Characteristics of Microbial Community in Rhizosphere Soil of Mangrove Forest Under Freshwater Stress
-
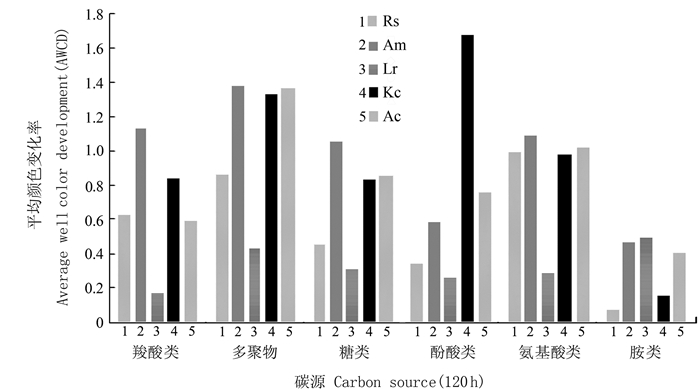
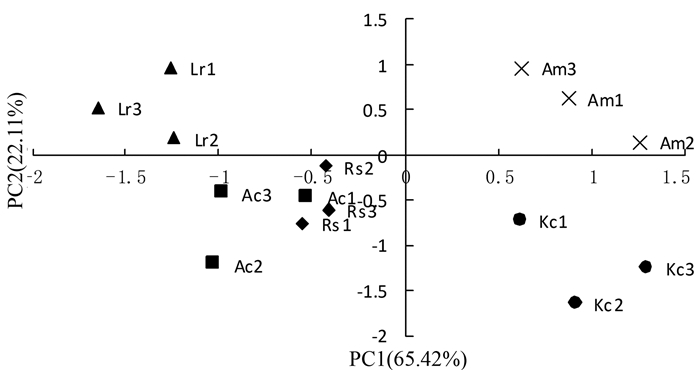
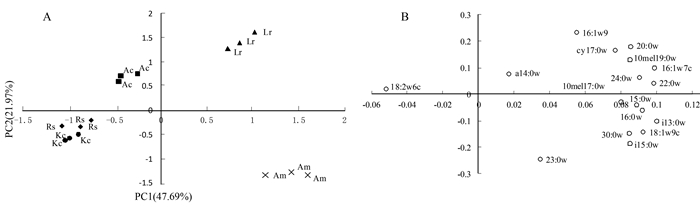
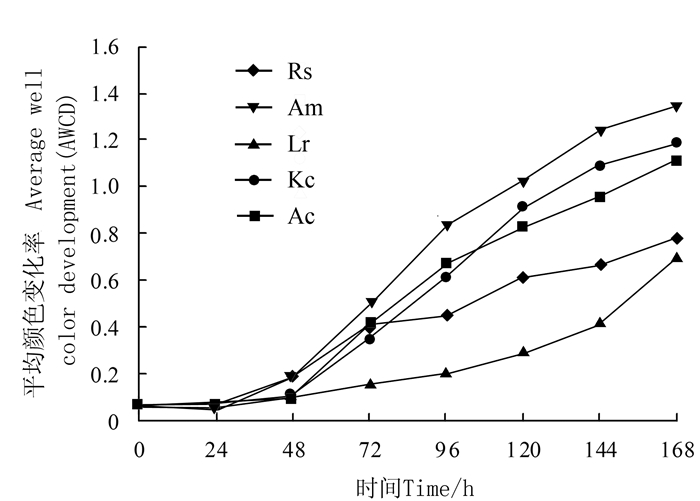
摘要:目的 探讨红树植物在淡水环境中土壤微生态变化,评价红树植物适应性,为红树林在淡水区域引种和推广提供理论基础。方法 采用Biolog-ECO微平板技术和磷脂脂肪酸标记法(PLFA),探讨淡水驯化条件下红海榄(Rs)、白骨壤(Am)、拉关木(Lr)、秋茄(Kc)、桐花树(Ac)5种不同红树植物根际土壤微生物群落结构特征,揭示红树林根际土壤微生物群落结构对淡水胁迫的响应规律。结果 研究结果表明:5种红树植物土壤理化性质差异显著;代表微生物整体代谢活性的平均颜色变化率(AWCD)由高到低顺序为Am > Kc > Ac > Rs > Lr,Am土壤微生物代谢活性最强;5种红树植物根际土壤微生物利用碳源类型最多为多聚物;而采用PLFA分析微生物群落结构,5种红树植物共检测到17种PLFA生物标记,16:0含量最高,Am土壤总PLFA含量显著高于其他4种红树植物;土壤特征微生物分布量最大是细菌;主成分分析表明Lr、Am位于同一主成分,与Biolog研究结果类似。结论 淡水驯化条件下红树植物土壤质量明显优于无红树林裸滩(CK),5种红树植物根际土壤微生物群落结构存在差异,多聚物是根际土壤微生物的主要利用碳源。表征细菌的生物标记含量最多,在根际土壤微生物中起主导作用的依然是细菌。Abstract:Objective In order to provide a theoretical basis for the introduction and promotion of mangroves in freshwater areas, we explored the micro-ecological changes and adaptability of mangrove plants in freshwater environments.Method To explore the microbial community structure characteristics of rhizosphere soil of 5 different mangrove plants, including Rhizophora stylosa(Rs), Avicennia marina(Am), Laguncularia racemose(Lr), Kandelia candel(Kc) and Aegiceras corniculatum(Ac), we performed the study by using Biolog-ECO micro plate (BIOLOG) and phospholipid fatty acid (PLFA) for revealing the response of microbial community structure to freshwater stress.Result The results showed that the soil physical and chemical properties were significantly different among 5 mangrove plants. The average well color development (AWCD) values from high to low were as follows:Am > Kc > Ac > Rs > Lr, and value of Am was the highest among 5 treatments. Ploymers was the most utilized carbon source. The PLFAs analysis was performed to explore the changes in the abundance of soil microbes. The results showed that a total of 17 kinds of PLFA were detected in 5 mangrove plants, and the highest content of PLFAs was 16:0, moreover, the total PLFAs content of Am was significantly higher than the other plants; the group-specific PLFAs in 5 soil samples showed the same trend that content of bacteria reached the maximum. Principal component analysis showed that Lr and Am soils distributed in the same principal component, which was similar to the results of BIOLOG.Conclusion The results indicated that soil of 5 plants was significantly better than unplanted mangrove soil (CK). The microbial community structure of rhizosphere soil was significantly different among mangrove plants. Soil microorganisms of 5 treatments showed the highest utilization of polymers, moreover, biomarkers of bacteria showed the same trend in 5 treatments.
-
Keywords:
- mangrove forest /
- fresh water /
- soil microorganisms /
- Biolog /
- PLFA
-
-
表 1 5种红树植物基本生长状况
Table 1 Basic growth status of 5 varieties of mangrove plants
红树植物
Mangrove plant平均株高
Average plant height/m平均地径
Average ground diameter/cm树龄
Tree age/a红海缆Rhizophora stylosa 0.57 1.12 2 白骨壤Avicennia marina 1.75 1.82 2 拉关木Laguncularia racemose 1.58 1.78 2 秋茄Kandelia candel 0.36 1.70 2 桐花Aegiceras corniculatum 0.77 1.28 2 表 2 不同红树植物土壤理化性质
Table 2 Physiochemical properties of soils planted with different mangrove plants
红树植物
Mangrove plant土壤
pHSoil pH全氮
Total nitrogen
/(g·kg-1)全磷
Total phosphorus
/(g·kg-1)全钾
Total potassium
/(g·kg-1)速效钾
Available potassium
/(mg·kg-1)速效磷
Available phosphorus
/(mg·kg-1)碱解氮
Available nitrogen
/(mg·kg-1)Rs 4.86±0.01d 2.18±0.07cd 0.13±0.01d 1.05±0.02b 138.50±3.19d 2.41±0.18bc 20.53±2.83b Am 5.09±0.03b 2.51±0.02bc 0.13±0.01d 1.02±0.02b 171.48±2.40c 2.37±0.09c 32.43±1.46a Lr 5.09±0.02b 2.65±0.17b 0.15±0.003c 1.03±0.02b 244.70±2.28b 2.46±0.01bc 34.53±4.66a Kc 5.05±0.03b 2.13±0.07cd 0.17±0.002b 1.14±0.02a 245.31±64.72b 3.14±0.24a 16.80±1.85b Ac 5.00±0.02c 3.75±0.49a 0.18±0.004a 0.93±0.11c 382.69±7.56a 2.65±0.07b 35.23±4.45a CK 6.12±0.03a 2.11±0.04d 0.05±0.001e 0.62±0.01d 106.72±14.70d 1.18±0.15d 8.63±1.07c 注:同列数据后不同字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05),表 3、6同。
Note: Different letters after the same column of data indicate significant difference (P < 0.05), the same as table 3 and 6.表 3 不同红树植物根际土壤微生物群落多样性指数
Table 3 Microbial diversity indices of rhizosphere soils of different mangrove plants
红树植物
Mangrove plantSimpson指数
Simpson indexShannon-wiener指数
Shannon-wiener index均匀度指数
Pielou indexBrillouin指数
Brillouin indexMcIntosh指数
McIntosh indexRs 0.97±0.004b 3.97±0.07cd 0.80±0.01cd 2.75±0.04b 1.00±0.02b Am 0.98±0.003ab 4.57±0.11a 0.92±0.02a 3.55±0.17a 0.99±0.03b Lr 1.00±0.01a 3.76±0.17d 0.76±0.03d 2.11±0.28c 1.09±0.03a Kc 0.97±0.003b 4.19±0.29bc 0.85±0.06bc 3.09±0.48ab 0.96±0.04ab Ac 0.99±0.02ab 4.41±0.09ab 0.89±0.02ab 3.29±0.13a 0.96±0.05ab 表 4 不同红树植物根际土壤微生物各PLFA种类及含量
Table 4 Types and contents of PLFAs in rhizosphere soils of different mangrove plants
序号
No.生物标记
Biomarkers微生物类型
Microbial group红树植物Different mangrove plants/(μg·g-1) Rs Am Lr Kc Ac 1 a14:0w 革兰氏阳性细菌G+ 7.31a 4.26b 4.08b 0 2.40c 2 i13:0w 革兰氏阳性细菌G+ 3.53c 10.61a 8.03b 8.15b 4.85c 3 i15:0w 革兰氏阳性细菌G+ 0 15.31a 0 0 2.28b 4 16:1w7c 革兰氏阴性细菌G- 8.00c 12.94a 12.65a 7.37c 11.49b 5 16:1w9 革兰氏阴性细菌G- 9.32c 13.19bc 23.12a 14.49b 0 6 cy17:0w 革兰氏阴性细菌G- 0 3.91b 4.25a 3.01c 4.10ab 7 10mel17:0w 放线菌actinomycete 5.38b 7.08a 5.34b 2.88c 6.03ab 8 10mel19:0w 放线菌actinomycete 7.52bc 9.91ab 11.37a 4.67d 6.28cd 9 15:0 细菌bacteria 9.71bc 4.20d 14.50a 11.67b 7.71c 10 16:0 细菌bacteria 32.11cd 47.93a 42.96b 36.48c 28.31d 11 20:0 细菌bacteria 2.99b 0 0 0 5.97a 12 22:0 细菌bacteria 5.68b 10.53a 3.88c 4.50bc 4.06c 13 23:0 细菌bacteria 4.87b 9.70a 0 5.09b 0 14 30:0 细菌bacteria 18.41b 5.18c 7.78c 25.09a 18.10b 15 24:0 细菌bacteria 11.67c 17.50a 4.81d 6.89d 14.55b 16 18:2w6c 真菌fungi 22.51a 0 0 0 0 17 18:1w9 真菌fungi 0 28.29a 11.24b 8.67b 10.68b 注:同行数据后不同字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。表 5同。
Note: Different letters after the same line indicate significant difference (P < 0.05), the same as table 5.表 5 不同红树植物根际土壤特征微生物类群PLFA含量
Table 5 PLFA content of microbial populations in rhizosphere soils of different mangrove plants
特征微生物类群
Microbial groups不同红树植物Different mangrove plants/(μg·g-1) Rs Am Lr Kc Ac 细菌bacteria 61.56c 77.53a 69.12b 82.83a 50.35d 革兰氏阳性细菌G+ 10.85bc 30.17a 12.11b 8.15d 9.53cd 革兰氏阴性细菌G- 17.32d 30.04b 40.02a 24.87c 15.59d 真菌fungi 22.51b 28.29a 11.25c 10.68c 8.67c 放线菌actinomycete 13.11b 17.65a 16.72a 7.88b 12.30c 革兰氏阳性细菌/革兰氏阴性细菌G+/G- 0.63b 1.01a 0.31c 0.33c 0.21d 真菌/细菌fungi/bacteria 0.37a 0.37a 0.16c 0.10d 0.21b 正常饱和磷脂脂肪酸/单烯不饱和磷脂脂肪酸Ns/ms 4.24a 1.75c 1.58c 2.93b 2.94b 表 6 不同红树植物根际土壤微生物群落多样性指数
Table 6 Diversity indices of microbial communities in soils planted with different mangroves
红树植物类型
mangrove typesSimpson指数
Simpson indexShannon-wiener指数
Shannon-wiener indexPielou均匀度指数
Pielou indexBrillouin指数
Brillouin indexMcIntosh指数
McIntosh indexRs 0.89±0.003b 3.60±0.02c 0.90±0.005b 3.60±0.02c 0.67±0.005b Am 0.90±0.0005a 3.72±0.01a 0.91±0.003a 3.72±0.01a 0.69±0.0008a Lr 0.90±0.002b 3.67±0.02b 0.90±0.005b 3.67±0.02b 0.68±0.003b Kc 0.88±0.003c 3.52±0.01d 0.88±0.006c 3.52±0.02d 0.66±0.004c Ac 0.90±0.002a 3.71±0.01a 0.91±0.002a 3.71±0.01a 0.69±0.003a 表 7 红树植物土壤理化性质与PLFA标记的相关性
Table 7 Correlation between physiochemical properties and PLFA markers in rhizosphere soils of different mangrove plants
因子
Factors土壤
pHSoil pH全氮
Total nitrogen
/(g·kg-1)全磷
Total phosphorus
/(g·kg-1)全钾
Total potassium
/(g·kg-1)速效钾
Available potassium
/(mg·kg-1)速效磷
Available phosphorus
/(mg·kg-1)碱解氮
Available nitrogen
/(mg·kg-1)细菌bacteria 0.17 0.75** -0.01 0.73** -0.52* 0.35 0.79** 革兰氏阳性菌G+ 0.43 -0.20 -0.67** -0.05 -0.44 -0.47 0.27 革兰氏阴性菌G- 0.61* 0.27 -0.11 -0.31 -0.48 0.11 0.76** 真菌fungi -0.12 -0.42 -0.87** 0.06 -0.58* -0.75** -0.08 放线菌Actinomycete 0.43 -0.53* -0.68** 0.27 -0.41 -0.63* 0.14 注:*为显著相关P < 0.05;**为极显著相关P < 0.01。
Note:* Indicates the correlation is significan,P<0.05;** Indicates the correlation is highly significant,P<0.01. -
[1] 林鹏.中国红树林生态系[M].北京:科学出版社, 1997. LIN P.Mangrove Ecosystem in China[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 1997.(in Chinese)
[2] 辛琨, 颜葵, 李真, 等.海南岛红树林湿地土壤有机碳分布规律及影响因素研究[J].土壤学报, 2014(5): 1078-1086. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8642684 XIN K, YAN K, LI Z, et al.Distribution of Soil Organic Carbon and Its Influencing Factors in Mangrove Wetland of Hainan Island[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2014(5): 1078-1086.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8642684
[3] 林鹏.中国红树林湿地与生态工程的几个问题[J].中国工程科学, 2003, 5(6): 33-38. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2003.06.005 LIN P.The Characteristics of Mangrove Wetlands and Some Ecological Engineering Questions in China[J]. Chinese Engineering Science, 2003, 5(6): 33-38.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2003.06.005
[4] 张祥霖, 石盛莉, 潘根兴, 等.互花米草入侵下福建漳江口红树林湿地土壤生态化学变化[J].地球科学进展, 2008(9): 974-981. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2008.09.009 ZHANG X L, SHI S L, PAN G X, et al.Soil Ecochemical Changes of Mangrove Wetland in Minjiang Estuary of Fujian Province under the Invasion of Spartina alterniflora[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2008(9): 974-981.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2008.09.009
[5] 陈玉军, 陈文沛, 郑松发, 等.广东番禺红树林造林研究[J].生态科学, 2001, 20(z1): 25-31. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stkx200101005 CHEN Y J, CHEN W P, ZHENG S F, et al.Researches on the Mangrove Plantation in Panyu, Guangdong[J]. Ecological science, 2001, 20(z1): 25-31.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stkx200101005
[6] 杨盛昌, 陆文勋, 邹祯, 等.中国红树林湿地:分布、种类组成及其保护[J].亚热带植物科学, 2017, 46(4): 301-310. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7791.2017.04.001 YANG S C, LU W X, ZHOU Z, et al.Mangrove Wetlands: Distribution, Species Composition and Protection in China[J]. Subtropical Plant Science, 2017, 46(4): 301-310.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7791.2017.04.001
[7] 董雪, 李昆, 向洪勇, 等.淡水驯化后桐花树幼苗对人工污水的净化效果研究[J].生态科学, 2014, 33(3): 426-432. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stkx201403005 DONG X, LI K, XIANG H Y, et al.Purification effects of freshwater adapted Aegiceras corniculatum seedlings on sewage[J]. Ecological science, 2014, 33(3): 426-432.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=stkx201403005
[8] WALL D H, MOORE J C.Interactions Underground: Soil biodiversity, mutualism, and ecosystem processes[J]. Bioscience, 1999, 49(2): 109-117. DOI: 10.2307/1313536
[9] 吴林坤, 林向民, 林文雄.根系分泌物介导下植物-土壤-微生物互作关系研究进展与展望[J].植物生态学报, 2014, 38(3): 298-310. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwstxb201403009 WU L K, LIN X M, LIN W X.Advances and perspective in research on plant-soil-microbe interactions mediated by root exudates[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2014, 38(3):298-310.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwstxb201403009
[10] MUMMEY D L, STAHL P D, BUYER J S.Microbial biomarkers as an indicator of ecosystem recovery following surface mine reclamation[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2002, 21(3): 251-259. DOI: 10.1016/S0929-1393(02)00090-2
[11] LUO L, WU R, GU J D, et al.Influence of mangrove roots on microbial abundance and ecoenzyme activity in sediments of a subtropical coastal mangrove ecosystem[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2018, 132: 10-17. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0964830518303494
[12] 刘涛, 刁治民, 祁永青, 等.根际微生物及对植物生长效应的初步研究[J].青海草业, 2008, 17(4): 41-44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1445.2008.04.010 LIU T, DIAO Z M, QI Y Q, et al.The Primary Advances in Rhizosphere Microbiology[J]. Qinghai Prataculture, 2008, 17(4):41-44.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1445.2008.04.010
[13] LIU J, PENG M, LI Y.Phylogenetic diversity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria and the nifH gene from mangrove rhizosphere soil[J]. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 2012, 58(4): 531-539. DOI: 10.1139/w2012-016
[14] 徐友林, 刘敏, 黄惠琴, 等.八门湾红树林土壤可培养真菌的多样性分析[J].热带作物学报, 2013, 34(1): 181-187. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rdzwxb201301033 XU Y L, LIU M, HUANG H Q, et al.Diversity of Culturable Fungi in the Mangrove Soil in Bamen Bay[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2013, 34(1):181-187.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rdzwxb201301033
[15] 蒋莲秀, 吴越, 陈建宏, 等.6株红树林根际土壤放线菌的分离鉴定及活性测定[J].中国病原生物学杂志, 2017(6): 513-518. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgjscbfzzz201706007 JIANG L X, WU Y, CHEN J H, et al.Identification of six Actinomycetes strains isolated from mangrove rhizosphere soil and determination of their activity[J]. Journal of Pathogen Biology, 2017(6):513-518.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgjscbfzzz201706007
[16] 伍思宇, 周阳, 胡哲, 等.海南东寨港红树林土壤微生物群落结构及多样性研究[C]//第17次全国环境微生物学学术研讨会论文摘要集, 2014: 187. WU S Y, ZHOU Y, HU Z, et al.Microbial Community Structure and Diversity of Mangrove Soil in Dongzhai Harbor, Hainan Province: The 17th National Symposium on Environmental Microbiology, 2014[C]//The 17th National Symposium on Environmental Microbiology, 2014: 187.(in Chinese)
[17] 陈权.不同演替阶段红树林主要底栖生物的群落结构特征[D].北京: 中国科学院大学, 2013. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y2370097 CHEN Q.Community structure characteristics of major benthic organisms in mangroves at different successional stages[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2013.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y2370097
[18] WANG C, XU X X, QU Z, et al.Micromonospora rhizosphaerae sp.nov., isolated from mangrove rhizosphere soil[J]. International Journal of Systematic & Evolutionary Microbiology, 2011, 61(2): 320. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0222103738/
[19] ZHANG L, WANG K L, YIN Q, et al.Ruegeria kandeliae sp.nov., isolated from the rhizosphere soil of a mangrove plant Kandelia candel[J]. International Journal of Systematic & Evolutionary Microbiology, 2018, 68(8):2653. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29949499
[20] LIU J, PENG M, LI Y.Phylogenetic diversity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria and the nifH gene from mangrove rhizosphere soil[J]. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 2012, 58(4): 531-539. DOI: 10.1139/w2012-016
[21] TOMLINSON P B.The botany of mangroves[J]. Quarterly Review of Biology, 1987, 52(4): 238. DOI: 10.2307-2438597/
[22] 魏美娥, 刘永金, 罗钦, 等.5种红树植物在淡水区域引种适应性分析[J].现代农业科技, 2011(1): 242-243. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2011.01.166 WEI M E, LIU Y J, LUO Q, et al.Adaptability Analysis of 5 Mangrove Plants Introduced in Fresh Water Areas[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2011(1):242-243.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2011.01.166
[23] 贺建, 陈桂珠, 罗航.四种红树林植物的淡水驯化试验[J].生态科学, 1999, 18(3): 12-15. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8873.1999.03.003 HE J, CHEN G Z, LUO H.Preliminary Study on Taming Four Kinds of Mangrove Plants in Fresh Water[J]. Ecological Science, 1999, 18(3):12-15.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8873.1999.03.003
[24] 刁俊明, 孙卿, 陈桂珠.淡水驯化对桐花树光合生理特性的影响[J].植物研究, 2010, 30(4): 416-423. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MBZW201004008.htm DIAO J M, SUN Q, CHEN G Z.Photosynthetic Characteristics of Aegiceras comiculatum Seedlings under Fresh Water Adaptation[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2010, 30(4):416-423.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MBZW201004008.htm
[25] 刁俊明, 刘惠娜, 郑云旋, 等.淡水驯化对桐花树幼苗叶片生长生理指标的影响[J].海洋环境科学, 2010, 29(3): 364-367. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2010.03.017 DIAO J M, LIU H N, ZHENG Y X, et al.Effect of aclimation in fresh water on physilological characteristics of leaves of Aegiceras corniculatum seedlings[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2010, 29(3):364-367.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2010.03.017
[26] 刁俊明, 曾宪录, 陈桂珠.干旱胁迫对桐花树生长和生理指标的影响[J].林业科学研究, 2014, 27(3): 423-428. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykxyj201403021 DIAO J M, ZENG X L, CHEN G Z.Effects of Drought Stress on the Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Aegiceras corniculatum[J]. Forest Research, 2014, 27(3):423-428.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykxyj201403021
[27] 刁俊明, 曾宪录.光强对桐花树根系生长和根系活力的影响[J].嘉应学院学报, 2013, 31(8): 68-75. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jydxxb201308015 DIAO J M, ZENG X L.Effects of light intensity on root growth and root vigor of Aegiceras corniculatum[J]. Journal of Jiaying University, 2013, 31(8):68-75.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jydxxb201308015
[28] 任延丽.人工湿地中三种红树植物生理生态特性研究[D].广州: 华南师范大学, 2005. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10574-2005081449.htm REN Y L.Studies on eco-physiological and ecological characteristics of Three mangrove species in constructed wetland[D]. Guangzhou: South China Normal University, 2005.(in Chinese) http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10574-2005081449.htm
[29] 罗穗华.红树植物人工湿地处理生活污水的净化效应及其机理研究[D].广州: 中山大学, 2005. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10558-2005116745.htm LUO S H.Study on the purification effect and mechanism of domestic wastewater in mangrove plants constructed wetland[D]. Guangzhou: Sun Yat-sen University, 2005.(in Chinese) http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10558-2005116745.htm
[30] 刁俊明, 邹嫣娉, 陈桂珠.淡水培养对桐花树幼苗生长发育的影响[J].林业科学研究, 2010, 23(3): 387-392. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykxyj201003012 DIAO J M, ZHOU Y P, CHEN G Z.Effect of Fresh Water Cultivation on the Growth and Development of Aegiceras corniculatum Seedlings[J]. Forest Research, 2010, 23(3):387-392.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykxyj201003012
[31] 彭玉华, 谭长强, 何琴飞, 等.台湾桤木与不同树种混交初期土壤理化性质的对比分析[J].中南林业科技大学学报, 2018, 38(11): 22-28. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/znlxyxb201811005 PENG Y H, TAN C Q, HE Q F, et al.Comparison on soil properties of mixed Alnus formosana plantations[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2018, 38(11):22-28.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/znlxyxb201811005
[32] 白世红, 丁新景, 马风云, 等.黄河三角洲盐碱地人工刺槐混交林细根分布研究[J].中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26(1):116-124. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stnyyj201801013 BAI S J, DING X J, MA F Y, et al.Fine root distribution in mixed Robinia pseudoacacia plantations in saline soils of the Yellow River Delta[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2018, 26(1):116-124.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stnyyj201801013
[33] 王颖, 宗宁, 何念鹏, 等.青藏高原高寒草甸不同海拔梯度下土壤微生物群落碳代谢多样性[J].生态学报, 2018, 38(16): 5837-5845. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201816022 WANG Y, ZONG N, HE N P, et al.Soil microbial functional diversity patterns and drivers along an elevation gradient on Qinghai-Tibet, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(16):5837-5845.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201816022
[34] 王颖.青藏高原高寒草甸不同海拔土壤微生物功能多样性[D].邯郸: 河北工程大学, 2018. WANG Y.Soil Microbial Functional Diversity at Different Elevations in Alpine Meadows of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[D]. Handan: Hebei University of Engineering, 2018.(in Chinese)
[35] 吴则焰, 林文雄, 陈志芳, 等.武夷山不同海拔植被带土壤微生物PLFA分析[J].林业科学, 2014, 50(7): 105-112. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykx201407015 WU Z Y, LIN W X, CHEN Z F, et al.Phospholipid Fatty Acid Analysis of Soil Microbes at Different Elevation of Wuyi Mountains[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2014, 50(7):105-112.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/lykx201407015
[36] 郑洁, 刘金福, 吴则焰, 等.闽江河口红树林土壤微生物群落对互花米草入侵的响应[J].生态学报, 2017, 37(21): 7293-7303. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201721027 ZHENG J, LIU J F, WU Z Y, et al.Soil microbial community of mangrove forests and its responses to the invasion of spartina alterniflora in the Minjiang River Estuary[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(21):7293-7303.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201721027
[37] 曹永昌, 杨瑞, 刘帅, 等.秦岭典型林分夏秋两季根际与非根际土壤微生物群落结构[J].生态学报, 2017, 37(5): 1667-1676. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201705031 CAO Y C, YANG R, LIU S, et al.Characteristics of microbial community in forest soil between rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere in summer and autumn in Qinling Mountains, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(5):1667-1676.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201705031
[38] 金映虹, 吴红萍, 谭方正, 等.不同红树植物类群土壤微生物功能多样性的研究[J].生态环境学报, 2017, 26(8): 1292-1300. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tryhj201708003 JIN Y H, WU H P, TAN F Z, et al.Study on Functional Diversity of Soil Microorganism in Different Mangrove Plants Based on Biolog-ECO Technology[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 2017, 26(8):1292-1300.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tryhj201708003
[39] MCKINLEY V L, PEACOCK A D, WHITE D C.Microbial community PLFA and PHB responses to ecosystem restoration in tallgrass prairie soils[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 2005, 37(10): 1946-1958. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0038071705001033
[40] 付丽娜, 汪娅婷, 王星, 等.三七连作根际微生物多样性研究[J].云南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 33(2):198-207. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNDX201802005.htm FU L N, WANG Y T, WANG X, et al.The Study on Microbial Diversity of Rhizosphere in Continuous Cropping System of Panax notoginseng[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 33(2):198-207.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNDX201802005.htm
[41] 韩维栋, 高旭东.湛江湾红树林土壤理化性质的研究[J].中国农学通报, 2013(31): 27-31. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgnxtb201331005 HAN W D, GAO X D.Study on the Soil Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Mangrove Forest in Zhanjiang Bay[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2013(31):27-31.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgnxtb201331005
[42] 陈粤超, 王占印, 许方宏, 等.不同类型的红树林土壤养分和生态化学计量特征比较[J].桉树科技, 2016, 33(1): 32-37. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3172.2016.01.006 CHEN Y C, WANG Z Y, XU F H, et al.Studies on Soil Nutrients and Ecological Stoichiometry of Different Types of Mangroves[J]. Eucalypt Science & Technology, 2016, 33(1):32-37.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3172.2016.01.006
[43] 徐海, 陈少波, 张素霞, 等.红树林土壤基本特征及发展前景[J].安徽农业科学, 2008, 36(4): 1496-1497. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2008.04.099 XU H, CHEN S B, ZHANG S X, et al.Basic Characteristics and Development Prospect of Mangrove Soil and Its Correlation with Mangrove[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2008, 36(4):1496-1497.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2008.04.099
[44] 王岳坤, 洪葵.红树林土壤细菌群落16S rDNA V3片段PCR产物的DGGE分析[J].微生物学报, 2005, 45(2): 201-204. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-6209.2005.02.009 WANG Y K, HONG K.Mangrove soil community analysis using DGGE of 16S rDNA V3 fragment polymerase chain reaction products[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2005, 45(2):201-204.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-6209.2005.02.009
[45] 张燕燕, 曲来叶, 陈利顶.Biolog EcoPlateTM实验信息提取方法改进[J].微生物学通报, 2009, 36(7): 1083-1091. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-WSWT200907026.htm ZHANG Y Y, QU L Y, CHEN L D.An Amendment on Information Extraction of Biolog EcoPlateTM[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2009, 36(7): 1083-1091.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-WSWT200907026.htm
[46] 姚琦, 尤青, 李媛宏, 等.海南东寨港红树林土壤微生物功能多样性[J].应用与环境生物学报, 2017, 23(5): 857-861. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yyyhjswxb201705013 YAO Q, YOU Q, LI Y H, et al.Functional diversity of soil microorganisms in the soil in Dongzhaigang mangrove wetlands in Hainan[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 2017, 23(5): 857-861.(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yyyhjswxb201705013
[47] KRISTENSEN E, HAESE R R, KOSTKA J E.9. Interactions Between Microorganisms and Intertidal Plant Communities[M]. American Geophysical Union, 2013.
[48] 殷萌清, 冯建祥, 黄小芳, 等.天然及人工红树林土壤微生物群落结构分析[J].生态科学, 2017, 36(5): 1-10. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stkx201705001 YIN M Q, FENG J X, HUANG X F, et al.Soil microbial community structure in natural and transplanted mangrove(Kandelia obovata) forests[J]. Ecological Science, 2017, 36(5): 1-10.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stkx201705001
[49] WANG C, XU X X, QU Z, et al.Micromonospora rhizosphaerae sp.nov., isolated from mangrove rhizosphere soil[J]. International Journal of Systematic & Evolutionary Microbiology, 2011, 61(2): 320-324. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0222103738/
[50] 王秀丽, 周亮, 许诗琳, 等.福建九龙江口不同林龄拉关木人工林凋落物组成及季节动态[J].应用海洋学学报, 2017(4): 519-527. DOI: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2017.04.007 WANG X L, ZHOU L, XU S L, et al.Composition and seasonal dynamics of litterfall in different ages of Laguncularia racemosa plantations in Jiulong River estuary, Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2017(4): 519-527.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2017.04.007
[51] 张骥诚, 梁嘉庆, 俞锦锋, 等.白骨壤重金属耐受性相关基因AmNramp3的克隆与分析[J].厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 56(3): 331-338. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xmdxxb201703004 ZHANG J C, LIANG J Q, YU J F, et al.Cloning and Analysis of Heavy Metal Tolerance-associated Gene Am Nramp 3 in Avicennia marina (Forsk.)Vierh[J]. Journal of Xiamen University(Natural Science), 2017, 56(3): 331-338.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xmdxxb201703004
[52] 王淼, 曲来叶, 马克明, 等.罕山土壤微生物群落组成对植被类型的响应[J].生态学报, 2014, 34(22): 6640-6654. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201422027 WANG M, QU L Y, MA K M, et al.Response of soil microbial community composition to vegetation types[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(22): 6640-6654.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201422027
[53] NOAH F, ROBERT B J.The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006, 103(3): 626-631. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0507535103
[54] 李庆赟, 殷萌清, 陈淑文, 等.红树林人工修复区根际微生物群落结构分析[J].现代生物医学进展, 2016, 16(8): 1401-1405. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/swcx201608001 LI Q Y, YIN M Q, CHEN S W, et al.Rhizohphere Microbial Community Analysis of Artificial Mangrove Restoration Area[J]. Progress in Modern Biomedicine, 2016, 16(8): 1401-1405.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/swcx201608001
[55] BERG G, SMALLA K.Plant species and soil type cooperatively shape the structure and function of microbial communities in the rhizosphere[J]. Fems Microbiology Ecology, 2010, 68(1): 1-13. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=6e80a55bc0ddcd3e803eec72fde4d494




 下载:
下载: