Carbon, Nitrogen, and Enzyme Activity in Saline-alkali Soil on Songnen Plain as Affected by Land Use
-
摘要:目的 探究不同土地利用方式对盐碱地土壤肥力及微生物活性的影响,旨在为盐碱地改良及生态修复提供科学依据。方法 以吉林西部松嫩平原为例,分析农耕水田(N1)、农耕旱田(N2)、湿地(S)、草地(C)等4种土地利用方式土壤中有机碳、全氮、蔗糖酶、脲酶、碱性磷酸酶、过氧化氢酶的变化特征及相互关系。结果 不同土地利用方式的土壤有机碳含量为N1:9.70~16.27 g·kg−1、N2:3.85~11.58 g·kg−1、S:2.14~2.97 g·kg−1、C:5.25~11.24 g·kg−1;全氮含量为N1:1.83~2.32 g·kg−1、N2:0.45~0.76 g·kg−1、S:0.34~1.28 g·kg−1、C:0.88~2.04 g·kg−1;碳氮比为N1:2.29~7.11、N2:8.89~15.28、S:2.00~6.42 、C:4.20~5.97 ,不同土地利用方式的土壤酶活性均表现为脲酶(60.64~286.49 μmol·d−1·mg−1)>碱性磷酸酶(9.22~48.05 μmol·d−1·mg−1)>过氧化氢酶(9.14~9.68 μmol·d−1·mg−1)>蔗糖酶(0.06~7.82 μmol·d−1·mg−1),并呈现出伴随土层加深土壤酶活性逐渐降低的趋势。相关分析结果表明,土壤蔗糖酶与碳氮比呈显著相关(P<0.05),脲酶与碳氮比呈极显著相关(P<0.01),碱性磷酸酶与有机碳呈极显著相关(P<0.01)、与全氮呈显著相关(P<0.05),过氧化氢酶与全氮呈极显著相关(P<0.01)、与碳氮比呈显著相关(P<0.05)。冗余分析结果表明,土壤蔗糖酶、脲酶主要受土壤pH值和容重调控,土壤碱性磷酸酶、过氧化氢酶主要受土壤含水量和电导率调控。结论 土壤有机碳、全氮含量及酶活性在不同土地利用方式间具有较明显的差异,在垂直土层上呈现表层土壤高于深层土壤的规律性分布;农耕水田土地利用方式的土壤有机物质累积量和肥力优于农耕旱田、湿地和草地,证明种植水稻在一定程度上可改善盐碱土壤的肥力及微生物活性,有利于生态环境的改善和修复。Abstract:Objective Fertility and enzymatic activity of the saline-alkali soil in relation to land use were analyzed for ecological improvements and restoration.Method At sites on Songnen Plain in western Jilin province, the effects on organic carbon, total nitrogen, invertase, urease, alkaline phosphatase, and catalase of the saline-alkali soils under different types of land use as paddy farming field (N1), dry farming field (N2), wetland (S), and grassland (C) were compared.Result The organic carbon contents in the soils ranged 9.70–16.27 g·kg−1 under N1, 3.85–11.58 g·kg−1 under N2, 2.14–2.97 g·kg−1 under S, and 5.25–11.24 g·kg−1 under C. and the total nitrogen, 1.83–2.32 g·kg−1 under N1, 0.45–0.76 g·kg−1 under N2, 0.34–1.28 g·kg−1 under S, and 0.88–2.04 g·kg−1 under C. and the total T/N, 2.29–7.11 under N1, 8.89–15.28 under N2, 2.00–6.42 under S, and 4.20–5.97 under C. The activities of various enzymes were urease (60.64–286.49 μmol·d−1·mg−1)>alkaline phosphatase (9.22–48.05 μmol·d−1·mg−1)>catalase (9.14–9.68 μmol·d−1·mg−1)>sucrase (0.06–7.82 μmol·d−1·mg−1) and decreased along the depth of the soil layers. The invertase significantly correlated with C/N at P<0.05, the urease with C/N at P<0.01, the alkaline phosphatase with the organic C at P<0.01 and with the total nitrogen at P<0.05, while the catalase with total nitrogen at P<0.01 and with C/N at P<0.05. The redundant analysis indicated that the activities of invertase and urease were mainly regulated by the pH and bulk density, while those of alkaline phosphatase and catalase largely affected by the moisture content and electric conductivity of the soil.Conclusion Land use exerted significant effects on the organic carbon, total nitrogen, and enzyme activity in the saline-alkali soils which gradually decreased from the surface to the deeper layers. Paddy farming on the land fostered the nutrient accumulation and increased the enzymatic activities in the soil. Thus, the type of land use was considered more ecologically friendly than wetland or grassland for the regions of saline-alkali soil.
-
Keywords:
- land uses /
- organic carbon /
- total nitrogen /
- enzyme activity /
- saline-alkali soil
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】盐碱土壤是我国主要的后备土壤资源之一,对于盐碱土壤的改良利用和生态建设一直是人们关注的热点,探究盐碱区的土地利用方式与土壤碳、氮及酶活性之间的关系,对于合理开发利用盐碱土壤具有重要的理论意义和实际意义。【前人研究进展】土壤有机碳含量与土壤物质循环及能量流动关系密切,任何土壤碳库储量的微细变化,都能导致大气CO2浓度的显著变化[1]。土壤全氮包括所有形式的有机和无机氮素,是标志土壤氮素总量和供应植物有效氮素的源和库,综合反映了土壤的氮素状况[2]。不同土地利用方式的土壤,其外界有机物质的输入量及转化效应不同,进而影响到土壤的碳、氮含量。大量研究表明,土壤酶活性易受环境中物理、化学及生物因素的影响, 可以反映土壤状态和动态变化,且对土壤碳、氮含量有一定的影响[3]。同时,土壤中的有机碳可以促进土壤酶及微生物的活动,并且供应土壤微生物所需的能量和养分。脲酶的酶促产物——氨是植物氮素来源之一[4],土壤有机质、总氮等都与土壤脲酶活性相关[5];蔗糖酶是可以表征土壤生物活性的水解酶,可以作为评价土壤熟化程度和土壤肥力水平的一个指标[6];碱性磷酸酶与土壤肥力关系密切[7-8];过氧化氢酶活性与土壤呼吸强度和微生物活动有关,可以反映土壤微生物活动过程的强度,故研究不同土地利用方式对土壤碳、氮及酶活性的影响是土壤环境质量研究的重要内容[9]。松嫩平原盐碱土是世界三大盐碱土集中分布区之一,且盐碱程度呈逐年增加之态势,使得农作物产量下降、草地退化、生态环境日趋恶化[10]。以往的研究主要集中在盐碱土壤改良后土壤物理、化学性质的变化[11-13]。【本研究切入点】从土壤碳、氮及酶活性差异的角度探讨盐碱区不同土地利用方式对土壤性质影响的相关研究结果鲜见报道。【拟解决的关键问题】以吉林西部松嫩平原为例,分析不同土地利用方式(农耕水田、农耕旱田、湿地、荒草地)土壤中碳、氮,以及蔗糖酶、脲酶、碱性磷酸酶、过氧化氢酶的变化特征及相互关系,阐明不同土地利用方式对土壤肥力及微生物的影响,为优化该区域土地利用、提高地力及防止土壤退化提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 研究区概况
松嫩平原西部是苏打盐碱化最严重的地区,盐碱地面积约96.87×104 hm2,其中轻度盐碱地6.07×104 hm2、中度盐碱地46.40×104 hm2、重度盐碱地44.40×104 hm2 [14]。该区属半干旱半湿润的大陆性季风气候区,受西风带和东亚夏季天气系统的影响,气候敏感,四季差异明显,春季干旱少雨,夏季炎热多雨,秋季凉爽,冬季漫长寒冷[14]。该区经历了多次沙漠化和盐碱荒漠化的正逆演变过程,形成了大面积的盐碱土沉积。研究区位于吉林西部松嫩平原内,该地区主要土地利用方式为农田(农耕旱田、农耕水田)、 荒草地(以下简称草地)、湿地等。
1.2 土壤样品采集
根据土壤类型图和土地利用方式类型图,结合实地调查,于2018年7月采集样品。每种土地利用方式中分别设置6个20 m2样方,按照S形采样法采集0~10、10~20、20~30、30~40、40~50 cm土层土壤样品,现场将每个采样点相同土层的样品混匀,去除土壤中植物残体和根系,置于塑封袋中,于4 ℃冰盒中保存。带回实验室后自然风干,过1.00 、0.25 mm筛,装袋备用。采样点基本信息见表1。
表 1 样地基本信息Table 1. Relevant information on sampled fields土地利用方式
Land use
type经度
Longitude纬度
LatitudepH 鲜土含水率
Water
content/%容重
Bulk density/
(g·cm−3)电导率
Conductivity/
(ms·cm−1)碱化度
exchangeable sodium
percentage/%主要植被
Main
vegetation农耕水田
Paddy farming field(N1)E124°54′50″ N45°18′26″ 8.29 50 0.83 0.21 7.11 水稻 rice 农耕旱田
Dry farming field(N2)E124°18′70″ N45°48′22″ 8.56 43 1.02 0.20 7.23 玉米 corn 湿地 Wetland(S) E124°48′45″ N45°14′38″ 7.88 55 0.46 0.25 7.02 芦苇 reed 草地 Grassland(C) E124°42′33″ N45°11′16″ 8.98 39 1.53 0.16 8.56 碱蓬 Suaeda glauca Bge 1.3 样品分析方法
有机碳采用重铬酸钾外加热法[15],全氮采用过硫酸钾氧化–紫外分光光度法[16],脲酶活性采用苯酚钠–次氯酸钠比色法、碱性磷酸酶采用磷酸苯二钠比色法、过氧化氢酶采用高锰酸钾滴定法[17],蔗糖酶活性采用3,5-二硝基水杨酸比色法测定[18]。
1.4 数据处理
采用SPSS 20.0软件进行单因素方差分析,采用最小差数法(LSD)进行差异显著性分析,通过Pearson(双侧)相关分析判断土壤碳、氮、酶之间的相关性。利用Canoco5.0软件进行冗余分析,探究土壤各指标之间的关系。运用WPS软件进行制图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同土地利用方式的土壤碳、氮含量
不同土地利用方式间的土壤有机碳(SOC)、全氮(TN)及碳氮比(C/N)变化见表2。不同土地利用方式土壤有机碳、全氮、碳氮比的差异性表现一致。土壤有机碳含量农耕水田为9.70~16.27 g·kg−1,农耕旱田为3.85~11.58 g·kg−1,湿地为2.14~2.97 g·kg−1,草地为5.25~11.24 g·kg−1;0~10 cm土层土壤有机碳含量的差异表现为:农耕水田>农耕旱田>草地>湿地。土壤全氮含量农耕水田为1.83~2.32 g·kg−1,农耕旱田为0.45~0.76 g·kg−1,湿地为0.34~1.28 g·kg−1,草地为0.88~2.04 g·kg−1;0~10 cm土层土壤全氮含量的差异表现为:农耕水田>草地>湿地>农耕旱田。土壤碳氮比农耕水田为2.29~7.11,农耕旱田为8.89~15.28,湿地为2.00~6.42,草地为4.20~5.97;0~10 cm土层土壤碳氮比的差异表现为:农耕旱田>农耕水田>草地>湿地。
表 2 不同土地利用方式土壤碳、氮垂直分布特征Table 2. Vertical distribution of carbon and nitrogen in soils of varied land uses土地利用方式
Land use type土层
siol layer/cm有机碳
SOC/(g·kg−1)全氮
TN/(g·kg−1)碳氮比
C/N农耕水田 Paddy farming field(N1) 0~10 16.27±0.31 a(a) 2.32±0.05 a(a) 7.01±0.27a(a) 10~20 15.38±0.56 b(a) 2.16±0.02 ab(a) 7.11±0.31a(a) 20~30 11.70±0.38 c(a) 2.11±0.04 b(a) 5.55±0.10 b(a) 30~40 10.53±0.34 d(a) 1.95±0.05 b(a) 5.39±0.06 b(a) 40~50 9.70±0.15 e(a) 1.83±0.06 b(a) 2.29±0.20 c(a) 农耕旱田 Dry farming field(N2) 0~10 11.58±0.23 a(b) 0.76±0.04 a(b) 15.28±1.11 a(b) 10~20 7.61±0.39 b(b) 0.72±0.02 a(b) 10.58±0.73 b(b) 20~30 6.84±0.03 c(b) 0.61±0.02 b(b) 11.22±0.35 b(b) 30~40 6.44±0.12 c(b) 0.52±0.03 c(b) 12.43±0.95 c(b) 40~50 3.85±0.09 e(b) 0.45±0.10 c(b) 8.89±1.80 d(b) 湿地 Wetland(S) 0~10 2.97±0.25 a(c) 1.28±0.07a(c) 2.32±0.29 cd(c) 10~20 2.25±0.87 b(c) 1.11±0.11a(c) 2.00±0.70 d(c) 20~30 2.69±0.19 ab(c) 1.03±0.05 ab(c) 2.62±0.08 c(c) 30~40 2.30±0.09 b(c) 0.74±0.08 b(b) 3.13±0.24 b(c) 40~50 2.14±0.10 b(c) 0.34±0.08 c(b) 6.42±1.14 a(c) 草地 Grassland(C) 0~10 11.24±0.07a(b) 2.04±0.07a(a) 5.51±0.29ab(d) 10~20 10.11±0.29 b(d) 1.95±0.07a(a) 5.20±0.29 b(d) 20~30 7.68±0.18 c(d) 1.83±0.13 a(a) 4.20±0.40 d(c) 30~40 6.63±0.18 d(b) 1.25±0.01 b(c) 4.30±0.10 c(d) 40~50 5.25±0.16 e(d) 0.88±0.04 c(c) 5.97±0.22 a(c) 注:括号外的小写字母代表同一土地利用方式不同土层间在0.05水平上的差异显著性,括号内的小写字母代表同一土层不同土地利用方式间在0.05水平上的差异显著性。
Note: Lowercase letters outside brackets represent significant difference at 0.05 level for indices of different soil layers under same land use; lowercase letters inside brackets represent significant difference at 0.05 level for indices of same soil layer under different land use.分析不同土层土壤碳、氮含量的差异性,结果表明:土壤有机碳含量在农耕水田、农耕旱田、草地均表现为伴随土层加深而逐渐减少的趋势,而在湿地则表现为20~30 cm土层土壤有机碳含量高于10~20 cm与30~40 cm土层;土壤全氮含量,不同土地利用方式均表现为伴随土层加深逐渐减少,0~10 cm土层显著高于30~50 cm土层;碳氮比,农耕旱田的碳氮比显著高于农耕水田、湿地和草地(P<0.05),农耕水田、农耕旱田的碳氮比表现为0~10 cm土层显著高于40~50 cm土层(P<0.05),而湿地和草地的碳氮比则表现为 0~10 cm土层低于40~50 cm土层。
2.2 不同土地利用方式的土壤酶活性
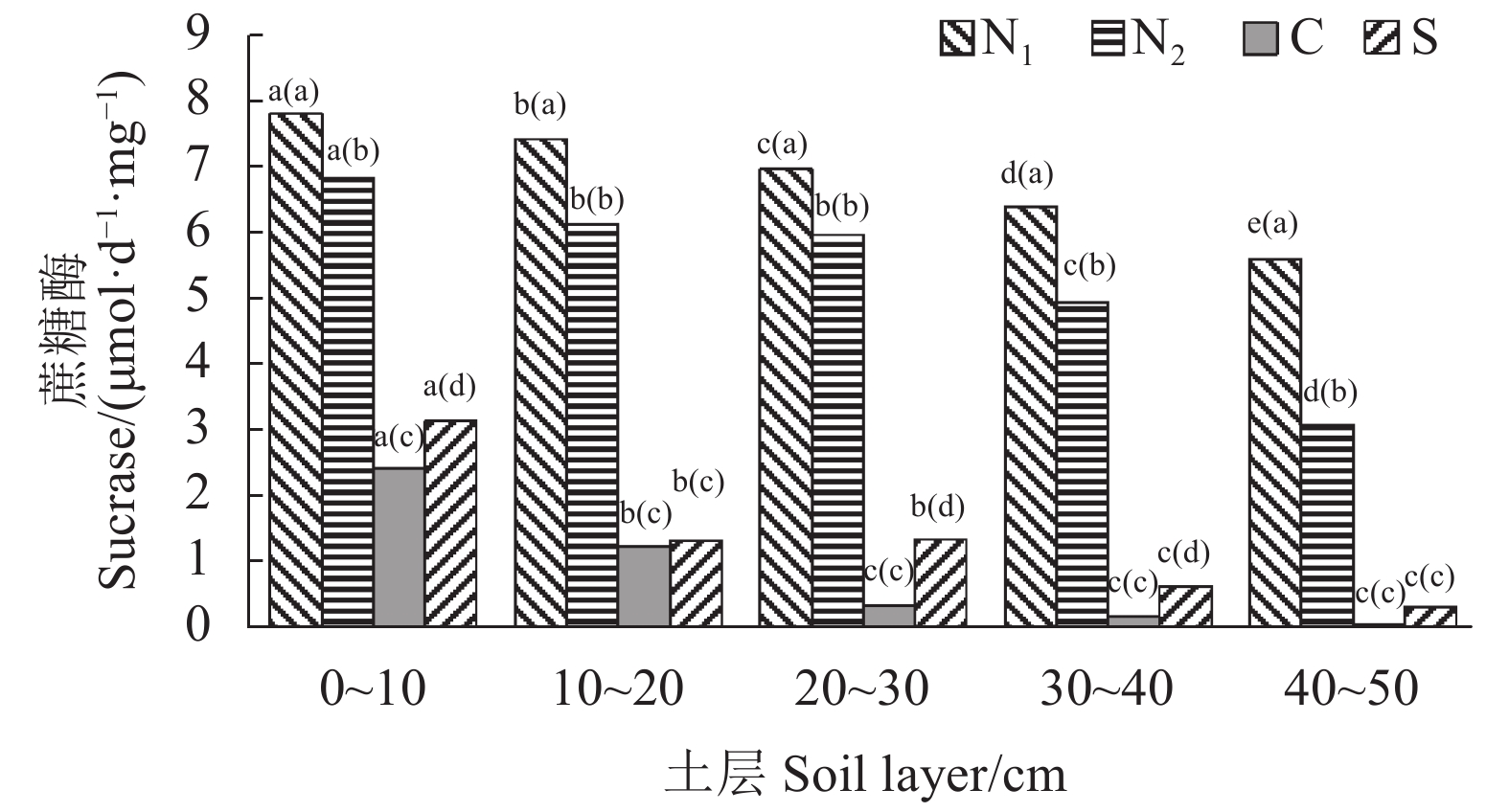
由图1可知,土壤蔗糖酶活性以农耕水田较高,显著高于其他土地利用方式(P<0.05),草地土壤蔗糖酶活性较低;从土壤剖面层看,表层土壤蔗糖酶活性高于深层土壤。
![]() 图 1 不同土地利用方式土壤蔗糖酶活性的垂直分布注:(1)N1为农耕水田、N2为农耕旱田、C为草地、S为湿地;(2)图中括号外的小字母代表同一土地利用方式不同土层间在0.05水平上的差异显著性,括号内的小字母代表同一土层不同土地利用方式间在0.05水平上的差异显著性(图2~4同)。Figure 1. Vertical distribution of sucrase in soils of varied land usesNote: (1) N1: farming paddy field; N2: farming dry land; C: grassland; S: wetland. (2) Data with lowercase letters outside brackets represent significant difference at 0.05 level on indices of different soil layers under same land use; those within brackets represent significant difference at 0.05 level under different land use at same soil layer. Same for Figs. 2-4.
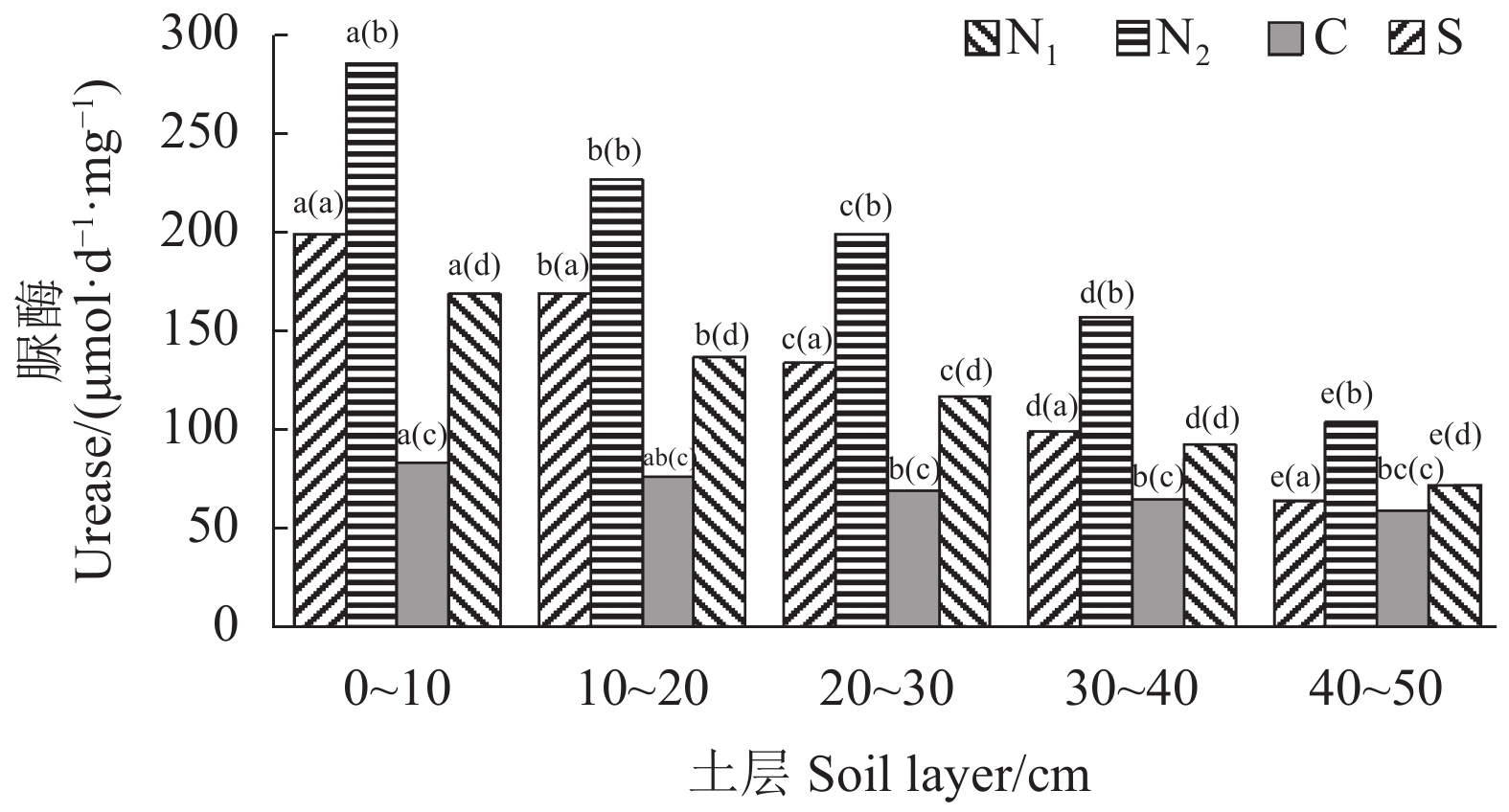
图 1 不同土地利用方式土壤蔗糖酶活性的垂直分布注:(1)N1为农耕水田、N2为农耕旱田、C为草地、S为湿地;(2)图中括号外的小字母代表同一土地利用方式不同土层间在0.05水平上的差异显著性,括号内的小字母代表同一土层不同土地利用方式间在0.05水平上的差异显著性(图2~4同)。Figure 1. Vertical distribution of sucrase in soils of varied land usesNote: (1) N1: farming paddy field; N2: farming dry land; C: grassland; S: wetland. (2) Data with lowercase letters outside brackets represent significant difference at 0.05 level on indices of different soil layers under same land use; those within brackets represent significant difference at 0.05 level under different land use at same soil layer. Same for Figs. 2-4.由图2可知,土壤脲酶活性以农耕旱田较高,显著高于其他土地利用方式(P<0.05),草地土壤脲酶活性较低;从土壤剖面层看,土壤脲酶活性呈现随土层加深而逐渐降低的趋势,且农耕水田、农耕旱田、湿地各土层脲酶活性差异显著(P<0.05)。
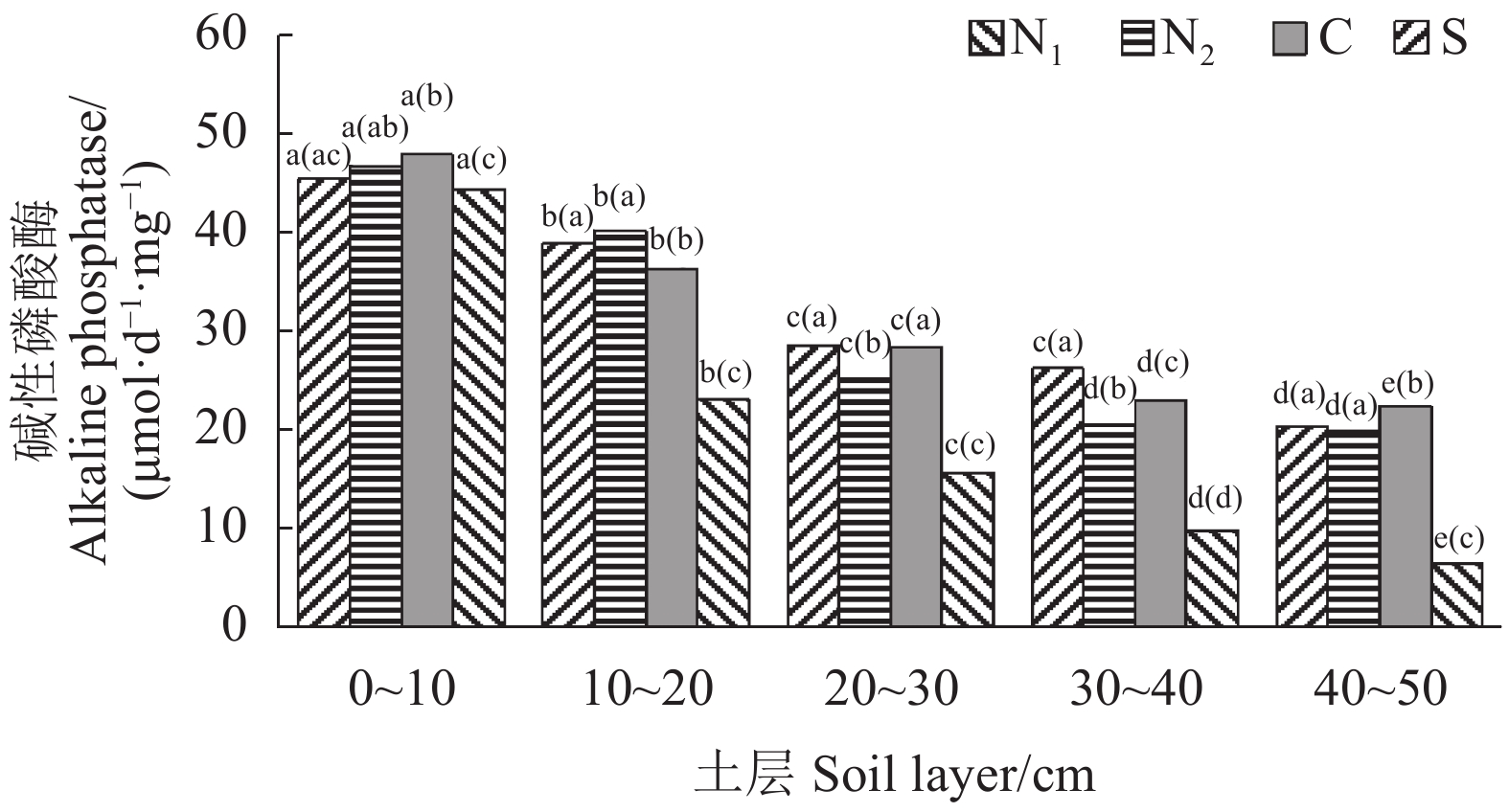
由图3可知,土壤碱性磷酸酶活性以湿地较低;从土壤剖面层看,土壤碱性磷酸酶活性呈现随土层加深而逐渐降低的趋势,但 0~10 cm、10~20 cm、40~50 cm土层农耕水田与农耕旱田之间的土壤碱性磷酸酶活性无显著差异;而20~30 cm、30~40 cm土层的农耕水田与农耕旱田之间的土壤碱性磷酸酶活性有显著差异(P<0.05)。
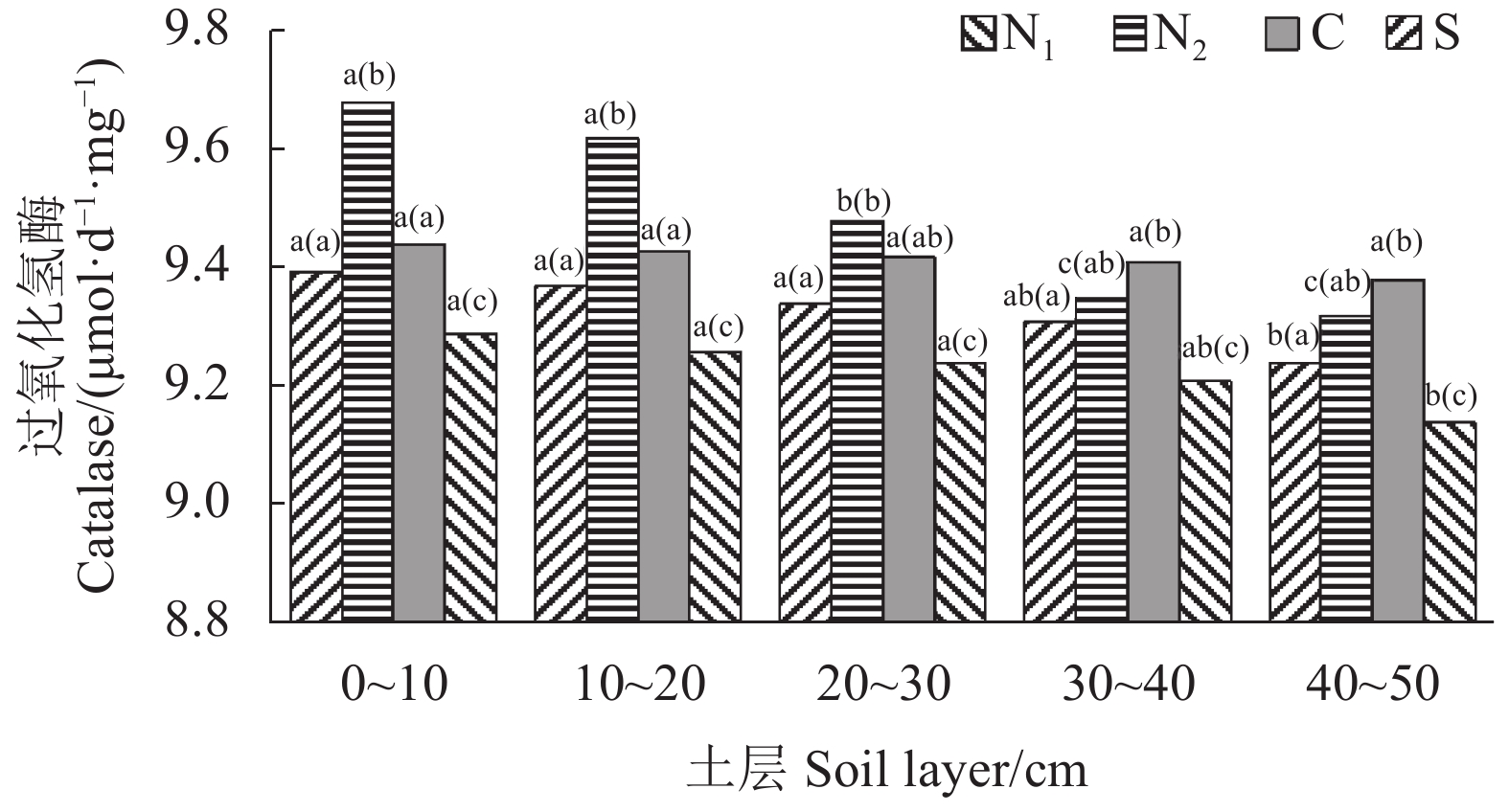
由图4可知,土壤过氧化氢酶活性以湿地较低,显著低于其他土地利用方式;从土壤剖面层看,同一土地利用方式的土壤过氧化氢酶活性呈现随土层加深而逐渐降低的趋势,0~30 cm土层农耕旱田土壤过氧化氢酶活性高于其他土地利用方式,30~50 cm土层草地土壤过氧化氢酶活性高于其他土地利用方式。
2.3 土壤碳、氮含量与土壤酶活性的相关性
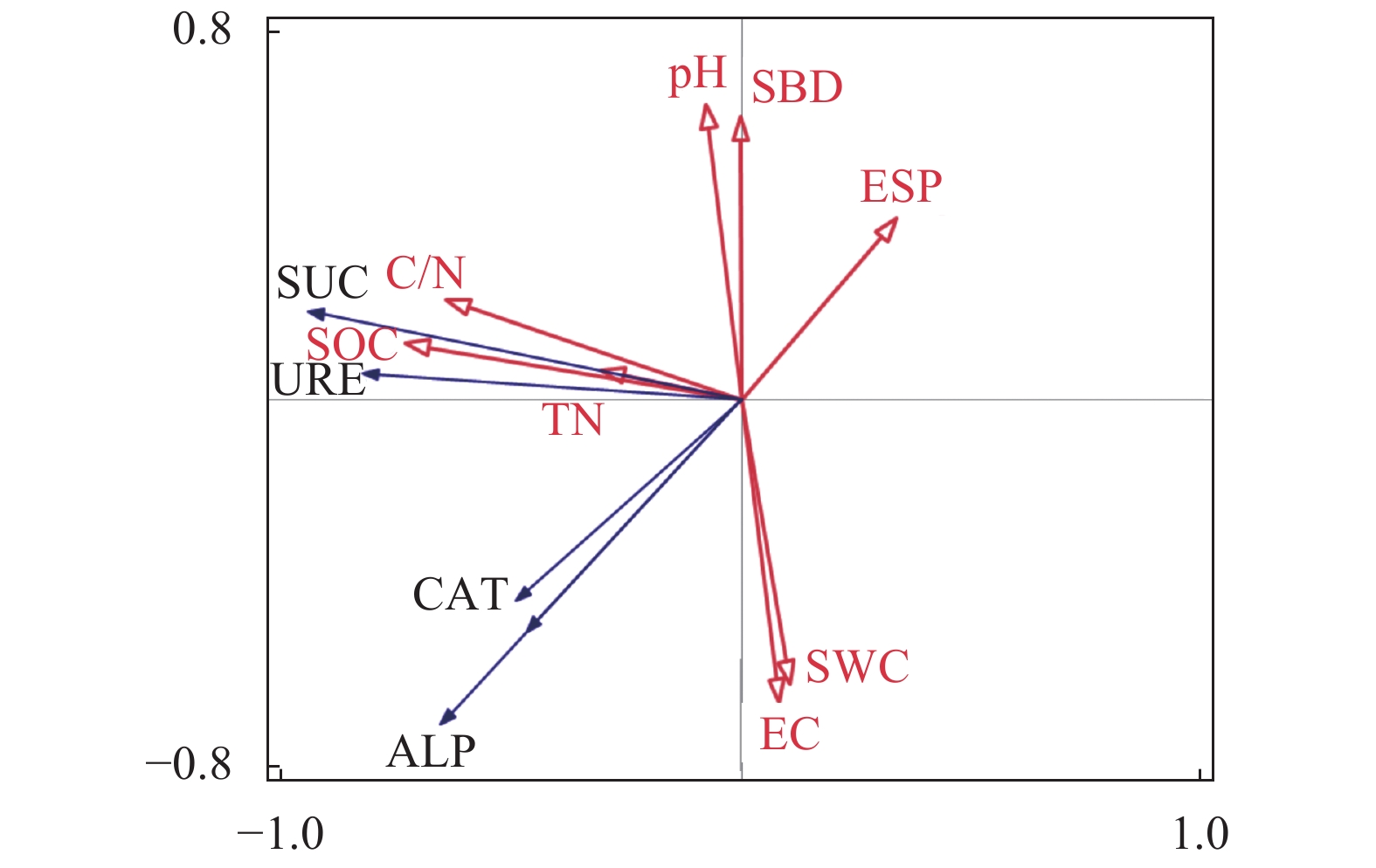
不同土地利用方式的土壤碳、氮含量与土壤酶活性的相关性如表3所示,土壤有机碳与碱性磷酸酶呈极显著负相关(P<0.01);土壤全氮与碱性磷酸酶呈显著负相关(P<0.05),与过氧化氢酶呈极显著负相关(P<0.01);土壤碳氮比与蔗糖酶、过氧化氢酶呈显著相关(P<0.05)、与脲酶呈极显著相关(P<0.01)。冗余分析结果(图5)表明,土壤蔗糖酶、脲酶主要受土壤pH值和容重调控,土壤碱性磷酸酶、过氧化氢酶受土壤含水量和电导率调控。
表 3 土壤碳、氮含量与土壤酶活性的相关性Table 3. Correlations among carbon, nitrogen, and enzyme activity of soil指标 Index SOC TN C/N SUC URE ALP CAT SOC 1 TN 0.607* 1 C/N 0.437 −0.443 1 SUC 0.531 0.086 0.583* 1 URE 0.552 −0.276 0.960** 0.771** 1 ALP − 0.824** −0.624* −0.191 −0.161 −0.246 1 CAT −0.272 −0.799** 0.620* 0.416 0.588* 0.528 1 注:(1)*表示显著相关(P<0.05),**表示极显著相关(P<0.01);(2)SOC:有机碳,TN:全氮,C/N:碳氮比,SUC:蔗糖酶,URE:脲酶,ALP:碱性磷酸酶,CAT:过氧化氢酶。
Note:(1) * indicates significant correlation (P <0.05), and ** significant correlation (P<0.01). (2) SOC: organic carbon, TN: total nitrogen,C/N: ratio of organic carbon to total nitrogen,SUC: sucrase,URE: urease, ALP: alkaline phosphatase, CAT: catalase.![]() 图 5 环境因子与土壤碳、氮含量及酶活性冗余分析注:SOC:有机碳,TN:全氮,C/N:碳氮比,SUC:蔗糖酶,URE:脲酶,ALP:碱性磷酸酶,CAT:过氧化氢酶,pH:pH值,SWC:鲜土含水率,SBD:容重,EC:电导率,ESP:碱化度。Figure 5. Redundancy analysis results on environmental factors, soil enzyme activities, carbon, and nitrogenNote: SOC: organic carbon,TN: total nitrogen, C/N: ratio of organic carbon to total nitrogen, SUC: sucrase,URE: urease,ALP: alkaline phosphatase, CAT: catalase,pH: soil pH, SWC: soil water content, SBD: soil bulk density, EC: electric conductivity, ESP: exchangeable sodium percentage.
图 5 环境因子与土壤碳、氮含量及酶活性冗余分析注:SOC:有机碳,TN:全氮,C/N:碳氮比,SUC:蔗糖酶,URE:脲酶,ALP:碱性磷酸酶,CAT:过氧化氢酶,pH:pH值,SWC:鲜土含水率,SBD:容重,EC:电导率,ESP:碱化度。Figure 5. Redundancy analysis results on environmental factors, soil enzyme activities, carbon, and nitrogenNote: SOC: organic carbon,TN: total nitrogen, C/N: ratio of organic carbon to total nitrogen, SUC: sucrase,URE: urease,ALP: alkaline phosphatase, CAT: catalase,pH: soil pH, SWC: soil water content, SBD: soil bulk density, EC: electric conductivity, ESP: exchangeable sodium percentage.3. 讨论
3.1 不同土地利用方式对土壤有机碳、全氮含量的影响
土壤有机碳、全氮含量与有机物料输入和输出关系密切,同时土壤性质、利用方式、耕作管理、地覆植被均会影响土壤有机碳、全氮的含量及分布[19-20]。本研究中,不同土地利用方式土壤有机碳、全氮含量随土层加深而呈现逐渐降低的趋势。究其原因主要是因为植物根系、土壤微生物、植物凋落物、农耕肥等是土壤有机碳、全氮的主要来源物质,表层土壤优先获得有机物料的输入,并逐步传导至深层土壤,因此表现为表层土壤的有机碳、全氮的累积量高于深层土壤[21-24]。不同土地利用方式中,各土层有机碳含量均值表现为农耕水田>农耕旱田>草地>湿地,说明盐碱土壤在人为耕作活动之后,通过农作物凋落物和有机肥等形式输入的碳素除了被植物吸收或者分解外,有更多的有机碳在土壤中累积。因此,农田耕作有利于提高盐碱稻田土壤有机碳的含量[25]。李新爱等[26]对亚热带喀斯特地区不同土地利用方式土壤全氮含量的变化进行研究表明,稻田土壤全氮含量显著高于旱地,本研究结果与之相似,也表现为农耕水田全氮含量高于农耕旱田。孙志高等[27]对三江平原地区不同土地利用方式的土壤全氮含量变化特征的研究表明,湿地土壤全氮含量高于农田,本研究结果也表现为0~10 cm土层的全氮含量湿地土壤高于农耕旱田。本研究中,土壤全氮与土壤有机碳之间具有明显的正耦合效应,这与前人研究结果一致,说明农业实践活动能够强烈地影响氮循环和碳存储[28-30]。其次,不同土地利用方式间,由于植被覆盖类型及枯枝落叶的差别较大,导致土壤氮素输入量不同。农耕水田土壤全氮含量高于其他土地利用方式,说明土壤氮素受水热条件影响明显,淹水状态及温度升高均能显著提高土壤中溶解性氮的累积[31]。普遍认为,土壤碳氮比与土壤有机碳分解速率成反比关系[32]。本研究4种土地利用方式的C/N值基本为2.00~15.28,其中农耕水田和农耕旱田的C/N值高于湿地和草地,这与土壤利用、水热条件及田间管理有一定关系,受人为干扰的土壤碳氮比普遍高于未受干扰的土壤[33]。C/N 值的升高对土壤微生物的繁殖速度和分解活动有一定的限制作用,使有机质和有机氮的分解矿化速度减慢,土壤固定有机碳能力提高。
3.2 不同土地利用方式对土壤酶活性的影响
酶活性是影响土壤养分转化的主要生物因素,对其碳、氮储量及运转速率影响明显。与此同时,土壤中养分含量的变化影响土壤的酶活性[34]。本研究中,不同土地利用方式对土壤酶活性有显著影响,其中:湿地土壤的过氧化氢酶和碱性磷酸酶活性低于其他3种土地利用方式;农田(农耕水田、农耕旱田)的蔗糖酶和脲酶活性高于湿地和草地。这是由于农耕过程中施用肥料,能刺激植物根系生长,且农田枯落物数量较多,可促使植物根系和微生物分泌更多转化酶[35]。
本研究中,不同土地利用方式间4种土壤酶活性均表现为表层土壤高于深层土壤,这与前人的研究结果基本一致[36-37]。不同土地利用方式土壤机械组成也不同,表现为土壤紧实度、通透性及肥力状况上的差异[38-39]。而土壤机械组成与土壤含水率、土壤孔隙度等密切相关,不同土地利用方式会影响到土壤理化性质,从而对土壤酶活性产生反馈作用。因此,pH值、含水率、孔隙度间接影响了酶活性[40]。
3.3 土壤碳、氮变化主控因素分析
在不同的土壤环境中,酶及微生物活性是区别不同土壤生态环境的重要指标,在促使土壤有机物质转化中不仅显示其专性特性,同时存在共性关系,氮素与碳素的相互转化亦受到影响[41]。土壤类型、气候条件、农田管理措施等环境因子的不同均会对土壤理化性质、酶活性造成影响,万忠梅等[42]对三江平原湿地进行研究,结果表明,土壤酶的变化是对环境因子的综合响应,这种变化对土壤碳循环过程产生直接影响。本研究从不同土地利用方式的角度分析酶活性及部分理化指标对其土壤碳氮变化的影响,结果表明,不同土地利用方式土壤酶活性具有明显差异,且土壤有机碳含量与碱性磷酸酶活性显著相关,土壤全氮含量与碱性磷酸酶、过氧化氢酶活性显著相关。土壤酶既参与有机物质的合成,又参与有机物的分解。土壤有机质在微生物和酶的作用下形成复杂而较稳定的大分子有机化合物。过氧化氢酶、磷酸酶均为与碳转化密切相关的酶,参与土壤碳氮循环和转化。表层土壤受到水分、植物根系等影响,微生物活性较强,直接影响到土壤碳的累积和转化,而酶促反应释放的低分子糖,是微生物的碳源和能源[43]。腐殖质可与酶结合,对土壤酶形成物理保护,促进或抑制酶促反应。Batra、Farnkenberger 等[44-45]研究表明,盐分的增加会降低土壤酶的活性。本研究中,不同利用方式土壤盐碱化程度差异明显,草地土壤碱化度较高,垦殖后土壤碱化度降低,pH值也均在8以上,但土壤碳、氮、酶之间均呈现显著正相关,说明土壤酶参与了垦殖后土壤生态系统中的绝大部分能源循环和能量转化过程,土壤碳库的稳定性与酶活性之间存在响应模式,即使在较高的盐碱化情况下,酶的生物化学作用仍可以促进土壤碳的转化。不同利用方式下土壤酶活性存在差异,使碳、氮等有机化合物的转化进程发生改变,也在一定程度上反映出不同的土壤肥力水平。农田与湿地、草地根本区别在于是否存在人为活动的影响,农田施用有机肥能增加土壤有效养分,调节土壤pH值,优化土壤微生物群落的结构组成[46]。由于盐碱草地的碱化度较高,因此土壤肥力较低,而农耕水田在人为耕作活动下,土壤的碱化度得到改善,同时,施用有机肥使土壤具有了较高的碳、氮值和酶活性。因此,分析典型盐碱土区不同土地利用方式间的碳、氮含量及酶活性的变化,不仅反映其差异性,同时也说明了人为耕作活动可促进提高土壤肥力和养分固持能力。
4. 结论
土壤有机碳、全氮含量及酶活性在不同土地利用方式间具有较明显的差异,在垂直土层上呈表层土壤高于深层土壤的规律性分布;农耕水田土地利用方式的土壤有机物质累积量和肥力均优于湿地和草地,证明种植水稻在一定程度上可改善盐碱土壤的肥力及微生物活性,有利于生态环境的改善和修复。
-
图 1 不同土地利用方式土壤蔗糖酶活性的垂直分布
注:(1)N1为农耕水田、N2为农耕旱田、C为草地、S为湿地;(2)图中括号外的小字母代表同一土地利用方式不同土层间在0.05水平上的差异显著性,括号内的小字母代表同一土层不同土地利用方式间在0.05水平上的差异显著性(图2~4同)。
Figure 1. Vertical distribution of sucrase in soils of varied land uses
Note: (1) N1: farming paddy field; N2: farming dry land; C: grassland; S: wetland. (2) Data with lowercase letters outside brackets represent significant difference at 0.05 level on indices of different soil layers under same land use; those within brackets represent significant difference at 0.05 level under different land use at same soil layer. Same for Figs. 2-4.
图 5 环境因子与土壤碳、氮含量及酶活性冗余分析
注:SOC:有机碳,TN:全氮,C/N:碳氮比,SUC:蔗糖酶,URE:脲酶,ALP:碱性磷酸酶,CAT:过氧化氢酶,pH:pH值,SWC:鲜土含水率,SBD:容重,EC:电导率,ESP:碱化度。
Figure 5. Redundancy analysis results on environmental factors, soil enzyme activities, carbon, and nitrogen
Note: SOC: organic carbon,TN: total nitrogen, C/N: ratio of organic carbon to total nitrogen, SUC: sucrase,URE: urease,ALP: alkaline phosphatase, CAT: catalase,pH: soil pH, SWC: soil water content, SBD: soil bulk density, EC: electric conductivity, ESP: exchangeable sodium percentage.
表 1 样地基本信息
Table 1 Relevant information on sampled fields
土地利用方式
Land use
type经度
Longitude纬度
LatitudepH 鲜土含水率
Water
content/%容重
Bulk density/
(g·cm−3)电导率
Conductivity/
(ms·cm−1)碱化度
exchangeable sodium
percentage/%主要植被
Main
vegetation农耕水田
Paddy farming field(N1)E124°54′50″ N45°18′26″ 8.29 50 0.83 0.21 7.11 水稻 rice 农耕旱田
Dry farming field(N2)E124°18′70″ N45°48′22″ 8.56 43 1.02 0.20 7.23 玉米 corn 湿地 Wetland(S) E124°48′45″ N45°14′38″ 7.88 55 0.46 0.25 7.02 芦苇 reed 草地 Grassland(C) E124°42′33″ N45°11′16″ 8.98 39 1.53 0.16 8.56 碱蓬 Suaeda glauca Bge 表 2 不同土地利用方式土壤碳、氮垂直分布特征
Table 2 Vertical distribution of carbon and nitrogen in soils of varied land uses
土地利用方式
Land use type土层
siol layer/cm有机碳
SOC/(g·kg−1)全氮
TN/(g·kg−1)碳氮比
C/N农耕水田 Paddy farming field(N1) 0~10 16.27±0.31 a(a) 2.32±0.05 a(a) 7.01±0.27a(a) 10~20 15.38±0.56 b(a) 2.16±0.02 ab(a) 7.11±0.31a(a) 20~30 11.70±0.38 c(a) 2.11±0.04 b(a) 5.55±0.10 b(a) 30~40 10.53±0.34 d(a) 1.95±0.05 b(a) 5.39±0.06 b(a) 40~50 9.70±0.15 e(a) 1.83±0.06 b(a) 2.29±0.20 c(a) 农耕旱田 Dry farming field(N2) 0~10 11.58±0.23 a(b) 0.76±0.04 a(b) 15.28±1.11 a(b) 10~20 7.61±0.39 b(b) 0.72±0.02 a(b) 10.58±0.73 b(b) 20~30 6.84±0.03 c(b) 0.61±0.02 b(b) 11.22±0.35 b(b) 30~40 6.44±0.12 c(b) 0.52±0.03 c(b) 12.43±0.95 c(b) 40~50 3.85±0.09 e(b) 0.45±0.10 c(b) 8.89±1.80 d(b) 湿地 Wetland(S) 0~10 2.97±0.25 a(c) 1.28±0.07a(c) 2.32±0.29 cd(c) 10~20 2.25±0.87 b(c) 1.11±0.11a(c) 2.00±0.70 d(c) 20~30 2.69±0.19 ab(c) 1.03±0.05 ab(c) 2.62±0.08 c(c) 30~40 2.30±0.09 b(c) 0.74±0.08 b(b) 3.13±0.24 b(c) 40~50 2.14±0.10 b(c) 0.34±0.08 c(b) 6.42±1.14 a(c) 草地 Grassland(C) 0~10 11.24±0.07a(b) 2.04±0.07a(a) 5.51±0.29ab(d) 10~20 10.11±0.29 b(d) 1.95±0.07a(a) 5.20±0.29 b(d) 20~30 7.68±0.18 c(d) 1.83±0.13 a(a) 4.20±0.40 d(c) 30~40 6.63±0.18 d(b) 1.25±0.01 b(c) 4.30±0.10 c(d) 40~50 5.25±0.16 e(d) 0.88±0.04 c(c) 5.97±0.22 a(c) 注:括号外的小写字母代表同一土地利用方式不同土层间在0.05水平上的差异显著性,括号内的小写字母代表同一土层不同土地利用方式间在0.05水平上的差异显著性。
Note: Lowercase letters outside brackets represent significant difference at 0.05 level for indices of different soil layers under same land use; lowercase letters inside brackets represent significant difference at 0.05 level for indices of same soil layer under different land use.表 3 土壤碳、氮含量与土壤酶活性的相关性
Table 3 Correlations among carbon, nitrogen, and enzyme activity of soil
指标 Index SOC TN C/N SUC URE ALP CAT SOC 1 TN 0.607* 1 C/N 0.437 −0.443 1 SUC 0.531 0.086 0.583* 1 URE 0.552 −0.276 0.960** 0.771** 1 ALP − 0.824** −0.624* −0.191 −0.161 −0.246 1 CAT −0.272 −0.799** 0.620* 0.416 0.588* 0.528 1 注:(1)*表示显著相关(P<0.05),**表示极显著相关(P<0.01);(2)SOC:有机碳,TN:全氮,C/N:碳氮比,SUC:蔗糖酶,URE:脲酶,ALP:碱性磷酸酶,CAT:过氧化氢酶。
Note:(1) * indicates significant correlation (P <0.05), and ** significant correlation (P<0.01). (2) SOC: organic carbon, TN: total nitrogen,C/N: ratio of organic carbon to total nitrogen,SUC: sucrase,URE: urease, ALP: alkaline phosphatase, CAT: catalase. -
[1] 潘根兴, 李恋卿, 张旭辉. 土壤有机碳库与全球变化研究的若干前沿问题——兼开展中国水稻土有机碳固定研究的建议 [J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2002, 25(3):100−109. PAN G X, LI L Q, ZHANG X H. Perspectives on issues of soil carbon pools and global change—With suggestions for studying organic carbon sequestration in paddy soils of China [J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2002, 25(3): 100−109.(in Chinese)
[2] 王建伟, 刘少敏, 罗汉东, 等. 不同类型肥料对油茶林地土壤氮库的影响 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2019, 34(5):606−612. WANG J W, LIU S M, LUO H D, et al. Effects of fertilizer type on nitrogen in plantation soil and camellia oleifera plant [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 34(5): 606−612.(in Chinese)
[3] 周际海, 郜茹茹, 魏倩, 等. 旱地红壤不同土地利用方式对土壤酶活性及微生物多样性的影响差异 [J]. 水土保持学报, 2020, 34(1):327−332. ZHOU J H, GAO R R, WEI Q, et al. Effects of different land use patternson enzyme activities and nicrobial diversityin upland red soil [J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 34(1): 327−332.(in Chinese)
[4] 李亚娟, 刘静, 徐长林, 等. 不同退化程度对高寒草甸土壤无机氮及脲酶活性的影响 [J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(10):45−53. DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2018098 LI Y J, LIU J, XU C L, et al. Effects of different grassland degradation levels on inorganic nitrogen and urease activity in alpine meadow soils [J]. Acta Pratica Sinica, 2018, 27(10): 45−53.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2018098
[5] 张知晓, 泽桑梓, 户连荣, 等. 土壤脲酶活性调控因素和脲酶活性细菌系统发育研究 [J]. 西部林业科学, 2018, 47(1):65−73. ZHANG Z X, ZE S Z, HU L R, et al. Regulatory factors of soil urease activity and phylogenetic analysis of urease bacteria [J]. Journal of West China Forestry Science, 2018, 47(1): 65−73.(in Chinese)
[6] 蒋永梅, 师尚礼, 田永亮, 等. 高寒草地不同退化程度下土壤微生物及土壤酶活性变化特征 [J]. 水土保持学报, 2017, 31(3):244−249. JIANG Y M, SHI S L, TIAN Y L, et al. Characteristics of soil microorganism and soil enzyme activities in alpine meadows under different degrees of degradation [J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 31(3): 244−249.(in Chinese)
[7] 李冰, 李玉双, 魏建兵, 等. 沈北新区不同土地利用类型土壤磷酸酶活性特征及其影响因素分析 [J]. 生态科学, 2019, 38(4):48−55. LI B, LI Y S, WEI J B, et al. Analysis of activity characteristics and influencing factors of soil phosphatase in different types of land in Shenyang North new area [J]. Ecological Science, 2019, 38(4): 48−55.(in Chinese)
[8] 曹婷婷, 郭振. 土壤酶活性与土壤肥力关系的研究进展 [J]. 农业科学, 2019, 9(6):444−448. DOI: 10.12677/HJAS.2019.96066 CAO T T, GUO Z. Research advance of the relationship between soil enzyme activity and soil fertility in forest land [J]. Hans Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 9(6): 444−448.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.12677/HJAS.2019.96066
[9] NNY B, CHOTTE J L, PATE E, et al. Use of soil enzyme activities to monitor soil quality in natural and improved fallows in semi-arid tropical regions [J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2001, 18(3): 229−238. DOI: 10.1016/S0929-1393(01)00159-7
[10] 赵可夫, 张万钧, 范海, 等. 改良和开发利用盐渍化土壤的生物学措施 [J]. 土壤通报, 2001, 32(Z1):115−119. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2001.z1.031 ZHAO K F, ZHANG W J, FAN H, et al. Biological measures for utilization and development of salinized soil [J]. Cheinese Journal of Soil Science, 2001, 32(Z1): 115−119.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3945.2001.z1.031
[11] 孔祥清, 韦建明, 常国伟, 等. 生物炭对盐碱土理化性质及大豆产量的影响 [J]. 大豆科学, 2018, 37(4):647−651. KONG X Q, WEI J M, CHANG G W, et al. Effect of biochar on the physical and chemical properties of saline-alkali soil and soybean yield [J]. Soybean Science, 2018, 37(4): 647−651.(in Chinese)
[12] 程科. 土体有机重构对盐碱地土壤理化特征的影响 [J]. 农业科学, 2018, 8(10):1192−1199. DOI: 10.12677/HJAS.2018.810175 CHENG K. Effect of organic reconstitution of soil on physical and chemical characteristics of saline soil [J]. Hans Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 8(10): 1192−1199.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.12677/HJAS.2018.810175
[13] 秦都林, 王双磊, 刘艳慧, 等. 滨海盐碱地棉花秸秆还田对土壤理化性质及棉花产量的影响 [J]. 作物学报, 2017, 43(7):1030−1042. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2017.01030 QIN D L, WANG S L, LIU Y H, et al. Effects of cotton stalk returning on soil physical and chemical properties and cotton yield in coastal saline-alkali soil [J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2017, 43(7): 1030−1042.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2017.01030
[14] 刘禹晴. 吉林西部盐碱地区稻田土壤有机碳矿化特征和动力学模拟研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2019. LIU Y Q. Study of characteristics of soil organic carbon mineralization in saline-alkali paddy fields and dynamic simulation in western Jilin province[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2019.(in Chinese)
[15] 李娜, 汤洁, 张楠, 等. 冻融作用对水田土壤有机碳和土壤酶活性的影响 [J]. 环境科学与技术, 2015, 38(10):1−6. LI N, TANG J, ZHANG N, et al. Soil organic carbon and its relationship with enzyme during freezing-thawing-cyclesin paddy soil [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 38(10): 1−6.(in Chinese)
[16] 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000: 25–96. [17] 关松荫. 土壤酶及其研究法[M]. 北京: 农业出版社1986. [18] 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 1999: 106–110. [19] 王义祥, 叶菁, 王成己, 等. 不同经营年限对柑橘果园土壤有机碳及其组分的影响 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2014, 23(10):1574−1580. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.10.002 WANG Y X, YE J, WANG C J, et al. Effect of different cultivation years on soil organic carbon pools in citrus orchards [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2014, 23(10): 1574−1580.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.10.002
[20] 张晗, 欧阳真程, 赵小敏, 等. 江西省不同农田利用方式对土壤碳、氮和碳氮比的影响 [J]. 环境科学报, 2018, 38(6):2486−2497. ZHANG H, OUYANG Z C, ZHAO X M, et al. Effects of different land use types on soil organic carbon, nitrogen and ratio of carbon to nitrogen in the plow layer of farmland soil in Jiangxi Province [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(6): 2486−2497.(in Chinese)
[21] 张晓东, 李忠, 张峰. 新疆艾比湖地区不同土地利用类型土壤养分及活性有机碳组分研究 [J]. 水土保持研究, 2017, 24(5):55−62. ZHANG X D, LI Z, ZHANG F. Variation of soil nutrients and soil active organic carbon under different land use patterns in Aibinur Lake region of Xinjiang [J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 24(5): 55−62.(in Chinese)
[22] 魏鸿鹏, 李志刚, 张蕾, 等. 土地利用方式对土壤有机碳与易氧化碳的影响 [J]. 内蒙古民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 32(3):226−232. WEI H P, LI Z G, ZHANG L, et al. Effects of land use types on soil organic carbon and readily oxidizable carbon [J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia University for Nationalities(Natural Sciences), 2017, 32(3): 226−232.(in Chinese)
[23] 王燕, 包翔, 王明玖, 等. 科尔沁沙地不同草地利用方式下土壤粒度和有机碳分布特征 [J]. 水土保持通报, 2019, 39(6):84−89, 97. WANG Y, BAO X, WANG M J, et al. Characteristics of soil particle size and organic carbon distribution under different grassland utilization modes in Horqin sandy land [J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 39(6): 84−89, 97.(in Chinese)
[24] 李燕, 赵志忠, 吴丹, 等. 海南岛东部地区不同土地利用方式土壤有机碳的分布特征 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2018, 33(8):820−827. LI Y, ZHAO Z Z, WU D, et al. Organic carbon distribution in soils of various land-use patterns in Eastern Hainan [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 33(8): 820−827.(in Chinese)
[25] 刘骞, 汤洁, 王静静, 等. 吉林西部盐碱稻田土壤有机碳及活性组分时空分布特征 [J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2019, 49(9):44−53. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9369.2019.09.006 LIU Q, TANG J, WANG J J, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of soil organic carbon and active components in saline-alkali paddy fields in Western Jilin [J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2019, 49(9): 44−53.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9369.2019.09.006
[26] 李新爱, 肖和艾, 吴金水, 等. 喀斯特地区不同土地利用方式对土壤有机碳、全氮以及微生物生物量碳和氮的影响 [J]. 应用生态学报, 2006, 17(10):1827−1831. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2006.10.011 LI X A, XIAO H A, WU J S, et al. Effects of land use type on soil organic carbon, total nitrogen, and microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen contents in Karst region of South China [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2006, 17(10): 1827−1831.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2006.10.011
[27] 孙志高, 刘景双, 李新华. 三江平原不同土地利用方式下土壤氮库的变化特征 [J]. 农业系统科学与综合研究, 2008, 24(3):270−274. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0068.2008.03.004 SUN Z G, LIU J S, LI X H. Changes of nitrogen storage in soil under different land uses in the Sanjiang Plain [J]. System science and Comprehensive in agriculture, 2008, 24(3): 270−274.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0068.2008.03.004
[28] SCHWAGER S J, MIKHAILOVA E A. Estimating variability in soil organic carbon storage using the method of statistical differentials [J]. Soil ence, 2002, 167(3): 194−200.
[29] ABER J D, DRISCOLL C T. Effects of land use, climate variation, and N deposition on N cycling and C storage in northern hardwood forests [J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 1997, 11(4): 639−648. DOI: 10.1029/97GB01366
[30] ABER J D, OLLONGER S V, DRISCOLL C T. Modeling nitrogen saturation in forest ecosystems in response to land use and atmospheric deposition [J]. Ecological Modelling, 1997, 101(1): 61−78. DOI: 10.1016/S0304-3800(97)01953-4
[31] 田飞飞, 纪鸿飞, 王乐云, 等. 施肥类型和水热变化对农田土壤氮素矿化及可溶性有机氮动态变化的影响 [J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(10):4717−4726. TIAN F F, JI H F, WANG L Y, et al. Effects of various combinations of fertilizer, soil moisture, and temperature on nitrogen mineralization and soluble organic nitrogen in agricultural soil [J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(10): 4717−4726.(in Chinese)
[32] MANZONI S, JACKSON R B, TROFYMOW J A, et al. The global stoichiometry of litter nitrogen mineralization [J]. Science, 2008, 321: 684−686. DOI: 10.1126/science.1159792
[33] OGUTU Z A. An investigation of the influence of human disturbance on selected soil nutrients in Narok District, Kenya [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 1999, 58(1): 39−60. DOI: 10.1023/A:1006083011646
[34] 宝日玛, 峥嵘, 周梅, 等. 大兴安岭火烧迹地土壤微生物生物量及酶活性研究 [J]. 内蒙古农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 37(4):77−83. BAO R M, ZHENG R, ZHOU M, et al. Study on soil microbial biomass and enzyme activities of burned areas in great hinggan mountains. [J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University(Natural Science Edition), 2016, 37(4): 77−83.(in Chinese)
[35] 王玉琴, 尹亚丽, 李世雄. 不同退化程度高寒草甸土壤理化性质及酶活性分析 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(6):1108−1116. WANG Y Q, YIN Y L, LI S X. Physicochemical properties and enzymatic activities of alpine meadow at different degradation degrees [J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 2019, 28(6): 1108−1116.(in Chinese)
[36] 杨成德, 陈秀蓉, 龙瑞军, 等. 东祁连山高寒草地牧草返青期土壤酶活性特征 [J]. 草地学报, 2010, 18(3):308−313. YANG C D, CHEN X R, LONG R J, et al. Characteristics of soil enzymatic activity during forage green-up period of alpine grasslands in the Eastern Qilian mountain areas [J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2010, 18(3): 308−313.(in Chinese)
[37] 胡雷, 王长庭, 王根绪, 等. 三江源区不同退化演替阶段高寒草甸土壤酶活性和微生物群落结构的变化 [J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(3):8−19. DOI: 10.11686/cyxb20140302 HU L, WANG C T, WANG G X, et al. Changes in the activities of soil enzymes and microbial community structure at different degradation successional stages of alpine meadows in the headwater region of three rivers, China [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(3): 8−19.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.11686/cyxb20140302
[38] 潘琇, 王亮, 谢拾冰, 等. 温州稻田耕层土壤机械组成与理化性状的相关研究 [J]. 浙江农业科学, 2009, 1(6):1194−1197. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0528-9017.2009.06.055 PAN X, WANG L, XIE S B, et al. A study on the soil mechanical composition and physical and chemical properties of ploughing layer in Wenzhou paddy field [J]. Jouranl of ZheJiang Agricultural Science, 2009, 1(6): 1194−1197.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0528-9017.2009.06.055
[39] 孟庆英, 张春峰, 贾会彬, 等. 不同机械改土方式对白浆土物理特性及酶活性的影响 [J]. 土壤学报, 2016, 53(2):552−559. MENG Q Y, ZHANG C F, JIA H B, et al. Effects of mechanical soil amelioration method on physical properties of and enzyme activity in planosol [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2016, 53(2): 552−559.(in Chinese)
[40] 乔赵崇, 赵海超, 黄智鸿, 等. 冀北坝上不同土地利用对土壤微生物量碳氮磷及酶活性的影响 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(3):498−505. QIAO Z C, ZHAO H C, HUANG Z H, et al. Effects of different land uses on soil microbial biomass, carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and enzyme activities in the plateau of north Hebei [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(3): 498−505.(in Chinese)
[41] JORGE P F, CARMEN T C, MARIA C L, et al. Intra-annual variation in biochemical properties and the biochemical equilibrium of different grassland soils under contrasting management and climate [J]. Biology & Fertility of Soils, 2011, 47(6): 633−645.
[42] 万忠梅, 宋长春. 三江平原小叶章湿地土壤酶活性的季节动态 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2010, 19(5):1215−1220. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2010.05.040 WAN Z M, SONG C C. Seasonal dynamics of soil enzyme activity in Xiaoyezhang wetland in Sanjiang plain [J]. Journal of Ecological Environment, 2010, 19(5): 1215−1220.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2010.05.040
[43] GIANFREDA L, RAO M A, PIOTROWSKA A, et al. Soil enzyme activities as affected by anthropogenic alterations: intensive agricultural practices and organic pollution [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2005, 341(1-3): 265−279. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.10.005
[44] BATRA L, MANNA M C. Dehydrogenase activity and microbial biomass carbon in salt-affected soils of semiarid and arid regions [J]. Arid Soil Research and Rehabilitation, 1997, 11: 295−303. DOI: 10.1080/15324989709381481
[45] FRANKENBERGER W T, BINGHAM F T. Influence of salinity on soil enzyme activities [J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1982, 46: 1173−1177. DOI: 10.2136/sssaj1982.03615995004600060011x
[46] 宁川川, 王建武, 蔡昆争, 等. 有机肥对土壤肥力和土壤环境质量的影响研究进展 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2016, 25(1):175−181. NING C C, WANG J W, CAI K Z, et al. The effects of organic fertilizers on soil fertility and soil environmental quality: A review [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2016, 25(1): 175−181.(in Chinese)
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 李志娟,肖宇童,吕佳霖,徐琪,董雄德. 不同土地利用方式对黄河(河南段)桃花峪滩区土壤酶活性的影响. 湿地科学. 2024(06): 922-929 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 马子钰,马文林. 秸秆还田对中国农田土壤固碳效应影响的研究. 土壤. 2023(01): 205-210 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王敬宽,吕鹏超,张楷悦,高枫舒,张强,柳新伟. 不同土地利用方式对盐碱地土壤团聚体及碳氮含量的影响. 山东农业科学. 2023(10): 86-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 贾雪莹,王佩将,田志杰,银海杏,贾文茹. 不同土地利用类型盐碱土无机磷组分及其影响因素. 生态学杂志. 2023(12): 2972-2978 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 袁佳宝,宋艳宇,刘桢迪,朱梦圆,程小峰,马秀艳,陈宁,李晓宇. 松嫩平原芦苇湿地土壤酶活性剖面分布特征及其微生物养分限制指示作用. 生态环境学报. 2023(12): 2141-2153 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 傅庆林,朱芸,郭彬,刘琛,林义成,裘高扬,李华. 稻麦轮作对滨海盐土土壤肥力的影响. 浙江农业科学. 2022(06): 1135-1138 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 梁启斌,李瑞琳,李佳琛,侯磊,王艳霞. 洱海罗时江小流域林地—农田—河岸带土壤碳氮磷化学计量特征. 西南农业学报. 2022(11): 2587-2594 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 史永亮,蒋桂欣. 不同农业土地利用方式对土壤有机碳和全氮的分布影响. 江西农业学报. 2022(12): 101-106 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)




 下载:
下载: