A Rapid Method for Identifying Stem Blight Resistance of Asparagus
-
摘要:目的
建立芦笋抗茎枯病快速鉴定方法,为芦笋抗病育种及抗病品种的筛选应用提供技术支持。
方法分别采用毒素浸种法、毒素浸根法、分生孢子悬浮液浸种法、分生孢子悬浮液灌根法和田间自然诱发法测定7个芦笋品种对芦笋茎枯病的抗病性。
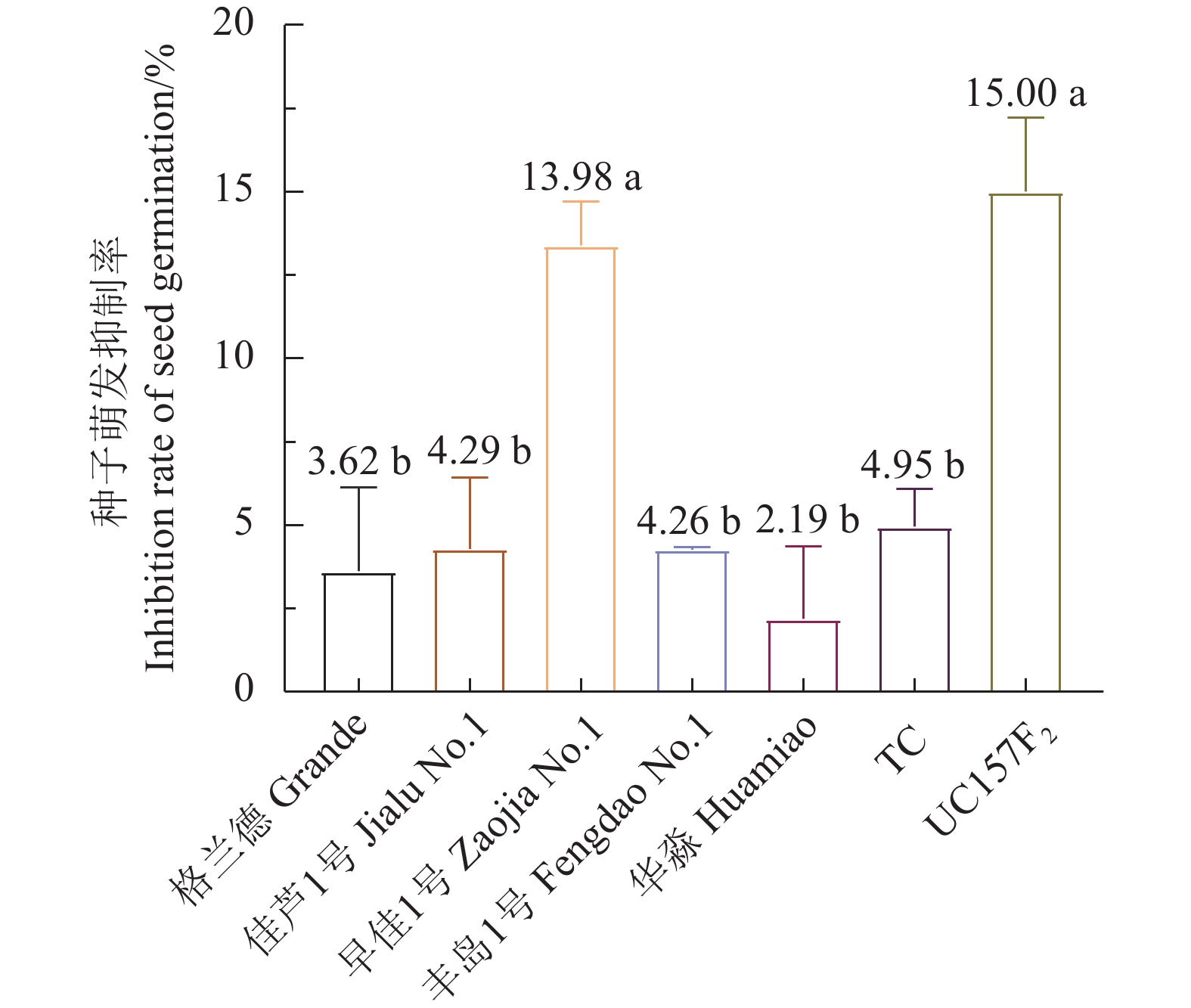
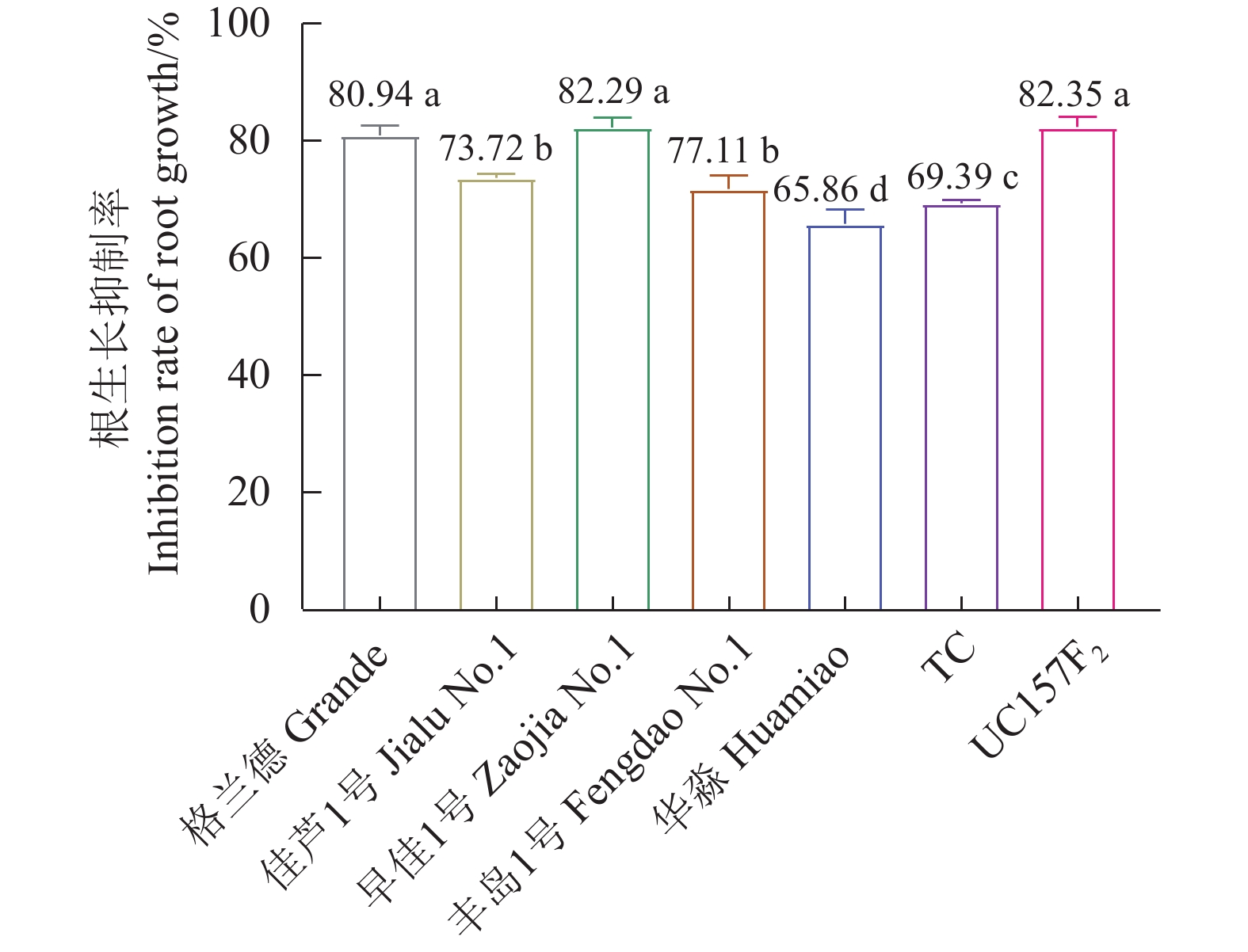
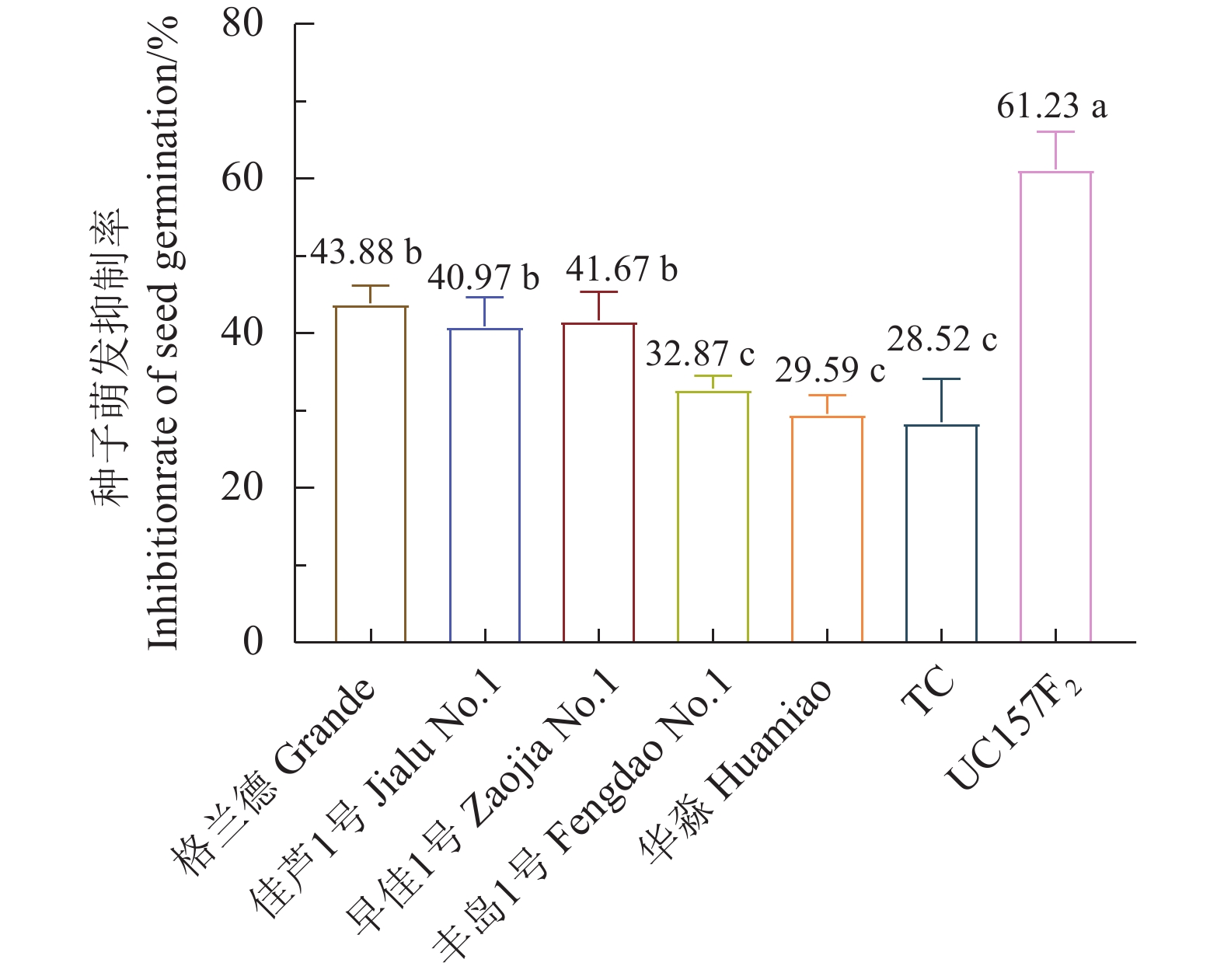
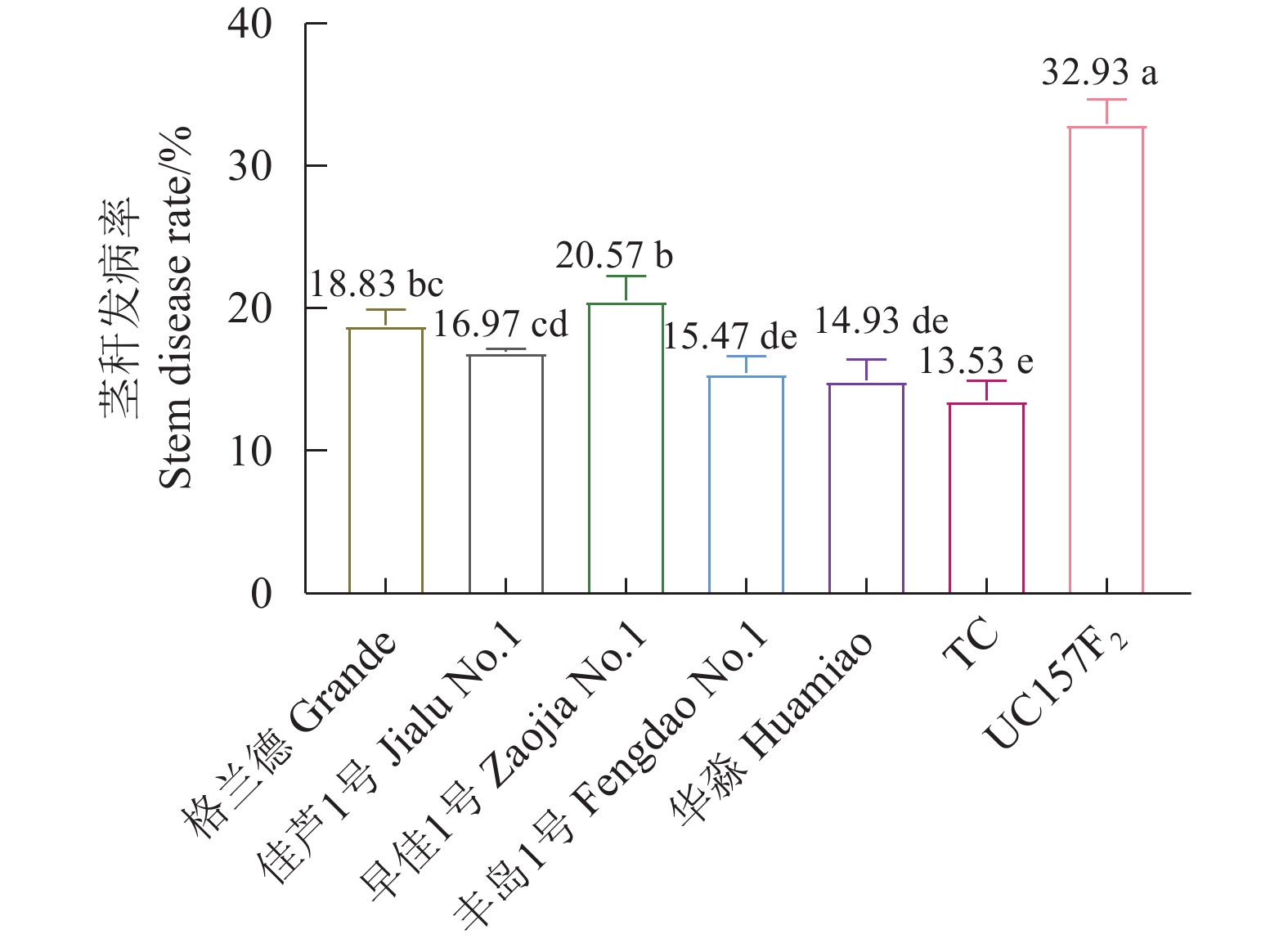
结果芦笋茎枯病菌毒素浸种24 h对格兰德、佳芦1号、早佳1号、丰岛1号、华淼、TC和UC157F2的种子萌发抑制率分别为3.62%、4.29%、13.98%、4.26%、2.19%、4.95%和15.00%,可将7个供试品种划分为感病和中抗2个类型,UC157F2和早佳1号为感病品种,其他品种表现为中抗。毒素原液浸根处理对格兰德、佳芦1号、早佳1号、丰岛1号、华淼、TC和UC157F2的根生长抑制率分别为80.94%、73.72%、82.29%、71.77%、65.86%、69.39%和82.35%,可将供试的7个芦笋品种划分为感病、中感和中抗3个类型,UC157F2、早佳1号和格兰德为感病品种,佳芦1号和丰岛1号为中感品种,TC和华淼为中抗品种。芦笋茎枯病菌分生孢子悬浮液浸种对供试芦笋种子萌发抑制作用较强,其中1.0×105个孢子·mL−1的分生孢子悬浮液浸种处理对格兰德、佳芦1号、早佳1号、丰岛1号、华淼、TC和UC157F2的种子萌发抑制率分别为43.88%、40.97%、41.67%、32.87%、29.59%、28.52%和61.23%,可将7个供试品种分为感病、中感和中抗3个类型,UC157F2为感病品种,格兰德、早佳1号和佳芦1号为中感品种,丰岛1号、华淼和TC为中抗品种。分生孢子悬浮液灌根后所有供试品种的发病率均在80%以上,不能有效区分供试品种的抗病性。田间自然诱发法可将7个供试品种划分为感病、中感和中抗3个类型,UC157F2为感病品种,早佳1号、格兰德和佳芦1号为中感品种,丰岛1号、华淼和TC为中抗品种。
结论病菌分生孢子悬浮液浸种法对芦笋品种的抗茎枯病鉴定结果与田间自然诱发法鉴定结果在0.01水平上显著相关,可以与田间自然诱发法相结合快速准确鉴定芦笋种质资源对茎枯病的抗性水平。
Abstract:ObjectiveA method was developed to rapidly evaluate the resistance of an asparagus cultivar to stem blight.
MethodSeven asparagus cultivars with varying degrees of resistance to stem blight were selected for the study. To artificially induce the disease, (1) the asparagus seeds and/or roots were soaked in an aqueous solution containing the mycotoxin produced by Phomopsis asparagi, (2) the asparagus seeds were submerged in P. asparagi spore suspension, or (3) the asparagus roots were irrigated with an aqueousP. asparagi spore suspension to compare with (4) the natural induction on asparagus plants in the field. Seed germination and seedling root growth were monitored to grade the disease resistance or susceptibility of each asparagus variety.
ResultAfter 24h soaking in an aqueous solution containing mycotoxin, the seeds of Grande, Jialu No. 1, Zaojia No. 1, Fengdao No. 1, Huamiao, TC and UC157F2 displayed inhibited germination at the rates of 3.62%, 4.29%, 13.98%, 4.26%, 2.19%, 4.95% and 15.00%, respectively. Accordingly, UC157F2 and Zaojia No. 1 were classified as the susceptible varieties and the remainders moderately resistant ones. As the root growth of Grande, Jialu No. 1, Zaojia No. 1, Fengdao No. 1, Huamiao, TC and UC157F2 plants affected by an exposure to mycotoxin were inhibited at the rates of 80.94%, 73.72%, 82.29%, 71.77%, 65.86%, 69.39% and 82.35%, respectively, the asparagus cultivars UC157F2, Zaojia No. 1 and Grande were grouped in the susceptible class, Jialu No. 1 and Fengdao No. 1 in the moderately susceptible class, and TC and Huamiao in the moderately resistant class. The significant inhibition on germination by soaking the seeds in suspension of 1.0×105 P. asparagi spores·mL−1 was at a rate of 43.88% on the Grande seeds, 40.97% on the Jialu No. 1 seeds, 41.67% on the Zaojia No. 1 seeds, 32.87% on the Fengdao No. 1 seeds, 29.59% on the Huamiao seeds, 28.52% on the TC seeds, and 61.23% on the UC157F2 seeds. The results placed UC157F2 in the susceptible, Grande, Zaojia No. 1 and Jialu No. 1 in the moderately susceptible, and Fengdao No. 1, Huamiao and TC in the moderately resistant classifications. When the plants were irrigated with the P. asparagi spore suspension, the disease incidence on all tested asparagus was greater than 80% and not adequate to differentiate the resistance grades. Finally, in comparison, the stem blight-induced UC157F2 plants in the field was the susceptible cultivar, whereas Zaojia No. 1, Grande, Jialu No. 1 and Fengdao No. 1 were the moderately susceptible and Huamiao and TC the moderately resistant varieties.
ConclusionOf the various methods for comparing resistance to stem blight of asparagus varieties, soaking the seeds in P. asparagi spore suspension rendered the classification closest to that obtained by the field induction (P<0.01). Therefore, along with field observation, it could be reliably applied to quickly estimate the disease resistance of an asparagus cultivar.
-
Keywords:
- Asparagus officinalis L. /
- asparagus stem blight /
- resistance /
- identification method
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】堆肥发酵是在微生物作用下将不可溶的大分子有机物矿质化、腐殖化和无害化的复杂化学过程。在这个过程中碳和氮是最重要的两种元素,是微生物生长和繁殖的主要物质和能量来源,是保障堆肥发酵顺利进行的关键[1]。堆肥过程中,在微生物作用下大分子有机氮和碳经过一系列复杂的生化反应,分解成小分子的溶解性有机氮和碳,这些小分子碳和氮被微生物吸收利用,再经过微生物作用完成腐殖化过程[1-6]。因此,可溶性有机碳和氮既是堆肥过程的中间产物,又是最终能被作物吸收利用的组分,其含量在一定程度上反映了大分子有机碳氮的降解效率,也间接反映了微生物的活跃程度和堆肥发酵的腐熟速率及程度,研究可溶性碳和氮含量的变化对揭示堆肥过程物料的物质转化规律具有重要的意义。【前人研究进展】堆肥过程中围绕碳氮变化的研究表明,硝态氮则呈逐渐增加趋势[6-8];而全氮、总有机氮[8]、铵态氮[6,7,9]、总有机碳[10]、可溶性有机碳[5,10]呈逐渐降低趋势,氮素形态由有机态向无机态转化、稳定态向有效态转化、铵态向硝态转化[8],碳素形态则由大分子有机态向小分子有机碳转化[3]。添加外源菌剂是商品化生产有机肥的常用方式之一。研究表明,添加外源微生物菌剂能提高发酵效果、缩短发酵周期、提高堆肥品质[11-13]。高云航等[8]研究发现,添加低温复合菌使堆肥物料中的铵态氮含量明显降低,硝态氮含量增高,促进氮的转化。王义祥等[10]研究发现,添加EM 菌剂的堆肥处理比未添加EM 菌剂处理的碳素损失高,添加EM 菌剂可以加速有机质的矿化分解和提高腐殖质化指数。单德鑫等研究表明,添加外源微生物会降低牛粪堆肥前期全氮和酸水解氮的含量,加速有机态氮矿化[2]。王守红等[9]研究认为,菌剂添加不当会增加堆肥过程氮的损失。可见不同的菌剂产生的效果不尽相同。【本研究切入点】奶牛是家畜中粪尿排放量最多的动物,一头600 kg体重、日产奶量20 kg的成年奶牛,一昼夜排粪量和尿量分别可达30 kg和22 kg[14]。目前,关于牛粪堆肥研究主要集中在工艺条件、影响因素以及外源菌剂对堆肥效果的影响等方面[6-9],但对半发酵的牛床垫料堆肥研究得还远远不够。目前市场上商品化的微生物菌剂种类繁多,其作用也不尽相同。【本研究切入点】本研究以使用3年的奶牛场牛床垫料为原料,随机选了市面上常用的4种微生物菌剂作为发酵添加剂,研究不同菌剂作用下半发酵牛床垫料发酵过程可溶性氮和碳含量的变化,通过可溶性氮、碳含量的动态变化揭示其降解效率和转化规律,为发酵床垫料的肥料化应用提供基础数据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
本试验所用堆肥原料主料来自于福建省南平市长富第15牧场,为该牧场使用了3年的牛床垫料,垫料使用过程未添加外源菌剂。试验材料为牛床垫料、猪粪、甘蔗渣按7∶2∶1的比例配合而成,其主要养分含量如表1所示。本试验所用菌剂共4种,介绍如下:菌剂1:EM原露,由乳酸菌、酵母菌、放线菌、丝状菌、光合细菌等5大菌群80种以上的微生物组合,适用于动植物废弃物的发酵;菌剂2:百丰畜禽宝菌剂,以乳酸菌、酵母菌、芽孢杆菌、醋酸菌和放线菌等为主,适用于畜禽粪便发酵和除臭;菌剂3:丰力净菌剂,主要由放线菌、酵母菌、乳酸菌和丝状真菌等复合菌组成,适用于畜禽粪便发酵和除臭;菌剂4:国龙生物床菌剂,主要由芽孢杆菌、乳酸菌、酵母菌、纳豆菌等多种发酵床专用菌及生物活性酶制剂复配而成,主要应用于微生物原位和异位发酵床。所有菌剂的有效活菌数均大于80亿cuf·g−1,除EM菌剂外,其他3种菌剂均为粉剂。
表 1 堆肥原料的基本组分Table 1. Major physiochemical properties of compost materials原料 Raw material N/% P2O5/% K2O/% C/% C/N 含水量 Water content% 质量分数 Mass faction% 牛床垫料 Cow bed material 1.68 0.78 0.92 38.17 22.68 60 70 猪粪 Pig manure 2.04 2.05 0.90 40.02 19.62 70 20 甘蔗渣 Sugar cane residue 0.39 0.09 0.25 41.00 105.00 42 10 1.2 试验设计
本试验在南平市顺元农业发展有限公司的有机肥厂进行。堆肥处为有顶棚但四周无墙体的空旷场地,地表为水泥地。在堆肥处堆5个圆锥形堆垛,每堆原料约为10 t,加入微生物菌剂50 kg,比例为原料的0.5%,原料和菌剂的添加为一层料一层菌剂,最后再用铲车翻堆直至菌剂与原料混合均匀,进行堆垛发酵。试验设置5个处理,处理1:EM菌剂,记为EM;处理2:百丰畜禽宝菌剂,记为BF;处理3:丰力净菌剂,记为FLJ;处理4:国龙生物床菌剂,记为GR;处理5:不加菌剂,对照(CK)。发酵过程中每隔5 d翻堆原料,10 、20 、30 、40 和50 d分别取样,鲜样取回后置于4 ℃冰箱保存,1周内测完所有指标。
1.3 试验方法
称取过1 mm筛的鲜土10 g,加入2M KCl提取液提取土壤溶液,参照鲁如坤[15]《土壤农业化学分析方法》采用比色法测定NO3−-N和NH4+-N含量;采用TOC分析仪测定提取液的可溶性全氮(STN)、可溶性全碳(STC)和可溶性有机碳(SOC)含量,可溶性有机氮SON=TSN-(NH4+-N)-(NO3−-N),SOC+SIC=STC。
1.4 数据处理
数据采用Excel 2016整理,用统计分析软件SPSS 12.0进行统计分析,处理间数据采用单因素方差分析法进行方差分析,用Duncan新复极差法进行多样本比较。数据用“平均值±标准差”表示,差异显著性水平p < 0.05。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 双因素方差分析
菌剂和发酵时间共同作用下牛床垫料发酵过程铵态氮(NH4+-N)、硝态氮(NO3−-N)、可溶性有机氮(SON)、可溶性总碳(STC)和可溶性有机碳(SOC)的双因素方差分析如表2所示。菌剂、发酵时间及菌剂和发酵时间的共同作用对牛粪污垫料发酵过程的可溶性氮(NH4+-N、NO3−-N和SON)及可溶性碳(STC和SOC)的影响均差异显著(p<0.05),表明使用菌剂会对牛粪污垫料发酵过程可溶性氮和碳产生显著影响。
表 2 双因素方差分析结果Table 2. Results of two-way analysis variance因素 Factor NH4+-N NO3−-N SON STC SOC F Sig. F Sig. F Sig. F Sig. F Sig. 校正模型 Correction model 52.504 0.000 30.92 0.000 12.301 0.000 9.526 0.000 70.97 0.000 菌剂 Inoculants 33.61 0.000 9.432 0.000 12.28 0.000 8.275 0.000 234.3 0.000 取样时间 Sampling time 219.86 0.000 96.237 0.000 42.869 0.000 31.8 0.000 59.42 0.000 菌剂×取样时间 Inoculants×Sampling time 14.414 0.000 20.002 0.000 4.667 0.000 4.256 0.000 32.42 0.000 2.2 菌剂对牛粪污垫料发酵过程可溶性氮的影响
菌剂对牛粪污垫料发酵过程可溶性氮含量的影响如图1和表3所示。与CK相比,添加4种菌剂显著提高了牛粪污发酵过程的NH4+-N和SON含量,表明添加4种菌剂后促进大分子氮的降解,增加了NH4+-N和SON含量,但有增加氨挥发的风险。其中GR处理的NH4+-N和SON含量最高,显著高于其他3种菌剂处理,表明GR对垫料的降解能力最强,但在降解垫料的过程中生成的铵态氮含量也最高,氨挥发的风险也最大,这可能与该菌剂中含产氨菌有关。从各时期来看,发酵10~20 d,EM处理NH4+-N含量较CK显著降低,而发酵50 d则显著提高;发酵10 、30 和50 d,BF处理NH4+-N含量较CK显著提高;整个发酵期,FLJ处理NH4+-N含量与CK相比差异不显著;发酵10~50 d,GR处理的牛粪污垫料NH4+-N含量较CK显著提高(图1-A)。发酵40~50 d,EM处理SON含量较CK显著提高;发酵30~50 d,BF、FLJ和GR处理SON含量也较CK显著提高(图1-C)。添加菌剂显著降低了牛粪污发酵过程NO3−-N含量,其中BF处理的NO3−-N含量最低。从各时期来看,发酵30~40d,EM、BF、FLJ和GR处理NO3−-N含量较CK显著降低,而发酵50 d EM处理NO3−-N含量则较CK显著增加(图1-B)。
表 3 不同处理样品NH4+-N、NO3−-N、SON、STC和SOC含量Table 3. Contents of NH4+-N, NO3−-N,SON, STC, and SOC in treatment samples项目Item NH4+-N NO3−-N SON STC SOC CK 0.810±0.132 d 0.837±0.123 a 1.309±0.165 d 11.301±0.440 bc 11.104±0.484 b EM 1.101±0.155 cd 0.601±0.088 b 1.879±0.203 c 10.606±0.794 c 8.968±0.433 c BF 1.592±0.200 b 0.491±0.044 b 2.124±0.164 bc 12.259±0.502 b 12.692±0.405 a FLJ 1.379±0.179 bc 0.589±0.063 b 2.257±0.227 b 12.534±0.642 b 13.743±0.772 a GR 2.094±0.322 a 0.591±0.083 b 2.825±0.319 a 14.135±0.736 a 8.394±0.440 c 注:表中同列数字后不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),下同。表中不同菌剂处理可溶性氮和碳的含量为5次取样的平均值。
Note: Data with different lowercase letters on same column mean significant difference at p<0.05. Contents of soluble nitrogen and carbon are average of 5 replicates.2.3 菌剂对垫料发酵过程可溶性碳含量的影响
菌剂对牛粪污垫料发酵过程STC和SOC含量的影响如图2和表3所示。添加菌剂对牛粪污发酵过程STC含量有增加作用,其中GR处理达到显著水平,较CK显著提高;而SOC含量的变化则无明显的规律性,其中BF和FLJ 2种菌剂处理牛粪污发酵过程SOC含量较CK显著增加,而EM和GR处理效果相反,较CK显著降低。从各时期来看,与CK相比,发酵10 d,BF和FLJ处理显著提高了牛粪污垫料的STC含量,发酵20 d,EM、FLJ和GR 3种菌剂处理的STC含量显著提高;发酵30 d,4种菌剂处理均显著提高了STC含量;而发酵40 d和50 d,菌剂处理后牛粪污垫料的STC含量有一个降低趋势(图 2-A)。表明在发酵前半段,菌剂处理有利于促进堆料中碳水化合物的分解,提高牛STC含量,后期随可溶性碳含量的提高,其在堆料中含量达到饱和,因此腐殖化作用强于分解作用,可溶性碳被微生物吸收利用转化为相对复杂的含碳化合物[10],后半段则表现为降低STC含量。对SOC而言,与CK相比,4种菌剂处理对牛粪污垫料发酵过程SOC含量有增加作用,且在发酵10、20、30和50 d,EM、FB、FLJ菌剂处理牛粪污垫料的SOC含量较CK显著提高,发酵40 d,4种菌剂处理均显著提高了牛粪污垫料的SOC含量(图 2-B),表明添加菌剂后能促进大分子有机氮的分解,产生更多的SOC。
2.4 不同形态氮和碳随发酵时间变化的回归方程
不同发酵时间对垫料发酵过程铵态氮(NH4+-N)、硝态氮(NO3−-N)、可溶性有机氮(SON)、可溶性总碳(STC)和可溶性有机碳(SOC)的影响如表4所示。铵态氮含量随发酵时间的延长表现为先升后降的变化趋势。发酵初期,无机氮被矿化分解生成铵态氮,因此铵态氮含量增加,随着发酵时间延长,微生物大量繁殖,铵态氮被吸收利用或生成氨气挥发,因此含量降低。硝态氮则随着发酵时间延长呈增加趋势,表明整个发酵过程硝化作用持续增强。发酵20 d,牛粪污垫料中的铵态氮含量最高,发酵50 d硝态氮含量最高,而SON含量则随着发酵时间延长显著增加,其中发酵50 d粪污垫料中的SON含量最高,这可能与大分子有机氮被分解有关。STC和SOC含量的变化随着发酵时间延长呈先增后降的趋势,发酵20 d和30 d,牛粪污垫料STC含量最高,发酵40 d和50 d,STC和SOC含量最低。表明发酵前期,垫料含碳物质分解作用增强,后期腐殖化作用强于分解作用,因此STC和SOC含量降低。
表 4 不同取样时间NH4+-N、NO3--N、SON、STC和SOC含量Table 4. Contents of NH4+-N, NO3−-N,SON, STC, and SOC in samples at different sampling times取样时间 Sampling time/d NH4+-N NO3−-N SON STC SOC 10 0.841±0.120 c 0.295±0.042 c 0.891±0.156 d 10.647±0.472 b 12.748±0.427 a 20 3.387±0.121 a 0.352±0.042 c 1.651±0.154 c 15.494±0.466 a 11.100±0.427 b 30 1.844±0.120 b 0.393±0.042 c 2.022±0.158 b 14.235±0.466 a 11.173±0.427 b 40 0.818±0.120 c 0.810±0.042 b 2.176±0.165 b 9.098±0.466 c 9.754±0.444 c 50 0.087±0.120 d 1.258±0.042 a 3.654±0.154 a 11.36±0.466 b 9.86±0.427 c 注:表中不同取样时间可溶性氮和碳的含量为所有处理在该时间的平均值。
Note: Contents of soluble nitrogen and carbon at different sampling times are average of all treatments.不同形态氮和碳随发酵时间变化的回归方程如表5所示。铵态氮、硝态氮、SON、STC和SOC含量与发酵时间的关系能用3次函数方程拟合,R2分别为0.583、0.401、0.347、0.285和0.611,且p=0.000<0.05,表明回归方程有统计学意义。
表 5 不同形态氮和碳随发酵时间变化的回归方程Table 5. Regression equation for dynamic changes of different forms of nitrogen and carbon at various fermentation times碳/氮形态 Carbon/nitrogen form 回归方程/Regression equation R2 F Sig. NH4+-N y=−6.538+1.08x−0.037x2+0.0001x3 0.583 102.46 0.000 NO3−-N y=1.761−0.246x+0.012x2+0.0001x3 0.401 49.18 0.000 SON y=−1.581+0.351x−0.012x2+0.0001x3 0.347 37.78 0.000 STC y=−9.831+3.00x−0.108x2+0.001x3 0.285 29.301 0.000 SOC y=11.378−0.313x+0.019x2+0.001x3 0.611 115.14 0.000 注:x为时间,y为不同形态碳氮含量。
Note: x: sampling time; y: different forms of nitrogen and carbon.3. 讨论
碳是堆肥过程中关键的元素,其形态和含量的变化能反应堆肥的进程及腐熟化程度。菌剂能促进堆肥过程中有机碳的降解,改变堆肥中的碳素形态[16] 。本研究发现,添加菌剂促进了可溶性总碳含量的提高,由于菌剂使用能减少总碳的消耗[16],这可能是导致可溶性总碳含量提高的原因。本研究还发现,随着发酵时间的延长,可溶性总碳呈先增后降的变化趋势,这与王义祥等[10]的研究结果一致,他们的研究认为添加EM 菌剂可加速有机质的矿化分解和提高腐殖质化指数。不添加任何辅料时,牛粪自身进行发酵过程中有机碳降解不彻底,而菌剂作用可以促进有机碳的降解,提高堆肥中可溶性碳的含量,有机碳含量的提高也可能意味着以其它形式损耗的碳减少。在4种菌剂中,国龙生物床菌剂的效果最明显,其作用后堆肥中可溶性总碳的含量最高。本研究还发现,不同的菌剂对可溶性有机碳的影响无明显的规律性。李杰等研究表明,添加不同菌剂对有机碳降解的效果不尽相同[16],这与本研究的结果一致。
氮素是堆肥过程中变化最大的元素之一,其变化包括氮的分解和固定。堆肥发酵过程中大分子有机氮被微生物降解和转化,产生小分子有机氮、无机氮和气态氮,再经过微生物固定继续参与氮循环,因此微生物是影响堆肥氮含量的最重要因素[17]。本研究结果表明,添加菌剂后显著增加了铵态氮含量,降低了硝态氮含量,这与高云航等[8]研究的结果一致。马丽红等[18]研究表明,堆肥中氨化细菌数量变化与堆肥中氨气挥发和氨态氮含量都极显著正相关关系,表明添加菌剂可能促进氨化细菌数量增加,进而导致铵态氮含量增加,但也存在增加氨挥发的风险。本研究还发现,牛粪污垫料发酵过程铵态氮呈先降低趋势,而硝态氮则呈增加趋势,这与刘超等[6]研究的结果一致。堆肥高温期氨化细菌数据大幅度增加,而降温期硝化细菌数量增加幅度较大[18],这是导致发酵过程铵态氮含量降低和硝态氮含量增加的主要原因。本研究的结果表明,添加菌剂后显著增加了可溶性有机氮的含量,且可溶性有机氮随着发酵时间延长呈增加趋势。可溶性有机氮含量的变化反映了大分子有机氮到小分子氮的转化过程和降解程度[19],菌剂使用后增加了可溶性有机氮含量,表明添加菌剂促进了垫料氮的降解和转化。
菌剂是影响畜禽粪便发酵的重要因素之一,目前市场上发酵菌剂种类繁多,效果不尽相同[9]。本研究选用的4种菌剂对牛粪垫料发酵过程的可溶性氮和碳含量都有显著影响,表明添加菌剂对大分子氮和碳的降解均产生显著影响。生物床菌剂(GR)主要应用于原位发酵床,在本研究中将其用于堆肥后,NH4+-N、SON、和STC的含量均最高,表明该菌剂降解牛粪垫料的能力最强,氨氮挥发的风险最大;而BF和FLJ两种菌剂作用后堆肥垫料NH4+-N、SON、和STC的含量次之,且SOC含量最高,表明这2种菌剂降解牛粪垫料的能力也很强,但NH4+-N较GR处理显著降低,这可能与BF和FLJ两种菌剂添加了除臭组分有关。而在本研究中EM菌对可溶性氮和碳的影响效果最差。因此,选择堆肥发酵菌剂时,应综合考虑降解能力和减少氨气的产生。
-
图 1 芦笋茎枯病菌毒素浸种24 h对芦笋种子萌发的抑制率
不同小写字母表示经Duncan氏新复极差法检验差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。
Figure 1. Germination inhibition rate of asparagus seeds soaked in mycotoxin-containing solution for 24 h
Those with different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at P<0.05 by Duncan’s new multiple range test. Same for below.
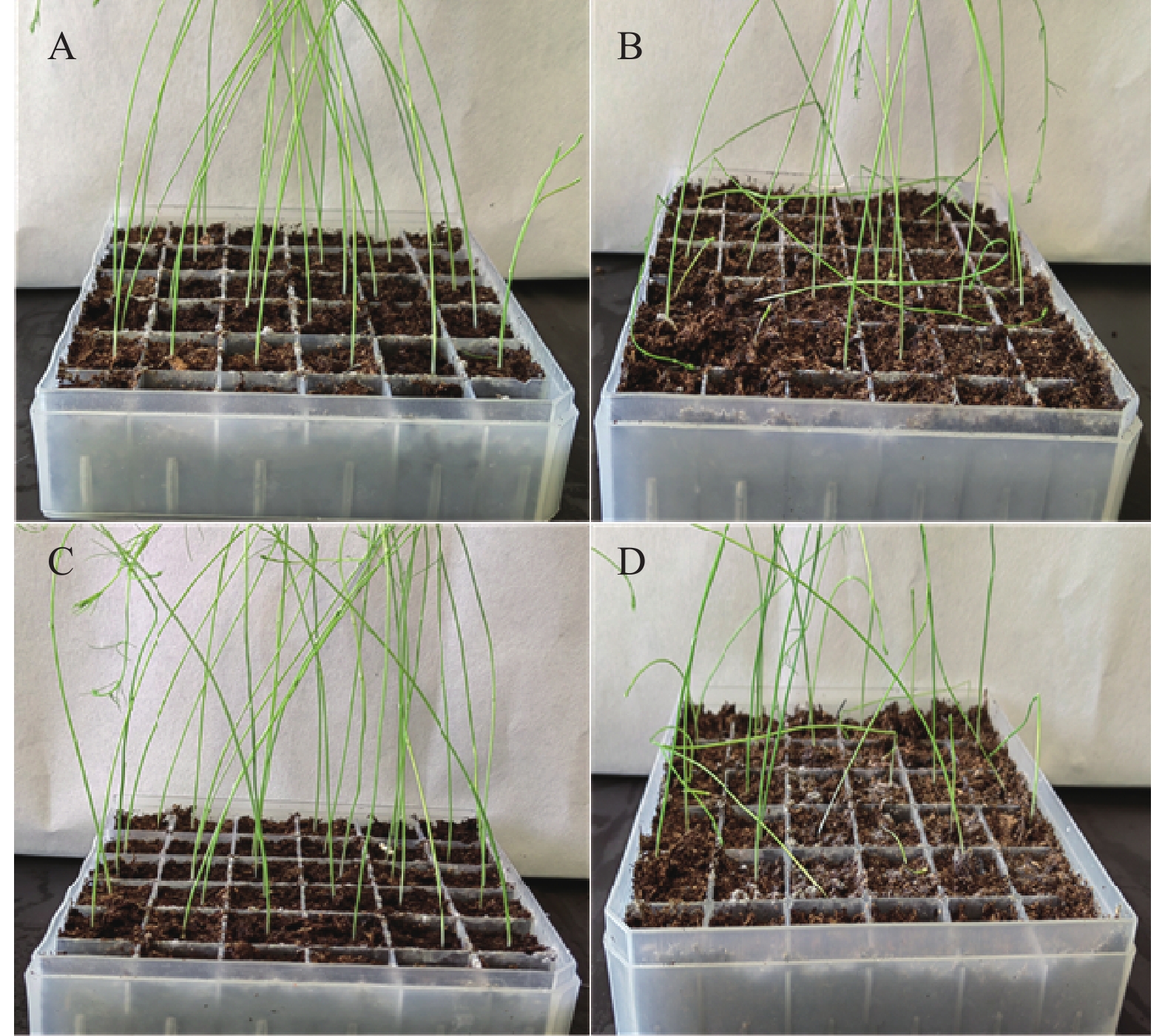
图 4 芦笋茎枯病菌1.0×103个孢子·mL−1孢子悬浮液灌根处理的发病结果
A:TC对照;B:TC分生孢子悬浮液灌根;C:UC157F2对照;D:UC157F2分生孢子悬浮液灌根。
Figure 4. Disease incident of asparagus plants with roots irrigated with 1.0×103P. asparagi spores·mL−1 suspension
A: TC control; B: TC roots irrigated with P. asparagi spore suspension; C: UC157F2 control; D: UC157F2 roots irrigated with P. asparagi spore suspension.
表 1 芦笋茎枯病菌毒素不同浸种时间对芦笋种子萌发率的影响
Table 1 Effect of soaking time in mycotoxin-containing solution on asparagus seed germination rate
浸种时间
Soaking time/h种子萌发率
Germination rate of seed /%格兰德
Grande佳芦1号
Jialu No.1早佳1号
Zaojia No.1丰岛1号
Fengdao No.1华淼
HuamiaoTC UC157F2 2 90.67a 92.00a 94.00a 92.00a 90.00a 92.67ab 90.67ab 4 91.33a 92.00a 91.33b 92.00a 90.67a 90.67ab 88.00bc 8 90.00a 91.33a 89.33b 92.00a 89.33a 92.00ab 85.33cd 16 88.00a 90.67a 84.67c 89.33a 90.67a 92.67ab 82.67de 24 89.33a 89.33a 82.00d 90.00a 89.33a 89.33b 79.33e 0 (CK) 92.00a 93.33a 94.67a 94.00a 91.33a 94.00a 93.33a 同列数据后不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。下同。
Data with different lowercase letters on a column indicate significant differences at P<0.05. Same for below.表 2 不同浓度芦笋茎枯病菌毒素浸根对芦笋根生长的影响
Table 2 Effect of soaking in solutions containing varied concentrations of mycotoxin on growth of asparagus roots
粗毒素原液与水体积比
Volume ratio of toxin to water根生长抑制率
The inhibition rate of root growth/%格兰德
Grande佳芦1号
Jialu No.1早佳1号
Zaojia No.1丰岛1号
Fengdao No.1华淼
HuamiaoTC UC157F2 1∶0 80.94a 73.72a 82.29a 71.77a 65.86a 69.39a 82.35a 7∶1 74.96b 68.58b 77.12b 67.99b 62.30b 64.60b 77.78b 3∶1 68.99c 64.56c 72.83c 63.02c 58.45c 60.95c 74.75c 1∶1 65.45d 60.85d 68.32d 58.61d 54.54d 55.60d 70.22d 1∶3 60.82e 57.12e 63.80e 53.59e 49.11e 50.54e 66.54e 1∶7 57.28f 55.10f 59.58f 46.00f 43.44f 46.61f 60.77f 表 3 不同浓度芦笋茎枯病菌分生孢子悬浮液浸种对芦笋种子萌发率的影响
Table 3 Effect on germination rate of seeds soaked in varied P. asparagi spore suspensions
分生孢子
悬浮液浓度
Concentration of
spore suspension
/(孢子·mL-1)种子萌发率
Germination rate of seed/%格兰德
Grande佳芦1号
Jialu
No.1早佳1号
Zaojia
No.1丰岛1号
Fengdao
No.1华淼
HuamiaoTC UC-
157F21.0×103 68.00b 68.00b 66.00b 73.33b 77.33b 80.00b 49.33b 1.0×104 60.67c 61.33bc 60.67bc 69.33bc 72.00c 72.00b 44.00bc 1.0×105 52.00d 56.67c 56.00c 62.67c 66.67d 68.67b 36.67c 0 (CK) 92.67a 96.00a 96.00a 93.33a 94.67a 96.00a 94.67a 表 4 不同鉴定方法的相关性
Table 4 Correlation between evaluation methods for disease resistance of asparagus
抗性鉴定方法
Resistance-identification
methods毒素浸种法
Soaking seed
with mycotoxin毒素浸根法
Soaking root
with mycotoxin分生孢子悬浮液浸种法
Soaking seed
with spore suspension分生孢子悬浮液灌根法
Irrigating root
with spore suspension自然诱发法
Field natural
induction method毒素浸种法
Soaking seed with mycotoxin1 0.768** 0.911** 0.267 0.703** 毒素浸根法
Soaking root with mycotoxin0.768** 1 0.682** 0.327 0.682** 分生孢子悬浮液浸种法
Soaking seed with spore suspension0.911** 0.682** 1 0.373 0.761** 分生孢子悬浮液灌根法
Irrigating root with spore suspension0.267 0.327 0.373 1 0.540* 田间自然诱发法
Field natural induction method0.703** 0.682** 0.761** 0.540* 1 **表示在0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关;*表示在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关。
** indicates significant correlation at P<0.01 (bilateral); * indicates significant correlation at P<0.05 (bilateral). -
[1] DEHGHAN-SHAHREZA F, BELADI-MOUSAVI S S, RAFIEIAN-KOPAEI M. Medicinal plants and diabetic kidney disease; an updated review on the recent findings [J]. Immunopathologia Persa, 2016, 2(1): 1−6.
[2] RUSJAN D, MIKULIC-PETKOVSEK M. Double maturation raisonnée: The impact of on-vine berry dehydration on the berry and wine composition of Merlot (Vitis vinifera L. ) [J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2017, 97(14): 4835−4846. DOI: 10.1002/jsfa.8354
[3] 孙强, 赵凤, 兰波, 等. 芦笋茎枯病菌致病机制的研究进展 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2023, 51(3):6−10. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2023.03.002 SUN Q, ZHAO F, LAN B, et al. Research progress on the pathogenic mechanism of Asparagus stem blight pathogen [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 51(3): 6−10. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2023.03.002
[4] 刘志恒, 孙俊, 杨红, 等. 芦笋茎枯病菌生物学特性的研究 [J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2008, 39(3):301−304. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1700.2008.03.010 LIU Z H, SUN J, YANG H, et al. Biological characteristics of Phomopsis asparagi the pathogen of Asparagus stem blight [J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2008, 39(3): 301−304. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1700.2008.03.010
[5] SHI N N, RUAN H C, GAN L, et al. Evaluating the sensitivities and efficacies of fungicides with different modes of action against Phomopsis asparagi [J]. Plant Disease, 2020, 104(2): 448−454. DOI: 10.1094/PDIS-05-19-1040-RE
[6] 杜宜新, 阮宏椿, 石妞妞, 等. 福建省稻瘟病菌对主要抗瘟基因及主栽品种的致病性分析 [J]. 植物保护学报, 2016, 43(3):442−451. DU Y X, RUAN H C, SHI N N, et al. Pathogenicity analysis of Magnaporthe grisea against major Pi-genes and main rice varieties in Fujian Province [J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2016, 43(3): 442−451. (in Chinese)
[7] 中华人民共和国农业部. 水稻品种试验稻瘟病抗性鉴定与评价 技术规程: NY/T 2646—2014[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2015. [8] 程蓬, 郭璇, 辛秀丽, 等. 83份西农系小麦品种(系)抗性鉴定及抗病基因分子检测 [J]. 植物保护学报, 2024, 51(1):237−248. CHENG P, GUO X, XIN X L, et al. Disease resistance evaluation and molecular detection of resistance genes of 83 Xinong wheat varieties(lines) [J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2024, 51(1): 237−248. (in Chinese)
[9] SONODA T, URAGAMI A, KAJI K. Evaluation of Asparagus officinalis cultivars for resistance to stem blight by using a novel inoculation method [J]. HortScience, 1997, 32(6): 1085−1086. DOI: 10.21273/HORTSCI.32.6.1085
[10] 杨迎青, 李湘民, 孟凡, 等. 芦笋茎枯病抗性鉴定方法的建立及芦笋抗病种质资源的筛选 [J]. 植物病理学报, 2012, 42(6):649−654. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0412-0914.2012.06.014 YANG Y Q, LI X M, MENG F, et al. Establishment of a resistance-identification method on Asparagus stem blight and evaluation of Asparagus officinalis germplasms [J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 2012, 42(6): 649−654. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0412-0914.2012.06.014
[11] 阮宏椿, 石妞妞, 杜宜新, 等. 9个芦笋品种在福建的适应性分析 [J]. 农学学报, 2017, 7(11):31−34. DOI: 10.11923/j.issn.2095-4050.cjas17010013 RUAN H C, SHI N N, DU Y X, et al. 9 Asparagus varieties in Fujian: Adaptability analysis [J]. Journal of Agriculture, 2017, 7(11): 31−34. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11923/j.issn.2095-4050.cjas17010013
[12] 李俊萍, 乜兰春, 王珊珊, 等. 茎枯病菌毒素制备及对芦笋愈伤组织抗性诱导的研究 [J]. 植物病理学报, 2016, 46(1):140−144. LI J P, NIE L C, WANG S S, et al. Phomopsis asparagi toxin preparation and the resistance induction on Asparagus callus by the pathogen toxin [J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 2016, 46(1): 140−144. (in Chinese)
[13] 孙丽萍, 时焦, 孟坤, 等. 利用赤星病菌毒素快速高通量鉴定烟草抗性种质的方法研究 [J]. 中国烟草科学, 2014, 35(1):80−84. SUN L P, SHI J, MENG K, et al. Investigation on the method of rapid identifying resistant tobacco germplasms to Alternaria alternata by using its mycotoxins [J]. Chinese Tobacco Science, 2014, 35(1): 80−84. (in Chinese)
[14] 杨迎青, 兰波, 胡水秀, 等. 几种因素对芦笋茎枯病菌分生孢子器和分生孢子产生量的影响 [J]. 植物保护学报, 2015, 42(4):517−522. YANG Y Q, LAN B, HU S X, et al. Effects of several factors on the production of pycnidia and conidia in Asparagus stem blight pathogen [J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2015, 42(4): 517−522. (in Chinese)
[15] 孙大元, 张景欣, 陈冠州, 等. 空间诱变选育抗稻瘟病水稻品种研究进展与展望 [J]. 核农学报, 2017, 31(2):271−279. DOI: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2017.02.0271 SUN D Y, ZHANG J X, CHEN G Z, et al. Achievements and perspective outlook of space induced mutation breeding for the rice blast resistance [J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 31(2): 271−279. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2017.02.0271
[16] 丁燕芳, 平文丽, 孙计平, 等. 烟草黑胫病抗性鉴定方法比较及其相关性分析 [J]. 湖北农业科学, 2017, 56(18):3477−3480. DING Y F, PING W L, SUN J P, et al. Comparison of methods to identify resistance to tobacco black shank disease and their correlation analysis [J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 56(18): 3477−3480. (in Chinese)
[17] 贺红, 温雁鹰, 许仕仰, 等. 广藿香抗青枯病鉴定方法的研究 [J]. 广州中医药大学学报, 2011, 28(3):301−305. HE H, WEN Y Y, XU S Y, et al. Study on bacterial-wilt-resistance identification methods for Pogostemon cablin (Blanco) Benth [J]. Journal of Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2011, 28(3): 301−305. (in Chinese)
[18] 王铭, 臧丽丽, 范凯, 等. 黄萎病菌毒素联合法鉴定棉花对黄萎病的抗性 [J]. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(9):1678−1688. DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2015.09.02 WANG M, ZANG L L, FAN K, et al. A combined identification method for the Verticillium wilt resistance in cotton by using pathogen toxin [J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015, 48(9): 1678−1688. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2015.09.02
[19] 周淼平, 姚金保, 张鹏, 等. 小麦幼苗纹枯病抗性评价新方法 [J]. 江苏农业学报, 2017, 33(1):61−66. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2017.01.010 ZHOU M P, YAO J B, ZHANG P, et al. New method for the resistance evaluation of wheat sharp eyespot in seedling [J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 33(1): 61−66. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2017.01.010
[20] 兰海燕. 几种向日葵菌核病抗性鉴定方法的比较 [J]. 植物保护, 2000, 26(6):26−28. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.2000.06.011 LAN H Y. Comparison of several identification methods of sunflower resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum [J]. Plant Protection, 2000, 26(6): 26−28. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.2000.06.011
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 姚展杏,王超,林寅盛,赵丹,张嘉家,伍辉吉,朱婉君,张济培,陈济铛. 鹅星状病毒Ⅰ型与Ⅱ型双重荧光定量PCR检测方法的建立与应用. 中国家禽. 2025(01): 64-70 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 谢军,张硕,王安平,吴植,吴双,朱善元. 鹅星状病毒Ⅰ型荧光定量PCR检测方法的建立及应用. 中国动物传染病学报. 2023(03): 106-112 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 姚鑫炎,杨惠湖,李文俊,曾繁聪,黄淑坚,车艺俊,张雪莲. 鹅星状病毒病原学、流行病学及宿主免疫应答的研究进展. 中国家禽. 2022(06): 107-113 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张帆帆,李海琴,谭美芳,杨群,涂凌云,康冬柳,罗士仙,黄奕雯,曾艳兵,谭佳,黄江南,谢金防,韦启鹏,康昭风. 鹅星状病毒衣壳蛋白间接ELISA检测方法的建立. 中国预防兽医学报. 2022(08): 850-854+887 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)




 下载:
下载: