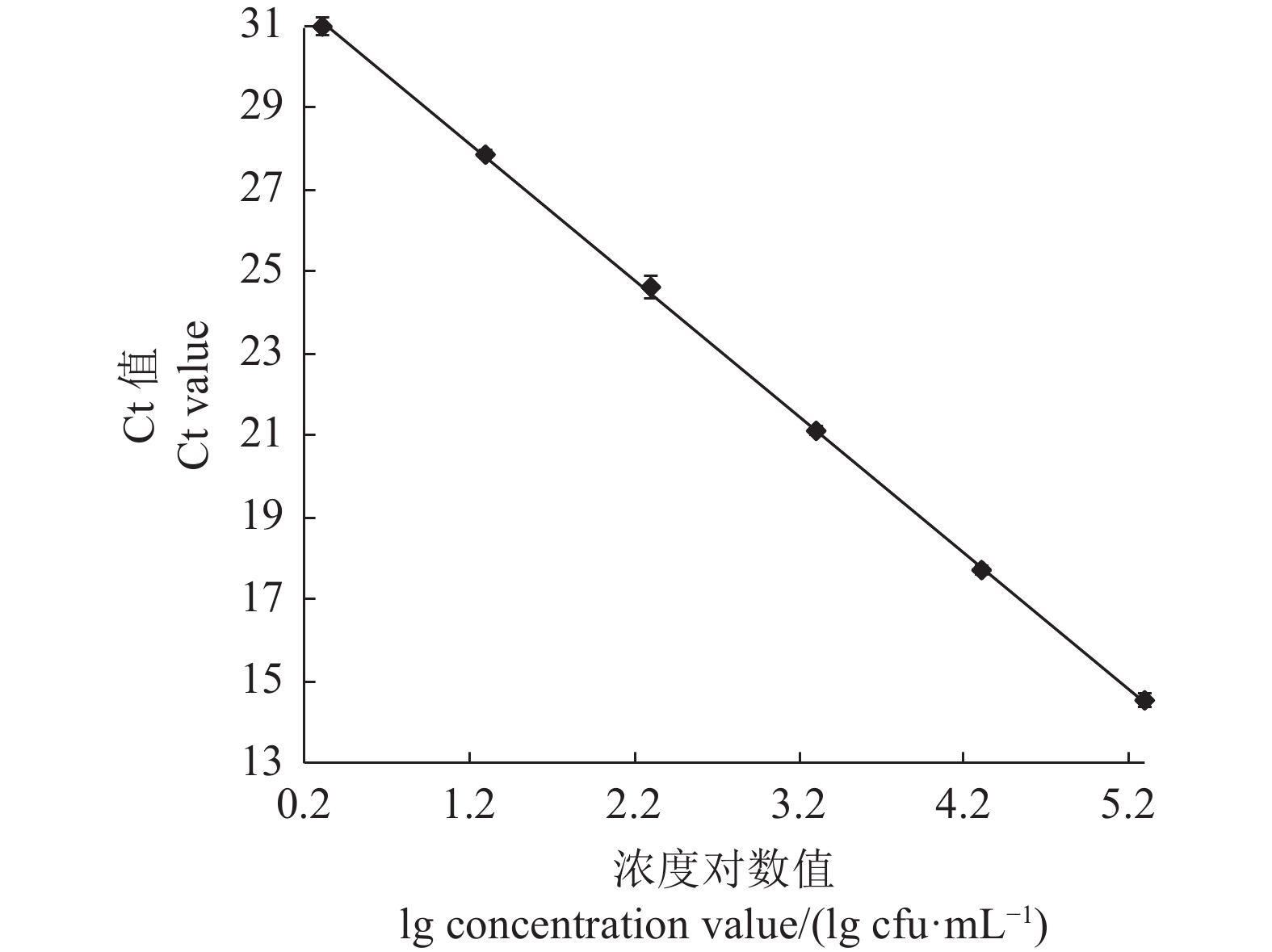
SYBR Green I RT-PCR Assay for Quantitative Detection of Salmonella in Irrigation Water
-
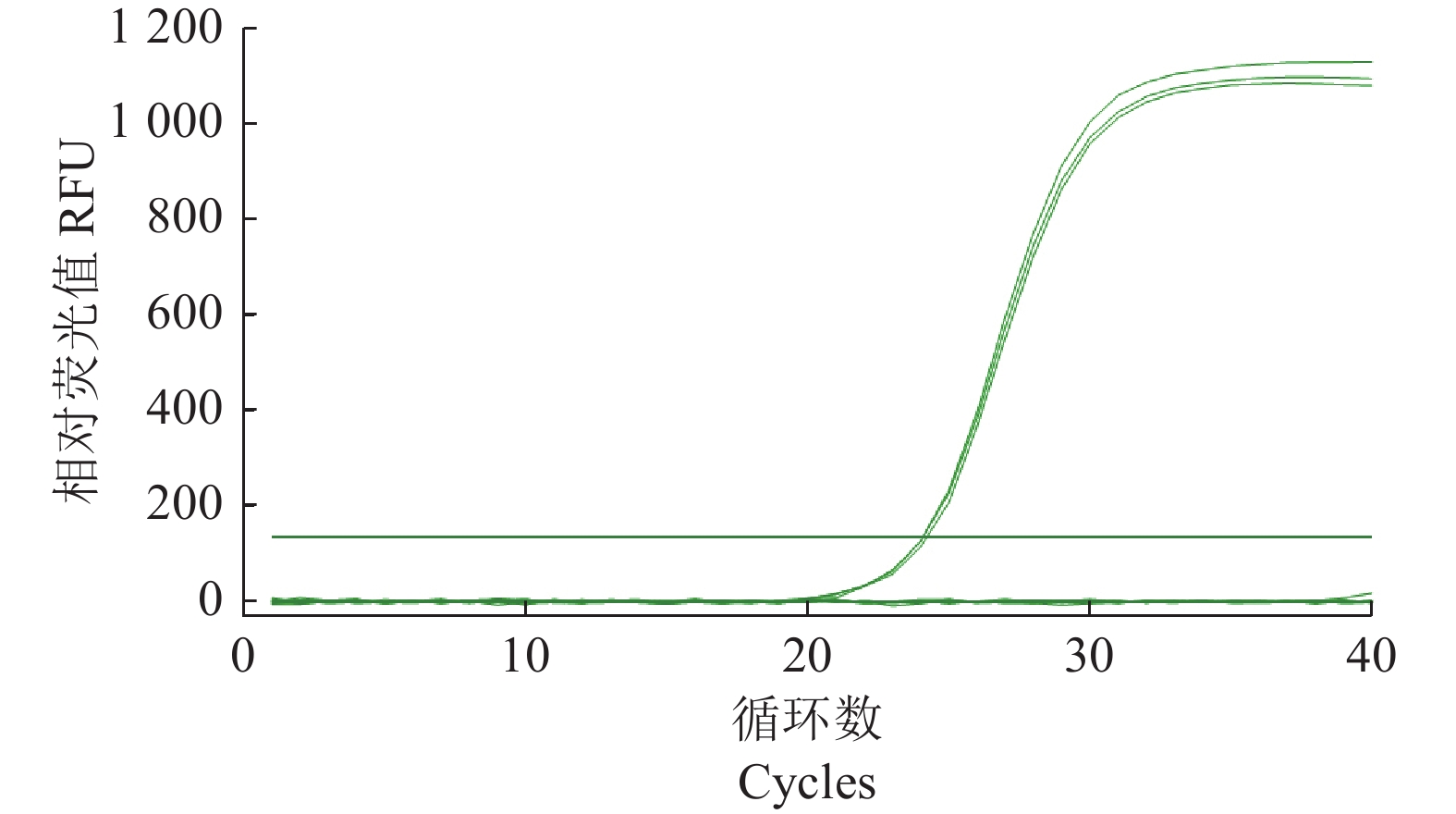
摘要:目的 建立基于SYBR Green I嵌合染料法的灌溉水源中沙门氏菌实时荧光定量PCR(Quantitative Real-time PCR, qPCR)检测方法。方法 以沙门氏菌侵袭蛋白A (invA)基因为靶基因,设计1对特异性qPCR检测引物,在对qPCR反应体系和反应条件进行优化后,通过特异性实验和灵敏度实验对qPCR方法进行验证,并制作灌溉水源中沙门氏菌qPCR定量标准曲线,最后与国标方法对比检测灌溉水源中沙门氏菌污染来验证该方法的准确性。结果 经过优化的qPCR检测方法灵敏度检测结果显示最低检测限量为1×10−1 pg·μL−1,特异性检测结果显示具有良好的特异性,干扰菌株对本qPCR检测方法无影响,所制作的qPCR扩增标准曲线在2×100~2×105 cfu·mL−1有较好的线性关系,相关系数为0.999 6,能对沙门氏菌进行准确的定量分析。该方法在与国标方法对比检测灌溉水源中沙门氏菌污染时具有同等准确性。结论 本研究建立的基于SYBR Green I嵌合荧光法的实时荧光定量PCR检测方法,可以满足灌溉水源中沙门氏菌的定量检测要求。Abstract:Objective A SYBR Green I-based quantitative RT-PCR (qPCR) method was developed for detecting salmonella in irrigation water.Method For the methodology development a pair of primers were designed based on the sequences of the invasion protein A gene (invA) of Salmonella. qPCR reaction conditions were optimized, the assay tested for specificity and sensitivity, and a standard curve of amplification constructed. Test results on a specimen of contaminated irrigation water using the qPCR assay were compared for detection accuracy with those obtained from the national standard method.Result The newly developed qPCR assay showed a minimum detection limit of 1×10−1pg·μL−1 and free of interference from genomic nucleic acids of non-target microbes. The constructed linear standard curve between 2×100cfu·mL−1 and 2×105 cfu·mL−1 had a high correlation coefficient of 0.999 6. The assay demonstrated same accuracy as did the national standard method in detecting salmonella in irrigation water.Conclusion The newly established qPCR assay could be adequately applied for salmonella detection in agriculture irrigation water.
-
Keywords:
- Quantitative RT-PCR /
- Irrigated water /
- Salmonella
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】儿茶素类化合物具有抗衰老、抗炎症、抗菌、抗病毒及抗氧化等功效[1-2],是茶叶生物化学研究最广泛、最深入的一类物质。儿茶素类主要包括表儿茶素(EC)、表没食子儿茶素(EGC)、表儿茶素没食子酸酯(ECG)和表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(EGCG),其中,EGCG抗氧化性最为突出[3-4]。表没食子儿茶素-3-O(3-O-甲基)没食子酸酯(EGCG3″Me)是在20世纪末从茶叶中新发现的一种天然被修饰的儿茶素物质,相较于其他常见的EGCG、EGC、ECG和EC,它的抗过敏和消炎等药理作用更强,尤其是花粉过敏反应的抑制效果极佳[5]。福建省为我国最大产茶省,茶树栽培历史悠久,野生茶树种质资源尤其丰富[6-8]。对福建野生茶树资源进行系统全面的儿茶素组分测定及分析,筛选出高EGCG、高EGCG3″Me等特异资源,对福建野生茶树资源的高效利用与甲基化儿茶素的研究具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】近年的研究发现,EGCG经甲基化、酰基化、糖苷化修饰后,其消炎、抗过敏性等药理作用会被显著提高[9-12]。日本学者研究显示红富贵、红富士和红誉这3个茶树品种中EGCG3″Me含量可超过1%[13]。近年来,我国茶叶科技工作者也通过筛选,发现了一系列含有此类甲基化儿茶素的种质资源[14-15]。例如,Jin等[6]在福建省南部发现一类白芽茶富含EGCG3″Me,陈潇敏等[16-17]对福建省大田、云霄茶树品种资源进行生化成分分析,发现两地的茶树品种资源均含有EGCG3″Me,并筛选出儿茶素组分特异资源。【本研究切入点】本课题组在福建省境内不同区域共收集获得43份野生茶树资源,已对其嘌呤生物碱组分进行测定及系统分析[18],其儿茶素组分则有待进一步研究。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究通过对课题组在福建省云霄、大田等7个县(市、区)搜集到的43份野生茶树种质资源儿茶素组分的系统分析,进而筛选获得其中高EGCG、高EGCG3″Me的特异茶树种质,旨在为高功能成分茶树品种选育和高EGCG、高EGCG3″Me产品的研发奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 供试材料
以43份福建野生茶树资源和8个主要栽培品种,共51份种质资源为供试茶样。 43份福建野生茶树资源样品(野生茶)采集自福建云霄、大田、尤溪、蕉城、诏安、漳平以及安溪等7个产区,8个常规生产栽培品种分别为福鼎大白茶、福云6号、黄旦、黄观音、黄金芽、龙井43、白叶1号及嘉茗1号,均采集自武夷学院茶树种质资源圃(北纬27°44′20″,东经117°59′51″)。供试材料信息见表1。采集过程参照《茶树种质资源描述规范和数据标准》[19],于2021年采摘春季第1轮茶树新梢的一芽二叶,冷冻干燥后粉碎过60目筛。
表 1 供试茶树种质资源信息Table 1. Information on tea germplasms种质资源类型
Type of germplasm resources来源
Source site种质数
Germplasm
number/份茶树种质资源样品
Samples of tea plant germplasm resources福建野生茶树资源
Wild tea resources of Fujian蕉城 Jiaocheng 3 蕉城1号—蕉城3号(JC01—JC03) 云霄 Yunxiao 6 云霄1号—云霄6号(YX01—YX06) 大田 Datian 6 大田1号—大田6号(DT01—DT06) 尤溪 Youxi 6 尤溪汤川1号—尤溪汤川6号(TC01—TC06) 安溪 Anxi 1 安溪苦茶(AX01) 诏安 Zhaoan 10 诏安1号—诏安10号(ZA01—ZA10) 漳平 Zhangping 11 漳平1号—漳平11号(ZP01—ZP11) 栽培品种
Cultivated variety武夷学院茶树种质资源圃
Tea germplasm resource nursery of Wuyi University8 福鼎大白茶(FD)、福云6号(FY6)、黄旦(HD)、金观音(JGY)、黄金芽(HJY)、龙井43(LJ43)、白叶1号(BY1)、嘉茗1号(JM1) 1.2 标准品与试剂
表没食子儿茶素-3-O-(3-O-甲基)没食子酸酯[(−)-epigallocatechin-3-O-(3-O-methylgallate), EGCG3″Me]、儿茶素(Catechin,C)、表儿茶素(Epicatechin,EC)、表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(Epigallocatechingallicacid,EGCG)、表没食子儿茶素(Epigallocatechin,EGC)、没食子儿茶素(Gallocatechin,GC)、表儿茶素没食子酸酯(Epicatechingallate,ECG)、没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(Callocatechingallate,GCG)、儿茶素没食子酸酯(Catechingallate,CG)标样(纯度≥98%,上海,源叶生物科技有限公司),甲醇(色谱级,上海默克化工技术有限公司),甲酸(色谱级,中国国药集团化学试剂有限公司),水为超纯水。
1.3 仪器设备
UltiMate 3000 高效液相色谱仪(美国,赛默飞世尔科技公司),二级管阵列检测器(DAD),C18反相色谱柱(5 µm,4.6 mm×250 mm)(中国,广州菲罗门公司);AB204-N分析天平(美国,梅特勒公司);超纯水系统(中国,Medium Touch,上海和泰仪器有限公司)。KQ-800E型超声波清洗器(中国,昆山市超声仪器有限公司);MS3 basic涡旋振荡仪[中国,艾卡(广州)仪器有限公司]。
1.4 儿茶素组分测定
参照王丽丽等[20]的高效液相色谱法。前处理:称取0.200 g粉碎样(过100目筛),加30 mL甲醇,涡旋,室温下超声提取30 min,4 ℃,10 000 r·min−1冷冻离心5 min,上清液过0.22 µm有机相微孔滤膜。色谱条件:流动相A为0.2%甲酸-水溶液(V∶V),流动相B为甲醇;流速1.00 mL·min−1;柱温,40 ℃;进样量10 µL。梯度洗脱条件,0~2 min,88% A;2 ~10 min,88%~75% A;10~15 min,75% ~73% A;15~25 min,73%~68% A;25~30 min,68% A;30~32 min,68%~88% A。检测器波长280 nm。
1.5 数据处理
每个参试资源品种,分别采集3批次,测定后,以“平均值±标准偏差”表示其儿茶素组分含量;使用Microsoft Excle 2018(美国,Microsoft公司)进行数据处理及表格制作;以Origin 2018(美国,OriginLab公司)制作折线图;采用SIMCA P14.1软件 (瑞典,Umetrics AB公司)进行正交偏最小二乘法判别分析(OPLS-DA)。使用MetaboAnalyst 5.0(https://www.metaboanalyst.ca.)在线分析平台进行聚类热图的绘制。儿茶素总量(Total catechins,TC)=EGCG3″Me+ECG+EGCG+GCG+CG+C+GC+EGC+EC。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 福建野生茶树资源儿茶素组分含量分析
通过对43份福建野生茶树资源儿茶素组分进行基本的统计分析,9种儿茶素组分标准品及样品的液相色谱图见图1,统计结果见表2,表明茶样中EGCG含量均为最高,YX06、ZP01中则富含EGCG3″Me;GCG、CG、GC在供试样中含量均较低或未检出。
![]() 图 1 标准品及参试样品的色谱注:(1)A:质量浓度为400 μg·mL混合标准工作液;B.:大田4号(DT04);C:云霄6号(YX06);D:漳平1号(ZP01)(2)峰号和组分依次对应为:1. GC,2. EGC,3. C,4. EGCG,5. EC,6. GCG,7. EGCG3′Me,8. ECG,9. CG。Figure 1. Chromatograms of standards and test samplesNote: (1)A: STD400; B: DT04; C: YX06; D: ZP01. (2) Peak number and respective component are 1 for GC, 2 for EGC, 3 for C, 4 for EGCG, 5 for EC, 6 for GCG, 7 for EGCG3″Me, 8 for ECG, and 9 for CG.表 2 43份福建野生茶树资源及8个栽培品种儿茶素组分含量Table 2. Catechins in 43 wild tea germplasms in Fujian and 8 cultivated varieties
图 1 标准品及参试样品的色谱注:(1)A:质量浓度为400 μg·mL混合标准工作液;B.:大田4号(DT04);C:云霄6号(YX06);D:漳平1号(ZP01)(2)峰号和组分依次对应为:1. GC,2. EGC,3. C,4. EGCG,5. EC,6. GCG,7. EGCG3′Me,8. ECG,9. CG。Figure 1. Chromatograms of standards and test samplesNote: (1)A: STD400; B: DT04; C: YX06; D: ZP01. (2) Peak number and respective component are 1 for GC, 2 for EGC, 3 for C, 4 for EGCG, 5 for EC, 6 for GCG, 7 for EGCG3″Me, 8 for ECG, and 9 for CG.表 2 43份福建野生茶树资源及8个栽培品种儿茶素组分含量Table 2. Catechins in 43 wild tea germplasms in Fujian and 8 cultivated varieties(单位:mg·g−1) 编号 Number 简单儿茶素 Simple catechins 酯型儿茶素 Ester catechins 总量 Total EC C EGC GC EGCG3″Me ECG EGCG GCG CG JC01 10.33±0.53 1.04±0.05 42.91±2.05 — 9.77±1.04 15.13±0.70 68.36±2.94 — — 147.54 JC02 8.08±0.62 0.75±0.19 41.18±0.50 — 15.05±1.77 13.76±1.04 76.00±5.38 — — 154.82 JC03 6.90±0.65 0.58±0.1 22.76±1.44 — 8.93±0.84 12.96±0.91 53.27±3.89 — — 105.40 YX01 2.12±0.39 0.91±0.13 8.46±0.76 — 4.96±0.49 14.06±1.20 58.38±5.58 — — 88.89 YX02 2.72±0.26 1.15±0.14 9.12±0.70- — 5.00±0.67 11.43±1.28 65.50±7.14 — — 94.92 YX03 8.97±0.26 1.49±0.03 31.23±0.57 — 9.57±1.03 21.83±0.57 111.20±2.70 — — 174.72 YX04 4.90±0.17 10.33±0.33 7.91±0.11 — 11.08±0.35 20.28±0.72 90.32±3.00 — — 144.82 YX05 10.61±0.47 1.69±0.11 31.09±0.65 — 25.54±0.44 26.88±0.62 125.53±2.83 — — 221.34 YX06 10.55±0.95 1.77±0.38 41.17±2.65 — 33.65±1.70 30.87±0.47 142.27±2.32 — — 260.28 DT01 0.84±0.12 — 6.06±1.52 — 3.54±1.01 13.93±3.97 72.56±15.87 — — 96.93 DT02 — 1.33±0.47 4.02±0.52 — 6.30±0.92 13.01±1.68 74.63±12.11 — — 99.29 DT03 5.50±0.41 2.23±0.06 23.70±1.97 — 12.84±0.31 24.00±1.01 160.70±5.39 — — 228.97 DT04 5.69±0.34 2.40±0.22 19.47±1.08 — 14.13±0.52 25.58±1.35 179.35±8.97 — — 246.62 DT05 5.24±0.11 — 28.43±0.63 — 16.45±0.71 16.55±0.42 148.72±3.84 — — 215.39 DT06 6.27±0.23 1.49±0.06 28.21±0.93 — 5.39±1.45 22.21±0.79 174.76±6.47 — — 238.33 TC01 5.03±0.26 4.28±0.40 14.17±0.62 4.61±0.36 7.91±0.75 24.75±1.55 116.26±10.32 — — 177.01 TC02 13.98±0.60 6.77±0.51 30.18±2.31 9.08±0.68 7.33±0.30 37.53±1.98 132.71±8.28 0.49±0.06 — 238.07 TC03 5.29±0.04 4.82±0.31 2.49±0.34 8.74±0.40 18.11±0.50 35.58±0.98 140.70±4.19 — — 215.73 TC04 4.01±0.87 3.58±0.18 10.97±0.36 5.62±0.27 20.70±1.95 20.64±0.96 119.47±7.15 — — 184.99 TC05 9.11±0.14 5.24±0.09 26.77±0.36 7.98±0.18 4.23±0.06 29.51±2.69 159.92±0.85 0.58±0.05 — 243.34 TC06 10.18±0.27 6.09±0.24 27.25±0.74 8.40±0.21 5.59±0.20 29.02±0.62 150.96±3.55 0.84±0.01 — 238.33 AX01 8.37±0.09 1.40±0.03 27.27±0.23 — 13.01±0.88 23.42±0.50 141.10±5.44 — — 214.57 ZA01 1.63±0.40 4.76±0.33 5.50±0.32 1.37±0.29 14.34±1.33 21.01±1.67 109.04±8.67 — — 157.65 ZA02 2.54±0.20 3.32±0.30 8.85±0.60 — 7.16±0.69 16.80±0.76 83.23±5.88 — — 121.90 ZA03 2.10±0.60 2.18±0.33 7.65±0.78 — 7.96±1.25 11.27±1.25 84.86±10.54 — — 116.02 ZA04 2.02±0.90 2.10±0.62 7.31±2.26 — 12.01±4.49 10.72±3.40 70.31±18.71 — — 104.47 ZA05 0.76±0.31 1.80±0.78 1.95±0.99 — 2.17±1.30 8.23±4.10 23.32±12.15 — — 38.23 ZA06 1.52±0.84 2.87±1.65 4.43±2.19 — 5.28±4.02 10.51±4.92 33.64±0.52 — — 58.25 ZA07 3.85±0.35 2.58±0.49 10.07±0.86 — 9.54±0.61 21.13±1.14 112.40±9.71 — — 159.57 ZA08 2.44±0.30 2.22±0.29 8.36±0.86 — 21.03±3.22 27.15±3.69 127.84±17.55 — — 189.04 ZA09 2.07±0.34 — 10.66±2.41 — 8.78±1.48 12.11±2.03 96.41±16.49 — — 130.03 ZA10 4.16±0.81 0.92±0.21 25.28±3.69 — 12.00±4.61 20.77±5.09 171.15±16.58 — — 241.99 ZP01 4.36±0.98 2.21±0.91 21.02±5.08 — 20.66±3.93 24.9±1.05 186.87±3.11 — — 260.02 ZP02 6.23±1.50 1.96±0.60 25.43±5.12 — 13.19±5.88 33.84±5.28 168.17±1.65 — — 248.82 ZP03 7.55±0.96 0.91±0.27 24.42±1.24 — 14.78±1.61 22.01±3.17 80.89±0.20 — — 150.56 ZP04 4.82±0.61 0.77±0.14 20.55±1.29 — 6.19±0.45 17.36±1.26 145.36±13.28 — — 195.05 ZP05 4.93±0.87 1.95±0.20 18.01±2.28 — 19.42±2.89 33.30±4.43 180.00±1.31 — — 257.61 ZP06 4.98±0.32 1.17±0.09 26.17±2.63 — 21.08±1.44 19.24±1.44 114.62±11.29 — — 187.26 ZP07 6.08±0.24 1.51±0.15 26.18±1.75 — 20.98±0.43 24.89±0.31 135.34±1.42 — — 214.98 ZP08 5.90±0.16 1.23±0.09 22.20±1.15 — 15.39±0.17 23.62±0.43 134.92±1.67 — — 203.26 ZP09 3.37±0.31 2.27±0.62 9.88±1.95 — 28.18±0.73 29.07±0.57 114.05±2.98 — — 186.82 ZP10 2.97±0.25 1.88±0.05 15.05±1.20 — 19.71±1.60 16.87±1.40 141.88±12.84 — — 198.36 ZP11 19.35±0.03 3.20±0.07 40.95±1.12 — 11.25±0.06 38.33±0.18 102.64±0.37 — — 215.72 FD 7.51±0.69 1.13±0.11 17.84±1.44 — — 14.12±0.80 61.36±5.69 — — 101.96 FY6 13.08±0.34 1.48±0.02 32.42±0.89 3.21±0.03 — 27.09±1.04 78.02±2.54 — — 155.30 JGY 8.78±0.41 2.01±0.64 28.79±5.02 — 1.55±0.11 17.44±0.19 94.31±1.52 — — 152.88 HD 9.08±0.45 1.74±0.26 24.01±2.39 — 1.65±0.03 20.75±0.63 73.60±1.95 — — 130.83 HJY 12.65±0.58 2.08±0.16 29.46±1.39 — — 19.87±0.78 57.01±1.90 — — 121.07 LJ43 9.24±0.27 — 26.68±1.87 — — 16.56±0.55 63.16±2.00 — — 115.64 BY1 8.46±0.12 1.39±0.14 49.42±2.93 — — 9.10±0.41 59.48±3.13 — — 127.85 JM1 9.46±0.63 1.56±0.03 38.96±1.42 — — 13.11±0.93 67.73±4.41 — — 130.82 注:“—”表示未检出。
Note: “—” indicates not detected.对43份福建野生茶树资源及8个栽培品种儿茶素组分含量进行描述统计分析,结果见表3,从儿茶素组分的构成上看,43份福建野生茶树资源与8个栽培品种相同,是以表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(EGCG)为主要组分,均未检测到儿茶素没食子酸酯(CG),含有少量的没食子儿茶素(GC)和没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(GCG)。与栽培品种不同的是,在43份福建野生茶树资源中,均检出表没食子儿茶素-3-O-(3-O-甲基)没食子酸酯(EGCG3″Me),其中以云霄6号(YX06)含量最高,为33.65 mg·g−1,而在栽培品种中,金观音(JGY)和黄旦(HD)含有少量的表没食子儿茶素-3-O-(3-O-甲基)没食子酸酯(EGCG3″Me),其余栽培品种均未检测该物质。可见,福建野生茶树资源富含表没食子儿茶素-3-O-(3-O-甲基)没食子酸酯(EGCG3″Me)。
表 3 福建野生茶树特异资源的筛选Table 3. Selection of tea germplasms from wild resources found in Fujian资源类型
Gemplasm type资源名称
Gemplasm name高儿茶素 High catechin
(>200 mg·g−1)YX06(260.28)、ZP01(260.02)、ZP05(257.51)、ZP02(248.82)、DT04(246.62)、TC05(243.34) ZA10(241.99)、TC06(238.33)、DT06(238.33)、TC02(238.07)、DT03(228.97)、YX05(221.34) TC03(215.73)、ZP11(215.72)、DT05(215.39)、ZP07(214.98)、AX01(214.57)、ZP08(203.26) 高EGCG High EGCG
(>150 mg·g-1)ZP01(186.87)、ZP05(180.00)、DT04(179.35)、DT06(174.76)、ZA10(171.15)、ZP02(168.17) 、DT03(160.70)、TC05(159.92)、TC06(150.96) 高EGCG3"Me High EGCG3''Me(>20 mg·g−1) YX06(33.65)、ZP09(28.18)、YX05(25.54)、ZP06(21.08)、ZA08(21.03)、ZP07(20.98) TC04(20.70)、ZP01(20.66) 以43份福建野生茶树资源和8个栽培品种儿茶素各组分含量的平均值为数据,绘制柱状图并进行t检验,结果如图2所示。福建野生茶树资源与栽培品种在非酯型儿茶素含量中均无明显差异,其中,福建野生茶树资源的没食子儿茶素(GC)和儿茶素(C)含量略高于栽培品种,而表没食子儿茶素(EGC)和表儿茶素(EC)含量略低于栽培品种。福建野生茶树资源的酯型儿茶素含量均高于栽培品种,其中表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(EGCG)和表没食子儿茶素-3-O-(3-O-甲基)没食子酸酯(EGCG3″Me)极显著高于栽培品种。
2.2 正交偏最小二乘判别分析 (OPLS-DA)
对福建野生茶树资源和栽培品种的儿茶素组分进行OPLS-DA分析。在图3-A中,除了漳平11号(ZP11)以外,其余福建野生茶树资源与栽培品种可以较好区分。其中福建野生茶树资源与栽培品种金观音(JGY)、黄旦(HD)、福鼎大白茶(FD)距离较近,与栽培品种龙井43(LJ43)、白叶1号(BY1)、嘉茗1号(JM1)、黄金芽(HJY)距离较远。由图3-B可知,福建野生茶树资源的主要标志物为表没食子儿茶素-3-O-(3-O-甲基)没食子酸酯(EGCG3″Me)、表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(EGCG),栽培品种含量较高的为表没食子儿茶素(EGC)、表儿茶素(EC)。如图3-C所示,共有4种化合物的 VIP (Variable importance for the projection,VIP)值大于1,变量VIP值由高至低依次是表没食子儿茶素-3-O-(3-O-甲基)没食子酸酯(EGCG3″Me)、表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(EGCG)、表儿茶素(EC)、表没食子儿茶素(EGC)、表儿茶素没食子酸酯(ECG)、儿茶素(C)、没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(GCG)和没食子儿茶素(GC)。此外,VIP大于1的4种化合物在因子载荷图(图3-B)中均属于离两类资源较近的变量。
2.3 聚类热图可视化分析
为直观展示儿茶素组分在福建野生茶树资源及栽培品种间的差异,对所测数据进行聚类热图可视化分析,颜色偏向红色说明含量越高。如图4所示,43份福建野生茶树资源中有12份与栽培品种聚为A类,以诏安和蕉城地区的种质居多。其中,蕉城地区的3份种质的儿茶素组分含量与栽培品种最为接近,如图中区域1所示,其表儿茶素(EC)、表没食子儿茶素(EGC)和儿茶素(C)含量较高,而其他物质含量均较低。B类为剩余的31份福建野生茶树资源,其与栽培品种具有明显的区分,如图中区域2所示,其表没食子儿茶素-3-O-(3-O-甲基)没食子酸酯(EGCG3″Me)、表儿茶素没食子酸酯(ECG)和表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(EGCG)含量较高。
2.4 特异性福建野生茶树资源筛选
根据儿茶素组分测定结果,参照王新超[21]的茶树特异资源筛选指标,从43份福建野生茶树资源中筛选出一批在儿茶素组分上比较特异的资源,包括18份高儿茶素茶树资源,9份高EGCG茶树资源,8份高EGCG3″Me茶树资源(表3),这些特异资源可以作为育种亲本用于之后的育种研究。
3. 讨论与结论
儿茶素组分是茶树次生物质代谢产物的重要成分,对茶叶的色、香、味品质的形成有重要作用[3]。鉴定茶树种质资源中的儿茶素组分含量及分布特征,对有针对性地开发利用资源具有重要意义。儿茶素组分又可划分为酯型儿茶素与非酯型儿茶素(简单儿茶素),其与茶叶滋味、茶叶保健功效密切相关。酯型儿茶素较非酯型儿茶素苦涩味更重,抗氧化效果更加突出[22]。本研究结果表明,在福建野生茶树品种资源中,酯型儿茶素的含量均高于栽培品种,其中EGCG和EGCG3″Me含量极显著高于栽培品种。此外,通过正交偏最小二乘判别分析及聚类热图分析发现,福建野生茶树品种资源与栽培品种的主要差异物质为EGCG和EGCG3″Me,这与前人的研究结果相似[15,23]。从产区之间分析发现,蕉城地区与栽培品种聚为A类,其EGCG3″Me、ECG、EGCG均较低,但EGC和EC含量较高。尤溪汤川、安溪及漳平地区的茶树品种资源聚为B类,该类群各儿茶素组分含量均较高,特别是EGCG3″Me、ECG、EGCG含量。而诏安、云霄及大田野生茶树在A、B两类均有分布,不同茶树种质资源间儿茶素含量变化较大,无明显区域特征。由此可见,福建野生茶树品种资源富含丰富的EGCG和EGCG3″Me,具有较高的开发利用价值。
EGCG3″Me是EGCG甲基化产物,也是茶叶中最为常见的一种甲基化儿茶素,相比于EGCG,具有更强的抗氧化和抗衰老等保健功效[5]。茶叶中EGCG3″Me的含量因茶树种质的不同有很大差异,并且高含量EGCG3″Me茶树种质资源的分布具有一定的区域性特征[24]。吕海鹏等[24]对国内200多份高茶多酚茶树种质展开调研,发现在福建、广东两地具有较多含有EGCG3″Me的茶树种质。本研究中的43份福建野生茶树种质资源中均检测出EGCG3″Me,其中含量大于10 mg·g−1有24份资源,大于20 mg·g−1有8份资源,含量最高的为云霄6号(33.65 mg·g−1)。随着茶学领域的研究进入后基因组时代,茶树次生物的代谢机理也逐渐深入到分子层面的研究阶段[25-26]。但对于茶树甲基化EGCG形成机理的研究因缺少富含EGCG3″Me的试验材料而严重受阻[13],而此次筛选鉴定出富含EGCG3″Me的种质资源,将为茶树高甲基化EGCG形成机理研究以及发掘茶树特异种质资源提供试验材料。
福建野生茶树种质资源丰富,对其儿茶素组分构成进行系统性评估,并从中筛选出高儿茶素茶树资源(>200 mg·g−1)18份,高EGCG茶树资源(>150 mg·g−1)9份,高EGCG3″Me茶树资源(>20 mg·g−1)8份,为优异茶树种质资源的开发利用提供依据。
-
表 1 供试菌株
Table 1 Salmonella strains applied for experimentation
序号
No.菌株名称
Strains name拉丁学名
Scientific name of strains菌株编号
Strains number菌株来源
Source of strains1 鼠伤寒沙门氏菌 Salmonella typhimurium 1.1174 CGMCC 2 金黄色葡萄球菌 Staphylococcus aureus 25923 ATCC 3 大肠埃希氏菌 Escherichia coli 25922 ATCC 4 阿氏肠杆菌 Enterobacter asburiae 1.876 CGMCC 5 大肠埃希氏菌O157:H7 Escherichia coli O157:H7 10907 CICC 6 单核细胞增生李斯特氏菌 Listeria monocytogenes 1.9136 CGMCC 7 英诺克李斯特氏菌 Listeria innocua 1.2990 CGMCC -
[1] YANG B W, QU D, ZHANG X L, et al. Prevalence and characterization of Salmonella serovars in retail meats of marketplace in Shaanxi, China [J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 2010, 141(1/2): 63−72.
[2] OLAIMAT A N, HOLLEY R A. Factors influencing the microbial safety of fresh produce: A review [J]. Food Microbiology, 2012, 32(1): 1−19. DOI: 10.1016/j.fm.2012.04.016
[3] WANG Y, YANG B W, WU Y, et al. Molecular characterization of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis on retail raw poultry in six provinces and two National cities in China [J]. Food Microbiology, 2015, 46: 74−80. DOI: 10.1016/j.fm.2014.07.012
[4] 方敏, 郑华英, 郭爱玲, 等. 自市售生食蔬菜胡萝卜中检出沙门菌报告 [J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2006, 16(12):1537. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8685.2006.12.067 FANG M, ZHENG H Y, GUO A L, et al. Report on Salmonella detection from raw vegetable carrots on the market [J]. Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory Technology, 2006, 16(12): 1537.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8685.2006.12.067
[5] 李秀桂, 黄彦, 唐振柱, 等. 南宁市生食蔬菜中病原菌污染监测 [J]. 应用预防医学, 2008, 14(6):361−363. LI X G, HUANG Y, TANG Z Z, et al. Monitoring of pathogenic bacteria pollution in raw vegetables in Nanning city [J]. Journal of Applied Preventive Medicine, 2008, 14(6): 361−363.(in Chinese)
[6] 吕新, 陈丽华, 李玥仁. 福州市生食蔬菜沙门氏菌污染状况分析 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2016, 31(3):297−300. LV X, CHEN L H, LI Y R. Salmonella contamination of raw vegetables in Fuzhou [J]. Fujian J Agricl Sci, 2016, 31(3): 297−300.(in Chinese)
[7] SANT'ANA A S, BARBOSA M S, DESTRO M T, et al. Growth potential of Salmonella spp. and Listeria monocytogenes in nine types of ready-to-eat vegetables stored at variable temperature conditions during shelf-life [J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 2012, 157(1): 52−58. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2012.04.011
[8] ILIC S, RAJIĆ A, BRITTON C J, et al. A scoping study characterizing prevalence, risk factor and intervention research, published between 1990 and 2010, for microbial hazards in leafy green vegetables [J]. Food Control, 2012, 23(1): 7−19. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2011.06.027
[9] SCALLAN E, HOEKSTRA R M, MAHON B E, et al. An assessment of the human health impact of seven leading foodborne pathogens in the United States using disability adjusted life years [J]. Epidemiology and Infection, 2015, 143(13): 2795−2804. DOI: 10.1017/S0950268814003185
[10] PARKER J S, WILSON R S, LEJEUNE J T, et al. An expert guide to understanding grower decisions related to fresh fruit and vegetable contamination prevention and control [J]. Food Control, 2012, 26(1): 107−116. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2011.12.025
[11] SCALLAN E, HOEKSTRA R M, ANGULO F J, et al. Foodborne illness acquired in the United States: Major pathogens [J]. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 2011, 17(1): 7−15. DOI: 10.3201/eid1701.P11101
[12] 吕新, 刘兰英, 陈丽华, 等. 可视化环介导恒温扩增法检测蔬菜产地环境灌溉水源中沙门氏菌 [J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2021, 12(2):492−498. LV X, LIU L Y, CHEN L H, et al. Determination of Salmonella in irrigated water of vegetable producing environment by visual loop-mediated isothermal amplification method [J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2021, 12(2): 492−498.(in Chinese)
[13] GONZÁLEZ-ESCALONA N, BROWN E W, ZHANG G D. Development and evaluation of a multiplex real-time PCR (qPCR) assay targeting ttrRSBCA locus and invA gene for accurate detection of Salmonella spp. in fresh produce and eggs [J]. Food Research International, 2012, 48(1): 202−208. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodres.2012.03.009
[14] SIALA M, BARBANA A, SMAOUI S, et al. Screening and detecting Salmonella in different food matrices in southern Tunisia using a combined enrichment/real-time PCR method: Correlation with conventional culture method [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017, 8: 2416. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02416
[15] BAI J F, TRINETTA V, SHI X R, et al. A multiplex real-time PCR assay, based on invA and pagC genes, for the detection and quantification of Salmonella enterica from cattle lymph nodes [J]. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 2018, 148: 110−116. DOI: 10.1016/j.mimet.2018.03.019
[16] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. 食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 沙门氏菌检验: GB 4789.4—2016[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. [17] 李光伟, 邱杨, 肖性龙, 等. 沙门氏菌荧光实时定量PCR检测试剂的研制及应用 [J]. 微生物学通报, 2007, 34(3):496−499. LI G W, QIU Y, XIAO X L, et al. Research and application on detection of Salmonella sp. by FQ-PCR [J]. Microbiology, 2007, 34(3): 496−499.(in Chinese)
[18] 杨滴, 赵宇明, 秦鹏钧, 等. 肉制品中蜡样芽胞杆菌实时荧光PCR检测方法的研究 [J]. 肉类工业, 2017(6):49−52. YANG D, ZHAO Y M, QIN P J, et al. Study on real-time fluorescent PCR detection method of cerea spore bacilli in meat products [J]. Meat Industry, 2017(6): 49−52.(in Chinese)
[19] 包海燕, 岳喜庆, 武俊瑞, 等. 基于实时荧光PCR技术快速检测饲料中的蜡样芽孢杆菌 [J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2020, 51(3):349−354. BAO H Y, YUE X Q, WU J R, et al. Rapid detection of Bacillus cereus in feed by real-time PCR [J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2020, 51(3): 349−354.(in Chinese)
[20] 张晓君, 陈丽, 毕可然, 等. 副溶血弧菌的SYBR Green Ⅰ实时定量PCR检测方法建立 [J]. 食品科学, 2012, 33(8):203−206. ZHANG X J, CHEN L, BI K R, et al. Development of SYBR green-based ⅠReal-time quantitative PCR for detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus [J]. Food Science, 2012, 33(8): 203−206.(in Chinese)
[21] 陈琳, 周青青, 顾青, 等. 实时定量PCR法快速检测水产品中的副溶血性弧菌 [J]. 浙江农业学报, 2019, 31(5):823−828. CHEN L, ZHOU Q Q, GU Q, et al. Detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in seafood products by real-time quantitative PCR assay [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2019, 31(5): 823−828.(in Chinese)
[22] 周慧平, 唐连飞, 蔡文杰, 等. 奶粉中阴沟肠杆菌实时荧光PCR快速检测方法建立 [J]. 检验检疫学刊, 2016, 26(3):10−13. ZHOU H P, TANG L F, CAI W J, et al. Rapid detection of Enterobacter cloacae in powdered milk by real-time PCR [J]. Journal of Inspection and Quarantine, 2016, 26(3): 10−13.(in Chinese)
[23] 林艳艳, 邢子伟, 谭翰清. 单核细胞增生李斯特菌hlyA基因实时荧光PCR的建立与研究 [J]. 中国热带医学, 2017, 17(12):1184−1188. LIN Y Y, XING Z W, TAN H Q. Establishment and application of real-time PCR for hlyA gene of Listeria monocytogenes [J]. China Tropical Medicine, 2017, 17(12): 1184−1188.(in Chinese)
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 陈荣平. 不同茶树种质武夷岩茶滋味成分的靶向代谢组分析. 茶叶学报. 2024(06): 19-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: