Factors Affecting Soil Organic Carbon on Farmland in Fujian Analyzed by Geodetector Model
-
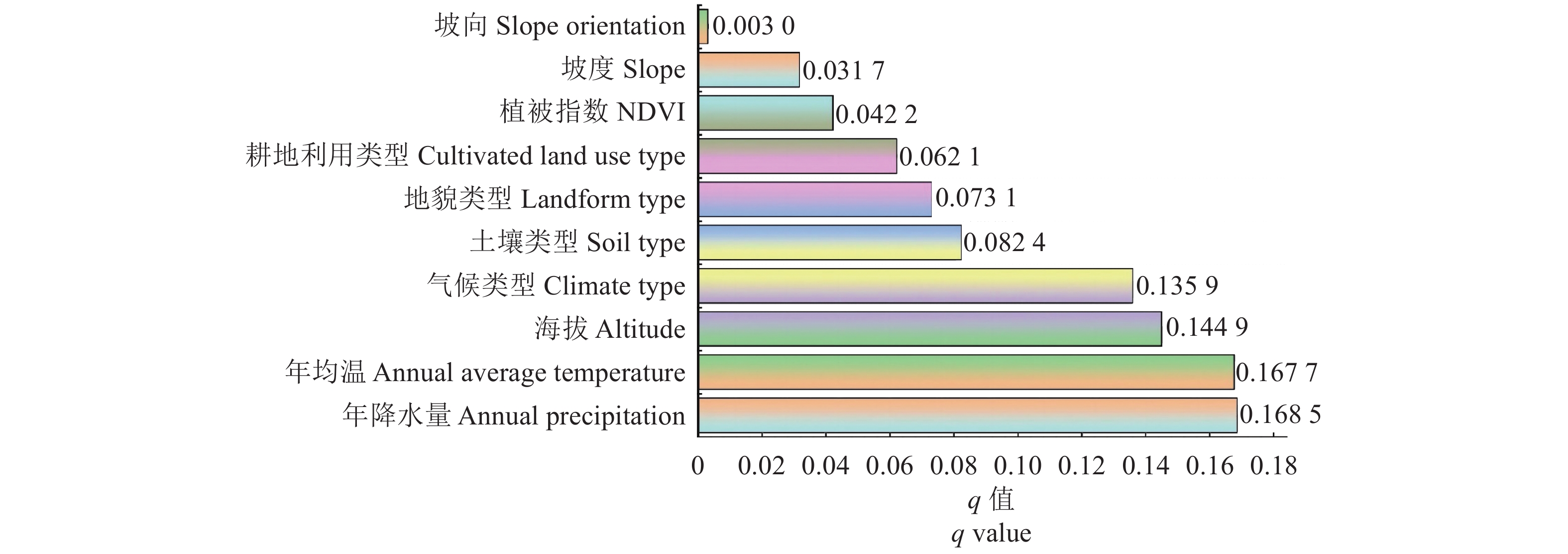
摘要:目的 探明福建省耕地土壤有机碳(Soil organic carbon, SOC)的空间分布及其影响因素。方法 基于福建省3万多个耕地土壤调查样点数据,利用皮尔逊相关系数、随机森林模型计算SOC影响因素的重要性,并通过地理探测器模型分析影响全省耕地土壤有机碳空间分布的因素。结果 2008年福建省耕地土壤有机碳样点数据的范围在0.12~67.28 g·kg−1,呈现东南部沿海低、西部和中部高的空间格局。3种模型中地理探测器模型的分析结果最全面和客观。地理探测器模型的因子探测器结果表明气候相关因素是福建省耕地土壤有机碳含量空间分异性的主要影响因子,各影响因子按解释程度前六名分别为:年降水量(
0.1685 )>年均温(0.1677 )>海拔(0.1499 )>气候类型(0.1359 )>土壤类型(0.0824 )>地貌类型(0.0731 )。通过交互探测器进一步发现年降水量与年均温的交互作用对SOC空间分异的解释程度最大(0.1941 ),其次为年降水量与土壤类型(0.1923 )、年降水量与耕地利用类型(0.1918 )。结论 强烈的因子交互作用表明,福建省耕地土壤有机碳含量空间分异性是由多种因子共同作用影响而非单一因子决定,对SOC进行研究需要考虑其复杂的空间分异特征。本研究可为提高耕地土壤的空间使用效率、合理布局农业生产提供科学依据。Abstract:Objective Explore the spatial distribution and influencing factors of soil organic carbon (SOC) in cultivated land in Fujian Province.Method Based on the data generated from over 30,000 survey sites on farmland in Fujian, Pearson correlation coefficient and random forest model were employed to derive key factors affecting the SOC. The geodetector model was used to analyze the spatial SOC distribution in the province.Result The data on SOC of the province in 2008 ranged between 0.12 and 67.28 g·kg−1 with a spatial pattern of being low in the southeast coastal areas and high in the west and central regions. The geodetector model was shown to render the most comprehensive and objective analysis among the three models tested. It concluded the climate-related conditions to be the major factors affecting the spatial differentiation of SOC on the farmland with top 6 rankings of: annual precipitation (0.168 5)>annual average temperature (0.167 7)>altitude (0.144 9)>climate type (0.135 9)>soil type (0.082 4)>landform type (0.073 1). The interactive detectors further revealed the interaction between the annual precipitation and annual average temperature to exert the greatest influence on the SOC spatial differentiation (0.194 1), while the annual precipitation and soil type (0.192 3) and the annual precipitation and cultivated land use type (0.1918) followed.Conclusion Multiple factors affected the SOC on the farmland in Fujian in the past. For improving the spatial utilization efficiency and bettering the agriculture production layout on the land, it seemed imperative that all various factors highlighted in this study be taken into serious considerations.-
Keywords:
- soil organic carbon /
- geodetector /
- spatial distribution /
- influencing factors /
- interaction
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】芦笋(Asparagus officinalis L.)又名石刁柏,是百合科(Liliaceae)天门冬属(Asparagus)多年生宿根植物,具有抗肿瘤和抗氧化等功效,是世界公认的高级保健蔬菜,享有“蔬菜之王”美誉[1−2]。芦笋茎枯病由天门冬拟茎点霉菌[Phomopsis asparagi(Sacc.)Bubak]侵染引起,主要为害芦笋茎秆,在中国、日本、泰国和印尼等亚洲国家芦笋种植区每年均有发生,严重影响芦笋的产量和品质[3−4]。目前,施用杀菌剂是防治芦笋茎枯病的有效手段,但面临着病原菌抗药性、食品安全和环境污染等问题[5]。利用作物品种的抗病性是防治作物病害最经济、有效和安全的措施[6]。芦笋是多年生作物,生产周期长,一次种植可采收10年,建立快速准确的芦笋抗茎枯病鉴定方法,选育抗病品种,对芦笋产业健康发展具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】开展品种抗病性鉴定是选育作物抗病品种的重要一环。我国对水稻、小麦、玉米和大豆等大宗作物的主要病害都建立了稳定可靠的抗病性鉴定方法,形成了国家作物品种抗病性鉴定技术规程[7−8]。在芦笋抗茎枯病的抗性鉴定方面,Sonoda等[9]报道了一种芦笋茎部接种的抗病性鉴定方法,但操作复杂、用时长、受环境条件影响大、重复性差。杨迎青等[10]采用苗期人工接种的方法鉴定了31份芦笋种质资源的抗病性水平,缩短了芦笋抗茎枯病鉴定的时间。阮宏椿等[11]采用苗期人工接种的鉴定方法测定了9个主栽品种对芦笋茎枯病的抗病性。苗期人工接种法具有鉴定结果稳定的优点,但仍需要完成播种、定植等繁杂工作,占用温棚面积大,耗时较长,难以针对大批量品种或育种材料开展抗病性鉴定。【本研究切入点】采用田间自然诱发或苗期人工接种法鉴定芦笋的抗病性,工作量大、耗时长,难以快速从大量种质资源中筛选出抗性材料。芦笋抗茎枯病快速准确鉴定方法还有待深入探讨。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究拟通过评价芦笋茎枯病菌毒素浸种法和浸根法、分生孢子悬浮液浸种法和分生孢子悬浮液灌根法等4种方法与田间自然诱发法对供试芦笋品种抗病性鉴定结果的一致性,建立芦笋抗茎枯病快速准确鉴定的新方法,为芦笋抗病育种和茎枯病的防治提供技术支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 供试材料
供试菌株:供试芦笋茎枯病菌菌株FJ58采集自福建省莆田市涵江区庄边镇吉云村,由福建省农业科学院植物保护研究所分离鉴定,测定致病性并保存。
供试芦笋品种:格兰德、佳芦1号、早佳1号、丰岛1号、华淼、TC和UC157F2(感病对照品种),由福建省农业科学院植物保护研究所收集并保存。
供试培养基:马铃薯葡萄糖琼脂培养基(PDA培养基),取200 g马铃薯进行切片,加水煮沸20 min,过滤,上清液加入葡萄糖20 g、琼脂粉16 g,加热至琼脂粉完全溶解,加水定容至
1000 mL,在121 ℃下高压湿热灭菌25 min。马铃薯葡萄糖培养基(PDB培养基),取200 g马铃薯进行切片,加水煮沸20 min,过滤,上清液加入葡萄糖20 g,加水定容至1000 mL,在121 ℃下高压湿热灭菌25 min。1.2 方法
1.2.1 芦笋茎枯病菌孢子悬浮液的制备
芦笋茎枯病菌孢子悬浮液的制备参照杨迎青等[10]的方法 ,并稍作修改。将保存于滤纸片上的芦笋茎枯病菌菌株FJ58转至PDA培养基平板上,28 ℃培养5 d,用直径5 mm的打孔器在菌落边缘打取菌饼,将菌饼转入PDA培养基平板,28 ℃培养14 d,用毛刷和适量无菌水洗下分生孢子器,用灭菌镊子捏碎分生孢子器,释放分生孢子,过滤后血球计数板测定分生孢子浓度,分别配制成1.0×103、1.0×104、1.0×105个孢子·mL−1的分生孢子悬浮液,置于4 ℃冰箱保存,备用。
1.2.2 芦笋茎枯病菌毒素的制备
参照李俊萍等[12]的方法,并稍作修改。将芦笋茎枯病菌菌株FJ58转至PDA培养基平板上,28 ℃培养5 d,用直径5 mm的打孔器在菌落边缘打取菌饼,将菌饼转入装有PDB培养基的三角瓶中,28 ℃、150 r·min−1振荡培养7 d,用灭菌滤纸过滤后收集滤液,并用细菌过滤器(0.22 μm)过滤,收集芦笋茎枯病菌粗毒素液。将芦笋茎枯病菌粗毒素液用无菌水稀释,分别配制成芦笋茎枯病菌粗毒素原液∶无菌水(体积比)=1∶0、7∶1、3∶1、1∶1、1∶3和1∶7的稀释液,置于4 ℃冰箱保存备用。
1.2.3 芦笋茎枯病菌毒素浸种法
将供试芦笋种子用10% H2O2浸泡消毒15 min,用无菌水冲洗3次后,然后分别用无菌水浸种22、20、16、8、0 h,再放入芦笋茎枯病菌FJ58的毒素中分别浸泡2、4、8、16、24 h,每个处理的浸种时间均为24 h,同时设无菌水浸种24 h的处理为对照。每处理50粒种子,3次重复。将浸种处理后的种子置于装有灭菌泥炭土的育苗盒中,将育苗盒置于28 ℃、相对湿度90%、光周期12L∶12D的培养箱内培育14 d,调查种子萌发率,计算茎枯病菌毒素对芦笋种子的萌发抑制率。采用DPS 9.5软件Duncan's新复极差法(P < 0.05)进行芦笋种子的萌发抑制率差异显著性分析,并根据试验结果以毒素浸种24 h对芦笋种子的萌发抑制率评价芦笋品种的抗病性[13]。高抗(HR):种子萌发抑制率=0%;抗病(R):0%<种子萌发抑制率≤1%;中抗(MR):1%<种子萌发抑制率≤5%;中感(MS):5%<种子萌发抑制率≤10%;感病(S):10%<种子萌发抑制率≤15%;高感(HS):15%<种子萌发抑制率。
1.2.4 芦笋茎枯病菌毒素浸根法
将供试芦笋种子用10% H2O2浸泡消毒15 min,用无菌水冲洗3次,然后放入无菌水浸泡24 h,置于28 ℃、90%相对湿度的培养箱中催芽3 d,将萌芽的种子置于育苗盒空穴中。每粒芦笋种子分别加入制备的不同芦笋茎枯病毒素稀释液2 mL,以无菌水作对照,每处理30粒种子,3次重复。将育苗盒置于28 ℃、相对湿度90%、光周期12L∶12D的培养箱内培育7 d观察并测量根长,计算不同茎枯病菌毒素稀释液对芦笋根生长的抑制率。采用DPS 9.5软件Duncan's新复极差法(P < 0.05)进行芦笋根生长的抑制率差异显著性分析,并根据试验结果以毒素原液对芦笋根生长的抑制率评价芦笋品种的抗病性。高抗(HR):芦笋根生长的抑制率≤50%;抗病(R):50%<芦笋根生长的抑制率≤60%;中抗(MR):60%<芦笋根生长的抑制率≤70%;中感(MS):70%<芦笋根生长的抑制率≤80%;感病(S):80%<芦笋根生长的抑制率≤90%;高感(HS):90%<芦笋根生长的抑制率。
1.2.5 芦笋茎枯病菌孢子悬浮液浸种法
将供试芦笋种子用10% H2O2浸泡消毒15 min,然后用无菌水冲洗3次,分别放入芦笋茎枯病菌1.0×103、1.0×104、1.0×105个孢子·mL−1分生孢子悬浮液中浸泡15 min,以无菌水浸泡为对照,每处理30粒种子,3次重复。将处理后种子置于装有灭菌泥炭土的育苗盒中,将育苗盒置于28 ℃、90%相对湿度、光周期12L∶12D的培养箱内培育14 d,调查种子萌发率。计算茎枯病菌对芦笋种子的萌发抑制率。采用DPS 9.5软件Duncan's新复极差法(P < 0.05)进行芦笋种子的萌发抑制率差异显著性分析,并根据试验结果以1.0×105个孢子·mL−1的分生孢子悬浮液浸种对种子萌发的抑制率评价芦笋品种的抗病性。高抗(HR):种子萌发抑制率=0%;抗病(R):0%<种子萌发抑制率≤20%;中抗(MR):20%<种子萌发抑制率≤40%;中感(MS):40%<种子萌发抑制率≤60%;感病(S):60%<种子萌发抑制率≤80%;高感(HS):80%<种子萌发抑制率。
1.2.6 芦笋茎枯病菌孢子悬浮液灌根法
将供试芦笋种子用10% H2O2浸泡消毒15 min,用无菌水冲洗3次,然后放入无菌水浸泡24 h,置于28 ℃、90%相对湿度的培养箱中催芽3 d,将处理后的种子置于装有灭菌泥炭土的育苗盒中,将育苗盒置于28 ℃、相对湿度90%、光周期12L∶12D的培养箱内培育14 d,分别用芦笋茎枯病菌1.0×103、1.0×104、1.0×105个孢子·mL−1的分生孢子悬浮液灌根接种,每株芦笋幼苗接种2 mL,以无菌水灌根为对照,每处理30株幼苗,3次重复。灌根处理3 d后逐日观察记载各处理的发病株数,计算发病率。采用DPS 9.5软件Duncan's新复极差法(P < 0.05)进行发病率差异显著性分析,并根据试验结果以1.0×103个孢子·mL−1分生孢子悬浮液灌根的发病率评价芦笋品种的抗病性。高抗(HR):发病率=0%;抗病(R):0%<发病率≤5%;中抗(MR):5%<发病率≤15%;中感(MS):15%<发病率≤30%;感病(S):30%<发病率≤45%;高感(HS):45%<发病率。
1.2.7 田间自然诱发法
将供试芦笋品种60 d苗龄的植株移栽种植于常年发生茎枯病的病圃中,60 d后五点取样,每点随机取10丛,观察记载各供试品种植株发病的茎秆数和调查总茎秆数,计算发病率。采用DPS 9.5软件Duncan's新复极差法(P < 0.05)进行发病率差异显著性分析,以发病率评价芦笋品种的抗病性,评价标准同1.2.6。
1.2.8 数据处理
按下列公式分别计算种子萌发率、种子萌发抑制率、根长抑制率和发病率。
种子萌发率/%=萌发的种子数/种子总数×100 (1) 种子萌发抑制率/%=(对照萌发率−处理萌发率)/对照萌发率×100 (2) 根长抑制率/%=(对照根长−处理根长)/对照根长×100 (3) 发病率/%=发病茎秆数/调查总茎秆数×100 (4) 采用SPSS 19.0分析各方法鉴定结果的相关性。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 芦笋茎枯病菌毒素浸种法
华淼、格兰德、佳芦1号和丰岛1号用芦笋茎枯病菌毒素原液浸种2、4、8、16、24 h的种子萌发率与对照差异不显著;早佳1号和UC157F2种子萌发率与芦笋茎枯病菌毒素浸种时间成反比,其中浸种4、8、16、24 h的萌发率显著低于对照;TC用茎枯病菌毒素浸种24 h的萌发率显著低于对照(表1)。芦笋茎枯病菌毒素浸种24 h对格兰德、佳芦1号、早佳1号、丰岛1号、华淼、TC和UC157F2种子萌发抑制率分别为3.62%、4.29%、13.98%、4.26%、2.19%、4.95%和15.00%,对早佳1号和UC157F2种子萌发抑制率显著高于其他供试品种。供试的7个品种被划分为感病和中抗2个类型,感病品种为UC157F2和早佳1号;中抗品种为格兰德、佳芦1号、丰岛1号、华淼和TC(图1)。
表 1 芦笋茎枯病菌毒素不同浸种时间对芦笋种子萌发率的影响Table 1. Effect of soaking time in mycotoxin-containing solution on asparagus seed germination rate浸种时间
Soaking time/h种子萌发率
Germination rate of seed /%格兰德
Grande佳芦1号
Jialu No.1早佳1号
Zaojia No.1丰岛1号
Fengdao No.1华淼
HuamiaoTC UC157F2 2 90.67a 92.00a 94.00a 92.00a 90.00a 92.67ab 90.67ab 4 91.33a 92.00a 91.33b 92.00a 90.67a 90.67ab 88.00bc 8 90.00a 91.33a 89.33b 92.00a 89.33a 92.00ab 85.33cd 16 88.00a 90.67a 84.67c 89.33a 90.67a 92.67ab 82.67de 24 89.33a 89.33a 82.00d 90.00a 89.33a 89.33b 79.33e 0 (CK) 92.00a 93.33a 94.67a 94.00a 91.33a 94.00a 93.33a 同列数据后不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。
Data with different lowercase letters on a column indicate significant differences at P<0.05. Same for below.![]() 图 1 芦笋茎枯病菌毒素浸种24 h对芦笋种子萌发的抑制率不同小写字母表示经Duncan氏新复极差法检验差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。Figure 1. Germination inhibition rate of asparagus seeds soaked in mycotoxin-containing solution for 24 hThose with different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at P<0.05 by Duncan’s new multiple range test. Same for below.
图 1 芦笋茎枯病菌毒素浸种24 h对芦笋种子萌发的抑制率不同小写字母表示经Duncan氏新复极差法检验差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。Figure 1. Germination inhibition rate of asparagus seeds soaked in mycotoxin-containing solution for 24 hThose with different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at P<0.05 by Duncan’s new multiple range test. Same for below.2.2 芦笋茎枯病菌毒素浸根法
芦笋茎枯病菌毒素浸根处理对芦笋根生长的抑制率与毒素浓度成正比,粗毒素原液∶无菌水(体积比)=1∶0、7∶1、3∶1、1∶1、1∶3和1∶7等6个处理对芦笋根生长抑制率差异达显著水平,其中毒素∶无菌水=1∶0浸根处理对芦笋根生长抑制率显著强于其他处理(表2)。毒素∶无菌水=1∶0浸根处理对格兰德、佳芦1号、早佳1号、丰岛1号、华淼、TC和UC157F2的根生长抑制率分别为80.94%、73.72%、82.29%、71.77%、65.86%、69.39%和82.35%,对华淼和TC根生长抑制率显著低于其他供试品种,而对UC157F2、格兰德和早佳1号的根生长抑制率则显著高于其他品种。供试的7个品种被划分为感病、中感和中抗3个类型,感病品种为UC157F2、早佳1号和格兰德;中感品种为佳芦1号和丰岛1号;中抗品种为TC和华淼(图2)。
表 2 不同浓度芦笋茎枯病菌毒素浸根对芦笋根生长的影响Table 2. Effect of soaking in solutions containing varied concentrations of mycotoxin on growth of asparagus roots粗毒素原液与水体积比
Volume ratio of toxin to water根生长抑制率
The inhibition rate of root growth/%格兰德
Grande佳芦1号
Jialu No.1早佳1号
Zaojia No.1丰岛1号
Fengdao No.1华淼
HuamiaoTC UC157F2 1∶0 80.94a 73.72a 82.29a 71.77a 65.86a 69.39a 82.35a 7∶1 74.96b 68.58b 77.12b 67.99b 62.30b 64.60b 77.78b 3∶1 68.99c 64.56c 72.83c 63.02c 58.45c 60.95c 74.75c 1∶1 65.45d 60.85d 68.32d 58.61d 54.54d 55.60d 70.22d 1∶3 60.82e 57.12e 63.80e 53.59e 49.11e 50.54e 66.54e 1∶7 57.28f 55.10f 59.58f 46.00f 43.44f 46.61f 60.77f 2.3 芦笋茎枯病菌分生孢子悬浮液浸种法
芦笋茎枯病菌1.0×103、1.0×104、1.0×105个孢子·mL−1的分生孢子悬浮液浸种处理对供试7个芦笋品种的种子萌发均有较强的抑制作用,种子萌发率与对照相比均达显著水平。1.0×103、1.0×104、1.0×105个孢子·mL−1的分生孢子悬浮液浸种处理后格兰德和华淼种子萌发率差异均达显著水平。1.0×103、1.0×104个孢子·mL−1的分生孢子悬浮液浸种处理后对佳芦1号、早佳1号、丰岛1号和UC157F2的种子萌发率影响均不显著;1.0×104、1.0×105个孢子·mL−1的分生孢子悬浮液浸种处理对这4个品种种子萌发率差异影响也均不显著,而1.0×103、1.0×105个孢子·mL−1的分生孢子悬浮液浸种处理对这4个品种种子萌发率差异均达显著水平。1.0×103、1.0×104、1.0×105个孢子·mL−1的分生孢子悬浮液浸种处理对TC的种子萌发影响差异不显著。1.0×105个孢子·mL−1的分生孢子悬浮液浸种处理对格兰德、佳芦1号、早佳1号、丰岛1号、华淼、TC和UC157F2的种子萌发抑制率分别为:43.88%、40.97%、41.67%、32.87%、29.59%、28.52%和61.23%,供试的7个品种被分为感病、中感和中抗3个类型,感病品种为UC157F2;中感品种为格兰德、佳芦1号和早佳1号;中抗品种为TC、华淼和丰岛1号(表3、图3)。
表 3 不同浓度芦笋茎枯病菌分生孢子悬浮液浸种对芦笋种子萌发率的影响Table 3. Effect on germination rate of seeds soaked in varied P. asparagi spore suspensions分生孢子
悬浮液浓度
Concentration of
spore suspension
/(孢子·mL-1)种子萌发率
Germination rate of seed/%格兰德
Grande佳芦1号
Jialu
No.1早佳1号
Zaojia
No.1丰岛1号
Fengdao
No.1华淼
HuamiaoTC UC-
157F21.0×103 68.00b 68.00b 66.00b 73.33b 77.33b 80.00b 49.33b 1.0×104 60.67c 61.33bc 60.67bc 69.33bc 72.00c 72.00b 44.00bc 1.0×105 52.00d 56.67c 56.00c 62.67c 66.67d 68.67b 36.67c 0 (CK) 92.67a 96.00a 96.00a 93.33a 94.67a 96.00a 94.67a 2.4 芦笋茎枯病菌分生孢子悬浮液灌根法
用芦笋茎枯病菌1.0×103个孢子·mL−1的分生孢子悬浮液灌根处理,格兰德、佳芦1号、早佳1号、丰岛1号、华淼、TC和UC157F2的发病率分别为87.33%、84.67%、89.33%、88.00%、83.33%、82.00%和86.00%;用1.0×104、1.0×105个孢子·mL−1的分生孢子悬浮液灌根处理,供试芦笋品种发病率均达100%,不能有效区分供试品种的抗病性(图4)。
![]() 图 4 芦笋茎枯病菌1.0×103个孢子·mL−1孢子悬浮液灌根处理的发病结果A:TC对照;B:TC分生孢子悬浮液灌根;C:UC157F2对照;D:UC157F2分生孢子悬浮液灌根。Figure 4. Disease incident of asparagus plants with roots irrigated with 1.0×103P. asparagi spores·mL−1 suspensionA: TC control; B: TC roots irrigated with P. asparagi spore suspension; C: UC157F2 control; D: UC157F2 roots irrigated with P. asparagi spore suspension.
图 4 芦笋茎枯病菌1.0×103个孢子·mL−1孢子悬浮液灌根处理的发病结果A:TC对照;B:TC分生孢子悬浮液灌根;C:UC157F2对照;D:UC157F2分生孢子悬浮液灌根。Figure 4. Disease incident of asparagus plants with roots irrigated with 1.0×103P. asparagi spores·mL−1 suspensionA: TC control; B: TC roots irrigated with P. asparagi spore suspension; C: UC157F2 control; D: UC157F2 roots irrigated with P. asparagi spore suspension.2.5 田间自然诱发鉴定法
在田间自然诱发的情况下,供试品种格兰德、佳芦1号、早佳1号、丰岛1号、华淼、TC和UC157F2的发病率分别为18.83%、16.97%、20.57%、15.47%、14.93%、13.53%和32.93%。UC157F2最感病,发病率显著高于其他品种,其后依次为早佳1号、格兰德、佳芦1号、丰岛1号、华淼和TC。根据品种发病率差异水平,将供试的7个品种划分为感病、中感和中抗3个类型,感病品种为UC157F2;中感品种为早佳1号、格兰德、佳芦1号和丰岛1号;中抗品种为华淼和TC(图5)。
2.6 不同鉴定方法相关性分析
芦笋茎枯病菌毒素浸种法、毒素浸根法和分生孢子悬浮液浸种法均与田间自然诱发法在0.01水平上显著相关,其中分生孢子悬浮液浸种法与田间自然诱发法的相关系数最大,为0.761。孢子悬浮液灌根法与自然诱发法在0.05水平上显著相关,相关系数为0.540;孢子悬浮液灌根法与毒素浸种法、毒素浸根法、孢子悬浮液浸种法的相关性均不显著。芦笋茎枯病菌毒素浸种法、毒素浸根法和孢子悬浮液浸种法的鉴定结果均在0.01水平上显著相关(表4)。
表 4 不同鉴定方法的相关性Table 4. Correlation between evaluation methods for disease resistance of asparagus抗性鉴定方法
Resistance-identification
methods毒素浸种法
Soaking seed
with mycotoxin毒素浸根法
Soaking root
with mycotoxin分生孢子悬浮液浸种法
Soaking seed
with spore suspension分生孢子悬浮液灌根法
Irrigating root
with spore suspension自然诱发法
Field natural
induction method毒素浸种法
Soaking seed with mycotoxin1 0.768** 0.911** 0.267 0.703** 毒素浸根法
Soaking root with mycotoxin0.768** 1 0.682** 0.327 0.682** 分生孢子悬浮液浸种法
Soaking seed with spore suspension0.911** 0.682** 1 0.373 0.761** 分生孢子悬浮液灌根法
Irrigating root with spore suspension0.267 0.327 0.373 1 0.540* 田间自然诱发法
Field natural induction method0.703** 0.682** 0.761** 0.540* 1 **表示在0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关;*表示在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关。
** indicates significant correlation at P<0.01 (bilateral); * indicates significant correlation at P<0.05 (bilateral).3. 讨论与结论
芦笋茎枯病是芦笋生产上最主要的病害,造成芦笋产量和品质下降[14]。利用抗病品种是防治芦笋茎枯病的重要措施,而在抗病品种培育中,育种亲本、后代群体与新品种(系)的抗病性评判都依赖抗病性鉴定[15]。目前,国内外对芦笋茎枯病的抗病性缺乏系统性、持续性的研究。芦笋抗病性鉴定通常采用田间病圃自然诱发的方法,而田间温度、降雨、湿度等自然条件的变化会直接影响鉴定结果的准确性,且试验用地大、鉴定周期长、工作量大。因此,建立快速准确鉴定芦笋抗茎枯病的方法对筛选和利用抗性材料,培育抗病品种,有效防控芦笋茎枯病具有重要意义。
芦笋茎枯病菌毒素浸种法对芦笋种子的萌发率和出苗率有一定的影响,其中对早佳1号和UC157F2的种子萌发抑制率有较显著影响,对其他供试品种的种子萌发抑制率均在5%以下,这可能与芦笋种子有坚硬皮壳包裹,毒素难以接触胚芽有关。孙丽萍等[13]研究结果也表明,毒素浸种法不能有效鉴定烟草种质对赤星病的抗性。 丁燕芳等[16]研究表明用毒素浸种法鉴定烟草种质对黑胫病抗性简单灵活,可进行多批量的初期筛选,但需注意因种子质量问题(低发芽率)造成“假感病”现象,影响了毒素浸种法的判定效果。本研究采用病菌毒素对种子萌发抑制率评价供试品种的抗病性,消除了因种子质量差造成的“假感病”现象,但仍需注意种子皮壳厚度及坚硬程度对毒素浸种鉴定的影响,选择适宜的浸种时间。
毒素浸根法与田间病圃自然诱发法相比具有简单易行和不易受环境影响等特点[17]。本研究发现,芦笋根生长的抑制率与芦笋茎枯病菌毒素浓度成正比,毒素原液对所有供试芦笋品种根的生长抑制率均在65%以上,对有效区分品种的抗感性有一定的影响。贺红等[17]采用0.6×108 cfu·mL−1 的青枯菌液制备的毒素浸根处理广藿香植株,可较快表现出青枯病的症状,缩短抗病鉴定的过程。王铭等[18]研究表明毒素浸根法鉴定棉花抗黄萎病时最适毒素浓度为15 μg·mL−1,在此浓度下,毒素浸根法的鉴定结果与田间病圃法鉴定结果较一致。在烟草黑胫病抗性鉴定中,毒素浸根法可以初步鉴别抗、感病品种,但是存在不能区分中感和中抗烟草品种的缺陷[16]。棉花黄萎病菌和烟草青枯病菌都侵染寄主的维管束,病菌毒素通常具有较强的致病或致枯作用,病菌毒素处理后寄主快速表现病害症状。可见,毒素浸根法对病菌或毒素造成系统性病害的作物抗性鉴定比较适用,而毒素浓度是影响鉴定结果的关键因素。
本研究采用分生孢子悬浮液灌根处理,1.0×103个孢子·mL−1的分生孢子悬浮液处理下供试芦笋品种的发病率均在80%以上,而1.0×104个孢子·mL−1的分生孢子悬浮液处理下供试芦笋品种的发病率达100%,这种结果不能有效区分供试品种对茎枯病的抗病性。这与芦笋茎枯病菌具有较强的致病性有关,分生孢子悬浮液灌根后病菌孢子快速萌发侵染芦笋幼嫩的根和茎,迅速造成枯萎。周淼平等[19]采用纹枯病菌菌丝体悬浮液浸种小麦种子法测定了小麦对纹枯病的抗病性,鉴定结果与田间幼苗纹枯病抗性鉴定结果有较高的相关性,且操作简便,重复性好。兰海燕[20]认为通过向日葵种子与菌核共培养,根据种子皮壳对病原菌的抗病能力鉴定向日葵对菌核病抗性的方法准确率高,且在播种前即可在室内快速大量进行定向选择,该鉴定方法的生化依据是抗病种子的皮壳上酚的含量比不抗病的高2~3倍。本研究中,芦笋茎枯病菌分生孢子悬浮液浸种法与田间自然诱发法的抗病性鉴定结果相关系数为0.761,一致性较高,可以与田间自然诱发法相结合用于快速筛选芦笋抗茎枯病种质资源。
-
表 1 各连续性因素与土壤有机碳相关分析
Table 1 Correlation between continuity factors and SOC
指标
Index土壤有机碳
Soil organic carbon年均温
Annual average temperature年降水量
Annual precipitation坡度
Slope坡向
Slope orientation海拔
Altitude归一化植被指数
NDVI土壤有机碳 Soil organic carbon 1 年均温 Annual average temperature −0.333** 1 年降水量 Annual precipitation 0.380** −0.878** 1 坡度 Slope 0.138** −0.404** 0.387** 1 坡向 Slope orientation −0.044** 0.041** −0.062** −0.133** 1 海拔 Altitude 0.284** −0.868** 0.703** 0.477** 0.062** 1 归一化植被指数 NDVI 0.134** −0.398** 0.391** 0.381** −0.129** 0.317** 1 **表示在P <0.01级别相关性显著。
** indicates significant correlation at P<0.01.表 2 不同影响因子下的福建省耕地土壤有机碳含量分级
Table 2 Classification of SOC on farmland in Fujian under various affecting factors
分级分类
Graded
classification年均温
Annual
average
temperature/
℃年降水量
Annual
precipitation/
mm坡度
Slope/(°)坡向
Slope
orientation/
(°)海拔
Altitude/
m归一化
植被指数
NDVI气候类型
Climate
type地貌类型
Landform
type耕地利用类型
Cultivated land
use type土壤类型
Soil
type1 10.00~17.16 1041 ~1232 0~3 −1~2 1~112 −1~−0.09 中亚热带
Middle
subtropical zone平原台地
Plain platform灌溉水田
Irrigated
paddy fields水稻土
Paddy
soil2 17.16~17.95 1232 ~1338 3~5 2~6 112~244 −0.09~0.13 南亚热带
South
subtropical zone丘陵
Hill旱地
Dry land赤红壤
Lateritic
red soil3 17.95~18.73 1338 ~1438 5~8 6~18 244~376 0.13~0.35 小起伏山地
Small undulating
mountains望天田
Non-irrigated
paddy field红壤
Red earth4 18.73~19.51 1438 ~1531 8~12 18~50 376~508 0.35~0.57 中起伏山地
Medium undulating
mountain水浇地
Irrigated
land风砂土
Aeolian sandy soil5 19.51~20.29 1531 ~1644 12~17 50~134 508~639 0.57~1 大起伏山地
Great undulating
mountains菜地
Vegetable
field滨海盐土
Coastal saline
soil6 20.29~21.08 1644 ~184817~60 134~360 639~ 1348 潮土
Tidal
soil7 >21.08 黄壤
Yellow
soil8 紫色土
Purple
soil9 石灰土
Limestone
soil根据最优参数地理探测器计算结果,年均温、海拔和NDVI采用标准差分类法,分为7类、6类和5类;年降水量采用自然间距分类法,分为6类;坡度采用分位数分类法,分为6类;坡向采用几何间隔分类法,分为6类。
According to calculation results of optimal geographic detector parameters, annual average temperature, altitude, and NDVI are classified using standard deviation classification method, which is divided into 7 categories, 6 categories, and 5 categories, respectively; annual precipitation is classified into 6 categories using natural interval classification method; slope is classified into 6 categories using quantile classification method; slope orientation adopts geometric interval classification method, which is divided into 6 categories.表 3 气候因素对土壤有机碳的影响
Table 3 Impact of climate factors on SOC
指标
Index等级
Grade样点数量
Number of
sample points土壤有机碳
Soil organic carbon/(g·kg−1)标准差
Standard deviation/
(g·kg−1)变异系数
Coefficient of
variation/%最小值
Minimum value最大值
Maximum value平均值
Average value年均温
Annual average
temperature/ ℃10.00≤年均温
Annual average temperature<17.163337 0.17 50.69 17.74 7.35 41.43 17.16≤年均温
Annual average temperature<17.952934 1.28 43.44 17.41 5.59 32.10 17.95≤年均温
Annual average temperature<18.735883 1.39 43.15 17.46 5.55 31.79 18.73≤年均温
Annual average temperature<19.515857 0.12 67.28 17.07 6.16 36.09 19.51≤年均温
Annual average temperature<20.294838 0.58 43.85 16.66 6.04 36.25 20.29≤年均温
Annual average temperature<21.085428 0.19 37.12 11.79 5.48 46.48 21.08≤年均温
Annual average temperature3082 0.20 32.89 10.57 4.99 47.21 年降水量
Annual
precipitation/mm1041 ≤年降水量
Annual precipitation<1232 5598 0.19 35.50 10.56 4.50 42.61 1232 ≤年降水量
Annual precipitation<1338 3720 0.58 62.93 13.64 5.87 43.04 1338 ≤年降水量
Annual precipitation<1438 5165 0.12 41.76 16.61 5.77 34.74 1438 ≤年降水量
Annual precipitation<1531 6552 1.16 43.85 17.06 5.56 32.59 1531 ≤年降水量
Annual precipitation<1644 8094 0.17 67.28 17.69 6.14 34.71 1644 ≤年降水量
Annual precipitation<18482230 2.38 50.69 17.70 8.02 45.31 气候类型
Climate type中亚热带
Middle subtropical zone21274 0.17 67.28 17.27 6.14 35.56 南亚热带
South subtropical zone10085 0.12 39.61 12.17 5.73 47.08 表 4 不同土壤类型、耕地利用和地貌类型下的土壤有机碳分布
Table 4 Effects of soil types, farmland use, and landform types on SOC
指标
Index类型
Type样点数量
Number of
sample points土壤有机碳
Soil organic carbon/(g·kg−1)标准差
Standard deviation/
(g·kg−1)变异系数
Coefficient of
variation/%最小值
Minimum value最大值
Maximum value平均值
Average value土壤类型
Soil type水稻土
Paddy soil27997 0.12 67.28 16.16 6.28 39.86 赤红壤
Lateritic red soil1831 0.58 30.80 9.72 4.72 48.56 红壤
Red earth912 1.22 43.85 15.68 6.56 41.84 风砂土
Aeolian sandy soil225 0.58 21.27 5.31 3.56 67.04 滨海盐土
Coastal saline soil175 0.99 27.20 7.91 5.10 64.48 潮土
Tidal soil108 1.80 30.97 11.56 5.55 48.01 黄壤
Yellow soil79 3.60 49.36 17.06 8.96 52.52 紫色土
Purple soil32 6.90 31.15 15.92 5.19 32.60 耕地利用类型
Cultivated land use type灌溉水田
Irrigated paddy fields23936 0.12 67.28 16.21 6.30 38.86 旱地
Dry land3434 0.58 50.69 11.64 6.58 56.53 望天田
Non-irrigated paddy field3288 0.17 42.92 16.57 5.75 34.70 水浇地
Irrigated land552 1.39 38.80 10.74 5.58 51.96 菜地
Vegetable field149 1.69 34.80 11.35 6.42 56.56 地貌类型
Landform type平原台地
Plain platform6942 0.19 50.11 12.36 6.44 52.10 丘陵
Hill8377 0.45 67.28 16.46 6.44 39.13 小起伏山地
Small undulating mountains14921 0.12 62.93 16.63 6.04 36.32 中起伏山地
Medium undulating mountain1119 1.39 38.34 16.39 5.74 35.02 表 5 地形因素对土壤有机碳的影响
Table 5 Impact of terrain factors on SOC
指标
Index等级
Grade样点数量
Number of sample points土壤有机碳
Soil organic carbon/(g·kg−1)标准差
Standard
deviation/(g·kg−1)变异系数
Coefficient of
variation/%最小值
Minimum value最大值
Maximum value平均值
Average value坡度
Slope/(°)0≤坡度 Slope <3 5243 0.41 67.28 13.60 6.52 47.94 3≤坡度 Slope <5 5218 0.19 43.85 14.57 6.77 46.46 5≤坡度 Slope <8 5213 0.58 49.88 15.93 6.54 41.05 8≤坡度 Slope <12 5217 0.93 45.19 16.41 6.22 37.90 12≤坡度 Slope <17 5241 1.39 49.36 16.69 6.06 36.31 17≤坡度 Slope≤60 5227 0.12 62.93 16.58 6.04 36.43 坡向
Slope orientation /(°)−1≤坡向 Slope orientation <2 391 1.16 50.69 14.54 6.84 47.04 2≤坡向 Slope orientation <6 309 2.73 38.74 16.21 6.20 38.25 6≤坡向 Slope orientation <18 956 1.10 41.18 15.31 6.18 40.37 18≤坡向 Slope orientation <50 3376 0.99 50.11 16.10 6.56 40.75 50≤坡向 Slope orientation≤134 9924 0.20 62.93 15.99 6.43 40.21 134≤坡向 Slope orientation≤360 16403 0.12 67.28 15.35 6.47 42.15 海拔 Altitude/m 1≤海拔 Altitude<112 9598 0.19 43.85 11.87 5.73 48.27 112≤海拔 Altitude<244 5080 1.16 67.28 17.41 6.29 36.13 244≤海拔 Altitude<376 5341 1.28 62.93 17.33 5.51 31.79 376≤海拔 Altitude<508 4197 0.12 43.44 16.87 5.56 32.96 508≤海拔 Altitude<639 2932 0.17 42.75 17.20 5.75 33.43 639≤海拔 Altitude≤ 1348 4211 2.20 50.69 17.56 7.07 40.26 -
[1] 王兴, 钟泽坤, 王佳懿, 等. 黄土高原撂荒草地土壤碳库对两年增温增雨的响应 [J]. 土壤学报, 2023, 60(2):523−534. WANG X, ZHONG Z K, WANG J Y, et al. Responses of soil carbon pool of abandoned grassland on the Loess Plateau to two-years warming and increased precipitation [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2023, 60(2): 523−534. (in Chinese)
[2] 李园园, 王蕾, 刘琪璟, 等. 新疆喀纳斯自然保护区森林碳储量及碳密度变化 [J]. 干旱区研究, 2019, 36(5):1136−1145. LI Y Y, WANG L, LIU Q J, et al. Changes of carbon storage and carbon density of forests in the kanas national nature reserve, Xinjiang [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2019, 36(5): 1136−1145. (in Chinese)
[3] 张维理, KOLBE H, 张认连. 土壤有机碳作用及转化机制研究进展 [J]. 中国农业科学, 2020, 53(2):317−331. DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2020.02.007 ZHANG W L, KOLBE H, ZHANG R L. Research progress of SOC functions and transformation mechanisms [J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2020, 53(2): 317−331. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2020.02.007
[4] WANG S, ZHUANG Q L, JIA S H, et al. Spatial variations of soil organic carbon stocks in a coastal hilly area of China [J]. Geoderma, 2018, 314: 8−19. DOI: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.10.052
[5] LI Q Q, ZHANG H, JIANG X Y, et al. Spatially distributed modeling of soil organic carbon across China with improved accuracy [J]. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, 2017, 9(2): 1167−1185. DOI: 10.1002/2016MS000827
[6] TENG M J, ZENG L X, XIAO W F, et al. Spatial variability of soil organic carbon in Three Gorges Reservoir area, China [J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 599/600: 1308−1316. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.085
[7] MA H H, PENG M, YANG Z, et al. Spatial distribution and driving factors of soil organic carbon in the Northeast China Plain: Insights from latest monitoring data [J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2024, 911: 168602. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.168602
[8] 李艾雯, 冉敏, 宋靓颖, 等. 四川盆地耕地表层土壤有机碳含量空间分布特征及其影响因素 [J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2023, 32(5):1102−1112. LI A W, RAN M, SONG L Y, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of cropland topsoil organic carbon content in the Sichuan Basin [J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2023, 32(5): 1102−1112. (in Chinese)
[9] 张勇, 史学正, 赵永存, 等. 滇黔桂地区土壤有机碳储量与影响因素研究 [J]. 环境科学, 2008, 29(8):2314−2319. ZHANG Y, SHI X Z, ZHAO Y C, et al. Estimates and affecting factors of soil organic carbon storages in Yunnan-Guizhou-guangxi region of China [J]. Environmental Science, 2008, 29(8): 2314−2319. (in Chinese)
[10] SUN T, TONG W J, CHANG N J, et al. Estimation of soil organic carbon stock and its controlling factors in cropland of Yunnan Province, China [J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2022, 21(5): 1475−1487. DOI: 10.1016/S2095-3119(21)63620-1
[11] LUO Y L, WANG K, LI H X, et al. Application of a combinatorial approach for soil organic carbon mapping in hills [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 300: 113718. DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113718
[12] BAI Y X, ZHOU Y C. The main factors controlling spatial variability of soil organic carbon in a small Karst watershed, Guizhou Province, China [J]. Geoderma, 2020, 357: 113938. DOI: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.113938
[13] 程金, 黄文卿, 张世昌, 等. 福建省表层土壤有机碳密度空间分布及影响因素分析 [J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2023, 40(4):805−816. CHENG J, HUANG W Q, ZHANG S C, et al. Spatial distribution and influencing factors of topsoil organic carbon density in Fujian Province, China [J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2023, 40(4): 805−816. (in Chinese)
[14] ZHAO B H, LI Z B, LI P, et al. Spatial distribution of soil organic carbon and its influencing factors under the condition of ecological construction in a hilly-gully watershed of the Loess Plateau, China [J]. Geoderma, 2017, 296: 10−17. DOI: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.02.010
[15] 林景亮. 福建土壤[M]. 福州: 福建科学技术出版社, 1991. [16] 国土资源部. 国土资源部关于印发试行《土地分类》的通知[L]. 2001-08-21. [17] 陈中星, 张楠, 张黎明, 等. 福建省土壤有机碳储量估算的尺度效应研究 [J]. 土壤学报, 2018, 55(3):606−619. CHEN Z X, ZHANG N, ZHANG L M, et al. Scale effects of estimation of soil organic carbon storage in Fujian Province, China [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2018, 55(3): 606−619. (in Chinese)
[18] 姚彩燕, 刘绍贵, 乔婷, 等. 基于时空变异的旱地土壤有机碳高效采样策略研究 [J]. 土壤学报, 2021, 58(3):638−648. YAO C Y, LIU S G, QIAO T, et al. Strategy for efficient sampling of upland soil based on spatiotemporal variation of the soil [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2021, 58(3): 638−648. (in Chinese)
[19] PENG S Z, DING Y X, LIU W Z, et al. 1 km monthly temperature and precipitation dataset for China from 1901 to 2017 [J]. Earth System Science Data, 2019, 11(4): 1931−1946. DOI: 10.5194/essd-11-1931-2019
[20] 金林, 李研. 几种相关系数辨析及其在R语言中的实现 [J]. 统计与信息论坛, 2019, 34(4):3−11. JIN L, LI Y. Discrimination of several correlation coefficients and their implementation in R software [J]. Statistics & Information Forum, 2019, 34(4): 3−11. (in Chinese)
[21] BREIMAN L. Random forests [J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45: 5−32. DOI: 10.1023/A:1010933404324
[22] LIAW A, WIENER M. Classification and regression by randomForest [J]. R news, 2002, 2(3): 18−22.
[23] WANG J F, LI X H, CHRISTAKOS G, et al. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun region, China [J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2010, 24(1): 107−127. DOI: 10.1080/13658810802443457
[24] 王劲峰, 徐成东. 地理探测器: 原理与展望 [J]. 地理学报, 2017, 72(1):116−134. WANG J F, XU C D. Geodetector: Principle and prospective [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2017, 72(1): 116−134. (in Chinese)
[25] SONG Y Z, WANG J F, GE Y, et al. An optimal parameters-based geographical detector model enhances geographic characteristics of explanatory variables for spatial heterogeneity analysis: Cases with different types of spatial data [J]. GIScience & Remote Sensing, 2020, 57(5): 593−610.
[26] LI Q Q, YUE T X, WANG C Q, et al. Spatially distributed modeling of soil organic matter across China: An application of artificial neural network approach [J]. CATENA, 2013, 104: 210−218. DOI: 10.1016/j.catena.2012.11.012
[27] JIANG R, WU P, SONG Y Z, et al. Factors influencing the adoption of renewable energy in the U. S. residential sector: An optimal parameters-based geographical detector approach [J]. Renewable Energy, 2022, 201: 450−461. DOI: 10.1016/j.renene.2022.09.084
[28] JENKINSON D S, ADAMS D E, WILD A. Model estimates of CO2 emissions from soil in response to global warming [J]. Nature, 1991, 351: 304−306. DOI: 10.1038/351304a0
[29] REYNA-BOWEN L, LASOTA J, VERA-MONTENEGRO L, et al. Distribution and factors influencing organic carbon stock in mountain soils in Babia góra National Park, Poland [J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(15): 3070. DOI: 10.3390/app9153070
[30] DAVIDSON E A, JANSSENS I A. Temperature sensitivity of soil carbon decomposition and feedbacks to climate change [J]. Nature, 2006, 440: 165−173. DOI: 10.1038/nature04514
[31] 丰思捷, 赵艳云, 李元恒, 等. 内蒙古典型草原表层土壤有机碳储量差异及影响因素 [J]. 中国草地学报, 2019, 41(2):116−120. FENG S J, ZHAO Y Y, LI Y H, et al. The differences and influencing factors of topsoil organic carbon storage in typical steppe of inner Mongolia [J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2019, 41(2): 116−120. (in Chinese)
[32] 周晓宇, 张称意, 郭广芬. 气候变化对森林土壤有机碳贮藏影响的研究进展 [J]. 应用生态学报, 2010, 21(7):1867−1874. ZHOU X Y, ZHANG C Y, GUO G F. Effects of climate change on forest soil organic carbon storage: A review [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2010, 21(7): 1867−1874. (in Chinese)
[33] ZHANG X F, ADAMOWSKI J F, LIU C F, et al. Which slope aspect and gradient provides the best afforestation-driven soil carbon sequestration on the China’s Loess Plateau? [J]. Ecological Engineering, 2020, 147: 105782. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2020.105782
[34] 丁金梅, 王维珍, 米文宝, 等. 宁夏草地土壤有机碳空间特征及其影响因素 [J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43(5):1913−1922. DING J M, WANG W Z, MI W B, et al. Spatial characteristics of soil organic carbon in grassland of Ningxia and its influencing factors [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43(5): 1913−1922. (in Chinese)
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(2)








 下载:
下载: