Disease and Insect Resistance Genes in Premium Sterile Line Funong A
-
摘要:目的
分析福农A中的抗病虫基因,为该不育系更好地应用于育种生产提供理论依据。
方法以福农A及亲本福稻B、华航丝苗为材料,利用抗稻瘟病基因分子标记检测各材料中抗稻瘟病基因情况,并应用高密度芯片检测抗白叶枯病、抗病毒及抗褐飞虱基因情况。PCR扩增获得福农A及亲本福稻B、华航丝苗中的抗稻瘟病基因,进行序列比对分析。植株培养至三叶一心期,喷雾接稻瘟病菌并取样,采用 SYBR Green I 荧光定量 PCR(qRT-PCR) 分析抗稻瘟病基因的表达模式。
结果福农A及亲本福稻B、华航丝苗中均含有稻瘟病抗性基因Pib、Pia、Pid3和Pid2,但均不含Pi9、Pi54、Pigm、Pit、Pi2;另外,福农A和华航丝苗中含有Pi5,而福稻B中含有Pita和Pi37。福农A及亲本福稻B和华航丝苗中均含有抗白叶枯病基因Xa21和抗黄色斑驳病毒病基因Rymv1;福农A及华航丝苗中含持久性抗水稻条叶枯病毒基因STV11;但它们中均不含抗褐飞虱基因Bph14、Bph15、Bph18、 Bph26、 Bph6、 Bph9。扩增获得的 Pi5、Pia、Pib、Pid3、Pid2基因序列长分别为5 672、2 597、5 532、2 865、
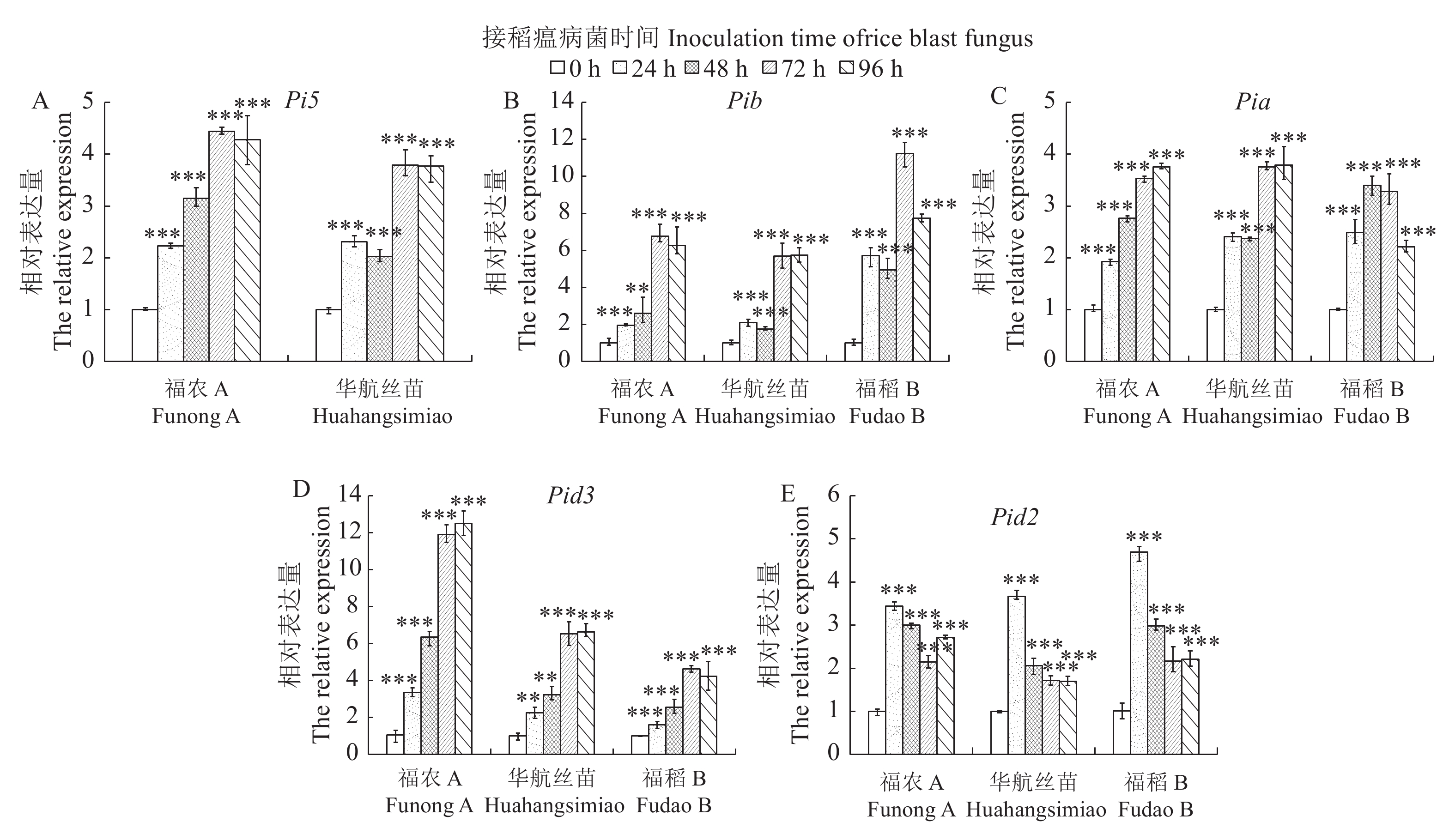
3847 bp;福农A与亲本华航丝苗中的Pi5基因序列完全一致;福农A和亲本华航丝苗、福稻B中的Pia、Pib基因序列均完全一致;福农A和华航丝苗中的Pid3和Pid2基因序列完全一致,而它们与福稻B的序列分别有2个和5个碱基差异。在福农A中,抗稻瘟病基因Pi5和Pib的表达明显受稻瘟病菌的诱导,接菌72 h时表达量最高;Pia和Pid3的表达随接菌时间的延长而逐渐升高,接菌96 h时表达量最高;Pid2的表达先升高后降低,且在接菌24 h时表达量最高。结论水稻三系不育系福农A中含有稻瘟病抗性基因Pi5、Pib、Pia、Pid3和Pid2,抗白叶枯病基因Xa21、抗黄色斑驳病毒病基因Rymv1及持久性抗水稻条叶枯病毒基因STV11。因此,该不育系有望应用于多抗基因的聚合育种研究。
Abstract:ObjectiveDisease and insect resistance genes in Funong A, a three-line indica cytoplasmic male sterile line, were analyzed for breeding applications.
MethodGenomic DNA of Funong A, Fudao B, and Huahangsimiao rice germplasms was extracted by CTAB method followed by detection of blast resistance genes with molecular markers. Resistance genes related to bacterial blight, viral diseases, and brown planthopper infestation were analyzed by high density chip detection method. Blast resistance genes of the lines were obtained by PCR and sequenced for comparison. Specimens were collected at 0, 24, 48, 72, and 96 h after a blast fungus inoculation for extraction of total RNA using Trizol method. Gene expression was determined by SYBR Green I qRT-PCR.
ResultFunong A, Fudao B, and Huahangsimiao were found to contain the blast resistance genes Pib, Pia, Pid3, Pid2, bacterial blight resistance gene Xa21, and yellow mottle virus resistance gene Rymv1. Furthermore, Funong A and Huahangsimiao had the blast resistance gene Pi5 and the stripe virus resistance gene STV11, while Fudao B consisted of the blast resistance genes Pita and Pi37. However, no brown planthopper resistance genes were detected in them. The fragments of Pi5, Pia, Pib, Pid3, and Pid2 were 5 672 bp, 2 597 bp, 5 532 bp, 2 865 bp, and 3 847 bp in length, respectively. The sequences of Pi5, Pid3, and Pid2 in Funong A were similar to those in Huahangsimiao, but 2 bases differed from Pid3 and 5 from Pid2 of Fudao B. In Funong A, the expressions of rice blast resistance genes Pi5 and Pib were significantly induced by the blast fungus with a peak occurred 72 h after inoculation. The expressions of Pia and Pid3 increased gradually with time after inoculation to peak in 96 h. The expression of Pid2 rose initially to a maximum in 24 h and then declined.
ConclusionThe three-line indica cytoplasmic male sterile line Funong A carried the blast resistance genes Pi5, Pib, Pia, Pid3, and Pid2, which were significantly induced by the blast fungus. The line also contained the bacterial blight resistance gene Xa21, yellow mottle virus resistance gene Rymv1, and stripe virus resistance gene STV11 but none of the insect resistance genes.
-
Keywords:
- Funong A /
- blast resistance gene /
- sequential analysis /
- gene expression
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】福建是全国著名的产茶大省,2017年毛茶产量45.2万t,产值235亿元,毛茶产量和产值均位居全国第一。茶产业作为福建七大优势特色产业之一,在福建现代农业中的地位不可替代。武夷山是中国乌龙茶的发源地,自20世纪80年代武夷岩茶被评为中国十大名茶以来,武夷山茶产业迅猛发展,已成为武夷山的主导产业和特色产业,在农村经济发展、农民就业和社会稳定方面发挥了极为重要的作用。武夷山茶园主要是由荒山荒坡和集体林地开垦而来,土壤大多呈酸性,腐质层厚,适宜茶树生长,新开垦茶园茶树长势良好,茶叶品质优良。由于经年的水土流失,茶园土壤肥力逐渐衰退,多数茶园在投产20年左右茶叶产量品质大幅下降,形成了低产衰老茶园,大大降低了茶园的经济效益[1]。土壤微生物作为土壤生态系统的重要组成部分,参与大约90%的土壤反应过程[2],对土壤化学特性的变化反应敏感,其特征可作为生物指标指示土壤质量,评价土壤肥力[3-4]。了解不同种植年限茶园土壤微生物的变化情况,对茶园土壤肥力衰退研究具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】由于土壤微生物在土壤有机质分解、土壤矿质营养循环等方面的重要作用,不少科学工作者对茶园土壤微生物展开研究。李俊强等[5]的研究结果表明,6种不同施肥模式对茶树根际土壤微生物数量有显著影响,与对照(不施肥)相比,均增加了茶树根际土壤微生物量碳、氮和土壤酶活性。王秀青等[6]的研究发现,现代茶园的微生物的总数量高于古茶园,但各微生物数量与茶园土壤养分质量分数之间相关性无统计学意义。林生等[1, 7]的研究发现,随着茶树种植年限的增加,茶树根际土壤的微生物群落结构发生了较大的变化,体现在微生物群落的多样性降低,适应于贫瘠条件与低代谢能力的种群增多。武夷山作为福建省茶叶主产区,有较多学者对该地茶园土壤理化特征进行研究,涉及的理化特征包括土壤有机质[8]、酸度[9]、重金属[10]等。然而,关于武夷山茶园土壤微生物的研究则鲜见报道。【本研究切入点】课题组前期在武夷山茗上缘茶业有限公司试验茶场开展农产品质量安全技术服务,服务过程中了解到该茶场种植多年的茶树茶叶的产量和品质均有所下降,种植多年的老茶园土壤肥力也呈下降趋势。众所周知,茶叶产量和品质与土壤肥力密切相关,肥沃的茶园土壤是实现茶园优质高产的基本保证[11]。也有研究表明,随着茶树种植时间的延长,茶树根际土壤有益微生物降低、病原菌增多,茶叶产量下降,品质降低[12]。那么,种植多年的茶园土壤肥力与土壤微生物之间是否存在着一定的联系,涉及该方面的研究报道较少。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究以武夷山茗上缘茶业有限公司试验茶场中不同种植年限茶树根际土壤为研究对象,分析不同种植年限茶树根际土壤可培养微生物数量及其肥力指标的变化,了解土壤微生物数量与肥力之间的关系,为茶园土壤改良和稳定生产奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 供试土壤
供试土壤样品取自福建省武夷山茗上缘茶业有限公司试验茶园。武夷山市位于福建省西北部(东经117°37′22″~118°19′44″、北纬27°27′31″~28°04′49″),是中国著名的茶叶产区,也是中国乌龙茶和红茶的发祥地。当地气候属中亚热带季风湿润气候区,年均气温19.7℃,年均降雨量1 960 mm左右。试验茶园位于武夷山市区近郊的“小武夷”风景区,采用统一管理模式,全年耕作措施基本一致。供试土壤采集于2017年3月29日,天气阴,最低气温13℃,最高气温21℃,土壤含水量介于10.40%~19.45%。
以茶树根际土壤为研究对象,在距离茶树主茎半径约30 cm的范围内取土,采样深度为0~15 cm和15~30 cm。采用多点混合采样法采集未种植茶树的土壤(CK),5年生(Y5)、10年生(Y10)和15年生(Y15)茶树根际土壤。剔除土壤样品中的残留根系、石块及其他杂质后,四分法混匀,装入无菌聚乙烯封口袋,放入冰盒内带回实验室。带回的土壤样品一部分风干,过筛后用于土壤理化指标的测定;一部分置于冷藏室,用于可培养微生物数量的测定。
1.2 土壤可培养微生物测定
通过稀释平板法[13]测定土壤中可培养微生物数量。采用营养琼脂培养基培养细菌,混菌法接种后在28℃光照培养箱中培养24 h,计算细菌菌落数;采用马铃薯-葡萄糖琼脂(PDA)培养基培养真菌,刮刀法接种后在28℃光照培养箱中培养48 h,计算真菌菌落数。试验结果以CFU·g−1干土表示。试验设3个重复。
1.3 土壤理化指标测定
土壤pH 值采用1 mol·g−1氯化钾浸提,电位法测定[14];有机质的测定采用重铬酸钾容量法;全氮测定采用半微量凯氏定氮法;全磷测定采用硫酸-高氯酸消煮法;全钾测定采用氢氧化钠碱熔-火焰光度法;碱解氮的测定采用碱解扩散法;有效磷的测定采用碳酸氢钠法;速效钾的测定采用醋酸铵-火焰光度计法[15]。每个指标测定均设空白对照处理,每个样品设3个重复。
1.4 数据处理分析
利用Microsoft Excel 2007、SPSS17.0和Canoco 5软件进行数据的统计分析和作图。采用单因素方差分析(Oneway-ANOVA)和多重比较(LSD)法分析样品之间的差异性(α=0.05)。采用冗余分析(RDA)研究土壤样品可培养微生物数量和理化指标之间的相关性。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同种植年限茶树根际土壤的可培养微生物数量变化特征
采用传统的平板计数法对不同种植年限茶树根际土壤的可培养微生物数量进行测定,结果见图1和图2。从图1可以看出,茶树根际土壤的可培养细菌数量介于2.43×104~1.14×105 CFU·g−1。从不同土层来看,同一年限15~30 cm土层的可培养细菌数量低于0~15 cm土层的可培养细菌数量;方差分析结果表明,Y5不同土层之间可培养细菌数量差异显著(P<0.05),而CK、Y10和Y15各自不同土层之间的可培养细菌数量差异不显著。从种植年限来看,0~15 cm土层和15~30 cm土层的茶树根际土壤可培养细菌数量均呈现Y10>CK>Y5>Y15的趋势,且Y15的可培养细菌数量显著低于其他年限样品(Y5-2除外)中的可培养细菌数量(P<0.05)。
![]() 图 1 不同种植年限茶树根际土壤的可培养细菌数量变化注:图中样品名称后面的“-1”和“-2”表示不同采样深度的土壤样品。“-1”代表采样深度为0~15 cm的土壤样品;“-2”代表采样深度为15~30 cm的土壤样品。图中不同小写字母表示样品间差异显著( P <0.05)。下同。Figure 1. Bacterial plate count of soil specimens from areas of different tea-planting yearsNote: The "-1" and "-2" following the sample name indicate soil samples with different sampling depths. “-1” means the soil sampling depth is from 0 to 15 cm; “-2” means the soil sampling depth is from 15 to 30 cm. Different lowercases in the picture indicate significant difference at 0.05 level among different samples. The same below.
图 1 不同种植年限茶树根际土壤的可培养细菌数量变化注:图中样品名称后面的“-1”和“-2”表示不同采样深度的土壤样品。“-1”代表采样深度为0~15 cm的土壤样品;“-2”代表采样深度为15~30 cm的土壤样品。图中不同小写字母表示样品间差异显著( P <0.05)。下同。Figure 1. Bacterial plate count of soil specimens from areas of different tea-planting yearsNote: The "-1" and "-2" following the sample name indicate soil samples with different sampling depths. “-1” means the soil sampling depth is from 0 to 15 cm; “-2” means the soil sampling depth is from 15 to 30 cm. Different lowercases in the picture indicate significant difference at 0.05 level among different samples. The same below.从图2可以看出,茶树根际土壤的可培养真菌数量为5.07×104~2.39×105 CFU·g−1。从不同土层来看,同一年限15~30 cm土层的可培养真菌数量同样均低于0~15 cm土层的可培养真菌数量。方差分析结果表明,Y5和Y15不同土层之间可培养真菌数量差异显著(P<0.05),而CK和Y10不同土层之间可培养真菌数量则差异不显著。从种植年限来看,0~15 cm土层茶树根际土壤可培养真菌数量表现为Y5-1>Y15-1>Y10-1>CK-1,且CK-1的可培养真菌数量显著低于Y5-1、Y15-1和Y10-1(P<0.05);15~30 cm土层茶树根际土壤可培养真菌数量则表现为Y10-2>Y5-2>CK-2>Y15-2,且Y10-2的可培养真菌数量显著高于Y5-2、CK-2和Y15-2(P<0.05)。
2.2 不同种植年限茶树根际土壤肥力分析
测定土壤样品pH值和有机质、全氮、全磷、全钾、碱解氮、速效磷、速效钾等肥力指标。不同种植年限茶树根际土壤理化性质见表1。从表1可以看出,茶树根际土壤pH值随种植年限变化不大,为3.14~3.36;同一种植年限pH值15~30 cm土层大于或等于0~15 cm土层的趋势。有机质含量介于18.34~30.00 g·kg−1,0~15 cm土层有机质含量呈现Y5-1>CK-1>Y15-1>Y10-1的趋势,而15~30 cm土层有机质含量则表现为Y10-2>Y15-2>CK-2>Y5-2。全氮、全磷和全钾的含量分别为0.69~1.40 g·kg−1、0.59~0.98 g·kg−1和12.20~33.07 g·kg−1;0~15 cm土层全氮的含量呈现Y5-1>Y15-1>Y10-1>CK-1的趋势,15~30 cm土层全氮的含量则随着种植年限的增加而增加;0~15 cm土层全磷的含量随着种植年限的增加而降低,15~30 cm土层全磷的含量则表现为CK-2>Y10-2>Y15-2>Y5-2;0~15 cm土层全钾的含量随着种植年限的增加而降低,而15~30 cm土层全钾的含量则表现为Y5-2>CK-2>Y15-2>Y10-2。碱解氮、速效磷和速效钾的含量分别为84.17~110.38 mg·kg−1、50.50~63.99 mg·kg−1和77.87~273.15 mg·kg−1;0~15 cm土层碱解氮的含量呈现Y10-1>Y15-1>CK-1>Y5-1的趋势,而15~30 cm土层碱解氮的含量则随着种植年限的增加而增加;0~15 cm土层速效磷的含量表现为Y15-1>CK-1>Y10-1>Y5-1,15~30 cm土层速效磷的含量则表现为Y5-2>Y15-2>CK-2>Y10-2;0~15 cm土层和15~30 cm土层速效钾的含量均表现为Y15>Y10>CK>Y5。
表 1 不同种植年限茶树根际土壤理化性质Table 1. Physiochemical properties of soils from areas of different tea-planting years样品
samples全氮 Total
N/(g·kg−1)全磷 Total
P/(g·kg−1)全钾 Total
K/(g·kg−1)碱解氮 Available
N/(mg·kg−1)速效磷 Available
P/(mg·kg−1)速效钾 Available
K/(mg·kg−1)有机质 Organic
matter/(g·kg−1)pH CK-1 1.30±0.00 c 0.98±0.01 a 20.64±0.15 b 104.16±0.95 b 60.00±4.04 ab 102.96±0.44 d 26.15±0.40 b 3.21±0.00 d CK-2 0.69±0.01 f 0.82±0.05 bc 15.20±0.35 c 84.17±0.24 d 57.25±0.62 bc 85.94±1.20 de 25.37±1.16 bc 3.30±0.00 b Y5-1 1.40±0.00 a 0.84±0.03 b 14.03±0.09 d 102.98±0.24 bc 50.50±1.32 d 149.70±7.68 c 30.00±0.00 a 3.25±0.01 c Y5-2 0.88±0.04 e 0.61±0.02 d 33.07±0.18 a 85.18±1.66 d 58.17±0.97 abc 145.11±4.42 c 20.31±0.44 d 3.35±0.00 a Y10-1 1.31±0.01 c 0.74±0.05 c 12.25±0.13 g 110.38±0.24 a 52.67±0.33 cd 273.15±22.48 a 18.34±0.00 e 3.14±0.00 e Y10-2 1.12±0.00 d 0.65±0.03 d 12.67±0.00 f 101.47±0.48 c 56.47±0.48 bcd 222.57±0.00 b 28.82±1.55 a 3.14±0.01 e Y15-1 1.35±0.00 b 0.59±0.00 d 12.20±0.10 g 110.04±1.19 a 63.99±6.09 a 79.16±3.22 e 24.14±0.00 c 3.30±0.00 b Y15-2 1.29±0.00 c 0.62±0.03 d 13.65±0.06 e 104.66±0.24 b 58.04±0.16 abc 77.87±0.00 e 25.77±0.75 bc 3.36±0.01 a 注:表中同列不同小写字母表示样品间在P<0.05水平上差异显著。
Note: Different lowercases in the same column indicate significant difference at 0.05 level among different samples.根据行业标准《茶叶产地环境技术条件》(NY/T853-2004)[16],将茶园土壤肥力指标分为三级,Ⅰ级表示优良,Ⅱ级表示尚可,Ⅲ级表示较差。根据优质、高效、高产茶园土壤营养诊断指标[17],将茶园土壤pH值分为三级,Ⅰ级表示酸化,Ⅱ级表示适中,Ⅲ级表示不适宜。具体茶园土壤肥力评价标准见表2。根据茶园土壤肥力评价标准,对各肥力指标进行分级。不同种植年限茶树根际土壤肥力情况见表3。从表3看出,土壤pH值均处于Ⅰ级水平,说明采样点土壤酸化严重。所有样品的有机质含量均达到优良水平。从氮含量来看,全氮和碱解氮的变化趋势基本一致,0~15 cm土层的土壤肥力均达到优良水平;而15~30 cm土层的土壤肥力则表现为CK-2和Y5-2的肥力为尚可或较差,Y10和Y15的肥力达到优良。从磷含量来看,大多数样品的全磷和速效磷含量均达到优良水平(除了Y15-1全磷含量为尚可)。从钾含量来看,全钾含量均达优良水平,Y5和Y10的速效钾含量也为优良水平,CK的速效钾含量为尚可,而Y15的速效钾含量则为较差。
表 2 茶园土壤肥力评价标准Table 2. Evaluation standards on soil fertility at tea plantations划分等级
Classification评价指标 Evaluation indexes 全氮 Total
N/(g·kg−1)全磷 Total
P/(g·kg−1)全钾 Total
K/(g·kg−1)碱解氮 Available
N/(mg·kg−1)速效磷 Available
P/(mg·kg−1)速效钾 Available
K/(mg·kg−1)有机质 Organic
matter/(g·kg−1)pH Ⅰ级 >1.0 >0.6 >10 >100 >10 >120 >15 <4.5 Ⅱ级 0.8~1.0 0.4~0.6 5~10 50~100 5~10 80~120 10~15 4.5~5.5 Ⅲ级 <0.8 <0.4 <5 <50 <5 <80 <10 >5.5 表 3 不同种植年限茶树根际土壤肥力情况Table 3. Fertility of soils from areas of different tea-planting years样品 Samples 全氮 Total N 全磷Total P 全钾 Total K 碱解氮 Available N 速效磷 Available P 速效钾 Available K 有机质 Organic matter pH CK-1 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅱ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 CK-2 Ⅲ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅱ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅱ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Y5-1 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Y5-2 Ⅱ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅱ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Y10-1 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Y10-2 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Y15-1 Ⅰ级 Ⅱ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅲ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Y15-2 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅲ级 Ⅰ级 Ⅰ级 2.3 土壤微生物数量与肥力指标之间的相关性
采用冗余分析揭示不同种植年限茶树根际土壤样品可培养微生物数量和肥力指标之间的相关性,从而得到二维排序图(图3)。从图3可知,第1排序轴和第2排序轴的解释量分别为83.2%和16.8%,两轴累计解释量为100%,说明这两轴能够很好地反映土壤肥力指标对可培养微生物数量的影响。第1排序轴与pH(r=0.869)、速效磷(r=0.503)和全钾(r=0.285)正相关,与其他肥力指标负相关。第2排序轴与全氮(r=0.581)、碱解氮(r=0.552)、速效磷(r=0.310)和pH(r=0.130)正相关,与其他肥力指标负相关。
![]() 图 3 不同种植年限茶树根际土壤的可培养微生物数量与肥力指标的冗余分析注:图中Bacteria代表可培养细菌数量,Fungus代表可培养真菌数量,TN、TP和TK分别代表总氮、总磷和总钾,AN、AP和AK分别代表碱解氮、速效磷和速效钾,OM代表有机质,pH即pH值。Figure 3. RDA analysis on microbial counts and fertility indices in soils from areas of different tea-planting yearsNote: Bacteria means number of laboratory-cultured bacteria; Fungus means number of laboratory-cultured fungus; TN, TP and TK mean total nitrogen, total phosphorus and total potassium respectively; AN, AP and AK mean available nitrogen, available phosphorus and available potassium respectively; OM means organic matter; and pH means the value of pH.
图 3 不同种植年限茶树根际土壤的可培养微生物数量与肥力指标的冗余分析注:图中Bacteria代表可培养细菌数量,Fungus代表可培养真菌数量,TN、TP和TK分别代表总氮、总磷和总钾,AN、AP和AK分别代表碱解氮、速效磷和速效钾,OM代表有机质,pH即pH值。Figure 3. RDA analysis on microbial counts and fertility indices in soils from areas of different tea-planting yearsNote: Bacteria means number of laboratory-cultured bacteria; Fungus means number of laboratory-cultured fungus; TN, TP and TK mean total nitrogen, total phosphorus and total potassium respectively; AN, AP and AK mean available nitrogen, available phosphorus and available potassium respectively; OM means organic matter; and pH means the value of pH.从图3可以看出可培养细菌数量和可培养真菌数量与土壤肥力指标之间的关系。位于第三象限的可培养细菌数量主要受速效钾和全磷含量的影响,位于第二象限的可培养真菌数量主要受全氮和碱解氮含量的影响。然而,与可培养微生物数量相关性较强的环境因子在不同土壤样品中是有差异的。土壤样品Y10-1和Y10-2主要分布在第三象限,说明10年生茶树根际土壤样品主要受速效钾和全磷含量的影响,并且与它们呈正相关。土壤样品Y5-1和Y15-1主要分布在第二象限,与全氮和碱解氮含量呈正相关。土壤样品Y5-2和Y15-2主要分布在第一象限,与pH、速效磷和全钾含量呈正相关。
3. 讨论与结论
茶园土壤微生物具有固氮、释钾、解磷以及增强土壤保湿性等优点,它在促进土壤有机质的分解、土壤矿质营养循环、维持和提高土壤肥力等方面发挥着关键作用[18]。本研究采用稀释平板法对武夷山茗上缘茶业有限公司试验茶园不同种植年限茶树根际土壤的可培养微生物数量进行研究,结果表明,可培养微生物数量随着土层加深而减少;10年生茶树根际土壤可培养细菌数量最大,15年生茶树根际土壤可培养细菌数量显著低于其他(Y5-2除外)样品(P<0.05);不同种植年限茶树根际土壤的可培养真菌数量在不同土层表现出不一样的变化趋势。张仕颖等[17]对不同种植年限的玫瑰蜜葡萄根际土壤微生物数量进行了研究,发现微生物总数由大到小依次是6年>10年>3年>30年,随着种植年限的延长,微生物总量先增加后减少,葡萄根际土壤微生物活性在连作10年后不断下降。本试验中微生物数量的变化趋势与该结果基本相一致。
肥沃的茶园土壤是茶园优质高产的前提条件。本研究分析了土壤样品pH值和有机质、全氮、全磷、全钾、碱解氮、速效磷、速效钾等肥力指标,结果表明,茶树根际土壤pH值随种植年限变化不大为3.14~3.36;随着种植年限的增加,各项肥力指标的变化趋势不尽相同,0~15 cm土层的全磷和全钾含量随着种植年限的增加而降低,15~30 cm土层全氮和碱解氮的含量随着种植年限的增加而增加,其他的指标则在连续种植5年或10年的时候出现最高值或最低值。吴志丹等[9]调查分析了武夷山市60个茶园的土壤酸度指标,发现超过50%的土壤样品属于重度酸化土壤(pH<4.5),而本研究供试土壤均为重度酸化土壤。对茶园土壤各项肥力指标的研究,发现随着种植年限的增加,不同肥力指标呈现出不同的结果。林生等[7]研究了安溪不同年限(1、6和20年生)茶树土壤养分情况,发现全磷、速效磷和速效钾的含量随着种植年限的增加而降低,而有机质、全氮、全钾和碱解氮则呈现先增加再减少的趋势。这与本研究中0~15 cm土层全磷含量的变化趋势相一致,而其他指标的变化趋势则与之不完全一致。王秀青等[6]对古茶园和现代茶园土壤养分的研究表明,3座茶山古茶园土壤全氮、全磷、碱解氮和速效磷含量显著高于现代茶园。本研究中15~30 cm土层全氮和碱解氮也是随着种植年限的增加而增加,这可能主要是因为随着种植时间的延长,茶树凋落物、根系分泌物等归还土壤,导致两者含量逐年增加。
冗余分析揭示了不同种植年限茶树根际土壤可培养微生物数量和肥力指标之间的相关性,结果表明,土壤中可培养微生物数量主要受速效钾、全磷、全氮和碱解氮含量的影响。其中,可培养细菌数量主要受速效钾和全磷含量的影响,可培养真菌数量主要受全氮和碱解氮含量的影响。但与微生物数量相关性较强的环境因子在不同样品中是不同的。10年生茶树根际土壤样品主要受速效钾和全磷含量的影响。0~15 cm土层的5年生茶树根际土壤样品和15年生茶树根际土壤样品主要受全氮和碱解氮含量的影响。15~30 cm土层的5年生和15年生的茶树根际土壤样品主要受pH、速效磷和全钾含量的影响。张仕颖等[19]的研究发现,葡萄根际土壤的速效钾含量与微生物数量相关性强。王世强等[20]的研究也表明,调节茶园酸性土壤的pH值是提高茶园土壤微生物数量和活性的最好方法。土壤微生物主要通过改善土壤的理化性质等来影响土壤的肥力,土壤微生物的数量在一定程度上反映了土壤的肥力水平。了解茶园土壤微生物与肥力指标之间的相关性,有望通过调节土壤微生物来改良某些土壤肥力指标,或者通过调节某一肥力指标来调控特定类别土壤微生物,进而改良茶园土壤。本研究仅于2017年3月采集了不同种植年限茶树根际土壤样品进行分析,发现本次样品中土壤微生物数量和部分肥力指标之间存在着相关性。进一步明确该茶园土壤微生物与肥力之间的关系,还需于不同季节多次采集茶园土壤样品进行分析,并且对土壤微生物群落结构进行更深入的研究。
-
表 1 PCR及qRT-PCR引物
Table 1 Primers for PCR and qRT-PCR
引物
Primers引物序列(5′-3′)
Primer sequence(5′-3′)片段大小(抗/感)
Fragment size(Resistance/Susceptibility)/bp参考文献
ReferencePibdom F:GAACAATGCCCAAACTTGAGA 365 (R) /无 (S) [9] R:GGGTCCACATGTCAGTGAGC Pi9 F:GCTGTGCTCCAAATGAGGAT 291 (R) / 397 (S) [10] R:GCGATCTCACATCCTTTGCT Pi5 F:ATAGATCATGCGCCCTCTTG 206 (R)/307 (S) [10] R:TCATACCCCATTCGGTCATT Pi54 F:CAATCTCCAAAGTTTTCAGG 216 (R)/359 (S) [11] R:GCTTCAATCACTGCTAGACC Pita F:CTCCCTTGTTCGGTCAAAAA 467 (R)/850 (S) [10] YL155:AGCAGGTTATAAGCTAGGCC R:CCACATTGATGAAGCCCATA Pia F:GCGACTGACACTTTCAATAGC 175 (R)/206 (S) [12] R:CGGTAGAGCAATTTAGAAGCAG Pigm F:CAGAGCAGTAACAAACCCTA 750 (R)/ 1800 (S)[13] R:TCCGCAAGATCAACATTC Pit F:ATGATAACCTCATCCTCAATAAGT 733(R)/无 (S) [14] R:GTTGGAGCTACGGTTGTTCAG Pid3 F:TACTACTCATGGAAGCTAGTTCTC Bam H I, 148 (R)/ 178 (S) [15] R:AGCACTTCTTGACTACTGTCTGCCT Pi2 F:CAGCGATGGTATGAGCACAA 450 (R)/ 282 (S) [10] R:CGTTCCTATACTGCCACATCG Pi37 F:TCTTGAGGGTCCCAGTGTAC 1149 (R)/无(S)[16] R:CGAACAGTGGCTGGTATCTC Pid2 F:GCGTCGAAGATGTCCTGAAGCTCA 629(R)/无 (S) [17] R:GGCAGTCGTATTGCTGTGAA Pi5-DNA F: CCTTCTCTCTTCTCGTTCTCCTATTTCACA 5672 R: CAGTTGGTTTCTTGTAGGATTACAGGTCAGT Pia-DNA F:ACATTTTAGTCAACTCGCCTGTTCTTTT 2597 R:CAATCAGAAAGCAACAGGTCCAAATAAC Pib-DNA F:ACAAAATCCATTCAAAAATAGAACAGAGCA 5532 R:CACAGCCCCTCGGGTCCACAT Pid3-DNA F:AAGCGAGAAGGAAGTAACACCCAAGG 2865 R:AAGAATGAATGTCCTGACTGAAACCAACT Pid2-DNA F:CTGGGTTTGAAGAAAAGAATAAAGGGAGTG 3847 R:TGAAAATGATACTGAAAGGTCTGATGAAAA Pi5-qPCR F:TTCTGCTCGCTATCCAATCCAATG 173 R:TTTCTGTATGATGTTGTTTGCTTCTCCTC Pia-qPCR F:CCAGCCACTTGCTCTTGTTACCATAG 134 R:GCCGCATCCTTTCAAGTGTTTTATCA Pib-qPCR F:GGACAAGTGTTGGTGCTTCGGAG 176 R:CCTTGGGCTTTGATAAACACCGCT Pid3-qPCR F:AAGCAGTGGAGGTCGCCAAGTC 138 R:CGTCCTTGAACCGCTCGGCT Pid2-qPCR F:ACTAACTTCTTCCCTCCTGCGGCT 175 R:AAGATGCGAAACGAGTTGTATTCCC Actin150 F:AGTGTCTGGATTGGAGGAT 147 R:TCTTGGCTTAGCATTCTTG 表 2 抗病虫基因分析结果
Table 2 Analysis on disease and insect resistance genes
基因名称
Genes染色体
Chromosome表型
Phenotype探针类型
Probe type福农A
FunongA福稻B
FudaoB华航丝苗
Huahangsimiaoxa13 8 白叶枯抗性 单倍型 0.08 0.08 0.22 Xa21 11 白叶枯抗性 单倍型 1.00 1.00 1.00 Xa23 11 白叶枯抗性 单倍型 0.07 0.10 0.07 xa5 5 白叶枯抗性 单倍型 0.35 0.31 0.35 Xa7 6 白叶枯抗性 单倍型 0.11 0.44 0.11 Rymv1 4 抗黄色斑驳病毒病 SNP √ √ √ STV11 11 持久性抗水稻条叶枯病毒 SNP √ √ Bph14 3 褐飞虱抗性 单倍型 0.48 0.55 0.34 Bph15 4 褐飞虱抗性 单倍型 0.16 0.16 0.16 Bph18 12 褐飞虱抗性 单倍型 0.69 0.59 0.69 Bph26 12 褐飞虱抗性 单倍型 0.52 0.43 0.52 Bph6 4 褐飞虱抗性 单倍型 0.62 0.62 0.62 Bph9 12 褐飞虱抗性 单倍型 0.40 0.28 0.40 表格中探针类型为“SNP”的基因,样品编号下方的“√”表示与代表品种基因型一致,空格表示未检测到相关基因;表格中探针类型为“单倍型”的基因,样品编号下方的数字表示与标准样对比的相似度,“1.00”表示与标准样相似度达100%,样品中存在该基因。
For genes with probe type "SNP", a "√" sign under the code indicates a genotype consistent with reference, while without a sign, no related gene detected. For genes with probe type "haplotype",number represented similarity to reference sequence, and "1.00" indicates a 100% similarity to reference as gene existed in the sample. -
[1] 刘倩, 张国豪, 车万均, 等. 杂交水稻重要亲本农艺性状配合力遗传力分析 [J]. 广东农业科学, 2020, 47(1):1−8. LIU Q, ZHANG G H, CHE W J, et al. Analysis on combining ability and heritability in agronomic traits of key parents of hybrid rice [J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 47(1): 1−8. (in Chinese)
[2] 曹厚明, 晚莉, 袁驰, 等. 优质抗病香型籼稻三系不育系内香10A的选育与应用 [J]. 杂交水稻, 2023, 38(6):62−66. CAO H M, WAN L, YUAN C, et al. Breeding and application of aromatic indica CMS line Neixiang 10A with good grain quality and disease resistance [J]. Hybrid Rice, 2023, 38(6): 62−66. (in Chinese)
[3] 张云虎, 严志, 杨力, 等. 利用分子标记辅助选择技术改良三系不育系荃9311A稻瘟病抗性的研究 [J]. 杂交水稻, 2022, 37(1):19−24. ZHANG Y H, YAN Z, YANG L, et al. Studies on improving rice blast resistance of CMS line Quan 9311A by molecular marker-assisted technology [J]. Hybrid Rice, 2022, 37(1): 19−24. (in Chinese)
[4] 涂诗航, 连玲, 洪永河, 等. 籼型三系不育系‘福农A’的选育及其综合农艺性状分析 [J]. 农业生物技术学报, 2024, 32(3):701−711. TU S H, LIAN L, HONG Y H, et al. Breeding of the three-line indica cytoplasmic male sterile line ‘funong a’ and its comprehensive agronomic trait analysis [J]. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2024, 32(3): 701−711. (in Chinese)
[5] 谢旺有, 陈锦文, 谢少和, 等. 高产中抗稻瘟病杂交水稻新组合福农优039的选育 [J]. 杂交水稻, 2022, 37(6):64−66. XIE W Y, CHEN J W, XIE S H, et al. Breeding of new hybrid rice combination funongyou 039 with high yield and moderate blast resistance [J]. Hybrid Rice, 2022, 37(6): 64−66. (in Chinese)
[6] 黄伟群. 优质、抗病杂交稻福农优9802在南平市示范表现及高产栽培技术 [J]. 福建稻麦科技, 2020, 38(4):46−48. HUANG W Q. Demonstration of plant performance and high-yielding cultivation techniques of good quality and disease resistance hybrid rice combination funongyou 9802 in Nanping City [J]. Fujian Science and Technology of Rice and Wheat, 2020, 38(4): 46−48. (in Chinese)
[7] 陈锦文, 陈惠清, 李坤泰, 等. 优质抗病水稻新品种福农优404的选育[J]. 福建农业学报, 2022, 37(3): 283-290. CHEN J W, CHEN H Q, LI K T, et al. Breeding a high-quality, disease-resistant rice, funong you 404[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 37(3): 283-290. (in Chinese)
[8] 丁巧莲. 优质抗病杂交稻福农优101在建阳区种植表现及高产栽培技术 [J]. 福建稻麦科技, 2021, 39(3):58−60. DING Q L. Planting performance and high-yielding cultivation techniques of Funongyou 101 in jianyang district [J]. Fujian Science and Technology of Rice and Wheat, 2021, 39(3): 58−60.
[9] FJELLSTROM R, CONAWAY-BORMANS C A, MCCLUNG A M, et al. Development of DNA markers suitable for marker assisted selection of three Pi genes conferring resistance to multiple Pyricularia grisea pathotypes [J]. Crop Science, 2004, 44(5): 1790−1798. DOI: 10.2135/cropsci2004.1790
[10] 高利军, 高汉亮, 颜群, 等. 4个抗稻瘟病基因分子标记的建立及在水稻亲本中的分布 [J]. 杂交水稻, 2010, 25(S1):294−298. GAO L J, GAO H L, YAN Q, et al. Establishment of markers for four blast genes and marker distribution in rice parents [J]. Hybrid Rice, 2010, 25(S1): 294−298. (in Chinese)
[11] RAMKUMAR G, SRINIVASARAO K, MOHAN K M, et al. Development and validation of functional marker targeting an InDel in the major rice blast disease resistance gene Pi54 (Pikh) [J]. Molecular Breeding, 2011, 27(1): 129−135. DOI: 10.1007/s11032-010-9538-6
[12] OKUYAMA Y, KANZAKI H, ABE A, et al. A multifaceted genomics approach allows the isolation of the rice Pia-blast resistance gene consisting of two adjacent NBS-LRR protein genes [J]. The Plant Journal, 2011, 66(3): 467−479. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04502.x
[13] 梁毅, 杨婷婷, 谭令辞, 等. 水稻广谱抗瘟基因Pigm紧密连锁分子标记开发及其育种应用 [J]. 杂交水稻, 2013, 28(4):63−68,74. LIANG Y, YANG T T, TAN L C, et al. Development of the molecular marker tightly-linked with the broad-spectrum blast resistance gene pigm and its breeding practice in rice [J]. Hybrid Rice, 2013, 28(4): 63−68,74. (in Chinese)
[14] HAYASHI K, YASUDA N, FUJITA Y, et al. Identification of the blast resistance gene Pit in rice cultivars using functional markers [J]. TAG Theoretical and Applied Genetics Theoretische und Angewandte Genetik, 2010, 121(7): 1357−1367. DOI: 10.1007/s00122-010-1393-7
[15] SHANG J J, TAO Y, CHEN X W, et al. Identification of a new rice blast resistance gene, Pid3, by genomewide comparison of paired nucleotide-binding site: Leucine-rich repeat genes and their pseudogene alleles between the two sequenced rice genomes [J]. Genetics, 2009, 182(4): 1303−1311. DOI: 10.1534/genetics.109.102871
[16] 孙庚. 水稻抗瘟基因与稻瘟菌无毒基因的分布及稻瘟菌分子检测[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2012. SUN G. Distribution of resistance genes in rice and avirulence genes in rice blast fungus and molecule detection of Magnaporthe oryzae [D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2012. (in Chinese)
[17] 高利军, 邓国富, 高汉亮, 等. 水稻抗稻瘟病基因Pi-d2基因标签的建立与应用 [J]. 西南农业学报, 2010, 23(1):77−82. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4829.2010.01.017 GAO L J, DENG G F, GAO H L, et al. Establishment and application of gene tagging linked to rice blast resistance gene Pi-d2 [J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 23(1): 77−82. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4829.2010.01.017
[18] DENG Y W, ZHAI K R, XIE Z, et al. Epigenetic regulation of antagonistic receptors confers rice blast resistance with yield balance [J]. Science, 2017, 355(6328): 962−965. DOI: 10.1126/science.aai8898
[19] 陈贤, 赵延存, 明亮, 等. 水稻白叶枯病抗性相关基因的研究进展 [J]. 江苏农业学报, 2022, 38(5):1402−1410. CHEN X, ZHAO Y C, MING L, et al. Update of rice bacterial blight resistance genes [J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 38(5): 1402−1410. (in Chinese)
[20] 黄振, 彭勇, 杨定照, 等. 优质三系杂交水稻新品种隆晶优8129的选育 [J]. 湖南农业科学, 2023(10):15−18. HUANG Z, PENG Y, YANG D Z, et al. Breeding of a new quality three-line hybrid rice longjingyou 8129 [J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2023(10): 15−18. (in Chinese)
[21] 宋丰顺, 倪金龙, 张爱芳, 等. 水稻两系不育系1892S抗白叶枯病和抗稻瘟病分子改良 [J]. 分子植物育种, 2016, 14(6):1507−1515. SONG F S, NI J L, ZHANG A F, et al. Molecular improvement of male sterile line 1892S for resistance to rice blast and bacterial blight [J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2016, 14(6): 1507−1515. (in Chinese)
[22] 柳武革, 王丰, 李金华, 等. 水稻三系不育系的分子设计改良与应用 [J]. 广东农业科学, 2021, 48(10):69−77. LIU W G, WANG F, LI J H, et al. Improvement of three-line rice male sterile lines by molecular design and their application [J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 48(10): 69−77. (in Chinese)





 下载:
下载: