A Constant Temperature Fluorescent RPA Assay for Detecting Novel Muscovy Duck Parvovirus
-
摘要:目的
建立新型番鸭细小病毒(New-genotype muscovy duck parvovirus, N-MDPV)荧光RPA恒温检测方法,为基层提供可视化快速检测技术手段。
方法以N-MDPV的VP3基因保守片段为靶点,使用EXO荧光探针特定结合VP3基因保守片段,设计特异的RPA扩增引物并利用重组酶聚合酶扩增技术扩增目的基因,从而建立一种荧光RPA恒温检测N-MDPV的方法,确定反应体系的最佳反应时间和温度,分析该方法特异性和灵敏性;对收集的病料进行核酸检测,并与传统PCR和病毒分离鉴定方法检测结果进行比较。
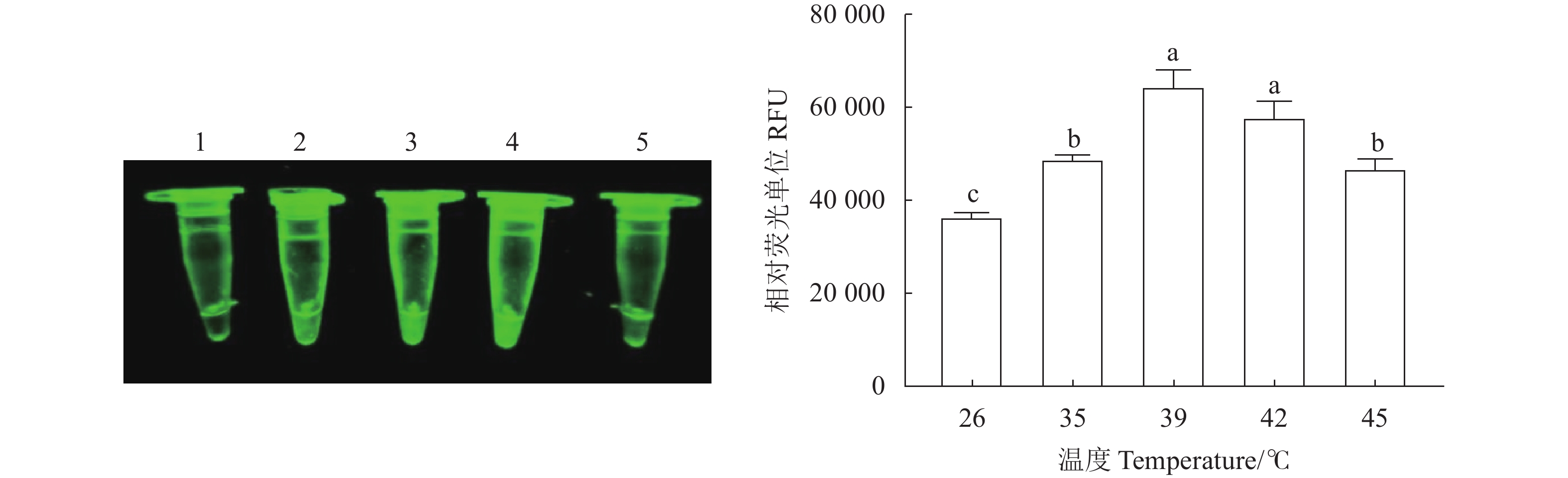
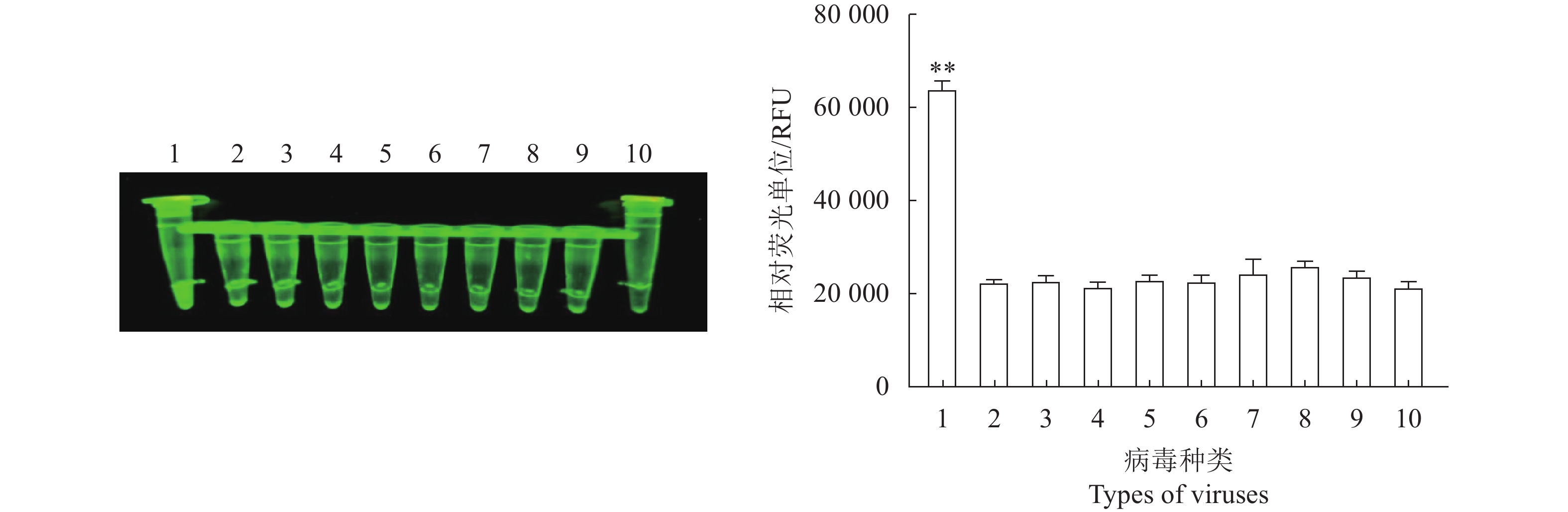
结果建立的荧光RPA恒温检测方法最佳反应温度为39 ℃,最佳反应时间为30 min;灵敏性高,最低核酸检测限度可达10 fg·μL−1;对新型番鸭细小病毒核酸进行特异性扩增,结果显示对鸭腺病毒3型(Duck adenovirus type 3, DAdV-3)、禽腺病毒4型(Fowl adenovirus serotype 4, FAdV-4)、鸭圆环病毒(Duck circovirus, DuCV)、鸭瘟病毒(Duck plague virus, DPV)、鸭病毒性肝炎病毒(Duck hepatitis virus, DHV)、鸭坦布苏病毒(Duck tembusu virus, DTMUV)和新型鸭呼肠孤病毒(Novel duck reovirus, NDRV)的核酸均未有发生交叉反应,特异性良好。利用本研究建立的RPA快检方法、传统PCR方法以及病毒分离鉴定方法对收集的38份鸭组织病料核酸样品进行检测,结果显示阳性率分别为36.8%(14/38)、36.8%(14/38)和31.6%(12/38);RPA检测后呈阳性的样品经PCR方法检测与病毒分离鉴定方法检测均呈现阳性,阳性符合率为100%。
结论该方法可以很好地应用于缺乏相应检测设备的基层进行新型番鸭细小病毒的大规模临床样本检测,为新型番鸭细小病毒的可视化快速检测提供技术手段。
-
关键词:
- 新型番鸭细小病毒 /
- RPA恒温检测 /
- 重组酶聚合酶扩增技术
Abstract:ObjectiveA constant temperature fluorescent RPA assay for detecting novel Muscovy duck parvovirus (N-MDPV) was developed.
MethodEXO fluorescent probes were specifically bound to the targeted conserved VP3 fragment of N-MDPV. RPA amplification primers were designed to amplify the segment by using recombinant enzyme polymerase. An assay for detecting N-MDPV was established with reaction time and temperature optimized and specificity, sensitivity, and accuracy tested on the collected nucleic acid of disease material in comparison with traditional PCR and virus isolation identification methods.
ResultThe optimized assay reaction temperature and time were 39 ℃ for 30 min to achieve a lowest sensitivity for nucleic acid detection at 10 fg·μL−1. The nucleic acid of N-MDPV was specifically amplified without any cross reaction with those of duck adenovirus type 3, fowl adenovirus type 4, duck circovirus, duck plague virus, duck hepatitis virus, duck tembusu virus, and novel duck reovirus. Along with the conventional PCR and the virus isolation and identification methods, the newly developed assay detected the nucleic acid on 38 duck tissue specimens with a positive rate of 36.8% (14/38) in comparison to those at 36.8% (14/38) for the PCR and 31.6% (12/38) for the isolation and identification method. In addition, 100% coincidence rates of the assay and the two other methods on positive samples as well as of the assay and the PCR on the positive clinical samples were secured.
ConclusionThe new RPA method to rapidly and visually detect N-MDPV demonstrated to be highly specific, sensitive, and accurate. It was deemed appropriate for clinical applications.
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】乡村是土地、人口、聚落等资源组合产生的具有自然、社会、经济特征的地域综合体,与城镇互促互进、共生共存,共同构成人类活动的主要空间。从人地关系地域系统角度看,乡村地域主要有三大功能:一是提供充足的资源品(农业生产空间);二是提供环境负熵流,容纳消解污染物(生态空间);三是提供理想栖居空间(聚落空间)[1]。改革开放以来,随着社会经济和城镇化的快速发展,由于不同地区和村庄自然资源的差异性、经济发展的不均衡性和社会需求的多样性,乡村空间结构和功能发生了调整[2−3]。乡村功能类型和功能价值与需求潜力存在巨大差距,尤其是受城市化进程影响较大的区域,乡村生产、生活和生态条件差距比较明显,其功能配置也存在显著差异[4]。《乡村振兴战略规划(2018-2022年)》提出,坚持乡村振兴和新型城镇化双轮驱动,统筹城乡国土空间开发格局,优化乡村生产生活生态空间,分类推进乡村振兴,打造各具特色的现代版“富春山居图”。如何优化乡村生产生活生态空间,分类推进乡村振兴成为困扰学者们的难点。乡村衰落,直接引发人、土地和聚落的空心化。从乡村空间结构和经济结构重构的动力机制出发,将农村空间、产业和组织结合,探索乡村重构的模式和道路,是新时期乡村空间重组的核心[5]。【前人研究进展】乡村发展水平综合评判是乡村发展转型类型划分的基础[6],乡村主导功能则是乡村转型发展类型划分的重要依据。长期以来,为了更深入地认识乡村和推进乡村发展,国内外学者们对乡村发展从评价尺度、评价方法、功能理论与发展内容等进行了大量的研究。在评价尺度上,大部分的学者主要从县域宏观尺度对乡村发展进行评价。崔悦怡等[7]以西部地区各省(自治区、直辖市)为尺度评价农村综合发展情况;贾晋等[8]、闫周府等[9]分别从省域层面测度和比较了乡村振兴发展水平;张挺等[10]对11省(市)的35个乡村进行了实证评价分析;韩磊等[11]从全国、区域、省级三个层面对农村发展进程进行测度和比较研究。在评价方法上,主要有数学模型等定量评价方法和GIS与RS的空间分析方法等。刘玉等[12]运用自组织映射神经网络法(SOFM)数学模型开展环渤海地区乡村地域功能分区;洪惠坤等[13]运用GIS技术和Dagum基尼系数法,对重庆市乡村空间功能值的空间非均衡及分布动态进行了实证研究;唐林楠等[14]借助BP神经网络模型揭示北京平谷区“生产-生活-生态”功能分异特征并运用Ward法划分乡村功能理论与发展内容上,Banski等[15]根据用地特征、社会服务、就业结构等指标,把波兰苏瓦乌基省划分为以农业为主导功能,以及以工业、旅游业、林业等为优势功能的6个功能类型;Willemen等[16]在把荷兰乡村地域划分为居住、文化等功能的基础上研究了乡村地域功能间的相互作用机制;Holmes等[17]提出多功能乡村转型理论,指出社会发展过程中人们对乡村生产、消费和生态的需求变化是驱使乡村功能不断转型的主要原因;杨忍等[18]基于国土空间“生产-生活-生态”三生功能理论,把乡村功能类型划分为农业生产功能、人居生活功能和生态保育功能等8种类型;刘彥随等[19]构建地域多功能性评价指标体系与指数分析模型,对中国县域经济发展、粮食生产、社会稳定、生态保育功能及其综合功能进行分级研究;刘自强等[20]分析了不同工业化发展阶段城市地域功能与乡村地域功能的演化轨迹,并以此把乡村发展阶段划分为维持生计型、产业驱动型与多功能主导型3个阶段;李平星等[21]以经济发达的江苏省为例,采用价值评价法核算1990—2010年乡村地域生态保育、农业生产、工业发展、社会保障功能及其综合价值,分析时间演变与空间分异规律。【本研究切入点】虽然国内外学者对乡村发展的研究成果辉煌,但在研究角度取向方面尚待进一步细化。一是大部分研究成果都是针对县域以上宏观层面,从行政村特别是连片村庄进行分析的更少。由于乡村的动态性、多样性、不整合性及相对性等因素[22],乡村评价受尺度影响显著,其尺度越小,越有助于科学揭示乡村发展的本质特征,越有助于深入揭示乡村特性与乡村发展之间的空间、经济和社会关联,因此乡村评价研究呈现出微观化和应用化趋势[23]。县域以上尺度的宏观评价分析经济发展的“人” “地”矛盾,对一定地理环境乡村振兴的乡村“病”药方就难以准确。村域尺度的乡村发展评价是对乡村“病”的直接“把脉”,是村庄乡村振兴定位和乡村发展类别判断的重要依据。二是鲜见涉及城市郊区的村域“三生”功能评价。城市近郊区是城乡融合的关键地带,识别该地区村庄功能与类型有助于统筹城乡发展格局[24]。【拟解决的关键问题】县(市)是中国经济社会功能比较完整的行政地域单元,行政村是农村经济社会活动与规划管理的基本单元,在一个县(市区)从村域进行乡村发展评价研究,能更深入揭示乡村发展特征及其存在的问题。为此本文以位于福州市城郊的晋安区北部59个村庄为例,将乡村发展要素分成生产、生活和生态三个方面,构建村级乡村发展评价体系,深入分析乡村发展演变的要素差异和空间特征,并通过乡村发展聚类特征状况,以“主导空间+辅助空间”的定位分析乡村振兴的空间开发格局,以期为形成因地制宜、循序渐进的乡村振兴策略,打造各具特色的现代“富春山居图”提供方法和思路。
1. 研究方法与数据来源
1.1 指标体系构建
综合考虑评价单元的完整性、评价方法的可操作性、数据资料的可获得性以及评价指标的稳定性,建立村域尺度乡村性评价指标体系,要素层包括生产、生活、生态三大功能,指标层包含25个指标(表1)。
表 1 “三生”功能乡村发展评价指标体系Table 1. Evaluation index for rural development of “Production-living-ecological” function要素层 Element 指标层 Index 计算方法 Description 权重 Weight 生产功能
Production function(PF)粮豆人均产量/t 村粮豆总产量/总人口数 1/9 蔬果人均产量/t 村蔬果总产量/总人口数 1/9 本村就业比例/% 留守就业人数/总人口数 1/9 产值人均数/元 村生产总值/总人口数 1/9 技术人口比例/% 村技能型人员数量/总人口数 1/9 合作社数量/个 村建立并实际运营的合作社数量 1/9 村外援人才状况 3年内平均村干部挂职和下派干部人数 1/9 乡贤情况 处科级以上领导+村人才学历(博士、硕士) 1/9 通村公路硬化率/% 村内公路硬化总里程/村内公路总里程 1/9 生活功能
Living function(LF)现代房屋户比例/% 1990年后建设且完好的房屋数量/总房屋数量 1/11 活动中心情况/个 各自然村活动中心数量和 1/11 学校教育方便性/个 幼儿园数量×0.5+小学数量×0.5 1/11 生活用品采购便利性/个 村内小卖部数量和 1/11 居民文化提升机会 图书角数量×0.5+(会堂或讲堂数量)×0.5 1/11 居民办事方便状况 村中有无居民服务中心 1/11 党员比例/% 村党员人数/总人口数 1/11 党员数量/人 村党员人数 1/11 人均纯收入/元 家庭纯收入总量和/村内总人口数 1/11 农村自来水状况/% 各自然村自来水开通比例 1/11 村卫生服务状况 村卫生服务站数量 1/11 生态功能
Ecological function(EF)森林覆盖率/% 森林总面积/村地域总面积 1/5 垃圾集中处理状况/% 自然村集中垃圾处理点覆盖比例 1/5 污水处理情况/% 各主要河流定期整治数/总河流数量 1/5 美丽乡村建设状况/分 按级别设定分值(国家级5、省级4、市级3、县级1) 1/5 村规民约制定状况 有无制定村规民约及针对性比例 1/5 (1)生产功能(Production function, PF)。该功能主要从农村产业发展的角度,以外部环境条件和内部发展能力两个方面构建指标。选取包括粮豆人均产量、蔬果人均产量、本村就业比例、人均产值、技术人口比例、合作社数量、村外援人才状况、乡贤情况和通村公路硬化率9个指标。
(2)生活功能(Living function, LF)。该功能主要反映村民生活基本功能和新时期现代生活提升需求,从硬件配套、经济水平和组织能力等方面综合构建。选取包括现代房屋户比例、活动中心、学校教育方便性、生活用品采购方便性、居民文化提升机会、居民办事方便状况、党员比例、党员数量、人均纯收入、农村自来水状况和村卫生服务状况11个评价指标。
(3)生态功能(Ecological function, EF)。该功能主要从自然环境条件和公共建设等角度,按照可持续发展的原则,构建包括森林覆盖率、垃圾集中处理状况、污水集中处理状况、美丽乡村建设状况和村规民约制定状况5个评价指标。
1.2 评价模型与指标权重
采用改进后的TOPSIS评价法[25]对区域内村庄的演变进行综合评价。首先整理调查数据,构建59行25列的原始数据矩阵,对其进行归一化处理使其无量纲化,然后找出方案中的最优方案和最劣方案,分别计算各评价对象与最优方案和最劣方案间的距离,获得各评价对象与最优方案的相对接近程度,以此作为评价优劣的依据。由于指标间的重要性判断带有主观因素,并且不同主体的看法也有差别,为了减少这方面的影响,指标间的权重分配采用平均法(表1)。
评价的主要步骤如下:
(1)同趋势化。综合评价中,有些指标是高优指标,有些指标是低势指标。用TOPSIS法进行评价时,要求所有指标方向一致。通常采用将低优指标高优化,对绝对数指标使用倒数法(
1/X ),对相对数低优指标使用差值法(1−X )。(2)指标无量纲化。为了消除指标计量单位的影响,要对指标实测值进行归一化处理,即无量纲化。设
(Xij)n×m 为同趋势化后的指标矩阵,(Zij)n×m 为归一化后的数据矩阵,则:Zij=Xij/√m∑i=1X2ij ,式中j=1,2,⋯,m 。(3)确定优先方案中的最优方案
Z+ 和最劣方案Z - 。若原始数据经同趋势化统一为高优指标,则:最优方案为:
Z+=(Z+1,Z+2,⋯,Z+m) 最劣方案为:
Z-=(Z-1,Z-2,⋯,Z-m) 其中,
Z+j=max ,Z_j^{\text{ - }} = \mathop {\min }\limits_{1 \leqslant i \leqslant n} \left\{ {{Z_{ij}}} \right\} ,式中j = 1,2, \cdots ,m 。(4)计算各评价对象与最优方案和最劣方案的加权欧氏距离
D_i^ + 和D_i^{{ - }} :D_i^ + = \sqrt {\sum\limits_{j = 1}^m {{{[{W_j}({Z_{ij}} - Z_{ij}^ + )]}^2}} } D_i^{\text{ - }} = \sqrt {\sum\limits_{j = 1}^m {{{[{W_j}({Z_{ij}} - Z_{ij}^{{ - }})]}^2}} } 式中
{W_j} 为各指标权重,i = 1,2, \cdots ,n 。(5)计算各评价对象与最优方案的接近程度
{C_i} :{C_i} = \frac{{D_i^ - }}{{D_i^ + + D_i^ - }} ,式中i = 1,2, \cdots ,n 。{C_i} \in [0,1] ,{C_i} 愈接近于1,表示第i 个评价对象越接近于最优水平;反之,{C_i} 愈接近于0,表示第i 个评价对象越接近于最劣水平。即{C_i} 值越大,评价结果越优。1.3 实证对象与数据来源
本研究实证对象为位于省会城市福州郊区的晋安区,该区包括3个街道6个乡镇,其中3个街道和3个乡镇已经基本城市化。全区常住人口85.5万人,其中农业人口约7万人,主要分布于宦溪、寿山和日溪3个乡镇。选取具有农村特征的宦溪、寿山和日溪3个乡镇59个村为样本。数据来源,一是社会经济数据来自《福州市晋安区统计年鉴》(2015—2018年),土地使用数据和空间地图来自于国土资源部门;二是通过发放调查问卷的方式获取,问卷填写对象主要为村书记和村主任,总共发放问卷59份,有效问卷59份。对于问卷中存在不清楚或未填写的问题,采取电话询问加以补充。
1.4 研究思路与方法
1.4.1 研究思路
随着我国经济发展水平的提高,城乡收入水平和公共服务供给能力的差异逐渐被拉大,乡村振兴要缩小这种差距,就要在经济活动中解决“人”和“地”的匹配问题。通过聚类分析方法剖析所有村庄的类型结构,同时结合村庄空间定位,围绕中心村形成“点—线—面”区域多村结合、联村共振的发展路径,促进农村产业发展和公共服务配套优化,特别是在农村一二三产融合发展模式下,更能促进乡村的振兴,从而逐步形成产权改革机制下的产业振兴、保留乡愁特色下的文化振兴、党建引领下的组织振兴、多主体共建下的人才振兴和自然谐发展下的生态振兴,形成板块式、连片化发展。
1.4.2 分类评价
以最显著要素为主导空间,其他要素为辅助空间,构造“主导空间+辅助空间=乡村类型”的乡村定位,将乡村分成“生活+生产、生活+生态、生活+生产+生态、生产+生活、生产+生态、生产+生活+生态、生态+生活、生态+生产、生态+生活+生产”9个类型(图1)。同时,将9个类型融入集聚提升、城镇转化、特色保护、搬迁撤并的村庄类型体系中,其中集聚提升包括“生活+生产、生产+生活、生活+生产+生态”、融入城镇包括“生活+生态”、特色保护包括“生产+生活+生态、生态+生活、生态+生活+生态”、搬迁撤并包括“生态+生态、生态+生产”,为乡村重构提供融合基础。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 评价结果
根据TOPSIS方法,得到晋安区北部山区各行政村乡村发展生产、生活和生态指数(图2),59个村的乡村发展总指数为0.18~0.48,表明晋安区北部村庄受省会城市对乡村资源吸纳影响,乡村弱化比较严重。从3个要素指标分析,生态指标最好,其次是生活指标,最后是生产指标。另外,3个要素的变异系数都比较大,全部大于20,生产要素的变异系数高达34.50,显示村之间发展不平衡。
2.2 空间特征分析
图3a反映了晋安区北部59个村总体指数情况和要素指数情况,为此进一步分析总指数和要素指数在地域空间的布局状况。
2.2.1 总指数的空间特征分析(RRI)
晋安区北部乡村发展评价指数(RRI)表现为北高南低的空间分布特征(图3a)。其中,低值区(RRI≤0.25)主要分布在宦溪镇镇政府所在地周边村庄和工业化开发比较大的村庄及一些交通不便的村庄,前两种村庄经济基础比较好、交通比较方便,城镇化水平比较高,第一产业比重低,后一种村庄除了生态不错,产业、区位和交通条件都比较弱。偏低值区(0.25<RRI≤0.35)为北峰山区村庄的主要部分,有34个村庄。区位和交通相对不错,主要分布于交通干线周边,资源要素比较丰富。高值区(RRI>0.35)主要是特色村庄,产业基础较好、交通条件优越、资源比较丰富且有特色。图3a显示,低值区和高值区的聚集程度不高,比较分散。而偏低值区的集聚程度比较高,特别是北部沿省道周边的村庄。从乡镇看,乡村发展指数为日溪乡(0.33)>寿山乡(0.29)>宦溪镇(0.25)。
2.2.2 生产要素的空间特征分析(PRI)
晋安区北部山区生产要素整体水平(PRI=0.26)低于总体发展水平(RRI=0.31),介于0.09~0.48,呈现中间低、南北两端高且发散趋势,空间分布差异显著(图3b),变异系数34.50。低值区(PRI≤0.25)包括27个(45.76%)行政村,这些村庄生产发展比较不足,客观原因是晋安区北部山区交通和自然条件相对不足,特别是因山区地貌限制交通受到很大制约;主观原因为晋安区位于省会城市郊区,改革开放后城市重点发展偏向于近郊的平原区,对远郊的山区发展关注不够。偏低值区(0.25<PRI≤0.35)有20个(33.90%)行政村。高值区(PRI>0.35)仅有12个(20.34%)行政村。乡镇生产要素水平排序为:日溪乡>寿山乡>宦溪镇。
2.2.3 生活要素的空间特征分析(LRI)
晋安区北部山区生活要素整体水平(LRI=0.34)高于总体发展水平(RRI=0.31),介于0.14~0.63,呈发散分布,空间分布差异显著(图3c),变异系数27.92。从指数分布区间看,低值区(LRI≤0.25)仅包括4个(45.76%)行政村,偏低值区(0.25<LRI≤0.35)有40个(33.90%)行政村,高值区(LRI>0.35)有15个(20.34%)行政村。量化分析结果,晋安区北部山区在城郊经济的带动下人均收入较高,其中务工收入有很大的贡献。在生活配套等方面,伴随美丽乡村建设,自来水入户、公路硬化、卫生服务等公共设施基本到位。但受不方便的交通条件、少而分散的耕地,以及陡峭的地形地貌,3个山区乡镇的人口仅有3.15万人,仅占晋安区总人口的6.76%,59个村户籍人口超过1000人的仅有3个,500人以下的有28个,随着外出人口的不断增加,村庄的常住人口不断减少,导致大部分的公共资源配套利用率低且逐步弱化,特别是在村级幼儿园和小学等教育资源配套方面具有很大的缺失。乡镇生活要素水平排序为:寿山乡>日溪乡>宦溪镇,其中日溪和寿山比较接近。
2.2.4 生态要素的空间特征分析(ERI)
北部山区生态要素整体水平(ERI=0.37)高于总体发展水平(RRI=0.31),介于0.17~0.66,呈东北高、西南低的趋势,空间分布差异相对较小(图3d),变异系数24.64。从指数分布区间看,低值区(ERI≤0.25)仅包括5个(45.76%)行政村,偏低值区(0.25<ERI≤0.35)有21个(33.90%)行政村,高值区(ERI>0.35)有33个(20.34%)行政村。从以上分析看,生态要素水平在3个要素指标中水平最佳。主要因素:一是晋安区北部山区的自然环境条件比较好,特别是森林覆盖率总体较高;二是通过美丽乡村建设的改造,不断提升环境整治、垃圾处理能力,生态环境持续优化。乡镇生态要素水平排序为:日溪乡>寿山乡>宦溪镇。
2.3 乡村多元发展类型分析
通过微观尺度的乡村发展评价结果(图3),可以得出59个村在生产、生活和生态的空间特征及其内部差异。通过(图1)的乡村定位方法,59个村的功能和类型如表2所示。
表 2 乡村功能与类型识别Table 2. Rural function and type identification主导空间
Dominant condition辅助空间
Auxiliary condition村庄类型
Village type村庄 Village 生活 Living 生产 集聚提升 岭头村、中心村、胜利村、前洋村 生态 融入城镇 宦溪村、日溪村、湖山村、垄头村、湖中村 生产+生态 集聚提升 红寮村、宜夏村、创新村、鹅鼻村、峨嵋村、寿山村、汶洋村、井后村、梓山村、降虎村、上寮村 生产 Production 生活 集聚提升 过仑村、江南竹村 生态 搬迁撤并 洲洋村、建立村 生活+生态 特色保护 叶洋村、点洋村、弥高村、恩顶茶场、山头顶村、 生态 Ecology 生活 特色保护 板桥村、石牌村、九峰村、芙蓉村、亥由村、溪下村、贵洋村、菜岭村、南洋村、山溪村 生产 搬迁撤并 上仑村、优山村、长基村、东坪村、增楼村、牛项村、黄土岗村、吾洋村、黄田村、
红庙村、沙溪村、大坂村、汶石村、南峰村、党洋村、铁坑村、万洋村、山秀园村生活+生产 特色保护 民义村、芹石村 2.3.1 以生活为主导的乡村发展类型
该类乡村发展有3种模式,分别是“生活+生产”“生活+生态”和“生活+(生产+生态)”。晋安区北部山区以生活为主导空间的行政村有20个。该类型村庄的特征主要表现为交通比较方便、人口相对密集、资源比较丰富。因此应结合空间邻近型乡村推进城乡空间一体化发展,破解城乡二元结构壁垒,充分利用公共服务资源和区域优势,大力发展乡村空间经济。从国家村庄类型划分看,这20个村庄可以分成集聚提升和融入城镇两类。其中集聚提升类村庄要在原有规模基础上改造提升、优化环境、保护保留乡村风貌,同时激活产业、提振人气、增添活力,建设宜居宜业的现代化村庄。融入城镇类村庄要做好基础设施互联互通、公共服务共建共享,在形态上保留乡村风貌,在景观配置上突出乡村特色,在治理上主动承接城市功能外溢,为城乡融合发展提供实践经验。
2.3.2 以生产为主导的乡村发展类型
该类乡村发展有3种模式,分别是“生产+生活”“生产+生态”和“生产+(生活+生态)”。晋安区北部山区以生产为主导空间的行政村有9个。该类型村庄的特征主要表现为农业资源和土地利用比较丰富,交通尚可,但生活条件相对滞后。因此乡村应通过资源市场化开发,积极培育优势产业,同时积极推进乡村空间重构,有效整合乡村产业、人口、土地、基础设施等要素,提高乡村经济发展活力,拓宽乡村居民的收入来源。从国家村庄类型划分看,主要是集聚提升、特色保护和搬迁撤并三类。其中集聚提升类村庄在要激活原有产业规模基础,发挥自身比较优势,强化主导产业支撑,走专业化村庄发展路径。特色保护类村庄要合理利用特色资源,发展特色产业和乡村旅游;同时要尊重原住居民生活形态和传统习惯,适当改善村庄基础设施和公共环境,形成特色资源保护与村庄发展的良性互促机制。搬迁撤并类主要为人口数量太少导致公共资源配置不足的村庄,可与就近中心村联结,通过农村集聚发展搬迁、易地搬迁、生态宜居搬迁等方式,统筹解决村民生计和优化区域生态保护等问题。
2.3.3 以生态为主导的乡村发展类型
该类乡村发展有3种模式,分别是“生态+生活”“生态+生产”和“生态+(生产+生活)”。晋安区北部山区以生态为主导空间的行政村有30个。该类型村庄的特征主要表现为资源比较丰富,但交通可达性不足、生活环境条件较差。因此该类型乡村主要在保护特色资源的前提下继续加强乡村产业特色化发展,如休闲度假区、观光农业区、生态旅游区等,不断提升乡村竞争力。对于条件比较脆弱的村庄,以环境保护为主,减少或限制开发。从国家村庄类型划分看,主要是特色保护和搬迁撤并两类。特色保护类村庄要尊重原住居民生活形态和传统习惯,促进村庄特色资源合理利用与生态保护相和谐,形成特色资源保护与村庄发展的良性互促机制。搬迁撤并类村庄要严格限制新建、扩建活动,可通过集聚发展搬迁、易地搬迁、生态宜居搬迁等方式,实施与就近中心村搬迁撤并,搬迁撤并后的村庄原址,因地制宜复垦或还绿,增加乡村生产生态空间。
2.4 村庄聚类分析与板块化发展识别
2.4.1 村庄聚类分析
根据村庄聚类结果,得到4个类别村庄(表3)。其中第一类村庄有9个,该类村庄基本属于条件比较突出,位置比较中心;第二类村庄有6个,第三类村庄有6个,这些村庄属于发展比较有优势或特色比较鲜明的村庄,村庄基本配套比较充足;第四类村庄有38个,该类村庄属于条件比较一般、资源和特色不是太突出。
表 3 聚类分析归类Table 3. Cluster analysis类型 Type 村庄 Village 一类 山溪村、红寮村、上寮村、中心村、垄头村、岭头村、宜夏村、宦溪村、日溪村 二类 鹅鼻村、石牌村、过仑村、降虎村、板桥村、黄土岗村 三类 叶洋村、上仑村、胜利村、长基村、优山村、创新村 四类 恩顶茶场、南洋村、增楼村、洲洋村、建立村、民义村、亥由村、黄田村、牛项村、弥高村、峨嵋村、湖山村、湖中村、溪下村、
前洋村、山头顶村、江南竹村、红庙村、沙溪村、吾洋村、贵洋村、菜岭村、九峰村、大坂村、芙蓉村、芹石村、寿山村、点洋村、
汶洋村、汶石村、南峰村、东坪村、党洋村、铁坑村、万洋村、井后村、梓山村、山秀园村2.4.2 村庄板块化发展识别
通过上述59个村的空间定位和聚类分析,按照“联村共振”区域板块化合并方法,晋安区北部山区59个村庄划分为12个板块(图4)。12个板块中,岭头板块、宦溪板块和捷坂板块包含的村庄达到8个,汶洋板块、党洋板块和日溪板块包含的村仅有3个。其中除了吾洋板块没有特色村,其他板块均有。
3. 结论与讨论
3.1 结论
本研究从村域微观尺度构建了乡村发展评价模型,对晋安区北部59个村从生产、生活和生态等要素进行分析与评价,把脉乡村;在评价的基础上根据要素显著情况进行空间定位,寻找“病根”;最后,通过聚类分析寻找中心村,结合村庄空间定位,形成以中心村为依托,“点—线—面”区域多村结合、联村共振的乡村振兴路径。结果如下:
(1)晋安区北部农村发展水平总体不高且不平衡,各要素发展水平空间差异明显。总体来看,要素间生产方面表现相当不足,生态环境和生活水平相对比较良好;要素内部发展水平较低的村庄主要分布在晋安区东南部的宦溪镇,西北面的寿山乡和日溪乡的村庄发展水平相对较高。
(2)由于地形地貌的限制,仅有少量分布在区域干道附近或地貌比较平坦的村庄,生活条件和产业发展较显著。其中生活显著的行政村有20个,这些村庄表现为交通比较方便、人口相对密集、资源比较丰富,可以集聚提升和融入城镇;生产显著的行政村有9个,这些村庄表现为农业资源和土地利用比较丰富,交通尚可、但生活条件比较不好,部分可以集聚提升和进行特色保护,部分搬迁撤并、消化生活功能;生态显著的行政村有30个,这些村庄表现为自然资源比较丰富,但交通可达性不足、生活环境条件较差,少量进行特色保护,大部分进行搬迁撤并。
(3)聚类分析后,晋安区中心村和生活显著的村庄耦合性高,结合交通、区位等条件,可以形成12个联村共振板块,形成板块式、连片化发展。在这些板块中,南部的板块由于村庄比较集中,形成的集聚板块村庄比较多。而远郊的日溪乡,形成的集聚板块村庄比较少,基本在3个村左右。
3.2 政策建议
我国是一个农业大国,乡村是我国的重要组成部分,新中国成立后,我国经历了工业化进程,乡村为工业和城市的发展做出了巨大贡献,但我国乡村面临着凋敝和衰落的客观事实。从2003年以来连续15年的中央一号文件都聚焦于“三农”问题,党的十七大和十八大分别提出了城乡统筹和城乡一体化的发展战略,党的十九大提出了乡村振兴战略,党的二十大作出了全面推进乡村振兴的战略部署,体现了党和政府对“三农”的高度重视。我国幅员辽阔,东西南北差异巨大,如何根据地区特点和特色,统筹城乡发展,激发乡村发展活力,增强乡村吸引力,解决人民日益增长的美好生活需要和不平衡不充分发展之间的矛盾,让农业成为有奔头的产业,让农民成为有吸引力的职业,让农村成为安居乐业的美丽家园,是我国区域化乡村振兴“三生”协调发展的主要问题,需要地方政府和学者们依据地方实际针对性规划设计,构建拥具有地域特色、协同互补、差异化发展的乡村振兴战略。针对城郊型乡村的“三生”协调发展,建议如下:
(1)在城乡发展关系上,必须重塑城乡关系,走城乡融合发展之路。要将乡村的生产、生活、生态等多重功能结合起来,构成具有自然、经济、社会特征的多村结合“联村共治”的人类活动空间地域综合体,达到与城镇互促互进、共生共存的发展格局。
(2)在产业经济发展上,一是利用当地资源禀赋和区位条件,因地制宜发展都市农业、循环农业、特色农业,开发智慧农业、现代设施农业等新业态模式,为城市提供丰富多元的绿色、优质农副产品;二是整合自然特色景观和乡村旅游资源,积极发展乡村休闲农业,满足市民对节假日休憩和旅游休闲的需求。
(3)在环境建设上,一是生态环境发展建设方面,必须坚持人与自然和谐共生,走乡村绿色发展之路;二是生活环境建设方面,减少简单式 “穿衣戴帽”的破坏运动,通过保留乡村原始特色,打造各具特色的现代版“富春山居图”;三是生产环境转变方面,通过新生代、专业化农民的引入和老农传统发展方式理念的再造,走健康和可持续的农产品生产。
-
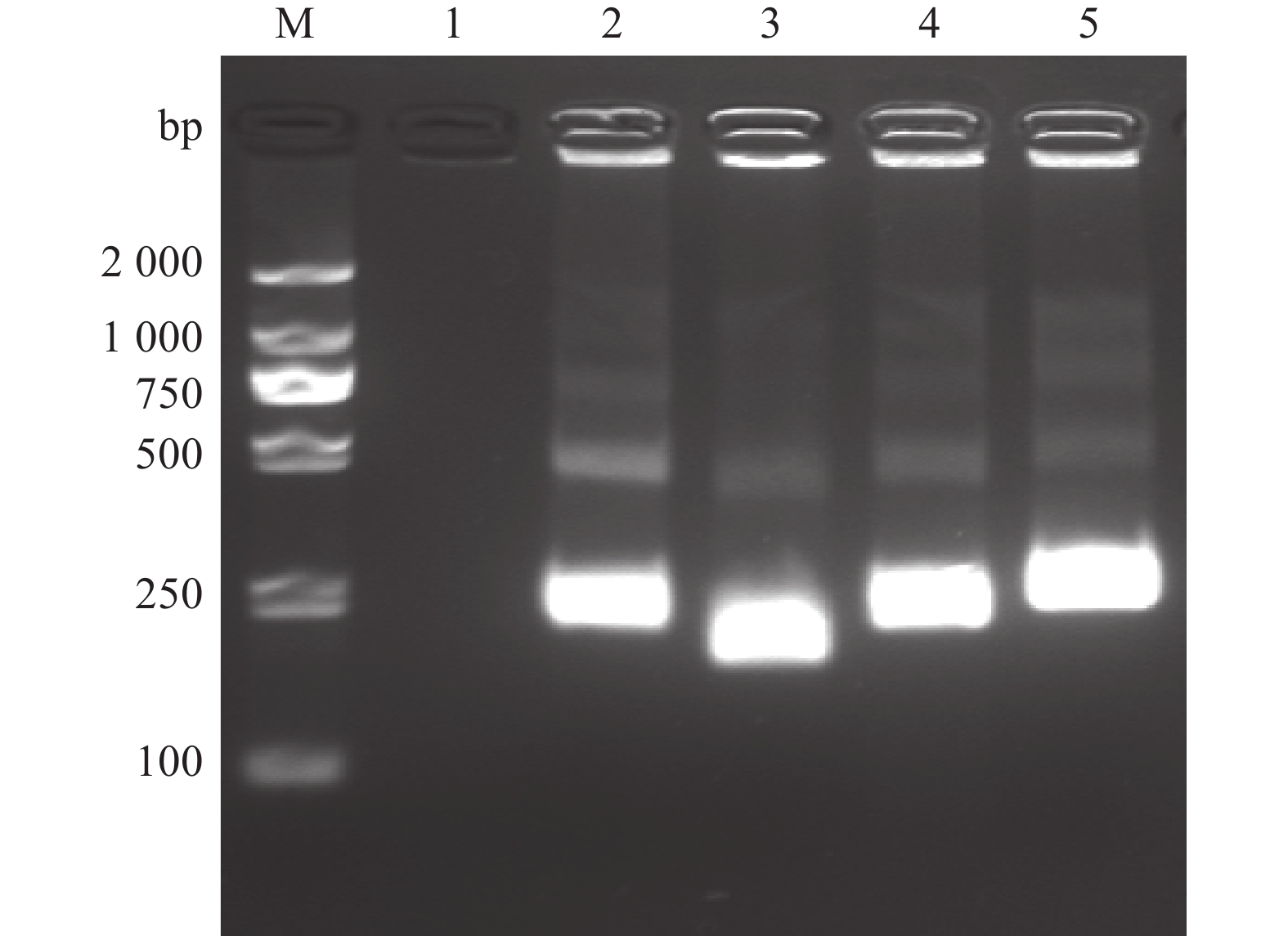
图 2 N-MDPV荧光RPA检测不同引物扩增结果
1~4(探针浓度4 μmol·L−1):N-MDPV-228F-228R、N-MDPV-193F-193R、N-MDPV-193F-230R、N-MDPV-193F-250R;5~8(探针浓度2 μmol·L−1):N-MDPV-228F-228R、N-MDPV-193F-193R、N-MDPV-193F-230R、N-MDPV-193F-250R;9~12(阴性对照):N-MDPV-228F-228R、N-MDPV-193F-193R、N-MDPV-193F-230R、N-MDPV-193F-250R。
Figure 2. Amplification of primers of RPA for N-MDPV
1–4 (with probe concentration at 4 μmol·L−1): N-MDPV-228F-228R, N-MDPV-193F-193R, N-MDPV-193F-230R, N-MDPV-193F-250R, respectively; 5–8 (with probe concentration at 2 μmol·L−1): N-MDPV-228F-228R, N-MDPV-193F-193R, N-MDPV-193F-230R, N-MDPV-193F-250R, respectively; 9–12 (negative control): N-MDPV-228F-228R, N-MDPV-193F-193R, N-MDPV-193F-230R, N-MDPV-193F-250R, respectively.
图 3 N- MDPV荧光RPA检测方法不同反应温度的扩增结果
1~5分别为26、35、39、42、45 ℃。不同小写字母表示不同温度之间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 3. Amplifications at varied reaction temperature of RPA for N-MDPV
1–5: 26, 35, 39, 42, and 45 ℃, respectively. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different temperatures at P<0.05.
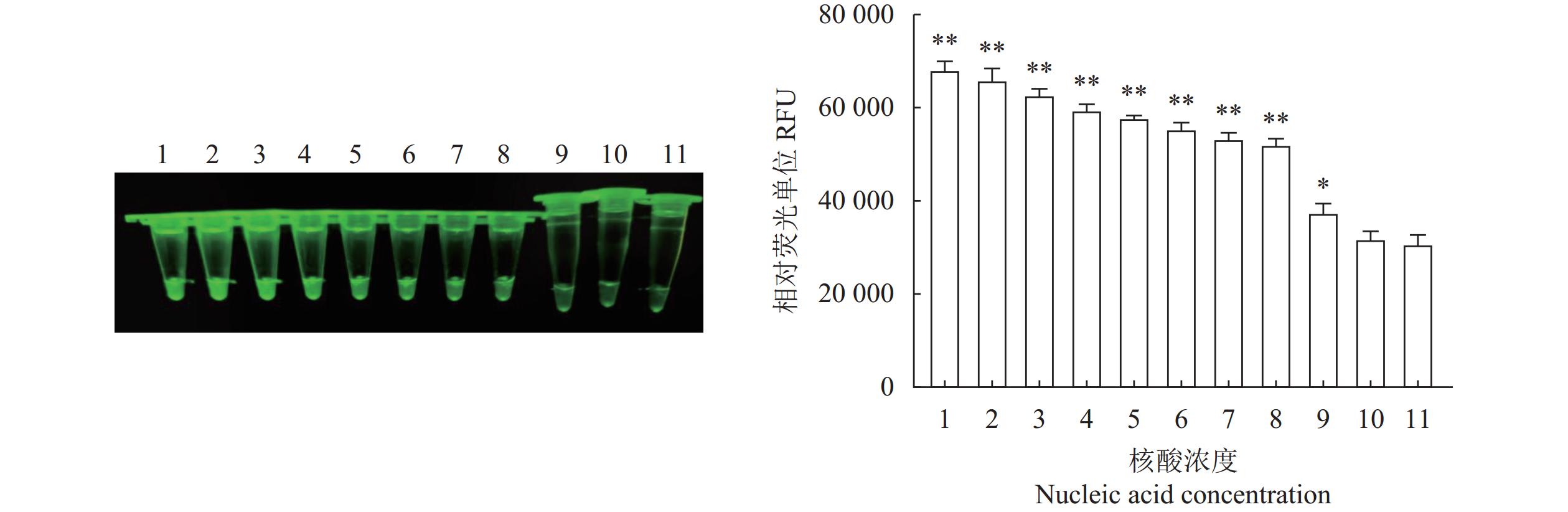
图 5 N-MDPV荧光RPA检测方法的敏感性
1:100 ng·μL−1;2:10 ng·μL−1;3:1 ng·μL−1;4:100 pg·μL−1;5:10 pg·μL−1;6:1 pg·μL−1;7:100 fg·μL−1;8:10 fg·μL−1;9:1 fg·μL−1;10:1 ag·μL−1;11:阴性对照。*、**:与阴性对照相比,差异显著(P<0.05)或极显著(P<0.01)。
Figure 5. Sensitivity of constant temperature fluorescent RPA assay
1: 100 ng·μL−1; 2: 10 ng·μL−1; 3: 1 ng·μL−1; 4: 100 pg·μL−1; 5: 10 pg·μL−1; 6: 1 pg·μL−1; 7: 100 fg·μL−1; 8: 10 fg·μL−1; 9: 1 fg·μL−1; 10: 1 ag·μL−1; 11: negative control; * and **: significant difference from negative control at P<0.05 and extremely significant difference from negative control at P<0.01, respectively.
图 6 N- MDPV荧光RPA检测方法的特异性
1:新型番鸭细小病毒;2:鸭腺病毒3型;3:禽腺病毒4型;4:鸭腺病毒3型+鸭坦布苏病毒;5:鸭瘟病毒;6:鸭病毒性肝炎病毒;7:鸭圆环病毒;8:鸭坦布苏病毒;9:新型鸭呼肠孤病毒;10:阴性对照。**:与阴性对照相比,差异极显著(P<0.01)。
Figure 6. Specificity of constant temperature fluorescent RPA assay
1: new-genotype muscovy duck parvovirus ; 2: duck adenovirus type 3; 3: fowl adenovirus serotype 4; 4: duck adenovirus type 3 + duck tembusu virus; 5: duck plague virus; 6: duck hepatitis virus; 7: duck circovirus; 8: duck tembusu virus; 9: novel duck reovirus; 10: negative control. **: extremely significant difference from negative control at P<0.01.
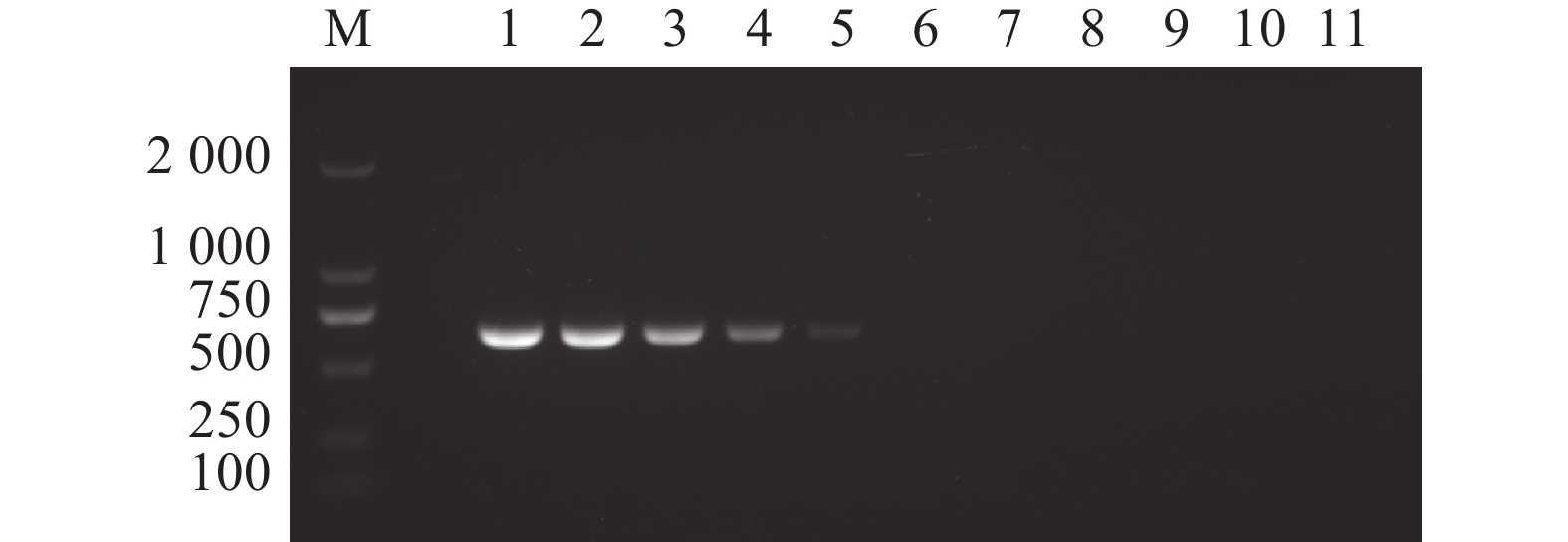
图 7 N-MDPV PCR 检测方法的敏感性
M:DL 2000 DNA分子质量标准;1:100 ng·μL−1;2:10 ng·μL−1;3:1 ng·μL−1;4:100 pg·μL−1;5:10 pg·μL−1;6:1 pg·μL−1;7:100 fg·μL−1;8:10 fg·μL−1;9:1 fg·μL−1;10:1 ag·μL−1;11:阴性对照。
Figure 7. Sensitivity of constant temperature fluorescent RPA assay
M: DL 2000 DNA marker; 1: 100 ng·μL−1; 2: 10 ng·μL−1; 3: 1 ng·μL−1; 4: 100 pg·μL−1; 5: 10 pg·μL−1; 6: 1 pg·μL−1; 7: 100 fg·μL−1; 8: 10 fg·μL−1; 9: 1 fg·μL−1; 10: 1 ag·μL−1; 11: negative control.
图 8 N-MDPV荧光RPA检测方法的敏感性
1:100 ng·μL−1;2:10 ng·μL−1;3:1 ng·μL−1;4:100 pg·μL−1;5:10 pg·μL−1;6:1 pg·μL−1;7:100 fg·μL−1;8:10 fg·μL−1;9:1 fg·μL−1;10:1 ag·μL−1;11:阴性对照。*、**:与阴性对照相比,差异显著(P<0.05)或极显著(P<0.01)。
Figure 8. Sensitivity of constant temperature fluorescent RPA assay
1: 100 ng·μL−1; 2: 10 ng·μL−1; 3: 1 ng·μL−1; 4: 100 pg·μL−1; 5: 10 pg·μL−1; 6: 1 pg·μL−1; 7: 100 fg·μL−1; 8: 10 fg·μL−1; 9: 1 fg·μL−1; 10: 1 ag·μL−1; 11: negative control; * and **: significant difference from negative control at P<0.05 and extremely significant difference from negative control at P<0.01. respectively.
表 1 N-MDPV的RPA引物和探针
Table 1 RPA primers and probes of N-MDPV
引物和探针
Primers and probes序列(5′-3′)
Sequence(5′-3′)N-MDPV-228F AGGCGCTTATGGCACCATGGGCCGCAATTGG N-MDPV-228R CCTAAAATATTTTGGGCTGGGATGCTGGAAG N-MDPV-193F ACTCACACAGAAGCAGAGGCTTCCAGCATCC N-MDPV-193R TAGTGTTTTGTTCATTCGTTACAGTCTTGCC N-MDPV-230R CCAAGAACATCAAGATCTGAACTCGTAGGAG N-MDPV-250R AAACCATTCCTGGTAAAGCTCCAAGAACATC N-MDPV-probe 5′ACAGATCTGGCAGCACTGCAGCAGGAATAA
AFGHQATTATGGTAACGGACG -C3 Spacer表 2 N-MDPV RPA 与 PCR 方法、病毒分离法临床样本检测结果比较
Table 2 Comparison between detections by constant temperature fluorescent RPA assay and PCR on clinical samples
检测方法
Detecting
Method样品数
No. of
samples阳性样品数
No. of
positive阴性样品数
No. of
negative阳性率
Positive
rate%RPA恒温检测
RPA constant
temperature detection38 14 24 36.8 常规 PCR
Conventional PCR38 14 24 36.8 病毒分离鉴定法
Virus isolation and
identification method38 12 26 31.6 -
[1] 林世棠, 郁晓岚, 陈炳钿, 等. 一种新的雏番鸭病毒性传染病的诊断 [J]. 中国畜禽传染病, 1991, 13(2):25−26. LIN S T, YU X L, CHEN B D, et al. Diagnosis of a new viral infectious disease in Muscovy duck [J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 1991, 13(2): 25−26. (in Chinese)
[2] 胡奇林, 吴振兖, 周文谟, 等. 雏番鸭细小病毒病的流行病学调查 [J]. 中国兽医杂志, 1993, 29(6):7−8. HU Q L, WU Z Y, ZHOU W M, et al. Epidemiological investigation of parvovirus disease in Muscovy ducks [J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 1993, 29(6): 7−8. (in Chinese)
[3] 黄瑜, 万春和, 傅秋玲, 等. 新型番鸭细小病毒的发现及其感染的临床表现 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2015, 30(5):442−445. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2015.05.004 HUANG Y, WAN C H, FU Q L, et al. The identity and clinic infectious symptoms of the new genotype Muscovy duck parvovirus [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 30(5): 442−445. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2015.05.004
[4] 孟婷, 朱善元, 夏文龙, 等. 番鸭细小病毒LAMP检测方法的建立 [J]. 中国动物传染病学报, 2019, 27(1):25−29. MENG T, ZHU S Y, XIA W L, et al. Development of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for detection of Muscovy duck parvovirus [J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Infectious Diseases, 2019, 27(1): 25−29. (in Chinese)
[5] EULER M, WANG Y J, OTTO P, et al. Recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid detection of Francisella tularensis [J]. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 2012, 50(7): 2234−2238. DOI: 10.1128/JCM.06504-11
[6] 刘孟啸, 蔡姝, 刘建钗, 等. 鸭腺病毒3型荧光RPA恒温快速检测方法的建立与应用 [J]. 中国兽药杂志, 2023, 57(11):8−15. LIU M X, CAI S, LIU J C, et al. Rapid detection of duck adenovirus type 3 based on isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification assay [J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Drug, 2023, 57(11): 8−15. (in Chinese)
[7] 袁嘉康, 李林岳, 庞俊增, 等. 猪流行性腹泻病毒RPA-LFD检测方法的建立 [J]. 中国兽医学报, 2023, 43(6):1127−1132. YUAN J K, LI L Y, PANG J Z, et al. Establishment of RPA-LFD method for detection of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus [J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2023, 43(6): 1127−1132. (in Chinese)
[8] ABD EL WAHED A, EL-DEEB A, EL-THOLOTH M, et al. A portable reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid detection of foot-and-mouth disease virus [J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(8): e71642. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071642
[9] 王建昌, 王金凤, 刘立兵, 等. 非洲猪瘟病毒RPA等温检测方法的建立 [J]. 中国动物检疫, 2016, 33(7):78−81,94. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-944X.2016.07.024 WANG J C, WANG J F, LIU L B, et al. Rapid and sensitive detection of African swine fever virus by recombinase polymerase amplification [J]. China Animal Health Inspection, 2016, 33(7): 78−81,94. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-944X.2016.07.024
[10] DAHER R K, STEWART G, BOISSINOT M, et al. Recombinase polymerase amplification for diagnostic applications [J]. Clinical Chemistry, 2016, 62(7): 947−958. DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2015.245829
[11] 万春和, 傅秋玲, 陈翠腾, 等. 基因重组型番鸭细小病毒FJM3的全基因组特征 [J]. 中国兽医学报, 2016, 36(11):1836−1841. WAN C H, FU Q L, CHEN C T, et al. Molecular characterization of the genome for recombinant Muscovy duck parvovirus strain FJM3 [J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2016, 36(11): 1836−1841. (in Chinese)
[12] 刘家森, 姜骞, 司昌德, 等. 番鸭细小病毒与鹅细小病毒PCR鉴别诊断方法的建立 [J]. 中国兽医科学, 2007, 37(6):469−472. LIU J S, JIANG Q, SI C D, et al. Establishment of PCR assay for differentiation of Muscovy duck parvovirus from goose parvovirus [J]. Veterinary Science in China, 2007, 37(6): 469−472. (in Chinese)
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 王沛然,张家林,高祥斌,涂佳才. 水肥耦合对‘聊红’椿幼苗生长特性的影响. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(02): 153-161 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王沛然,张家林,高祥斌,涂佳才. 水肥耦合对‘聊红’椿幼苗根系形态特征的影响. 山东农业科学. 2024(05): 87-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 尹明华,郭依瑶,李启诺,罗泽全,林文龙,熊姿雯. 信前胡烟草花叶病毒lncRNA测序鉴定、原核蛋白表达及其序列分析. 中国农学通报. 2024(21): 106-113 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: