Transcriptome Analysis on Pyroxsulam-resistance of Naked Barley
-
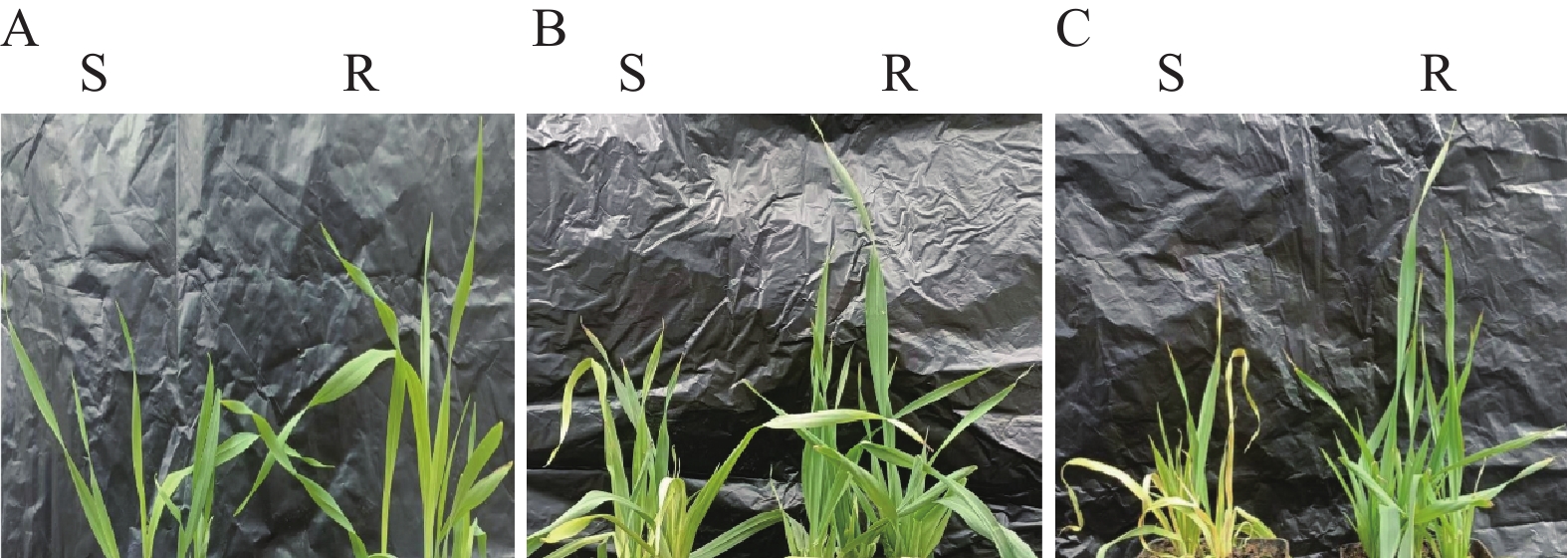
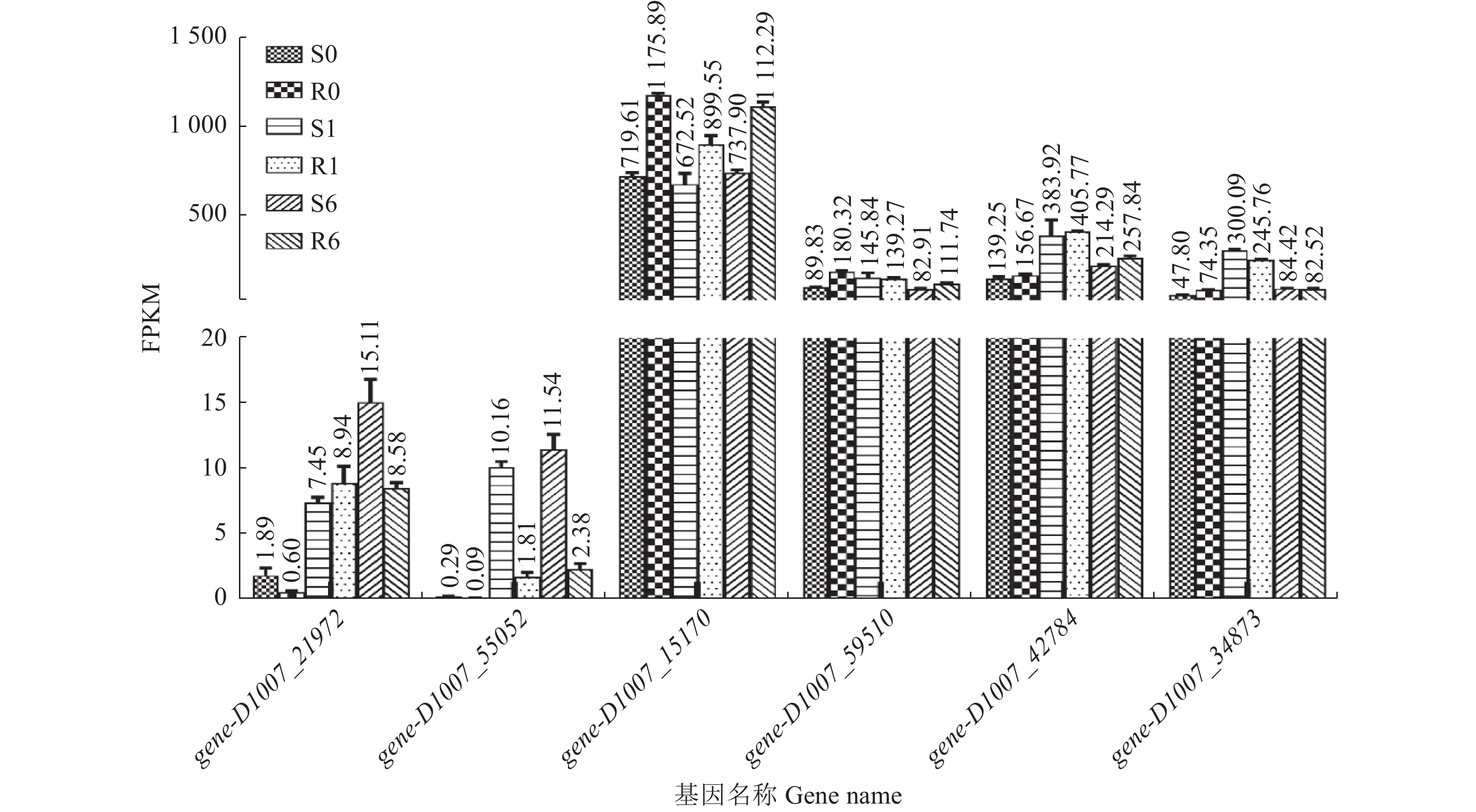
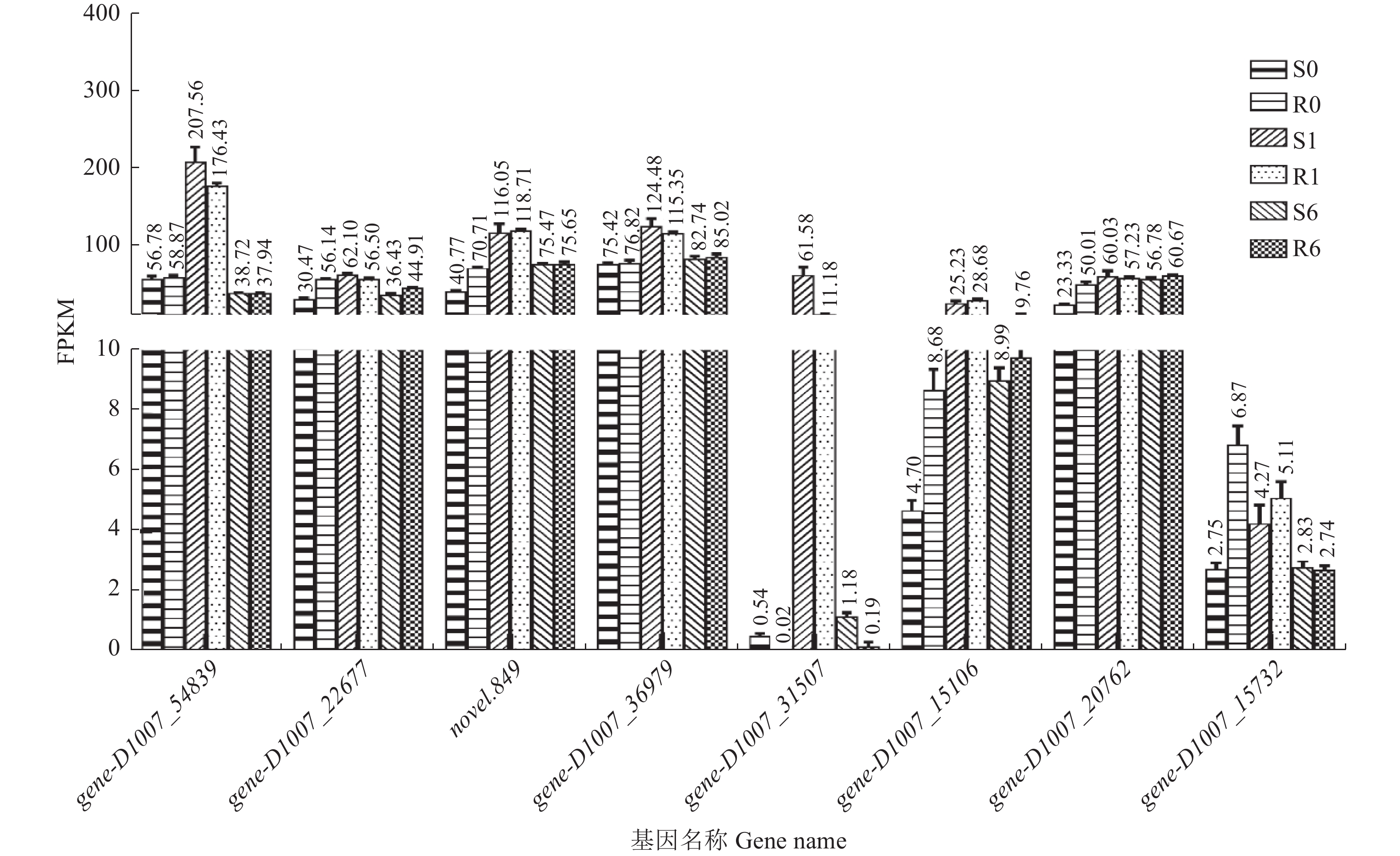
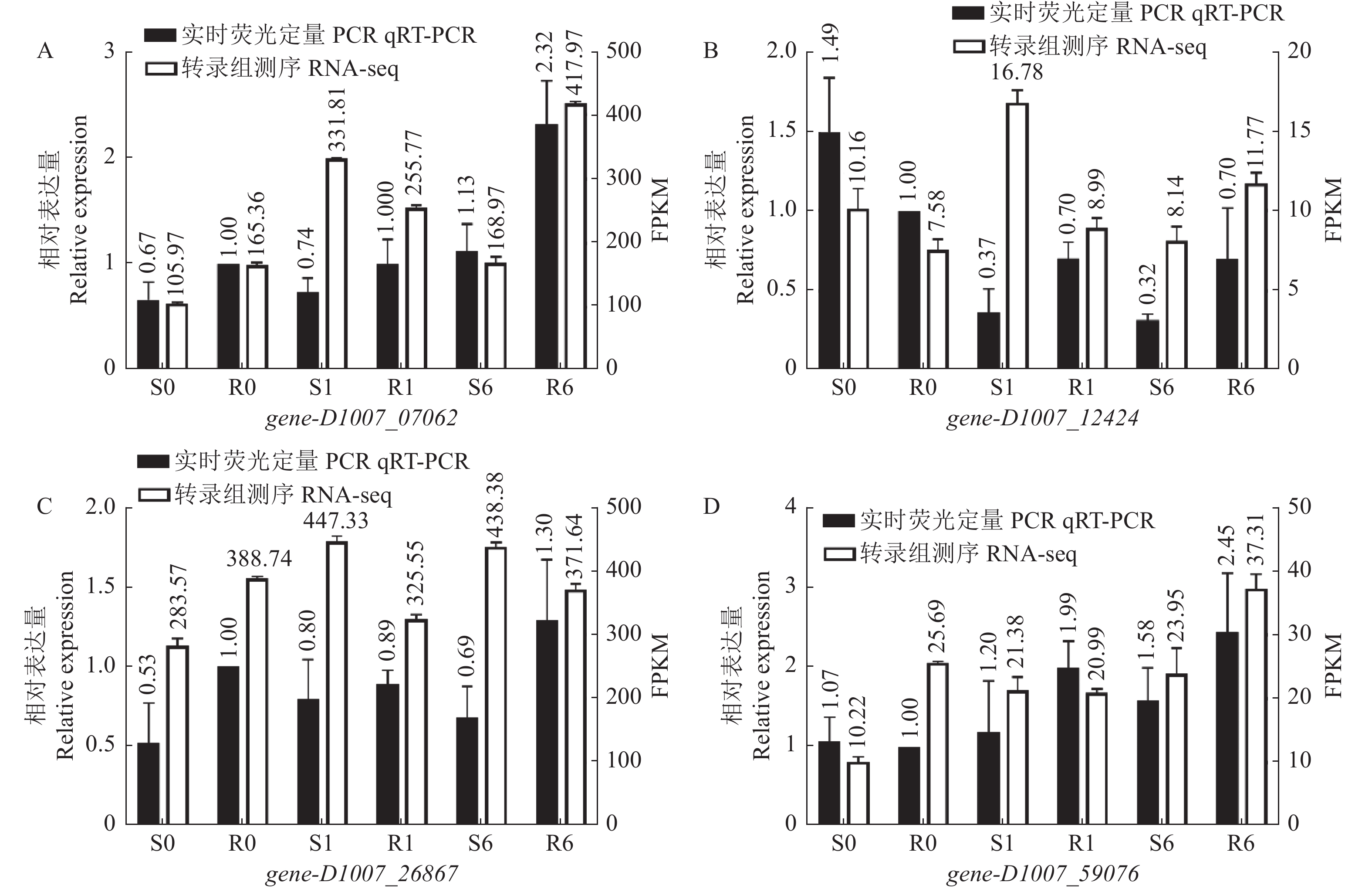
摘要:目的 挖掘青稞代谢啶磺草胺可能涉及的重要基因,明确青稞对啶磺草胺的代谢解毒机制,为啶磺草胺的科学使用和耐受除草剂的青稞品种选育提供理论基础。方法 以啶磺草胺处理0 、1 、6 d的敏感青稞品种青0160以及耐药青稞品种青0306的叶片为材料,借助高通量测序技术进行转录组测序结果分析。结果 GO富集分析结果表明,啶磺草胺处理前后差异表达基因均显著富集在光合作用上。KEGG富集分析表明,啶磺草胺处理1 d后,谷胱甘肽代谢途径中抗氧化剂相关基因以及苯丙素和吡啶生物碱生物合成途径中与应激相关基因显著富集;啶磺草胺处理6 d后,与维持细胞功能的一系列生物过程及氨基酸的生物合成和代谢相关的基因显著富集。进一步分析表明,两个品种中的SOD21972、POD55052、CAT15170、DHAR59510、APX42784、GR34873、GSTs849、GSTs36979、GSTs31507、GSTs15106、GSTs20762表达上调,PSⅡ55705、Cc31194、Cc17547、Cc17551、CYP12424受到抑制;其中POD55052在敏感青稞中表达量高于耐药青稞,SOD21972、CAT15170、DHAR59510、APX42784、GR34873、GSTs849、GSTs36979、GSTs31507、GSTs15106、GSTs20762、PSⅡ55705、Cc31194、Cc17547、Cc17551、CYP12424在耐药青稞中表达量高于敏感青稞,这些基因可能参与了青稞耐啶磺草胺机制。qRT-PCR相对表达量和转录组测序结果变化趋势基本一致,证明转录组测序结果具有可靠性。结论 明确了青稞对啶磺草胺的代谢解毒机制,为青稞耐受啶磺草胺提供分子基础,对啶磺草胺安全用药及选育青稞耐除草剂品种有重要意义。Abstract:Objective Key genes involved in the detoxification of pyroxsulam in naked barley were identified to facilitate breeding an herbicide-tolerant variety.Method Leaves of herbicide-sensitive Qing 0160 and herbicide-resistant Qing 0306 naked barley were treated with pyroxsulam for 0, 1, or 6 d prior to a high throughput transcriptome sequencing.Result The GO of the differentially expressed genes were significantly enriched in photosynthesis before as well as after the pyroxsulam treatment. Significant KEGG enrichment of the genes related to antioxidants in the glutathione metabolic pathway and the stress-related genes in the phenylpropanol and pyridine alkaloid biosynthesis pathways was observed 1d after the treatment. And 6 d afterward, the genes related to the biological processes that maintain the cell function as well as the biosynthesis and metabolism of amino acids were significantly enriched. Further analysis indicated that the expressions of SOD21972, POD55052, CAT15170, DHAR59510, APX42784, GR34873, GSTs849, GSTs36979, GSTs31507, GSTs15106, andGSTs20762 were upregulated, while PSⅡ55705, Cc31194, Cc17547, Cc17551, and CYP12424 downregulated. POD55052 in the herbicide-sensitive naked barley was highly expressed but not in the herbicide-resistant counterparts. On the other hand, the expressions of SOD21972, CAT15170, DHAR59510, APX42784, GR34873, GSTs849, GSTs36979, GSTs31507, GSTs15106, GSTs20762, PSⅡ55705, Cc31194, Cc17547, Cc17551, and CYP12424 were higher in the herbicide-resistant than in the herbicide-sensitive naked barley. It suggested that they might be involved in the pyroxsulam-resistance of the plants.Conclusion The basically same trend shown in this study on the gene express by qRT-PCR and the transcriptome sequencing unveiled the genes possibly associated with the pyroxsulam detoxification mechanism of naked barley. The information would facilitate the breeding of an herbicide-resistant variety.
-
Keywords:
- naked barley /
- pyroxsulam /
- transcriptome /
- drug resistance gene
-
0. 引 言
【研究意义】荷叶离褶伞(Lyophyllum decastes,Lyd),又称鹿茸菇,属于离褶伞科(Lyophyllaceae),离褶伞属(Lyophyllum,Ly),是一种木腐型珍贵食药用真菌[1-2]。荷叶离褶伞子实体分叉成丛生的细枝,菌盖外观似鹿茸切片[3],广泛分布于北半球温带的山区和丛林之中[2, 4]。荷叶离褶伞口感丝滑爽脆,子实体脂肪含量低,粗纤维成分高,富含人体所需的氨基酸和微量元素[2]。荷叶离褶伞子实体含有粗蛋白22.16%,粗脂肪2.69%,多糖44.29%,粗纤维8.66%,属于高蛋白低脂肪的食用菌[5]。荷叶离褶伞富含的致密型膳食纤维可改善人体肠道的消化能力[6-7],是近年来新兴的工厂化栽培药食兼用菌品种[8-10],且在我国已实现工厂化栽培[2]。当前荷叶离褶伞工厂化栽培仍存在着发菌较慢、成活较迟、易发生有害菌污染等问题[4],获得荷叶离褶伞优良品种是栽培成功的关键[11-13]。筛选出菌种纯度高、菌丝遗传性状稳定、生长活力强和普通培养基易于栽培的品种是当下荷叶离褶伞菌株市场化规模化袋式栽培生产的关键。将本地区与其他地区引进的荷叶离褶伞菌株进行基因组序列突变比对和菌丝形态分析研究,对丰富本地区荷叶离褶伞种质资源有重要意义。【前人研究进展】在自然环境下荷叶离褶伞自身能产生基因组序列突变,且在漫长的进化过程中逐渐累积突变,形成子实体和菌丝形态差异明显的菌株[1]。不同地区的地理气候环境差异较大,对自然突变的荷叶离褶伞有着不同的筛选机制,形成地区之间基因组序列差异较大的菌株,突出表现为菌丝生长和形态的多样性和差异性。荷叶离褶伞子实体由组织化的菌丝体构成,菌丝稳定的生长速度决定子实体的大小[2]。菌丝的生长活力和遗传性状以及将优良性状稳定遗传到子代受其基因序列控制,而基因序列的突变是产生菌丝形态差异的根本原因[4,6]。通过基因序列差异性获得菌丝形态遗传稳定的荷叶离褶伞菌株,能克服由外界不利环境胁迫造成菌丝变异生长的假阳性现象,加快获得菌丝形态优良的菌株。【本研究切入点】 传统分类方法通过子实体生长和菌丝形态对不同地区来源的荷叶离褶伞菌株进行筛选和建立菌种资源库,不但进度慢且无法明确菌丝变异的原因。鉴定到基因组序列碱基突变且变异菌丝稳定遗传是有效增加荷叶离褶伞菌株资源库的关键,而采取真菌18S rRNA(V4)和ITS(ITS1~ITS4)序列结合菌丝形态对不同地区的荷叶离褶伞进行鉴定尚无相关报道。【拟解决的关键问题】通过比较从上海、云南和吉林等地引进的荷叶离褶伞与福建本地栽培的荷叶离褶伞之间基因序列和菌丝生长的差异性,获得基因序列变异大且菌丝形态稳定遗传的荷叶离褶伞,为选育菌丝生长较快且适合工厂袋式栽培的荷叶离褶伞菌株提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
荷叶离褶伞菌株包括从云南、吉林和上海等地引进的Lyd-LR1、Lyd-LR6、Lyd-LR10、Lyd-LR15和Lyd-LR17,福建省本地工厂化栽培菌株Lyd-LRX和Lyd-LRY。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 荷叶离褶伞的纯化培养及电镜观察
荷叶离褶伞菌株均在实验室进行多次菌丝分离和继代培养。挑取荷叶离褶伞菌丝在PDA固体培养基上连续继代培养5次,获得纯化的菌丝体用于后续的菌丝生长试验。将相同量的菌丝块(直径<5 mm)接种至PDA固体培养基上暗培养10 d 和20 d(温度恒定在30 ℃,每个菌株5次重复),用化学方法制备扫描电镜观察样品,对荷叶离褶伞菌丝的生长情况和形态特征进行观察拍照。
1.2.2 荷叶离褶伞基因组DNA的提取
挑选荷叶离褶伞菌丝体(新鲜菌丝1 g左右)到研钵,加入液氮充分碾磨破碎,选取部分粉末转入2 mL离心管中,按照真菌基因组DNA提取试剂盒步骤提取荷叶离褶伞菌丝体DNA。提取的基因组DNA 经 1.20%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,确定荷叶离褶伞菌丝体DNA的完整性。
1.2.3 18S rRNA和ITS区段序列的PCR扩增和测序
配制Phanta Max Super-Fidelity DNA Polymerase(诺唯赞Vazyme Biotech, Co., Ltd#P505-d1, 中国)PCR反应试剂。PCR 反应体系(50 μL): 2×Phanta Max Buffer 25 μL, dNTPs 1 μL,引物(10 μmol·L−1)各 2 μL,DNA Polymerase 1 μL, DNA 模板1 μL (<50 ng), ddH2O 18 μL。PCR反应条件:95 °C变性 3 min;95 °C 变性15 s,55 °C 退火15 s,72 °C 延伸1 min,35 个循环;72 °C 总延伸5 min。对18S rRNA的V4变量区(623~853)和ITS1~ITS4区段分别进行PCR扩增。18S rRNA的引物序列为18S_3NDF(正向引物序列):5′ -GGCAAGTCTGGTGCCAG-3′;18S_V4_euk_R2(反向引物序列): 5′-ACGGTATCT(AG)ATC(AG)TCTTCG-3′。ITS区段引物序列为ITS1(正向引物序列): 5′-TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG-3′;ITS4(反向引物序列): 5′-TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC-3′。引物由上海生工生物工程有限公司合成。采用PCR仪Eppendorf 5331(德国eppendorf公司)进行PCR扩增,PCR产物用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,确定PCR产物的大小和特异性。PCR产物使用通用型DNA纯化回收试剂盒进行回收(TIANGEN DP214,天根生化科技有限公司,中国)。纯化的PCR产物送北京擎科生物科技有限公司进行测序分析。
1.2.4 18S rRNA和ITS序列的同源性比对
测序获得荷叶离褶伞18S rRNA的V4区序列和ITS的ITS1~ITS4区序列,去除杂峰序列后,登录NCBI Blast(https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi)并选用Nucleotide BLAST进行核酸序列同源性比对,同时在NCBI GenBank获得同源性较高(>90%)的部分荷叶离褶伞菌株序列编号(Accession)及其序列信息,使用生物软件DNAMAN 9进行多重序列比对。
1.2.5 构建系统发育进化树
采用MEGA 7.0.26(MolecularEvolutionary Genetics Analysis,http://www.megasoftware.net/)软件分别对18S rRNA(V4)和ITS(ITS1~ITS4)序列同源性较高的荷叶离褶伞序列构建系统进化树。用 ClustalW 进行多序列匹配比对,重复数(Bootstrap)为1000,以Neighbor-Joining(NJ)法构建系统发育进化树。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 荷叶离褶伞菌株18S rRNA-ITS同源性分析和多重序列比对
18S rRNA(V4)序列的NCBI Blast比对结果显示,外地离褶伞菌株(Lyd-LR1、Lyd-LR6、Lyd-LR10、Lyd-LR15和Lyd-LR17)、福建本地离褶伞菌株(Lyd-LRX和Lyd-LRY)与NCBI登录的荷叶离褶伞菌株(Lyd-PBM3069和Lyd-JM87/16)序列同源性为97.55%~98.88%(表1);与NCBI登录的离褶伞属菌株Ly-shimeji(D84555.1)、Ly-sp. MSG166、Ly-sp. PBM 2688、Ly-praslinense 10295、Ly-leucophaeatum HAe251和Ly-shimeji(D84553.1)的序列同源性为94.21%~100%。序列同源性均大于94%,确定试验菌株Lyd-LR1、Lyd-LR6、Lyd-LR10、Lyd-LR15和Lyd-LR17菌株为荷叶离褶伞。
表 1 荷叶离褶伞菌株的18S rRNA(V4)序列同源性分析Table 1. Homology of 18S rRNA (V4) sequences in Lyd strains(单位:%) 菌株 Strain Lyd-LR1 Lyd-LR6 Lyd-LR10 Lyd-LR15 Lyd-LR17 Lyd-LRX Lyd-LRY Lyd-PBM3069 98.45 98.22 98.88 99.11 98.48 98.66 98.21 Lyd-JM87/16 98.23 97.55 98.66 98.44 97.83 97.99 97.54 Ly-shimeji(D84555.1) 97.96 97.90 98.59 98.83 97.95 98.13 97.90 Ly-sp. MSG166 96.69 96.44 97.10 97.32 96.96 96.88 96.64 Ly-sp. PBM 2688 96.47 96.21 96.88 97.10 96.75 96.65 96.42 Ly-praslinense 10295 94.92 94.65 95.31 95.54 95.23 95.09 94.85 Ly-leucophaeatum HAe251 94.48 94.21 94.87 95.09 94.79 94.64 94.41 Ly-shimeji(D84553.1) 100.00 93.44 98.36 98.36 100.00 95.08 93.22 根据18S rRNA多重序列比对结果(图1),与NCBI登录菌株Lyd-PBM3069和Lyd-JM87/16相比较,外地荷叶离褶伞菌株Lyd-LR1、Lyd-LR6、Lyd-LR10、Lyd-LR15和Lyd-LR17以及福建本地荷叶离褶伞菌株Lyd-LRX和Lyd-LRY均发生4处碱基替换以及1处碱基缺失。与本地荷叶离褶伞菌株Lyd-LRX和Lyd-LRY相比较,外地荷叶离褶伞菌株Lyd-LR1、Lyd-LR6、Lyd-LR10、Lyd-LR15和Lyd-LR17部分发生3处碱基缺失/插入突变。外地荷叶离褶伞菌株Lyd-LR1、Lyd-LR6、Lyd-LR10、Lyd-LR15和Lyd-LR17在真菌非常保守的18S rRNA(V4)序列发生碱基替换和碱基缺失的多处突变,需继续以碱基突变概率较高的ITS(ITS1-ITS4)序列进一步分析外地荷叶离褶伞菌株的基因序列差异性。
ITS(ITS1-ITS4)序列NCBI Blast比对结果显示,与Lyd-LR1、Lyd-LR6、Lyd-LR10、Lyd-LR15、Lyd-LR17、Lyd-LRX和Lyd-LRY菌株序列均高度同源(>80%)的荷叶离褶伞菌株达到45个,但序列同源性下降至80.09%~90.33%(表2),提示菌株的ITS(ITS1–ITS4)序列已发生较高比例的碱基突变。根据ITS(ITS1–ITS4)多重序列比对结果,与NCBI登录菌株Lyd-Ld418和Lyd-ywy1相比较,Lyd-LR1、Lyd-LR6、Lyd-LR10、Lyd-LR15、Lyd-LR17、Lyd-LRX和Lyd-LRY菌株均发生基本相同的7处碱基替换、1处碱基缺失以及1处碱基插入。与本地荷叶离褶伞菌株Lyd-LRX和Lyd-LRY相比较,外地荷叶离褶伞菌株Lyd-LR1、Lyd-LR6、Lyd-LR10、Lyd-LR15和Lyd-LR17菌株均发生相同的5处碱基替换以及1处碱基插入。与其他荷叶离褶伞菌株相比较, Lyd-LR1、Lyd-LR6菌株发生更高的碱基突变(图2)。与NCBI登录荷叶离褶伞菌株相比,外地荷叶离褶伞菌株和福建本地荷叶离褶伞菌株的ITS(ITS1–ITS4)序列均发生较高比例的碱基替换和碱基缺失,且外地荷叶离褶伞菌株Lyd-LR1和Lyd-LR6的碱基突变明显高于其他荷叶离褶伞菌株,而Lyd-LR6菌株ITS(ITS1–ITS4)序列发生碱基替换和碱基缺失的突变比例高于Lyd-LR1菌株。
表 2 荷叶离褶伞菌株的ITS(ITS1–ITS4)序列同源性分析Table 2. Homology of ITS (ITS1–ITS4) sequences in Lyd strains(单位:%) 菌株
StrainLyd-LR1 Lyd-LR6 Lyd-LR10 Lyd-LR15 Lyd-LR17 Lyd-LRX Lyd-LRY Lyd-dcy2255 89.72 83.52 90.33 84.64 89.38 86.52 82.92 Lyd-ywy1 89.42 82.76 90.05 84.33 89.06 86.06 82.49 Lyd-Ld418 89.27 82.92 89.94 84.45 89.24 85.67 82.58 Lyd-060926 89.30 82.82 90.08 84.07 88.79 85.80 82.24 Lyd-060801 89.15 82.66 89.94 83.94 88.61 85.91 82.06 Lyd-061011 88.98 82.35 89.77 83.33 88.02 85.76 81.65 Lyd-iNAT 88.34 82.37 88.99 83.26 87.95 85.23 81.26 Lyd-22/14DMRJU 88.69 81.74 88.98 83.14 88.69 85.60 80.09 2.2 荷叶离褶伞菌株的18S rRNA-ITS系统发育进化树分析
为明确外地荷叶离褶伞菌株和福建本地荷叶离褶伞菌株之间的进化关系,同时根据NCBI Blast提供的同源性分析结果,选取部分NCBI登录的荷叶离褶伞、离褶伞属菌株和其食用菌[18S rRNA(V4)同源性>80%]进行系统发育进化树分析。18S rRNA(V4区)序列的进化树分析结果显示,外地荷叶离褶伞菌株(Lyd-LR1、Lyd-LR6、Lyd-LR10、Lyd-LR15和Lyd-LR17)聚为一类,再与福建本地荷叶离褶伞菌株(Lyd-LRX和Lyd-LRY)聚为一类,最后与NCBI登录的荷叶离褶伞菌株(Lyophyllum decastes PBM3069和Lyophyllum decastes JM87/16)聚合(图3),但均不与NCBI登录的其他食用菌进行聚合,说明外地荷叶离褶伞菌株在遗传距离上有着近似的亲缘关系,但与福建本地荷叶离褶伞已存在遗传进化上的差别,而与NCBI登录的荷叶离褶伞和其他食用菌有较远的遗传距离和亲缘关系。
ITS(ITS1–ITS4)序列的系统发育进化树分析结果显示,Lyd-LR1和Lyd-LR6菌株聚合在一起,而Lyd-LR10、Lyd-LR15、Lyd-LR17、Lyd-LRX和Lyd-LRY菌株聚合在一起,再与NCBI登录的荷叶离褶伞菌株进行聚合(图4)。从遗传距离和进化关系进行分析,外地荷叶离褶伞菌株Lyd-LR10、Lyd-LR15和Lyd-LR17与福建本地离褶伞菌株Lyd-LRX和Lyd-LRY亲缘关系更接近。Lyd-LR1和Lyd-LR6菌株保持相近的亲缘关系,与其他荷叶离褶伞菌株亲缘关系较远。外地荷叶离褶伞菌株Lyd-LR1和Lyd-LR6的遗传进化距离大于其他荷叶离褶伞菌株,表现出较远的种属亲缘关系。
2.3 荷叶离褶伞的菌丝体生长和菌丝形态观察
将外地荷叶离褶伞菌株(Lyd-LR1、Lyd-LR6、Lyd-LR10、Lyd-LR15和Lyd-LR17)接菌至PDA培养基暗培养10 d 和20 d(30 ℃)。在菌丝体生长的第10 天,Lyd-LR6菌株在生长圈边缘形成厚实的菌丝体且菌丝体生长的速度明显快于Lyd-LR1、Lyd-LR10、Lyd-LR15和Lyd-LR17菌株;Lyd-LR10和Lyd-LR17菌株的菌丝体生长速度基本一致;Lyd-LR1和Lyd-LR15菌株的菌丝体厚度较低且菌丝体生长速度慢于Lyd-LR6、Lyd-LR10和Lyd-LR17菌株(图5)。在菌丝体生长的第20天,Lyd-LR1菌株的菌丝体不能铺满整个培养基,菌丝呈现松散放射状且菌丝厚度较薄,生长较慢;Lyd-LR6厚实的菌丝体呈平铺状且铺满整个培养基,菌丝厚度较高且均一,生长速度较快;Lyd-LR10、Lyd-LR15、Lyd-LR17、Lyd-LRX和Lyd-LRY菌丝体生长基本相同且菌丝体铺满整个培养基,菌丝体厚度较高且呈现突起状,生长较为迅速(图5)。荷叶离褶伞的菌丝体生长结果显示,Lyd-LR6菌丝体生长迅速,而Lyd-LR1菌丝体生长缓慢。Lyd-LR1和Lyd-LR6菌株之间的菌丝体生长速度差别明显且均不同于Lyd-LR10、Lyd-LR15和Lyd-LR17菌株的菌丝体生长。
挑取生长20 d的外地荷叶离褶伞菌株菌丝体进行扫描电镜观察,Lyd-LR10、Lyd-LR15、Lyd-LR17、Lyd-LRX和Lyd-LRY菌株的菌丝形态基本相似,均为圆柱形的菌丝,菌丝饱满且交织在一起;Lyd-LR1菌株的菌丝呈现梭子状,菌丝生长不规则且有聚合生长的倾向;Lyd-LR6菌株的菌丝生长更加不规则且呈现凹陷状,菌丝明显聚合生长(图6)。与Lyd-LR10、Lyd-LR15、Lyd-LR17、Lyd-LRX和Lyd-LRY菌株相比较,Lyd-LR1和Lyd-LR6菌株的菌丝形态发生了明显的变异,且Lyd-LR6菌株的菌丝形态变异幅度大于Lyd-LR1菌株。
3. 讨论与结论
快速鉴定外地引进的菌株是提高荷叶离褶伞品种选育效率的重要手段。目前对荷叶离褶伞菌株的研究主要集中在改良栽培技术、营养成分分析、甾类和多糖等活性物质的提取纯化[14-16],缺乏对于不同地区来源的荷叶离褶伞菌株的有效快速鉴定。随着分子生物学的发展,通过PCR扩增部分基因组序列对不同地区的食用菌菌株进行鉴定和确定其种属关系及基因组碱基序列变异情况的方法逐渐成熟,为优良菌株的筛选提供快捷方法[17]。采用传统的形态学鉴定食用菌有易于观察和比较优势,但菌丝形态多样性易受到外界因素的影响而出现假阳性。根据基因组序列同源性的特征(>95%)可确定食用菌菌株之间的序列差异性和种属亲缘关系[18]。基因组碱基序列的鉴定方法通过分析碱基序列的突变而明确菌丝形态变异和菌丝体性状能遗传稳定的本质原因。利用菌体形态学和基因组序列测序结合的方法,鉴定了蘑菇属的双孢蘑菇(Agaricus bisporus),香菇属的香菇(Lentinula edodes)和小包脚菇属的草菇(Volvariella volvacea)[19],以及快速将野生菌鉴定为Paxillus ammoniavirescens[18]。基因组部分序列测序和菌丝形态的结合是鉴定食用菌新菌株的有效方法。真菌食用菌具有物种多样性和序列保守性,其18S rRNA(V4)序列在遗传进化上较为保守,而ITS(ITS1–ITS4)序列常发生较高概率的碱基突变,常用于快速鉴定食用菌的基因序列同源性、种属关系和碱基序列突变程度,为进一步分析菌丝形态变异提供依据。
外地引进的荷叶离褶伞菌株(Lyd-LR1、Lyd-LR6、Lyd-LR10、Lyd-LR15和Lyd-LR17)与福建本地的荷叶离褶伞菌株(Lyd-LRX和Lyd-LRY)以及NCBI登录的荷叶离褶伞菌株在18S rRNA-ITS序列的系统发育进化树均聚合在一起,且菌株间的18S rRNA 序列同源性大于97.55%,与离褶伞菌株的同源性也大于94.21%,确定此次从外地引进的食用菌均为荷叶离褶伞菌株。18S rRNA-ITS序列的同源性分析、多重序列比对和遗传进化树分析均显示外地荷叶离褶伞菌株(Lyd-LR1、Lyd-LR6、Lyd-LR10、Lyd-LR15和Lyd-LR17)和福建本地荷叶离褶伞菌株(Lyd-LRX和Lyd-LRY)存在较高比例的碱基序列突变,ITS序列同源性下降至80.09%~89.72%,从而明确外地荷叶离褶伞菌株已明显不同于福建本地荷叶离褶伞菌株以及NCBI登录的荷叶离褶伞菌株(45个)。这些外地引进的荷叶离褶伞菌株具有丰富本地区荷叶离褶伞菌株资源库的研究价值。ITS(ITS1–ITS4)的多重序列比对和遗传进化树显示Lyd-LR1和Lyd-LR6菌株的基因序列差异性和碱基序列突变比例明显区别于其他荷叶离褶伞菌株,且仅在Lyd-LR6菌株发生的碱基替换和碱基缺失明显高于Lyd-LR1、Lyd-LR10、Lyd-LR15、Lyd-LR17、Lyd-LRX和Lyd-LRY。菌丝体生长速度和菌丝形态进一步表明,Lyd-LR1梭子状不规则菌丝和松散放射状菌丝体以及Lyd-LR6凹陷状聚合生长菌丝和边缘厚实平铺状菌丝体,均不同于Lyd-LR10、Lyd-LR15和Lyd-LR17圆柱形饱满的菌丝和突起状菌丝体,且Lyd-LR6菌丝体生长速度明显快于Lyd-LR1,Lyd-LR6菌丝形态的变异程度也高于Lyd-LR1。基因组碱基序列高比例的突变是造成Lyd-LR1和Lyd-LR6菌株菌丝体生长速度和菌丝形态明显不同于Lyd-LR10、Lyd-LR15、Lyd-LR17、Lyd-LRX和Lyd-LRY的根本原因。而与Lyd-LR1菌株相比,Lyd-LR6菌株的碱基序列突变比例更高且碱基突变位置更多变(碱基替换和碱基缺失),使得Lyd-LR6菌株的菌丝形态明显区别于Lyd-LR1菌株。
-
表 1 Real-time qRT-PCR分析所用引物序列
Table 1 Sequence of primer for qRT-PCR analysis
基因名称
Gene name正向引物(5'–3′)
Forward primer(5'–3′)反向引物(5'–3′)
Reverse primer(5'–3′)gene_07062 CCAGTCAAGCATCAAAAGCA GCAGAAAGGCCACTGTTTTC gene_12424 CAAGGAGAGCGGTGCTAAAC AGCTCCTCTTGCAGCTTCTG gene_26867 GACGGAGATGTGCAGAGTGA GTGCTGGTTTCACCACCTTT gene_59076 ACCGCAGCATAGCAGAAGAT AAGGGAGAAGCACCAGTTCA Actin
(青稞
Hulless barley)CTATTCAGGCCGTGCTTTCC CCAGCGAGATCCAAACGAAG 表 2 差异表达基因显著富集KEGG途径
Table 2 Significantly enriched KEGG-pathway of DGEs
途径注释
Description of pathway差异表达基因
DEGs途径注释
Description of pathway差异表达基因
DEGsR0 vs S0 R6 vs S6 碳代谢 Carbon metabolism 139 核糖体 Ribosome 109 光合生物中的碳固定
Carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms41 氨基酸生物合成
Biosynthesis of amino acids90 丙酮酸代谢 Pyruvate metabolism 43 碳代谢 Carbon metabolism 101 氨基酸生物合成 Biosynthesis of amino acids 113 乙醛酸和二羧酸代谢
Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism36 乙醛酸和二羧酸代谢
Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism42 光合作用-天线蛋白
Photosynthesis - antenna proteins16 甘氨酸、丝氨酸和苏氨酸代谢
Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism39 光合生物的碳代谢
Carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms33 氧化磷酸化 Oxidative phosphorylation 63 光合作用 Photosynthesis 32 柠檬酸循环(TCA循环)
Citrate cycle (TCA cycle)33 甘氨酸、丝氨酸和苏氨酸代谢
Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism32 光合作用 Photosynthesis 40 丙氨酸、天冬氨酸和谷氨酸代谢
Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism23 光合作用-天线蛋白
Photosynthesis - antenna proteins16 精氨酸生物合成 Arginine biosynthesis 17 丁酸代谢 Butanoate metabolism 14 莨菪烷、哌啶和吡啶生物碱生物合成
Tropane, piperidine and pyridine alkaloid biosynthesis9 磷酸戊糖途径 Pentose phosphate pathway 31 2-氧代羧酸代谢
2-Oxocarboxylic acid metabolism22 R1 vs S1 丙酮酸代谢 Pyruvate metabolism 28 核糖体 Ribosome 50 烟酸和烟酰胺代谢
Nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism11 光合作用-天线蛋白
Photosynthesis -antenna proteins9 -
[1] 吕银花. 高海拔地区青稞田间主要杂草及其防除 [J]. 中国农业信息, 2014, (24):99−100. LV Y H. Main weeds in highland barley field at high altitude and their control [J]. China Agricultural Information, 2014(24): 99−100. (in Chinese)
[2] 闫栋, 罗振华, 胡有良, 等. 不同除草剂对青稞田野燕麦的防除及对青稞生长的影响 [J]. 生物技术通报, 2017, 33(9):166−171. YAN D, LUO Z H, HU Y L, et al. Effects of different herbicides on weed control and the growth, yield and quality of highland barley [J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2017, 33(9): 166−171. (in Chinese)
[3] 周兰兰, 朱君, 桑安平, 等. 高海拔区青稞田除草剂组合筛选试验 [J]. 甘肃农业科技, 2022, 53(8):88−92. ZHOU L L, ZHU J, SANG A P, et al. Study on screening experiment of highland barley herbicides in Gannan autonomous prefecture [J]. Gansu Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 53(8): 88−92. (in Chinese)
[4] 李亚东, 贺双, 田笑明, 等. 啶磺草胺对不同品种小麦生长发育的影响 [J]. 新疆农业科学, 2017, 54(4):682−693. LI Y D, HE S, TIAN X M, et al. Effects of pyroxsulam on growth and development of different varieties of wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 54(4): 682−693. (in Chinese)
[5] 罗思荃, 曹轩, 刘乐, 等. 啶磺草胺与双氟磺草胺协同防除冬小麦田杂草效果及对小麦产量的影响 [J]. 杂草学报, 2022, 40(1):69−76. LUO S Q, CAO X, LIU L, et al. Cooperative control effect of pyroxsulam with florasulam on weeds and influence on the winter wheat yield [J]. Journal of Weed Science, 2022, 40(1): 69−76. (in Chinese)
[6] 董雪. 不同小麦品种对除草剂啶磺草胺耐药性差异研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2014. DONG X. Study on difference of pyroxsulam tolerance of various wheat varieties[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2014. (in Chinese)
[7] 王丹丹. 不同小麦品种对甲基二磺隆等药剂的耐药性差异研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2019 WANG D D. Study on the difference in herbicide tolerance of wheat varieties to mesosulfuron-methyl and other herbicides[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2019. (in Chinese)
[8] 裴涛. 日本看麦娘(Alopecurus japonicas)对啶磺草胺的抗性研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2015. PEI T. Study on resistance of Alopecurus japonicus to pyroxulam[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2015. (in Chinese)
[9] 冯雨娟. 日本看麦娘(Alopecurus japonicus)对啶磺草胺的抗药性研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2016. FENG Y J. Study on resistance of Alopecurus japonicus to pyroxsulam[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2016. (in Chinese)
[10] 张宇翔, 朱亮, 魏有海. 不同青稞品种对7.5%啶磺草胺的耐药性分析 [J]. 青海大学学报, 2022, 40(2):14−19. ZHANG Y X, ZHU L, WEI Y H. Analysis of drug resistance of different Hordeum vulgare var nudum varieties to 7.5% pyroxsulam [J]. Journal of Qinghai University, 2022, 40(2): 14−19. (in Chinese)
[11] PERTEA M, KIM D, PERTEA G M, et al. Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown [J]. Nature Protocols, 2016, 11(9): 1650−1667.
[12] ANDERS S, HUBER W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data [J]. Genome Biology, 2010, 11(10): R106.
[13] BENJAMINI Y, HOCHBERG Y. On the adaptive control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing with independent statistics [J]. Journal of Educational and Behavioral Statistics, 2000, 25(1): 60−83.
[14] KANEHISA M, GOTO S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes [J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2000, 28(1): 27−30.
[15] 郭美俊. 谷子对除草剂抗性的生理特性及产量性状的影响[D]. 太谷: 山西农业大学, 2017. GUO M J. Effect of foxtail millet on physiological characteristics and yields characteristics of herbicides resistance[D]. Taigu: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2017. (in Chinese)
[16] 田敏, 饶龙兵, 李纪元. 植物细胞中的活性氧及其生理作用 [J]. 植物生理学通讯, 2005, 41(2):235−241. TIAN M, RAO L B, LI J Y. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and its physiological functions in plant cells [J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 2005, 41(2): 235−241. (in Chinese)
[17] 王荣华, 石雷, 汤庚国, 等. 渗透胁迫对蒙古冰草幼苗保护酶系统的影响 [J]. 植物学通报, 2003, 38(3):330−335. WANG R H, SHI L, TANG G G, et al. Effect of osmotic stress on activities of protective enzymes system in Agropyron mongolicum seedling [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2003, 38(3): 330−335. (in Chinese)
[18] 袁帅. 水稻与大豆对氯磺隆、胺苯磺隆胁迫的生化响应[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2009 YUAN S. The biochemical responses of rice and soybean to stress of chlorsulfuron and ethametsulfuron[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2009. (in Chinese)
[19] RADWAN D E M. Salicylic acid induced alleviation of oxidative stress caused by clethodim in maize (Zea mays L. ) leaves [J]. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 2012, 102(2): 182−188.
[20] KARUPPANAPANDIAN T, WANG H W, PRABAKARAN N, et al. 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid-induced leaf senescence in mung bean (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek) and senescence inhibition by co-treatment with silver nanoparticles [J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2011, 49(2): 168−177.
[21] 刘长乐, 郭月, 李芳芳, 等. 抗ALS类除草剂作物种质创制与利用研究进展 [J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2022, 23(2):333−345. LIU C L, GUO Y, LI F F, et al. Advances in development and utilization of crop germplasm resources resistant to ALS herbicides [J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2022, 23(2): 333−345. (in Chinese)
[22] YUAN J S, TRANEL P J, STEWART C N Jr. Non-target-site herbicide resistance: A family business [J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2007, 12(1): 6−13.
[23] 李向楠, 吴振兴, 陈坚剑, 等. 耐性和敏感两种类型鲜食玉米苗期施用硝磺草酮后的转录组分析 [J]. 农药学学报, 2021, 23(5):893−904. LI X N, WU Z X, CHEN J J, et al. RNA-Seq transcriptome analysis of fresh-eating maizes sensitive and tolerant to mesotrione in the seedling stage [J]. Chinese Journal of Pesticide Science, 2021, 23(5): 893−904. (in Chinese)
[24] 董雪, 梁友, 田笑明, 等. 不同小麦品种对啶磺草胺的耐药性差异 [J]. 新疆农业科学, 2014, 51(8):1474−1481. DONG X, LIANG Y, TIAN X M, et al. Difference of tolerance of different wheat varieties to pyroxsulam [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 51(8): 1474−1481. (in Chinese)
[25] 谢娜, 毕亚玲, 李凌绪, 等. 不同玉米品种对氯吡嘧磺隆的耐药性差异及其机制 [J]. 植物保护学报, 2012, 39(6):567−572. XIE N, BI Y L, LI L X, et al. Difference of tolerance and mechanism of various maize varieties to halosulfuron-methyl [J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2012, 39(6): 567−572. (in Chinese)
[26] 郭玉莲, 陶波, 翟喜海, 等. 不同玉米品种对氯嘧磺隆的耐药性差异及其机制 [J]. 植物保护学报, 2009, 36(4):366−370. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-7518.2009.04.015 GUO Y L, TAO B, ZHAI X H, et al. Drug resistance and mechanism between different maize varieties to chlorimuron-ethyl [J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2009, 36(4): 366−370. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-7518.2009.04.015
[27] 马春英. 不同品种谷子对单嘧磺隆和扑草净耐药性差异的生理机制[D]. 太谷: 山西农业大学. MA C Y. Physiological resistance mechanism of foxtail millet with different herbicide-resistance to monosulfuron and prometryn[D]. Taigu: Shanxi Agricultural University . (in Chinese)
[28] 毕亚玲, 李君君, 戴玲玲, 等. 杂草对除草剂非靶标抗性机理研究进展 [J]. 植物保护, 2020, 46(5):1−5,12. BI Y L, LI J J, DAI L L, et al. Research advances in non-target resistance mechanisms of weeds to herbicides [J]. Plant Protection, 2020, 46(5): 1−5,12. (in Chinese)
[29] 王正贵, 周立云, 郭文善, 等. 除草剂对小麦光合特性及叶绿素荧光参数的影响 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2011, 30(6):1037−1043. WANG Z G, ZHOU L Y, GUO W S, et al. Effects of herbicides on photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters in wheat leaves [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2011, 30(6): 1037−1043. (in Chinese)
[30] 侯丽丽, 邱毅, 孙惠敏, 等. 除草剂草甘膦对葡萄光合作用及叶绿素荧光特性的影响 [J]. 北方园艺, 2018, (13):57−62. HOU L L, QIU Y, SUN H M, et al. Effects of herbicide glyphosate on photosynthetic and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of grapes [J]. Northern Horticulture, 2018(13): 57−62. (in Chinese)
[31] 高贞攀, 郭平毅, 原向阳, 等. 苯磺隆和单嘧磺隆对张杂谷10号光合特性及产量构成的影响 [J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2015, 20(6):36−45. DOI: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2015.06.05 GAO Z P, GUO P Y, YUAN X Y, et al. Effects of Tribenuron-methyl and Monosulfuron application on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of Zhangza Gu 10 [J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2015, 20(6): 36−45. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2015.06.05
[32] 宋慧, 王涛, 邢璐, 等. 不同谷子品种喷施咪唑啉酮除草剂后的转录组分析[J/OL]. 作物杂志, 2023: 1-12. (2023-03-31). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1808.s.20230330.1542.009.html. SONG H, WANG T, XING L, et al. Transcriptome analysis of different foxtail millet(Setaria italica L.) varieties treated with imazapic herbicide[J/OL]. Crops, 2023: 1-12. (2023-03-31). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1808.s.20230330.1542.009.html.(in Chinese)




 下载:
下载: