Regulating JsTPS Promoters by JsMYB108 and JsMYB305 in Jasminum sambac
-
摘要:目的 探明茉莉香气合成相关转录因子JsMYB108和JsMYB305对3个萜烯合成酶基因JsTPS启动子的调控机制。方法 以茉莉叶片DNA为模板,采用染色体步移法克隆3个JsTPS基因的启动子片段,预测启动子序列顺式作用元件,并在此基础上将3个JsTPS基因启动子片段分别构建到报告载体pGWB433,单独转化烟草叶片或与pK7FWG2.0-JsMYB108、pK7FWG2.0-JsMYB305效应载体共同转化烟草叶片以检测JsMYB108和JsMYB305对3个TPS基因启动子的激活作用;同时,通过酵母单杂交实验进一步检验JsMYB108和JsMYB305与3个TPS基因启动子的结合作用。结果 克隆了3个JsTPS基因启动子片段,长度分别为 1 357、1 849、1 005 bp。这些序列中均含MYB识别位点,不同启动子序列包含不同顺式作用元件,如光反应元件、损伤响应元件、脱落酸诱导顺式作用元件等;叶片GUS染色和GUS活性检测结果显示3个JsTPS基因启动子片段均具有启动活性且JsMYB108和JsMYB305能不同程度地激活3个TPS基因启动子活性。JsMYB108使JsTPS1、JsTPS3、JsTPS4启动子活性增强至对照的1.96倍、6.47倍和4.15倍;JsMYB305使JsTPS1、JsTPS3、JsTPS4启动子活性增强至对照的1.57倍、15.18倍和3.12倍;酵母单杂交结果显示JsMYB108和JsMYB305能与JsTPS1、JsTPS3和JsTPS4启动子结合。结论 JsMYB108和JsMYB305可以不同程度激活JsTPS基因启动子活性,推测这2个转录因子在茉莉花萜烯香气合成和代谢过程具有一定作用。Abstract:Objective Regulation functions of JsMYB108 and JsMYB305 on the promoters of three terpene synthase genes (TPSs) relating to the aroma synthesis of jasmine were analyzed.Method The promoter fragments of JsTPSs were cloned by genome walking with the DNA of jasmine leaves as template to determine the sequences of the cis-acting elements in them. The fragments were constructed separately in the reporter vector pGWB433. Then, tobacco leaves were transformed with the reporter vector alone or with pK7FWG2.0-JsMYB108 and pK7FWG2.0-JsMYB305 effect vectors to detect the activation of JsMYB108 and JsMYB305 on the promoters. Binding of JsMYB108 and JsMYB305 to the promoters was verified by the yeast one-hybrid assay.Result The cloned promoter fragments of the three JsTPSs were 1 357 bp, 1 849 bp, and 1 005 bp with MYB recognition sites. The elements relating to light response, damage response, and abscisic acid induced cis-acting were predicted in different promoter sequences. The GUS staining and activity detection in tobacco leaves confirmed varying degrees of activity of the fragments by introducing JsMYB108 and JsMYB305. Comparing to control, JsMYB108 expanded the activities 1.96-fold on the promoter of JsTPS1, 6.47-fold on that of JsTPS3, and 4.15-fold on that of JsTPS4, while JsMYB305 did 1.57-fold, 15.18-fold, and 3.12-fold, respectively. The yeast one-hybrid assay further verified the bindings of JsMYB108 and JsMYB305 to JsTPS1, JsTPS3, and JsTPS4.Conclusion JsMYB108 and JsMYB305 could activate the promoters of JsTPS1, JsTPS3, andJsTPS4. These two transcription factors might play a key role in the synthesis and metabolism of aromatic terpenes in jasmine flowers.
-
Keywords:
- Jasminum sambac /
- transcription factors /
- TPS /
- promoter /
- regulation
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】茉莉花[Jasminum sambac (L.) Aiton]为木樨科(Oleaceae)素馨属(Jasminum)常绿灌木,现广泛植栽于亚热带地区[1],用于园林观赏、茉莉花茶窨制、香精香料制作及化妆品、食品添加等方面[2]。我国是世界上茉莉花产量最多的国家,栽培总面积占世界三分之二,年产量占世界总产量一半以上,因此茉莉花在我国南方农村经济发展中有着重要意义[3]。与南亚及东南亚国家茉莉花主要用于精油生产不同,我国茉莉鲜花基本上用于花茶生产,优质茉莉花茶每公斤原料需配 1.0~1.3 kg茉莉花,窨花配量的增加不仅大大提高了成本,也制约了增产提质工艺的优化,因此高香浓香型茉莉花的需求十分迫切。种质创新进程的缓慢导致茉莉花现有品种不多,栽培品种主要是单瓣茉莉和双瓣茉莉,双瓣茉莉因抗性强、易栽培、产量高,是目前生产上栽种面积最大的品种。为了明确茉莉花的香气形成规律及调控因素,探讨提高鲜花质量的技术措施,多年来科技工作者进行了诸多研究,但对起调控作用的关键分子及其作用方式的揭示一直未有突破。【前人研究进展】茉莉花挥发性香气主要为单萜、倍半萜、苯环类/苯丙烷类,以及其他微量物质如挥发性脂肪衍生物,其中,萜烯类物质为茉莉花香气中最多的一大类[4−7]。萜烯合成酶(Terpene synthase, TPS)处于萜类代谢途径下游,以香叶基焦磷酸(geranyl pyrophosphate,GPP)、橙花基焦磷酸(neryl pyrophosphate,NPP)、法尼基焦磷酸(farnesyl pyrophosphate,FPP)、香叶基香叶基焦磷酸(geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate,GGPP)为直接前体合成数量庞大、结构丰富的各种萜类化合物,是萜类代谢途径限速酶。TPS包括单萜合成酶、倍半萜合成酶和二萜合成酶等,是萜类生物合成过程中研究最多和最深入的酶类[8]。植物MYB转录因子是一大基因家族编码的调控因子,根据其蛋白序列及其作用分为29个亚族。它们广泛参与植物的生长发育、激素作用、抗性生理、细胞代谢活动以及次生代谢产物合成等基因调节网络[9]。如拟南芥花发育过程中,两个R2R3MYB转录因子MYB21和MYB24能够上调大多数花中(E)-β-石竹烯[(E)-β-caryophyllene]倍半萜合酶 TPS21 基因的表达[10]。在松柏科植物的防御反应中MYB14优先通过 MVA 途径和茉莉酸代谢调控挥发性萜类化合物生物合成[11]。酵母单杂交试验表明在桂花中OfMYB1调节OfPAL基因的表达,随后又证实OfWRKY3与OfCCD4 启动子互作,正调控其表达[12, 13]。这些研究都表明MYB转录因子在参与挥发性萜类代谢中具有重要的作用,然而MYB转录因子对于单萜类,倍半萜类合成途径以及萜烯类香气成分的调控方面的研究十分匮乏。【本研究的切入点】在茉莉中,我们前期通过转录组筛选、基因表达模式分析、亚细胞定位、烟草瞬时转化、酵母转化测定产物、酶学特征反应等锁定了3个和单萜和倍半萜合成相关的TPS基因,分别命名为JsTPS1、JsTPS3、JsTPS4(GenBank 登录号MW057921、MW057923、MW057924),其中JsTPS4为单萜合成酶,JsTPS1和JsTPS3为倍半萜合成酶(另文发表)。同时,前期研究结果显示JsMYB305和JsMYB108转录因子可以对茉莉茎段愈伤组织中3个JsTPS基因进行转录激活[14]。【拟解决的关键问题】深入研究这两个转录因子对3个TPS基因的调控作用,进一步分离3个TPS基因的启动子,并利用烟草瞬时转化系统和酵母单杂交系统进行研究,以期为深入探索JsMYB305和JsMYB108对JsTPS基因以及茉莉萜烯合成途径的调控奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 植物材料
以三年生双瓣茉莉植株为供试材料,栽培基质为泥碳∶蛭石:珍珠岩= 7 ∶ 3 ∶ 0.5(体积比)。盆栽茉莉种植于人工气候室,温度26 ℃/22 ℃(昼/夜),光周期为16 h/8 h(昼/夜),湿度为70%。GUS活性检测时,使用生长了4~6片叶片的本氏烟草(Nicotiana benthamiana)。本氏烟草种植于人工气候室,光周期为16 h/8 h(昼/夜),温度为26 ℃/22 ℃(昼/夜)。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 茉莉3个JsTPS基因启动子克隆及顺式作用元件分析
将JsTPS1、JsTPS3、JsTPS4的CDS序列在双瓣茉莉基因组中(本课题组测序)进行本地BLAST,获得了JsTPS3、JsTPS4基因的启动子序列,后续设计特异性引物(表1)对JsTPS3、JsTPS4基因的启动子序列进行PCR验证。
表 1 引物序列Table 1. Sequences of primers applied引物名称
Primer name引物序列(5′- 3′)
Primer sequences (5′- 3′)用途
UsageJsTPS1DNA-F ATGGGCAGCCAAGTTTATGCATC 扩增 DNA 序列
DNA amplificationJsTPS1DNA-R GAGATAGGGTTGTGGAACGCTA JsTPS1-GW-GSP1 ATTGTGCGAAGGTCCTCGTTTTGCTTGTAA 扩增启动子序列
Promoter sequence amplificationJsTPS1-GW-GSP2 GTTACGGAGCGTCGAGCAACTTCAATGC JsTPS1-PRO-F TTTCATAGGGAAATTGGTGC 验证启动子序列 JsTPS1-PRO-R TTATATCTAATCAAATGCTTCTAGC Confirming promoter sequence JsTPS3-PRO-F ATGACAAGGTATTAATGCTTGGCG JsTPS3-PRO-R TCTTGATATGTATTACTAGTAATTTAACAAC JsTPS4-PRO-F GTGATATTGATTCCAAATCTGGTC JsTPS4-PRO-R GATAACAAGTAAAACGGAAAATCAGG pAbAi-proJsTPS1-F AATTCGAGCTCGGTACCCGGGCACATTCAAGCTTGAAATACCGG 扩增酵母单杂启动子片段 pAbAi-proJsTPS1-R ATACAGAGCACATGCCTCGAGCAAGCGCATGTAAACGCTAGAC Amplification of promoter sequence
for yeast one hybridpAbAi-proJsTPS3-F AATTCGAGCTCGGTACCCGGGTGCATTTGGATGTAACATTAAAATCA pAbAi-proJsTPS3-R ATACAGAGCACAATGCCTCGAGGTCACATCATGGTTGTGACGAACA pAbAi-proJsTPS4-F AATTCGAGCTCGGTACCCGGGGCCGCCATAAGAAAATTCGG pAbAi-proJsTPS4-R ATACAGAGCACATGCCTCGAGGCTCGTGTACTACATATCGTTTATTAATTAC pAbAi-F GTTCCTTATATGTAGCTTTCGACA 验证上游片段-pAbAi pAbAi-R CCATCTCGAAAAAGGGTTTGCC Confirming cloning sequence in –pABAi vector pGADT7-JsMYB108-F gtaccagattacgctcatatgATGGAGCATCATGTTAAAGGAGATG 构建pGADT7-JsMYBs
Construction of pGADT7-JsMYBs vectorspGADT7-JsMYB108-R cagctcgagctcgatggatccCTACTGTTGTAGGAAATTCCACATGTC pGADT7-JsMYB305-F gtaccagattacgctcatatgATGGACAAGAAAATATGCAATAGCTC pGADT7-JsMYB305-R cagctcgagctcgatggatccTTAATCCCCATTAAGTAACTGGATGG pGADT7-F TAATACGACTCACTATAGGG 验证pGADT7-JsMYBs pGADT7-R AGATGGTGCACGATGCACAG Confirming the construction of
pGADT7-JsMYBs vectorsJsTPS1基因先根据CDS序列设计特异性引物扩增DNA片段,再根据DNA片段设计用于启动子克隆的JsTPS1-GW-GSP1(表1)进行扩增。方法参照Universal Genome Walker™ 2.0 User Manual(Clonetech)试剂盒,以试剂盒中的简并引物 AP1、AP2为上游引物分别和根据获得的DNA序列分别设计的GSP引物进行2轮巢式PCR ,回收目的条带连接至pEASY-T5 Zero 克隆载体(北京全式金),热激法转化大肠杆菌DH5α感受态细胞,菌液PCR验证后将阳性菌液送往铂尚生物技术(福州)有限公司测序。
根据测序结果设计引物用以验证启动子序列(表1),将获得的JsTPS1、JsTPS3和JsTPS4基因启动子序列,用PlantCARE(http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be /webtools/plantcare/html/)对克隆得到的序列进行顺式作用元件分析。
1.2.2 构建3个JsTPS基因启动子的报告载体
将PCR扩增大小无误后的目的片段进行产物回收(AxyPrepTMPCR Gel-CleanUp Kit),将纯化回收后的PCR产物与克隆载体相连(Zero BluntTMTOPOTM PCR Cloning Kit, Invitrogen),随后与TOPO入门载体(PENTR/SD/D-TOPO, Invitrogen)相连,转化,菌落验证,测序。将测序无误的TOPO-proJsTPSs进行质粒提取(Omega)后与pGWB433报告载体进行LR反应,体系包含150 ng TOPO-proJsTPSs载体,150 ng pGWB433,加H2O至8 μL,再加入2 μL LR ClonaseTM II Enzyme mix(Invitrogen),轻微涡旋后在25 ℃下反应1 h,加入1 μL Proteinase K solution 37 ℃反应10 min终止反应。将反应产物转化到大肠杆菌DH5α感受态细胞,挑取单克隆进行PCR鉴定,将阳性菌液送铂尚公司测序。将测序正确的pGWB433-proJsTPS1、pGWB433-proJsTPS3、pGWB433-proJsTPS4分别通过冻融法转入农杆菌GV3101 株系(实验室保存),PCR检测无误后备用。
1.2.3 烟草叶片瞬时表达
将长至四周左右生长健壮的本氏烟草用于瞬时表达试验。取适量保存的含pGWB433-proJsTPS1::GUS、pGWB433-proJsTPS3::GUS、pGWB433-proJsTPS4::GUS、pK7FWG2.0-JsMYB108、pK7FWG2.0-JsMYB305 质粒的农杆菌于10 mL LB液体培养基(含50 mg· L−1 Gen、50 mg·L−1 Rif、50 mg·L−1 Spec),28 ℃,200 r·min−1 振荡培养过夜,再取出适量菌液接种于50 mL LB液体培养基中于28 ℃、200 r·min−1振荡培养至OD600值为0.8~1.0。将菌液5 000 r·min−1离心10 min收集菌体,加入重悬液(1/2MS + 200 μmol·L−1 AS + 10 mmol·L−1 MES),暗培养3 h 之后,轻轻摇匀菌液,用10 mL无菌注射器吸取菌液,去掉针头,用注射口贴住叶背面,轻柔地注入菌液,直到肉眼观察到菌液完全浸染整个烟草叶片,吸干净叶片表面沾染的菌液,将浸染的叶片做好标记,暗培养 24~30 h后取样。以单独注射3个pGWB433-proJsTPS农杆菌的烟草 用以检测启动子活性。将pK7FWG2.0-JsMYB108,pK7FWG2.0-JsMYB305分别与3个pGWB433-proJsTPS共注射的烟草用以检测JsMYB108和JsMYB305对3个TPS基因启动子的激活作用。同时以注射含报告载体和空效应载体的农杆菌为阴性对照。以注射 pGWB433::GUS 叶片作为阳性对照。每个处理重复3次(每个处理设置的重复注射在不同植株的不同叶片上)。
1.2.4 烟草叶片GUS组织化学染色
用剪刀剪下暗处理48 h的烟草叶片,置于15 mL EP管中,根据 GUS 染色试剂盒(北京中科瑞泰生物科技有限公司)配置染液。并加入GUS 染色液直至彻底浸没植物组织,用锡箔纸包住,放入37 ℃恒温培养箱孵育过夜。次日去除 GUS 染色液,在离心管中加入75% 无水乙醇浸泡脱色,期间更换数次无水乙醇,直到叶片偏白为止,用Leica体式荧光显微镜(Leica M205 FA)拍照记录。
1.2.5 烟草叶片GUS活性检测
将注射后2 d的烟草叶片剪下用液氮研磨成粉状,加入1 mL GUS 酶提取液混匀。12 000 r·min−1、4 ℃ 离心10 min,上清即为GUS蛋白液,4 ℃保存。采用BIO-Rad蛋白浓度测定试剂盒(北京伯乐生物科技有限公司)法进行蛋白定量。GUS活性检测采用试剂盒[MarkerGene TM β-Glucuronidase (GUS) Reporter Gene Activity Detection Kit],结果以生成的4-MU的量与总蛋白含量和时间的比值(pmol·mg−1·min−1)表示。
1.2.6 上游目的片段诱饵载体的构建
基于已克隆出的TPS基因启动子序列,在MYB顺式元件附近截取200~250 bp 长度的片段设计引物(表1)。以pGWB433-proJsTPSs质粒为模板,进行启动子片段扩增,利用 Sma I和 Xho I 酶(赛默飞世尔科技公司)将pAbAi 诱饵载体酶切,使其打开为线型分子。使用pEASY-Basic Seamless Cloning and Assembly Kit(北京全式金生物科技有限公司)将启动子片段连接到线性化的pAbAi 载体上,反应体系和反应条件参照说明书。转化大肠杆菌DH5α,涂布于Amp筛选培养基37 ℃恒温培养箱过夜培养。随后挑取单克隆进行PCR检测,将阳性菌液送铂尚生物技术有限公司测序后提取质粒。
1.2.7 酵母单杂交自激活检测
利用Bstb I限制酶线性化pAbAi-JsTPSs重组质粒,纯化酶切后的片段将转化至酵母菌株Y1H-Gold,涂布于SD/-Ura(Coolaber)平板28 ℃恒温培养箱培养2~3 d。挑取单克隆,利用Matchmarker Insert Check PCR Mix I(Takara)进行PCR,检测上游片段-pAbAi重组质粒是否插入Y1H基因组中 ,将PCR鉴定阳性的单克隆在SD/-Ura培养基上进行划线,然后挑取单克隆置于SD/-Ura液体培养基中28 ℃、 200 r·min−1振荡过夜培养,将菌液OD600调至0.02,再稀释10倍和100倍,分别吸取5 μL点板至AbA(AureobasidinA, Coolaber)质量浓度为200 、250 、300、400、500、800 ng·mL−1的SD/-Ura平板,用于筛选合适的AbA浓度。酵母转化使用PEG/LiAc法,具体步骤参照Clontech产品使用手册。
1.2.8 酵母单杂交验证JsMYB108、JsMYB305与JsTPS的互作
根据已扩增出的JsMYB108和JsMYB305编码序列,设计特异性引物,进行PCR扩增,纯化PCR产物,与经Nde I和BamH I(赛默飞世尔科技公司)酶切后的pGADT7载体采用pEASY-Basic Seamless Cloning and Assembly Kit相连,引物序列见表1。将检测为阳性的酵母诱饵菌株Y1H-Gold[上游片段-pAbAi]制成酵母感受态,通过共转化的方法,将PGADT7-JsMYB108、PGADT7-JsMYB305质粒转入酵母感受态中,涂板于SD/-Leu/-Ura 平板28 ℃恒温培养箱培养2~3 d。挑取单克隆于SD/-Leu/-Ura 液体培养基28 ℃、200 r·min−1摇床过夜培养,而后将OD600调至均一后,分别稀释10倍、100倍、
1000 倍进行培养观察。2. 结果与分析
2.1 茉莉3个TPS基因启动子克隆
JsTPS3和JsTPS4启动子序列通过基因组序列直接设计引物扩增获得。JsTPS1基因用简并引物AP1与JsTPS1-GW-GSP1引物扩增获得约
1500 bp 片段。最后根据3个JsTPS基因的启动子序列,设计引物进行验证,获得了长度分别为1357 、1849、1005 bp的序列。2.2 pGWB433-proJsTPSs报告载体的构建及转化
将扩增的茉莉JsTPS1、JsTPS3和JsTPS4基因启动子的产物进行菌液PCR检测,获得片段长度与预期一致,说明报告载体pGWB433-proJsTPSs已成功构建。测序正确后提取重组质粒,并转化农杆菌GV3101株系,经PCR检测,片段大小无误,表明重组质粒已成功转化农杆菌GV3101。
2.3 茉莉JsTPS1、JsTPS3、JsTPS4基因启动子顺式作用元件分析
3个JsTPS基因启动子序列中均含有典型的保守顺式元件TATA-box 和CAAT-box 和光反应元件Box 4,且 JsTPS1、sTPS3、JsTPS4序列里都含有MYB结合位点,都含有G-Box、损伤响应元件WUN-motif、脱落酸诱导顺式作用元件ABRE、厌氧诱导调节元件ARE;JsTPS3和JsTPS4启动子序列都含有光反应元件G-box、ACE,脱落酸诱导顺式作用元件ABRE3a,茉莉酮酸甲酯顺式作用调节元件CGTCA-motif(表2)。
表 2 茉莉JsTPS1、JsTPS3和JsTPS4启动子序列中顺式作用元件预测Table 2. Predicted cis-acting elements in JsTPS1, JsTPS3, and JsTPS4 promoters顺式元件
Cis-element序列
Sequence位置 Position JsTPS1 JsTPS3 JsTPS4 G-Box
参与光响应的顺式作用调节CACGTT + 1157 − 1555 −846, −725 AuxRR-core
参与生长素的顺式作用调节元件GGTCCAT +345 ACE
参与光响应的顺式作用元件GACACGTATG −616 +503 TGACG-motif
茉莉酮酸甲酯反应性中涉及的顺式作用调节元件TGACG −261 −561,+ 1676 ,+863,
−1660 ,+1254 MBSI
MYB结合位点参与类黄酮生物合成基因的调控元件aaaAaaC(G/C)GTTA − 1318 I-box
光响应元件的一部分cCATATCCAAT −173 TGA-element
生长素反应元件AACGAC −153 − 1148 Box 4
涉及光响应性的保守 DNA 模板的一部分ATTAAT +136,− 1146 ,+449,
+413,+488+11,− 1246 ,−1083 ,+1711 ,
+869,+885,−1038 ,−1707 +188,+163 GC-motif
参与缺氧特异性诱导的调控CCCCCG + 1797 , −145−854,+172,−63 ARE
厌氧诱导必不可少的顺式作用元件AAACCA +374, −768 CCAAT-box
MYBHv1结合位点CAACGG −402 +894 CGTCA-motif
茉莉酮酸甲酯反应性中涉及的顺式作用调节元件CGTCA +261 − 1676 , +561, −863
+1660 , −1254 GATA-motif
光响应元件的一部分GATAGGA −582 −566 TATA-box
转录启动子周围−30个核心启动子元件TATA +40,− 1555 ,
+82,+1556 +726,+847,−434 ABRE
脱落酸反应性涉及的顺式作用元件ACGTG/TACGTGTC +213, − 1157 +619,
+618,+1130 A-box
顺式作用调节元件CCGTCC −46,−984 TATC-box
参与赤霉素反应的顺式作用元件TATCCCA −618 GT1-motif
光响应元件GGTTAA +58,−149,+100 TCA-element
水杨酸反应性涉及的顺式作用元件CCATCTTTTT − 1148 Sp1
光响应元件GGGCGG −350 GARE-motif
赤霉素反应元件TCTGTTG +1813 TGA-box
生长素反应元件的一部分TGACGTAA + 1254 3-AF1binding site
光响应元件TAAGAGAGGAA + 1092 AT1-motif
光响应模板的一部分AATTATTTTTTATT −252 TCT-motif
光响应元件的一部分TCTTAC −926 AE-box
光响应模块的一部分AGAAACTT −150 AT-rich element
富含AT的DNA结合蛋白的结合位点ATAGAAATCAA +282 O2-site
玉米醇溶蛋白代谢调控中涉及的顺式调控元件GATGA(C/T)(A/G)TG(A/G) −657 ABRE3a
参与脱落酸反应的顺式作用元件TACGTG +212,+618 +39 G-box
参与光响应的顺式作用调节TACGTG +212,+618,+ 1129 ,+1157 +39,−81,− 1555 MYB
MYB结构域CAACCA + 1295 −99,−1814,+ 1665 −447 MYB recognition site
MYB识别位点CCGTTG +402 −894 MYC
干旱诱导相关的顺式作用元件CATTTG −228,− 1170 ,+663−207, −482,
+457,+1334 +986 WUN-motif
损伤响应元件AAATTTCTT + 1253 as−1
水杨酸诱导型调控元件TGACG −261 +1822,−561,
+1676 ,+1254 Myb-binding site
MYB结合位点CAACAG +863,− 1660 W box
诱导子、受伤及病原体应答,结合 WRKY类转录因子TTGACC −1814 +858,+130 WRE3
顺式作用元件CCACCT +379 WUN-motif
损伤响应元件CAATTACAT −192 2.4 茉莉JsMYB108和JsMYB305转录因子对JsTPS启动子活性的影响
GUS染色结果表明,阴性对照组烟草未出现蓝色(图1A),转入35S::GUS载体的阳性对照组叶片被染成深蓝色(图1B),转入proJsTPS::GUS载体的处理组叶片呈现出不同程度的蓝色(图1 C、F、I),说明JsTPS1、JsTPS3和JsTPS4启动子均具有启动活性,能够启动GUS报告基因的表达。
![]() 图 1 JsMYB108和JsMYB305转录因子与3个JsTPS基因启动子共同转化烟草后的GUS组织化学染色结果A:阴性对照;B:阳性对照;C:单独注射proJsTPS1::GUS;D:proJsTPS1::GUS+35S::JsMYB108共同注射;E:proJsTPS1::GUS+35S::JsMYB305共同注射;F:单独注射proJsTPS3::GUS;G:proJsTPS3::GUS+35S::JsMYB108共同注射;H:proJsTPS3::GUS+35S::JsMYB305共同注射;I:单独注射proJsTPS4::GUS;J:proJsTPS4::GUS+35S::JsMYB108共同注射;K:proJsTPS4::GUS+35S::JsMYB305共同注射。图中标尺为1 mm。Figure 1. GUS histochemical staining on tobacco transformed with two JsMYB transcription factors and three JsTPS promotersA: negative control; B: positive control; C: single injection of proJsTPS1::GUS; D: co-injection of proJsTPS1::GUS+35S::JsMYB108; E: co-injection of proJsTPS1::GUS+35S::JsMYB305; F: single injection of proJsTPS3::GUS; G: co-injection of proJsTPS3::GUS+35S::JsMYB108; H: co-injection of proJsTPS3 ::GUS+35S::JsMYB305; I: single injection of proJsTPS4::GUS; J: co-injection of proJsTPS4::GUS+35S::JsMYB108; K: co-injection of proJsTPS4::GUS+35S::JsMYB305. Scale bar = 1 mm.
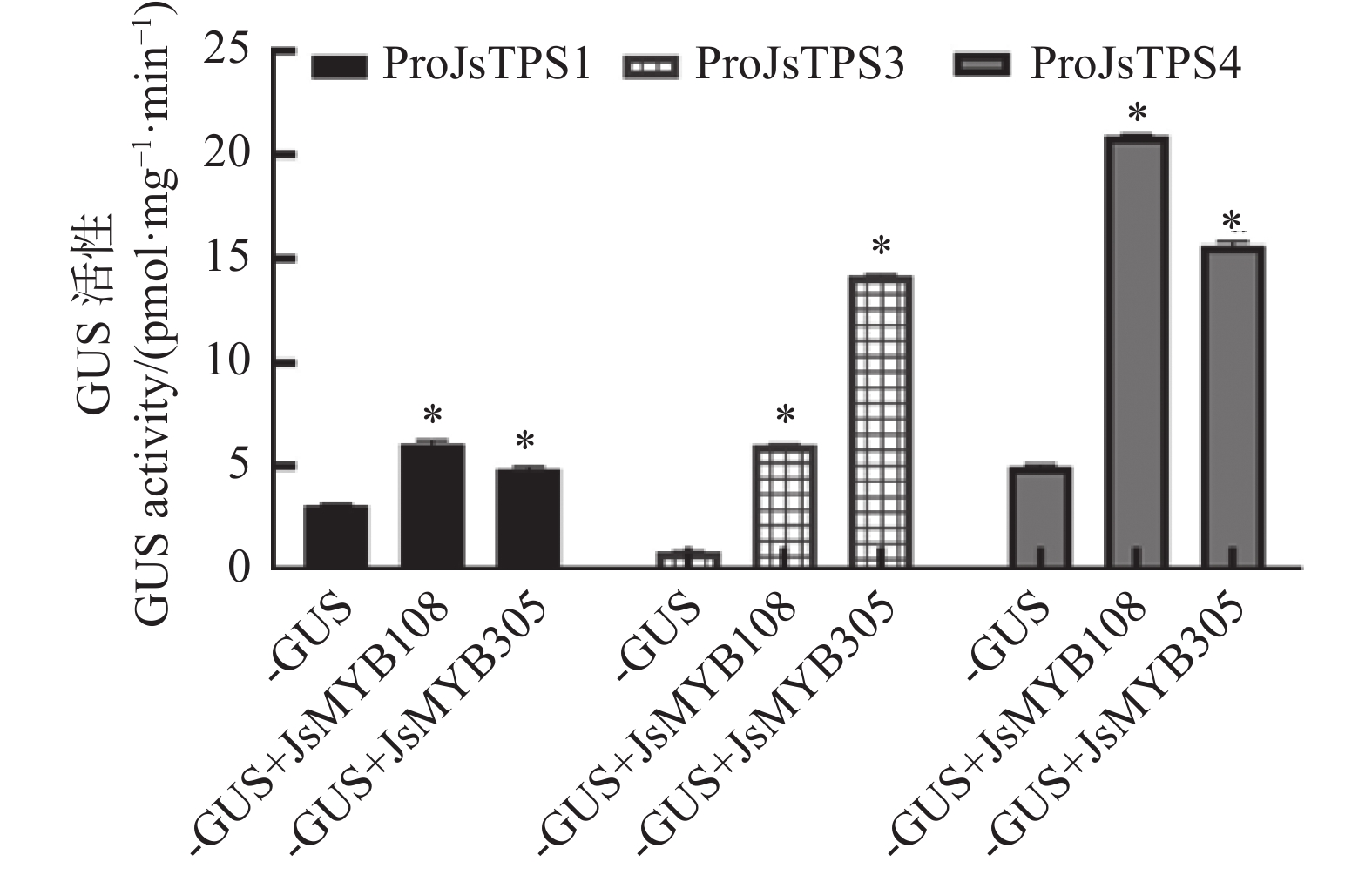
图 1 JsMYB108和JsMYB305转录因子与3个JsTPS基因启动子共同转化烟草后的GUS组织化学染色结果A:阴性对照;B:阳性对照;C:单独注射proJsTPS1::GUS;D:proJsTPS1::GUS+35S::JsMYB108共同注射;E:proJsTPS1::GUS+35S::JsMYB305共同注射;F:单独注射proJsTPS3::GUS;G:proJsTPS3::GUS+35S::JsMYB108共同注射;H:proJsTPS3::GUS+35S::JsMYB305共同注射;I:单独注射proJsTPS4::GUS;J:proJsTPS4::GUS+35S::JsMYB108共同注射;K:proJsTPS4::GUS+35S::JsMYB305共同注射。图中标尺为1 mm。Figure 1. GUS histochemical staining on tobacco transformed with two JsMYB transcription factors and three JsTPS promotersA: negative control; B: positive control; C: single injection of proJsTPS1::GUS; D: co-injection of proJsTPS1::GUS+35S::JsMYB108; E: co-injection of proJsTPS1::GUS+35S::JsMYB305; F: single injection of proJsTPS3::GUS; G: co-injection of proJsTPS3::GUS+35S::JsMYB108; H: co-injection of proJsTPS3 ::GUS+35S::JsMYB305; I: single injection of proJsTPS4::GUS; J: co-injection of proJsTPS4::GUS+35S::JsMYB108; K: co-injection of proJsTPS4::GUS+35S::JsMYB305. Scale bar = 1 mm.35S:: JsMYB108、35S:: JsMYB305与proJsTPSs::GUS共注射烟草的GUS染色结果显示,单独注射含proJsTPS1::GUS、proJsTPS3::GUS、proJsTPS4::GUS的菌液时,叶片中的GUS染色蓝色较浅(图1 C、F、I),而当proJsTPSs::GUS与35S:: JsMYB108和35S::JsMYB305共同转化时,叶片中GUS染色颜色不同程度的加深(图1D、E、G、H、J、K)。从叶片GUS染色深浅程度判断,JsMYB108对JsTPS4启动子活性有增强作用,JsMYB305对JsTPS3和 JsTPS4启动子活性有增强作用。
进一步GUS定量结果显示,JsMYB108使JsTPS1、JsTPS3和JsTPS4启动子活性分别上调为对照的1.96倍、6.47倍和4.15倍;JsMYB305使JsTPS1、JsTPS3和JsTPS4启动子活性分别上调为对照的1.57倍、15.18倍和3.12倍(图2)。以上结果说明JsMYB108和JsMYB305可以不同程度地增强3个JsTPS的启动子活性。
2.5 茉莉JsMYB108和JsMYB305转录因子与JsTPS启动子的酵母单杂交
2.5.1 启动子诱饵载体的构建及诱饵载体转化Y1H-Gold酵母感受态细胞
基于启动子上的MYB顺式作用元件,以pGWB433-proJsTPS1、pGWB433-proJsTPS3、 pGWB433-proJsTPS4质粒为模板,进行启动子片段扩增,得到3个候选上游片段(200 bp左右),进行纯化回收后与用Sma I、Xho I双酶切的载体pAbAi利用In-Fusion法进行构建。转化、涂板后进行菌液PCR检测,获得片段长度与预期一致,说明proJsTPSs-pAbAi已成功构建。将上述成功构建并测序正确的进行质粒提取,即获得上游片段-pAbAi的重组质粒,转化至 Y1H-Gold 酵母感受态细胞中,进行菌液 PCR (Matchmarker Insert Check PCR Mix I)验证,PCR的片段比原启动子片段大1.2 kb左右,说明3个上游片段-pAbAi 重组质粒全部成功转化至 Y1H-Gold 酵母基因组中。
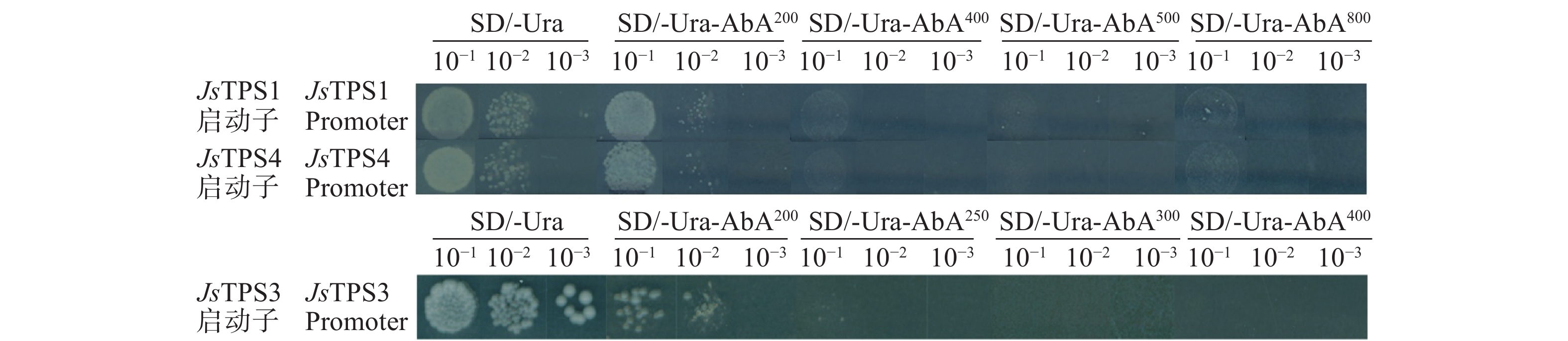
2.5.2 最低AbA抑制浓度筛选
Y1H[proJsTPS1-pAbAi]、Y1H[proJsTPS4-pAbAi]在AbA质量浓度为400 ng·mL−1下几乎没有菌落生长,而Y1H[proJsTPS3-pAbAi]在AbA浓度为250 ng·mL−1下几乎没有菌落生长,因此Y1H[proJsTPS1-pAbAi]、Y1H[proJsTPS4-pAbAi]选择400 ng·mL−1的AbA质量浓度进行后期互作试验,Y1H[proJsTPS3-pAbAi]选择250 ng·mL−1的AbA质量浓度进行后期互作试验(图3)。
2.5.3 酵母单杂验证JsMYB108和JsMYB305与JsTPS的互作
根据JsMYB108和JsMYB305基因序列,设计特异性引物,扩增出目的基因并构建酵母pGADT7-JsMYB108和pGADT7-JsMYB305载体。将检测为阳性的酵母诱饵菌株Y1H-Gold[上游片段-pAbAi]制成酵母感受态,通过共转化的方法,将pGADT7-JsMYB108和pGADT7-JsMYB305质粒分别转入酵母感受态中,涂于SD/-Leu/-Ura 平板28 ℃恒温培养箱培养2~3 d。挑取单克隆于SD/-Leu/-Ura 液体培养基28 ℃、200 r·min−1摇床过夜培养,而后观察培养结果。结果显示JsMYB108和JsMYB305与JsTPS1、JsTPS3、JsTPS4启动子均有互作(图4)。
3. 讨论与结论
转录水平的调控在高等植物基因的表达调控中发挥着重要的作用,并受到多种转录因子和顺式作用元件的相互协调影响[15]。目前研究转录因子与启动子之间作用的方法,主要包括染色质免疫共沉淀技术(Chromatin immunoprecipitation, ChIP)、DNase I足迹法(DNase I footprinting)、凝胶阻滞分析(Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay, EMSA)和酵母单杂交技术[16−19]。本研究主要使用转录激活和酵母单杂交技术分析2个MYB转录因子对3个TPS基因的调控功能。
通过分析茉莉JsTPS1、JsTPS3和JsTPS4基因启动子序列,发现JsTPS1、JsTPS3和 JsTPS4都有MYB结合位点,暗示它们可能受MYB转录因子的调控,后续的转录激活和酵母单杂试验也证实这3个基因的转录水平确实可受到JsMYB108和JsMYB305的调控。这与Liu[20]和李琴琴[21]发现卵叶牡丹(Paeonia qiui)中PqDFR和PqANS有很多MYB转录结合位点,且受PqMYB113正向调控的结果一致;相同的结果也在菊花(Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat.)中报道,CmDFR启动子上具有MYB结合位点,受到CmMYB6转录因子调控[22]。黄色金针菇FL19隐花色素基因Ffcry启动子包含有3个光响应元件,相应的,Ffcry基因在蓝光下表达量显著高于黑暗以及其他波长的光照条件[23];白桦BpPIN3启动了中有3个光响应元件,相应的,遮光胁迫诱导了BpPIN3基因的表达[24],本研究中,3个TPS基因启动子序列都含有光反应元件,其中JsTPS1、JsTPS3序列含有G-Box,JsTPS4序列含有I-box,JsTPS3序列含有ATCT-motif和Sp1,JsTPS1序列含有AE-box和AT1-motif,基于茉莉在夜间开始开放[25],且夜间萜类物质的香气释放量显著高于白昼[26],推测3个TPS基因可能也受光调控,但还需后续试验进行验证。
本研究中,GUS染色及活性检测结果表明JsMYB108和JsMYB305对JsTPS1、JsTPS3和JsTPS4启动子活性有不同程度的增强,且相比JsTPS1,对JsTPS3和JsTPS4启动子活性的调控更显著,可能是由于 JsTPS3和JsTPS4启动子区域中存在更多预测的MYB结合元件。此外, JsTPS1、JsTPS3和JsTPS4是茉莉单萜和倍半萜的合成的关键酶,JsMYB108和 JsMYB305对它们的表达有上调作用[14],对启动子活性有激活作用,推测JsMYB108和 JsMYB305可能对茉莉的单萜和倍半萜合成具有调控功能。类似的研究成果在多个物种中均有报道。拟南芥MYB21和MYC2 通过直接结合倍半萜合酶 AtTPS21 和 AtTPS11 的启动子激活它们的表达,影响倍半萜的合成量[27];番茄中SlMYB75 能够直接结合 MYBPLANT 和 MYBPZM 顺式调节元件并激活 LOXC、AADC2 和 TPS 基因的启动子,过表达SlMYB75可以提高果实中的一些萜挥发物的含量[28];铁皮石斛(Dendrobium officinale)中13个TPS基因可能受AP2/ERF、WRKY、MYB、bHLH和bZIP转录因子调控[29];蜡梅CpMYB2能结合在CpTPS1的启动子上,影响CpTPS1表达,从而影响蜡梅花中罗勒烯的合成[30]。本研究中,JsMYB108和 JsMYB305是否通过调控3个TPS基因的表达从而调控茉莉的单萜和倍半萜合成,还需要转基因功能验证。
酵母单杂交试验证实了JsMYB108和 JsMYB305确实与JsTPS1、JsTPS3和JsTPS4的启动子序列存在互作,与GUS染色结果相对应。JsTPS1、JsTPS3和JsTPS4启动子片段有着不同的最低AbA抑制浓度,这可能与这个序列中MYB位点位置或启动子序列长度不同有关。相似的结果在柱花草SgPAL3基因启动子活性研究中也有发现,启动子区域−2000~0 bp,−
1500 ~0 bp序列分别构建的诱饵载体自激活检测中在100、200、300、400、500 ng·mL−1 AbA下的自激活反应不同[31]。矮牵牛中至少有4个 R2R3-MYB 转录因子被证明在挥发性苯丙素/苯类化合物的产生和释放中起作用:PhMYB4 [32]、PhODO1 [33]、PhEOBII [34]、PhEOBI [35]。事实上,涉及多个 MYB 转录因子的协同相互作用或调控网络似乎是植物次生代谢的共同机制。如桃李(Prunus persica)果实颜色形成[36]、桃金娘(Vaccinium myrtillus)浆果花青素生物合成[37]、姜花(Hedychium coronarium)花挥发物产生[38]。本研究结果显示JsMYB108和 JsMYB305对JsTPS1、JsTPS3和JsTPS4均有调控,但尚不清楚这两个MYB 转录因子在萜类香气合成中是如何协调或相互作用的,为了揭示茉莉花萜类香气的调控机制,还需要通过体外DNA结合试验、芯片测序等实验手段,以及反向遗传学手段进一步研究JsMYB 转录因子及其下游基因的具体作用。
综上所述,本研究在获得茉莉萜烯合成酶基因JsTPS1、JsTPS3和JsTPS4启动子序列的基础上通过转录激活和酵母单杂交技术,证实茉莉JsMYB108和 JsMYB305对JsTPS1、JsTPS3和JsTPS4存在正向调控,它们可能在茉莉花萜烯类挥发物的产生中发挥调控作用。
-
图 1 JsMYB108和JsMYB305转录因子与3个JsTPS基因启动子共同转化烟草后的GUS组织化学染色结果
A:阴性对照;B:阳性对照;C:单独注射proJsTPS1::GUS;D:proJsTPS1::GUS+35S::JsMYB108共同注射;E:proJsTPS1::GUS+35S::JsMYB305共同注射;F:单独注射proJsTPS3::GUS;G:proJsTPS3::GUS+35S::JsMYB108共同注射;H:proJsTPS3::GUS+35S::JsMYB305共同注射;I:单独注射proJsTPS4::GUS;J:proJsTPS4::GUS+35S::JsMYB108共同注射;K:proJsTPS4::GUS+35S::JsMYB305共同注射。图中标尺为1 mm。
Figure 1. GUS histochemical staining on tobacco transformed with two JsMYB transcription factors and three JsTPS promoters
A: negative control; B: positive control; C: single injection of proJsTPS1::GUS; D: co-injection of proJsTPS1::GUS+35S::JsMYB108; E: co-injection of proJsTPS1::GUS+35S::JsMYB305; F: single injection of proJsTPS3::GUS; G: co-injection of proJsTPS3::GUS+35S::JsMYB108; H: co-injection of proJsTPS3 ::GUS+35S::JsMYB305; I: single injection of proJsTPS4::GUS; J: co-injection of proJsTPS4::GUS+35S::JsMYB108; K: co-injection of proJsTPS4::GUS+35S::JsMYB305. Scale bar = 1 mm.
表 1 引物序列
Table 1 Sequences of primers applied
引物名称
Primer name引物序列(5′- 3′)
Primer sequences (5′- 3′)用途
UsageJsTPS1DNA-F ATGGGCAGCCAAGTTTATGCATC 扩增 DNA 序列
DNA amplificationJsTPS1DNA-R GAGATAGGGTTGTGGAACGCTA JsTPS1-GW-GSP1 ATTGTGCGAAGGTCCTCGTTTTGCTTGTAA 扩增启动子序列
Promoter sequence amplificationJsTPS1-GW-GSP2 GTTACGGAGCGTCGAGCAACTTCAATGC JsTPS1-PRO-F TTTCATAGGGAAATTGGTGC 验证启动子序列 JsTPS1-PRO-R TTATATCTAATCAAATGCTTCTAGC Confirming promoter sequence JsTPS3-PRO-F ATGACAAGGTATTAATGCTTGGCG JsTPS3-PRO-R TCTTGATATGTATTACTAGTAATTTAACAAC JsTPS4-PRO-F GTGATATTGATTCCAAATCTGGTC JsTPS4-PRO-R GATAACAAGTAAAACGGAAAATCAGG pAbAi-proJsTPS1-F AATTCGAGCTCGGTACCCGGGCACATTCAAGCTTGAAATACCGG 扩增酵母单杂启动子片段 pAbAi-proJsTPS1-R ATACAGAGCACATGCCTCGAGCAAGCGCATGTAAACGCTAGAC Amplification of promoter sequence
for yeast one hybridpAbAi-proJsTPS3-F AATTCGAGCTCGGTACCCGGGTGCATTTGGATGTAACATTAAAATCA pAbAi-proJsTPS3-R ATACAGAGCACAATGCCTCGAGGTCACATCATGGTTGTGACGAACA pAbAi-proJsTPS4-F AATTCGAGCTCGGTACCCGGGGCCGCCATAAGAAAATTCGG pAbAi-proJsTPS4-R ATACAGAGCACATGCCTCGAGGCTCGTGTACTACATATCGTTTATTAATTAC pAbAi-F GTTCCTTATATGTAGCTTTCGACA 验证上游片段-pAbAi pAbAi-R CCATCTCGAAAAAGGGTTTGCC Confirming cloning sequence in –pABAi vector pGADT7-JsMYB108-F gtaccagattacgctcatatgATGGAGCATCATGTTAAAGGAGATG 构建pGADT7-JsMYBs
Construction of pGADT7-JsMYBs vectorspGADT7-JsMYB108-R cagctcgagctcgatggatccCTACTGTTGTAGGAAATTCCACATGTC pGADT7-JsMYB305-F gtaccagattacgctcatatgATGGACAAGAAAATATGCAATAGCTC pGADT7-JsMYB305-R cagctcgagctcgatggatccTTAATCCCCATTAAGTAACTGGATGG pGADT7-F TAATACGACTCACTATAGGG 验证pGADT7-JsMYBs pGADT7-R AGATGGTGCACGATGCACAG Confirming the construction of
pGADT7-JsMYBs vectors表 2 茉莉JsTPS1、JsTPS3和JsTPS4启动子序列中顺式作用元件预测
Table 2 Predicted cis-acting elements in JsTPS1, JsTPS3, and JsTPS4 promoters
顺式元件
Cis-element序列
Sequence位置 Position JsTPS1 JsTPS3 JsTPS4 G-Box
参与光响应的顺式作用调节CACGTT + 1157 − 1555 −846, −725 AuxRR-core
参与生长素的顺式作用调节元件GGTCCAT +345 ACE
参与光响应的顺式作用元件GACACGTATG −616 +503 TGACG-motif
茉莉酮酸甲酯反应性中涉及的顺式作用调节元件TGACG −261 −561,+ 1676 ,+863,
−1660 ,+1254 MBSI
MYB结合位点参与类黄酮生物合成基因的调控元件aaaAaaC(G/C)GTTA − 1318 I-box
光响应元件的一部分cCATATCCAAT −173 TGA-element
生长素反应元件AACGAC −153 − 1148 Box 4
涉及光响应性的保守 DNA 模板的一部分ATTAAT +136,− 1146 ,+449,
+413,+488+11,− 1246 ,−1083 ,+1711 ,
+869,+885,−1038 ,−1707 +188,+163 GC-motif
参与缺氧特异性诱导的调控CCCCCG + 1797 , −145−854,+172,−63 ARE
厌氧诱导必不可少的顺式作用元件AAACCA +374, −768 CCAAT-box
MYBHv1结合位点CAACGG −402 +894 CGTCA-motif
茉莉酮酸甲酯反应性中涉及的顺式作用调节元件CGTCA +261 − 1676 , +561, −863
+1660 , −1254 GATA-motif
光响应元件的一部分GATAGGA −582 −566 TATA-box
转录启动子周围−30个核心启动子元件TATA +40,− 1555 ,
+82,+1556 +726,+847,−434 ABRE
脱落酸反应性涉及的顺式作用元件ACGTG/TACGTGTC +213, − 1157 +619,
+618,+1130 A-box
顺式作用调节元件CCGTCC −46,−984 TATC-box
参与赤霉素反应的顺式作用元件TATCCCA −618 GT1-motif
光响应元件GGTTAA +58,−149,+100 TCA-element
水杨酸反应性涉及的顺式作用元件CCATCTTTTT − 1148 Sp1
光响应元件GGGCGG −350 GARE-motif
赤霉素反应元件TCTGTTG +1813 TGA-box
生长素反应元件的一部分TGACGTAA + 1254 3-AF1binding site
光响应元件TAAGAGAGGAA + 1092 AT1-motif
光响应模板的一部分AATTATTTTTTATT −252 TCT-motif
光响应元件的一部分TCTTAC −926 AE-box
光响应模块的一部分AGAAACTT −150 AT-rich element
富含AT的DNA结合蛋白的结合位点ATAGAAATCAA +282 O2-site
玉米醇溶蛋白代谢调控中涉及的顺式调控元件GATGA(C/T)(A/G)TG(A/G) −657 ABRE3a
参与脱落酸反应的顺式作用元件TACGTG +212,+618 +39 G-box
参与光响应的顺式作用调节TACGTG +212,+618,+ 1129 ,+1157 +39,−81,− 1555 MYB
MYB结构域CAACCA + 1295 −99,−1814,+ 1665 −447 MYB recognition site
MYB识别位点CCGTTG +402 −894 MYC
干旱诱导相关的顺式作用元件CATTTG −228,− 1170 ,+663−207, −482,
+457,+1334 +986 WUN-motif
损伤响应元件AAATTTCTT + 1253 as−1
水杨酸诱导型调控元件TGACG −261 +1822,−561,
+1676 ,+1254 Myb-binding site
MYB结合位点CAACAG +863,− 1660 W box
诱导子、受伤及病原体应答,结合 WRKY类转录因子TTGACC −1814 +858,+130 WRE3
顺式作用元件CCACCT +379 WUN-motif
损伤响应元件CAATTACAT −192 -
[1] 赵国飞, 罗理勇, 常睿, 等. 离体茉莉花释香过程的香气成分特征 [J]. 食品科学, 2015, 36(18):120−126. ZHAO G F, LUO L Y, CHANG R, et al. Aroma characteristics of jasmine during postharvest release of fragrance [J]. Food Science, 2015, 36(18): 120−126. (in Chinese)
[2] 齐香玉, 陈双双, 冯景, 等. 茉莉花实时荧光定量PCR内参基因的筛选与验证 [J]. 华北农学报, 2020, 35(6):22−30. QI X Y, CHEN S S, FENG J, et al. Selection and validation of candidate reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR in Jasminum sambac aiton [J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2020, 35(6): 22−30. (in Chinese)
[3] 侯彦林, 黄梅, 贾书刚, 等. 茉莉花种植适宜生境及高产产区研究[J/OL]. 吉林农业大学学报, https://doi.org/10.13327/j. jjlau.2021.1363. HOU Y L, HUANG M, JIA S G, et al. Study on suitable habitat and high yield producing area of jasmine[J/OL] Journal of Jilin Agricultural University. https://doi.org/10.13327/j.jjlau.2021.1363.
[4] 孙君, 陈桂信, 叶乃兴, 等. 茉莉花香气相关基因JsDXS及其启动子的克隆与表达分析 [J]. 园艺学报, 2014, 41(6):1236−1244. SUN J, CHEN G X, YE N X, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of deoxyoxylulose-5-phosphate synthase gene related to aroma from Jasminum sambac and isolation of its promoter [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2014, 41(6): 1236−1244. (in Chinese)
[5] 傅天龙, 郭晨, 傅天甫, 等. 福州8种主要茉莉花茶特征香气成分比较与分析 [J]. 茶叶科学, 2020, 40(5):656−664. FU T L, GUO C, FU T P, et al. Comparison and analysis of characteristic aroma components of eight main jasmine teas in Fuzhou [J]. Journal of Tea Science, 2020, 40(5): 656−664. (in Chinese)
[6] 张俊杰, 傅天龙, 傅天甫, 等. 福州茉莉花茶窨制次数与香气成分的关联分析 [J]. 茶叶科学, 2021, 41(1):113−121. ZHANG J J, FU T L, FU T F, et al. Correlation analysis of scenting times and aroma components of Fuzhou jasmine tea [J]. Journal of Tea Science, 2021, 41(1): 113−121. (in Chinese)
[7] 陈梅春, 林增钦, 郑梅霞, 等. 茉莉花茶香气品质评价指标的构建与研究 [J]. 茶叶通讯, 2021, 48(1):90−97. CHEN M C, LIN Z Q, ZHENG M X, et al. Construction and study on aroma quality evaluation index of jasmine tea [J]. Journal of Tea Communication, 2021, 48(1): 90−97. (in Chinese)
[8] 吴宏清, 王磊, 何欣, 等. 白木香倍半萜合成酶基因As-SesTPS的克隆及生物信息学与表达分析 [J]. 中草药, 2014, 45(1):94−101. WU H Q, WANG L, HE X, et al. Cloning of sesquiterpene synthase gene As-SesTPS from Aquilaria sinensis and analysis its bioinformatics and expression [J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2014, 45(1): 94−101. (in Chinese)
[9] ALLAN A C, ESPLEY R V. MYBs drive novel consumer traits in fruits and vegetables [J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2018, 23(8): 693−705. DOI: 10.1016/j.tplants.2018.06.001
[10] REEVES P H, ELLIS C M, PLOENSE S E, et al. A regulatory network for coordinated flower maturation [J]. PLoS Genetics, 2012, 8(2): e1002506. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002506
[11] BEDON F, BOMAL C, CARON S, et al. Subgroup 4 R2R3-MYBs in conifer trees: Gene family expansion and contribution to the isoprenoid- and flavonoid-oriented responses [J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2010, 61(14): 3847−3864. DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erq196
[12] HAN Y J, CHEN W C, YANG F B, et al. cDNA-AFLP analysis on 2 Osmanthus fragrans cultivars with different flower color and molecular characteristics of OfMYB1 gene [J]. Trees, 2015, 29(3): 931−940. DOI: 10.1007/s00468-015-1175-6
[13] HAN Y J, WU M, CAO L Y, et al. Characterization of OfWRKY3, a transcription factor that positively regulates the carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase gene OfCCD4 in Osmanthus fragrans [J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2016, 91(4/5): 485−496.
[14] 张月, 袁媛, 何弦, 等. 茉莉花JsMYB108和JsMYB305基因的克隆及其对TPS基因的激活作用 [J]. 热带作物学报, 2021, 42(6):1539−1548. ZHANG Y, YUAN Y, HE X, et al. Cloning of JsMYB108 and JsMYB305 and analysis of their activation on TPS gene in Jasminum sambac [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2021, 42(6): 1539−1548. (in Chinese)
[15] 聂丽娜, 夏兰琴, 徐兆师, 等. 植物基因启动子的克隆及其功能研究进展 [J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2008, 9(3):385−391. NIE L N, XIA L Q, XU Z S, et al. Progress on cloning and functional study of plant gene promoters [J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2008, 9(3): 385−391. (in Chinese)
[16] 王雪, 王盛昊, 于冰. 转录因子和启动子互作分析技术及其在植物应答逆境胁迫中的研究进展 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(33):112−119. WANG X, WANG S H, YU B. Interaction analysis of transcription factors and promoters and its application in response of plants to stress [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2021, 37(33): 112−119. (in Chinese)
[17] NEPH S, VIERSTRA J, STERGACHIS A B, et al. An expansive human regulatory lexicon encoded in transcription factor footprints [J]. Nature, 2012, 489(7414): 83−90. DOI: 10.1038/nature11212
[18] LANDT S G, MARINOV G K, KUNDAJE A, et al. ChIP-seq guidelines and practices of the ENCODE and modENCODE consortia [J]. Genome Research, 2012, 22(9): 1813−1831. DOI: 10.1101/gr.136184.111
[19] 孙宇航, 王宇祥. DNA与蛋白质的相互作用及其生物学研究方法 [J]. 生命科学, 2018, 30(5):585−592. SUN Y H, WANG Y X. Interaction and biological research methods of DNA-protein [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2018, 30(5): 585−592. (in Chinese)
[20] LIU X K, DUAN J J, HUO D, et al. The Paeonia qiui R2R3-MYB transcription factor PqMYB113 positively regulates anthocyanin accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana and tobacco [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 810990.
[21] 李琴琴, 董山榕, 罗建让, 等. 卵叶牡丹PqDFR和PqANS及启动子克隆与功能分析 [J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6):1256−1272. LI Q Q, DONG S R, LUO J R, et al. Cloning and functional analysis of PqDFR and PqANS genes and its promoters from Paeonia qiui [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1256−1272. (in Chinese)
[22] XIANG L L, LIU X F, LI X, et al. A novel bHLH transcription factor involved in regulating anthocyanin biosynthesis in chrysanthemums (Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat. ) [J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(11): e0143892. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143892
[23] 许畅, 罗兴超, 张豪, 等. 金针菇光受体隐花色素Ffcry基因的鉴定及其表达模式 [J]. 菌物学报, 2022, 41(6):962−970. XU C, LUO X C, ZHANG H, et al. Identification and expression pattern of photoreceptor cryptochrome Ffcry gene in Flammulina filiformis [J]. Mycosystema, 2022, 41(6): 962−970. (in Chinese)
[24] 陈坤, 方功桂, 穆怀志, 等. 白桦BpPIN3基因启动子序列及应答特性分析 [J]. 植物研究, 2022, 42(4):592−601. DOI: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2022.04.009 CHEN K, FANG G G, MU H Z, et al. Analysis of the promoter sequence and response characteristics of the BpPIN3 gene in Betula platyphylla [J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2022, 42(4): 592−601. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2022.04.009
[25] LU Y, LIU Z Y, LYU M L, et al. Characterization of JsWOX1 and JsWOX4 during callus and root induction in the shrub species Jasminum sambac [J]. Plants, 2019, 8(4): 79. DOI: 10.3390/plants8040079
[26] WANG Y T, ZHANG H L, WAN C, et al. Characterization of two BAHD acetyltransferases highly expressed in the flowers of Jasminum sambac (L.) Aiton [J]. Plants, 2021, 11(1): 13. DOI: 10.3390/plants11010013
[27] HONG G J, XUE X Y, MAO Y B, et al. Arabidopsis MYC2 interacts with DELLA proteins in regulating sesquiterpene synthase gene expression [J]. The Plant Cell, 2012, 24(6): 2635−2648. DOI: 10.1105/tpc.112.098749
[28] JIAN W, CAO H H, YUAN S, et al. SlMYB75, an MYB-type transcription factor, promotes anthocyanin accumulation and enhances volatile aroma production in tomato fruits [J]. Horticulture Research, 2019, 6: 22. DOI: 10.1038/s41438-018-0098-y
[29] LI N H, DONG Y X, LV M, et al. Combined analysis of volatile terpenoid metabolism and transcriptome reveals transcription factors related to terpene synthase in two cultivars of Dendrobium officinale flowers [J]. Frontiers in Genetics, 2021, 12: 661296. DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2021.661296
[30] 付雪梅, 陈绍元, 郭春燕, 等. CpMYB2和CpNAC1调控蜡梅花香基因CpTPS1的初步验证[J/OL]. 分子植物育种, 2022 (2022-05-12). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20220512.1132.016.html" target="_blank"> https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20220512.1132.016.html. FU X M, CHEN S Y, GUO C Y, et al. Preliminary verification of the regulation of winter sweet flower fragrance gene CpTPS1 by CpMYB2 and CpNCA1. [J/OL]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2022 (2022-05-12). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20220512.1132.016.html" target="_blank"> https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20220512.1132.016.html.(in Chinese [31] 戴镕徽, 高梦泽, 王芳, 等. 柱花草SgPAL3基因启动子的克隆及上游转录因子的筛选 [J]. 草地学报, 2024, 32(1):66−74. DAI R H, GAO M Z, WANG F, et al. Cloning of SgPAL3 gene promoter and screening of upstream transcription factors in Stylosanthes [J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2024, 32(1): 66−74. (in Chinese)
[32] COLQUHOUN T A, KIM J Y, WEDDE A E, et al. PhMYB4 fine-tunes the floral volatile signature of Petunia x hybrida through PhC4H [J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2011, 62(3): 1133−1143. DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erq342
[33] ADEBESIN F, WIDHALM J R, BOACHON B, et al. Emission of volatile organic compounds from Petunia flowers is facilitated by an ABC transporter [J]. Science, 2017, 356(6345): 1386−1388. DOI: 10.1126/science.aan0826
[34] SPITZER-RIMON B, FARHI M, ALBO B, et al. The R2R3-MYB-like regulatory factor EOBI acting downstream of EOBII regulates scent production by activating ODO1 and structural scent-related genes in Petunia [J]. The Plant Cell, 2012, 24(12): 5089−5105.
[35] VAN MOERKERCKE A, HARING M A, SCHUURINK R C. The transcription factor EMISSION OF BENZENOIDS II activates the MYB ODORANT1 promoter at a MYB binding site specific for fragrant petunias [J]. The Plant Journal, 2011, 67(5): 917−928. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04644.x
[36] ZHOU H, KUI L W, WANG F R, et al. Activator-type R2R3-MYB genes induce a repressor-type R2R3-MYB gene to balance anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin accumulation [J]. The New Phytologist, 2019, 221(4): 1919−1934. DOI: 10.1111/nph.15486
[37] KARPPINEN K, LAFFERTY D J, ALBERT N W, et al. MYBA and MYBPA transcription factors co-regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis in blue-coloured berries [J]. The New Phytologist, 2021, 232(3): 1350−1367. DOI: 10.1111/nph.17669
[38] KE Y G, ABBAS F, ZHOU Y W, et al. Auxin-responsive R2R3-MYB transcription factors HcMYB1 and HcMYB2 activate volatile biosynthesis in Hedychium coronarium flowers [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 710826. DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.710826




 下载:
下载: