Identification and Natural Antibacterial Agent of Mulberry Rot Pathogen
-
摘要:目的
分离鉴定桑葚果实腐烂的病原菌并筛选对其具有抑菌活性的植物提取物,为桑葚果腐病的绿色防控提供依据。
方法采用组织分离法分离病原菌并通过真菌形态学及分子生物学对病原菌进行鉴定;采用菌丝生长速率法测定54种植物提取物对桑葚果实腐烂病原菌的抑菌活性,筛选活性较好的提取物,通过浓度梯度进行毒力测定,最后通过显微观察活性较好的提取物(EC50)对菌丝形态的影响。
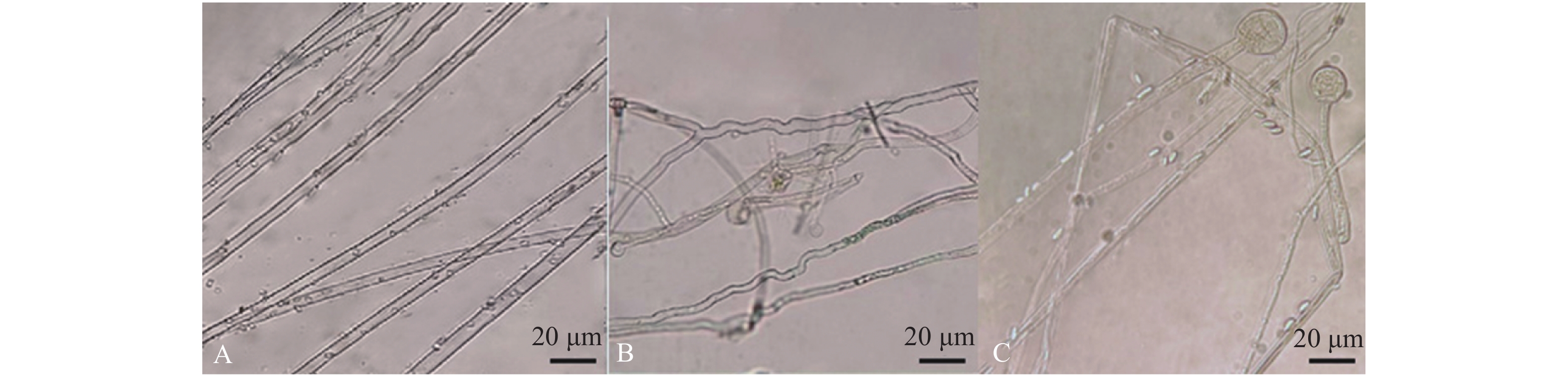
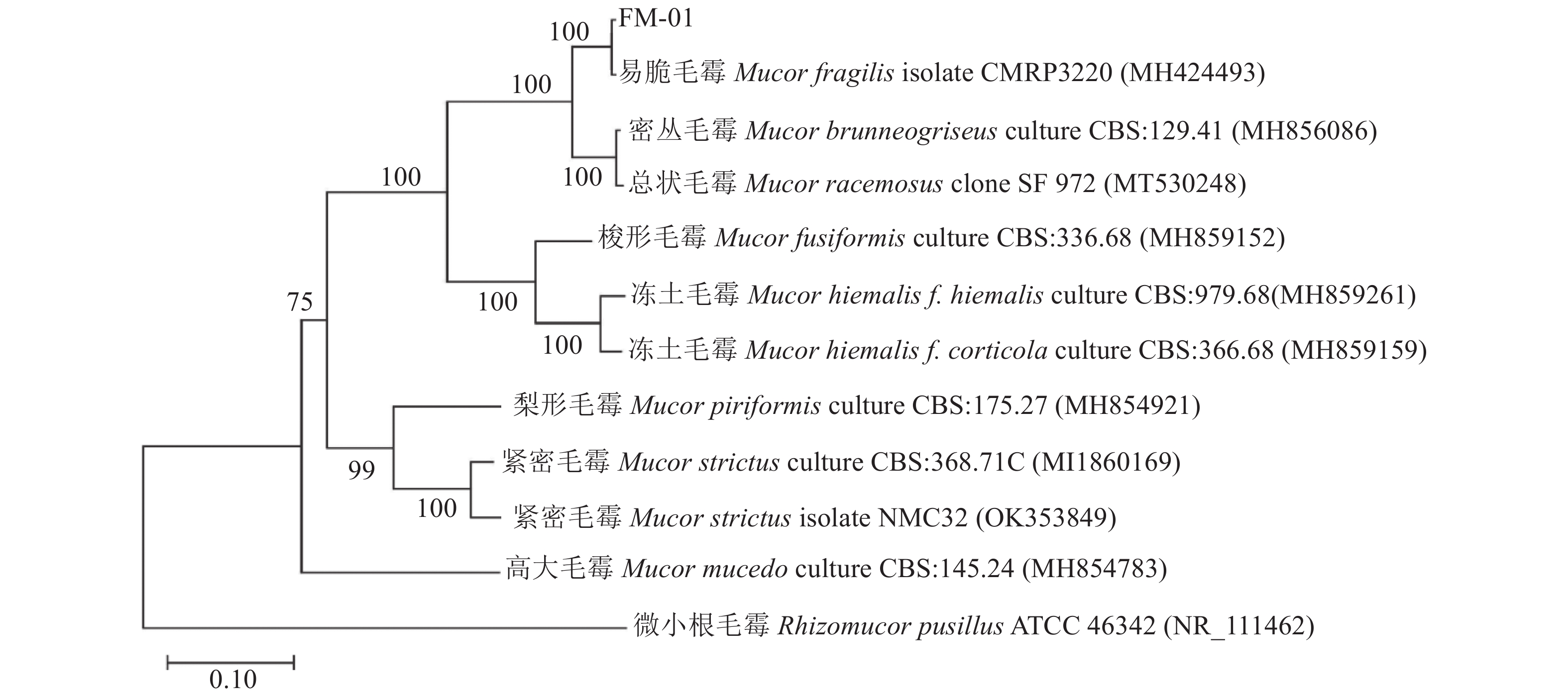
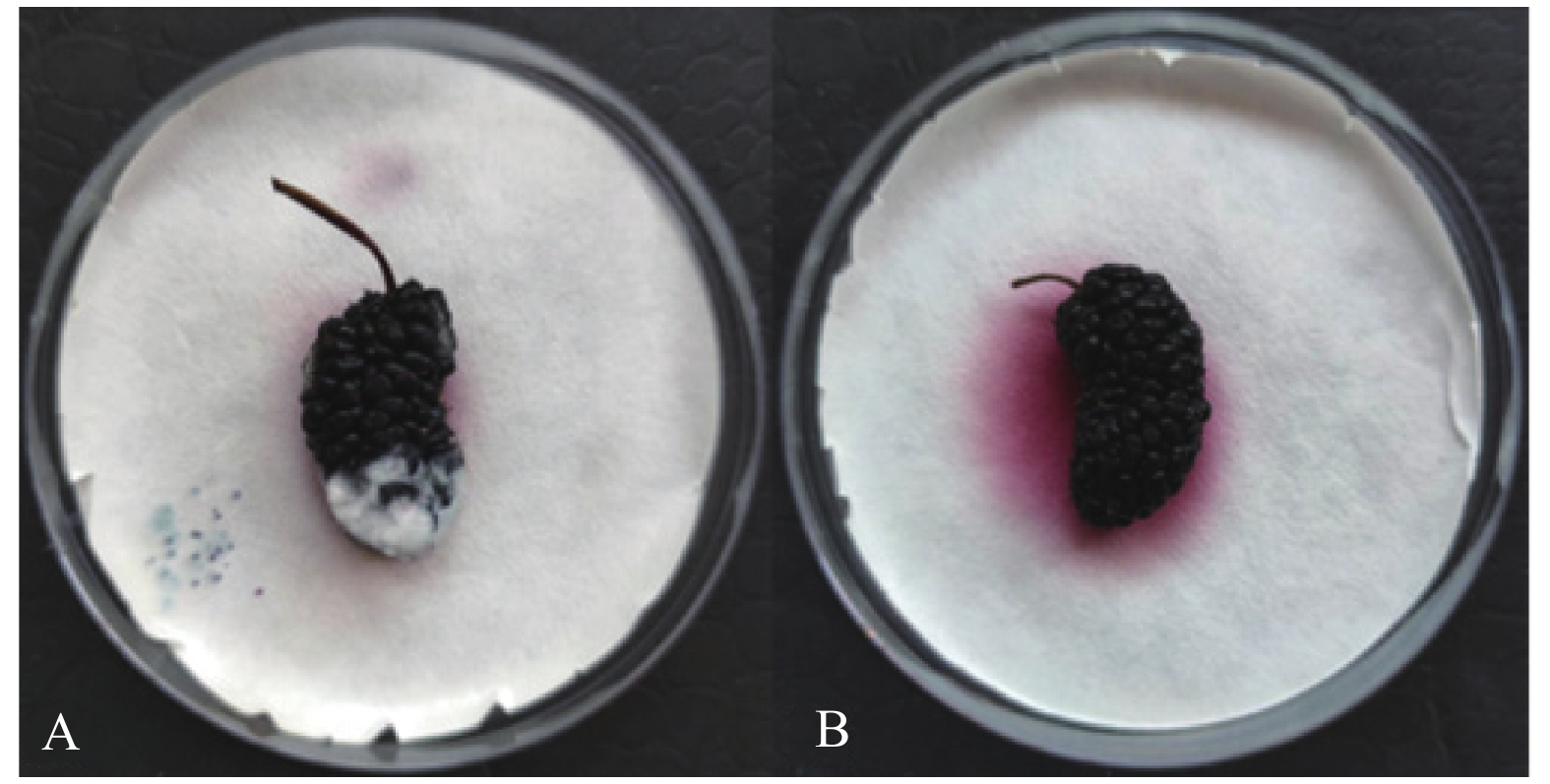
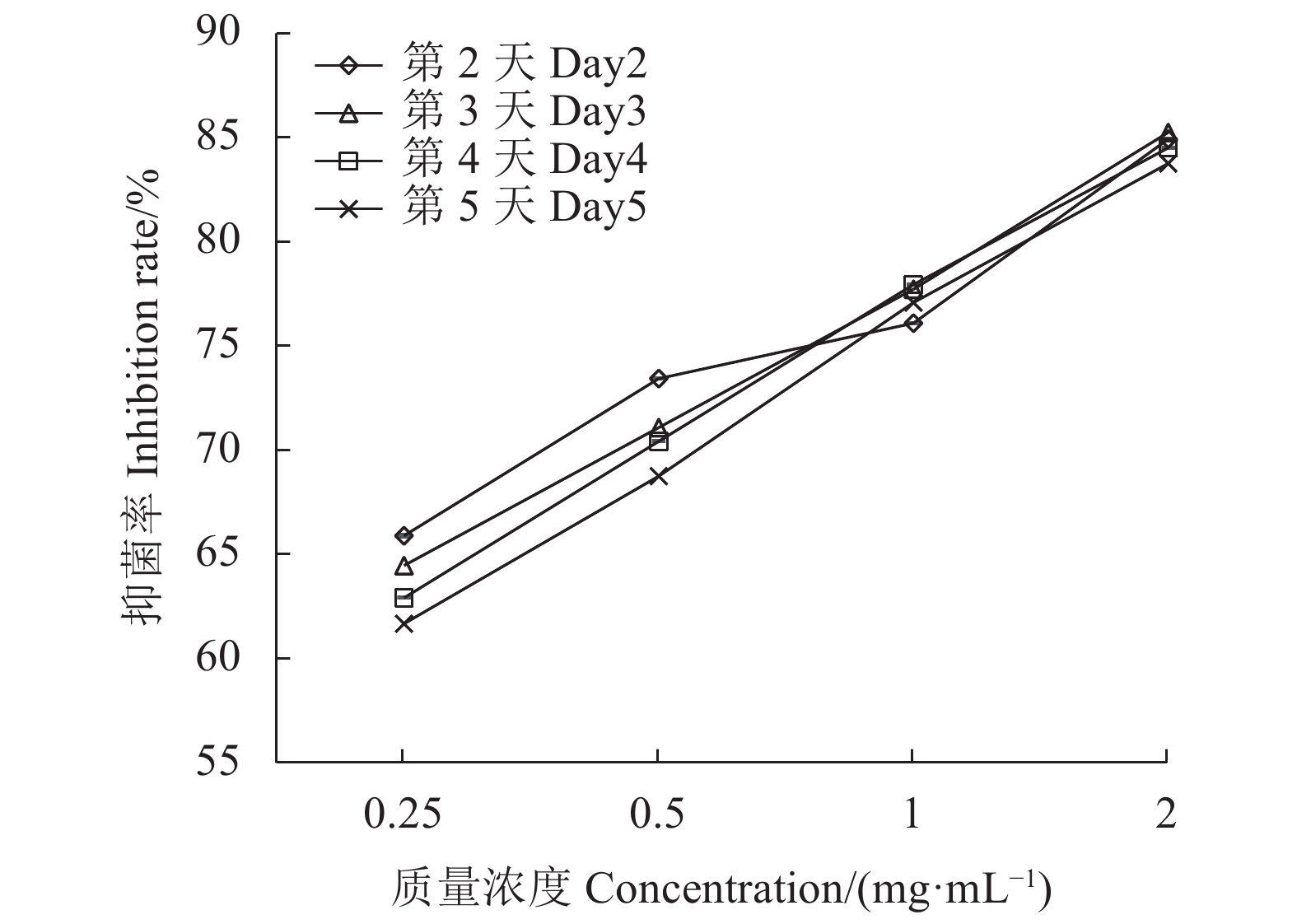
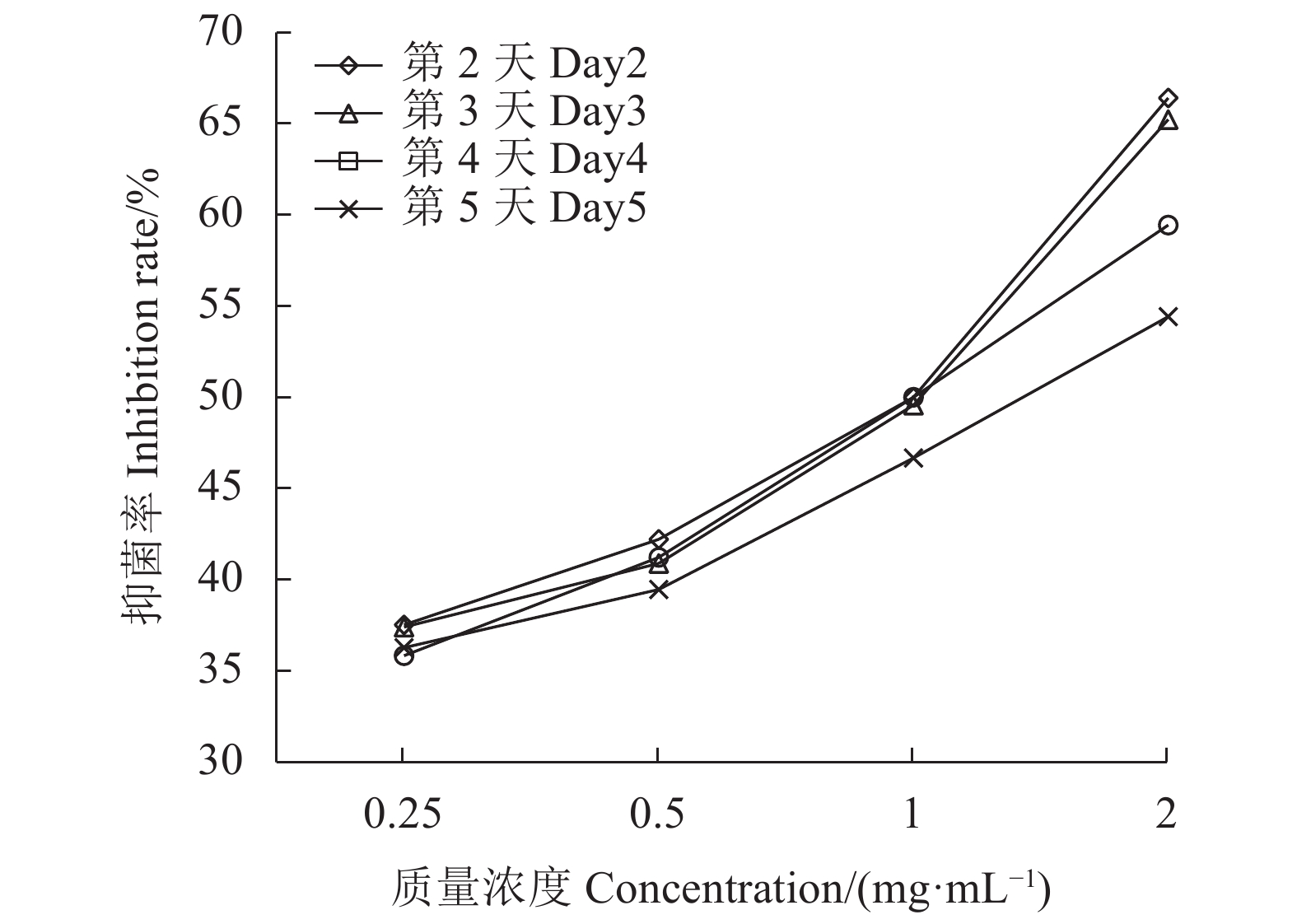
结果经形态及分子生物学鉴定该致病菌为易脆毛霉(Mucor fragilis);当提取物质量浓度为1 mg·mL−1时,青蒿和天蓝鼠尾草乙醇提取物对该菌株有较好的抑菌效果,抑菌率分别为77.72%和49.06%,经毒力测定其抑菌有效中浓度(EC50)分别为0.063、0.107 mg·mL−1;通过显微镜观察发现,青蒿乙醇提取物可导致病菌菌丝畸变,天蓝鼠尾草对病原菌菌丝形态无明显影响。
结论本研究发现青蒿和天蓝鼠尾草对桑葚果腐病菌易脆毛霉有较好的抑菌活性,青蒿提取物的抑菌活性尤为显著,EC50仅为0.063 mg·mL−1,具有进一步开发的价值。
Abstract:ObjectivePathogen of the fruit rot on mulberries was isolated and identified, and effective antibacterial plant extracts for the disease prevention and control selected.
MethodTissue separation method was applied to isolate potential pathogens from the infected mulberries. The morphology and molecular biology of the isolates were examined for pathogen identification. Antibacterial activity of 54 plant ethanol extracts was tested to compare the inhibition on the growth of the isolate mycelia. Virulence of the most potent extracts at gradient concentrations was determined along with microscopic observations.
ResultGrowth of the identified pathogen, Mucor fragilis was significantly inhibited at a rate of 77.72% by the extract of Artemisia caruifolia on a dosage of 1 mg·mL−1 rendering an EC50 at 0.063 mg·mL−1, and also at a rate of 49.06% by Salvia uliginosa with an EC50 at 0.107 mg·mL−1. In addition to a higher inhibition rate, the A. caruifolia extract induced significant mycelial distortions on the pathogens as shown under the microscope.
ConclusionSignificant antifungal activities against the mulberry rot-causing M. fragilis were found of the ethanol extracts of A. caruifolia and S. uliginosa. With a toxicity of EC50 at 0.063 mg·mL−1 and significant deformation on the mycelia of the pathogen, A. caruifolia was considered the choice candidate as a biocontrol agent against the disease.
-
Keywords:
- Mulberry rot disease /
- plant extracts /
- antibacterial activity /
- toxicity
-
多花黄精Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua是百合科黄精属植物,为中药黄精的原植物来源之一,具有补气养阴、健脾等功效,在临床上常用于治疗体倦乏力、脾胃气虚、精血不足、胃阴不足、须发早白、口干食少等,也可用于治疗肺结核、糖尿病、慢性肝炎等病,同时又是多种滋补性中成药或复方的重要组分[1-2],其药用价值可见一斑。福建省多花黄精野生资源尤为丰富,而长梗黄精Polygonatum filipes Merr.在原植物形态、生药性状与多花黄精极为相似[3],闽民间常把长梗黄精混作为黄精入药[4],给用药安全带来很大的隐患,目前两者之间的种质鉴别方法一般采用形态鉴别,由于气候、地理、土壤等自然因素的影响,形态鉴别往往缺乏准确性,因此,对多花黄精进行快速准确的鉴定显得尤为重要和迫切。简单重复序列间扩增多态性(inter-simple sequence repeat,ISSR)分子标记方法,可以灵敏、快速、高效地检测出基因组DNA的多态性,具有DNA用量少,耗时少,操作简单、成本较低,可重复性好等优点,适合大样本的检测[5],近年来在品种鉴定、种群遗传学、种质资源、分类学、种系发生学等方面研究中得到了广泛的应用,并成为构建种质遗传图谱的重要工具[6-10]。张红梅等建立了多花黄精ISSR反应体系[11],周晔等利用ISSR分子标记准确鉴别了黄精和卷叶黄精[5],但利用分子标记全面系统对多花黄精种质资源及其掺伪品鉴定、分类、构建分子遗传图谱和基因定位等方面的研究尚未见报道。本研究采用原植物鉴定、性状鉴定及ISSR等方法鉴别闽产多花黄精与长梗黄精,并分析其种质资源遗传多样性。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
2014年5月至2015年9月,收集福建福州、南平、三明、宁德等黄精属主分布区种质资源19份,19份样品均为野生种质资源,集中种植于福建中医药大学药用植物园,样品信息见表 1。
表 1 19份供试材料Table 1. Basic information on 19 germplasm samples样品 原产地 叶下面短毛 总花梗长
/cmS1 福建泰宁 无 3~4 S2 福建梅列 有 5~8 S3 福建沙县 有 6~8 S4 福建光泽1 有 6~8 S5 福建光泽2 有 5~8 S6 福建霞浦 无 3~4 S7 福建建瓯 无 2~4 S8 福建建阳 无 3~4 S9 福建尤溪 无 2~4 S10 福建柘荣 无 3~4 S11 福建永泰 无 3~4 S12 福建泉港 无 2~4 S13 福建松溪 无 3~4 S14 福建闽侯 有 6~8 S15 福建新罗 无 3~4 S16 福建上杭 无 3~4 S17 福建武夷山1 有 6~8 S18 福建武夷山2 无 2~4 S19 福建武夷山3 无 3~4 试验仪器包括PCR仪(BIO-RAD公司),凝胶成像分析系统(BIO-RAD公司),电泳仪(Thermo公司),低温冷冻离心机(Eppendorf公司),微量移液器(Eppendorf公司)。琼脂糖(Promega公司),EB(Fluka公司),DNA聚合酶(北京全式金公司),UBC801~UBC900(上海生工生物技术有限公司),异丙醇、氯仿、乙醇均为分析纯。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 性状及原植物鉴别
原植物鉴定本次收集的黄精属植物分布检索表如下[12]。
1.叶互生
2.根状茎圆柱状(即“节”不粗大, “节间”延伸较长);花丝近平滑至乳头状突起1.玉竹P. odoratum
2.根状茎姜状、连珠状或多少呈连珠状(即“节”粗大, “节间”较短缩);花丝全部两侧压扁, 具乳头状突起至具短绵毛
3.叶下面有短毛;总花梗细长, 长3~8 cm……………………………………………2.长梗黄精P. filipes
3.叶下面无毛;总花梗较粗短, 长1~4 cm…………………………………3.多花黄精P. cyrtonema
性状鉴别(1) 长梗黄精:根基圆柱形,节处有突出分支,直径0.6~4.0 cm。茎痕圆盘状,直径0.3~0.6 cm,环节明显,表面棕黄色、黄色或黄棕色,有细皱纹。气弱,味甜;(2) 多花黄精:根茎连珠状或块状,圆柱形,直径2.0~3.0 cm。茎痕明显,圆盘状,直径约1.0 cm。外环节明显,有众多须根。表面黄棕色,有细皱纹。质坚实,稍带柔韧,折断面颗粒状,有众多黄棕色维管束小点散列。气弱,味微甜[13-15]。
1.2.2 ISSR鉴定
(1) 样品基因组总DNA的提取和纯化:2016年6月,采集受试19份种质的嫩叶,每份样品随机选取10片,洗净,以本课题组建立的改良CTAB法分别提取新鲜或阴干样品总DNA,经琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,并用纯化DNA样品。
(2) 引物筛选及样品ISSR分析:以19个样品总DNA为模板,用UBC801~UBC900等100条ISSR引物进行多态性筛选。ISSR-PCR反应体系:总体积20 μL,包括50 ng模板DNA,1.0 U Taq DNA聚合酶,0.2 mmol·L-1 dNTPs,0.4 μmol·L-1引物,2.5 mmol·L-1 Mg2+。ISSR-PCR反应条件:94℃预变性5 min;94℃变性45 s,31~50℃退火1.5 min,72℃延伸1.5 min,35个循环;72℃延伸10 min;10℃保温。退火温度因扩增条带的效果而进行相应的调整。PCR扩增产物在加有EB的琼脂糖凝胶中电泳分离,电泳结果在成像系统拍照储存。
1.3 数据统计及分析
根据扩增产物条带的有无进行统计,有带记为1,无带记为0,建立所有位点的二元数据。应用Popgen 32软件进行遗传参数分析,计算样品之间的遗传距离和相似系数,利用NTSYSpc 2.1软件根据遗传距离用UPGMA法(Unweighted pair group mean average)聚类分析,构建系统树。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 性状及原植物鉴别
根据性状及原植物进行样品鉴别,种质1、6、7、8、9、10、11、12、13、15、16、18、19为多花黄精,种质2、3、4、5、14、17为长梗黄精。
2.2 DNA提取方法
在样品前处理上,考查了叶子不同处理方法(新鲜、阴干)、水浴时间、不同的震荡方法(机械、手动)、提取及纯化次数对DNA提取的影响。结果表明叶子阴干后提取效果较佳,故样品制备最终采用叶子阴干后提取,水浴1 h,手动振摇,纯化2次(如图 1)的方法。
2.3 扩增产物的多态性分析
以S1~S19共19份黄精属样品的总DNA为模板,建立ISSR-PCR反应体系,对UBC801~UBC900共100个随机引物进行多态性筛选,扩增产物经1.8%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳分离后,共选出11个多态性较理想的ISSR引物(表 2),每个引物扩增条带数在11~19条,条带大小在250~2 000 bp(图 2)。每条随机引物设置3次重复,11条引物扩增效果重复性好,共扩增出170条谱带,其中多态性谱带170条,多态性条带比率为100%,这表明受试黄精属样品在DNA水平上存在显著差异。
表 2 11条ISSR引物扩增条带数与多态性比率Table 2. Number and ratio of polymorphic bands amplified by 11 ISSR primers引物 引物序列 退火温
度/℃扩增
条带数多态性
条带数多态性
比率/%UBC807 AGA GAG AGA GAG AGA GT 52 13 13 100 UBC811 GAG AGA GAG AGA GAG AC 54 17 17 100 UBC818 CACACACACACACACAG 54 18 18 100 UBC820 GTG TGT GTG TGT GTG TC 54 14 14 100 UBC826 ACA CAC ACA CAC ACA CC 54 18 18 100 UBC827 ACA CAC ACA CAC ACA CG 54 11 11 100 UBC842 GAG AGA GAG AGA GAG AYG 51 15 15 100 UBC849 GTG TGT GTG TGT GTG TYA 53 19 19 100 UBC854 TCT CTC TCT CTC TCT CRG 51 12 12 100 UBC855 ACA CAC ACA CAC ACA CYT 53 14 14 100 UBC889 DBD ACA CAC ACA CAC AC 52 19 19 100 统计 170
(合计)170
(合计)100
(均值)注:R为碱基A或G;B为碱基C、G或T;D为碱基A、G或T;V为碱基A、C或G;H为碱基A、C或T。 2.4 相似系数和遗传距离分析
用Popgen 32软件分析得到受试19份样品的遗传相似度与遗传距离(表 3)。结果表明:供试黄精属种质资源相似系数值在0.604 9~0.824 4,平均遗传相似系数为0.702 0;遗传距离分布在0.193 1~0.502 7,平均遗传距离为0.355 7。在19个样品中,最大相似系数为0.824 4,是S6采自霞浦种质的多花黄精与S7采自建瓯种质的多花黄精,它们之间的遗传距离仅为0.193 1;而采自柘荣种质的多花黄精与武夷山1种质的长梗黄精之间的遗传相似系数仅为0.604 9,遗传距离为0.502 7。
表 3 Nei's遗传相似性(对角线上方)和遗传距离(对角线下方)Table 3. Nei's genetic identity (above diagonal line) and distance (below diagonal line)项目 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S 6 S7 S8 S9 S10 S11 S12 S13 S14 S15 S16 S17 S18 S19 S1 0.7317 0.6976 0.6683 0.6829 0.7073 0.6683 0.6829 0.6878 0.6927 0.6780 0.6634 0.6634 0.6683 0.7073 0.7024 0.6780 0.6829 0.7366 S2 0.3124 0.7415 0.7415 0.7463 0.6829 0.6732 0.6780 0.7122 0.6683 0.6537 0.6780 0.6585 0.7024 0.6829 0.6976 0.6732 0.6390 0.6732 S3 0.3602 0.2991 0.7171 0.6634 0.6878 0.7073 0.6829 0.7073 0.7122 0.6585 0.6829 0.6634 0.6976 0.6780 0.6732 0.6390 0.6244 0.6683 S4 0.4030 0.2991 0.3326 0.8195 0.6780 0.6976 0.6732 0.6878 0.6927 0.6683 0.6927 0.6732 0.7171 0.6683 0.6732 0.6878 0.6439 0.6683 S5 0.3814 0.2926 0.4104 0.1990 0.7512 0.7024 0.6878 0.6927 0.6488 0.6634 0.6878 0.6488 0.7610 0.6732 0.6878 0.7122 0.6878 0.6829 S6 0.3643 0.3814 0.3743 0.3885 0.2861 0.8244 0.8000 0.7659 0.7512 0.7268 0.7512 0.7220 0.6976 0.7268 0.7024 0.6683 0.7122 0.6976 S7 0.4030 0.3958 0.3463 0.3602 0.3532 0.1931 0.8195 0.7951 0.7610 0.6878 0.7610 0.7610 0.6878 0.7561 0.7610 0.6293 0.6927 0.6683 S8 0.3814 0.3885 0.3814 0.3958 0.3743 0.2231 0.1990 0.8000 0.7756 0.7805 0.7268 0.7659 0.6927 0.7610 0.7463 0.6537 0.6878 0.7024 S9 0.3743 0.3394 0.3463 0.3743 0.3672 0.2668 0.2293 0.2231 0.8098 0.7073 0.6927 0.8000 0.6488 0.7756 0.6927 0.6390 0.6634 0.6683 S10 0.3672 0.4030 0.3394 0.3672 0.4327 0.2861 0.2732 0.2541 0.2110 0.7415 0.7366 0.7659 0.6244 0.7317 0.7268 0.6049 0.6293 0.6634 S11 0.3885 0.4252 0.4 177 0.4030 0.4104 0.3191 0.3743 0.2478 0.3463 0.2991 0.7902 0.7317 0.6683 0.6780 0.7122 0.7073 0.6439 0.6878 S12 0.4104 0.3885 0.3814 0.3672 0.3743 0.2861 0.2732 0.3191 0.3672 0.3057 0.2354 0.7463 0.7220 0.6829 0.7463 0.7024 0.6878 0.6829 S13 0.4104 0.4177 0.4104 0.3958 0.4327 0.3258 0.2732 0.2668 0.2231 0.2668 0.3124 0.2926 0.6927 0.7317 0.7171 0.6537 0.6878 0.7024 S14 0.4030 0.3532 0.3602 0.3326 0.2732 0.3602 0.3743 0.3672 0.4327 0.4710 0.4030 0.3258 0.3672 0.6585 0.6634 0.7366 0.6829 0.7171 S15 0.3463 0.3814 0.3885 0.4030 0.3958 0.3191 0.2796 0.2732 0.2541 0.3124 0.3885 0.3814 0.3124 0.4177 0.7707 0.6683 0.7024 0.6780 S16 0.3532 0.3602 0.3958 0.3958 0.3743 0.3532 0.2732 0.2926 0.3672 0.3191 0.3394 0.2926 0.3326 0.4104 0.2604 0.7415 0.6976 0.7122 S17 0.3885 0.3958 0.4478 0.3743 0.3394 0.4030 0.4632 0.4252 0.4478 0.5027 0.3463 0.3532 0.4252 0.3057 0.4030 0.2991 0.7024 0.6878 S18 0.3814 0.4478 0.4710 0.4402 0.3743 0.3394 0.3672 0.3743 0.4104 0.4632 0.4402 0.3743 0.3743 0.3814 0.3532 0.3602 0.3532 0.7122 S19 0.3057 0.3958 0.4030 0.4030 0.3814 0.3602 0.4030 0.3532 0.4030 0.4104 0.3743 0.3814 0.3532 0.3326 0.3885 0.3394 0.3743 0.3394 2.5 聚类分析
利用NTSYSpc 2.1软件进行UPGMA聚类,得到树状聚类图(图 3),供试材料以相似系数0.68为分类界限,将19份样品分成2大类,4个亚类:Ⅰ1类有3个种质,分别为S1、S18和S19;Ⅰ2类有10个种质,分别为S6、S7、S8、S9、S10、S11、S12、S13、S15和S16;Ⅱ1类有5个种质,分别为S2、S4、S5、S14和S17;Ⅱ2类只有种质S3。
2.6 遗传多样性及分化分析
用Popgen 32软件对4个亚类的居群多样性进行分析,结果见表 4。从居群的有效等位基因数(Ne)、期望杂合度(H)、Shannon信息指数(Ⅰ)可以看出,Ⅰ2亚类多样性最高;在假设遗传遵循哈德温伯格平衡的条件下,黄精属4个亚类种水平的基因多样性Ht=0.4132,表明受试样品具有一定的遗传多样性和分化。
表 4 基于ISSR的黄精属遗传多样性Table 4. Genetic diversity of Polygonatum based on ISSR markers亚类 有效等位基
因数(Ne)期望杂合度
(H)Shannon信息
指数(Ⅰ)Ⅰ1 1.3473 0.1930 0.2763 Ⅰ2 1.3799 0.2257 0.3391 Ⅱ1 1.3741 0.2162 0.3180 Ⅱ2 1.0 0 0 种级All 1.4845 0.2823 0.4239 3. 讨论与结论
本研究釆用了11条引物对样品进行PCR扩增,共扩增出170条DNA条带,多态性条带百分率高达100%,表明样品种质之间存在高度的遗传多样性,这可能是种间或居群间变异大所致。从相似系数或遗传距离看种质亲缘关系,在19个样品中,亲缘关系最近的为霞浦种质与建瓯种质,它们都是多花黄精,说明它们之间的遗传差异很小;而采自柘荣种质的多花黄精与武夷山1种质的长梗黄精之间的亲缘关系最远,多花黄精和长梗黄精为黄精属不同植物品种,这可能是它们遗传差异较大的主要原因。从地理位置与相似系数看,霞浦种质与建瓯种质之间的遗传距离小于光泽1种质与光泽2种质,这表明黄精属种质资源间亲缘关系的远近不全由地理距离决定,其种质资源之间的基因交流可能还与地形地貌、生态气候、海拔经纬度、生物群落分布等自然因素及人类活动等社会因素密切相关,从而影响种质之间的亲缘关系[16-17]。
本研究的聚类结果可以把19个样品分成2大类,根据原植物的叶、根茎及总花梗等性状,把这2大类分别鉴定为多花黄精和长梗黄精,说明ISSR标记能有效揭示福建多花黄精和长梗黄精之间亲缘关系的精确性,能很好地将材料区分开来,与植物形态学分类相一致,这为黄精及其掺伪品精确鉴别提供参考依据。
19个受试样品的有效等位基因数(Ne)、期望杂合度(H)、Shannon信息指数(Ⅰ)分别为1.484 5、0.292 3、0.423 9,4个亚类种水平的基因多样性Ht=0.4132,说明黄精属植物居群内变异较大;在第Ⅰ类多花黄精的13个种质中,S1、S18和S19这3个种质聚集在一起,在遗传相似系数0.684处,分支于其余10个种质,而在Ⅱ类6个种质中,S3种质在遗传相似系数0.690处分支于其余5个种质,说明闽产多花黄精和长梗黄精遗传多样性处于较高水平,其种质资源基因库较为丰富,种质间有明显分化,有待于结合生物学特性、农艺性状、化学成分及其他分子标记技术进一步探讨研究[17]。
本试验建立了ISSR多花黄精和长梗黄精种质鉴定及遗传多样性分析的分子标记方法,该方法可重复性好,简便准确,成本较低,可以为黄精属种质鉴别提供新的方法与参考依据。
-
表 1 供试植物名录
Table 1 List of tested plants
序号
Number植物名称
Plants科
Family提取部位
Plant parts采集地点
Location1 牛尾蒿
Artemisia dubia菊科
Asteraceae全草 云南昆明 2 千里光
Senecio scandens菊科
Asteraceae全草 云南昆明 3 鱼眼草
Dichrocephala integrifolia菊科
Asteraceae全草 云南昆明 4 黑蒿
A. palustris菊科
Asteraceae地上部分 辽宁朝阳 5 茵陈蒿
A. capillaris菊科
Asteraceae地上部分 辽宁朝阳 6 小花鬼针草
Bidens parviflora菊科
Asteraceae地上部分 辽宁朝阳 7 全叶马兰
Aster pekinensis菊科
Asteraceae地上部分 辽宁朝阳 8 革命菜
Crassocephalum crepidioides菊科
Asteraceae全草 广西宾阳 9 藿香蓟
Ageratum conyzoides菊科
Asteraceae全草 广西宾阳 10 银胶菊
Parthenium hysterophorus菊科
Asteraceae全草 广西宾阳 11 香丝草
Erigeron bonariensis菊科
Asteraceae全草 广西宾阳 12 金腰箭
Synedrella nodiflora菊科
Asteraceae全草 广西宾阳 13 翼齿六棱菊
Laggera pterodonta菊科
Asteraceae全草 云南昆明 14 野蒿茼
Crassocephalum crepidioides菊科
Asteraceae全草 云南昆明 15 微甘菊
Mikania micrantha菊科
Asteraceae地上部分 云南德宏 16 青蒿
A. caruifolia菊科
Asteraceae地上部分 辽宁朝阳 17 天名精
Carpesium abrotanoides菊科
Asteraceae地上部分 云南昆明 18 紫茎泽兰
Ageratina adenophora菊科
Asteraceae地上部分 云南昆明 19 香青
Anaphalis sinica菊科
Asteraceae地上部分 云南昆明 20 土木香
Inula helenium菊科
Asteraceae地上部分 云南昆明 21 小鱼眼草
Dichrocephala benthamii菊科
Asteraceae地上部分 云南昆明 22 假臭草
Praxelis clematidea菊科
Asteraceae地上部分 云南昆明 23 火绒草
Leontopodium leontopodioides菊科
Asteraceae地上部分 辽宁朝阳 24 尼泊尔香青
Anaphalis nepalensis菊科
Asteraceae地上部分 云南昆明 25 钻叶紫菀
Symphyotrichum subulatum菊科
Asteraceae地上部分 云南昆明 26 芳香堆心菊
Helenium aromaticum菊科
Asteraceae地上部分 云南昆明 27 水棘针
Amethystea caerulea唇形科
Lamiaceae全草 辽宁朝阳 28 益母草
Leonurus japonicus唇形科
Lamiaceae全草 云南昆明 29 墨西哥鼠尾草
Salvia leucantha唇形科
Lamiaceae地上部分 云南昆明 30 香茶菜
Isodon amethystoides唇形科
Lamiaceae地上部分 云南昆明 31 天蓝鼠尾草
Salvia uliginosa唇形科
Lamiaceae地上部分 云南昆明 32 山薄荷
Dracocephalum moldavica唇形科
Lamiaceae全草 辽宁朝阳 33 马鞭草
Verbena officinalis马鞭草科
Verbenaceae全草 云南昆明 34 牛筋果
Harrisonia perforata芸香科
Rutaceae地上部分 云南昆明 35 臭椿
Ailanthus altissima苦木科
Simaroubaceae枝叶 辽宁朝阳 36 拔毒散
Sida szechuensis锦葵科
Malvaceae地上部分 云南昆明 37 土牛膝
Achyranthes aspera苋科
Amaranthaceae全草 云南昆明 38 土荆芥
Dysphania ambrosioides苋科
Amaranthaceae全草 云南昆明 39 粉花月见草
Oenothera rosea柳叶菜科
Onagraceae地上部分 云南昆明 40 黄花酢浆草
Oxalis pes-caprae酢浆草科
Oxalidaceae全草 云南昆明 41 荨麻
Urtica fissa荨麻科
Urtiaceae全草 云南昆明 42 女萎
Clematis apiifolia毛茛科
Ranunculaceae地上部分 云南昆明 43 老鹳草
Geranium wilfordii牻牛儿苗科
Geraniaceae全草 云南昆明 44 络石
Trachelospermum jasminoides夹竹桃科
Apocynaceae枝、叶 云南昆明 45 线萼山梗菜
Lobelia melliana桔梗科
Campanulaceae地上部分 云南昆明 46 黄精
Polygonatum sibiricum天门冬科
Asparagaceae地上部分 辽宁朝阳 47 曼陀罗
Datura stramonium茄科
Solanaceae枝、叶 云南昆明 48 忍冬
Lonicera japonica忍冬科
Caprifoliaceae地上部分 云南昆明 49 马桑
Coriaria nepalensis马桑科
Coriariaceae枝、叶 云南昆明 50 毛蕊花
Verbascum thapsus玄参科
Scrophulariaceae地上部分 云南昆明 51 紫红獐芽菜
Swertia punicea龙胆科
Gentianaceae全草 云南昆明 52 罗汉松
Podocarpus macrophyllus罗汉松科
Podocarpaceae枝、叶 云南昆明 53 假酸浆
Nicandra physalodes茄科
Solanaceae地上部分 云南昆明 54 角蒿
Incarvillea sinensis紫葳科
Bignoniaceae地上部分 辽宁朝阳 表 2 54种植物乙醇提取物对易脆毛霉的抑菌活性筛选
Table 2 Antifungal activities on M. fragilis of 54 plant ethanol extracts
植物
Plants抑菌率
Inhibition rate/%植物
Plants抑菌率
Inhibition rate/%青蒿 A. caruifolia 77.72±0.01 a 天蓝鼠尾草 S.uliginosa 49.06±0.02 b 茵陈蒿 A.capillaris 44.80±0.02 c 香青 A. sinica 40.22±0.02 d 香茶菜 I. amethystoides 38.75±0.04 d 紫茎泽兰 A.adenophora 31.14±0.01 e 全叶马兰 A. pekinensis 31.14±0.01 e 假臭草 P. clematidea 27.38±0.02 f 天名精 C. abrotanoides 27.71±0.03 f 芳香堆心菊 H.aromaticum 25.95±0.02 f 鱼眼菊 D. benthamii 22.65±0.00 g 牛尾蒿 A. dubia 22.62±0.01 g 黑蒿 A. palustris 22.31±0.01 g 土木香 I. helenium 19.81±0.03 gh 藿香蓟 A.conyzoides 19.81±0.00 gh 微甘菊 M. micrantha 18.86±0.02 he 尼泊尔香青 A. nepalensis 17.88±0.02 hei 牛筋果 H. perforata 16.03±0.02 eij 益母草 L. japonicus 15.24±0.02 ijk 假酸浆 N. physaloides 13.85±0.01 jkl 臭椿 A. altissima 13.33±0.02 jkl 小花鬼针草 B. parviflora 12.49±0.01 klm 罗汉松 P. macrophyllus 12.25±0.01 lm 女萎 C. apiifolia 11.57±0.04 lm 紫红獐牙菜 S. punicea 11.32±0.00 lm 香丝草 E.bonariensis 10.89±0.03 lmn 土牛膝 A. aspera 10.21±0.01 mn 山薄荷 D. moldavica 9.70±0.05 mn 火绒草 L. leontopodioides 8.25±0.03 no 土荆芥 C. ambrosioides 6.67±0.02 op 黄精 P. sibiricum 6.61±0.02 op 金腰箭 S. nodiflora 6.24±0.01 op 粉花月见草 O. rosea 5.80±0.02 op 络石 T. jasminoides 5.09±0.01 pq 银胶菊 P. hysterophorus 4.41±0.01 pqr 墨西哥鼠尾草 S. leucantha 3.78±0.02 qrs 黄花酢浆草 O. pes-caprae 3.61±0.02 qrs 水棘针 A. caerulea 2.66±0.03 rs 革命菜 C. crepidioides 1.78±0.02 rs 千里光 S. scandens 0.95±0.02 s 表中数据为 3 次重复的平均值,平均数±标准差,字母不同者表示差异达显著水平( P<0.05)。下同。
Data are presented as mean of 3 repeats±standard deviation; those with different alphabets indicate significant difference at P<0.05. Same for below.表 3 天蓝鼠尾草、青蒿乙醇提取物对易脆毛霉的抑菌毒力
Table 3 Toxicity on M. fragilis of A. carvifolia and S. uliginosa ethanol extracts
植物
Plants培养时间
Time/ d毒力回归方程
Toxicity regression
equation相关系数
R2EC50/
(mg·mL−1)青蒿
A.carvifolia2 y= 1.11x + 1.31 0.946 0.063 3 y = 1.27x +1.32 0.986 0.089 4 y = 1.29x +1.28 0.997 0.100 5 y = 1.30x + 1.22 0.995 0.113 天蓝鼠尾草
S.benth2 y = 1.29x + 0.16 0.924 0.760 3 y = 1.26x + 0.12 0.919 0.807 4 y = 1.08x + 0.02 0.988 0.952 5 y = 0.84x + 0.11 0.973 1.356 -
[1] 决登伟, 桑雪莲. 高压均质对桑葚汁中抗氧化成分与抗氧化活性的影响 [J]. 热带作物学报, 2017, 38(12):2261−2265. JUE D W, SANG X L. Effects of high-pressure homogenization treatment on the total antioxidants content and the antioxidant activity of mulberry juice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2017, 38(12): 2261−2265. (in Chinese)
[2] SAENSOUK S, SENAVONGSE R, PAPAYRATA C, et al. Evaluation of color, phytochemical compounds and antioxidant activities of mulberry fruit (Morus alba L. ) during ripening [J]. Horticulturae, 2022, 8(12): 1146. DOI: 10.3390/horticulturae8121146
[3] 陈春华, 唐炜, 殷军艺, 等. 桑葚多糖结构特征和生物活性研究进展 [J]. 中国食品学报, 2022, 22(5):367−382. CHEN C H, TANG W, YIN J Y, et al. Research progress on structure characteristics and biological activity of polysaccharide from fructus Mori [J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2022, 22(5): 367−382. (in Chinese)
[4] 杨舒, 黄徐英, 屠寒, 等. 桑葚花色苷对小鼠的抗疲劳作用 [J]. 食品工艺科技, 2023, 44(16):377−385 YANG S, HUANG X Y, TU H, et al. Anti-fatigue effects of mulberry anthocyanins in mice [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(16): 377−385.
[5] 浦冠勤, 黄艳君, 毛建萍, 等. 中国桑树病害名录(Ⅲ) [J]. 中国蚕业, 2012, 33(4):12−17. PU G Q, HUANG Y J, MAO J P, et al. List of mulberry diseases in China(Ⅲ) [J]. China Sericulture, 2012, 33(4): 12−17. (in Chinese)
[6] 张健. 桑椹防腐技术研究和桑树果用性状关联分析[D]. 镇江: 江苏科技大学, 2017. ZHANG J. Study on mulberry fruit preservation techniquesand association analysis of fruit traits in mulberry species[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, 2017. (in Chinese)
[7] 周建华, 朱志贤, 李勇, 等. 湖北省桑椹腐烂病病原菌鉴定 [J]. 湖北农业科学, 2018, 57(21):69−72. ZHOU J H, ZHU Z X, LI Y, et al. Identification of fruit rot pathogen on mulberry in Hubei Province [J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 57(21): 69−72. (in Chinese)
[8] 聂蓓蓓, 梁嘉俊, 包立军, 等. 桑椹果腐病的病原菌鉴定 [J]. 蚕业科学, 2020, 46(1):26−30. NIE B B, LIANG J J, BAO L J, et al. Identification of pathogen causing mulberry fruit rot disease [J]. Acta Sericologica Sinica, 2020, 46(1): 26−30. (in Chinese)
[9] 王飞, 杨瑾, 李绍建, 等. 丹参根腐病菌拮抗菌株贝莱斯芽胞杆菌Bv1-4的筛选及盆栽防效 [J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2023, 39(6):1398−1407. WANG F, YANG J, LI S J, et al. Screening of antagonistic isolate Bacillus velezensis Bv1-4 and its control effect against root rot disease on Salvia miltiorrhiza [J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2023, 39(6): 1398−1407. (in Chinese)
[10] 齐永霞, 陈方新, 丁克坚, 等. 安徽省油菜菌核病菌对菌核净的抗药性测定 [J]. 农药, 2006, 45(8):567−568,570. QI Y X, CHEN F X, DING K J, et al. Determining dimethachlon resistance of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in Anhui province [J]. Agrochemicals, 2006, 45(8): 567−568,570. (in Chinese)
[11] 李晓菲, 徐政. 植物源杀菌剂研究进展 [J]. 南方农业, 2018, 12(13):40−42,45. LI X F, XU Z. The research progress on botanical fungicides [J]. South China Agriculture, 2018, 12(13): 40−42,45. (in Chinese)
[12] 杨欣蕊, 廖艳凤, 赵鹏飞, 等. 植物源农药及其开发利用研究进展 [J]. 南方农业, 2022, 16(11):33−36. YANG X R, LIAO Y F, ZHAO P F, et al. Study progress in plant-source pesticides and their development and utilization [J]. South China Agriculture, 2022, 16(11): 33−36. (in Chinese)
[13] 谷少伟, 向伟, 周兵, 等. 麻黄提取物中抑制桑椹肥大性菌核病病原菌的活性成分分离鉴定 [J]. 蚕业科学, 2015, 41(5):833−838. GU S W, XIANG W, ZHOU B, et al. Separation and identification of active ingredients with inhibitory activity to the pathogen causing mulberry sorosus hypertrophic sclerote disease from Ephedra extract [J]. Science of Sericulture, 2015, 41(5): 833−838. (in Chinese)
[14] 郑泽林. 一株桑椹核盘菌的分离鉴定及其植物源抑菌剂的筛选[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2020. ZHENG Z L. Isolation and Identification of a Mulberry Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Screening of Plant-derived Bacteriostatic Agents[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2020.
[15] 王彩霞, 兰妍彦, 孟衍朴, 等. 87种植物提取物抑菌活性初步研究 [J]. 植物保护, 2023, 49(4):293−301,308. WANG C X, LAN Y Y, MENG Y P, et al. Antifungal activity of extracts from 87 plant species [J]. Plant Protection, 2023, 49(4): 293−301,308. (in Chinese)
[16] 苟亚峰, 刘爱勤, 孙世伟, 等. 23种植物提取物对胡椒瘟病病原菌的抑制作用 [J]. 植物保护, 2010, 36(6):128−131. GOU Y F, LIU A Q, SUN S W, et al. Inhibitory effects of 23 plant extracts against Phytophthora capsici [J]. Plant Protection, 2010, 36(6): 128−131. (in Chinese)
[17] 朱庆书, 赵文英, 殷其峰. 苍耳子中抑菌成分提取方法的比较 [J]. 青岛科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 29(5):413−414,418. ZHU Q S, ZHAO W Y, YIN Q F. Studies on extraction methods of antibacterial constituents from Xanthium sibiricum patr [J]. Journal of Qingdao University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 29(5): 413−414,418. (in Chinese)
[18] 郝梦超, 安超娜, 王乙颖, 等. 金银花黄酮的提取工艺及其药理活性研究进展 [J]. 饮料工艺, 2022, 25(5):71−75. HAO M C, AN C N, WANG Y Y, et al. Research Prospect on Extraction and Pharmacological Activity of Flavonoids from Lonicerae Japonica [J]. Beverage Industry, 2022, 25(5): 71−75.
[19] 尹沙亮, 钟珊, 刘奇志, 等. 草莓丝核菌根腐病病原菌鉴定及7种杀菌剂的抑菌作用测定 [J]. 植物保护, 2019, 45(4):132−136,148. YIN S L, ZHONG S, LIU Q Z, et al. Identification of Rhizoctonia species causing root rot of strawberry and inhibition effects of seven fungicides [J]. Plant Protection, 2019, 45(4): 132−136,148. (in Chinese)
[20] WEI G , ZHAO W , HU A , et al. Identification of a new pathogenic fungi causing sorghum leaf spot disease and its management using natural product and microorganisms [J] . Microorganisms, 2023, 11(6) . DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11061431.
[21] 罗建梅, 张兴怡, 伍建榕, 等. 植物提取物对油茶炭疽菌的抑菌活性筛选 [J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2022, 38(4):852−859. LUO J M, ZHANG X Y, WU J R, et al. Antifungal Activity of Plant extracts against Colletotrichum fructicola, Pathogen of Camellia oleifera [J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2022, 38(4): 852−859. (in Chinese)
[22] 关波, 张璇, 胡玉婵, 等. 新疆石河子地区甜樱桃采后腐烂致病真菌的分离鉴定 [J]. 微生物学通报, 2018, 45(11):2480−2487. GUAN B, ZHANG X, HU Y C, et al. Isolation and identification of pathogenic fungi in rotten sweet cherry from Shihezi, Xinjiang [J]. Microbiology China, 2018, 45(11): 2480−2487. (in Chinese)
[23] KHAN I H, JAVAID A. Mucor fragilis causing rot of Seychelles polebean in Pakistan [J]. Australasian Plant Pathology, 2022, 51(3): 359−362. DOI: 10.1007/s13313-022-00859-8
[24] 魏超, 代晓航, 郭灵安, 等. 草莓致腐霉菌的鉴定及其产毒能力研究 [J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2017, 8(5):1721−1726. WEI C, DAI X H, GUO L A, et al. Identification and toxin-producing capability of causing-spoilage fungi in strawberry [J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2017, 8(5): 1721−1726. (in Chinese)
[25] 刘德衍, 袁磊, 李国良, 等. 糖尿病合并毛霉菌感染致死亡法医学鉴定1例报告并文献复习 [J]. 青岛大学学报(医学版), 2022, 58(5):775−776. LIU D Y, YUAN L, LI G L, et al. Forensic identification of death caused by diabetes mellitus with mucormycosis infection: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Qingdao University (Medical Sciences), 2022, 58(5): 775−776. (in Chinese)
[26] EGIDI E, DELGADO-BAQUERIZO M, PLETT J M, et al. A few Ascomycota taxa dominate soil fungal communities worldwide [J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 2369. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-10373-z
[27] 肖立皓, 李海波, 黄玉欣, 等. 青蒿的化学成分研究Ⅰ [J]. 中国中药杂志, 2021, 46(5):1160−1167. XIAO L H, LI H B, HUANG Y X, et al. Research on chemical constituents from Artemisia annua Ⅰ [J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2021, 46(5): 1160−1167. (in Chinese)
[28] 宁睿, 李优琴, 王春梅, 等. 青蒿粗提物的抑菌活性研究 [J]. 江苏农业科学, 2007(3):61−63. [29] 霍焕燃. 青蒿提取物对四种植物病原镰刀菌的抑菌活性研究[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学, 2021. HUO H R. Study on the antifungal activity of Artemisia annua extracts against four plant pathogenic Fusarium [D]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University, 2021.
[30] 范敏. 三种鼠尾草属植物中二萜的化学成分及生物活性研究[D]. 昆明: 云南大学, 2018. FAN M. Studies on the diterpenoids constituents and their bioactivities of three species Salvia plant[D]. Kunming: Yunnan University, 2018. (in Chinese)
[31] 王芳, 李晓旭, 高瑾, 等. 墨西哥鼠尾草挥发油的抗菌活性研究 [J]. 西南林业大学学报, 2015, 35(5):92−96. WANG F, LI X X, GAO J, et al. Chemical constituents and anti-microbial activity of the essential oils from Salvia leucantha [J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University, 2015, 35(5): 92−96. (in Chinese)
[32] CÍSAROVÁ M, TANČINOVÁ D, MEDO J. Antifungal activity of lemon, Eucalyptus, thyme, oregano, sage and lavender essential oils against Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus tubingensis isolated from grapes [J]. Potravinarstvo Slovak Journal of Food Sciences, 2016, 10(1): 83−88. DOI: 10.5219/554
-
期刊类型引用(19)
1. 王多梅,胡冲,蒲婧哲,陈灵丽,杨建波,张亚中,张文娟. 基于LNA-TaqMan探针实时荧光定量PCR检测技术的药用黄精掺伪研究. 中国现代中药. 2024(03): 457-462 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 苏海兰,江保东,朱雁鸣,郑梅霞,陈宏,丁明月,牛雨晴,朱育菁. 黄精转录组SSR分子标记开发及种质遗传多样性分析. 中国农学通报. 2024(26): 30-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李亚萍,戴惠明,姜武,陈家栋,段晓婧,陶正明. 基于SRAP标记的不同产区黄精的遗传多样性. 浙江农林大学学报. 2023(03): 658-664 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘贺贺,石洪峰. 黄精属植物种质资源遗传多样性研究进展. 现代农业科技. 2023(17): 83-89 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 吴杰,宁伟. 两种玉竹根茎显微形态及同工酶谱带比对研究. 特产研究. 2023(05): 53-56+65 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 宋荣,宋静爽,欧立军,严蓓,周佳民,朱校奇,易自立. 不同地区多花黄精的ITS序列分析及近缘种聚类分析. 分子植物育种. 2022(01): 218-224 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 谢蕾,肖良俊,吴涛,李贤忠,苏包顺,刘志彤. 3种花色类型滇黄精的遗传关系研究. 浙江林业科技. 2022(02): 21-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 叶碧欢,杨阳,朱杰丽,石从广,陈友吾,胡传久,宋其岩,李海波. 基于比较转录组学的多花黄精黄酮类化合物合成基因表达分析. 食品与生物技术学报. 2022(04): 84-92 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 朱香梅,石雨荷,李晴,周日宝,童巧珍. 白术种质资源遗传多样性及连作障碍研究进展. 江苏农业科学. 2021(08): 43-48 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 石乃星,文国松,赵明富. 黄精属植物DNA分子鉴定技术应用研究进展. 植物遗传资源学报. 2021(05): 1209-1218 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 陈友吾,廖荣俊,叶碧欢,宋其岩,杨阳,李楠,李海波. 多花黄精转录组SSR位点分析及分子标记开发. 中草药. 2020(01): 182-189 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 周先治,饶宝蓉,高晖,陈阳,林永胜. 基于DNA条形码的多花黄精系统发育和变异位点分析研究. 中草药. 2020(15): 4003-4010 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 王晓云,张莲,曹岚,梁芳. 江西省锐尖山香圆亲缘关系与群体结构的ISSR分析. 中国实验方剂学杂志. 2020(15): 150-155 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 钱润,周骏辉,杨健,黄璐琦,袁媛. 中药材分子标记辅助育种技术研究进展. 中国中药杂志. 2020(20): 4812-4818 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 徐惠龙,孟静,范世明,徐伟,林羽. 基于转录组的多花黄精与长梗黄精代谢途径分析. 中药材. 2020(11): 2663-2668 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 叶碧欢,陈友吾,胡传久,宋其岩,廖荣俊,翁永发,杜国坚,李海波. 长梗黄精的SCAR分子鉴别. 中国药学杂志. 2019(20): 1647-1652 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 王志威,杜富强,张浪,王世梅,魏升华. 中药黄精及其易混品植物的分类鉴别研究进展. 北方园艺. 2019(24): 130-136 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 朱巧,邓欣,张树冰,梅时勇,陈小军,张冀芳,肖清明,黎宇. 黄精属6种植物的SSR遗传差异分析. 中国中药杂志. 2018(14): 2935-2943 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 杨丹丹,吴思宇,傅静,张莹,王孝勋. ISSR标记在中药和壮瑶药研究中应用进展. 壮瑶药研究季刊. 2018(01): 91-96+140 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(9)




 下载:
下载: