Effects of Melatonin Application on Physiology and Cell Wall of Bougainvillea Plant under Cold Stress
-
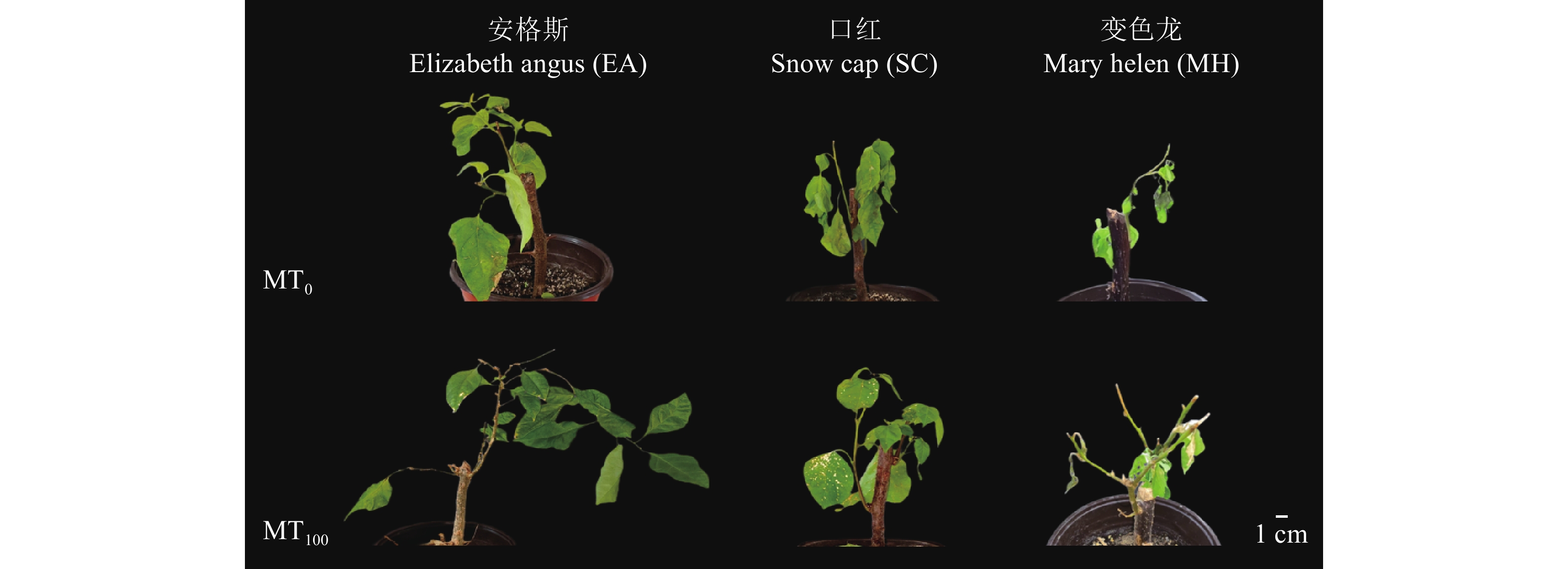
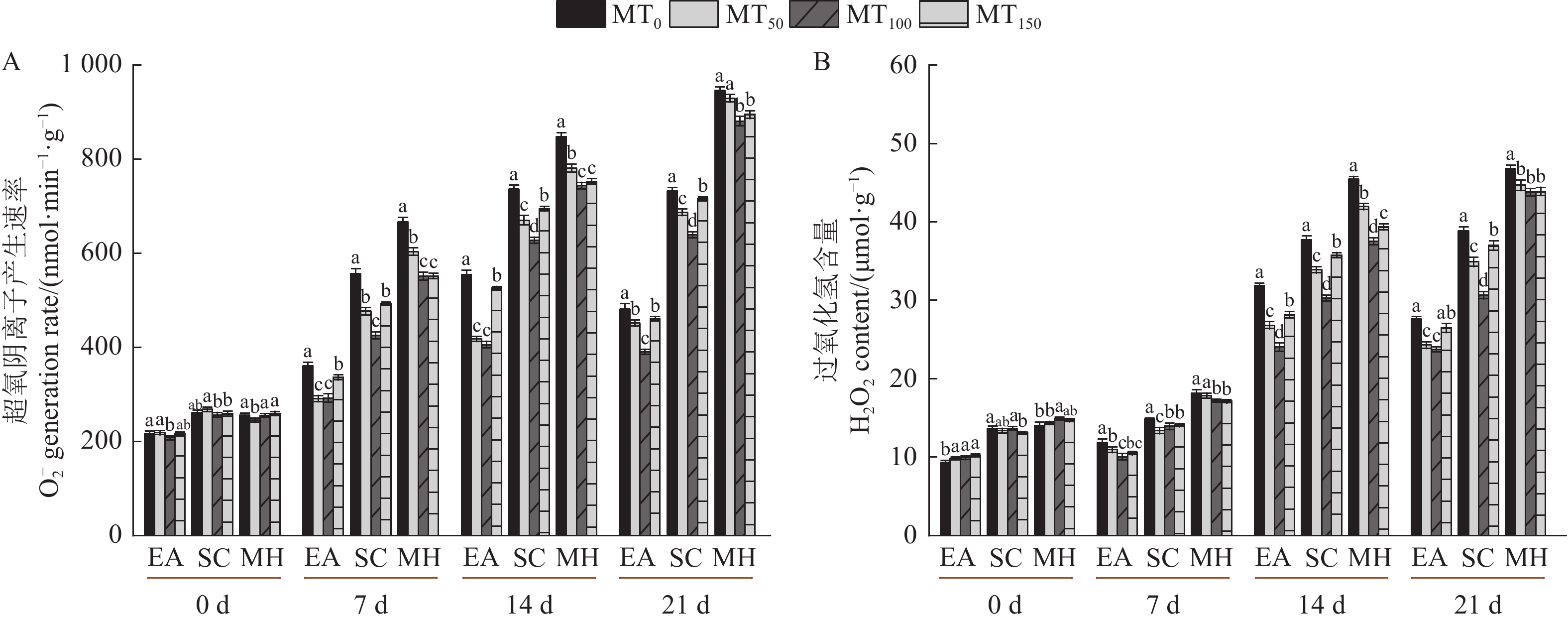
摘要:目的 研究褪黑素对低温逆境下三角梅生理生化及细胞壁组分的调控作用,为缓解低温对三角梅生长造成的不利影响提供理论依据。方法 以不同耐冷性的3个三角梅品种安格斯、口红、变色龙为供试材料,在4 ℃低温下对三角梅植株叶面施加不同浓度(0、50、100、150 µmol·L–1)的外源褪黑素,测定各处理组生长0、7、14、21 d的叶面积、叶绿素含量、叶绿素荧光参数[PSⅡ最大光化学量子产量(Fv/Fm)、表观电子传递速率(ETR)、光化学猝灭系数(qP)、非光化学猝灭系数(qN)]、抗氧化酶[超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化物酶(POD)和过氧化氢酶(CAT)]活性、膜脂过氧化产物[超氧阴离子(O2−)产生速率、过氧化氢(H2O2)含量]、渗透调节物质[可溶性糖(SS)、可溶性蛋白(SP)]含量、细胞壁组分[螯合型果胶(CSP)、碱溶性果胶(SSP)、半纤维素(HC)和纤维素(CE)]含量。结果 低温逆境下三角梅的正常生长发育受阻,叶绿素荧光参数失衡,膜脂过氧化加剧,细胞壁组分受到影响。而施加100 µmol·L–1的褪黑素能够有效地提升三角梅的生理活性,改善植株萎蔫程度,Fv/Fm与ETR降幅减小;抗氧化酶活性显著增加,强耐冷型品种安格斯较于0 d的SOD、POD、CAT最大可增加96.45%、104.35%、73.11%;H2O2含量、O2−生成速率对比同周期MT0最多下降21.07%、26.85%;细胞壁组分中CSP、SSP上升幅度增加,较于0 d最多可上涨22.55%、43.08%。结论 明确了外源褪黑素在生理特性方面对不同品种三角梅冷害的调控作用,外源施加适宜浓度的褪黑素可以有效缓解低温对三角梅生长的抑制,减轻光系统损伤,增强抗氧化酶活性,减缓膜脂氧化,并调节细胞壁各组分含量以维持其结构整体稳定,从而降低低温伤害,为探索褪黑素对冷害下植物的调控作用提供新思路。Abstract:Objective Effects of melatonin application on plant physiology and biochemistry as well as cell wall components of Bougainvillea plants under low temperature were studied.Method Bougainvillea leaves were sprayed with melatonin solutions in the concentrations of 0, 50, 100, and 150 µmol·L–1 at 4 ℃. Leaf area, chlorophyll content, chlorophyll fluorescence parameters at the optimal/maximal quantum yield of PSⅡ (Fv/Fm), apparent electron transfer rate (ETR), photochemical quenching coefficient (qP), non-photochemical quenching coefficient (qN)], activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD), and catalase (CAT), membrane lipid peroxidation products at the production rate of superoxide anion (O2−), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) content, osmotic adjustment soluble sugar (SS) and soluble protein (SP) as well as cell wall components including chelate pectin (CSP), alkali-soluble pectin (SSP), hemicellulose (HC), and cellulose (CE) of the plants were monitored weekly for 3 consecutive weeks from the beginning of treatments (MT0).Result At 4 ℃, the growth and development of Bougainvillea plants was hindered showing unbalanced chlorophyll fluorescence parameters, intensified membrane lipid peroxidation, and altered cell wall composition. The spray of 100 µmol·L−1 melatonin significantly enhanced the physiological activity, reduced wilting, Fv/Fm and ETR, increased activities of SOD, POD, and CAT (e.g., by 96.45%, 104.35%, and 73.11%, respectively, in Elizabeth Angus), decreased H2O2 content by 21.07% and O2− production rate by 26.85%, and raised CSP by 22.55% and SSP by 43.08% in the cell wall over those at MT0.Conclusion Melatonin regulated the physiology of Bougainvillea plants and effectively mitigated the growth inhibition by cold stress. The spray reduced the damage to the photosystem, enhance the antioxidant enzyme activity, retard the membrane lipid oxidation, and stabilize the cell wall of the plant suggesting a potential treatment for preventing serious harms by temperature decline in winter.
-
Keywords:
- Melatonin /
- Bougainvillea /
- cold stress /
- physiological response /
- cell wall composition
-
果树种质资源收集、利用、评价是育种创新的基础。本研究利用已公布的SSR分子标记,对收集保存于福州闽侯地区区试的50份桃种质 (育成品种、地方种质) 进行遗传分析,从DNA水平评估遗传多样性,并进一步探究福建地方种质与引进品种间的亲缘关系,为今后的遗传育种提供可靠的遗传背景信息。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
桃种质资源共50份,包括普通桃、油桃、蟠桃、观赏桃等4大类别。50份种质中,境内育成品种由原育种单位提供,福建地方种质资源由当地采集,其他种质由产地采集。供试材料信息见表 1。
表 1 50份供试桃种质资源基本信息Table 1. Basic information on 50 peach germplasmsstudied序号 样本 分类 来源地 1 03-1 白肉普通桃 北京林果所 2 96-3-54 白肉普通桃 北京林果所 3 瑞红 白肉普通桃 北京林果所 4 FlordingKing 黄肉普通桃 北京林果所 5 2-14W 油桃 北京林果所 6 5-32W 油桃 北京林果所 7 瑞光51 油桃 北京林果所 8 穆阳水蜜 (花粉正常) 白肉普通桃 福建福安产地 9 穆阳水蜜 (花粉败育) 白肉普通桃 福建福安产地 10 大久保 白肉普通桃 福建古田产地 (原产日本) 11 新川中岛白桃 白肉普通桃 福建古田产地 (原产日本) 12 晚白凤 白肉普通桃 福建古田产地 13 美香 白肉普通桃 福建古田产地 (原产日本) 14 梦富士 白肉普通桃 福建古田产地 15 古田甜桃 白肉普通桃 福建古田产地 16 丰黄 黄肉普通桃 福建建宁产地 17 锦绣 黄肉普通桃 福建建宁产地 18 春雪 白肉普通桃 福建闽侯产地 (原产美国) 19 台湾脆桃 白肉普通桃 福建闽侯产地 (原产巴西) 20 西选1号 白肉普通桃 福建永安产地 21 南方野生桃 (砧木) 白肉普通桃 福建闽侯 22 朝晖 白肉普通桃 江苏农科院园艺所 23 霞晖6号 白肉普通桃 江苏农科院园艺所 24 霞脆 白肉普通桃 江苏农科院园艺所 25 霞晖8号 白肉普通桃 江苏农科院园艺所 26 沙红 白肉普通桃 山东农科院 27 春元 白肉普通桃 山东农科院 28 春艳 白肉普通桃 山东农科院 29 锦园 黄肉普通桃 上海农科院 30 秋月 白肉普通桃 上海农科院 31 锦香 黄肉普通桃 上海农科院 32 沪油018 油桃 上海农科院 33 沪油004 油桃 上海农科院 34 沪油002 油桃 上海农科院 35 秦王 白肉普通桃 西北农林科技大学 36 小仙桃 白肉普通桃 浙江农科院 37 99-10-7 白肉普通桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 38 99-13-9 白肉普通桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 39 理想 白肉普通桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 40 NJC83 黄肉普通桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 41 33-20 油桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 42 中油8号 油桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 43 中油10号 油桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 44 早红2号 油桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 45 曙光 油桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 46 金霞 蟠桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 47 中农蟠10号 蟠桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 48 早露 蟠桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 49 红菊花 观赏桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 50 满天红 观赏桃 中国农科院郑州果树所 1.2 SSR扩增
CTAB法提取叶片DNA。从已发表的SSR引物中筛选出能在50份样本间稳定扩增、多态性好、基因组随机分布的16对蔷薇类SSR引物 (UDP96-05、UDP98-25、UDP98-407、BPPCT006、BPPCT008、BPPCT017、BPPCT023、BPPCT025、BPPCT028、BPPCT034、BPPCT038、CPPCT022、CPPCT026、CPPCT029、CPPCT042) 用于遗传分析。反应体系20 μL,扩增程序94℃预变性3 min,94℃预变性30 s,55℃退火30 s,72℃延伸30 s,30次循环;72℃延伸5 min;12℃保存。扩增结束后,加入微量上样缓冲液 (0.005%溴酚蓝,95%甲酰胺) 混匀,2 μL扩增产物聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳分离,电泳缓冲液为1×TBE,150 V稳压电泳1h。电泳结束后将胶块置于核酸染料染色5 min,去离子水漂洗,凝胶成像系统紫外成像留影。
1.3 统计分析
选取扩增清晰的条带。在相同迁移位置, 有条带记为“1”,无条带记为“0”,缺失或不清楚记为“9”,不同引物扩增的结果构成原始的“0,1”二元数据矩阵。利用PowerMarker Ver 3.25软件计算各标记的主要等位基因频率、多态性条带、基因多态性和多态性信息含量 (PIC)。利用NTSYS-pc 2.11软件,对供试群体遗传相似系数进行UPGMA聚类分析。利用DARwin软件进行基于遗传距离的因子分析和聚类分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 遗传多样性分析
由16对SSR标记所得多样性条带,计算出每个位点的等位基因频率变化范围为0.50~1.00,平均为0.77;基因多样性 (Gene Diversity) 变化范围为0.03~0.50,平均为0.30;PIC值变化范围为0.04~0.37,平均值为0.24。
依据聚类分析, 50份桃种质可主要划分为3个类群 (图 1)。A类群基本上为中晚熟桃种质, B类群主要是中早熟种质,C类群为超短低温早熟种质。其中,在A类群种质中,可进一步细分成2个小群,涵盖了北方、中原和南方产区的主栽品种。而在B类群种质中,则包含了早熟种质B2支群,该支群种质在福建暖湿地区表现良好,成熟期皆在6月中旬之前,早于目前福建主栽品种。C类群为需冷量极少的超短低温种质,在福州平原地区即可完成冬季休眠,表现极好。不过,虽然B2与C类群均为短需冷量种质,亲缘性较其他种质近,但仍为不同遗传起源。
2.2 系统进化分析
根据果实性状可粗分桃种质为:普通桃、油桃、蟠桃、观赏桃。油桃 (果皮表面无绒毛)、蟠桃 (果形扁平) 都源自普通桃祖先,受单基因质量性状控制。从本研究选取的50份桃种质的遗传多样性和系统进化角度分析,由图 1、图 2可知,育成的油桃、蟠桃品种的遗传背景与普通桃并未有太大区别,遗传基础来自普通桃亲本,因此油桃、蟠桃并未单独聚类成簇。而观赏桃则不同,观赏桃红菊花、满天红与鲜食桃遗传差异较大,其遗传基础明显异于鲜食桃,表明其起源不同。红菊花独立分支,其亲本必然异于鲜食桃,而另一观赏鲜食兼用品种满天红则是由鲜食桃与观赏桃亲本杂交而来,与鲜食桃具有一定的亲缘关系。
2.3 福建地方特色种质起源分析
亚热带湿热地区并不是桃的最适生长区,本地野生种质资源少、分布窄。目前福建省内绝大多数的栽培品种是由省外引入,特别是江浙沪等南方水蜜桃主产区。这些栽培品种经过数十年的生产、繁育、筛选后,开始逐渐出现遗传变化,形成了目前福建本地的一些特色地方种质。较为成功的有抗流胶病的西选一号[1]、高甜浓香的穆阳水蜜[2]、古田甜桃等。遗传分析表明:西选一号、穆阳水蜜应该是源自江浙地区的南方水蜜桃品种,位于A2分支中;本试验所采集的古田甜桃与美香桃关系密切,应该具有渊源,有可能是同物异名。
3. 讨论与结论
中国是世界上最大的桃生产和消费地区,桃产量和种植面积位居第一,占世界半数以上。随着桃基因组测序的完成,桃在亚洲特别是中国地区的起源、分支、进化路线已基本清楚,大样本桃资源的遗传分析结果相继发表[3-6]。本研究重点关注了在福建地区参与品种区域试验的各地广适优异育成品种、育成待认定品种及当地特色种质,以期为今后本地化育种工作提供理论参考依据。而SSR分子标记在桃遗传多样性的研究上得到广泛应用[7-10],技术成熟、结果可靠性高、成本适宜,在本研究中取得了良好的效果,初步界定出了重要的短低温种质类群及相应品种。
桃发源于北方地区,需要一定时间的低温休眠才能成花并分化出正常的配子细胞。进入南方后,冬季低温积累时数减少,为适应自然环境,桃逐步演化出低需冷量资源。从目前来看,在福建亚热带地区表现良好的短低温桃种质归属于B2和C 2个类群,其中C类群种质与南方野生桃亲缘最近,这证实了境外短低温种质 (如C类群Flord King、台湾脆桃) 遗传背景中带有中国南方桃低需冷量基因资源的报道。B2类群与南方野生桃亲缘次之,其低需冷量表现与南方野生桃可能也有一定关系。
在鲜食桃中,油桃和蟠桃所占比例较低,其果皮无毛、果形扁平性状是单基因控制的质量性状,分别定位于第5、6连锁群[11-12]。在育种实践中,人们可以通过孟德尔遗传规律,利用特定亲本培育出符合预期性状的油桃、蟠桃。由于这2个位点属于单基因质量性状位点,不与其他数量性状连锁,在育种群体后代中可以得到不同数量性状组合 (如果实品质、果实成熟期、抗性) 的油桃、蟠桃个体,遗传多样性丰富,带有鲜食亲本的绝大多数遗传背景。这也就是在本研究中,油桃、蟠桃遗传差异不明显,在聚类分析中散落分布于鲜食普通桃群体中的主要原因。
-
-
[1] QIN B, SHI Y S, TANG Q, et al. Study on the industry status of Chinese Bougainvillea and its popularization strategy in Guangxi [J]. Agricultural Research and Application, 2020, 33(6): 56−60.
[2] 张昭, 聂宇婷, 崔凯伦, 等. 褪黑素调控草类植物生长发育及抗逆性功能研究进展 [J]. 草地学报, 2023, 31(9):2571−2581. ZHANG Z, NIE Y T, CUI K L, et al. Research progress on the function of melatonin in regulating growth, development and stress resistance in herbaceous species [J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2023, 31(9): 2571−2581.
[3] SHI H T, CHEN Y H, TAN D X, et al. Melatonin induces nitric oxide and the potential mechanisms relate to innate immunity against bacterial pathogen infection in Arabidopsis [J]. Journal of Pineal Research, 2015, 59(1): 102−108. DOI: 10.1111/jpi.12244
[4] 蒋朝维, 吴俊杰, 姜浩, 等. 低温胁迫下烤烟幼苗对喷施外源褪黑素的生理响应 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2023, 51(21):62−66. JIANG C W, WU J J, JIANG H, et al. Physiological response of flue-cured tobacco seedlings to exogenous melatonin spray under low temperature stress [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 51(21): 62−66. (in Chinese)
[5] IMRAN M, LATIF KHAN A, SHAHZAD R, et al. Exogenous melatonin induces drought stress tolerance by promoting plant growth and antioxidant defence system of soybean plants [J]. AoB PLANTS, 2021, 13(4): plab026. DOI: 10.1093/aobpla/plab026
[6] MICHARD E, SIMON A A. Melatonin’s antioxidant properties protect plants under salt stress[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2020, 43(11): 2587-2590.
[7] LIU N, LI J W, LV J, et al. Melatonin alleviates imidacloprid phytotoxicity to cucumber (Cucumis sativus L. ) through modulating redox homeostasis in plants and promoting its metabolism by enhancing glutathione dependent detoxification [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 217: 112248. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112248
[8] 孙志娟, 刘文杰, 郑晓东, 等. 褪黑素对盐碱胁迫下平邑甜茶幼苗生长的影响及其机制 [J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8):1697−1710. SUN Z J, LIU W J, ZHENG X D, et al. Effects and functional mechanism of melatonin on the growth of Malus hupehensis seedlings under saline-alkali stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(8): 1697−1710. (in Chinese)
[9] 任利明, 谢芳, 丁飞, 等. 褪黑素对花椒幼苗低温伤害的缓解效应 [J]. 西北林学院学报, 2023, 38(4):34−43. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2023.04.05 REN L M, XIE F, DING F, et al. The mitigative effect of melatonin on Zanthoxylum bungeanum seedlings under chilling stress [J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2023, 38(4): 34−43. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2023.04.05
[10] 李方一, 黄璜, 官春云. 作物叶面积测量的研究进展 [J]. 湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 47(3):274−282. LI F Y, HUANG H, GUAN C Y. Review on measurement of crop leaf area [J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University (Natural Sciences), 2021, 47(3): 274−282. (in Chinese)
[11] SHIBAEVA T G, MAMAEV A V, SHERUDILO E G. Evaluation of a SPAD-502 plus chlorophyll meter to estimate chlorophyll content in leaves with interveinal chlorosis [J]. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology, 2020, 67(4): 690−696. DOI: 10.1134/S1021443720040160
[12] 努尔凯麦尔·木拉提, 杨亚杰, 帕尔哈提·阿布都克日木, 等. 小麦叶绿素含量测定方法比较 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2021, 49(9):156−159. NURKHEIMER M, YANG Y J, PARHATI A, et al. Comparative study on determination methods of chlorophyll content in wheat [J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 49(9): 156−159. (in Chinese)
[13] SEPEHRI E, HOSSEINI B, HEDAYATI A. The effect of iron oxide Nano-Particles on the production of tropane alkaloids, h6h gene expression and antioxidant enzyme activity in Atropa belladonna hairy roots [J]. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology, 2022, 69(6): 122. DOI: 10.1134/S1021443722060243
[14] TIMINS, PENG J, YU Z. Exogenous glycine betaine treatment enhances chilling tolerance of peach fruit during cold storage[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 2016: 104-110.
[15] 董扬. 低温胁迫对不同耐冷性糜子品种苗期耐冷性的影响 [J]. 作物杂志, 2023, 39(6):1−7 DONG Y. Effects of low temperature stress on cold tolerance of broomcorn millet varieties with different cold tolerance at seedling stage [J]. Crop Journal, 2023, 39(6): 1−7(in Chinese)
[16] 张治安, 陈展宇. 植物生理学实验技术[M]. 长春: 吉林大学出版社, 2008. [17] 沈蔡慰. 硼对铝胁迫下栝楼有机酸及细胞壁成分调控作用的探究[D]. 金华: 浙江师范大学, 2020 SHEN C W. Effects of boron on organic acids and cell wall components of Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim. under aluminum stress[D]. Jinhua: Zhejiang Normal University, 2020. (in Chinese)
[18] DAT J, VANDENABEELE S, VRANOVÁ E, et al. Dual action of the active oxygen species during plant stress responses [J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences: CMLS, 2000, 57(5): 779−795. DOI: 10.1007/s000180050041
[19] 王荣荣, 王海琪, 蒋桂英, 等. 2个不同抗旱性小麦品种耗水特征及根系生理特性对开花期干旱的响应 [J]. 水土保持学报, 2022, 36(4):253−264. WANG R R, WANG H Q, JIANG G Y, et al. Response of water consumption and root physiological characteristics of two different drought-tolerant wheat varieties to anthesis stage drought [J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022, 36(4): 253−264. (in Chinese)
[20] 李欠敏, 杨琳, 段巧红, 等. 外源褪黑素对低温胁迫下大白菜幼苗生长及生理特性的影响 [J]. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 52(2):182−186. LI Q M, YANG L, DUAN Q H, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin on the growth and physiological characteristics of Chinese cabbage seedlings under chilling stress [J]. Journal of Shandong Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 52(2): 182−186. (in Chinese)
[21] 尤鑫, 龚吉蕊. 叶绿素荧光动力学参数的意义及实例辨析 [J]. 西部林业科学, 2012, 41(5):90−94. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8246.2012.05.017 YOU X, GONG J R. Significance and application of chlorophyll fluorescence dynamics process parameters [J]. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 2012, 41(5): 90−94. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8246.2012.05.017
[22] 丁东霞, 李能慧, 李静, 等. 外源褪黑素对低温弱光胁迫下辣椒叶绿素荧光和抗氧化系统的影响 [J]. 浙江农业学报, 2022, 34(9):1935−1944. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2022.09.12 DING D X, LI N H, LI J, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin on chlorophyll fluorescence and antioxidant system of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) under low temperature and low light stress [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2022, 34(9): 1935−1944. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2022.09.12
[23] 朱晓丹. 不同乌菜品种在低温胁迫下的生理响应[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2017. ZHU X D. Physiological response of different cultivars of under low temperature stressin Brassica campestris L. ssp. Chinese (L.) Makino var rosularis Tsen et Lee[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese)
[24] AYYAZ A, FAROOQ M A, DAWOOD M, et al. Exogenous melatonin regulates chromium stress-induced feedback inhibition of photosynthesis and antioxidative protection in Brassica napus cultivars [J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2021, 40(11): 2063−2080. DOI: 10.1007/s00299-021-02769-3
[25] 白如意, 宋希梅, 沈健, 等. 叶面喷施褪黑素对低温胁迫下南瓜幼苗生长和生理特性的影响 [J]. 西北植物学报, 2023, 43(5):805−813. DOI: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2023.05.0805 BAI R Y, SONG X M, SHEN J, et al. Effect of foliar spraying melatonin on growth and physiological characteristics of pumpkin seedlings under cold stress [J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2023, 43(5): 805−813. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2023.05.0805
[26] SALADIN G, CLÉMENT C, MAGNÉ C. Stress effects of flumioxazin herbicide on grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) grown in vitro [J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2003, 21(12): 1221−1227. DOI: 10.1007/s00299-003-0658-x
[27] 唐鸿吕. 外源褪黑素对低温胁迫下甘蓝苗期生长、生理特性及成株产量的影响[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2022 TANG H L. Effects of exogenous melatonin on seedling growth, physiological characteristics and yield of cabbage under low temperature stress[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2022. (in Chinese)
[28] 宋静蕾, 潘晓帆, 裴家伟, 等. 红薯渣中不同果胶组分的提取及结构表征 [J]. 中国调味品, 2023, 48(8):24−32. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2023.08.005 SONG J L, PAN X F, PEI J W, et al. Extraction and structural characterization of different pectin components from sweet potato pomace [J]. China Condiment, 2023, 48(8): 24−32. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2023.08.005
[29] 陈立莉, 陈小爱, 徐飞, 等. 不同溶解性面包果果胶的理化、结构性质及抗氧化活性的比较 [J]. 现代食品科技, 2023, 22(5):168−172 CHEN L L, CHEN X A, XU F, et al. Physicochemical, structural properties and antioxidant activity of breadfruit pectin with different solubility [J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2023, 22(5): 168−172. (in Chinese)
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 乔雨轩,申潇潇,焦雪辉,周小娟,岳长平,史喜兵. 豫中地区46份桃种质的观赏性综合评价. 果树学报. 2024(02): 216-228 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 殷纪伟,韩贝贝,马莹雪,武星廷,徐振江,姜建福,陈昌文,韩瑞玺. 基于SSR分子标记的154份桃品种遗传多样性分析. 江苏农业科学. 2023(16): 18-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 史芳芳,梁武军,张延磊. 基于SSR标记的油桃品种需冷性分析. 安徽农业科学. 2020(07): 59-61 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 袁滨,柯丽娜,陈光祥,连燕萍,张志鸿,纪鹏伟,吴振强. 应用体细胞不亲和性试验和SSR方法综合鉴定闽南地区双孢蘑菇种质资源. 福建农业学报. 2020(09): 950-956 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 焦云,柴春燕,舒巧云. 基于SSR分子标记的早熟杨梅优株遗传多样性分析. 中国南方果树. 2019(04): 42-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 唐莹莹,杨祥燕,蔡元保,李穆,曾黎明,郑文武,邱文武,李季东,叶维雁. 澳洲坚果SSR-PCR反应体系优化及其应用. 福建农业学报. 2018(02): 154-158 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: