Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Community of Soil and Crop Yield under Rice-Tobacco-Milk Vetch Rotation Cropping
-
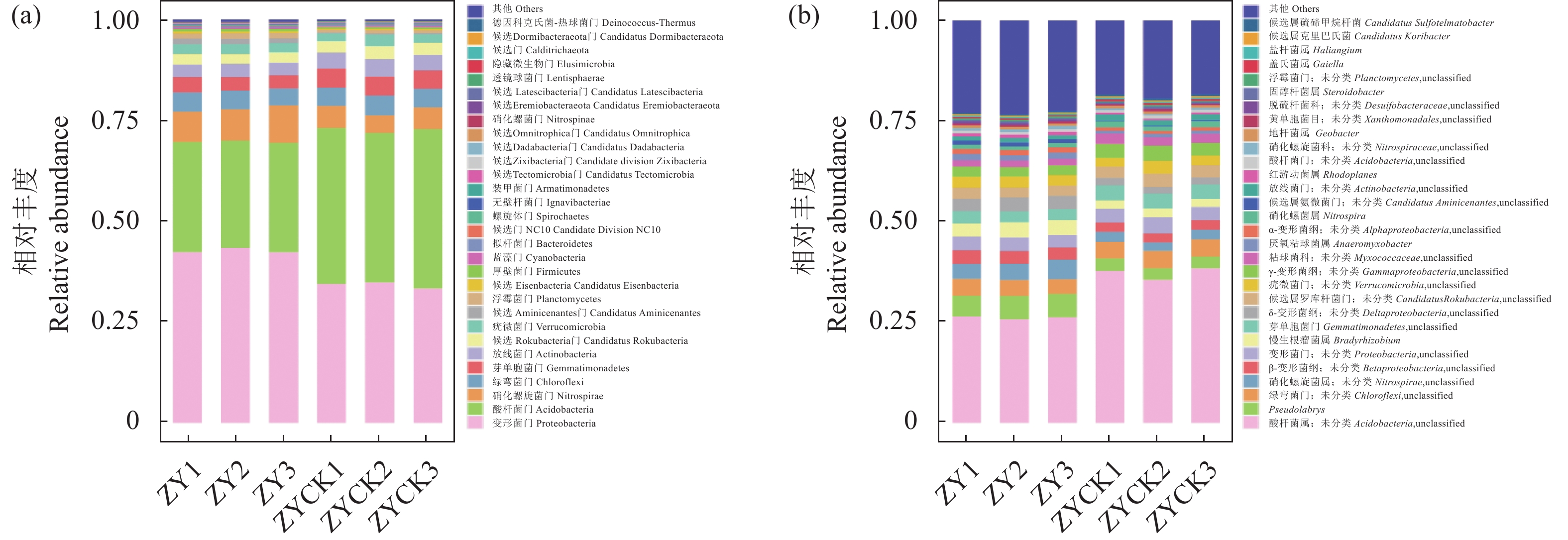
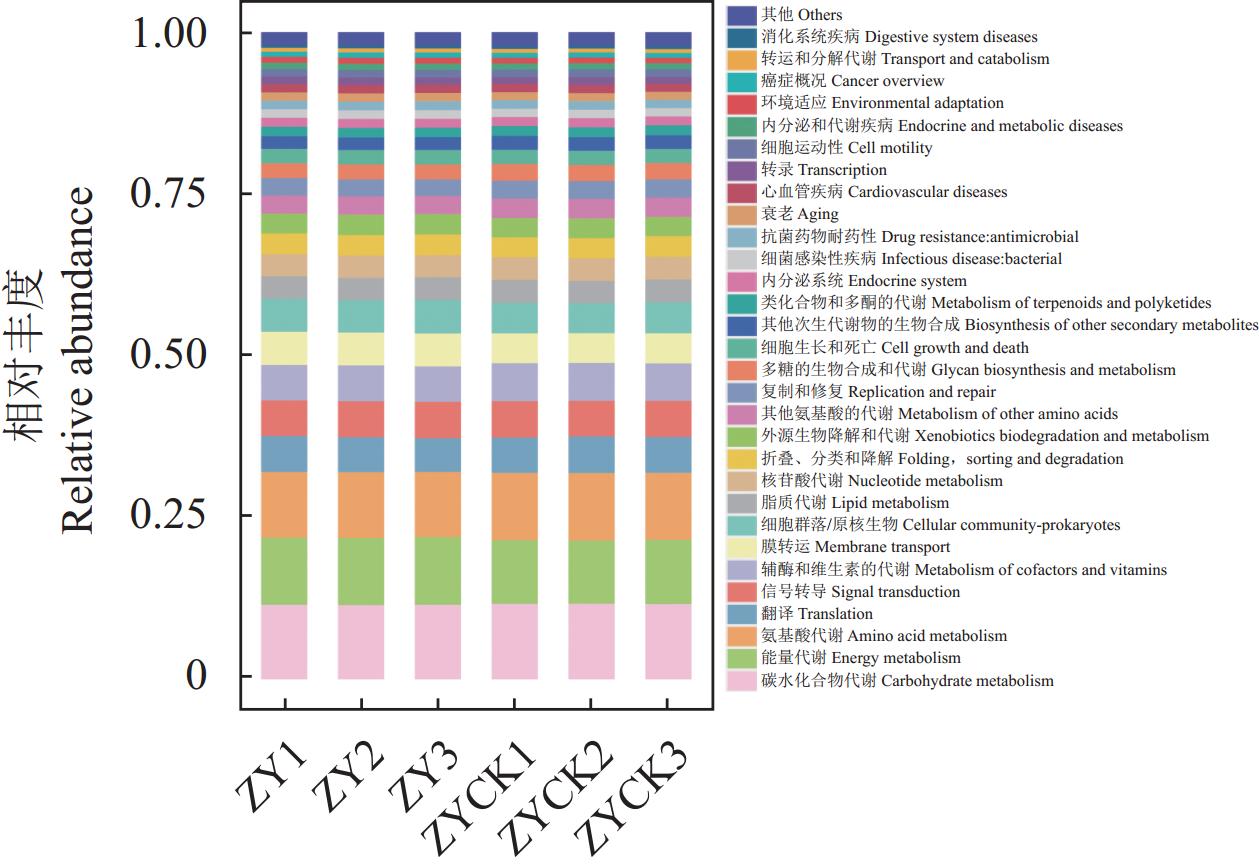
摘要:目的 研究烤烟-水稻-紫云英轮作模式下土壤理化性质和微生物群落结构组成变化,揭示紫云英对土壤肥力和微生物群落的影响,为紫云英的合理利用提供科学依据。方法 选取烤烟-水稻-紫云英3种植物连续轮作5年的田块土壤为处理样品,以烤烟-水稻2种作物轮作的田块土壤为对照;利用分光光度法测定土壤的常规理化性质,采用宏基因组测序等方法测定土壤微生物群落结构变化及功能预测分析。结果 在烤烟-水稻-紫云英轮作模式下,土壤有机质、全氮、全钾含量略上升,全磷含量变化不显著,速效氮、速效磷的含量显著增加,但速效钾含量明显减少;2023年烤烟、水稻年产量分别提高2.74%、4.67%;土壤微生物群落多样性明显提高,主要微生物为细菌界的变形菌门、硝化螺旋菌门和酸杆菌门微生物,与对照组相比,三者相对丰度分别上调8.67%、上调3.10%和下降11.57%;土壤微生物功能主要富集在碳水化合物代谢、能量代谢和氨基酸代谢3个通路中。结论 烤烟-水稻-紫云英轮作方式改善土壤的理化性质,提高作物产量,明确了轮作紫云英对土壤微生物物种丰富度和群落组成分布影响及其参与的主要代谢通路,为紫云英对土壤肥力和微生物群落影响的机制研究提供依据。Abstract:Objective Regulatory functions of milk vetch on soil fertility and microbial communities were studied to determine the potential of incorporating the shrub plant in rotation cropping with tobacco and rice for further land use improvement.Method Soil samples were collected from a field practicing tobacco-rice-milk vetch rotation cropping for 5 years and one of tobacco-rice as control. Physicochemical analysis on the soil using spectrophotometry and metagenomic sequencing on the microbial community were conducted.Result With milk vetch added to the tobacco-rice rotation cropping, the field soil increased significantly on the available nitrogen and phosphorus, rose slightly on the organic matter, total nitrogen, and total potassium, maintained a same level of total phosphorus, and reduced significantly on the available potassium. The yield of tobacco rose 2.74% and that of rice 4.67% in 2023. And the microbial diversity became significantly enriched by 8.67% and 3.10% but declined by 11.57% over control on the dominant kingdoms of Proteobacteria, Nitrospira, and Acidobacteria, respectively. The microbes in the soil were largely associated with carbohydrate, energy, and amino acid metabolisms.Conclusion By incorporating milk vetch in the rotation cropping of tobacco and rice, aside from the increased yields on the crops, the physiochemical properties of field soil were significantly improved as well.
-
Keywords:
- Milk vetch /
- rotation cropping /
- microorganisms /
- metagenomic /
- soil physicochemical properties
-
鸭瘟(Duck plague,DP),又名鸭病毒性肠炎(Duck viral enteritis,DVE),是由鸭瘟病毒(duck plague virus,DPV)引起的鸭、鹅、雁及其他雁形目禽类的急性、败血性、高度致死性传染病,是危害养鸭业的重要疾病之一,该病流行广泛,传播迅速,发病率和死亡率高,曾给世界各国造成巨大的经济损失[1-3]。
2015年以来,福建省不同日龄未免疫鸭瘟疫苗的番鸭群均不同程度发生疑似鸭瘟疫情,病程急、病鸭流泪、肿头、拉黄绿色稀便,剖检见肝脏肿大质脆边缘坏死、肠黏膜及淋巴环出血、食道和泄殖腔出血等,为明确其病原并采取有效控制措施减少损失,本课题组采集60~120日龄疑似鸭瘟病死番鸭的肝脾胰等组织进行病原分离,应用单抗间接免疫荧光抗体技术,PCR技术和动物回归试验等鉴定,现将结果报道如下。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 禽胚及细胞
番鸭胚和番鸭均购自福州山区健康番鸭场,番鸭胚成纤维细胞(MDEF)的制备按文献[1]的方法进行。
1.2 单克隆抗体及试剂盒
抗鹅细小病毒(GPV)单抗、抗雏番鸭细小病毒(MPV)单抗、抗鸭呼肠孤病毒(MDRV)单抗、抗鸭源副粘病毒(DPMV)和禽坦布苏病毒(TUMV)单抗等均为本课题组制备并保存;鸭瘟病毒荧光PCR检测试剂盒购于北京生科尚仪科技有限公司。
1.3 病料来源及处理
取疑似病死番鸭的肝、脾、胰腺等组织,剪碎研磨,以Hank′s液制成1:5匀浆,加双抗各1 000 U,4℃过夜,低温冻融3次,7 000 r·min-1离心10 min,将上清液经直径为0.22 μm的微孔滤膜过滤,收集滤液供病毒分离和核酸抽提用。
1.4 病毒分离
取长成单层的MDEF细胞,弃去营养液,接种上述病料滤液,37℃吸附1 h,倾去吸附液,以灭菌Hank′s冲洗3次后,加足量维持液(0.5%HL-2%小牛血清)。并设置未接种病料的细胞对照组,37℃继续培养,逐日观察细胞病变至7 d,置-20℃冻融3次,收获细胞。如上反复传代,观察病变情况。
1.5 病毒鉴定
1.5.1 血凝特性(HA)测定
按殷震法[1]进行,在37℃、pH 7.2的PBS缓冲液中测定分离毒对鸡、鸽红细胞的血凝性。
1.5.2 间接免疫荧光试验(IFA)鉴定
(1) 冰冻切片制备:取临床自然病鸭或人工感染病死鸭肝、脾、胰腺等组织在冰冻切片机中切成6 μm厚的薄片,冷丙酮固定15 min,晾干备用。
(2) 感染病毒的细胞板制备:将分离毒DP1d3适当稀释后接种于已成长单层的MDEF 96孔细胞培养板,于37℃、6%CO2培养,当细胞病变达30%时,弃去培养液,甩干。每孔加100 μL甲醇(预置-20℃)于4℃固定30 min,弃甲醇,用0.85%生理盐水洗涤3次,每孔100 μL, 每次5 min,甩干,置-20℃保存供IFA试验。
(3) IFA染色及观察:取上述冰冻切片或感染病毒的细胞板,按常规方法[4]分别以抗GPV、MPV、DRV、DPMV和TUMV单抗为一抗、羊抗鼠IgG-FITC为二抗进行间接荧光抗体试验检测,置荧光显微镜下观察,以出现亮绿色特异性荧光判为阳性。
1.5.3 荧光定量PCR鉴定
4份第3代细胞分离毒(DPVfj1、DPVfj2、DPVfj3、DPVfj4) 用DNA提取试剂盒提取病毒核酸,按照鸭瘟病毒荧光PCR检测试剂盒说明书操作,在实时荧光定量PCR仪(eppendorf公司)进行检测。并设阴阳性对照。
1.5.4 PCR及产物序列鉴定
第3代细胞毒(DP1d3) 提取核酸。根据已发表的鸭瘟病毒(JQ673560) gJ蛋白基因序列,设计了如下引物:gJ1:5′-atgtatacag acgttacggtc-3′,gJ2:5′-tcatac catacaaaggcatag-3′。利用TAKARA公司试剂进行PCR扩增,将回收的PCR产物与pMD-18T载体连接后转化到感受态细胞,进行重组质粒的筛选。鉴定后的重组质粒由TAKARA公司进行序列测定,应用分析软件对gJ基因进行分析和比较。
1.5.5 动物回归试验
30日龄健康雏番鸭15羽随机分为2组,其中健康对照组5羽,每羽腿肌注射正常MDEF细胞0.1 mL;攻毒组10羽,每羽腿部肌肉注射第3代细胞培养毒(DP1d3)0.1 mL。隔离饲养,每天观察并记录试验鸭发病和死亡情况,并从病死鸭中分离病毒。
1.5.6 番鸭同居感染试验
在1.5.2动物回归试验中,当攻毒组人工感染后第4 d出现死亡鸭时,移入10羽5日龄健康番鸭与攻毒组鸭同居饲养,每天观察并记录试验鸭发病和死亡情况,并从病死鸭中分离回收病毒。
1.5.7 病毒对鹅的致病性试验
将DP1d3经口服和腿部肌肉注射途径人工感染17日龄健康雏鹅6羽,0.8 mL·羽-1,每天观察并记录感染鹅发病和死亡情况,并从病死鹅中分离病毒。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 病毒分离结果
6份65~120日龄疑似病死番鸭肝脾组织匀浆上清,接种MDEF单层细胞培养并盲传至第3代,其中4份出现细胞病变,表现为局灶性细胞圆缩、随后病变范围逐渐扩大并脱落,部分细胞融合形成巨融合细胞(图 1)。随着传代代次增加,出现病变的时间亦随之缩短。暂将这4株病毒命名为DPVfj1、DPVfj2、DPVfj3、DPVfj4。
2.2 病毒鉴定结果
2.2.1 血凝性测定结果
血凝试验显示分离毒不能凝集鸡、鸽红细胞,提示分离毒无血凝特性。
2.2.2 IFA试验
人工病死番鸭肝、脾、胰腺等组织的冰冻切片和感染病毒的细胞板分别经抗GPV、MPV、MDRV、DPMV和TUMV单抗的IFA,均未出现特异性荧光,结果均为阴性。
2.2.3 荧光定量PCR鉴定结果
4份分离毒应用鸭瘟病毒荧光PCR检测试剂盒进行鉴定,扩增曲线如图 2所示,分离毒DPVfj1、DPVfj2、DPVfj3、DPVfj4、阳性对照、阴性对照CT值分别为19.32、19.45、24.9、22.8、21.71、none,判定4份分离毒均为鸭瘟病毒核酸阳性。
2.2.4 PCR及产物序列鉴定结果
对PCR产物的阳性重组质粒进行正、反向测序,得到长度为1 173 bp鸭瘟病毒gJ基因部分序列。经BLAST分析,该序列与多株鸭瘟病毒gJ蛋白基因序列(KJ549663、KF693236、JQ673560、KF487736、JQ647509、EU082088、FJ222443、JF999965、KF263690) 相似度均大于99%(图 3)。PCR产物序列进一步证实分离毒为鸭瘟病毒。
2.2.5 动物回归试验结果
人工感染组番鸭于接种分离毒后3 d出现精神沉郁,食欲废绝,渴欲增加,行走迟缓、喜卧等症状,第4 d出现死亡,10羽番鸭死亡6羽,第5 d接种鸭全部死亡,发病率和死亡率均为100%。剖检病死鸭出现与临床自然感染一致的病变,肝脏略肿大质脆出血、脾脏略肿大呈瘀黑色,特征性病变表现为肠黏膜出血环及出血点和泄殖腔出血点(图 4),并从病死鸭肝脾匀浆中分离到病毒。动物回归试验表明分离毒是该病的病原。
2.2.6 番鸭同居感染试验结果
5日龄番鸭与病鸭同居后第4 d开始发病,第6 d出现死亡,至第8 d 10羽番鸭死亡3羽,继续观察到25 d,发病率和死亡率均为30%,并从病死鸭肝脾匀浆中分离到病毒。同居感染试验结果表明直接接触是该病传播途径之一。
2.2.7 对鹅的致病性试验结果
17日龄健康雏鹅以细胞毒原液DP1d3(0.8 mL·羽-1)经口服和肌注途径人工感染后,每天观察至28 d,结果人工感染鹅未出现临床症状且生长发育良好,初步表明该分离毒对鹅不易感,无致病性。
3. 讨论
鸭瘟由Baudet于1923年首次在荷兰发现,随后陆续在许多养鸭国家暴发和流行[1-4]。该病病原是鸭瘟病毒,属疱疹病毒科a疱疹病毒亚科,核酸为线状双股DNA。在我国该病多见于成年种鸭和蛋鸭,其临床特征性症状是流泪,眼睑肿胀,两脚发软不能站立,下痢,头颈部肿大,俗称“大头瘟”,剖检可见食道和泄殖腔黏膜出血并伴有黄褐色假膜覆盖[4]。至今全国各地均有鸭瘟流行的报道,鸭瘟仍然是目前阻碍我国养鸭业发展的重要传染病之一[5-10]。
本研究应用MDEF从疑似鸭瘟病毒自然感染病死番鸭中分离到病毒,分离毒无血凝活性,能致MDEF产生细胞病变,经荧光定量PCR、gJ蛋白基因PCR及其产物序列测定均证实分离毒属于鸭瘟病毒,人工感染对鹅不易感,无致病性;对雏番鸭具有很强的致病性,发病率和死亡率均高达100%,动物回归能复制出与自然感染一致的病症,并能回收到病毒。提示该分离毒为鸭瘟病毒强毒株,但其全基因序列还有待进一步测定。
由于我省有十多年未发生鸭瘟疫情,养殖企业也不同程度忽视了鸭瘟疫苗免疫。然而2015年以来,我省不同日龄不同品种未免疫鸭瘟疫苗的鸭群均不同程度发生该病,发病率和病死率高,给养鸭业敲响了警钟。建议在加强日常饲养管理和生物安全措施的同时,应对鸭瘟疫苗的免疫予以足够重视,可根据疫区流行情况适当调整免疫程序(如疫源地在10日龄首免、间隔20 d加强免疫1次)。
-
表 1 2019—2023年试验田轮作方式
Table 1 Rotation cropping practiced at experimentation field from 2019 to 2023
年份
YearZY组
ZY GroupZYCK组
ZYCK Group2019 烤烟-水稻-紫云英 烤烟-水稻-休耕 2020 水稻-紫云英 水稻-休耕 2021 烤烟-水稻-紫云英 烤烟-水稻-休耕 2022 水稻-紫云英 水稻-休耕 2023 烤烟-水稻-紫云英 烤烟-水稻-休耕 表 2 土壤理化性质检测结果
Table 2 Physicochemical properties of soil
组别
GrouppH值
pH value有机质
Organic
matter/
(g·kg−1)全氮
Total
nitrogen/
(g·kg−1)全磷
Total
phosphorus/
(g·kg−1)全钾
Total
potassium/
(g·kg−1)速效氮
Available
nitrogen/
(mg·kg−1)速效磷
Available
phosphorus/
(mg·kg−1)速效钾
Available
potassium/
(mg·kg−1)ZY 5.85±0.01b 49.14±0.45a 2.77±0.04a 0.49±0.05b 13.80±1.09a 196.33±2.55a 23.80±1.03a 23.80±1.03a ZYCK 5.98±0.07a 43.87±0.72b 2.43±0.04b 0.52±0.04a 11.48±0.97b 177.89±1.48b 18.69±1.29b 18.69±1.29b 同列数据后不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Data with different lowercase letters on same column indicate significant differences at P<0.05.表 3 2023年作物产量对比
Table 3 Yields of crops in 2023
轮作模式
Crop Rotation Pattern烤烟(K326)
Tobacco(K326)水稻(甬优1540)
Rice(YongYou1540)产量
Yield /(kg·hm−2)增产率
Production
increase ratio/%化肥配施
Fertilizer dosage/
(kg ·hm−2)减施率
Reduction
rate/%产量
Yield /(kg·hm−2)增产率
Production
increase ratio/%化肥配施
Fertilizer dosage/
(kg ·hm−2)减施率
Reduction
rate/%烤烟-水稻-紫云英
Tobacco-Rice-Milk vetch9.00±0.18a 2.74 4 0 43.68±0.91a 4.67 4 14.35 烤烟-水稻
Tobacco-Rice8.76±0.15b — 4 — 41.73±0.47b — 4.67 — 表中每公顷作物产量为三组烟农(稻农)共60户收获作物产量的平均值。同列数据后不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著( P <0.05)。
Crop yield per hectare is averaged harvest of 3 tobacco/rice farmer groups of 60 households. Data with different lowercase letters on same column indicate significant differences at P <0.05.表 4 组装及基因预测结果
Table 4 Assembly and gene predictions
样品编号
Sample number读段
Clean reads/bpcontigs总数
Total contigs/个contigs总长
Contigs total length/bpcontigs平均长度
Contigs average length/bpN50/bp 开放阅读框ORF ZY1 41 140 450 53 533 37 145 783 693.9 653.0 71 335 ZY2 42 103 566 64 213 45 184 155 703.7 664.0 86 224 ZY3 40 249 302 61 491 43 430 673 706.3 664.0 82 535 ZYCK1 43 096 370 83 046 70 399 309 847.7 761.0 123 983 ZYCK2 39 600 220 51 862 43 618 116 841.0 765.0 76 974 ZYCK3 44 321 698 85 949 71 272 981 829.2 744.0 127 232 表 5 样品的物种丰度统计
Table 5 Statistics on microbial abundance of soils
样品编号
Sample number细菌
Bacteria/%古菌
Archaea/%真核生物
Eukaryotes/%病毒
Viruses/%未知物种
Unknown species/%ZY1 98.95 1.01 0.01 0.02 0.01 ZY2 99.02 0.95 0.01 0.02 0.01 ZY3 99.02 0.96 0.01 0.01 0.01 ZYCK1 99.39 0.58 0.01 0.01 0.01 ZYCK2 99.10 0.88 0.01 0.01 0.01 ZYCK3 99.13 0.84 0.01 0.02 0.01 表 6 土壤Alpha多样性分析结果
Table 6 Alpha diversity of soil
组别
Group香农指数
Shannon辛普森指数
Simpsoninv-辛普森指数
Inv-SimpsonZY1 5.105 0.929 13.996 ZY2 5.143 0.931 14.586 ZY3 5.089 0.928 13.980 ZYCK1 4.346 0.857 6.974 ZYCK2 4.473 0.874 7.911 ZYCK3 4.350 0.854 6.841 表 7 作物产量与微生物及土壤理化性状的相关系数
Table 7 Pearson correlation coefficients on crop yield, microbes, and soil physicochemical properties
菌种/参数
Strain/ParameterspH值
pH value有机质
Organic matter全氮
Total nitrogen全磷
Total phosphorus全钾
Total potassium速效氮
Available nitrogen速效磷
Available phosphorus速效钾
Available potassium水稻产量
Rice yield0.9556 − 0.9999* 0.6219 − 0.3675 − 0.3428 − 0.7555 − 0.9528 0.9746 烟草产量
Tobacco yield0.8665 − 0.9784 0.7799 − 0.5645 − 0.5425 − 0.5916 − 0.9964 1.0000** 变形菌门
Proteobacteria− 0.9995* 0.9602 − 0.3923 0.1081 0.0818 0.9020 0.8385 − 0.8805 酸杆菌门
Acidobacteria0.9545 − 0.8156 0.0691 0.2237 0.2494 − 0.9937 − 0.6135 0.6765 硝化菌门
Nitrospirae0.3692 − 0.6384 1.0000** − 0.9550 − 0.9469 0.0369 − 0.8337 0.7853 酸杆菌属
Acidobacterium0.9545 − 0.8529 0.1365 0.1572 0.1832 − 0.9838 − 0.6656 0.7249 Pseudolabrys − 0.4764 0.1812 0.6460 − 0.8399 − 0.8540 0.7905 − 0.1108 0.0284 硝化螺旋菌属
Nitrospirae0.2865 − 0.5686 0.9967* − 0.9773 − 0.9714 0.1243 − 0.7821 0.7281 -
[1] 唐治喜, 高菊生, 宋阿琳, 等. 用宏基因组学方法研究绿肥对水稻根际微生物磷循环功能基因的影响 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(9):1578−1590. DOI: 10.11674/zwyf.20052 TANG Z X, GAO J S, SONG A L, et al. Impact of green manure on microbial phosphorus cycling genes in rice rhizosphere as investigated by metagenomics [J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(9): 1578−1590. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11674/zwyf.20052
[2] 李科江, 张素芳, 贾文竹, 等. 半干旱区长期施肥对作物产量和土壤肥力的影响 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 1999, 5(1):21−25. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.1999.01.004 LI K J, ZHANG S F, JIA W Z, et al. Effect of long term fertilization on crop yield and soil fertility in semi arid area [J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 1999, 5(1): 21−25. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.1999.01.004
[3] 高菊生, 徐明岗, 董春华, 等. 长期稻-稻-绿肥轮作对水稻产量及土壤肥力的影响 [J]. 作物学报, 2013, 39(2):343−349. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2013.00343 GAO J S, XU M G, DONG C H, et al. Effects of long-term rice-rice-green manure cropping rotation on rice yield and soil fertility [J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2013, 39(2): 343−349. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2013.00343
[4] 叶协锋, 杨超, 李正, 等. 绿肥对植烟土壤酶活性及土壤肥力的影响 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2013, 19(2):445−454. DOI: 10.11674/zwyf.2013.0222 YE X F, YANG C, LI Z, et al. Effects of green manure in corporation on soil enzyme activities and fertility in tobacco-planting soils [J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2013, 19(2): 445−454. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11674/zwyf.2013.0222
[5] 王秀呈. 稻—稻—绿肥长期轮作对水稻土壤及根系细菌群落的影响[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2015. WANG X C. Effects of long-term rice-rice-green manure rotation on bacterial communities in rice soil and root system[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2015. (in Chinese)
[6] 方宇, 王飞, 贾宪波, 等. 绿肥配施减量化肥对土壤固氮菌群落的影响 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(9):1933−1941. DOI: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0509 FANG Y, WANG F, JIA X B, et al. Effect of green manure and reduced chemical fertilizer load on the community of soil nitrogen-fixing bacteria [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(9): 1933−1941. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0509
[7] 林多胡, 顾荣申. 中国紫云英[M]. 福州: 福建科学技术出版社, 2000. [8] KIM D J, CHUNG D S, BAI S C C, et al. Effects of soil selenium supplementation level on selenium contents of green tea leaves and milk vetch [J]. Preventive Nutrition and Food Science, 2007, 12(1): 35−39. DOI: 10.3746/jfn.2007.12.1.035
[9] ASAGI N, UENO H. Nitrogen dynamics in paddy soil applied with various 15N-labelled green manures [J]. Plant and Soil, 2009, 322(1): 251−262.
[10] 周影, 魏启舜, 管永祥, 等. 播种量对晚播紫云英生长及养分积累的效应 [J]. 土壤, 2020, 52(3):482−486. ZHOU Y, WEI Q S, GUAN Y X, et al. Effects of different sowing rates on growth and nutrient accumulation of later-sown Chinese milk vetch [J]. Soils, 2020, 52(3): 482−486. (in Chinese)
[11] 谢志坚, 周春火, 贺亚琴, 等. 21世纪我国稻区种植紫云英的研究现状及展望 [J]. 草业学报, 2018, 27(8):185−196. DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2017360 XIE Z J, ZHOU C H, HE Y Q, et al. A review of Astragalus sinicus in paddy fields in South China since 2000s [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2018, 27(8): 185−196. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2017360
[12] 黄晶, 刘淑军, 张会民, 等. 水稻产量对双季稻-不同冬绿肥轮作及环境的响应 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2016, 25(8):1271−1276. HUANG J, LIU S J, ZHANG H M, et al. The response of rice yields on long-term double cropping rice with different winter green manure rotation and environment [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2016, 25(8): 1271−1276. (in Chinese)
[13] XIE Z J, TU S X, SHAH F, et al. Substitution of fertilizer-N by green manure improves the sustainability of yield in double-rice cropping system in South China [J]. Field Crops Research, 2016, 188: 142−149. DOI: 10.1016/j.fcr.2016.01.006
[14] 谢志坚, 涂书新, 徐昌旭, 等. 紫云英还田对单季稻田氨挥发的影响 [J]. 核农学报, 2017, 31(8):1576−1584. DOI: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2017.08.1576 XIE Z J, TU S X, XU C X, et al. Effects of Chinese milk vetch on ammonia volatilization from single season rice fields in South China [J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 31(8): 1576−1584. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2017.08.1576
[15] 马守田, 冯荣成, 张黛静, 等. 有机物料替代部分氮肥对小麦光合特性及产量的影响 [J]. 河南农业科学, 2015, 44(2):48−51. MA S T, FENG R C, ZHANG D J, et al. Effects of replacing part of nitrogen fertilizer by organic materials on photosynthetic traits and yield of wheat [J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 44(2): 48−51. (in Chinese)
[16] 周国朋, 谢志坚, 曹卫东, 等. 稻草高茬-紫云英联合还田改善土壤肥力提高作物产量 [J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(23):157−163. DOI: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.23.020 ZHOU G P, XIE Z J, CAO W D, et al. Co-incorporation of high rice stubble and Chinese milk vetch improving soil fertility and yield of rice [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(23): 157−163. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.23.020
[17] 程会丹, 鲁艳红, 聂军, 等. 减量化肥配施紫云英对稻田土壤碳、氮的影响 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(6):1259−1270. DOI: 10.11654/jaes.2019-1356 CHENG H D, LU Y H, NIE J, et al. Effects of reducing chemical fertilizer combined with Chinese milk vetch on soil carbon and nitrogen in paddy fields [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(6): 1259−1270. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11654/jaes.2019-1356
[18] 刘小粉, 贺小思, 易柏宁, 等. 有机肥绿肥配施对水稻土有机碳组分和水稻产量的影响 [J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2020, (5):147−151. DOI: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.20045 LIU X F, HE X S, YI B N, et al. Effect of applying organic fertilizer and green manure on organic carbon fractions and rice yield in a paddy soil [J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2020(5): 147−151. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.20045
[19] 杨曾平, 高菊生, 郑圣先, 等. 长期冬种绿肥对红壤性水稻土微生物特性及酶活性的影响 [J]. 土壤, 2011, 43(4):576−583. YANG Z P, GAO J S, ZHENG S X, et al. Effects of long-term winter planting-green manure on microbial properties and enzyme activities in reddish paddy soil [J]. Soils, 2011, 43(4): 576−583. (in Chinese)
[20] 张珺穜, 曹卫东, 徐昌旭, 等. 种植利用紫云英对稻田土壤微生物及酶活性的影响 [J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2012, (1):19−25. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6257.2012.01.004 ZHANG J T, CAO W D, XU C X, et al. Effects of incorporation of milk vetch(Astragalus sinicus)on microbial populations and enzyme activities of paddy soil in Jiangxi [J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2012(1): 19−25. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6257.2012.01.004
[21] 肖嫩群, 张洪霞, 成壮, 等. 紫云英还田量对烟田土壤微生物及酶的影响 [J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2010, 18(4):711−715. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2010.00711 XIAO N Q, ZHANG H X, CHENG Z, et al. Effect of incorporation of Astragalus sinicus on microbe and enzyme dynamics in tobacco cultivated soils [J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2010, 18(4): 711−715. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2010.00711
[22] FALKOWSKI P G, FENCHEL T, DELONG E F. The microbial engines that drive Earth’s biogeochemical cycles [J]. Science, 2008, 320(5879): 1034−1039. DOI: 10.1126/science.1153213
[23] 万水霞, 唐杉, 王允青, 等. 紫云英还田量对稻田土壤微生物数量及活度的影响 [J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2013, (4):39−42. WAN S X, TANG S, WANG Y Q, et al. Effect of returning quantity of Astragalus sinicus to soil on quantity and activity of microbial in paddy soil [J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2013(4): 39−42. (in Chinese)
[24] ZHANG X X, ZHANG R J, GAO J S, et al. Thirty-one years of rice-rice-green manure rotations shape the rhizosphere microbial community and enrich beneficial bacteria [J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2017, 104: 208−217. DOI: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.10.023
[25] 李增强, 张贤, 王建红, 等. 紫云英施用量对土壤活性有机碳和碳转化酶活性的影响 [J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2018, (4):14−20. DOI: 10.11838/sfsc.20180403 LI Z Q, ZHANG X, WANG J H, et al. Effects of Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L. ) application rate on soil labile organic carbon and C-transformation enzyme activities [J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2018(4): 14−20. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11838/sfsc.20180403
[26] 朱强, 张静, 郭再华, 等. 稻草和紫云英联合还田下施氮水平对水稻产量及土壤氮素形态的影响 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(12):2177−2183. DOI: 10.11674/zwyf.20384 ZHU Q, ZHANG J, GUO Z H, et al. Effects of different nitrogen inputs on rice yield and soil nitrogen forms under incorporation of rice straw and Chinese milk vetch [J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(12): 2177−2183. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11674/zwyf.20384
[27] WANG Y F, LIU X M, BUTTERLY C, et al. pH change, carbon and nitrogen mineralization in paddy soils as affected by Chinese milk vetch addition and soil water regime [J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2013, 13(4): 654−663. DOI: 10.1007/s11368-012-0645-3
[28] 童跃伟, 屈利利, 符庆响, 等. 大别山南坡森林植物群落物种多样性及其与海拔因子的关系 [J]. 生态学报, 2024, 44(12):5307−5317. TONG Y W, QU L L, FU Q X, et al. Species diversity of forest plant communities on the southern slope of the Dabie Mountains and its relationship with altitude factors [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2024, 44(12): 5307−5317. (in Chinese)
[29] 颜志雷, 方宇, 陈济琛, 等. 连年翻压紫云英对稻田土壤养分和微生物学特性的影响 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2014, 20(5):1151−1160. DOI: 10.11674/zwyf.2014.0511 YAN Z L, FANG Y, CHEN J C, et al. Effect of turning over Chinese milk vetch(Astragalus sinicus L.) on soil nutrients and microbial properties in paddy fields [J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2014, 20(5): 1151−1160. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11674/zwyf.2014.0511
[30] 聂良鹏, 郭利伟, 郑春风, 等. 种植翻压紫云英配施化肥对稻田土壤理化性状和水稻产量的影响 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(27):65−69. DOI: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2020-0767 NIE L P, GUO L W, ZHENG C F, et al. Planting and incorporation of Chinese milk vetch coupled with chemical fertilizer application: Effects on the physical and chemical characters of paddy soil and rice yield [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2021, 37(27): 65−69. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2020-0767
[31] 王慧, 周国朋, 常单娜, 等. 湘北双季稻区种植翻压紫云英的氮肥减施效应 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(1):33−44. DOI: 10.11674/zwyf.2021292 WANG H, ZHOU G P, CHANG D N, et al. Nitrogen reduction effects in double rice by planting and returning Chinese milk vetch to the field in Northern Hunan Province [J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(1): 33−44. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11674/zwyf.2021292
[32] 常单娜, 王慧, 周国朋, 等. 赣北地区稻-稻-紫云英轮作体系减施化肥对水稻产量、氮素吸收及土壤供氮能力的影响 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2023, 29(8):1449−1460. DOI: 10.11674/zwyf.2022707 CHANG D N, WANG H, ZHOU G P, et al. Yield and nitrogen uptake of rice and soil nitrogen supply capacity under fertilizer reduction in a rice-rice-Chinese milk vetch rotation system, northern Jiangxi Province, China [J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2023, 29(8): 1449−1460. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11674/zwyf.2022707
[33] 张济世, 张琳, 丁丽, 等. 紫云英还田与化肥减量配施对土壤氮素供应和水稻生长的影响 [J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(10):1793−1803. DOI: 10.11674/zwyf.2022186 ZHANG J S, ZHANG L, DING L, et al. Effects of Chinese milk vetch incorporation and chemical fertilizer reduction on soil nitrogen supply and rice growth [J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2022, 28(10): 1793−1803. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11674/zwyf.2022186
[34] 吕玉虎, 郭晓彦, 李本银, 等. 翻压不同量紫云英配施减量化肥对土壤肥力和水稻产量的影响 [J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2017, (5):94−98. DOI: 10.11838/sfsc.20170516 LÜ Y H, GUO X Y, LI B Y, et al. Effects of the incorporation of various amounts of Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L. ) and reducing chemical fertilizer on soil fertility and rice yield [J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2017(5): 94−98. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11838/sfsc.20170516
[35] 何春梅, 钟少杰, 严建辉, 等. 紫云英翻压对葡萄产量品质与果园土壤理化性状及微生物量的影响 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2018, 33(11):1151−1157. HE C M, ZHONG S J, YAN J H, et al. Effect of Chinese milk vetch(Astragalus sinicus L. ) as a green manure on grape productivity and quality, nutrient contents, and microbiologic properties of vineyard soils [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 33(11): 1151−1157. (in Chinese)
[36] 林文星, 马鹏生, 王芳, 等. 基于宏基因组学研究分析农药对宁夏枸杞地微生物的影响 [J]. 北方园艺, 2023, (1):98−105. LIN W X, MA P S, WANG F, et al. Analysis of the effects of pesticides on microbial diversity of Lycium chinense l. in Ningxia based on macrogenomics [J]. Northern Horticulture, 2023(1): 98−105. (in Chinese)
[37] PHILIPPOT L, RAAIJMAKERS J M, LEMANCEAU P, et al. Going back to the roots: The microbial ecology of the rhizosphere [J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2013, 11(11): 789−799. DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro3109
[38] 刘进, 冀瑞卿, 李冠霖, 等. 红松和蒙古栎菌根系变形菌门细菌的群落多样性[J/OL]. 吉林农业大学学报, 2023: 1−9. LIU J, JI R Q, LI G L, et al. Diversity of Proteobacteria in the ectomycorrhizosphere of Pinus koraiensis and Quercus mongolica[J/OL]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2023: 1−9. (in Chinese)
[39] 钟珍梅. 圆叶决明对果园红壤可溶性氮及细菌群落动态变化的影响[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2019. ZHONG Z M. Effects of Cassia rotundifolia on the dynamic changes of soluble nitrogen and bacterial community in red soil of orchard[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2019. (in Chinese)
[40] 赵峥, 朱元宏, 周德平, 等. 不同轮作模式对稻田土壤肥力和微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2024,43(4): 874−885. ZHAO Z, ZHU Y H, ZHOU D P, et al. Effects of different rotation patterns on soil fertility and microbial community composition in a paddy field system[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2024, 43(4): : 874−885. (in Chinese)
[41] 王新月. 磷石膏污染农田土壤中镉、氟和磷的交互作用研究[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2022. WANG X Y. Study on the interaction of cadmium, fluorine and phosphorus in agricultural soil polluted by phosphogypsum[D]. Yaan: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2022. (in Chinese)
[42] 万水霞, 朱宏斌, 唐杉, 等. 紫云英与化肥配施对稻田土壤养分和微生物学特性的影响 [J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2015, (3):79−83. DOI: 10.11838/sfsc.20150314 WAN S X, ZHU H B, TANG S, et al. Effects of Astragalus sinicus manure and fertilizer combined application on soil nutrient and microbiological characteristics [J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2015(3): 79−83. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11838/sfsc.20150314
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 廖素凤,罗进凤,兰孜怡,黄婷婷,熊钒,杨志坚,许明,郑金贵. 基于UPLC-MS/MS的豆瓣菜酚酸类组分分析. 天然产物研究与开发. 2024(11): 1874-1888 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张今君,夏慧丽,方如意. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定红美人中8种酚酸化合物. 食品研究与开发. 2022(09): 169-175 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 卢专,黄永桥,于以竹,毛敏霞,简银池,吴新文. UPLC-MS/MS分析绿茶中12种酚酸类物质. 食品安全导刊. 2022(15): 53-56+61 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 姚娜,黄燕明,汪静,李雪银,陈桂生,王斌,康志英. 麸炒白术配方颗粒HPLC指纹图谱研究. 亚太传统医药. 2020(12): 78-83 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载: