Identification and Expressions of YUCCA Family in Passiflora edulis
-
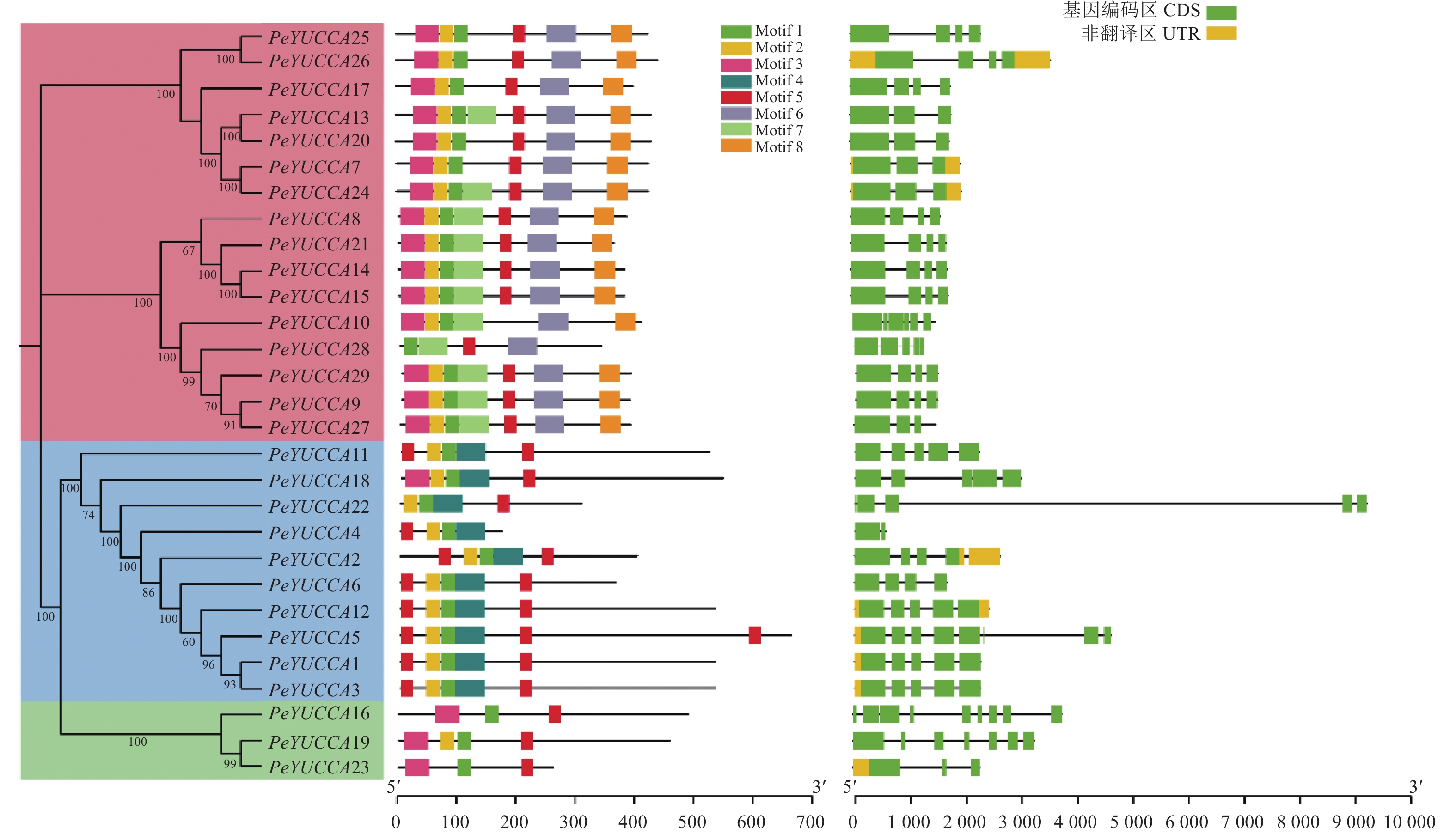
摘要:目的 黄素单加氧酶(YUCCA)基因是吲哚-3-乙酸(Indole-3-acetic acid, IAA)生物合成的主要限速酶基因之一,在植物生长发育中起着重要调控作用。本研究利用生物信息学方法对百香果(Passiflora edulis Sims.)YUCCA基因家族成员进行鉴定,以期揭示百香果YUCCA家族基因在激素响应中的功能,同时为YUCCA家族基因在其他物种中的生物信息学研究提供参考。方法 利用生物信息学方法分析百香果YUCCA基因编码蛋白质的理化性质和保守结构域,基因的染色体定位、基因结构、系统进化树、顺式作用元件等;利用qRT-PCR探究部分成员在植物生长调节剂IAA处理下的表达情况。结果 百香果基因组中共鉴定出29个YUCCA家族成员,不均匀分布于8条染色体,基因长度(552~9210 bp)存在明显差异,含有1~8个内含子,同时具有8个保守基序。通过系统进化树分析,发现百香果YUCCA基因家族可划分为3类,聚在同一分类中的百香果YUCCA基因具有高度的保守性,同时发现百香果的YUCCA基因与苜蓿(Medicago sativa L.)、拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)亲缘关系更近,而与水稻(Oryza sativa L.)的亲缘关系较远。顺式作用元件分析显示,百香果YUCCA基因家族启动子受多种激素所诱导,可响应多种逆境胁迫。转录组数据分析结果表明:PeYUCCA6、PeYUCCA11和PeYUCCA16在台农百香果和黄金百香果叶片中呈现较低表达或者不表达,其中PeYUCCA23在台农百香果和黄金百香果的表达量最高,推测该基因对百香果叶片的发育有较大影响。qRT-PCR分析结果表明,在100 μmol·L−1 IAA处理后,PeYUCCA7、PeYUCCA13、PeYUCCA17、PeYUCCA24 和PeYUCCA26基因表达量显著升高。结论 YUCCA基因家族成员在 IAA处理下的表达差异较大,YUCCA基因可能在植物生长调节剂IAA处理下的百香果生长发育和抵御逆境环境过程中发挥重要作用。
-
关键词:
- 百香果 /
- 吲哚-3-乙酸 /
- YUCCA 基因家族 /
- 生物信息学 /
- 定量分析
Abstract:Objective Bioinformatics of YUCCA family encoding the flavin-containing monooxygenase associated with biosynthesis of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) in passion fruit was studied.Methods Bioinformatic methods were applied to analyze the physicochemical properties, conserved domains, chromosome location, structure, phylogenetic tree, and cis-acting elements of the genes in Passiflora edulis Sims. qRT-PCR was used to determine the expressions of some members under IAA treatment.Results There were 29 YUCCA members unevenly distributed in 8 chromosomes of P. edulis. They significantly differed in length that ranged from 552 bp to 9210 bp and contained 1–8 introns and 8 conserved motifs. A phylogenetic tree analysis divided the family into three distinct categories, and within a same class the members were highly conservative. Genetically, the genes were more closely related to Medicago sativa L. and Arabidopsis thaliana than Oryza sativa L. The cis-acting element analysis indicated that the promoter of the family genes could be induced by various hormones and respond to various stresses. PeYUCCA6, PeYUCCA11, and PeYUCCA16 showed low or no expression in the leaves of Tainong and Golden Passion Fruit, but PeYUCCA23 had a high expression suggesting its predominant role in the plant development. The treatment of 100 μmol·L−1 IAA significantly elevated the expressions of PeYUCCA7, PeYUCCA13, PeYUCCA17, PeYUCCA24, and PeYUCCA26.Conclusion The expressions of YUCCAs in P. edulis varied greatly under IAA treatment. But as a family, the genes likely played an important role in the growth, development, and resistance to adverse environment of passion fruits.-
Keywords:
- Passiflora edulis Sims /
- IAA /
- YUCCA family /
- bioinformatics /
- quantitative analysis
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】土壤污染是当前我国乃至世界共同存在的环境污染问题,由于经济发展需求,人类的扰动破坏了土地原本的生态平衡,导致环境质量恶化[1]。通过颁布《土壤污染防治行动计划》,国家明确规定了在2020年和2035年被污染耕地安全利用率至少达90%和95%[2]。2014年,全国土壤环境质量公报显示,我国有19.4%的耕地土壤受到Cd、Pb、As、Cr、Hg等潜在有毒重金属污染[3]。水稻是广西主要的粮食作物,目前广西耕地土壤重金属污染严重,而且是多种重金属复合污染[4-5]。重金属污染土壤上水稻重金属含量状况不容忽视,自治区政府对水稻田土壤重金属污染问题高度重视[4]。因此,开展水稻重金属低积累技术及重金属污染水稻田修复研究,对实现重金属污染水稻田安全利用和粮食安全生产具有十分重要的意义。【前人研究进展】目前,减少重金属向水稻迁移和累积主要有两种方法,一是通过向土壤施用钝化剂使土壤重金属钝化或者叶面施用阻控剂来减少重金属向水稻迁移;另一种是筛选出适宜在当地种植的重金属低积累水稻品种来减少水稻体内的重金属含量[6-7]。有研究表明[8],不同水稻品种基因型不同,对As、Zn、Cd等重金属元素的富集能力存在明显差异。不同水稻品种对 Pb、Hg 的耐性和富集能力存在显著的基因型差异[9],通过不同品种水稻对重金属富集的差异,可以筛选出适应于在中低重金属污染稻田种植的低累积型水稻品种[10]。文典等[7]通过重金属低积累水稻品种筛选和化学修复手段结合的农田安全利用技术研究发现,采用化学钝化剂联合低累积水稻品种对减少稻米Cd含量效果显著,降低率40%~70%。水稻对土壤主要重金属镉、铅、铜、锌的富集规律研究发现,糙米对镉的富集系数最高,但影响糙米对镉富集的因素较为复杂,铅从土壤到糙米的迁移能力逐渐降低[11]。施用阻控剂可以有效降低水稻籽粒中的重金属含量[12-13]。学者研究发现水稻叶面喷施硅肥和硒肥可以显著降低稻米中Cd含量[13],有研究发现,补施硒肥可有效降低稻米中Pb、Cd、Cr、Hg等重金属含量,提高籽粒营养成分,施用适量叶面肥可以有效降低水稻体内重金属的含量,但不同水稻品种施用叶面肥对水稻积累重金属的影响有所不同[14-16]。【本研究切入点】目前关于不同水稻品种对重金属迁移和积累的差异,主要是以研究筛选水稻Cd低累积品种为主,而对于As、Pb、Cr低累积水稻品种的报道较少[14, 16],而事实上土壤环境中重金属的污染常是多种重金属的复合污染[17-18]。且目前关于水稻品种筛选和叶面肥组合处理对多个重金属的影响报道较少[14, 16]。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究在广西德保县某重金属污染水稻田进行,选用10个广西主要种植的水稻品种,以及含有硒元素、硅元素的两种叶面肥,通过大田试验分析水稻糙米Cd、As、Pb、Cr等4种重金属的影响,了解不同水稻品种对重金属Cd、As、Pb、Cr的累积情况,施用叶面肥对水稻糙米累积重金属的影响,为安全利用重金属污染稻田区域提供研究基础,为水稻粮食安全生产提供试验依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验设计
本研究在广西德保县某重金属污染水稻田进行。试验选用10个(表1)广西广泛种植的晚稻品种,每个品种设置施用含硒叶面肥(Se)(处理A)、含硅叶面肥(Si)(处理B)及CK等3个处理,完全随机区组试验,一共30个处理,120个小区,每个小区面积为20 m2。2020年7月25日播种前施用复合肥做基肥[每个小区施用6 kg,(N+P2O5+K2O)≥48%,质量比为N:P2O5:K2O=26:10:12]。2020年8月3日,进行人工移植。2020年9月21日,原液稀释100倍后采用人工喷洒的方式喷洒叶面肥,10月4日,按照第一次的浓度进行第二次喷洒。德保试验田土壤pH为7.66,总镉含量为2.33 mg·kg−1,总砷含量为10.86 mg·kg−1,总铬含量为0.35 mg·kg−1,铅含量为67.32 mg·kg−1。硒肥主要成分为有机硒(有机硒≥85 g·L−1),其余组分为水不溶物(≤10 g·L−1)、Na(≤10 g·L−1);硅肥主要成分为有机硅(有机硅≥120 g·L−1),其余组分为N、P2O5、K2O,(N+P2O5+K2O)≥170 g·L−1。两种阻控剂Cd含量均<10 mg·kg−1,Hg含量均<5 mg·kg−1,As含量均<10 mg·kg−1,Pb含量均<10 mg·kg−1,Cr含量均<50 mg·kg−1。
表 1 供试水稻品种Table 1. Rice varieties under study品种 Varieties 编号Number 来源Source 桂育12
Guiyu 12D-1 当地农资店
Local agricultural materials store华浙优1号
Huazheyou No.1D-2 广西农科院提供
Provided by Guangxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences68优金占
68 YoujinzhangD-3 凯丰优158
Kaifengyou 158D-4 裕丰优158
Yufengyou 158D-5 y两优143
y Lliangyou 143D-6 荃香优822
Quanxiangyou 822D-7 又香优龙丝苗
Youxiang youlongsimiaoD-8 又香优雅丝苗
Youxiang youyasimiaoD-9 野香优明月丝苗
Yexiangyou mingyuesimiaoD-10 1.2 采样方法与样品分析
2020年11月在水稻进入收获期后,每个小区采用五点法混合采样5株水稻样品,先用离子水冲洗干净,在水稻自然风干后,脱壳成糙米。所有植物样品粉碎后用自封袋保存。在采集植物样品的同时,每个小组采集一个土壤混合样品,样品自然风干后,研磨过100目筛装入自封备用。所有样品交由广西西大检测有限公司检测重金属总含量(As为无机砷)(对于未检出的数据均采用检出限值0.001 mg·kg−1表示,样品中仅重金属Pb存在未检出)。重金属的富集按下列公式计算:
富集系数(BCF)= m1/m2
式中,m1为植株重金属含量(mg·kg−1);m2为土壤重金属含量(mg·kg−1)。
1.3 数据分析
运用 IMB SPSS 19.0进行数据分析统计,通过Duncan法进行显著差异性分析(重金属Cr、Pb部分通过Duncan法和最小显著性差异LSR法两种分析方法结合进行显著性分析)。通过Microsoft Office Excel 2016 进行图的制作。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同品种水稻糙米重金属含量
图1(a)所示,10个品种水稻糙米Cd含量在0.1350~0.2520 mg·kg−1,均值为0.1812 mg·kg−1,水稻糙米Cd含量最低的品种是桂育12,含量最高的品种是野香优明月丝苗,其中凯丰优158、又香优雅丝苗、野香优明月丝苗3个品种水稻糙米Cd含量显著高于其他品种。10个品种水稻中,共有3个水稻品种Cd含量超过GB/T 5009.15-2014(≤0.2 mg·kg−1)。图1(b)所示,10个品种水稻糙米As含量在0.2000~0.3950 mg·kg−1,均值为0.2643 mg·kg−1,水稻糙米As含量最低的品种是裕丰优158,含量最高的品种是又香优雅丝苗,其中桂育12、又香优雅丝苗两个品种水稻糙米As含量显著高于凯丰优158、裕丰优158、荃香优822。10个品种水稻中,共有9个水稻品种As含量超过GB/T 5009.11—2014(≤0.2 mg·kg−1)。图1(c)所示,10个品种水稻糙米Pb含量在0.0010~0.0268 mg·kg−1,均值为0.0036 mg·kg−1,10个品种水稻中,仅有华浙优1号检测出Pb含量,且10个水稻品种Pb含量远低于GB/T 5009.12—2014(≤0.2 mg·kg−1)。图1(d)所示,10个品种水稻糙米Cr含量在0.0046~0.0521 mg·kg−1,均值为0.0185 mg·kg−1,水稻糙米Cr含量最低的品种是荃香优822,含量最高的品种是又香优龙丝苗,又香优龙丝苗水稻糙米Cr含量显著高于桂育12、华浙优1号、68优金占、Y两优143、荃香优822等5个品种。10个品种糙米Cr含量均远低于GB/T 5009.123—2014(≤1.0 mg·kg−1)。
2.2 不同叶面肥处理对水稻糙米重金属含量的影响
表2 所示,经过叶面肥处理后,10个品种水稻糙米Cd含量均低于对照组,糙米Cd含量均低于国家标准要求GB/T 5009.15—2014(≤0.2 mg·kg−1)。喷洒硒肥(Se)和喷洒硅肥(Si)后,10个品种水稻糙米Cd含量均值分别为0.1000 mg·kg−1和0.1010mg·kg−1,含量均显著低于对照组Cd含量0.1812 mg·kg−1,除华浙优1号和y两优143两个品种外,其他品种喷洒硒肥(Se)和喷洒硅肥(Si)后糙米Cd含量均显著低于其对照处理。由表3 所示,喷洒硒肥(Se)后,10个品种水稻糙米As含量在0.1900~0.2850 mg·kg−1,平均值为0.2195 mg·kg−1,显著低于对照处理0.2643 mg·kg−1,相较于对照处理含量降低了17.1%,其中除裕丰优158外,其他水稻品种糙米As含量均低于对照处理,且桂育12糙米As含量显著低于其对照处理;喷洒硒肥(Se)后,仅野香优明月丝苗、荃香优822、凯丰优158、Y两优143等4个品种糙米As含量低于GB/T 5009.11—2014(≤0.2 mg·kg−1)。喷洒硅肥(Si)后,10个品种水稻糙米As含量在0.1425~0.2650 mg·kg−1,平均值为0.1850 mg·kg−1,显著低于对照处理0.2643 mg·kg−1,相较于对照处理含量降低了30.0%,10个品种水稻糙米As含量均低于对照组,且桂育12和68优金占糙米As含量显著低于对照处理。喷洒硅肥(Si)后,除又香优雅丝苗外,其他9个品种糙米As含量均低于GB/T 5009.11—2014(≤0.2 mg·kg−1)。表4所示,经过叶面肥处理后,10个品种水稻糙米中仅有喷洒硅肥(Si)处理中,品种桂育12检测出Pb含量,且相较于对照处理0.001 mg·kg−1(检出线)升高了1580%,但与对照相比差异不显著。施用硒叶面肥(Se)(处理A)、施用硅叶面肥(Si)(处理B)及CK等3个处理,10个水稻品种Pb含量均远低于GB/T 5009.12—2014(≤0.2 mg·kg−1)。如表5所示,10个品种喷施叶面肥后糙米Cr含量相较于对照处理有明显差异,但差异不显著。喷洒硒肥(Se)后,10个品种水稻糙米Cr含量在0.0076~0.0741 mg·kg−1,平均值为0.0257 mg·kg−1,相较于对照处理0.0185 mg·kg−1含量增加了39.1%,但差异不显著。喷洒硅肥(Si)后,10个品种水稻糙米Cr含量在0.0039~0.0361 mg·kg−1,平均值为0.0183 mg·kg−1,相较于对照处理0.0185 mg·kg−1,含量降低了1.2%。施用硒叶面肥(Se)(处理A)、施用硅叶面肥(Si)(处理B)及CK等3个处理,10个水稻品种Cr含量均远低于GB/T 5009.123—2014(≤1.0 mg·kg−1)。
表 2 不同处理水稻糙米Cd含量Table 2. Cd content of brown rice under treatments品种
VarietiesCK 处理A Treatment A 处理B Treatment B 含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)降幅
Decline/%含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)降幅
Decline/%D-1 0.1350±0.0173 a 0.0900±0.0141 b −33.3 0.0825±0.0150 b −38.9 D-2 0.1500±0.0365 a 0.0950±0.0054 a −36.7 0.0975±0.0450 a −35.0 D-3 0.1675±0.005 a 0.0975±0.025 b −41.8 0.0975±0.0125 b −41.8 D-4 0.2350±0.0369 a 0.1025±0.0095 b −56.4 0.1025±0.020 b −56.4 D-5 0.1500±0.0141 a 0.0975±0.0325 b −35.0 0.0950±0.0173 b −36.7 D-6 0.1575±0.0411 a 0.1275±0.0530 a −19.0 0.1400±0.0315 a −11.1 D-7 0.1700±0.0336 a 0.1000±0.0291 b −41.2 0.0850±0.0054 b −50.0 D-8 0.1675±0.0221 a 0.1050±0.0253 b −37.3 0.0975±0.0170 b −41.8 D-9 0.2275±0.0403 a 0.0825±0.0093 b −63.7 0.0950±0.0191 b −58.2 D-10 0.2520±0.0346 a 0.1025±0.0184 b −59.3 0.1175±0.0330 b −53.4 平均值 Average 0.1812±0.047 a 0.1000±0.0254 b −44.8 0.1010±0.0264 b −44.3 同行数据后不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05),下同。
Data with different letters on the same column indicate significant difference between different varieties (P<0.05). Same for the following tables.表 3 不同处理水稻糙米As含量Table 3. As content of brown rice from different treatment groups品种
VarietiesCK 处理A Treatment A 处理B Treatment B 含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)降幅
Decline/%含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)降幅
Decline/%D-1 0.3125±0.0298 a 0.2250±0.0443 b −28.0 0.1425±0.0614 c −54.4 D-2 0.2800±0.0182 a 0.2450±0.0732 a −12.5 0.1950±0.0983 a −30.4 D-3 0.2625±0.015 a 0.2025±0.0222 ab −22.9 0.1725±0.0670 b −34.3 D-4 0.2275±0.0394 a 0.1925±0.0355 a −15.4 0.1675±0.1092 a −26.4 D-5 0.2000±0.0483 a 0.2325±0.0386 a 16.3 0.1800±0.0680 a −10.0 D-6 0.2375±0.1105 a 0.1900±0.0495 a −20.0 0.1675±0.0570 a −29.5 D-7 0.2200±0.0270 a 0.1950±0.0793 a −11.4 0.1800±0.0742 a −18.2 D-8 0.2625±0.0531 a 0.2250±0.0544 a −14.3 0.1825±0.0680 a −30.5 D-9 0.3950±0.0369 a 0.2850±0.0420 a −27.8 0.2650±0.1283 a −32.9 D−10 0.2450±0.0412 a 0.1975±0.0872 a −19.4 0.1975±0.0580 a −19.4 平均值 Average 0.2643±0.068 a 0.2195±0.0572 b −17.1 0.1850±0.07845 c −30.0 表 4 不同处理水稻糙米Pb含量Table 4. Pb content of brown rice from different treatment groups品种
VarietiesCK 处理A Treatment A 处理B Treatment B 含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)降幅
Decline/%含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)降幅
Decline/%D-1 0.0010±0 a 0.0010±0 a 0 0.0168±0.031 a 1580.0 D-2 0.0268±0.0516 a 0.0010±0 a −96.3 0.0010±0 a −96.3 D-3 0.0010±0 a 0.0010±0 a 0 0.0010±0 a 0.0 D-4 0.0010±0 a 0.0010±0 a 0 0.0010±0 a 0.0 D-5 0.0010±0 a 0.0010±0 a 0 0.0010±0 a 0.0 D-6 0.0010±0 a 0.0010±0 a 0 0.0010±0 a 0.0 D-7 0.0010±0 a 0.0010±0 a 0 0.0010±0 a 0.0 D-8 0.0010±0 a 0.0010±0 a 0 0.0010±0 a 0.0 D-9 0.0010±0 a 0.0010±0 a 0 0.0010±0 a 0.0 D-10 0.0010±0 a 0.0010±0 a 0 0.0010±0 a 0.0 平均值 Average 0.0035±0.016 a 0.0010±0 a −72.1 0.0025±0.010 a −27.9 表 5 不同处理水稻糙米Cr含量Table 5. Cr content of brown rice from different treatment groups品种
VarietiesCK 处理A Treatment A 处理B Treatment B 含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)降幅
Decline/%含量
Content/(mg·kg−1)降幅
Decline/%D-1 0.0051±0.0082 a 0.0144±0.0149 a 182.4 0.0178±0.0217 a 249.0 D-2 0.0097±0.0120 a 0.0335±0.045 a 245.4 0.0070±0.0119 a −27.8 D-3 0.0051±0.0081 a 0.0341±0.0421 a 568.6 0.0248±0.0307 a 386.3 D-4 0.0226±0.0284 a 0.0741±0.1362 a 227.9 0.0315±0.0523 a 39.4 D-5 0.0166±0.0109 a 0.0224±0.0078 a 34.9 0.0361±0.0512 a 117.5 D-6 0.0103±0.0127 a 0.0076±0.0082 a −26.2 0.0173±0.0266 a 68.0 D-7 0.0046±0.0071 a 0.0201±0.0134 a 337.0 0.0049±0.0078 a 6.5 D-8 0.0521±0.0452 a 0.0123±0.0076 a −76.4 0.0227±0.0375 a −56.4 D-9 0.0339±0.0241 a 0.0102±0.0065 a −69.9 0.0171±0.0207 a −49.6 D-10 0.0253±0.0422 a 0.0291±0.0504 a 15.0 0.0039±0.0057 a −84.6 平均值 Average 0.0185±0.025 a 0.0257±0.0481a 39.1 0.0183±0.0290a −1.2 2.3 不同处理对水稻糙米重金属富集的影响
如表6所示,10个品种水稻中,水稻糙米Cd、As、Pb、Cr的平均富集系数分别为0.0884、0.0195、0.00012、0.0003,水稻糙米对Cd的富集系数明显高于As、Pb、Cr,水稻糙米对As的富集系数明显高于Pb、Cr两种重金属,水稻糙米对Cr的富集系数高于Pb。
表 6 不同品种水稻糙米重金属的富集系数Table 6. Enrichment coefficients on heavy metals in brown rice of different varieties品种
VarietiesCd As Pb Cr D-1 0.0601 0.0229 0.00003 0.0001 D-2 0.0684 0.0205 0.00089 0.0001 D-3 0.0901 0.0187 0.00004 0.0001 D-4 0.1065 0.0163 0.00003 0.0003 D-5 0.0677 0.0151 0.00003 0.0002 D-6 0.0733 0.0169 0.00003 0.0001 D-7 0.0767 0.0164 0.00003 0.0001 D-8 0.0784 0.0208 0.00003 0.0007 D-9 0.1056 0.0286 0.00004 0.0005 D-10 0.1178 0.0190 0.00003 0.0003 如表7所示,经过叶面肥处理后水稻糙米Pb、Cr的富集系数差异不显著。硒肥(Se)、硅肥(Si)2个处理水稻糙米Cd的富集系数分别为0.0446、0.0444,较于对照组(CK)处理Cd的富集系数分别降低了47.2%和47.4%,差异显著。硒肥(Se)、硅肥(Si)处理水稻糙米As的富集系数分别为0.0186、0.0158,较于对照组(CK)处理As的富集系数分别降低了4.6%和19.0%,施用硅肥(Si)水稻糙米As的富集系数显著低于其他处理。
表 7 不同处理对水稻糙米重金属富集系数的影响Table 7. Enrichment coefficients on heavy metals in brown rice from different treatment groups处理
Treatment富集系数BCF Cd As Pb Cr CK 0.0844 a 0.0195 a 0.00012 a 0.0003 a 处理A Treatment A 0.0446 b 0.0186 a 0.00003 a 0.0004 a 处理B Treatment B 0.0444 b 0.0158 b 0.00009 a 0.0003 a 注:同列数据后不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Note: Data with different letters on same column indicate significant difference at P<0.05.3. 讨论
研究表明,不同水稻品种糙米对重金属As、Cd、Cr、Pb的积累不同,不同水稻品种对As、Cd、Cr、Pb的吸收富集能力也存在差异[19-21]。本研究发现10个品种水稻糙米对As、Cd、Cr、Pb的吸收存在较大差异,凯丰优158、又香优雅丝苗、野香优明月丝苗3个品种水稻糙米Cd含量明显高于其他品种,且3个品种Cd含量均超过GB/T 5009.15—2014(≤0.2 mg·kg−1)。10个水稻品种中,裕丰优158的As含量低于其他品种,且仅裕丰优158糙米As含量低于GB/T 5009.11—2014(≤0.2 mg·kg−1)。另外研究发现10个品种水稻中,仅有华浙优1号检测出Pb含量,10个品种水稻糙米Cr含量虽有差异,但最高值0.0521 mg·kg−1远低于GB/T 5009.123—2014(≤1.0 mg·kg−1),仅为标准要求≤1.0 mg·kg−1的5.21%,可能是由于当地气候及土壤因素影响,10个品种糙米对Pb和Cr的累积均不高,具体原因有待进一步探究。
陈慧茹等[14, 22]在研究土壤Cd、Cr、Pb元素向水稻的迁移特征时发现,Cd元素在水稻植株中的富集能力最强,其次分别是Cr和Pb。这与本次研究结果一致。10个品种水稻中,糙米对Cd的富集系数均明显高于As、Pb、Cr,水稻糙米对As的富集系数明显高于Pb、Cr两种重金属,水稻糙米对Cr的富集系数高于Pb。As、Cd、Cr、Pb在水稻糙米中的富集能力为Cd>As>Cr>Pb。
相关研究证明[23],适当喷洒硅、硒叶面肥可抑制重金属如Cd、As、Pb在水稻糙米中的积累。这是由于硒能与镉结合生成一种低毒性、较稳定的复合物,同时较难被植物根系吸收和积累,因此植物对镉的吸收量降低;另一方面硅可促进植株叶片的叶绿素含量增加,降低细胞膜的透性,从而提高了水稻的抵抗能力;植物吸收的硅元素沉积在了地上部进而阻止了Cd向地上部的迁移[24-26]。在张世杰等的研究中,同样发现在施加叶面硅肥处理中,水稻地上部的As浓度显著降低,在一定程度上能降低水稻砷毒害作用[27]。本研究中,喷洒硒肥(Se)和喷洒硅肥(Si)后均可以有效降低糙米Cd含量,糙米Cd含量分别下降了44.8%和44.2%,富集系数分别降低了47.2%和47.4%,叶面肥均可以显著降低糙米对镉的吸收和富集。研究发现两种叶面肥对糙米吸收砷的影响存在明显差异,喷洒硒肥(Se)后10个品种水稻糙米As含量均有所降低,但仅有野香优明月丝苗、荃香优822、凯丰优158、Y两优143 4个品种糙米As含量低于GB/T 5009.11—2014(国家标准要求≤0.2 mg·kg−1)。与喷洒硒肥(Se)后效果不同,喷洒硅肥(Si)后,除又香优雅丝苗外其他9个品种糙米As含量均低于GB/T 5009.11—2014(国家标准要求≤0.2 mg·kg−1)。另外研究发现,喷洒叶面肥后对水稻糙米Pb含量影响较小。不同处理水稻糙米Cr含量均远低于GB/T 5009.123—2014(≤1.0 mg·kg−1),但相同处理条件下数据误差较大,且喷洒叶面肥后不仅不会降低糙米的Cr含量,还会出现稻米Cr含量增加的情况,具体原因有待探究。
4. 结论
(1)10个品种糙米对As、Cd、Cr重金属的累积存在明显差异。其中桂育12水稻品种糙米Cd含量最低,裕丰优158水稻品种糙米As含量最低,荃香优822水稻品种糙米Cr含量最低,10个品种水稻中,仅有华浙优1号检测出Pb含量。桂育12、裕丰优158、荃香优822可分别作为Cd、As、Cr低累积品种推广种植。
(2)10个水稻品种糙米中As、Cd、Cr、Pb在水稻糙米中的富集能力为Cd>As>Cr>Pb。
(3)两种叶面肥均能显著降低水稻糙米镉含量,降低水稻糙米对Cd的富集能力,但对水稻糙米Pb无显著影响。
(4)两种叶面肥对水稻糙米富集As的能力影响不同,施用硅肥(Si)对水稻糙米As含量降低效果更明显。
因此,选用适合的品种可以减少水稻糙米对重金属的累积,施用硅肥(Si)可显著降低As在水稻糙米中的累积,叶面喷施硒肥(Se)和硅肥(Si)均可以很好地阻控在水稻糙米中Cd的富集。
-
表 1 YUCCA基因家族成员实时荧光定量PCR引物
Table 1 Primers for qRT-PCR on YUCCAs in passion fruit
基因
Gene正向引物序列(5'-3')
Forward primer(5'-3')反向引物序列(5'-3')
Reverse primer (5'-3')Pe60S AGGTGGGTAACAGGATTATC TGGCTGTCTTTTGGTGCTG PeYUCCA7 GGGAAGAAAGTGCTGGTCGT TGTCAACGAGCCAAAGTGGT PeYUCCA13 TGCCAGAGTTTGTGGGGTTG TGGGCAAGACATGAACCGAG PeYUCCA17 GTTGGGTGCGGCAATTCAG GTTGGCAGCTAGAAGGAGGA PeYUCCA24 TGTCTGAGTTTGGTGGCGAT TCTCGGCAGAACGTGAACC PeYUCCA25 GGGGACCTATTCTGCACACC GCATCTCTTGGGGCAAAACG PeYUCCA26 GGGAATGGAGGTGTGTTTGGA ACACATGGACAGCCCGAAAG 表 2 百香果YUCCA基因家族成员
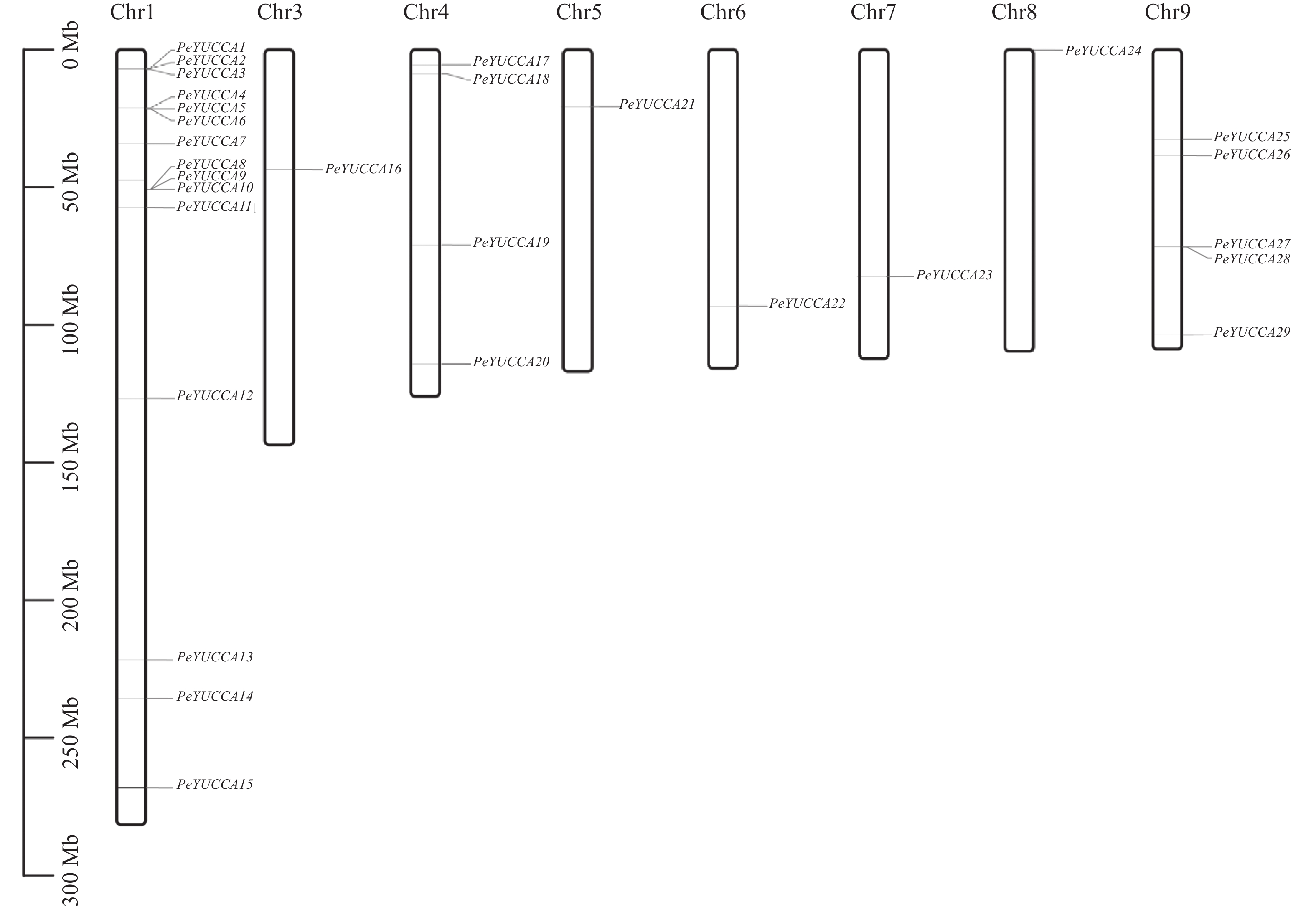
Table 2 YUCCAs in passion fruit
基因ID
Gene name基因名称
Gene ID基因全长
Full length of genes/bp编码区长度
Coding area length/bpG+C含量
C+G content/%A+T含量
A+T content/%PeYUCCA1 ZX.01G0002140 2265 1593 41 59 PeYUCCA2 ZX.01G0002210 2612 1200 40 60 PeYUCCA3 ZX.01G0002240 2263 1593 41 59 PeYUCCA4 ZX.01G0004710 552 516 43 57 PeYUCCA5 ZX.01G0004780 4609 1977 38 62 PeYUCCA6 ZX.01G0004800 1651 1092 40 60 PeYUCCA7 ZX.01G0017780 1964 1275 43 57 PeYUCCA8 ZX.01G0025770 1602 1155 42 58 PeYUCCA9 ZX.01G0025830 1450 1152 42 58 PeYUCCA10 ZX.01G0025850 1412 1215 42 58 PeYUCCA11 ZX.01G0029730 2216 1557 42 58 PeYUCCA12 ZX.01G0086000 2409 1593 41 59 PeYUCCA13 ZX.01G0115230 1809 1293 43 57 PeYUCCA14 ZX.01G0126750 1718 1146 40 60 PeYUCCA15 ZX.01G0137550 1733 1146 40 60 PeYUCCA16 ZX.03G0007260 3263 1374 40 60 PeYUCCA17 ZX.04G0004260 1787 1200 43 57 PeYUCCA18 ZX.04G0005300 2979 1629 37 63 PeYUCCA19 ZX.04G0017390 2275 783 39 61 PeYUCCA20 ZX.04G0031510 1769 1293 44 56 PeYUCCA21 ZX.05G0003260 1706 1092 40 60 PeYUCCA22 ZX.06G0015980 9210 918 41 59 PeYUCCA23 ZX.07G0012040 3758 1467 40 60 PeYUCCA24 ZX.08G0000090 1981 1275 44 56 PeYUCCA25 ZX.09G0006460 2339 1275 43 57 PeYUCCA26 ZX.09G0011010 3589 1323 44 56 PeYUCCA27 ZX.09G0020980 1460 1164 41 59 PeYUCCA28 ZX.09G0021020 1263 1023 39 61 PeYUCCA29 ZX.09G0026980 1457 1161 41 59 表 3 百香果YUCCA蛋白的理化性质
Table 3 Physicochemical properties of YUCCA protein in passion fruit
蛋白名称
Protein氨基酸数量
Number of amino acid分子量
Molecular weight/Da等电点
pI不稳定指数
Instability index脂肪系数
Aliphatic index平均亲水指数
Grand average of hydropathicityPeYUCCA1 530 60025.48 8.79 36.52 91.96 −0.108 PeYUCCA2 399 44952.88 8.77 36.33 90.35 −0.132 PeYUCCA3 530 59901.36 8.86 36.45 93.25 −0.089 PeYUCCA4 171 19496.11 6.70 33.86 83.74 −0.353 PeYUCCA5 658 74050.52 8.60 38.14 93.92 −0.1 PeYUCCA6 363 40948.6 8.44 33.65 97.19 0.006 PeYUCCA7 424 47517.87 8.70 50.74 88.47 −0.163 PeYUCCA8 384 42813.29 8.51 35.85 82.99 −0.164 0PeYUCCA9 384 42248.58 8.39 36.22 83.49 −0.142 PeYUCCA10 404 44826.99 9.10 35.42 94.03 −0.082 PeYUCCA11 519 59666.11 8.66 46.14 80.58 −0.17 PeYUCCA12 530 59791.11 8.80 34.27 93.25 −0.104 PeYUCCA13 430 48121.4 8.21 48.71 90.4 −0.109 PeYUCCA14 381 43169.1 9.36 36.67 87.98 −0.239 PeYUCCA15 381 43196 9.26 37.02 85.43 −0.251 PeYUCCA16 457 52147.09 5.61 43.24 85.67 −0.361 PeYUCCA17 399 44585.34 8.88 41.46 89.65 −0.242 PeYUCCA18 542 61911.37 7.57 45.29 86.48 −0.18 PeYUCCA19 260 29366.12 5.62 37.73 80.46 −0.345 PeYUCCA20 430 48033.36 9.36 47.03 84.72 −0.237 PeYUCCA21 363 41357.16 9.25 38.59 85.62 −0.23 PeYUCCA22 305 35045.45 8.69 39.78 81.77 −0.216 PeYUCCA23 488 55653.62 5.65 50.21 76.6 −0.449 PeYUCCA24 424 47483.77 8.70 49.26 87.1 −0.191 PeYUCCA25 424 47495.97 8.64 48.26 84.15 −0.124 PeYUCCA26 440 48908.67 8.59 44.73 87.07 −0.122 PeYUCCA27 388 42840.19 8.20 37.54 81.88 −0.173 PeYUCCA28 340 37800.42 7.63 32.03 89.35 −0.094 PeYUCCA29 386 42561 8.37 34.48 85.08 −0.145 -
[1] 贾利霞, 齐艳华. 生长素代谢、运输及信号转导调控水稻粒型研究进展 [J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3):263−275. DOI: 10.11983/CBB21227 JIA L X, QI Y H. Advances in the regulation of rice(Oryza sativa)grain shape by auxin metabolism, transport and signal transduction [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(3): 263−275. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11983/CBB21227
[2] 李中华. 多组学数据揭示棉花纤维发育转换期的遗传调控机制和重要代谢物[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2021. LI Z H. Multiomics data reveal the genetic regulation mechanism and important metabolites of cotton fiber development transition period[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2021. (in Chinese)
[3] 莫福磊, 束艺, 陈秀玲, 等. 基于全基因组的番茄YUCCA基因家族生物信息学分析 [J]. 分子植物育种, 2020, 18(10):3159−3163. MO F L, SHU Y, CHEN X L, et al. Bioinformatics analysis of tomato YUCCA gene family based on whole genome [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2020, 18(10): 3159−3163. (in Chinese)
[4] 刘华彬, 张秦莹, 门淑珍. YUCCA基因家族在拟南芥胚胎发育过程中的表达模式研究 [J]. 南开大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 50(4):1−7. LIU H B, ZHANG Q Y, MEN S Z. The expression patterns of YUCCA during embryo development in Arabidopsis [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Nankaiensis, 2017, 50(4): 1−7. (in Chinese)
[5] 李莉萍. 西番莲综合开发利用研究进展 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2012, 40(28):13840−13843,13846. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2012.28.062 LI L P. Research progress of comprehensive development and utilization of passionflower [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 40(28): 13840−13843,13846. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2012.28.062
[6] LI C B, XIN M, LI L, et al. Characterization of the aromatic profile of purple passion fruit (Passiflora edulis Sims) during ripening by HS-SPME-GC/MS and RNA sequencing [J]. Food Chemistry, 2021, 355: 129685. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129685
[7] FONSECA A M A, GERALDI M V, JUNIOR M R M, et al. Purple passion fruit (Passiflora edulis f. edulis): A comprehensive review on the nutritional value, phytochemical profile and associated health effects [J]. Food Research International, 2022, 160: 111665. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111665
[8] XU M X, LI A D, TENG Y, et al. Exploring the adaptive mechanism of Passiflora edulis in Karst areas via an integrative analysis of nutrient elements and transcriptional profiles [J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 185. DOI: 10.1186/s12870-019-1797-8
[9] XIA Z Q, HUANG D M, ZHANG S K, et al. Chromosome-scale genome assembly provides insights into the evolution and flavor synthesis of passion fruit (Passiflora edulis Sims) [J]. Horticulture Research, 2021, 8: 14. DOI: 10.1038/s41438-020-00455-1
[10] CHENG Y F, DAI X H, ZHAO Y D. Auxin biosynthesis by the YUCCA flavin monooxygenases controls the formation of floral organs and vascular tissues in Arabidopsis [J]. Genes & Development, 2006, 20(13): 1790−1799.
[11] YAMAMOTO Y, KAMIYA N, MORINAKA Y, et al. Auxin biosynthesis by the YUCCA genes in rice [J]. Plant Physiology, 2007, 143(3): 1362−1371. DOI: 10.1104/pp.106.091561
[12] LI W L, ZHAO X Y, ZHANG X S. Genome-wide analysis and expression patterns of the YUCCA genes in maize [J]. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 2015, 42(12): 707−710. DOI: 10.1016/j.jgg.2015.06.010
[13] ZHAO B L, HE L L, JIANG C, et al. Lateral Leaflet Suppression 1 (LLS1), encoding the MtYUCCA1 protein, regulates lateral leaflet development in Medicago truncatula [J]. The New Phytologist, 2020, 227(2): 613−628. DOI: 10.1111/nph.16539
[14] 袁美同, 李绍信, 纪丕钰, 等. 梨YUCCA基因家族的鉴定与生物信息学分析 [J]. 分子植物育种, 2021, 19(19):6328−6337. YUAN M T, LI S X, JI P Y, et al. Identification and bioinformatics analysis of YUCCA gene family in Pyrus [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2021, 19(19): 6328−6337. (in Chinese)
[15] 李志谦, 邹东方, 李靖雯, 等. 葡萄YUCCA家族基因的鉴定及在穗梗褪绿过程中的表达分析 [J]. 河南农业大学学报, 2022, 56(2):254−261. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2340.2022.2.hennannydxxb202202010 LI Z Q, ZOU D F, LI J W, et al. Genome-wide identification of YUCCA gene family in grape and expression analysis during rachis degreening [J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural University, 2022, 56(2): 254−261. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2340.2022.2.hennannydxxb202202010
[16] 张倩倩, 田守蔚, 张洁, 等. 西瓜YUCCA基因家族鉴定及在果实成熟过程中的表达分析 [J]. 中国蔬菜, 2019, (3):21−29. ZHANG Q Q, TIAN S W, ZHANG J, et al. Identification of YUCCA gene family and expression analysis during watermelon fruit ripening process [J]. China Vegetables, 2019(3): 21−29. (in Chinese)
[17] ZHANG Y Y, MAO Q S, MA R J, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the PpYUCCA gene family in weeping peach trees (Prunus persica ‘Pendula’) [J]. Horticulturae, 2022, 8(10): 878. DOI: 10.3390/horticulturae8100878
[18] MA D N, DONG S S, ZHANG S C, et al. Chromosome-level reference genome assembly provides insights into aroma biosynthesis in passion fruit (Passiflora edulis) [J]. Molecular Ecology Resources, 2021, 21(3): 955−968. DOI: 10.1111/1755-0998.13310
[19] CHEN C J, CHEN H, ZHANG Y, et al. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data [J]. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(8): 1194−1202. DOI: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
[20] 何锐杰, 方庭, 余伟军, 等. 西番莲查尔酮合成酶(CHS)基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达模式 [J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2022, 28(4):1066−1075. HE R J, FANG T, YU W J, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the CHS gene family in passion fruit [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2022, 28(4): 1066−1075. (in Chinese)
[21] TRIPATHI P, TAYADE R, MUN B G, et al. Silicon application differentially modulates root morphology and expression of PIN and YUCCA family genes in soybean (Glycine max L. ) [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 842832. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.842832
[22] 梁栋. IAA和BR参与干旱胁迫影响烟草侧根发育的研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2021. LIANG D. Study on IAA and BR participating in drought stress affecting tobacco lateral root development[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2021. (in Chinese)
[23] 李真. 毛白杨PtoWOX11/12a基因的抗逆功能研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2017. LI Z. Functional characterization of A PtoWOX11/12a gene in stress resistance of Populus tomentosa[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2017. (in Chinese)
[24] 李孟湛. SAUR15调控植物侧根及不定根发育的功能及分子机理研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2022. LI M Z. Functions and molecular mechanisms of SAUR15 in regulating development of plant lateral and adventitious roots[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2022. (in Chinese)
[25] 阚东阳, 柯学, Walid Ghidan, 等. 拟南芥图位克隆快速初定位系统的建立 [J]. 西南农业学报, 2018, 31(9):1765−1771. KAN D Y, KE X, WALID G, et al. Establishment of rapid initial localization system of Arabidopsis based on map-based cloning [J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 31(9): 1765−1771. (in Chinese)
[26] 丁义峰. 生长素相关基因调控桃果实成熟分子机制研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2018. DING Y F. Molecular mechanism of auxin related genes regulating peach fruit ripening[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2018. (in Chinese)
[27] ABEL S, NGUYEN M D, THEOLOGIS A. The PS-IAA4/5-like family of early auxin-inducible mRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana [J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 1995, 251(4): 533−549. DOI: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0454
[28] YAMAGUCHI N, WINTER C M, WU M F, et al. Gibberellin acts positively then negatively to control onset of flower formation in Arabidopsis [J]. Science, 2014, 344(6184): 638−641. DOI: 10.1126/science.1250498
[29] 金晓蕾. 外源激素对甜荞开花结实的影响及调控机制研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2019. JIN X L. Effect and regulation mechanism of exogenous hormones on flowering and fruiting in common buckwheat[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2019. (in Chinese)
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 张容慧,张秀锦,柴冠群,范成五,何腾兵,秦松. 贵州青黄泥田重金属元素低积累水稻品种筛选. 中国稻米. 2024(01): 75-83 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈光明,张敏,史朝艾,曹坳程,王秋霞,颜冬冬,方文生,李园. 土壤活化技术的研究进展与展望. 现代农药. 2024(01): 32-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 郑晶,鲍广灵,陶荣浩,吴承龙,马友华,叶文玲. 基施与叶面施硒肥对富硒镉污染农田水稻降镉增硒的效应. 农业环境科学学报. 2024(05): 974-982 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. Wangbiao Lu,Guangneng Zeng,Weijun Luo,Jiangju Song,Maofei Ni,Shuangqin Guo,Qi Zhang,Chengling Huang,Cheng Yang,Haijun Du,Shijie Wang. Can soil remediation agents synergistically mitigate rice Cd content and CH_4 emission from karst paddies?. Acta Geochimica. 2024(06): 1123-1132 .  必应学术
必应学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: