Identification and Expressions of YUCCA Family in Passiflora edulis
-
摘要:目的 黄素单加氧酶(YUCCA)基因是吲哚-3-乙酸(Indole-3-acetic acid, IAA)生物合成的主要限速酶基因之一,在植物生长发育中起着重要调控作用。本研究利用生物信息学方法对百香果(Passiflora edulis Sims.)YUCCA基因家族成员进行鉴定,以期揭示百香果YUCCA家族基因在激素响应中的功能,同时为YUCCA家族基因在其他物种中的生物信息学研究提供参考。方法 利用生物信息学方法分析百香果YUCCA基因编码蛋白质的理化性质和保守结构域,基因的染色体定位、基因结构、系统进化树、顺式作用元件等;利用qRT-PCR探究部分成员在植物生长调节剂IAA处理下的表达情况。结果 百香果基因组中共鉴定出29个YUCCA家族成员,不均匀分布于8条染色体,基因长度(552~9210 bp)存在明显差异,含有1~8个内含子,同时具有8个保守基序。通过系统进化树分析,发现百香果YUCCA基因家族可划分为3类,聚在同一分类中的百香果YUCCA基因具有高度的保守性,同时发现百香果的YUCCA基因与苜蓿(Medicago sativa L.)、拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)亲缘关系更近,而与水稻(Oryza sativa L.)的亲缘关系较远。顺式作用元件分析显示,百香果YUCCA基因家族启动子受多种激素所诱导,可响应多种逆境胁迫。转录组数据分析结果表明:PeYUCCA6、PeYUCCA11和PeYUCCA16在台农百香果和黄金百香果叶片中呈现较低表达或者不表达,其中PeYUCCA23在台农百香果和黄金百香果的表达量最高,推测该基因对百香果叶片的发育有较大影响。qRT-PCR分析结果表明,在100 μmol·L−1 IAA处理后,PeYUCCA7、PeYUCCA13、PeYUCCA17、PeYUCCA24 和PeYUCCA26基因表达量显著升高。结论 YUCCA基因家族成员在 IAA处理下的表达差异较大,YUCCA基因可能在植物生长调节剂IAA处理下的百香果生长发育和抵御逆境环境过程中发挥重要作用。
-
关键词:
- 百香果 /
- 吲哚-3-乙酸 /
- YUCCA 基因家族 /
- 生物信息学 /
- 定量分析
Abstract:Objective Bioinformatics of YUCCA family encoding the flavin-containing monooxygenase associated with biosynthesis of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) in passion fruit was studied.Methods Bioinformatic methods were applied to analyze the physicochemical properties, conserved domains, chromosome location, structure, phylogenetic tree, and cis-acting elements of the genes in Passiflora edulis Sims. qRT-PCR was used to determine the expressions of some members under IAA treatment.Results There were 29 YUCCA members unevenly distributed in 8 chromosomes of P. edulis. They significantly differed in length that ranged from 552 bp to 9210 bp and contained 1–8 introns and 8 conserved motifs. A phylogenetic tree analysis divided the family into three distinct categories, and within a same class the members were highly conservative. Genetically, the genes were more closely related to Medicago sativa L. and Arabidopsis thaliana than Oryza sativa L. The cis-acting element analysis indicated that the promoter of the family genes could be induced by various hormones and respond to various stresses. PeYUCCA6, PeYUCCA11, and PeYUCCA16 showed low or no expression in the leaves of Tainong and Golden Passion Fruit, but PeYUCCA23 had a high expression suggesting its predominant role in the plant development. The treatment of 100 μmol·L−1 IAA significantly elevated the expressions of PeYUCCA7, PeYUCCA13, PeYUCCA17, PeYUCCA24, and PeYUCCA26.Conclusion The expressions of YUCCAs in P. edulis varied greatly under IAA treatment. But as a family, the genes likely played an important role in the growth, development, and resistance to adverse environment of passion fruits.-
Keywords:
- Passiflora edulis Sims /
- IAA /
- YUCCA family /
- bioinformatics /
- quantitative analysis
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】生长素作为最早被发现的一种植物生长类激素[1],在植物的胚胎发育、器官生成以及向性生长等生物学过程中发挥关键作用[2] 。吲哚-3-乙酸(Indole-3-acetic acid, IAA)是植物体内生长素存在的主要形式[3]。IAA合成途径包括色氨酸依赖途径和非色氨酸依赖途径,目前关于前者的研究较多。遗传和生化研究表明黄素单加氧酶(YUCCA)是色氨酸依赖途径中的限速酶,催化吲哚-3-丙酮酸(Indoble-3-pyruvate, IPA)生成IAA[4],对生长素的合成起重要作用。目前,全球具有超过500种西番莲植物,百香果作为其中60种可食用的水果之一,受到全球各地消费者们的喜爱[5]。百香果兼具食用、药用和观赏价值 [6−9]。因此,针对百香果YUCCA家族基因进行全基因组分析,探讨该家族基因在生长素响应中的潜在作用,对揭示百香果YUCCA蛋白的生物学功能具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】作为一个多基因家族,YUCCA家族成员已在许多植物中得到鉴定,包括拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)[10]、水稻(Oryza sativa L.)[11]、玉米[12](Zea mays L.)、苜蓿(Medicago sativa L.) [13]、梨(Pyrus sorotina.)[14]等。已有研究表明YUCCA家族成员广泛参与植物的生长发育、逆境胁迫响应等多种生物过程,如葡萄(Vitis vinifera L.)中鉴定出10个YUCCA家族成员,YUCCA1和YUCCA8可能参与葡萄采后贮藏过程中穗梗的褪绿[15];西瓜(Citrullus lanatus)中有10个YUCCA家族成员,ClYUCCA4 及 ClYUCCA10c可能参与调控西瓜果实的成熟[16];桃 (Prunus persica)中鉴定出11个YUCCA家族成员,PpYUCCA6/12可能参与其垂枝性状的形成[17]。【本研究切入点】截至目前,YUCCA基因家族成员已在20多种植物中得到鉴定,但百香果中YUCCA基因家族的研究还鲜见报道,其研究还有待深入,在其生长过程中YUCCA家族基因是否参与调控生长发育过程未见报道。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究基于百香果基因组,利用生物信息学方法对YUCCA基因家族进行全基因组鉴定,分析基因的染色体定位、基因结构、编码蛋白的理化性质、保守基序、系统进化树等理化信息,并利用转录组数据分析其在不同品种叶片中的表达模式;利用qRT-PCR分析家族成员对IAA的响应模式,可为百香果YUCCA 基因功能验证提供一定的理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 百香果 YUCCA 基因家族鉴定
从国家基因库生命大数据平台(China National GeneBank DataBase, CNGBdb)下载百香果全基因组数据,获取百香果基因组序列[18];从拟南芥基因组数据库TAIR下载 9个拟南芥YUCCA 基因的蛋白质序列,利用TBtools软件[19]进行BlastP比对,阈值设置为1×10−5,以此获得百香果中YUCCA 基因家族候选蛋白序列;利用CDD 和SMART 数据库对所有候选基因的蛋白质序列结构域进行鉴定,去除不含或含有不完整结构域的蛋白序列,最终获得29个百香果YUCCA 候选基因,并按照其在染色体上的位置进行命名。
1.2 百香果YUCCA 家族成员编码蛋白质理化性质和保守基序
通过 ExPASy(https://web. Expasy.org/protparam/)在线网站对百香果YUCCA基因家族蛋白质的理化性质进行分析。使用 MEME在线网站(https://meme-suite. org/meme/tools/meme)对百香果YUCCA蛋白质保守基序进行分析,基序数设置为8,利用 TBtools对保守基序的结果进行可视化分析。
1.3 百香果YUCCA 家族成员的染色体定位、基因结构和系统进化树
利用TBtools软件进行百香果YUCCA基因家族成员染色体定位并进行数据可视化。利用MEGA 7. 0软件中的Neighbour-Joining(NJ)系统发育方法构建系统发育树,bootstrap 设为1000,利用在线网站 iTOL(https://itol.embl.de/itol.cgi)对系统进化树进行优化。
1.4 百香果YUCCA家族成员启动子的顺式作用元件
利用TBtools软件对百香果 YUCCA 基因编码区序列上游2000 bp序列进行提取,使用在线软件Plant CARE(http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html)分析预测顺式作用元件,利用TBtools软件对结果进行可视化。
1.5 百香果YUCCA基因家族成员表达模式
基于从NCBI获得的公共转录组数据(PRJNA634206)分析百香果YUCCA基因家族成员在不同品种(台农百香果和黄金百香果)叶片中的表达模式,基于FPKM(每千个碱基的转录每百万映射读取的碎片)定量分析各基因表达水平,并利用TBtools软件绘制特异性表达热图。
1.6 IAA处理及qRT-PCR分析
选择3个月苗龄且长势基本一致的台农百香果幼苗为试验对象,处理组喷施100 μmol·L −1 IAA于叶片上,对照组喷施超纯水,处理组及对照组各处理3株幼苗,处理6 h后取材,选取每株植物从上往下第3片叶,液氮冷冻,于−80 ℃冰箱保存,用于后续荧光定量PCR试验。参照何锐杰等[20]的方法进行 RNA 提取和 qRT-PCR 分析,所用引物序列见表1,内参基因为Pe60S基因,所用试剂为SYBR GreenⅠMaster Mix(Takara),所用仪器为LightCycler 96 Real-Time PCR Systems(Roche),采用2−ΔΔCT方法计算相对表达量。
表 1 YUCCA基因家族成员实时荧光定量PCR引物Table 1. Primers for qRT-PCR on YUCCAs in passion fruit基因
Gene正向引物序列(5'-3')
Forward primer(5'-3')反向引物序列(5'-3')
Reverse primer (5'-3')Pe60S AGGTGGGTAACAGGATTATC TGGCTGTCTTTTGGTGCTG PeYUCCA7 GGGAAGAAAGTGCTGGTCGT TGTCAACGAGCCAAAGTGGT PeYUCCA13 TGCCAGAGTTTGTGGGGTTG TGGGCAAGACATGAACCGAG PeYUCCA17 GTTGGGTGCGGCAATTCAG GTTGGCAGCTAGAAGGAGGA PeYUCCA24 TGTCTGAGTTTGGTGGCGAT TCTCGGCAGAACGTGAACC PeYUCCA25 GGGGACCTATTCTGCACACC GCATCTCTTGGGGCAAAACG PeYUCCA26 GGGAATGGAGGTGTGTTTGGA ACACATGGACAGCCCGAAAG 1.7 数据处理
利用 SPSS 21.0 软件中的 Duncan’s 新复极差法对试验数据进行显著性分析。利用Prism 9.1软件绘制柱形图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 百香果YUCCA基因家族成员鉴定
从表2可知,从百香果基因组中筛选获得29个YUCCA基因家族候选成员,并根据其在染色体上的位置分别命名为PeYUCCA1~PeYUCCA29。基因长度552(PeYUCCA4)~9210 (PeYUCCA22)bp,平均长度4881 bp;编码区长度516(PeYUCCA4)~1977 (PeYUCCA5)bp,平均长度1247 bp;C+G含量37%(PeYUCCA18)~44%(PeYUCCA20)。
表 2 百香果YUCCA基因家族成员Table 2. YUCCAs in passion fruit基因ID
Gene name基因名称
Gene ID基因全长
Full length of genes/bp编码区长度
Coding area length/bpG+C含量
C+G content/%A+T含量
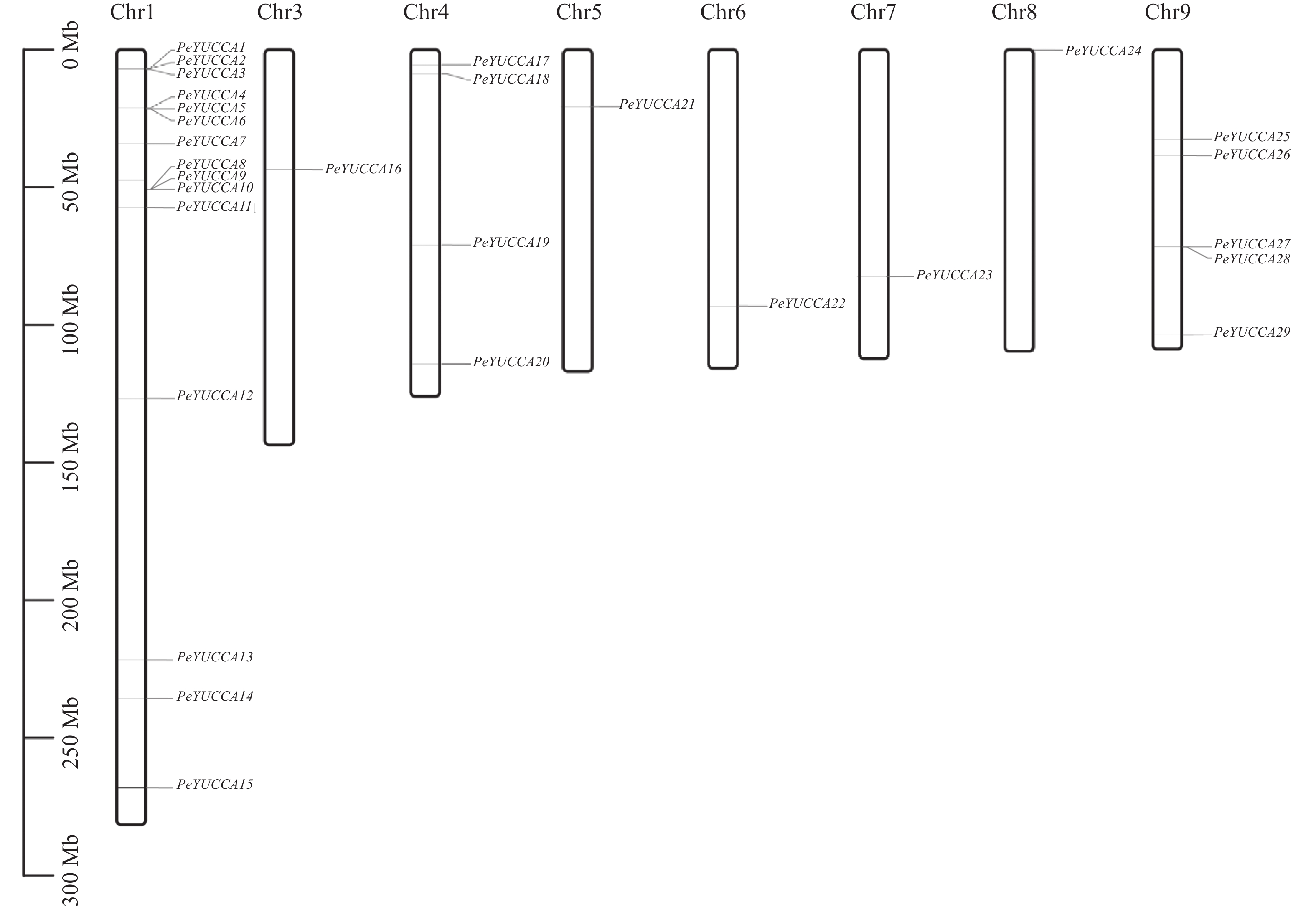
A+T content/%PeYUCCA1 ZX.01G0002140 2265 1593 41 59 PeYUCCA2 ZX.01G0002210 2612 1200 40 60 PeYUCCA3 ZX.01G0002240 2263 1593 41 59 PeYUCCA4 ZX.01G0004710 552 516 43 57 PeYUCCA5 ZX.01G0004780 4609 1977 38 62 PeYUCCA6 ZX.01G0004800 1651 1092 40 60 PeYUCCA7 ZX.01G0017780 1964 1275 43 57 PeYUCCA8 ZX.01G0025770 1602 1155 42 58 PeYUCCA9 ZX.01G0025830 1450 1152 42 58 PeYUCCA10 ZX.01G0025850 1412 1215 42 58 PeYUCCA11 ZX.01G0029730 2216 1557 42 58 PeYUCCA12 ZX.01G0086000 2409 1593 41 59 PeYUCCA13 ZX.01G0115230 1809 1293 43 57 PeYUCCA14 ZX.01G0126750 1718 1146 40 60 PeYUCCA15 ZX.01G0137550 1733 1146 40 60 PeYUCCA16 ZX.03G0007260 3263 1374 40 60 PeYUCCA17 ZX.04G0004260 1787 1200 43 57 PeYUCCA18 ZX.04G0005300 2979 1629 37 63 PeYUCCA19 ZX.04G0017390 2275 783 39 61 PeYUCCA20 ZX.04G0031510 1769 1293 44 56 PeYUCCA21 ZX.05G0003260 1706 1092 40 60 PeYUCCA22 ZX.06G0015980 9210 918 41 59 PeYUCCA23 ZX.07G0012040 3758 1467 40 60 PeYUCCA24 ZX.08G0000090 1981 1275 44 56 PeYUCCA25 ZX.09G0006460 2339 1275 43 57 PeYUCCA26 ZX.09G0011010 3589 1323 44 56 PeYUCCA27 ZX.09G0020980 1460 1164 41 59 PeYUCCA28 ZX.09G0021020 1263 1023 39 61 PeYUCCA29 ZX.09G0026980 1457 1161 41 59 利用 TBtools对百香果全基因组信息进行染色体定位分析,结果(图1)表明 29个YUCCA 基因在8条染色体上均有分布,在1号染色体上的YUCCA 基因家族成员最多,有15个,9号和4号染色体次之,分别有5个和 4个成员,3、5、6、7、8号染色体上最少,均有1个成员。
2.2 百香果YUCCA基因家族成员编码蛋白序列特征
从表3可知,百香果 YUCCA 家族成员蛋白编码171~658 个氨基酸残基,其中PeYUCCA4氨基酸残基数量最少,PeYUCCA5氨基酸残基数量最多;其蛋白质的相对分子质量29366.12(PeYUCCA19)~74050.52(PeYUCCA5)Da,与氨基酸残基数量变化范围较为一致。29个PeYUCCA蛋白的等电点pI为5.61~9.36,其中3个PeYUCCA蛋白(PeYUCCA4、PeYUCCA16和PeYUCCA19)为酸性蛋白,pI小于7,剩余蛋白均为碱性蛋白质;不稳定系数在 32.03~50.74,其中 PeYUCCA7、PeYUCCA11、PeYUCCA13、PeYUCCA16、PeYUCCA17、PeYUCCA18、PeYUCCA20、PeYUCCA23、PeYUCCA24、PeYUCCA25、PeYUCCA26的不稳定系数值大于40,是不稳定蛋白;亲水性指数在−0.449~0.006,仅PeYUCCA6为疏水性蛋白,其余28个PeYUCCA蛋白均为亲水性蛋白,亲水性蛋白在PeYUCCA基因家族中占有较大的比例;蛋白脂溶指数在76.6~97.19,其中 PeYUCCA6脂肪系数最大,为97.19,PeYUCCA23脂肪系数最小,为76.6。
表 3 百香果YUCCA蛋白的理化性质Table 3. Physicochemical properties of YUCCA protein in passion fruit蛋白名称
Protein氨基酸数量
Number of amino acid分子量
Molecular weight/Da等电点
pI不稳定指数
Instability index脂肪系数
Aliphatic index平均亲水指数
Grand average of hydropathicityPeYUCCA1 530 60025.48 8.79 36.52 91.96 −0.108 PeYUCCA2 399 44952.88 8.77 36.33 90.35 −0.132 PeYUCCA3 530 59901.36 8.86 36.45 93.25 −0.089 PeYUCCA4 171 19496.11 6.70 33.86 83.74 −0.353 PeYUCCA5 658 74050.52 8.60 38.14 93.92 −0.1 PeYUCCA6 363 40948.6 8.44 33.65 97.19 0.006 PeYUCCA7 424 47517.87 8.70 50.74 88.47 −0.163 PeYUCCA8 384 42813.29 8.51 35.85 82.99 −0.164 0PeYUCCA9 384 42248.58 8.39 36.22 83.49 −0.142 PeYUCCA10 404 44826.99 9.10 35.42 94.03 −0.082 PeYUCCA11 519 59666.11 8.66 46.14 80.58 −0.17 PeYUCCA12 530 59791.11 8.80 34.27 93.25 −0.104 PeYUCCA13 430 48121.4 8.21 48.71 90.4 −0.109 PeYUCCA14 381 43169.1 9.36 36.67 87.98 −0.239 PeYUCCA15 381 43196 9.26 37.02 85.43 −0.251 PeYUCCA16 457 52147.09 5.61 43.24 85.67 −0.361 PeYUCCA17 399 44585.34 8.88 41.46 89.65 −0.242 PeYUCCA18 542 61911.37 7.57 45.29 86.48 −0.18 PeYUCCA19 260 29366.12 5.62 37.73 80.46 −0.345 PeYUCCA20 430 48033.36 9.36 47.03 84.72 −0.237 PeYUCCA21 363 41357.16 9.25 38.59 85.62 −0.23 PeYUCCA22 305 35045.45 8.69 39.78 81.77 −0.216 PeYUCCA23 488 55653.62 5.65 50.21 76.6 −0.449 PeYUCCA24 424 47483.77 8.70 49.26 87.1 −0.191 PeYUCCA25 424 47495.97 8.64 48.26 84.15 −0.124 PeYUCCA26 440 48908.67 8.59 44.73 87.07 −0.122 PeYUCCA27 388 42840.19 8.20 37.54 81.88 −0.173 PeYUCCA28 340 37800.42 7.63 32.03 89.35 −0.094 PeYUCCA29 386 42561 8.37 34.48 85.08 −0.145 2.3 百香果YUCCA 基因结构和保守基序分析
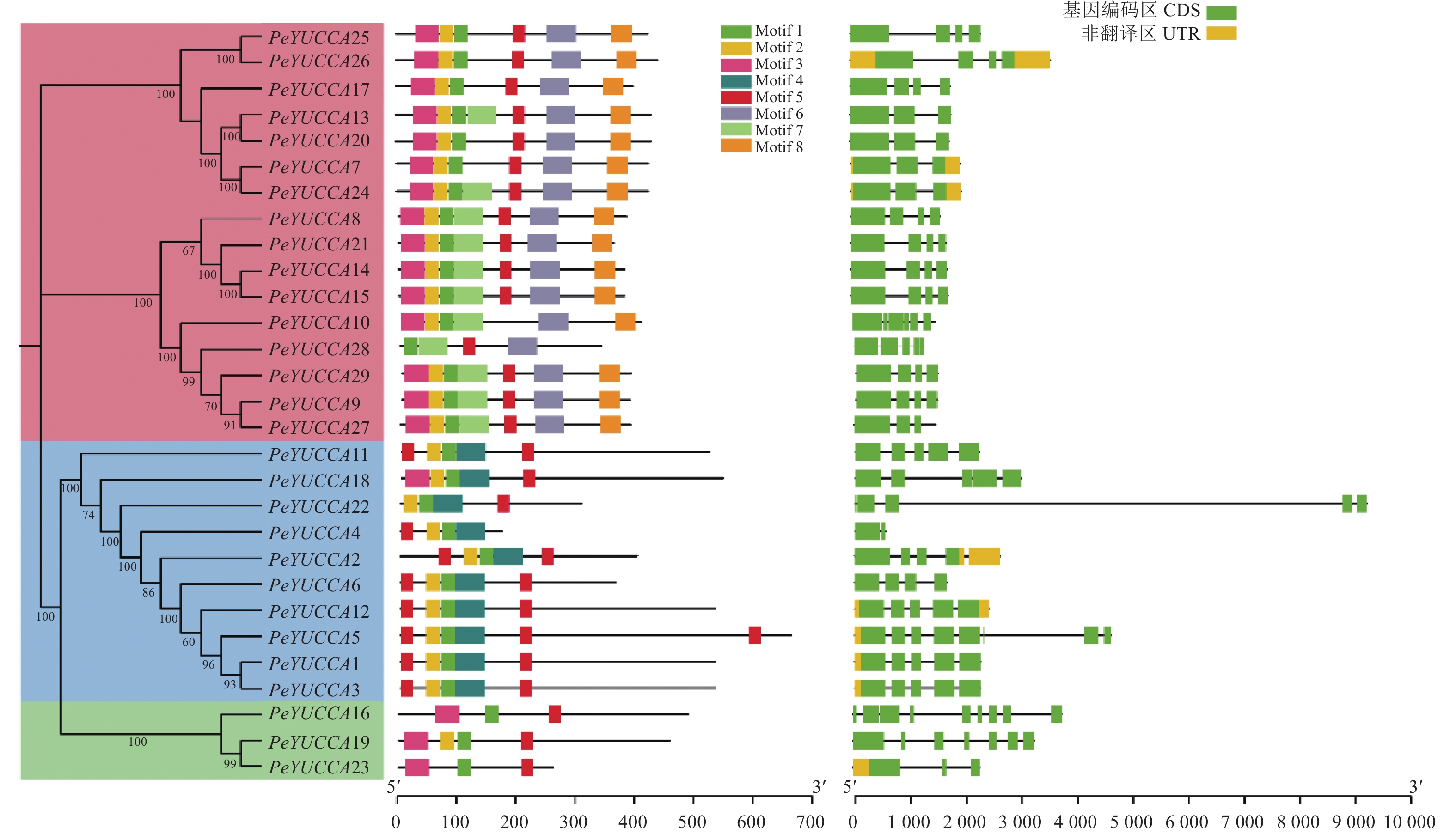
图2表明,百香果YUCCA 基因家族成员的内含子数量存在一定的差异,其中PeYUCCA4的内含子数量最少,只有1个,而PeYUCCA23内含子数量最多,有8个,大部分成员的内含子数量为3~4个。通过对氨基酸保守基序分析发现,百香果YUCCA 基因家族成员编码的蛋白质中共有8个motif,motif 1和motif 5为YUCCA 基因家族成员共同拥有,显示2个基序为29个YUCCA蛋白较保守的基序。
2.4 百香果 YUCCA 基因家族成员蛋白的系统进化
为进一步了解百香果YUCCA家族成员的生物学作用,使用MEGA7软件对拟南芥、水稻、苜蓿和百香果的YUCCA家族共68个成员的蛋白序列建立系统进化树,结果如图3所示,YUCCA家族可以划分为3大分支Class I、Class II和Class III,多数百香果YUCCA蛋白单独聚集在Class I和Class II上,剩余百香果YUCCA蛋白跟拟南芥及苜蓿聚集在Class III上,如PeYUCCA17和AtYUCCA4蛋白聚集在Class III的分支上,PeYUCCA25和MtYUCCA11蛋白聚为一支,说明百香果YUCCA和拟南芥及苜蓿有着较近的亲缘关系,跟水稻的亲缘关系相对最远。另外可以发现,PeYUCCA19和PeYUCCA23蛋白聚为一支,PeYUCCA1和PeYUCCA3蛋白聚为一支,这些PeYUCCA蛋白有着较短的进化距离,说明PeYUCCA19和PeYUCCA23蛋白、PeYUCCA1和PeYUCCA3蛋白的亲缘关系更为接近。
2.5 百香果 YUCCA 基因家族成员启动子顺式作用元件
启动子顺式作用元件结果显示:百香果YUCCA基因家族成员的启动子区域包含多种顺式作用元件,如脱落酸诱导元件、水杨酸诱导元件、赤霉素诱导元件、生长素响应元件和茉莉酸甲酯响应元件。这些元件提示YUCCA基因可能在响应多种植物激素时发挥作用,参与生长和发育过程。除PeYUCCA19之外,其他28个YUCCA基因家族成员都含有厌氧诱导元件,表明YUCCA基因家族可能在低氧条件下发挥一定的作用,可能与根部或其他组织的适应性生长有关。同时有27个YUCCA基因家族成员含有酸响应作用元件,表明YUCCA基因家族的表达可能受到酸性环境的调控,可能与酸性环境下的生长发育过程有关(图4)。此外,还存在光响应作用元件、胁迫元件、低温响应元件以及防御和应激响应元件,表明YUCCA基因家族可能在植物的光周期和应对不利环境胁迫时发挥作用。
2.6 百香果YUCCA基因家族表达模式
百香果YUCCA基因家族表达模式分析结果(图5)显示:PeYUCCA6、PeYUCCA11和PeYUCCA16在台农百香果和黄金百香果叶片中呈现较低表达或者不表达, PeYUCCA1、PeYUCCA3、PeYUCCA5和PeYUCCA6在台农百香果叶片中的表达量高于黄金百香果。PeYUCCA23在台农百香果叶片和黄金百香果的叶片表达量均最高,推测该基因对百香果叶片的发育有较大影响。
2.7 IAA处理对百香果YUCCA基因家族成员表达的影响
为了解百香果YUCCA基因对IAA的响应情况,利用qRT-PCR技术,选择与拟南芥亲缘关系较近的6个百香果YUCCA基因家族成员进行表达量分析。结果(图6)显示: IAA处理下百香果叶片中5个基因(PeYUCCA7、PeYUCCA13、PeYUCCA17、PeYUCCA24 和PeYUCCA26)表达量呈现显著上升。
3. 讨论
YUCCA基因编码是植物内源生长素生物合成途径中的关键酶,在植物的生长发育、植株体型形成、组织器官分化以及响应环境刺激等方面发挥重要作用,已成为植物生物学领域的重要研究课题之一 [21]。近年来的研究表明YUCCA基因参与了植物根部的生长素分布和根发育的调控机制,并讨论了其在根发育中的重要性,强调了该基因在根部生长和架构中的作用。例如,过表达YUCCA1基因可导致水稻出现不定根,侧根的数量明显增多[22−23]。同时,研究发现YUCCA基因在根发育的早期表达水平较低,在根生长的中后期发挥着重要的调控作用,尤其是不定根形成后表达显著上调[24]。至今,在百香果属植物中尚未有YUCCA基因相关的研究报道,因此,在百香果属植物中鉴定和研究YUCCA基因具有重要的研究意义。YUCCA 基因通常为多基因成员家族,如在拟南芥、草莓(Fragaria raananassa Duch.)等植物中均是多基因家族,在百香果属植物中亦存在多基因家族情况。本研究从百香果中共鉴定到29 个 YUCCA 基因,基因数量多于拟南芥(14个),推测百香果在生长发育的进化过程中可能出现了该家族基因大量复制现象,导致数量远远超出模式植物拟南芥。
由于目前西番莲科中除了百香果外还未有其他物种基因组信息进行了破译,因此本研究仅进行了百香果YUCCA家族成员与拟南芥、水稻等模式物种YUCCA家族成员的聚类分析。研究表明,百香果基因家族分为三大类Class I、Class II和Class III,AtYUCCA4和PeYUCCA17蛋白聚集在同一支上,而AtYUCCA1、AtYUCCA4蛋白双突变体显示拟南芥在开花期间的植物器官受到阻碍,未能形成完整的开花器官[25],推测PeYUCCA17蛋白可能与百香果花器官发育有关。YUCCA11启动子区转座子插入可能会导致桃果实性状硬化[26];MtYUCCA11和PeYUCCA25蛋白聚集在一支,推测PeYUCCA25蛋白可能与百香果的果实硬化有关;聚类在同一支上的基因成员大多具有相似数量的motif,在蛋白结构上存在保守性以及功能相似性。
通过qRT-PCR技术分析植物生长调节剂IAA对百香果YUCCA基因家族的影响,结果显示在100 μmol·L−1 IAA处理下,除PeYUCCA25基因外,其余5个基因表达量均显著上升,表明百香果PeYUCCA基因家族成员可能参与了生长素响应进程而参与植物生长发育过程,同样拟南芥和水稻的YUCCA基因家族成员也表现出对植物生长调节剂IAA的调控浓度和时间不同的表达模式差异[27],推测认为这种差别可能与组织的特异性以及生长素依赖性转录和转录后的调节模式有关。
启动子顺式作用元件分析发现百香果YUCCA基因家族成员的启动子上包含一个或多个激素类诱导元件,而激素在植物开花过程中发挥重要作用。如在低温情况下赤霉素能够促进拟南芥开花[28],甜荞(Fagopyrum esculentum Moench)中喷施6-BA可以使开花时间提前,提高开花株数和结实率[29]。综上,百香果YUCCA基因家族的潜在多功能性,使得它们可能在植物的生长、发育和适应性响应中发挥关键作用,并且受到多种植物激素和环境因素的调控,这对于进一步研究YUCCA基因在百香果中的功能和调控机制提供了重要线索。
-
表 1 YUCCA基因家族成员实时荧光定量PCR引物
Table 1 Primers for qRT-PCR on YUCCAs in passion fruit
基因
Gene正向引物序列(5'-3')
Forward primer(5'-3')反向引物序列(5'-3')
Reverse primer (5'-3')Pe60S AGGTGGGTAACAGGATTATC TGGCTGTCTTTTGGTGCTG PeYUCCA7 GGGAAGAAAGTGCTGGTCGT TGTCAACGAGCCAAAGTGGT PeYUCCA13 TGCCAGAGTTTGTGGGGTTG TGGGCAAGACATGAACCGAG PeYUCCA17 GTTGGGTGCGGCAATTCAG GTTGGCAGCTAGAAGGAGGA PeYUCCA24 TGTCTGAGTTTGGTGGCGAT TCTCGGCAGAACGTGAACC PeYUCCA25 GGGGACCTATTCTGCACACC GCATCTCTTGGGGCAAAACG PeYUCCA26 GGGAATGGAGGTGTGTTTGGA ACACATGGACAGCCCGAAAG 表 2 百香果YUCCA基因家族成员
Table 2 YUCCAs in passion fruit
基因ID
Gene name基因名称
Gene ID基因全长
Full length of genes/bp编码区长度
Coding area length/bpG+C含量
C+G content/%A+T含量
A+T content/%PeYUCCA1 ZX.01G0002140 2265 1593 41 59 PeYUCCA2 ZX.01G0002210 2612 1200 40 60 PeYUCCA3 ZX.01G0002240 2263 1593 41 59 PeYUCCA4 ZX.01G0004710 552 516 43 57 PeYUCCA5 ZX.01G0004780 4609 1977 38 62 PeYUCCA6 ZX.01G0004800 1651 1092 40 60 PeYUCCA7 ZX.01G0017780 1964 1275 43 57 PeYUCCA8 ZX.01G0025770 1602 1155 42 58 PeYUCCA9 ZX.01G0025830 1450 1152 42 58 PeYUCCA10 ZX.01G0025850 1412 1215 42 58 PeYUCCA11 ZX.01G0029730 2216 1557 42 58 PeYUCCA12 ZX.01G0086000 2409 1593 41 59 PeYUCCA13 ZX.01G0115230 1809 1293 43 57 PeYUCCA14 ZX.01G0126750 1718 1146 40 60 PeYUCCA15 ZX.01G0137550 1733 1146 40 60 PeYUCCA16 ZX.03G0007260 3263 1374 40 60 PeYUCCA17 ZX.04G0004260 1787 1200 43 57 PeYUCCA18 ZX.04G0005300 2979 1629 37 63 PeYUCCA19 ZX.04G0017390 2275 783 39 61 PeYUCCA20 ZX.04G0031510 1769 1293 44 56 PeYUCCA21 ZX.05G0003260 1706 1092 40 60 PeYUCCA22 ZX.06G0015980 9210 918 41 59 PeYUCCA23 ZX.07G0012040 3758 1467 40 60 PeYUCCA24 ZX.08G0000090 1981 1275 44 56 PeYUCCA25 ZX.09G0006460 2339 1275 43 57 PeYUCCA26 ZX.09G0011010 3589 1323 44 56 PeYUCCA27 ZX.09G0020980 1460 1164 41 59 PeYUCCA28 ZX.09G0021020 1263 1023 39 61 PeYUCCA29 ZX.09G0026980 1457 1161 41 59 表 3 百香果YUCCA蛋白的理化性质
Table 3 Physicochemical properties of YUCCA protein in passion fruit
蛋白名称
Protein氨基酸数量
Number of amino acid分子量
Molecular weight/Da等电点
pI不稳定指数
Instability index脂肪系数
Aliphatic index平均亲水指数
Grand average of hydropathicityPeYUCCA1 530 60025.48 8.79 36.52 91.96 −0.108 PeYUCCA2 399 44952.88 8.77 36.33 90.35 −0.132 PeYUCCA3 530 59901.36 8.86 36.45 93.25 −0.089 PeYUCCA4 171 19496.11 6.70 33.86 83.74 −0.353 PeYUCCA5 658 74050.52 8.60 38.14 93.92 −0.1 PeYUCCA6 363 40948.6 8.44 33.65 97.19 0.006 PeYUCCA7 424 47517.87 8.70 50.74 88.47 −0.163 PeYUCCA8 384 42813.29 8.51 35.85 82.99 −0.164 0PeYUCCA9 384 42248.58 8.39 36.22 83.49 −0.142 PeYUCCA10 404 44826.99 9.10 35.42 94.03 −0.082 PeYUCCA11 519 59666.11 8.66 46.14 80.58 −0.17 PeYUCCA12 530 59791.11 8.80 34.27 93.25 −0.104 PeYUCCA13 430 48121.4 8.21 48.71 90.4 −0.109 PeYUCCA14 381 43169.1 9.36 36.67 87.98 −0.239 PeYUCCA15 381 43196 9.26 37.02 85.43 −0.251 PeYUCCA16 457 52147.09 5.61 43.24 85.67 −0.361 PeYUCCA17 399 44585.34 8.88 41.46 89.65 −0.242 PeYUCCA18 542 61911.37 7.57 45.29 86.48 −0.18 PeYUCCA19 260 29366.12 5.62 37.73 80.46 −0.345 PeYUCCA20 430 48033.36 9.36 47.03 84.72 −0.237 PeYUCCA21 363 41357.16 9.25 38.59 85.62 −0.23 PeYUCCA22 305 35045.45 8.69 39.78 81.77 −0.216 PeYUCCA23 488 55653.62 5.65 50.21 76.6 −0.449 PeYUCCA24 424 47483.77 8.70 49.26 87.1 −0.191 PeYUCCA25 424 47495.97 8.64 48.26 84.15 −0.124 PeYUCCA26 440 48908.67 8.59 44.73 87.07 −0.122 PeYUCCA27 388 42840.19 8.20 37.54 81.88 −0.173 PeYUCCA28 340 37800.42 7.63 32.03 89.35 −0.094 PeYUCCA29 386 42561 8.37 34.48 85.08 −0.145 -
[1] 贾利霞, 齐艳华. 生长素代谢、运输及信号转导调控水稻粒型研究进展 [J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3):263−275. DOI: 10.11983/CBB21227 JIA L X, QI Y H. Advances in the regulation of rice(Oryza sativa)grain shape by auxin metabolism, transport and signal transduction [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(3): 263−275. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11983/CBB21227
[2] 李中华. 多组学数据揭示棉花纤维发育转换期的遗传调控机制和重要代谢物[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2021. LI Z H. Multiomics data reveal the genetic regulation mechanism and important metabolites of cotton fiber development transition period[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2021. (in Chinese)
[3] 莫福磊, 束艺, 陈秀玲, 等. 基于全基因组的番茄YUCCA基因家族生物信息学分析 [J]. 分子植物育种, 2020, 18(10):3159−3163. MO F L, SHU Y, CHEN X L, et al. Bioinformatics analysis of tomato YUCCA gene family based on whole genome [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2020, 18(10): 3159−3163. (in Chinese)
[4] 刘华彬, 张秦莹, 门淑珍. YUCCA基因家族在拟南芥胚胎发育过程中的表达模式研究 [J]. 南开大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 50(4):1−7. LIU H B, ZHANG Q Y, MEN S Z. The expression patterns of YUCCA during embryo development in Arabidopsis [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Nankaiensis, 2017, 50(4): 1−7. (in Chinese)
[5] 李莉萍. 西番莲综合开发利用研究进展 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2012, 40(28):13840−13843,13846. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2012.28.062 LI L P. Research progress of comprehensive development and utilization of passionflower [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 40(28): 13840−13843,13846. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2012.28.062
[6] LI C B, XIN M, LI L, et al. Characterization of the aromatic profile of purple passion fruit (Passiflora edulis Sims) during ripening by HS-SPME-GC/MS and RNA sequencing [J]. Food Chemistry, 2021, 355: 129685. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129685
[7] FONSECA A M A, GERALDI M V, JUNIOR M R M, et al. Purple passion fruit (Passiflora edulis f. edulis): A comprehensive review on the nutritional value, phytochemical profile and associated health effects [J]. Food Research International, 2022, 160: 111665. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111665
[8] XU M X, LI A D, TENG Y, et al. Exploring the adaptive mechanism of Passiflora edulis in Karst areas via an integrative analysis of nutrient elements and transcriptional profiles [J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 185. DOI: 10.1186/s12870-019-1797-8
[9] XIA Z Q, HUANG D M, ZHANG S K, et al. Chromosome-scale genome assembly provides insights into the evolution and flavor synthesis of passion fruit (Passiflora edulis Sims) [J]. Horticulture Research, 2021, 8: 14. DOI: 10.1038/s41438-020-00455-1
[10] CHENG Y F, DAI X H, ZHAO Y D. Auxin biosynthesis by the YUCCA flavin monooxygenases controls the formation of floral organs and vascular tissues in Arabidopsis [J]. Genes & Development, 2006, 20(13): 1790−1799.
[11] YAMAMOTO Y, KAMIYA N, MORINAKA Y, et al. Auxin biosynthesis by the YUCCA genes in rice [J]. Plant Physiology, 2007, 143(3): 1362−1371. DOI: 10.1104/pp.106.091561
[12] LI W L, ZHAO X Y, ZHANG X S. Genome-wide analysis and expression patterns of the YUCCA genes in maize [J]. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2015, 42(12): 707−710. DOI: 10.1016/j.jgg.2015.06.010
[13] ZHAO B L, HE L L, JIANG C, et al. Lateral Leaflet Suppression 1 (LLS1), encoding the MtYUCCA1 protein, regulates lateral leaflet development in Medicago truncatula [J]. The New Phytologist, 2020, 227(2): 613−628. DOI: 10.1111/nph.16539
[14] 袁美同, 李绍信, 纪丕钰, 等. 梨YUCCA基因家族的鉴定与生物信息学分析 [J]. 分子植物育种, 2021, 19(19):6328−6337. YUAN M T, LI S X, JI P Y, et al. Identification and bioinformatics analysis of YUCCA gene family in Pyrus [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2021, 19(19): 6328−6337. (in Chinese)
[15] 李志谦, 邹东方, 李靖雯, 等. 葡萄YUCCA家族基因的鉴定及在穗梗褪绿过程中的表达分析 [J]. 河南农业大学学报, 2022, 56(2):254−261. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2340.2022.2.hennannydxxb202202010 LI Z Q, ZOU D F, LI J W, et al. Genome-wide identification of YUCCA gene family in grape and expression analysis during rachis degreening [J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural University, 2022, 56(2): 254−261. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2340.2022.2.hennannydxxb202202010
[16] 张倩倩, 田守蔚, 张洁, 等. 西瓜YUCCA基因家族鉴定及在果实成熟过程中的表达分析 [J]. 中国蔬菜, 2019, (3):21−29. ZHANG Q Q, TIAN S W, ZHANG J, et al. Identification of YUCCA gene family and expression analysis during watermelon fruit ripening process [J]. China Vegetables, 2019(3): 21−29. (in Chinese)
[17] ZHANG Y Y, MAO Q S, MA R J, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the PpYUCCA gene family in weeping peach trees (Prunus persica ‘Pendula’) [J]. Horticulturae, 2022, 8(10): 878. DOI: 10.3390/horticulturae8100878
[18] MA D N, DONG S S, ZHANG S C, et al. Chromosome-level reference genome assembly provides insights into aroma biosynthesis in passion fruit (Passiflora edulis) [J]. Molecular Ecology Resources, 2021, 21(3): 955−968. DOI: 10.1111/1755-0998.13310
[19] CHEN C J, CHEN H, ZHANG Y, et al. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data [J]. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(8): 1194−1202. DOI: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
[20] 何锐杰, 方庭, 余伟军, 等. 西番莲查尔酮合成酶(CHS)基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达模式 [J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2022, 28(4):1066−1075. HE R J, FANG T, YU W J, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the CHS gene family in passion fruit [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2022, 28(4): 1066−1075. (in Chinese)
[21] TRIPATHI P, TAYADE R, MUN B G, et al. Silicon application differentially modulates root morphology and expression of PIN and YUCCA family genes in soybean (Glycine max L. ) [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 842832. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.842832
[22] 梁栋. IAA和BR参与干旱胁迫影响烟草侧根发育的研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2021. LIANG D. Study on IAA and BR participating in drought stress affecting tobacco lateral root development[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2021. (in Chinese)
[23] 李真. 毛白杨PtoWOX11/12a基因的抗逆功能研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2017. LI Z. Functional characterization of A PtoWOX11/12a gene in stress resistance of Populus tomentosa[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2017. (in Chinese)
[24] 李孟湛. SAUR15调控植物侧根及不定根发育的功能及分子机理研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2022. LI M Z. Functions and molecular mechanisms of SAUR15 in regulating development of plant lateral and adventitious roots[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2022. (in Chinese)
[25] 阚东阳, 柯学, Walid Ghidan, 等. 拟南芥图位克隆快速初定位系统的建立 [J]. 西南农业学报, 2018, 31(9):1765−1771. KAN D Y, KE X, WALID G, et al. Establishment of rapid initial localization system of Arabidopsis based on map-based cloning [J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 31(9): 1765−1771. (in Chinese)
[26] 丁义峰. 生长素相关基因调控桃果实成熟分子机制研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2018. DING Y F. Molecular mechanism of auxin related genes regulating peach fruit ripening[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2018. (in Chinese)
[27] ABEL S, NGUYEN M D, THEOLOGIS A. The PS-IAA4/5-like family of early auxin-inducible mRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 1995, 251(4): 533−549. DOI: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0454
[28] YAMAGUCHI N, WINTER C M, WU M F, et al. Gibberellin acts positively then negatively to control onset of flower formation in Arabidopsis [J]. Science, 2014, 344(6184): 638−641. DOI: 10.1126/science.1250498
[29] 金晓蕾. 外源激素对甜荞开花结实的影响及调控机制研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2019. JIN X L. Effect and regulation mechanism of exogenous hormones on flowering and fruiting in common buckwheat[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2019. (in Chinese)




 下载:
下载: