A Concise Phenotype-based Collection of Phalaenopsis Germplasms
-
摘要:目的
基于表型性状构建蝴蝶兰初级核心种质,为蝴蝶兰资源的保存利用和品种选育提供理论依据。
方法以210份蝴蝶兰种质资源为材料,对32个表型性状进行调查,其中包括13个质量性状和19个数量性状。采用3种取样方法(随机取样法、优先取样法、偏离度取样法)、2种遗传距离(欧氏距离、马氏距离)、3种取样比例(20%、25%、30%)和8种聚类方法(最短距离法、最长距离法、中间距离法、重心法、不加权类平均法、可变类平均法、可变法、离差平方和法),探讨最佳取样策略,构建核心种质。利用均值差异百分率(Mean difference percentage, MD)、方差差异百分率(Variance difference percentage, VD)、极差符合率(Range coincidence rate, CR)和变异系数变化率(Variation coefficient change rate, VR)对备选核心种质进行评价,利用均值、极值比较分析和主成分分析对核心种质进行确认。
结果优先取样法能够使核心种质更具代表性,欧式距离优于马氏距离,25%为最佳取样比例,最优聚类方法为最长距离法,最终抽提出52份材料的初级核心种质。构建的核心种质各项评价参数优秀,能够代表原始种质的遗传多样性,主成分信息得到保留,并且很好地去除了原种质的遗传冗余。
结论构建的蝴蝶兰初级核心种质可以优先作为后续蝴蝶兰种质资源研究的材料,为种质的保存和利用提供理论基础。
Abstract:ObjectiveA concise collection of Phalaenopsis germplasms based on their phenotypic traits was preliminarily assembled to facilitate conservation and utilization of the natural resource.
MethodsTwo hundred and ten Phalaenopsis germplasms encompassing 32 phenotypes, including 13 qualitative and 19 quantitative traits, were included in this study. The random, preferred, and deviation sampling methods, the Euclidean and Mahalanobis genetic distances, the 20%, 25%, and 30% sampling ratios as well as the single, complete, median, centroid, unweighted, weighted, flexible, and ward clustering methods were employed in comparison to optimize the selection process. The information obtained was scrutinized with evaluations on the mean difference percentage (MD), variance difference percentage (VD), range coincidence rate (CR), and variation coefficient change rate (VR). It was further verified by the mean and extreme comparative analyses and principal component analysis to arrive at a concise and representative collection of the germplasms.
ResultsThe germplasms for the collection were eventually gathered by means of the preferred sampling at the Euclidean distance and 25% sampling ratio with the complete clustering. Out of the 210 germplasms, 52 selected cultivars were deemed to statistically represent the genetic diversity of the current collection with all the principal components on phenotypic traits preserved without redundancy.
ConclusionThe collection of Phalaenopsis germplasms assembled by this study was concise and representative of the resource presently in stock. It covered all key phenotypes needed to be preserved for future studies and applications.
-
Keywords:
- Phalaenopsis /
- germplasm collection /
- phenotypic traits /
- sampling methods
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】蝴蝶兰(Phalaenopsis)为兰科(Orchidaceae)蝴蝶兰属(Phalaenopsis)多年生草本植物,因其优美的姿态、丰富艳丽的花色、高雅的气质,被誉为“兰花皇后”,备受市场青睐[1]。蝴蝶兰最早由德国科学家Rumphius在安纹岛上发现,至今已拥有丰富的种质资源[2]。随着品种的不断引进栽培,我国蝴蝶兰种质资源保存数量逐渐庞大,增加了种质资源管理的费用和特异性种质筛选的难度,为此构建蝴蝶兰品种资源的核心种质、充分挖掘利用蝴蝶兰资源优势、保障品种资源工作的延续性并推动育种创新具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】核心种质的概念最早由Frankel[3]提出,随后Brown[4]对核心种质的概念进行了完善和总结。目前核心种质的研究引起了国内外很多学者的重视,已经在许多农作物上应用,如水稻(Oryza sativa L.)[5−6]、玉米(Zea mays L.)[7]、马铃薯(Solanum tuberosum L.)[8]、番茄(Solanum lycopersicum L.)[9]等,部分观赏植物,如菊花(Chrysanthemum × morifolium Ramat)[10−11]、望春玉兰[Yulania biondii (Pamp.) D. L. Fu][12]、紫薇(Lagerstroemia indica L.)[13]、建兰[Cymbidium ensifolium (L.) Sw.][14]等也进行了核心种质的构建。同时,有关核心种质的取样比例、取样策略以及有效性评价等理论研究也取得了长足的进展,为核心种质的构建及代表性评价提供了理论依据[15−18]。国内外研究者对蝴蝶兰种质资源进行了广泛的收集与利用[19−20]。李佐等[21] 对构建蝴蝶兰核心种质的方法进行了初步探讨。【本研究切入点】但基于表型性状构建蝴蝶兰初级核心种质构建的系统研究鲜有报道。【拟解决对关键问题】本研究基于收集的210份蝴蝶兰资源,通过对其32个表型性状进行调查分析,系统比较3种组内取样方法、2种遗传距离、8种聚类方法和3种取样规模,初步构建适宜的蝴蝶兰初级核心种质,以期为蝴蝶兰种质资源利用和品种选育提供理论依据和亲本选择。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 供试材料
以福建省农业科学院花卉研究中心收集并保存的210份蝴蝶兰资源为材料,表型性状的调查于2023—2024年进行。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 数据的收集和整理
调查的32个性状包括19个数量性状和13个质量性状(表1),主要依据《植物新品种特异性、一致性和稳定性测试指南——蝴蝶兰》(NY/T2230—2012)[22]的要求进行观测、测量并记录,同时对质量性状进行赋值(表2)。
表 1 蝴蝶兰性状及代码Table 1. Codes of Phalaenopsis phenotypic traits代码 Code 性状Traits 代码 Code 性状Traits C1 植株大小 Plant length/cm C17 花序梗数量 Peduncle number/个 C2 叶片长度 Leaf length/cm C18 合蕊柱长度 Gynostemium length/cm C3 叶片宽度 Leaf width/cm C19 合蕊柱粗度 Gynostemium thickness/cm C4 花序长度 Inflorescence length/cm C20 叶片形状 Leaf shape C5 花数量 Flower number/朵 C21 叶片上表面颜色 Color of the upper side of leaf C6 花序梗长度 Peduncle length/cm C22 叶片花青甙显色 Anthocyanin coloration of leaf C7 花序梗粗度 Peduncle thickness/cm C23 叶片厚度 Leaf thickness C8 花梗长度 Pedicel length/cm C24 叶片表面纹理 Leaf surface texture C9 花长度 Flower length/cm C25 花序类型 Inflorescence type C10 花宽度 Flower width/cm C26 花序梗表面颜色 Surface color of peduncle C11 萼片长度 Dorsal sepal length/cm C27 花瓣排列方式 Petal arrangement C12 萼片宽度 Dorsal sepal width/cm C28 花香味 Scent of flower C13 花瓣长度 Petal length/cm C29 中萼片颜色数量 Number of middle sepal colors C14 花瓣宽度 Petal width/cm C30 侧萼片颜色数量 Number of lateral sepal colors C15 中裂片长度 Apical lobe length/cm C31 花瓣颜色数量 Number of petal colors C16 中裂片宽度 Apical lobe width/cm C32 花蜡质 Waxiness of flower 表 2 蝴蝶兰质量性状分级与赋值Table 2. Classification and codes of qualitative Phalaenopsis traits性状 Traits 赋值 Assigning value 叶片形状
Leaf shape披针形=1,窄卵圆形=2,椭圆形=3,窄倒卵圆形=4,倒卵圆形=5
lanceolate=1,narrowly oval=2,elliptical=3,narrowly inverted ovoid=4,obovoid=5叶片上表面颜色
Color of the upper side of leaf浅绿色=1,中等绿色=2,深绿色=3,灰绿色=4
light green=1,medium green=2,dark green=3,greyish green=4叶片花青甙显色
Anthocyanin coloration of leaf无=1,有=2
no=1,yes=2叶片厚度
Leaf thickness薄=1,中=2,厚=3
thin=1,medium=2,thick=3叶片表面纹理
Leaf surface texture无=1,有=2
no=1,yes=2花序类型
Inflorescence type单生花=1,总状花序=2,圆锥花序=3
solitary=1,raceme=2,panicle=3花序梗表面颜色
Surface color of peduncle浅绿色=1,中等绿色=2,深绿色=3,灰绿色=4,红褐色=5,褐色=6
light green=1,medium green=2,dark green=3,greyish green=4,reddish brown=5,brown=6花瓣排列方式
Petal arrangement分开=1,相接=2,重叠=3
separate=1,adjacent=2,overlapping=3花香味
Scent of flower无=1,有=2
no=1,yes=2中萼片颜色数量
Number of middle sepal colors1种=1,2种=2,3种=3,3种以上=4
1 color=1,2 colors=2,3 colors=3,more than 3 colors=4侧萼片颜色数量
Number of lateral sepal colors1种=1,2种=2,3种=3,3种以上=4
1 color=1,2 colors=2,3 colors=3,more than 3 colors=4花瓣颜色数量
Number of petal colors1种=1,2种=2,3种=3,3种以上=4
1 color=1,2 colors=2,3 colors=3,more than 3 colors=4花蜡质
Waxiness of flower无=1,有=2
no=1,yes=21.2.2 数据分组和聚类分析
采用Excel2016计算32个性状的基础指标,包括平均值、标准差、最大值、最小值和变异系数;采用QGA2.0构建核心种质[23-24];采用SPSS25.0进行t检验和主成分分析。
1.2.3 取样策略
通过3种取样方法(随机取样法、优先取样法、偏离度取样法)、2种遗传距离(欧氏距离、马氏距离)、3种取样比例(20%、25%、30%)和8种聚类方法(最短距离法、最长距离法、中间距离法、重心法、不加权类平均法、可变类平均法、可变法、离差平方和法)构建出144份备选核心种质。
1.2.4 核心种质评价
利用均值差异百分率(Mean difference percentage, MD)、方差差异百分率(Variance difference percentage, VD)、极差符合率(Range coincidence rate, CR)和变异系数变化率(Variation coefficient change rate, VR)对备选核心种质进行评价,以MD小于20%、CR大于80%为最低标准,同时VD和VR的值越高越好[25−27],确定蝴蝶兰初级核心种质的最佳构建策略。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 最佳构建策略的确定
基于排列组合构建出的144份备选核心种质,利用MD、VD、CR、VR进行评价(表3)。
表 3 144个备选核心种质的评价参数Table 3. Parameters for evaluating 144 candidate germplasms取样比例
Sample ratio遗传距离
Genetic distance聚类方法
Cluster method多次聚类随机取样法
Multiple cluster random
sampling method多次聚类优先取样法
Multiple cluster preferred sampling method多次聚类偏离度取样法
Multiple cluster deviation
sampling methodMD VD CR VR MD VD CR VR MD VD CR VR 20% 欧氏距离
Euclidean distanceSingle 3.13 18.75 91.34 111.47 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 9.38 28.13 97.96 119.58 Complete 0.00 15.63 89.52 107.99 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 0.00 37.50 98.02 120.42 Median 0.00 9.38 90.43 108.20 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 3.13 15.63 95.28 114.72 Centroid 3.13 15.63 91.48 112.49 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 0.00 15.63 95.69 113.18 Unweighted 0.00 6.25 93.92 109.68 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 0.00 15.63 94.49 119.55 weighted 0.00 15.63 89.88 106.84 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 0.00 31.25 95.39 116.32 Flexible 3.13 12.50 86.44 105.95 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 0.00 28.13 94.05 116.58 Ward 0.00 15.63 90.43 110.29 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 0.00 43.75 95.43 117.14 马氏距离
Mahalanobis distanceSingle 6.25 15.63 90.77 110.74 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 21.88 53.13 96.81 116.87 Complete 0.00 6.25 90.36 107.11 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 3.13 46.88 96.18 121.91 Median 3.13 15.63 90.28 109.75 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 9.38 53.13 97.08 120.88 Centroid 21.88 25.00 93.94 115.19 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 40.63 50.00 97.34 114.20 Unweighted 0.00 9.38 89.96 104.78 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 3.13 53.13 95.31 122.61 weighted 0.00 9.38 90.15 105.21 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 0.00 53.13 94.04 117.15 Flexible 0.00 9.38 84.82 99.43 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 0.00 53.13 92.76 118.25 Ward 0.00 15.63 88.01 110.22 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 3.13 50.00 96.31 124.36 25% 欧氏距离
Euclidean distanceSingle 3.13 18.75 94.06 108.15 3.13 46.88 100.00 116.83 9.38 21.88 97.99 116.42 Complete 0.00 9.38 90.33 107.97 0.00 37.50 100.00 118.20 0.00 15.63 98.02 117.14 Median 0.00 6.25 91.10 104.70 18.75 37.50 100.00 113.46 0.00 12.50 96.03 111.96 Centroid 3.13 12.50 92.52 108.82 0.00 28.13 100.00 116.11 0.00 12.50 96.19 110.06 Unweighted 0.00 9.38 96.02 106.98 0.00 37.50 100.00 117.18 0.00 15.63 96.02 116.94 weighted 0.00 9.38 91.54 104.42 0.00 34.38 100.00 116.48 0.00 12.50 95.83 112.31 Flexible 3.13 12.50 89.51 104.44 0.00 34.38 100.00 116.41 0.00 15.63 95.61 113.33 Ward 0.00 12.50 92.22 107.95 0.00 34.38 100.00 117.65 0.00 21.88 95.49 113.83 马氏距离
Mahalanobis distanceSingle 3.13 15.63 93.96 108.25 3.13 43.75 100.00 116.84 25.00 43.75 97.80 114.64 Complete 0.00 6.25 92.49 104.49 18.75 21.88 100.00 113.25 3.13 43.75 96.18 117.74 Median 12.50 15.63 90.96 106.71 6.25 37.50 100.00 114.98 12.50 50.00 97.65 116.36 Centroid 25.00 40.63 94.40 111.51 6.25 34.38 100.00 114.99 12.50 50.00 97.80 115.74 Unweighted 0.00 9.38 91.23 105.90 3.13 21.88 100.00 115.20 0.00 43.75 95.72 119.67 weighted 0.00 6.25 90.32 102.42 0.00 31.25 100.00 115.65 0.00 34.38 94.04 114.45 Flexible 0.00 6.25 89.18 102.02 9.38 43.75 100.00 115.10 0.00 43.75 94.37 115.04 Ward 0.00 12.50 88.99 105.98 0.00 28.13 100.00 113.91 0.00 46.88 97.06 118.15 30% 欧氏距离
Euclidean distanceSingle 3.13 18.75 94.06 105.70 6.25 28.13 100.00 113.08 9.38 18.75 98.45 115.29 Complete 0.00 12.50 91.83 106.48 0.00 28.13 100.00 115.17 0.00 15.63 98.51 115.55 Median 0.00 6.25 92.13 104.42 3.13 21.88 100.00 110.75 0.00 12.50 97.82 109.50 Centroid 0.00 9.38 93.09 106.86 0.00 18.75 100.00 112.80 0.00 12.50 96.23 108.23 Unweighted 0.00 9.38 96.82 105.33 0.00 21.88 100.00 114.35 0.00 9.38 98.03 113.32 weighted 0.00 15.63 92.98 102.65 0.00 25.00 100.00 114.54 0.00 12.50 95.94 110.04 Flexible 0.00 15.63 90.92 104.92 0.00 21.88 100.00 113.34 0.00 12.50 95.69 111.23 Ward 0.00 12.50 93.17 107.20 0.00 25.00 100.00 114.83 0.00 18.75 96.00 111.83 30% 马氏距离
Mahalanobis distance最短距离法Single 9.38 15.63 94.73 107.77 0.00 31.25 100.00 113.80 15.63 40.63 97.80 113.30 最长距离法Complete 0.00 9.38 93.56 105.10 6.25 21.88 100.00 113.05 0.00 43.75 97.32 115.64 中间距离法Median 0.00 9.38 93.50 106.51 3.13 21.88 100.00 112.91 6.25 40.63 97.65 113.08 重心法Centroid 31.25 43.75 95.09 110.91 21.88 37.50 100.00 113.00 12.50 40.63 97.80 111.99 类平均法Unweighted 0.00 9.38 92.31 105.21 0.00 25.00 100.00 111.08 3.13 46.88 96.20 116.42 可变类平均法weighted 0.00 9.38 94.73 105.33 0.00 18.75 100.00 112.31 0.00 18.75 94.52 112.03 可变法Flexible 0.00 6.25 90.23 103.40 3.13 25.00 100.00 112.42 0.00 40.63 94.84 113.80 离差平方和法Ward 0.00 15.63 92.36 107.50 0.00 21.88 100.00 111.19 0.00 37.50 97.06 116.19 MD:均值差异百分率,VD:方差差异百分率, CR:极差符合率,VR:变异系数变化率;最短距离法,最长距离法,中间距离法,重心法,类平均法,可变类平均法,可变法,离差平方和法。
MD:mean difference percentage; VD:variance difference percentage; CR: range coincidence rate; VR:variation coefficient change rate;single,complete,median,centroid,unweighted,weighted,flexible,and ward clustering methods.2.1.1 取样方法的确定
对3种取样方法进行比较,随机取样法MD均值最低,但VD、CR和VR均值也最低;优先取样法虽然MD均值略高于偏离度取样法,但VD、CR和VR均值均大于另外两种方法,且CR均为100%,因此在取样方法上选择优先取样法进行初级核心种质的构建。
2.1.2 遗传距离的确定
在优先取样法的基础上,对欧氏距离和马氏距离进行比较,发现欧氏距离的MD均值低于马氏距离,VD和VR高于马氏距离,两种遗传距离CR均为100%,因此选择欧氏距离进行核心种质的构建更加合适。
2.1.3 取样比例的确定
在优先取样法、欧氏距离的基础上,取样比例为20%时,所有聚类方法的4个评价指标均相同且MD均不为0,随着取样比例的增加,MD均值降低,同时VD、VR也降低,取样比例为30%时,虽然MD最低,但VD降低较多,综合考虑取样比例为25%时MD较低,且VD、VR较高。
2.1.4 聚类方法的确定
在优先取样法、欧氏距离和25%取样比例的基础上,比较8种聚类方法,发现在MD为0、CR为100%的6种聚类方法中,最长距离法和类平均法的VD均为37.5%,其中最长距离法的VR最高,为118.2%,因此最长距离法是构建初级核心种质的最优方法。
综上所述,选择“优先取样法+欧氏距离+25%的取样比例+最长距离法”的策略构建蝴蝶兰初级核心种质。
2.2 初级核心种质的验证
2.2.1 原始种质与核心种质的比较分析
对原始种质与核心种质的均值、极值、方差和变异系数进行对比,如表4所示。结果表明:核心种质与原始种质相比,所有性状的均值无显著差异;最大值、最小值均一致,极差符合率为100%;32个性状中有31个方差高于原始种质,所有性状的变异系数均高于原始种质,说明核心种质的遗传变异高于原始种质,有较好的代表性。
表 4 原始种质与核心种质遗传差异比较Table 4. Genetic differences between entire and representative collection of germplasms性状
Traits类别
Categories均值
MeanP值
P value显著性
Significance方差
VarianceP值
P value显著性
Significance极差
Range变异系数
CV/%C1 原始种质 Original 29.98 0.98 NS 47.67 0.02 S* 42.5 23.03 核心种质 Core 29.94 73.40 42.5 28.62 C2 原始种质 Original 16.21 0.89 NS 12.59 0.01 S* 21.67 21.89 核心种质 Core 16.31 19.83 21.67 27.31 C3 原始种质 Original 6.70 0.63 NS 2.41 0.00 S** 11.17 23.17 核心种质 Core 6.54 5.00 11.17 34.20 C4 原始种质 Original 14.71 0.53 NS 94.34 0.07 NS 40.06 66.01 核心种质 Core 15.71 127.87 40.06 71.99 C5 原始种质 Original 11.31 0.90 NS 55.47 0.40 NS 33 65.87 核心种质 Core 11.16 58.05 33 68.27 C6 原始种质 Original 19.13 0.25 NS 126.63 0.10 NS 49.83 58.82 核心种质 Core 21.23 166.13 49.83 60.71 C7 原始种质 Original 0.47 0.34 NS 0.05 0.00 S** 2.93 46.54 核心种质 Core 0.52 0.15 2.93 75.11 C8 原始种质 Original 32.85 0.46 NS 383.95 0.06 NS 86.63 59.65 核心种质 Core 35.19 528.77 86.63 65.34 C9 原始种质 Original 5.43 0.14 NS 2.58 0.01 S** 8.2 29.58 核心种质 Core 5.90 4.30 8.2 35.13 C10 原始种质 Original 5.83 0.21 NS 3.58 0.01 S* 10.57 32.46 核心种质 Core 6.28 5.71 10.57 38.03 C11 原始种质 Original 2.98 0.14 NS 0.84 0.03 S* 4.73 30.75 核心种质 Core 3.20 1.22 4.73 34.61 C12 原始种质 Original 2.11 0.14 NS 0.67 0.01 S* 4.07 38.66 核心种质 Core 2.34 1.07 4.07 44.26 C13 原始种质 Original 2.70 0.18 NS 0.77 0.03 S* 4.83 32.46 核心种质 Core 2.89 1.14 4.83 36.94 C14 原始种质 Original 2.85 0.17 NS 2.20 0.03 S* 6.6 52.05 核心种质 Core 3.18 3.27 6.6 56.85 C15 原始种质 Original 1.73 0.41 NS 0.28 0.00 S** 3.27 30.66 核心种质 Core 1.64 0.56 3.27 45.41 C16 原始种质 Original 1.45 0.60 NS 0.39 0.01 S* 3.17 43.04 核心种质 Core 1.38 0.61 3.17 56.65 C17 原始种质 Original 1.71 0.33 NS 0.74 0.47 NS 4.66 50.24 核心种质 Core 1.58 0.74 4.66 54.58 C18 原始种质 Original 1.01 0.21 NS 0.02 0.00 S** 1.17 15.03 核心种质 Core 1.05 0.04 1.17 20.15 C19 原始种质 Original 0.45 0.35 NS 0.06 0.00 S** 3.54 56.28 核心种质 Core 0.51 0.22 3.54 91.93 C20 原始种质 Original 2.72 0.47 NS 1.19 0.11 NS 4 40.10 核心种质 Core 2.60 1.54 4 47.79 C21 原始种质 Original 1.85 0.75 NS 0.61 0.33 NS 3 42.33 核心种质 Core 1.81 0.67 3 45.22 C22 原始种质 Original 1.19 0.13 NS 0.16 0.08 NS 1 33.10 核心种质 Core 1.29 0.21 1 35.51 C23 原始种质 Original 1.90 0.58 NS 0.42 0.30 NS 2 34.17 核心种质 Core 1.96 0.47 2 34.92 C24 原始种质 Original 1.14 0.85 NS 0.12 0.36 NS 1 30.74 核心种质 Core 1.15 0.13 1 31.58 C25 原始种质 Original 2.41 0.19 NS 0.25 0.46 NS 2 20.86 核心种质 Core 2.31 0.26 2 21.94 C26 原始种质 Original 2.86 0.22 NS 2.24 0.13 NS 5 52.38 核心种质 Core 3.15 2.84 5 53.42 C27 原始种质 Original 1.07 0.27 NS 0.12 0.00 S** 2 32.53 核心种质 Core 1.15 0.29 2 46.64 C28 原始种质 Original 1.32 0.71 NS 0.22 0.45 NS 1 35.41 核心种质 Core 1.29 0.21 1 35.51 C29 原始种质 Original 2.00 0.88 NS 0.36 0.14 NS 3 29.95 核心种质 Core 2.02 0.45 3 33.24 C30 原始种质 Original 2.22 0.69 NS 0.49 0.40 NS 3 31.54 核心种质 Core 2.27 0.51 3 31.60 C31 原始种质 Original 2.04 0.47 NS 0.38 0.10 NS 3 30.09 核心种质 Core 2.12 0.50 3 33.30 C32 原始种质 Original 1.75 0.18 NS 0.19 0.17 NS 1 24.97 核心种质 Core 1.65 0.23 1 29.05 NS表示无显著差异;S*表示显著水平;S**表示极显著水平;P值表示判定假设检验结果的参数。
NS: No significant difference; S*: significant difference; S**: extremely significant difference; P: parameter for evaluating hypothesis test result.2.2.2 主成分分析
对原始种质和核心种质进行了主成分分析,详见表5。结果表明原始种质和核心种质都提取了9个特征根大于1的主成分,累积贡献率分别为77.122%和81.666%,说明构建的核心种质可以有效地减少遗传冗余。
表 5 原始种质与核心种质主成分分析比较Table 5. Principal components on phenotypic traits of entire and representative collection of germplasms主成分
Component原始种质 Original collection 核心种质 Core collection 特征根
Characteristic-root贡献率/%
Contribution rate累积贡献率/%
Cumulative contribution rate特征根
Characteristic-root贡献率/%
Contribution rate累积贡献率/%
Cumulative contribution rate1 10.352 32.351 32.351 10.212 31.913 31.913 2 3.500 10.936 43.287 4.273 13.354 45.267 3 2.421 7.565 50.853 2.779 8.684 53.951 4 1.901 5.941 56.793 2.050 6.408 60.358 5 1.664 5.200 61.993 1.674 5.231 65.590 6 1.515 4.734 66.726 1.522 4.758 70.348 7 1.203 3.758 70.485 1.311 4.096 74.443 8 1.086 3.394 73.879 1.229 3.840 78.283 9 1.038 3.243 77.122 1.083 3.383 81.666 2.2.3 聚类分析
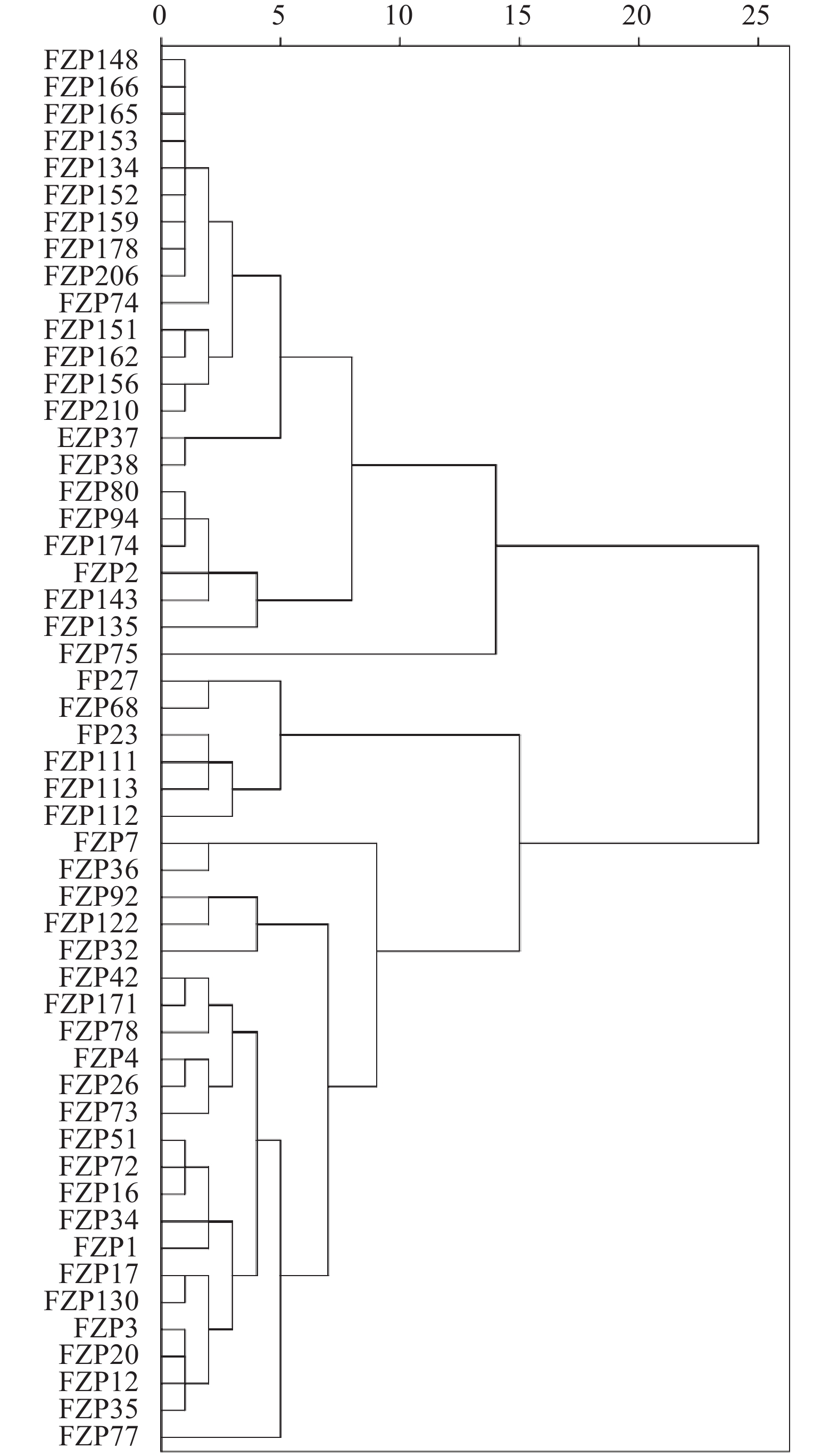
对构建的蝴蝶兰初级核心种质进行聚类分析,详见图1。结果表明在遗传距离为10时,可以将52份蝴蝶兰种质分为4大类群。类群1包括22份种质,为植株大小较小、花序及花序梗长较短、花朵大小较小的小花型蝴蝶兰;类群2包括1份种质,其植株大小较大、叶片长宽及花序较长,且叶片宽度最宽;类群3包括6份种质,为花序及花序梗较长、花朵大小较大的大花型蝴蝶兰;类群4包括23份种质,为植株大小、花朵大小介于类群1和类群3的中花型蝴蝶兰。
3. 讨论
种质资源是品种选育的物质基础,很多育种工作者和科研工作者已经对种质资源进行了广泛的收集,但种质资源繁杂、数量庞大,往往会增加育种工作量,因此,构建优良的核心种质,可以深入了解种质资源的遗传背景,提高品种选育效率。目前构建核心种质的数据来源主要有表型性状和分子标记,资源群体具有良好的遗传变异范围和多样性分布时,应优先使用表型性状构建初级核心种质[10]。对于观赏植物而言,应重点收集花色、花型、花香等方面的观赏性状[25]。
取样方法是核心种质研究的重点。目前常用的取样方法有随机取样法、优先取样法、偏离度取样法等。彭枫等[28]研究表明优先取样法是构建菠菜核心种质的最佳取样方法;陈建华等[29]研究表明优先取样法是构建酸枣核心种质的最佳取样方法。本研究在对比3种取样方法后,得出了相同的结论。目前应用分类学方法计算遗传距离最为常用的是马氏距离和欧式距离。本研究通过对比两种遗传距离,发现欧式距离更适于构建蝴蝶兰初级核心种质,这与郎彬彬等[30]的研究结果相似。
聚类分析常应用于种质资源亲缘关系研究[31]。常见的聚类方法有最短距离法、最长距离法、中间距离法、重心法、不加权类平均法、可变类平均法、可变法、离差平方和法。对于不同的作物,构建核心种质的聚类方法也有所不同:赵欣蕊等[8]的研究表明最短距离法对构建马铃薯核心种质效果最佳;赵立民等[11]通过比较发现离差平方和法最适于构建切花小菊核心种质。本研究比较了8种聚类方法,发现最长距离法是构建蝴蝶兰初级核心种质的最优方法。
取样比例的大小根据作物种类、原种质群体大小和群体组成而定。一般而言,取样比例为原始材料的5%~30%。由于园艺作物保存的种质规模远不及农作物,其取样比例一般为10%~30%[32]。侯志强等[33]在构建菊芋核心种质时发现,当取样低于15%时,表型性状丢失较多;而规模增大为30%时,核心种质多样性指数最大,但VD和VR较小。本研究对3种取样比例(20%、25%、30%)比较后发现:取样比例为20%时,随着取样比例的增加,MD均值降低,同时VD、VR也降低,取样比例为30%时,虽然MD最低,但VD降低较多,综合考虑取样比例为25%时MD较低,且VD、VR较高,这与侯志强等[33]的研究结果相似。
检验核心种质是否具有代表性是验证核心种质构建有效与否的关键,通常用均值、极值、方差和变异系数等评价核心种质的代表性[34]。HU等[35]认为当均值差异百分率小于20%,极差符合率参数大于80%时,为合理的核心种质。王建成等[36]和刘遵春等[25]的研究表明:均值差异百分率越小,方差差异百分率、极差符合率和变异系数变化率越大,对原始种质的代表性越强。
4. 结论
本研究利用210份蝴蝶兰种质资源材料的32个表型性状数据进行初级核心种质构建,发现优先取样法、欧式距离、最长距离法和25%的取样比例是构建蝴蝶兰初级核心种质的最优方法,最终筛选获得包含52份材料的初级核心种质。之后对原始种质与核心种质的均值、极值、方差和变异系数进行对比,并进行了主成分分析,结果表明构建的初级核心种质各项评价参数优秀,能够代表原始种质的遗传多样性,主成分信息得到保留,并很好地去除了原种质的遗传冗余,可以优先作为后续蝴蝶兰种质资源研究的材料。
-
表 1 蝴蝶兰性状及代码
Table 1 Codes of Phalaenopsis phenotypic traits
代码 Code 性状Traits 代码 Code 性状Traits C1 植株大小 Plant length/cm C17 花序梗数量 Peduncle number/个 C2 叶片长度 Leaf length/cm C18 合蕊柱长度 Gynostemium length/cm C3 叶片宽度 Leaf width/cm C19 合蕊柱粗度 Gynostemium thickness/cm C4 花序长度 Inflorescence length/cm C20 叶片形状 Leaf shape C5 花数量 Flower number/朵 C21 叶片上表面颜色 Color of the upper side of leaf C6 花序梗长度 Peduncle length/cm C22 叶片花青甙显色 Anthocyanin coloration of leaf C7 花序梗粗度 Peduncle thickness/cm C23 叶片厚度 Leaf thickness C8 花梗长度 Pedicel length/cm C24 叶片表面纹理 Leaf surface texture C9 花长度 Flower length/cm C25 花序类型 Inflorescence type C10 花宽度 Flower width/cm C26 花序梗表面颜色 Surface color of peduncle C11 萼片长度 Dorsal sepal length/cm C27 花瓣排列方式 Petal arrangement C12 萼片宽度 Dorsal sepal width/cm C28 花香味 Scent of flower C13 花瓣长度 Petal length/cm C29 中萼片颜色数量 Number of middle sepal colors C14 花瓣宽度 Petal width/cm C30 侧萼片颜色数量 Number of lateral sepal colors C15 中裂片长度 Apical lobe length/cm C31 花瓣颜色数量 Number of petal colors C16 中裂片宽度 Apical lobe width/cm C32 花蜡质 Waxiness of flower 表 2 蝴蝶兰质量性状分级与赋值
Table 2 Classification and codes of qualitative Phalaenopsis traits
性状 Traits 赋值 Assigning value 叶片形状
Leaf shape披针形=1,窄卵圆形=2,椭圆形=3,窄倒卵圆形=4,倒卵圆形=5
lanceolate=1,narrowly oval=2,elliptical=3,narrowly inverted ovoid=4,obovoid=5叶片上表面颜色
Color of the upper side of leaf浅绿色=1,中等绿色=2,深绿色=3,灰绿色=4
light green=1,medium green=2,dark green=3,greyish green=4叶片花青甙显色
Anthocyanin coloration of leaf无=1,有=2
no=1,yes=2叶片厚度
Leaf thickness薄=1,中=2,厚=3
thin=1,medium=2,thick=3叶片表面纹理
Leaf surface texture无=1,有=2
no=1,yes=2花序类型
Inflorescence type单生花=1,总状花序=2,圆锥花序=3
solitary=1,raceme=2,panicle=3花序梗表面颜色
Surface color of peduncle浅绿色=1,中等绿色=2,深绿色=3,灰绿色=4,红褐色=5,褐色=6
light green=1,medium green=2,dark green=3,greyish green=4,reddish brown=5,brown=6花瓣排列方式
Petal arrangement分开=1,相接=2,重叠=3
separate=1,adjacent=2,overlapping=3花香味
Scent of flower无=1,有=2
no=1,yes=2中萼片颜色数量
Number of middle sepal colors1种=1,2种=2,3种=3,3种以上=4
1 color=1,2 colors=2,3 colors=3,more than 3 colors=4侧萼片颜色数量
Number of lateral sepal colors1种=1,2种=2,3种=3,3种以上=4
1 color=1,2 colors=2,3 colors=3,more than 3 colors=4花瓣颜色数量
Number of petal colors1种=1,2种=2,3种=3,3种以上=4
1 color=1,2 colors=2,3 colors=3,more than 3 colors=4花蜡质
Waxiness of flower无=1,有=2
no=1,yes=2表 3 144个备选核心种质的评价参数
Table 3 Parameters for evaluating 144 candidate germplasms
取样比例
Sample ratio遗传距离
Genetic distance聚类方法
Cluster method多次聚类随机取样法
Multiple cluster random
sampling method多次聚类优先取样法
Multiple cluster preferred sampling method多次聚类偏离度取样法
Multiple cluster deviation
sampling methodMD VD CR VR MD VD CR VR MD VD CR VR 20% 欧氏距离
Euclidean distanceSingle 3.13 18.75 91.34 111.47 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 9.38 28.13 97.96 119.58 Complete 0.00 15.63 89.52 107.99 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 0.00 37.50 98.02 120.42 Median 0.00 9.38 90.43 108.20 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 3.13 15.63 95.28 114.72 Centroid 3.13 15.63 91.48 112.49 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 0.00 15.63 95.69 113.18 Unweighted 0.00 6.25 93.92 109.68 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 0.00 15.63 94.49 119.55 weighted 0.00 15.63 89.88 106.84 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 0.00 31.25 95.39 116.32 Flexible 3.13 12.50 86.44 105.95 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 0.00 28.13 94.05 116.58 Ward 0.00 15.63 90.43 110.29 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 0.00 43.75 95.43 117.14 马氏距离
Mahalanobis distanceSingle 6.25 15.63 90.77 110.74 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 21.88 53.13 96.81 116.87 Complete 0.00 6.25 90.36 107.11 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 3.13 46.88 96.18 121.91 Median 3.13 15.63 90.28 109.75 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 9.38 53.13 97.08 120.88 Centroid 21.88 25.00 93.94 115.19 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 40.63 50.00 97.34 114.20 Unweighted 0.00 9.38 89.96 104.78 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 3.13 53.13 95.31 122.61 weighted 0.00 9.38 90.15 105.21 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 0.00 53.13 94.04 117.15 Flexible 0.00 9.38 84.82 99.43 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 0.00 53.13 92.76 118.25 Ward 0.00 15.63 88.01 110.22 3.13 40.63 100.00 119.45 3.13 50.00 96.31 124.36 25% 欧氏距离
Euclidean distanceSingle 3.13 18.75 94.06 108.15 3.13 46.88 100.00 116.83 9.38 21.88 97.99 116.42 Complete 0.00 9.38 90.33 107.97 0.00 37.50 100.00 118.20 0.00 15.63 98.02 117.14 Median 0.00 6.25 91.10 104.70 18.75 37.50 100.00 113.46 0.00 12.50 96.03 111.96 Centroid 3.13 12.50 92.52 108.82 0.00 28.13 100.00 116.11 0.00 12.50 96.19 110.06 Unweighted 0.00 9.38 96.02 106.98 0.00 37.50 100.00 117.18 0.00 15.63 96.02 116.94 weighted 0.00 9.38 91.54 104.42 0.00 34.38 100.00 116.48 0.00 12.50 95.83 112.31 Flexible 3.13 12.50 89.51 104.44 0.00 34.38 100.00 116.41 0.00 15.63 95.61 113.33 Ward 0.00 12.50 92.22 107.95 0.00 34.38 100.00 117.65 0.00 21.88 95.49 113.83 马氏距离
Mahalanobis distanceSingle 3.13 15.63 93.96 108.25 3.13 43.75 100.00 116.84 25.00 43.75 97.80 114.64 Complete 0.00 6.25 92.49 104.49 18.75 21.88 100.00 113.25 3.13 43.75 96.18 117.74 Median 12.50 15.63 90.96 106.71 6.25 37.50 100.00 114.98 12.50 50.00 97.65 116.36 Centroid 25.00 40.63 94.40 111.51 6.25 34.38 100.00 114.99 12.50 50.00 97.80 115.74 Unweighted 0.00 9.38 91.23 105.90 3.13 21.88 100.00 115.20 0.00 43.75 95.72 119.67 weighted 0.00 6.25 90.32 102.42 0.00 31.25 100.00 115.65 0.00 34.38 94.04 114.45 Flexible 0.00 6.25 89.18 102.02 9.38 43.75 100.00 115.10 0.00 43.75 94.37 115.04 Ward 0.00 12.50 88.99 105.98 0.00 28.13 100.00 113.91 0.00 46.88 97.06 118.15 30% 欧氏距离
Euclidean distanceSingle 3.13 18.75 94.06 105.70 6.25 28.13 100.00 113.08 9.38 18.75 98.45 115.29 Complete 0.00 12.50 91.83 106.48 0.00 28.13 100.00 115.17 0.00 15.63 98.51 115.55 Median 0.00 6.25 92.13 104.42 3.13 21.88 100.00 110.75 0.00 12.50 97.82 109.50 Centroid 0.00 9.38 93.09 106.86 0.00 18.75 100.00 112.80 0.00 12.50 96.23 108.23 Unweighted 0.00 9.38 96.82 105.33 0.00 21.88 100.00 114.35 0.00 9.38 98.03 113.32 weighted 0.00 15.63 92.98 102.65 0.00 25.00 100.00 114.54 0.00 12.50 95.94 110.04 Flexible 0.00 15.63 90.92 104.92 0.00 21.88 100.00 113.34 0.00 12.50 95.69 111.23 Ward 0.00 12.50 93.17 107.20 0.00 25.00 100.00 114.83 0.00 18.75 96.00 111.83 30% 马氏距离
Mahalanobis distance最短距离法Single 9.38 15.63 94.73 107.77 0.00 31.25 100.00 113.80 15.63 40.63 97.80 113.30 最长距离法Complete 0.00 9.38 93.56 105.10 6.25 21.88 100.00 113.05 0.00 43.75 97.32 115.64 中间距离法Median 0.00 9.38 93.50 106.51 3.13 21.88 100.00 112.91 6.25 40.63 97.65 113.08 重心法Centroid 31.25 43.75 95.09 110.91 21.88 37.50 100.00 113.00 12.50 40.63 97.80 111.99 类平均法Unweighted 0.00 9.38 92.31 105.21 0.00 25.00 100.00 111.08 3.13 46.88 96.20 116.42 可变类平均法weighted 0.00 9.38 94.73 105.33 0.00 18.75 100.00 112.31 0.00 18.75 94.52 112.03 可变法Flexible 0.00 6.25 90.23 103.40 3.13 25.00 100.00 112.42 0.00 40.63 94.84 113.80 离差平方和法Ward 0.00 15.63 92.36 107.50 0.00 21.88 100.00 111.19 0.00 37.50 97.06 116.19 MD:均值差异百分率,VD:方差差异百分率, CR:极差符合率,VR:变异系数变化率;最短距离法,最长距离法,中间距离法,重心法,类平均法,可变类平均法,可变法,离差平方和法。
MD:mean difference percentage; VD:variance difference percentage; CR: range coincidence rate; VR:variation coefficient change rate;single,complete,median,centroid,unweighted,weighted,flexible,and ward clustering methods.表 4 原始种质与核心种质遗传差异比较
Table 4 Genetic differences between entire and representative collection of germplasms
性状
Traits类别
Categories均值
MeanP值
P value显著性
Significance方差
VarianceP值
P value显著性
Significance极差
Range变异系数
CV/%C1 原始种质 Original 29.98 0.98 NS 47.67 0.02 S* 42.5 23.03 核心种质 Core 29.94 73.40 42.5 28.62 C2 原始种质 Original 16.21 0.89 NS 12.59 0.01 S* 21.67 21.89 核心种质 Core 16.31 19.83 21.67 27.31 C3 原始种质 Original 6.70 0.63 NS 2.41 0.00 S** 11.17 23.17 核心种质 Core 6.54 5.00 11.17 34.20 C4 原始种质 Original 14.71 0.53 NS 94.34 0.07 NS 40.06 66.01 核心种质 Core 15.71 127.87 40.06 71.99 C5 原始种质 Original 11.31 0.90 NS 55.47 0.40 NS 33 65.87 核心种质 Core 11.16 58.05 33 68.27 C6 原始种质 Original 19.13 0.25 NS 126.63 0.10 NS 49.83 58.82 核心种质 Core 21.23 166.13 49.83 60.71 C7 原始种质 Original 0.47 0.34 NS 0.05 0.00 S** 2.93 46.54 核心种质 Core 0.52 0.15 2.93 75.11 C8 原始种质 Original 32.85 0.46 NS 383.95 0.06 NS 86.63 59.65 核心种质 Core 35.19 528.77 86.63 65.34 C9 原始种质 Original 5.43 0.14 NS 2.58 0.01 S** 8.2 29.58 核心种质 Core 5.90 4.30 8.2 35.13 C10 原始种质 Original 5.83 0.21 NS 3.58 0.01 S* 10.57 32.46 核心种质 Core 6.28 5.71 10.57 38.03 C11 原始种质 Original 2.98 0.14 NS 0.84 0.03 S* 4.73 30.75 核心种质 Core 3.20 1.22 4.73 34.61 C12 原始种质 Original 2.11 0.14 NS 0.67 0.01 S* 4.07 38.66 核心种质 Core 2.34 1.07 4.07 44.26 C13 原始种质 Original 2.70 0.18 NS 0.77 0.03 S* 4.83 32.46 核心种质 Core 2.89 1.14 4.83 36.94 C14 原始种质 Original 2.85 0.17 NS 2.20 0.03 S* 6.6 52.05 核心种质 Core 3.18 3.27 6.6 56.85 C15 原始种质 Original 1.73 0.41 NS 0.28 0.00 S** 3.27 30.66 核心种质 Core 1.64 0.56 3.27 45.41 C16 原始种质 Original 1.45 0.60 NS 0.39 0.01 S* 3.17 43.04 核心种质 Core 1.38 0.61 3.17 56.65 C17 原始种质 Original 1.71 0.33 NS 0.74 0.47 NS 4.66 50.24 核心种质 Core 1.58 0.74 4.66 54.58 C18 原始种质 Original 1.01 0.21 NS 0.02 0.00 S** 1.17 15.03 核心种质 Core 1.05 0.04 1.17 20.15 C19 原始种质 Original 0.45 0.35 NS 0.06 0.00 S** 3.54 56.28 核心种质 Core 0.51 0.22 3.54 91.93 C20 原始种质 Original 2.72 0.47 NS 1.19 0.11 NS 4 40.10 核心种质 Core 2.60 1.54 4 47.79 C21 原始种质 Original 1.85 0.75 NS 0.61 0.33 NS 3 42.33 核心种质 Core 1.81 0.67 3 45.22 C22 原始种质 Original 1.19 0.13 NS 0.16 0.08 NS 1 33.10 核心种质 Core 1.29 0.21 1 35.51 C23 原始种质 Original 1.90 0.58 NS 0.42 0.30 NS 2 34.17 核心种质 Core 1.96 0.47 2 34.92 C24 原始种质 Original 1.14 0.85 NS 0.12 0.36 NS 1 30.74 核心种质 Core 1.15 0.13 1 31.58 C25 原始种质 Original 2.41 0.19 NS 0.25 0.46 NS 2 20.86 核心种质 Core 2.31 0.26 2 21.94 C26 原始种质 Original 2.86 0.22 NS 2.24 0.13 NS 5 52.38 核心种质 Core 3.15 2.84 5 53.42 C27 原始种质 Original 1.07 0.27 NS 0.12 0.00 S** 2 32.53 核心种质 Core 1.15 0.29 2 46.64 C28 原始种质 Original 1.32 0.71 NS 0.22 0.45 NS 1 35.41 核心种质 Core 1.29 0.21 1 35.51 C29 原始种质 Original 2.00 0.88 NS 0.36 0.14 NS 3 29.95 核心种质 Core 2.02 0.45 3 33.24 C30 原始种质 Original 2.22 0.69 NS 0.49 0.40 NS 3 31.54 核心种质 Core 2.27 0.51 3 31.60 C31 原始种质 Original 2.04 0.47 NS 0.38 0.10 NS 3 30.09 核心种质 Core 2.12 0.50 3 33.30 C32 原始种质 Original 1.75 0.18 NS 0.19 0.17 NS 1 24.97 核心种质 Core 1.65 0.23 1 29.05 NS表示无显著差异;S*表示显著水平;S**表示极显著水平;P值表示判定假设检验结果的参数。
NS: No significant difference; S*: significant difference; S**: extremely significant difference; P: parameter for evaluating hypothesis test result.表 5 原始种质与核心种质主成分分析比较
Table 5 Principal components on phenotypic traits of entire and representative collection of germplasms
主成分
Component原始种质 Original collection 核心种质 Core collection 特征根
Characteristic-root贡献率/%
Contribution rate累积贡献率/%
Cumulative contribution rate特征根
Characteristic-root贡献率/%
Contribution rate累积贡献率/%
Cumulative contribution rate1 10.352 32.351 32.351 10.212 31.913 31.913 2 3.500 10.936 43.287 4.273 13.354 45.267 3 2.421 7.565 50.853 2.779 8.684 53.951 4 1.901 5.941 56.793 2.050 6.408 60.358 5 1.664 5.200 61.993 1.674 5.231 65.590 6 1.515 4.734 66.726 1.522 4.758 70.348 7 1.203 3.758 70.485 1.311 4.096 74.443 8 1.086 3.394 73.879 1.229 3.840 78.283 9 1.038 3.243 77.122 1.083 3.383 81.666 -
[1] 朱根发. 蝴蝶兰种质资源及杂交育种进展[J]. 广东农业科学,2015,42(5) :31–38. ZHU G F. Progress in germplasm resources and crossbreeding of Phalaenopsis[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences,2015,42(5) :31–38. (in Chinese)
[2] 许申平,张腾飞,廖飞雄,等. 蝴蝶兰种质资源与育种研究[J]. 中国园艺文摘,2010,26(5) :27–30. XU S P,ZHANG T F,LIAO F X,et al. A review on studies of Phalaenopsis germplasm resources and breeding[J]. Chinese Horticulture Abstracts,2010,26(5) :27–30. (in Chinese)
[3] FRANKEL O. Genetic perspectives of germplasm conservation[M]. Cambridge:Cambridge University Press,1984:161–170.
[4] BROWN A H D. Core collections:A practical approach to genetic resources management[J]. Genome,1989,31(2) :818−824. DOI: 10.1139/g89-144
[5] TANAKA N,SHENTON M,KAWAHARA Y,et al. Investigation of the genetic diversity of a rice core collection of Japanese landraces using whole-genome sequencing[J]. Plant &; Cell Physiology,2021,61(12) :2087–2096.
[6] 朱业宝,王金英,江川. 水稻种质资源核心种质的研究进展[J]. 江西农业学报,2023,35(4) :27–32. ZHU Y B,WANG J Y,JIANG C. Research progress in core collection of rice germplasm resources[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi,2023,35(4) :27–32. (in Chinese)
[7] 李永祥,李会勇,扈光辉,等. 玉米应用核心种质的构建与应用[J]. 植物遗传资源学报,2023,24(4) :911–916. LI Y X,LI H Y,HU G H,et al. Construction and utilization of applied core collection in maize[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources,2023,24(4) :911–916. (in Chinese)
[8] 赵欣蕊,陈啸天,薛薇,等. 基于表型性状分析构建冀北地区马铃薯核心种质[J]. 核农学报,2024,38(5) :805–818. ZHAO X R,CHEN X T,XUE W,et al. Construction of core potato germplasm resources in north Hebei based on phenotypic traits[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2024,38(5) :805–818. (in Chinese)
[9] 郑福顺,王晓敏,李国花,等. 基于表型性状的宁夏番茄种质资源核心种质构建[J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版) ,2021,47(2) :171–181. ZHENG F S,WANG X M,LI G H,et al. Core collection construction of Ningxia tomato germplasm resources based on phenotypic traits[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture and Life Sciences) ,2021,47(2) :171–181. (in Chinese)
[10] 李嘉伟,苏江硕,张飞,等. 基于表型性状构建传统菊花核心种质[J]. 中国农业科学,2021,54(16) :3514–3526. LI J W,SU J S,ZHANG F,et al. Construction of core collection of traditional Chrysanthemum morifolium based on phenotypic traits[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2021,54(16) :3514–3526. (in Chinese)
[11] 赵立民,李嘉伟,张飞,等. 基于表型数据构建切花小菊核心种质[J]. 园艺学报,2022,49(10) :2273–2284. ZHAO L M,LI J W,ZHANG F,et al. Construction of a core collection of spray cut Chrysanthemum based on phenotypic data[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2022,49(10) :2273–2284. (in Chinese)
[12] 秦子璐,徐正康,戴晓港,等. 望春玉兰种质资源遗传多样性分析与核心种质构建[J]. 园艺学报,2024,51(8) :1823–1832. QIN Z L,XU Z K,DAI X G,et al. Genetic diversity analysis and core collection construction of Magnolia biondii germplasm[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2024,51(8) :1823–1832. (in Chinese)
[13] 张林娟,李向茂,奉树成. 紫薇种质资源与应用研究进展[J]. 广东农业科学,2024,51(2) :81–91. ZHANG L J,LI X M,FENG S C.Research progress on germplasm resources and application of Lagerstroemia indica[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences,2024,51(2) :81–91.(in Chinese)
[14] 陈明堃,陈璐,孙维红,等. 建兰种质资源遗传多样性分析及核心种质构建[J]. 园艺学报,2022,49(1) :175–186. CHEN M K,CHEN L,SUN W H,et al. Genetic diversity analysis and core collection of Cymbidium ensifolium germplasm resources[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2022,49(1) :175–186. (in Chinese)
[15] 张保青,黄玉新,周珊,等. 广西割手密核心种质构建与关联分析[J]. 华中农业大学学报 ,2024,43(5) :75–81. ZHANG B Q,HUANG Y X,ZHOU S,et al. Construction and association analysis of core germplasm for Saccharum spontaneum L. in Guangxi[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University,2024,43 (5) :75–81. (in Chinese)
[16] 陈妍,杨午,万坤,等. 基于表型多样性构建山西大豆地方品种核心种质[J]. 中国油料作物学报,2025,47(1) :105–114. CHEN Y,YANG W,WAN K,et al.Establishment of soybean core collection based on phenotypic characters in Shanxi Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences,2025,47(1) :105–114.(in Chinese)
[17] 丁艺冰,辛旭霞,冯智尊,等. 东北春播区糜子核心种质及其DNA分子身份证构建[J]. 作物学报,2024,50(5) :1181–1192. DING Y B,XIN X X,FENG Z Z,et al. Core germplasm and DNA molecular identity card of proso millet in Northeast Spring sowing region in China[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica,2024,50(5) :1181–1192. (in Chinese)
[18] 明军,张启翔,兰彦平. 梅花品种资源核心种质构建[J]. 北京林业大学学报,2005,27(2) :65–69. MING J,ZHANG Q X,LAN Y P. Core collection of Prunus mume sieb. et zucc[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2005,27(2) :65–69. (in Chinese)
[19] 陈剑锋,钟声远,陈宇华,等. 基于花表型性状的蝴蝶兰品种资源多样性研究[J]. 热带作物学报,2023,44(3) :494–505. CHEN J F,ZHONG S Y,CHEN Y H,et al. Research on diversity of Phalaenopsis germplasm resources based on flowers phenotype traits[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops,2023,44(3) :494–505. (in Chinese)
[20] 王钦,黄捷,涂松,等. 蝴蝶兰不同品种表型性状遗传多样性分析[J]. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学) ,2023,43(6) :8–18. WANG Q,HUANG J,TU S,et al. Analysis of phenotypic genetic diversity of various Phalaenopsis varieties[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University (Natural Sciences) ,2023,43(6) :8–18. (in Chinese)
[21] 李佐,肖文芳,尤毅,等. 蝴蝶兰核心种质构建初探[J]. 广东农业科学,2013,40(1) :46–49. LI Z,XIAO W F,YOU Y,et al. Preliminary establishment of core collection for Phalaenopsis[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences,2013,40(1) :46–49. (in Chinese)
[22] 中华人民共和国农业部. 植物新品种特异性、一致性和稳定性测试指南 蝴蝶兰:NY/T 2230—2012[S]. 北京:中国农业出版社,2013. [23] 胡晋,徐海明,朱军. 保留特殊种质材料的核心库构建方法[J]. 生物数学学报,2001,16(3) :348–352. HU J,XU H M,ZHU J. A method of constructing core collection reserving special germplasm materials[J]. Journal of Biomathematics,2001,16(3) :348–352. (in Chinese)
[24] 徐海明,胡晋,朱军. 构建作物种质资源核心库的一种有效抽样方法[J]. 作物学报,2000,26(2) :157–162. XU H M,HU J,ZHU J. An efficient method of sampling core collection from crop germpl asm[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica,2000,26(2) :157–162. (in Chinese)
[25] 刘遵春,张春雨,张艳敏,等. 利用数量性状构建新疆野苹果核心种质的方法[J]. 中国农业科学,2010,43(2) :358–370. LIU Z C,ZHANG C Y,ZHANG Y M,et al. Study on method of constructing core collection of Malus sieversii based on quantitative traits[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2010,43(2) :358–370. (in Chinese)
[26] 刘艳阳,梅鸿献,杜振伟,等. 基于表型和SSR分子标记构建芝麻核心种质[J]. 中国农业科学,2017,50(13) :2433–2441. LIU Y Y,MEI H X,DU Z W,et al. Construction of core collection of sesame based on phenotype and molecular markers[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2017,50(13) :2433–2441. (in Chinese)
[27] 刘娟,廖康,赵世荣,等. 利用ISSR分子标记构建新疆野杏核心种质资源[J]. 中国农业科学,2015,48(10) :2017–2028. LIU J,LIAO K,ZHAO S R,et al. The core collection construction of Xinjiang wild apricot based on ISSR molecular markers[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2015,48(10) :2017–2028. (in Chinese)
[28] 彭枫,李阳,戴雨柔,等. 基于表型性状的菠菜核心种质构建[J]. 上海师范大学学报(自然科学版) ,2022,51(1) :9–19. PENG F,LI Y,DAI Y R,et al. Construction of spinach’s core germplasms based on its phenotypic traits[J]. Journal of Shanghai Normal University (Natural Sciences) ,2022,51(1) :9–19. (in Chinese)
[29] 陈建华,曲凯伦,张云程,等. 基于表型性状的酸枣核心种质构建[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报,2024,55(2) :176–186. CHEN J H,QU K L,ZHANG Y C,et al. Construction of Ziziphus jujuba var. spinosa core collection based on phenotypic traits[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University,2024,55(2) :176–186. (in Chinese)
[30] 郎彬彬,黄春辉,朱博,等. 基于果实相关性状的江西野生毛花猕猴桃初级核心种质的构建方法研究[J]. 果树学报,2016,33(7) :794–803. LANG B B,HUANG C H,ZHU B,et al. Study on the method of constructing a primary core collection of Jiangxi wild Actinidia eriantha based on fruit traits[J]. Journal of Fruit Science,2016,33(7) :794–803. (in Chinese)
[31] PEETERS J P,MARTINELLI J A. Hierarchical cluster analysis as a tool to manage variation in germplasm collections[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics,1989,78(1) :42–48.
[32] 缪黎明,王神云,邹明华,等. 园艺作物核心种质构建的研究进展[J]. 植物遗传资源学报,2016,17(5) :791–800. MIAO L M,WANG S Y,ZOU M H,et al. Review of the studies on core collection for horticultural crops[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources,2016,17(5) :791–800. (in Chinese)
[33] 侯志强,王丽慧,赵孟良,等. 基于表型数据的菊芋核心种质初步构建[J]. 分子植物育种,2021,19(10) :3463–3472. HOU Z Q,WANG L H,ZHAO M L,et al. Preliminary construction of core collection of Jerusalem artichoke based on phenotypic data[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding,2021,19(10) :3463–3472. (in Chinese)
[34] 崔艳华,邱丽娟,常汝镇,等. 黄淮夏大豆(G. max) 初选核心种质代表性检测[J]. 作物学报,2004,30(3) :284–288. CUI Y H,QIU L J,CHANG R Z,et al. Representative test for primary core collection of summer sowing soybeans in Huanghuai region of China[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica,2004,30(3) :284–288. (in Chinese)
[35] HU J,ZHU J,XU H M. Methods of constructing core collections by stepwise clustering with three sampling strategies based on the genotypic values of crops[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics,2000,101(1) :264−268.
[36] 王建成,胡晋,张彩芳,等. 建立在基因型值和分子标记信息上的水稻核心种质评价参数[J]. 中国水稻科学,2007,21(1) :51–58. WANG J C,HU J,ZHANG C F,et al. Evaluating parameters of rice core collections based on genotypic values and molecular marker information[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science,2007,21(1) :51–58. (in Chinese)




 下载:
下载: