Analysis on the difference of main quality components of Jinmudan tea in different tea seasons
-
摘要:目的
本研究旨在揭示金牡丹茶的主要品质特征及其春、夏、秋3季中不同茶类(红茶、乌龙茶、白茶、黄茶及绿茶)的主要品质成分差异情况,探究不同茶季金牡丹茶主要特征代谢物间的关联特性以及可用于区分不同茶季的主要代谢物。
方法以不同茶季的‘金牡丹’鲜叶制成的红茶、乌龙茶、黄茶、白茶及绿茶为供试材料,基于生化测定、高效液相色谱法以及AQC衍生液质联用法对供试茶样的生化成分进行测定分析。
结果金牡丹夏茶的茶多酚和儿茶素含量显著高于其它茶季。而春茶中氨基酸含量最高,夏茶最低。金牡丹茶的儿茶素组成以EGC、EGCG、ECG及GC为主。相关性分析表明,季节因素对金牡丹茶的化学成分具有显著影响。基于OPLS-DA判别模型,在不同茶季的金牡丹红茶、乌龙茶、白茶、黄茶及绿茶中分别筛选出12、15、15、17、17种差异代谢产物,这些代谢物可作为区分春、夏、秋茶的潜在标志。
结论本研究明确了金牡丹茶在不同茶类和茶季中的滋味品质化学特征,揭示了其不同茶季的主要特征代谢物的变化规律,为提升金牡丹鲜叶原料的利用率及优化金牡丹茶品质提供了科学依据。
Abstract:ObjectiveThis study is aimed at uncovering the main quality traits of Jinmudan tea and the variances in quality components among different tea types (black tea, oolong tea, white tea, yellow tea, and green tea) in spring, summer, and autumn. It also explores the correlation characteristics among the main characteristic metabolites of Jinmudan tea in different tea seasons and the main metabolites that can be used to distinguish between different tea seasons.
MethodsEmploying black tea, oolong tea, yellow tea, white tea and green tea made from fresh leaves of 'Jinmudan' in different tea seasons as test materials, the biochemical components of tea samples were determined through conventional biochemical determination, high performance liquid chromatography and mass linking of AQC derivatives.
ResultsThe content of tea polyphenols and catechins in Jinmudan summer tea is significantly higher than that in other seasons. In contrast, the amino acid content is highest in spring tea and lowest in summer tea. The catechin composition of Jinmudan tea is dominated by EGC, EGCG, ECG, and GC. Correlation analysis indicates that seasonal factors have a significant impact on the chemical composition of Jinmudan tea. Based on the OPLS-DA discriminant model, 12, 15, 15, 17, and 17 differential metabolites were screened from Jinmudan black tea, oolong tea, white tea, yellow tea, and green tea, respectively, across different seasons. These metabolites can serve as potential markers for distinguishing spring, summer, and autumn teas.
ConclusionThis study clarified the chemical characteristics of taste quality in Jinmudan tea across different tea types and seasons, and reveals the variation patterns of its major characteristic metabolites in different tea seasons. It provides a scientific basis for improving the utilization rate of Jinmudan fresh tea leaves and optimizing the quality of Jinmudan tea.
-
Keywords:
- Jinmudan /
- types of tea /
- tea season /
- taste /
- quality chemistry
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】兔出血症2型(rabbit hemorrhagic disease Type 2, RHD-2)是由兔出血症病毒2型(rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus serum type 2, RHdV-2)引起的一种新型高度接触传染性、急性致死性传染病。新型毒株的RHdV-2的感染性更强,感染范围更广,不同日龄和品种的家兔、野兔均可被感染[1−3]。RHD-2具有较高发病率和致死率[4],且国内尚未研制出可靠的商品化疫苗供生产使用,一旦发病将严重影响养兔业的健康发展。当前,我国养兔规模化程度仍然十分低,散养户是养兔业的主力。散养户普遍存在技术力量弱、不会操作检测仪器等问题。RHdV-2感染已对我国养兔也造成了巨大经济损失,如何在养殖场特别是散养户进行快速准确的诊断对于科学防控该病具有十分重要的意义。通过建立快速且准确的检测方法,可以有效识别并控制传染源,从而防止疫情的进一步扩散。【前人研究进展】目前,重组酶介导的核酸等温扩增(recombinase aided amplification, RAA)与CRISPR/Cas13a技术联用在病原检测领域已逐渐展现出其巨大的应用潜力。该法先对目标序列进行RAA扩增以获得大量的检测模板,再利用CRISPR系统对其进行特异性识别以激活Cas13a蛋白来剪切反应体系中的荧光探针,从而实现对低载量样品的快速准确检测[5−6]。作为病原检测研究领域的一个热门方向,RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a检测方法通过结合RAA法和CRISPR/Cas13a技术,在灵敏度和特异性方面实现了显著提升。一些学者已经利用这种方法开发出了快速检测动物疫病病原微生物的新方法,如禽腺病毒 4 型[7]、猪流行性腹泻病毒[8]、口蹄疫病毒[9]和禽流感病毒[10]。虽然国内已经建立多种针对RHdV-2的诊断技术,但是均需要一定的专业知识和仪器设备,难以在养殖场一线应用。有研究根据RHdV-2的保守序列VP60,建立了实时荧光定量聚合酶链反应(real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction, qPCR)检测方法[11],酶联免疫吸附技术(enzyme Linked Immunosorbent assay, ELISA)也可用于检测RHdV-2抗原或抗体[12],这些方法虽然其灵敏度和特异性也较好,但它们均需较为昂贵的配备仪器和过长的反应时间。【本研究切入点】本实验室前期建立了基于RAA的侧流层析试纸(lateral flow device, LFD)方法[13],用于RHdV-2的特异性检测,然而RAA的扩增效率易受引物设计、模板序列及其他因素的制约,限制了其检测灵敏度和稳定性。近年来,CRISPR-Cas核酸酶的精准切割特性为核酸检测提供了新的技术突破,多项研究[14−15]通过联合RAA与CRISPR-Cas系统,显著提升了检测的灵敏度和特异性,并结合LFD实现了检测结果的可视化。基于此,本研究创新性地整合了RAA与CRISPR/Cas13a技术,首次建立了一种兔出血症病毒2型可视化诊断方法RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a(cpf1)-LFD。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究在本实验室前期研究的重组酶等温扩增结合侧流层析试纸条方法[13]的基础上,结合CRISPR/Cas13a技术,建立了新的RHdV-2检测方法,这种方法具备高度的灵敏度和特异性,操作简单,可实现在实验室和基层养殖场现场的快速检测,同时利用LFD实现结果可视化,为RHdV-2的诊断提供高效准确的检测方法。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
1.1.1 重组质粒与临床样本
RHdV-2(KU991797.1)VP60重组质粒、RHdV-1(DQ205345.1)VP60重组质粒均由擎科股份有限公司进行合成。31份临床样本由本实验室保存,来自闽侯、武平、大田、连江等多个兔场,病兔主要表现急性死亡,实质器官有出血,采集脾脏淋巴结等实质器官。
1.1.2 主要试验试剂
总RNA提取试剂盒(ER501-01)(北京全式金生物有限公司);RAA核酸扩增试剂盒,RAA核酸扩增试剂盒(试纸条法)(T00R01)(江苏奇天基因生物科技有限公司);一次性核酸检测试纸条(JY0301,北京宝盈同汇生物技术有限公司);1xPBS(兰杰柯科技有限公司);LwaCas13a蛋白(C2C2)(广州美格生物有限公司);HiScribeT7快速高效 RNA 合成试剂盒(New England Biolabs);重组RNase抑制剂(荷瑞生物);RNA纯化试剂盒(DP412,天根生物有限公司);LwaCas13a 10×reaction buffer:200 mmol·L−1 HEPES-NaOH(pH6.8),600 mmol·L−1 NaCl,60 mmol·L−1 MgCl2,10 mmol·L−1 DTT。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 RAA引物、crRNA设计与合成
RAA特异性引物和RAA-LFD探针按照文献[13]报道的序列合成。在已扩增的特异且保守序列范围内,首先识别符合条件的PAM序列,继而设计长度为20~23 nt的间隔区序列构成LwaCas13a-crRNA,间隔区序列位于PAM序列之后,同时确保LwaCas13a-crRNA目标序列内3'端的PFS序列由A、C、U组成,且目标序列不与RAA引物重叠,最终,将间隔区序列进行Blast分析比对确定其保守特异性。crRNA的单链DNA(即ssDNA)由擎科股份有限公司进行合成。
Lwacas13a-crRNA合成步骤:将crRNA的单链DNA作为模板与相应引物通过PCR扩增获得大量crRNA的双链DNA(即dsDNA),使用琼脂凝胶回收试剂盒回收目的条带进行纯化,纯化产物通过T7 HiScribe T7高效RNA合成试剂盒37 ℃过夜转录,转录产物使用RNA纯化试剂盒纯化后通过nanodrop 2000测定RNA浓度置于−80 ℃保存。CRISPR-Cas13a相关序列见表1。
表 1 CRISPR-Cas13a crRNA及相关引物Table 1. CRISPR-Cas13a crRNA and related primers基因
Genes序列5'-3'
Sequences (5’-3’)Cas13a crRNA1 TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGGATTTAGACTACCCCAAAAACGAAGGGGACTAAAACACTCATAAGCCTGCATGGTCGTGACGTA Cas13a crRNA2 TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGGATTTAGACTACCCCAAAAACGAAGGGGACTAAAACGGTGGTGGTGGGTTGGGGGTTGCTCGGT 斜体为T7启动子序列,下划线碱基为重复序列区。
The italicized sequence represents the T7 promoter, and the underlined bases indicate the repetitive sequence region.PCR 25 μL反应体系:2×San Taq PCR Master Mix (含蓝色染料)12.5 μL,crRNA-dsDNA 1 μL,上下游引物各1 μL(10 μmol·L−1),ddH2O 9.5 μL。PCR反应过程:95 ℃预变性5 min;95 ℃变性30 s,56 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃延伸15 s,30个循环;72 ℃延伸10 min。
转录体系:T7 mix 2 μL,NTP mix 10 μL,模板1 μg,ddH2O补齐至20 μL。
1.2.2 RAA-LFD反应体系
根据RAA核酸扩增试剂盒说明书,选择50 μL体系进行扩增。反应体系为:缓冲液25 μL,纯水15.7 μL,正向与反向引物各取2.1 μL,探针取0.6 μL,乙酸镁(280 mmol·L−1)2.5 μL,模板3 μL。
1.2.3 Cas13a试纸条法反应条件的确立
(1) RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a (Cpf1)-LFD体系优化。1.5 μL crRNA(300 ng·μL−1)与50 nmol·L−1 Cas13a蛋白进行反应,选择反应效果最佳体系为CRISPR-Cas13a反应体系。该体系的总体积为50 µL,包括以下成分:10×反应缓冲液5 µL,crRNA(浓度为300 ng·µL−1)1.5 µL,探针(浓度为10 μmol·L−1)2 µL,模板2.5 µL,LwaCAS13a蛋白(浓度为1 μmol·L−1)3.5 µL,NTP混合物2.5 µL,RNA酶(浓度为300U·µL−1)5 µL,T7混合物0.5 µL,以及双蒸水27.5 µL。
(2)RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a-LFD反应时间优化。基于上述Cas13a体系对RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a-LFD反应时间进行优化,每5 min一个间隔,设置反应时间为10~25 min,Cas13a试纸条法通过试纸条观察结果。
1.2.4 RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a (Cpf1)-LFD试纸条法检测敏感性的评价
RHdV-2 VP60重组质粒经检测其质粒浓度为6.7×103 copies·μL−1,用1×PBS梯度稀释得到6.7×103、6.7×102、6.7×101、6.7×10−1、6.7×10−2 copies·μL−1 5个浓度梯度,以不同浓度的重组质粒为模板进行扩增,扩增产物与Cas13a蛋白以及crRNA等试剂再进行一定时间恒温反应,反应产物经LFD显示,分析敏感性试验结果。
1.2.5 RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a (Cpf1)-LFD检测RHdV-2特异性评价
RHdV-2 VP60重组质粒(6.7×105 ng·μL−1)、RHdV-1 VP60重组质粒(6.7×105 ng·μL−1)为模板进行RAA扩增,产物与Cas13a蛋白以及crRNA再进行一定时间恒温反应,反应产物经LFD显示。
1.2.6 RNA的提取
根据总RNA提取试剂盒说明进行操作提取,具体步骤:将单份临床兔病料75 mg与1 mL Trans Zol混合并研磨裂解样品,后加入200 μL RNA Extraction Agent,振荡混匀5 min后放于4 ℃高速离心机10 000 r·min−1离心15 min;吸取无色水相部分与同体积无水乙醇混合后加入离心柱后离心;重复加入CB9(500 μL)并离心;重复加入WB9(500 μL)并离心;离心去除剩余乙醇,使用75 μL纯水洗脱后,将提取的RNA保存于-80 ℃保存。
1.2.7 临床样品的检测
提取31份临床样本病料的总RNA,应用建立的RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a(Cpf1)-LFD 法分别对31份临床样品进行RAA扩增反应,扩增产物经LFD显示结果。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 Cas13-crRNA筛选结果
分别以crRNA1和crRNA2为探针对同一阳性样本进行检测,结果如图1A和图1B所示,crRNA1显示出更明显的检测线(T线),并且Image J定量分析(图1C)可见crRNA1与crRNA2之间的信号强度差异显著(P<0.05),说明crRNA1具有更高的信号强度。综上后续选择crRNA1进行试验。
![]() 图 1 Cas13a-crRNA筛选结果A:试纸条;B:Image J定量图;C:样品条带定量柱状图。1:crRNA 1;2: crRNA 2;N:阴性对照。C:质控线;T:检测线;* 表示与对照相比差异显著 P < 0.05。Figure 1. Cas13-crRNA screening resultsA: test strip image; B: image J quantification graph; C: sample band quantification bar chart. 1: crRNA1; 2: crRNA2; N: negative control. C: quality control Line; T:test line; * indicates a statistically significant difference with control (P < 0.05).
图 1 Cas13a-crRNA筛选结果A:试纸条;B:Image J定量图;C:样品条带定量柱状图。1:crRNA 1;2: crRNA 2;N:阴性对照。C:质控线;T:检测线;* 表示与对照相比差异显著 P < 0.05。Figure 1. Cas13-crRNA screening resultsA: test strip image; B: image J quantification graph; C: sample band quantification bar chart. 1: crRNA1; 2: crRNA2; N: negative control. C: quality control Line; T:test line; * indicates a statistically significant difference with control (P < 0.05).2.2 RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a (Cpf1)-LFD反应时间优化
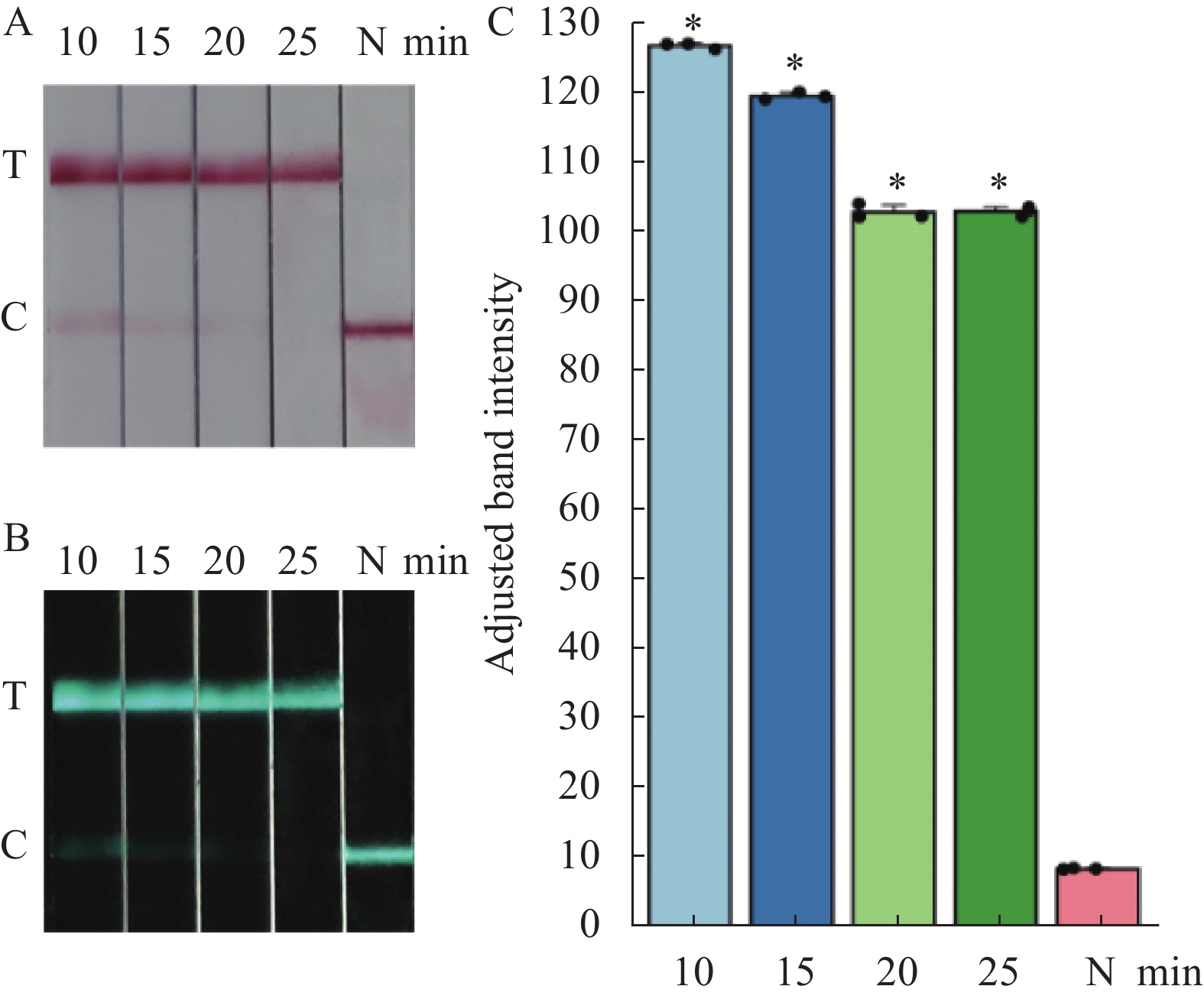
从图2中可以看出,在RAA基础反应30 min后,仅再需10 min,RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a(Cpf1)-LFD即可检测出RHdV-2,且显色明显,从量化柱状图可知,反应时间为10 min时,数值最高(P<0.05),综合分析可知10 min时即可达到较佳检测效果,故后续反应时间均釆用10 min。
![]() 图 2 不同反应时间RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a(Cpf1)-LFD扩增产物A:试纸条图;B:Image J定量图;C:样品条带定量柱状图。10、15、20、25分别为 10、15、20、25 min 扩增产物; N阴性对。C:质控线;T:检测线;*表示与对照相比差异显著(P < 0.05)。Figure 2. Analysis of RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a(Cpf1)-LFD amplification products at different reaction timeA: test strip image; B: image J quantification graph; C: sample band quantification bar chart. 10, 15, 20, 25: amplification products for 10, 15, 20, 25 min with the standard plasmid as template; N: negative control. C: quality control line; T: test line; * indicates significant difference with control (P < 0.05).
图 2 不同反应时间RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a(Cpf1)-LFD扩增产物A:试纸条图;B:Image J定量图;C:样品条带定量柱状图。10、15、20、25分别为 10、15、20、25 min 扩增产物; N阴性对。C:质控线;T:检测线;*表示与对照相比差异显著(P < 0.05)。Figure 2. Analysis of RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a(Cpf1)-LFD amplification products at different reaction timeA: test strip image; B: image J quantification graph; C: sample band quantification bar chart. 10, 15, 20, 25: amplification products for 10, 15, 20, 25 min with the standard plasmid as template; N: negative control. C: quality control line; T: test line; * indicates significant difference with control (P < 0.05).2.3 RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a (Cpf1)-LFD敏感性
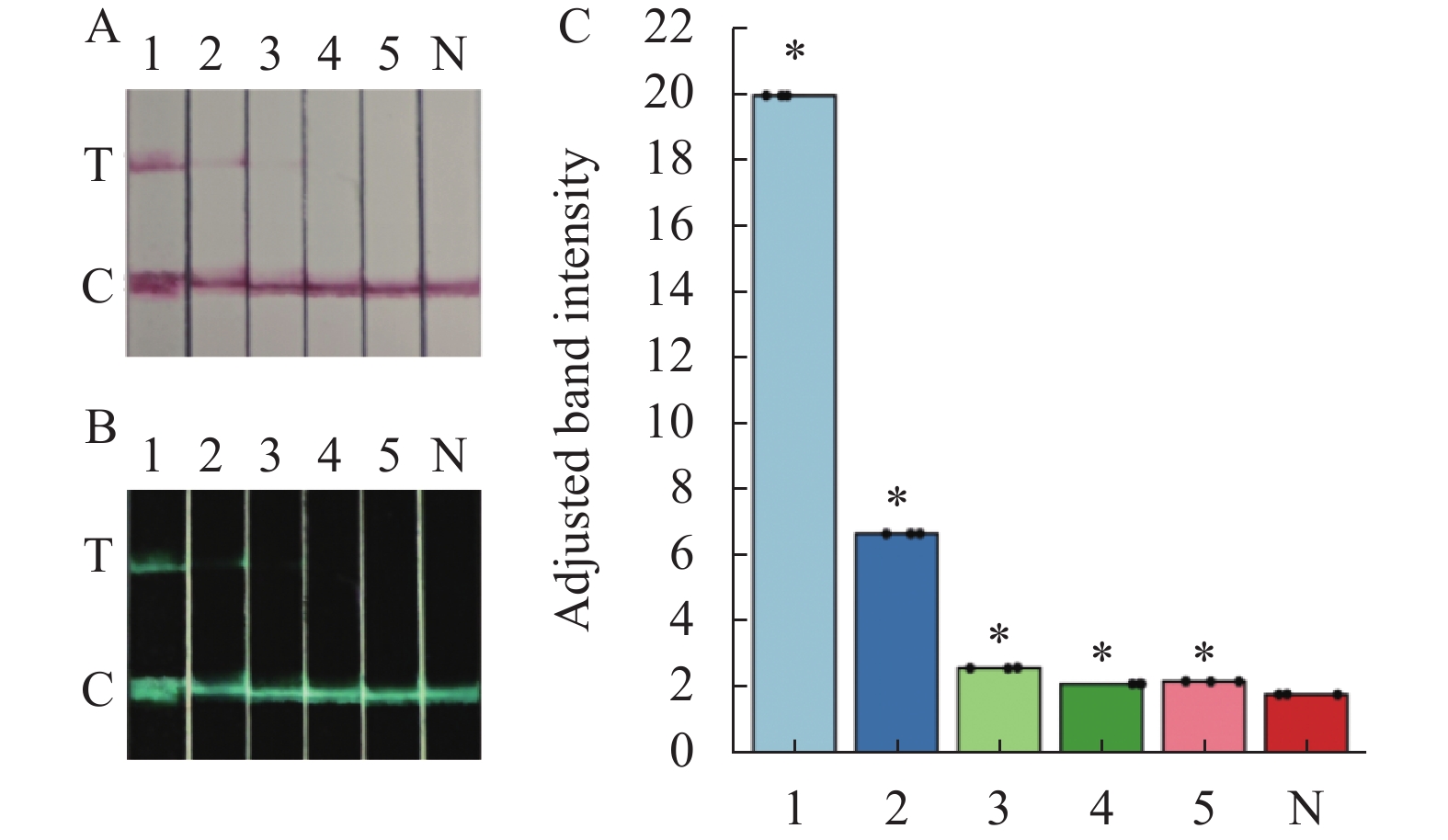
Cas13a试纸条法对RHdV-2 RNA最低可检值可达6.7×101 copies·μL−1,结合量化结果(图3)综合分析在质粒浓度为6.7×101 ng·μL−1时阳性结果最亮且数值最高(P<0.05),阴性对照结果为阴性。
![]() 图 3 Cas13a敏感性试验结果A:试纸条图;B:Image J定量图;B:样品条带定量柱状图。1:6.7×103 copies·μL−1;2:6.7×102 copies·μL−1;3:6.7×101 copies·μL−1;4:6.7×10−1 copies·μL−1;5:6.7×10−2 copies·μL−1;N:阴性;* 表示与对照相比差异显著(P < 0.05)。Figure 3. Sensitivity test results about Cas13aA: test strip image; B: image J quantification graph; C: sample band quantification bar chart. 1: 6.7×103 copies·μL−1; 2: 6.7×102 copies·μL−1; 3: 6.7×101 copies·μL−1; 4: 6.7×10−1 copies·μL−1; 5: 6.7×10−2 copies·μL−1; N: negative control; * indicates significant difference with control (P < 0.05).
图 3 Cas13a敏感性试验结果A:试纸条图;B:Image J定量图;B:样品条带定量柱状图。1:6.7×103 copies·μL−1;2:6.7×102 copies·μL−1;3:6.7×101 copies·μL−1;4:6.7×10−1 copies·μL−1;5:6.7×10−2 copies·μL−1;N:阴性;* 表示与对照相比差异显著(P < 0.05)。Figure 3. Sensitivity test results about Cas13aA: test strip image; B: image J quantification graph; C: sample band quantification bar chart. 1: 6.7×103 copies·μL−1; 2: 6.7×102 copies·μL−1; 3: 6.7×101 copies·μL−1; 4: 6.7×10−1 copies·μL−1; 5: 6.7×10−2 copies·μL−1; N: negative control; * indicates significant difference with control (P < 0.05).2.4 RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a (Cpf1)-LFD特异性试验结果
如图4可知,RHdV-1结果为阴性,RHdV-2在试纸条检测中呈现强阳性,因此所建立的方法特异性优异。
![]() 图 4 Cas13特异性检测结果A:试纸条图;B:Image J定量图; B:样品条带定量柱状图。1:RHdV-2;2:RHdV-1;N:阴性对照;*表示与对照相比差异显著(P < 0.05)。Figure 4. Cas13a specific test resultsA: test strip image; B: image J quantification graph; C: sample band quantification bar chart. 1: RHdV-2; 2: RHdV-1; N: negative control; * indicates significant difference with control (P < 0.05).
图 4 Cas13特异性检测结果A:试纸条图;B:Image J定量图; B:样品条带定量柱状图。1:RHdV-2;2:RHdV-1;N:阴性对照;*表示与对照相比差异显著(P < 0.05)。Figure 4. Cas13a specific test resultsA: test strip image; B: image J quantification graph; C: sample band quantification bar chart. 1: RHdV-2; 2: RHdV-1; N: negative control; * indicates significant difference with control (P < 0.05).2.5 RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a (Cpf1)-LFD法检测结果
对31份不同兔场收集的病死兔脾脏组织进行RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a (Cpf1)-LFD试纸条检测,如图5可知,所有样品在C位置均有条带,表明所有样品均合格,样品4、10、13、15、18、19、22、24、27、29在T位置出现了较为明显的条带,并且Image J定量分析(图5C)可见样品4、10、13、15、18、19、22、24、27、29的条带强度与其他样品相比差异显著(P<0.05),表明样品4、10、13、15、18、19、22、24、27、29均为阳性样品,RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a (Cpf1)-LFD法的阳性检出率为30.3%。
![]() 图 5 RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a (Cpf1)-LFD临床样品检测结果A:试纸条图;B:Image J定量图;C:样品条带定量柱状图。1~31分别为样品编号; N为阴性对照;*表示与对照相比差异显著(P < 0.05)。Figure 5. Clinical samples detected by RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a (Cpf1)-LFDA: test strip image; B: image J quantification graph; C: sample band quantification bar chart. 1—31 are sample numbers; N: negative control; * indicates significant difference with control (P < 0.05).
图 5 RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a (Cpf1)-LFD临床样品检测结果A:试纸条图;B:Image J定量图;C:样品条带定量柱状图。1~31分别为样品编号; N为阴性对照;*表示与对照相比差异显著(P < 0.05)。Figure 5. Clinical samples detected by RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a (Cpf1)-LFDA: test strip image; B: image J quantification graph; C: sample band quantification bar chart. 1—31 are sample numbers; N: negative control; * indicates significant difference with control (P < 0.05).3. 讨论与结论
自2010年在法国首次发现RHdV-2以来[4],该病毒已在全球范围内流行。2020年,中国四川省首次报告了RHD2病例[16]。RHdV-2对养兔业构成严重威胁,但目前缺乏有效的商业疫苗。因此,开发可靠的病原学检测技术对于控制RHdV-2传播、减轻其对养兔业和生态系统的影响至关重要。
王波[17]在其研究中建立的检测RHdV-2的SYBR Green Ⅰ实时荧光定量RT-PCR方法检测限度达到68个拷贝数,而本研究中我们构建的RHdV-2核酸试纸条检测方法对兔出血症病毒RNA的最低检测限为6.7×101 copies·μL−1,说明本研究建立的方法灵敏度与实时荧光定量RT-PCR方法相当。同时,应用该方法进行检测,结果显示RHdV-1结果为阴性,RHdV-2则呈现强阳性,说明该方法特异性良好,与RHdV-1血清型核酸无交叉反应。本研究使用新建立的RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a (Cpf1)-LFD方法对本实验室前期研究中保存的31份疑似阳性临床样品[13]进行检测后,阳性率从19.2%提高到了30.3%,说明新方法在检测RHdV-2方面具有更高的有效性和准确性。近年来,关于RHdV-2检测方法的研究主要集中在RT-PCR技术上。尽管部分研究[18−19]开发的检测方法能够达到1×101 copies·μL−1的高灵敏度,但这些方法通常需要较长的反应时间,并且依赖于专业设备来判读结果,这限制了它们在临床快速检测RHDV-2中的应用。相比之下,本研究建立的检测方法在40 min内即可完成,并且通过试纸条直接显示结果,使得结果判读变得快速且直观。但本研究建立的方法也存在不足之处,反应过程中需要开盖转移RAA反应产物作为体系中的模板,易产生气溶胶污染。目前已有RAA-CAS一管反应法,将RAA反应试剂与Cas相关试剂一次性加入一个管内,反应时间相应缩短,减少气溶胶污染。然而,一管法灵敏性较低,这可能与RAA中反应蛋白酶接触Cas相关试剂影响了蛋白酶的活性,后期是否可以通过改变体系内试剂浓度进行一管反应还需进一步研究。
本研究前期通过RHdV两种血清型基因组对比,发现RHdV-2的VP60基因最为保守,将其设定为检测靶序列,合成特异性引物,建立了RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a(cpf1)-LFD检测方法。该方法具有敏感性强、特异性高、操作简易等优点,可实现对RHdV-2快速检测,可为RHdV-2的预防与早期诊断、控制提供便捷技术,规避兔养殖业面临巨大疫病风险,助力养兔业蓬勃发展。
-
图 1 不同茶季金牡丹5大类茶主要特征代谢物相关性分析。春茶(A)、夏茶(B)、秋茶(C)
*代表0.01<P值<0.05,**代表 0.001<P值<0.01,***代表0.0001<P值<0.001.
Figure 1. Correlation analysis of major characteristic metabolites in 5 types of Jinmudan tea in different tea seasons. Spring tea(A), Summer tea(B), Autumn tea(C)
Statistical significance is indicated as follows: * for 0.01 < P < 0.05, ** for 0.001 < P < 0.01, and *** for 0.0001 < P < 0.001.
图 2 不同茶季金牡丹5大类茶主要特征代谢物OPLS-DA与聚类热图综合分析。
OPLS-DA得分图、OPLS-DA置换检验图及VIP聚类热图:红茶(A),乌龙茶(B),白茶(C),黄茶(D),绿茶(E)
Figure 2. Comprehensive analysis of OPLS-DA and cluster heat map of main characteristic metabolites of multiple tea types of Jinmudan in different tea seasons.
OPLS-DA Score Plot, OPLS-DA Permutation Test Plot, and VIP Cluster Heatmap for: Black Tea (A), Oolong Tea (B), White Tea (C), Yellow Tea (D), Green Tea (E).
表 1 不同茶季金牡丹5大茶类主要生化成分含量
Table 1 Content of main biochemical components of 5 types of Jinmudan tea in different tea seasons
生化名称
Biochemical茶季
Tea season红茶
Black tea乌龙茶
Oolong Tea白茶
White tea黄茶
Yellow tea绿茶
Green tea水浸出物(%) 春茶 47.23±0.58c 46.31±0.26c 52.00±0.61b 54.01±0.34a 53.14±0.83a 夏茶 43.56±0.22d 46.73±0.13c 51.05±0.72b 53.10±0.83a 53.97±0.50a 秋茶 39.40±0.01d 45.41±0.01c 49.47±0.01b 51.95±0.00a 53.32±0.00a 茶多酚(%) 春茶 18.14±0.64e 23.66±0.40d 26.60±0.12c 28.92±0.62b 31.34±0.32a 夏茶 20.00±0.61d 25.40±0.43c 31.03±0.40b 31.87±0.28b 34.63±0.16a 秋茶 17.44±0.51e 25.22±0.67d 29.31±0.42c 30.86±0.31b 33.02±0.41a 氨基酸总量(%) 春茶 1.72±0.06e 2.69±0.12d 4.64±0.07a 3.01±0.07c 3.95±0.16b 夏茶 1.24±0.03e 1.72±0.04d 2.90±0.06b 1.87±0.01c 3.14±0.05a 秋茶 1.60±0.03d 2.35±0.08c 4.04±0.20a 2.42±0.03c 3.56±0.08b 酚氨比 春茶 10.53±0.61a 8.80±0.28b 6.24±0.09d 8.83±0.24b 8.23±0.43c 夏茶 16.14±0.84a 14.80±0.64c 10.66±0.24d 15.70±0.24b 10.62±0.04d 秋茶 10.88±0.30b 10.74±0.46c 7.27±0.36e 12.74±0.41a 9.28±0.35d 茶黄素(%) 春茶 0.21±0.01a 0.04±0.01b 0.04±0.00b 0.03±0.00c - 夏茶 0.14±0.01a 0.03±0.00b 0.02±0.00c 0.02±0.00c 秋茶 0.10±0.00a 0.04±0.00b 0.03±0.00c 0.03±0.00c 茶红素(%) 春茶 2.26±0.07a 1.61±0.09b 1.20±0.02d 1.23±0.07c - 夏茶 1.87±0.07a 1.38±0.10b 0.77±0.03d 1.08±0.08c 秋茶 2.36±0.16a 1.44±0.00b 0.93±0.02d 1.15±0.03c 茶褐素(%) 春茶 1.92±0.04a 1.17±0.04b 0.77±0.04d 1.12±0.02c - 夏茶 2.10±0.03a 1.13±0.04b 0.75±0.01d 0.92±0.05c 秋茶 1.63±0.00a 1.62±0.01b 0.90±0.02d 1.05±0.08c “-”表示未检测出;同列数据右上角标相同字母表示同行数据差异不显著(P>0.05),不同小写字母表示同行数据差异显著(P<0.05),下同。
“-” indicates that the substance was not detected. Within the same column, values sharing the same superscript letters are not significantly different (P>0.05), while those with different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05). The same convention applies to the following tables.表 2 不同茶季金牡丹5大类茶儿茶素及生物碱含量
Table 2 Contents of catechins and alkaloids in 5 types of Jinmudan tea different tea seasons
组分名称
Component茶季
Tea Season红茶
Black Tea乌龙茶
Oolong Tea白茶
White Tea黄茶
Yellow Tea绿茶
Green Tea儿茶素(mg·g−1) EGC 春茶 1.53±0.16d 11.59±0.38c 9.26±0.28bc 18.03±0.78a 13.05±0.89b 夏茶 1.32±0.08e 19.18±1.76c 7.66±0.52d 23.60±1.75b 30.92±1.70a 秋茶 1.46±0.07d 16.85±0.31b 7.78±0.13c 17.21±0.55b 19.76±0.47a C 春茶 1.24±0.04d 1.37±0.04c 1.93±0.13b 1.84±0.01b 2.53±0.10a 夏茶 1.47±0.06e 1.62±0.06d 2.48±0.05b 2.29±0.06c 4.68±0.11a 秋茶 1.51±0.07c 1.61±0.04c 2.05±0.15ab 1.88±0.01bc 2.30±0.04a EGCG 春茶 1.82±0.19d 27.83±1.15c 60.73±0.92b 56.03±0.78b 72.25±0.74a 夏茶 3.26±0.06d 40.87±0.85c 77.61±0.70b 63.21±1.92b 90.72±0.19a 秋茶 1.04±0.17e 28.48±2.20d 58.80±1.17b 50.42±3.14c 67.27±2.81a EC 春茶 0.58±0.13d 5.16±0.38b 2.22±0.16c 6.03±0.52a 6.56±1.17a 夏茶 0.22±0.01e 6.69±0.45c 1.95±0.31d 8.19±0.48b 10.75±0.08a 秋茶 0.15±0.03c 5.28±0.35a 2.48±0.1b 5.74±0.54a 5.92±0.59a EGCG3″Me 春茶 0.10±0.01d 4.16±0.38c 5.36±0.21b 4.36±0.37c 6.20±0.05a 夏茶 0.69±0.07c 4.17±0.42b 3.97±0.69b 5.94±0.53a 6.35±1.14a 秋茶 0.64±0.17c 5.21±0.70a 5.34±0.25a 3.72±0.33b 4.05±0.42b ECG 春茶 1.61±0.06e 6.50±0.36d 20.70±0.10a 14.35±0.71c 15.84±0.81b 夏茶 2.81±0.09e 10.74±0.26d 16.70±0.58c 18.28±1.67b 23.05±0.37b 秋茶 1.39±0.16c 7.69±0.61b 13.16±0.66a 11.47±1.10a 12.63±1.40a GCG 春茶 0.06±0.01d 0.18±0.02c 0.23±0.07c 0.37±0.05b 0.47±0.05a 夏茶 0.04±0.02e 0.93±0.03c 0.79±0.06d 1.08±0.07b 1.25±0.01a 秋茶 0.20±0.04b 0.45±0.03b 0.45±0.16b 1.43±0.28a 1.53±0.08a GC 春茶 4.44±0.11a 2.50±0.19c 3.01±0.34b 0.47±0.04d 0.38±0.04d 夏茶 3.65±0.07a 0.92±0.11c 3.46±0.15a 0.83±0.04c 1.83±0.30b 秋茶 3.71±0.03a 1.03±0.11c 2.57±0.08b 0.53±0.05d 0.51±0.05d TECs 春茶 4.07±0.21d 38.43±1.01c 76.35±18.57b 75.12±1.03b 94.76±0.67a 夏茶 6.80±0.03e 56.53±1.28d 99.28±0.79b 88.52±3.78c 121.36±0.58a 秋茶 3.27±0.20e 41.83±3.34d 77.74±1.11b 67.05±2.64c 85.48±4.69a TSCs 春茶 7.80±0.21c 20.05±1.09b 17.50±1.44b 26.36±0.87b 22.52±1.96a 夏茶 6.67±0.21e 28.40±2.28c 15.55±0.87d 34.91±2.28b 48.18±1.92a 秋茶 6.84±0.21d 24.78±1.49b 14.89±0.38c 25.37±0.50b 28.49±1.01a TCs 春茶 11.87±0.38d 58.48±1.27c 93.85±17.19b 101.49±1.89b 117.27±2.23a 夏茶 13.46±0.24e 84.93±1.49d 114.83±0.87c 123.43±6.05b 169.54±2.40a 秋茶 10.10±0.22d 66.61±4.80c 92.63±1.03b 92.41±2.40b 113.97±5.71a 生物碱(mg·g−1) TB 春茶 0.48±0.09d 0.73±0.00c 0.91±0.03b 0.88±0.03b 1.52±0.11a 夏茶 0.34±0.02d 0.61±0.04c 1.32±0.11b 1.39±0.08b 1.65±0.08a 秋茶 0.34±0.03d 0.51±0.05c 1.17±0.06a 0.70±0.07b 1.25±0.04a CAF 春茶 16.16±1.12e 18.87±0.82d 33.39±0.38a 26.81±0.58c 31.96±0.20b 夏茶 13.56±0.60e 29.81±1.24d 39.69±1.24b 32.62±0.11c 42.81±0.92a 秋茶 9.84±0.55d 12.53±0.71c 30.88±1.56a 23.70±1.68b 24.26±0.65b 总量 春茶 16.64±1.21e 19.61±0.83d 34.30±0.37a 27.69±0.62c 33.47±0.22b 夏茶 13.90±0.62e 30.42±1.28d 41.01±1.35b 34.00±0.17c 44.46±0.97a 秋茶 10.18±0.55d 13.04±0.67c 32.06±1.62a 24.40±1.74b 25.51±0.69b 表 3 不同茶季金牡丹5大类茶氨基酸含量及TAV值
Table 3 The amino acid content and TAV value of 5 kinds of Jinmudan tea in different tea seasons
氨基酸
Amino acid阈值
Threshold
(mg·g−1)茶季
Tea season氨基酸含量
Amino Acid Content(mg·g−1)TAV值
TAV Value红茶
Black tea乌龙茶
Oolong tea白茶
White tea黄茶
Yellow tea绿茶
Green tea红茶
Black tea乌龙茶
Oolong tea白茶
White tea黄茶
Yellow tea绿茶
Green teaMet 0.30 春茶 0.05±0.01ab 0.04±0.00b 0.04±0.00b 0.04±0.00ab 0.05±0.01a 0.15±0.03ab 0.12±0.02b 0.13±0.01ab 0.14±0.01ab 0.16±0.02a 夏茶 0.02±0.00c 0.05±0.01a 0.04±0.01b 0.02±0.01c 0.04±0.00ab 0.07±0.00c 0.16±0.02a 0.10±0.03bc 0.08±0.02c 0.13±0.00ab 秋茶 0.05±0.00a 0.04±0.00b 0.04±0.00bc 0.04±0.00bc 0.03±0.00c 0.17±0.01a 0.14±0.01b 0.12±0.01bc 0.13±0.01bc 0.12±0.01c Arg 0.50 春茶 0.50±0.09b 0.41±0.04b 0.96±0.11a 0.53±0.01b 0.53±0.04b 1.01±0.18b 0.82±0.07b 1.57±0.45a 1.06±0.03b 1.07±0.08b 夏茶 0.28±0.05b 0.29±0.08b 0.28±0.03b 0.61±0.06a 0.52±0.15a 0.57±0.11b 0.58±0.16b 0.80±0.47ab 1.22±0.11a 1.04±0.31ab 秋茶 0.46±0.02bc 0.45±0.00c 0.80±0.05a 0.43±0.01c 0.51±0.03b 0.92±0.03b 0.90±0.00b 1.35±0.42a 0.86±0.02b 1.02±0.05ab Lys 0.50 春茶 0.40±0.05c 0.30±0.02d 1.50±0.04a 0.68±0.02b 0.72±0.06b 0.80±0.10bc 0.60±0.04c 2.42±0.92a 1.35±0.05bc 1.45±0.11b 夏茶 0.16±0.03c 0.17±0.02c 0.27±0.05ab 0.34±0.08a 0.22±0.05b 0.31±0.06b 0.34±0.05b 0.60±0.21a 0.68±0.15a 0.45±0.09ab 秋茶 0.60±0.16b 0.59±0.12b 0.87±0.00a 0.51±0.08b 0.64±0.02b 1.20±0.33ab 1.18±0.25ab 1.56±0.31a 1.01±0.16b 1.28±0.04ab Tyr 0.91 春茶 0.73±0.12b 0.53±0.04c 1.04±0.13a 0.57±0.01bc 1.17±0.14a 0.80±0.13bc 0.59±0.04c 0.96±0.32b 0.63±0.02c 1.28±0.15a 夏茶 0.42±0.08b 0.26±0.04bc 0.61±0.13a 0.22±0.02c 0.68±0.14a 0.46±0.09b 0.29±0.05b 0.49±0.25b 0.24±0.02b 0.75±0.15a 秋茶 0.51±0.06c 0.34±0.06d 1.31±0.09a 0.59±0.03c 1.16±0.03b 0.56±0.07b 0.38±0.06b 1.21±0.49a 0.65±0.03b 1.27±0.04a Leu 1.90 春茶 0.39±0.06c 0.26±0.02d 0.46±0.03b 0.61±0.01a 0.67±0.03a 0.21±0.03c 0.14±0.01d 0.27±0.05b 0.32±0.01a 0.35±0.02a 夏茶 0.72±0.12bc 0.04±0.01d 0.93±0.19a 0.61±0.01c 0.81±0.05ab 0.38±0.06ab 0.02±0.00c 0.39±0.07ab 0.32±0.00b 0.43±0.02a 秋茶 0.37±0.06c 0.42±0.04c 0.69±0.08b 0.86±0.11a 0.44±0.11c 0.19±0.03b 0.22±0.02b 0.4±0.11a 0.45±0.06a 0.23±0.06b Trp 0.90 春茶 0.57±0.12b 0.56±0.06b 0.56±0.04b 0.59±0.03b 0.75±0.03a 0.64±0.13b 0.63±0.07b 0.61±0.02b 0.66±0.03b 0.84±0.03a 夏茶 0.44±0.05bc 0.61±0.09ab 0.53±0.17bc 0.38±0.10c 0.74±0.04a 0.49±0.06b 0.68±0.10ab 0.54±0.25b 0.42±0.11b 0.83±0.05a 秋茶 0.36±0.07c 0.70±0.12a 0.70±0.06a 0.53±0.01b 0.70±0.03a 0.40±0.08c 0.77±0.13a 0.72±0.14ab 0.58±0.01b 0.77±0.03a Val 0.40 春茶 0.48±0.05c 0.40±0.04c 1.19±0.09a 0.73±0.02b 1.21±0.12a 1.20±0.11c 1.00±0.10c 2.52±0.64a 1.81±0.05b 3.03±0.30a 夏茶 0.43±0.05c 0.24±0.08c 1.74±0.49a 0.93±0.08b 1.17±0.25b 1.07±0.11bc 0.61±0.21c 3.28±1.37a 2.31±0.21b 2.93±0.62a 秋茶 0.46±0.05c 0.77±0.13b 0.71±0.02b 0.80±0.11b 1.33±0.08a 1.15±0.14c 1.92±0.33b 1.94±0.34b 2.01±0.28b 3.32±0.20a Ile 0.90 春茶 0.70±0.07d 0.49±0.02e 0.87±0.05c 1.06±0.04b 1.32±0.10a 0.78±0.08c 0.54±0.03d 1.04±0.17b 1.18±0.05b 1.47±0.11a 夏茶 0.36±0.07b 0.38±0.00b 0.72±0.02a 0.44±0.03b 0.49±0.13b 0.4±0.07b 0.43±0.00b 0.69±0.18a 0.48±0.03ab 0.54±0.15ab 秋茶 0.68±0.09b 0.28±0.03c 0.63±0.29b 0.59±0.11b 1.23±0.06a 0.75±0.10b 0.31±0.03c 0.78±0.30b 0.66±0.12b 1.37±0.07a His 0.20 春茶 0.16±0.01c 0.20±0.02bc 0.25±0.02b 0.24±0.00b 0.35±0.05a 0.82±0.04c 1.02±0.11bc 1.20±0.01b 1.18±0.02b 1.77±0.24a 夏茶 0.09±0.03b 0.07±0.06b 0.15±0.08ab 0.16±0.02ab 0.22±0.02a 0.47±0.16bc 0.34±0.28c 0.67±0.37bc 0.79±0.10ab 1.10±0.08a 秋茶 0.08±0.02b 0.11±0.04b 0.15±0.09b 0.11±0.05b 0.36±0.01a 0.40±0.10c 0.56±0.20c 0.92±0.25b 0.55±0.24c 1.78±0.05a Ala 0.60 春茶 0.62±0.10b 0.61±0.06b 1.45±0.17a 0.59±0.07b 0.67±0.02b 1.04±0.17b 1.02±0.10b 1.90±0.74a 0.99±0.11b 1.11±0.03b 夏茶 0.76±0.10a 0.45±0.06b 0.86±0.01a 0.55±0.09b 0.76±0.19a 1.27±0.17ab 0.75±0.10c 1.32±0.21a 0.91±0.14bc 1.26±0.31ab 秋茶 0.59±0.10c 0.81±0.05b 1.10±0.07a 0.82±0.07b 0.35±0.05d 0.98±0.17c 1.34±0.08b 1.70±0.32a 1.37±0.11b 0.58±0.08d Pro 3.00 春茶 0.33±0.11b 0.20±0.05c 0.47±0.05a 0.35±0.02b 0.43±0.02ab 0.11±0.04a 0.07±0.02b 0.15±0.03a 0.12±0.01a 0.14±0.01a 夏茶 0.48±0.12b 0.43±0.06b 0.68±0.03a 0.27±0.03c 0.42±0.09b 0.16±0.04ab 0.14±0.02ab 0.18±0.07a 0.09±0.01b 0.14±0.03ab 秋茶 0.69±0.03b 0.59±0.08b 0.84±0.12a 0.43±0.03c 0.26±0.03d 0.23±0.01a 0.2±0.03ab 0.22±0.08a 0.14±0.01bc 0.09±0.01c Thr 2.60 春茶 0.57±0.02d 0.55±0.05d 0.71±0.06c 0.86±0.00b 1.10±0.11a 0.22±0.01c 0.21±0.02c 0.29±0.04b 0.33±0.00b 0.42±0.04a 夏茶 0.49±0.08b 0.31±0.13b 0.90±0.11a 0.53±0.23b 1.10±0.05a 0.19±0.03c 0.12±0.05c 0.33±0.05b 0.20±0.09c 0.42±0.02a 秋茶 0.54±0.08b 0.54±0.03b 0.83±0.13a 0.6±0.05b 0.88±0.06a 0.21±0.03b 0.21±0.01b 0.31±0.06a 0.23±0.02b 0.34±0.02a Ser 1.50 春茶 1.54±0.15c 1.54±0.15c 2.58±0.05a 2.25±0.06b 2.20±0.11b 1.03±0.10c 1.03±0.10c 1.66±0.11a 1.50±0.04b 1.47±0.08b 夏茶 0.90±0.09b 0.76±0.17b 1.60±0.37a 1.51±0.03a 1.48±0.15a 0.60±0.06b 0.51±0.11b 1.14±0.13a 1.01±0.02a 0.98±0.10a 秋茶 1.12±0.15c 1.07±0.12c 2.14±0.08a 2.09±0.02a 1.83±0.12b 0.75±0.10c 0.72±0.08c 1.44±0.04a 1.40±0.02a 1.22±0.08b Asp 1.00 春茶 1.33±0.25b 0.76±0.11c 1.32±0.08b 0.52±0.10c 2.64±0.37a 1.33±0.25b 0.76±0.11bc 1.01±0.52bc 0.52±0.10c 2.64±0.37a 夏茶 0.35±0.11b 0.06±0.05c 0.37±0.18b 0.19±0.09bc 1.05±0.02a 0.35±0.11b 0.06±0.05c 0.31±0.23b 0.19±0.09bc 1.05±0.02a 秋茶 2.31±0.12a 1.04±0.09b 0.93±0.06b 0.64±0.13c 2.29±0.08a 2.31±0.12a 1.04±0.09b 0.81±0.26bc 0.64±0.13c 2.29±0.08a Asn 1.00 春茶 0.61±0.06c 0.66±0.07c 2.27±0.09a 1.47±0.08b 1.42±0.08b 0.61±0.06c 0.66±0.07c 1.96±0.47a 1.47±0.08b 1.42±0.08b 夏茶 0.46±0.12c 0.18±0.04d 1.21±0.24a 0.79±0.07b 0.77±0.20b 0.46±0.12b 0.18±0.04c 0.99±0.17a 0.79±0.07a 0.77±0.20a 秋茶 0.32±0.05c 0.39±0.06c 1.74±0.04a 1.20±0.10b 1.14±0.03b 0.32±0.05c 0.39±0.06c 1.58±0.26a 1.20±0.10b 1.14±0.03b Thea 4.18 春茶 5.73±0.23e 14.02±0.13d 25.50±0.10a 15.20±0.57c 18.97±0.09b 1.37±0.05c 3.35±0.03b 5.55±1.76a 3.64±0.14b 4.54±0.02ab 夏茶 4.32±0.20c 9.55±0.39b 15.93±0.63a 8.85±0.35b 16.30±1.10a 1.03±0.05c 2.29±0.09b 3.23±1.06a 2.12±0.08b 3.90±0.26a 秋茶 5.22±0.14d 11.82±0.53c 24.61±1.52a 11.07±0.07c 17.96±0.98b 1.25±0.03c 2.83±0.13bc 4.77±1.86a 2.65±0.02c 4.3±0.23ab Glu 0.30 春茶 0.83±0.09d 1.08±0.08c 0.81±0.09d 1.41±0.05b 2.08±0.11a 2.75±0.31c 3.60±0.28c 3.51±1.16c 4.70±0.18b 6.94±0.37a 夏茶 0.45±0.05d 0.76±0.04b 0.30±0.03e 0.60±0.06c 1.70±0.08a 1.49±0.18d 2.54±0.12b 1.30±0.47d 2.00±0.19c 5.66±0.28a 秋茶 0.49±0.03d 0.68±0.05c 0.61±0.12cd 1.19±0.07b 1.59±0.03a 1.63±0.11c 2.28±0.17c 2.46±1.10c 3.97±0.25b 5.30±0.09a Gln 0.50 春茶 0.86±0.03d 3.52±0.45a 0.94±0.05d 1.48±0.03c 2.12±0.19b 1.71±0.07d 7.04±0.91a 2.23±0.68cd 2.97±0.06c 4.23±0.38b 夏茶 0.54±0.05d 2.02±0.15a 0.55±0.04d 0.98±0.07c 1.86±0.03b 1.08±0.11c 4.04±0.30a 1.42±0.61bc 1.96±0.15b 3.73±0.07a 秋茶 0.50±0.04e 2.27±0.04a 0.82±0.01d 1.31±0.09c 2.06±0.02b 1.00±0.07e 4.54±0.08a 1.90±0.45d 2.62±0.17c 4.11±0.04b β-ABA NF 春茶 0.37±0.02b 0.31±0.03c 0.73±0.04a 0.39±0.02b 0.42±0.04b NF 夏茶 0.43±0.04bc 0.14±0.05d 0.74±0.02a 0.37±0.02c 0.46±0.06b 秋茶 0.36±0.04b 0.24±0.04c 0.41±0.07ab 0.11±0.02d 0.45±0.02a GABA NF 春茶 0.35±0.01bc 0.31±0.03c 0.51±0.05a 0.40±0.01b 0.46±0.03a NF 夏茶 0.25±0.03c 0.33±0.01bc 0.49±0.03a 0.28±0.09c 0.40±0.02b 秋茶 0.21±0.01c 0.27±0.04ab 0.34±0.06ab 0.23±0.12bc 0.37±0.06a Orn NF 春茶 0.12±0.01b 0.16±0.03ab 0.22±0.03a 0.15±0.03ab 0.20±0.05a NF 夏茶 0.05±0.02b 0.07±0.01b 0.05±0.00b 0.05±0.02b 0.18±0.02a 秋茶 0.11±0.01a 0.07±0.02b 0.14±0.03a 0.07±0.01b 0.07±0.01b 合计 NF 春茶 17.25±0.58e 26.92±1.22d 46.38±0.73a 30.13±0.71c 39.48±1.58b NF 夏茶 12.40±0.32e 17.17±0.41d 28.96±0.60b 18.66±0.13c 31.36±0.53a 秋茶 16.02±0.33d 23.49±0.77c 40.42±2.00a 24.23±0.27c 35.64±0.80b “NF”表示没找到阈值。
"NF" denotes that the threshold was not found -
[1] 叶乃兴. 茶学概论[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2021. [2] CHEN S, LI M H, ZHENG G Y, et al. Metabolite profiling of 14 Wuyi rock tea cultivars using UPLC-QTOF MS and UPLC-QqQ MS combined with chemometrics [J]. Molecules, 2018, 23(2): 104. DOI: 10.3390/molecules23020104
[3] 唐梦婷, 廖献盛, 吴先寿, 等. 金牡丹不同茶类夏秋茶香气品质差异分析 [J]. 食品科学, 2025, 46(2):171−182. DOI: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20240525-209 TANG M T, LIAO X S, WU X S, et al. Differences in aroma quality of different types of jinmudan tea made from tea leaves harvested in summer and autumn [J]. Food Science, 2025, 46(2): 171−182. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20240525-209
[4] TANG M T, LIAO X S, XU M T, et al. Comprehensive investigation on the flavor difference in five types of tea from JMD (Camellia sinensis ‘Jinmudan’) [J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2025, 105(2): 990−1002. DOI: 10.1002/jsfa.13890
[5] XU J, HU F L, WANG W, et al. Investigation on biochemical compositional changes during the microbial fermentation process of Fu brick tea by LC–MS based metabolomics [J]. Food Chemistry, 2015, 186: 176−184. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.12.045
[6] 魏明秀. 茶树新品系金茗早、凤阳紫芽、长乐大叶品种特性研究[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2022. WEI M X. Study on the characteristics of three novel tea variety for Jinmingzao, Fengyang-ziya and Changle-day [D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2022. (in Chinese)
[7] 徐梦婷. 寿宁金牡丹红茶的品质化学解析[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2024. XU M T. Chemical analysis of quality of Shouning Jinmudan black tea[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2024. (in Chinese)
[8] DEKA H, BARMAN T, DUTTA J, et al. Catechin and caffeine content of tea (Camellia sinensis L.) leaf significantly differ with seasonal variation: A study on popular cultivars in North East India [J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 2021, 96: 103684. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfca.2020.103684
[9] 毛娟, 王文海, 洛英, 等. 西藏墨脱县6个茶树品种春夏两季化学品质差异分析 [J]. 食品科学, 2024, 45(10):10167−10174. MAO J, WANG W H, LOB S, et al. Variations in chemical quality among spring and summer tea made from six cultivars grown in Motuo County, Tibet [J]. Food Science, 2024, 45(10): 10167−10174. (in Chinese)
[10] DAI W D, QI D D, YANG T, et al. Nontargeted analysis using ultraperformance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry uncovers the effects of harvest season on the metabolites and taste quality of tea (Camellia sinensis L. ) [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2015, 63(44): 9869−9878. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b03967
[11] 王江花. 不同采摘季节对清香型铁观音成分的影响 [J]. 蚕桑茶叶通讯, 2023(3):21−24. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1253.2023.03.009 WANG J H. The impact of different harvesting seasons on the composition of Qingxiang-type Tieguanyin tea [J]. Newsletter of Sericulture and Tea, 2023(3): 21−24. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1253.2023.03.009
[12] 罗军武. 茶学实验技术[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2020: 29–82. [13] 徐梦婷, 魏明秀, 陈潇敏, 等. 寿宁长叶1号等茶树新品系儿茶素和氨基酸组分分析 [J]. 茶叶学报, 2022, 63(1):20−26. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4872.2022.01.004 XU M T, WEI M X, CHEN X M, et al. Catechins and amino acids in shouningchangye No. 1 and other new tea varieties [J]. Acta Tea Sinica, 2022, 63(1): 20−26. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4872.2022.01.004
[14] ZHOU P, ZHAO F, CHEN M J, et al. Determination of 21 free amino acids in 5 types of tea by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC–MS/MS) using a modified 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate (AQC) method [J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 2019, 81: 46−54. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfca.2019.05.007
[15] FANG K X, XIA Z Q, LI H J, et al. Genome-wide association analysis identified molecular markers associated with important tea flavor-related metabolites [J]. Horticulture Research, 2021, 8(1): 42. DOI: 10.1038/s41438-021-00477-3
[16] ROTZOLL N, DUNKEL A, HOFMANN T. Quantitative studies, taste reconstitution, and omission experiments on the key taste compounds in morel mushrooms (Morchella deliciosa Fr. ) [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2006, 54(7): 2705−2711. DOI: 10.1021/jf053131y
[17] LI M W, SHEN Y, LING T J, et al. Analysis of differentiated chemical components between zijuan purple tea and Yunkang green tea by UHPLC-orbitrap-MS/MS combined with chemometrics [J]. Foods, 2021, 10(5): 1070. DOI: 10.3390/foods10051070
[18] 伊晓云, 李晓嫚, 曾建明. 氮肥和留养时间对夏秋茶生长和品质的影响 [J]. 茶叶学报, 2023, 64(4):14−20. YI X Y, LI X M, ZENG J M. Effects of nitrogen fertilization and retention time on growth and quality of summer and autumn teas [J]. Acta Tea Sinica, 2023, 64(4): 14−20. (in Chinese)
[19] CAO Q Q, ZOU C, ZHANG Y H, et al. Improving the taste of autumn green tea with tannase [J]. Food Chemistry, 2019, 277: 432−437. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.10.146
[20] 梅黎青, 徐雨琴, 刘庆辉, 等. 婺源茶树群体种的适制性研究及品质评价 [J]. 食品研究与开发, 2024, 45(2):51−57. DOI: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2024.02.008 MEI L Q, XU Y Q, LIU Q H, et al. Study on the processing suitability and quality evaluation of Wuyuan tea landraces [J]. Food Research and Development, 2024, 45(2): 51−57. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2024.02.008
[21] ASTILL C, BIRCH M R, DACOMBE C, et al. Factors affecting the caffeine and polyphenol contents of black and green tea infusions [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2001, 49(11): 5340−5347. DOI: 10.1021/jf010759+
[22] 王辉, 杨霁虹, 张晓磊, 等. 蒸汽处理对黟县黑毛茶风味品质的影响 [J]. 食品工业科技, 2024, 45(22):97−106. WANG H, YANG J H, ZHANG X L, et al. Effect of steam treatment on the flavor quality of Yixian dark tea [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2024, 45(22): 97−106. (in Chinese)
[23] 唐梦婷, 廖献盛, 谷梦雅, 等. 基于HS-SPME-GC-MS分析三种茶坯窨制桂花茶的香气成分 [J]. 现代食品科技, 2024, 40(3):247−258. TANG M T, LIAO X S, GU M Y, et al. Analysis of aromatic compounds in three types of tea dhools scented with Osmanthus using HS-SPME-GC-MS [J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2024, 40(3): 247−258. (in Chinese)
[24] YU Z M, YANG Z Y. Understanding different regulatory mechanisms of proteinaceous and non-proteinaceous amino acid formation in tea (Camellia sinensis) provides new insights into the safe and effective alteration of tea flavor and function [J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2020, 60(5): 844−858. DOI: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1552245
[25] LE GALL G, COLQUHOUN I J, DEFERNEZ M. Metabolite profiling using (1)H NMR spectroscopy for quality assessment of green tea, Camellia sinensis (L.) [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2004, 52(4): 692−700. DOI: 10.1021/jf034828r




 下载:
下载: