Vector Construction and Immunogenicity of S and N Gene DNA Vaccine for TGEV
-
摘要:目的
构建猪传染性胃肠炎病毒(transmissible gastroenteritis virus, TGEV)S、N基因的DNA疫苗载体,并进行免疫原性试验,为猪传染性胃肠炎(transmissible gastroenteritis, TGE)的防控和DNA疫苗研究提供技术支撑和基础数据。
方法扩增S基因的A位点、D位点和N基因,并将N基因(单独)、A位点和D位点(融合)克隆至pCDNA3.1-His-C构建重组疫苗载体,运用生物信息学软件预测分析S(A-D)蛋白、N蛋白二级结构组成、三级构像、亚细胞定位和优势B细胞抗原表位。将构建成功的重组载体分别转染至PK-15细胞进行间接免疫荧光试验,运用共聚焦检测重组蛋白的表达分布情况。将重组疫苗载体单独或联合免疫小鼠,运用间接ELISA检测IgG抗体水平。
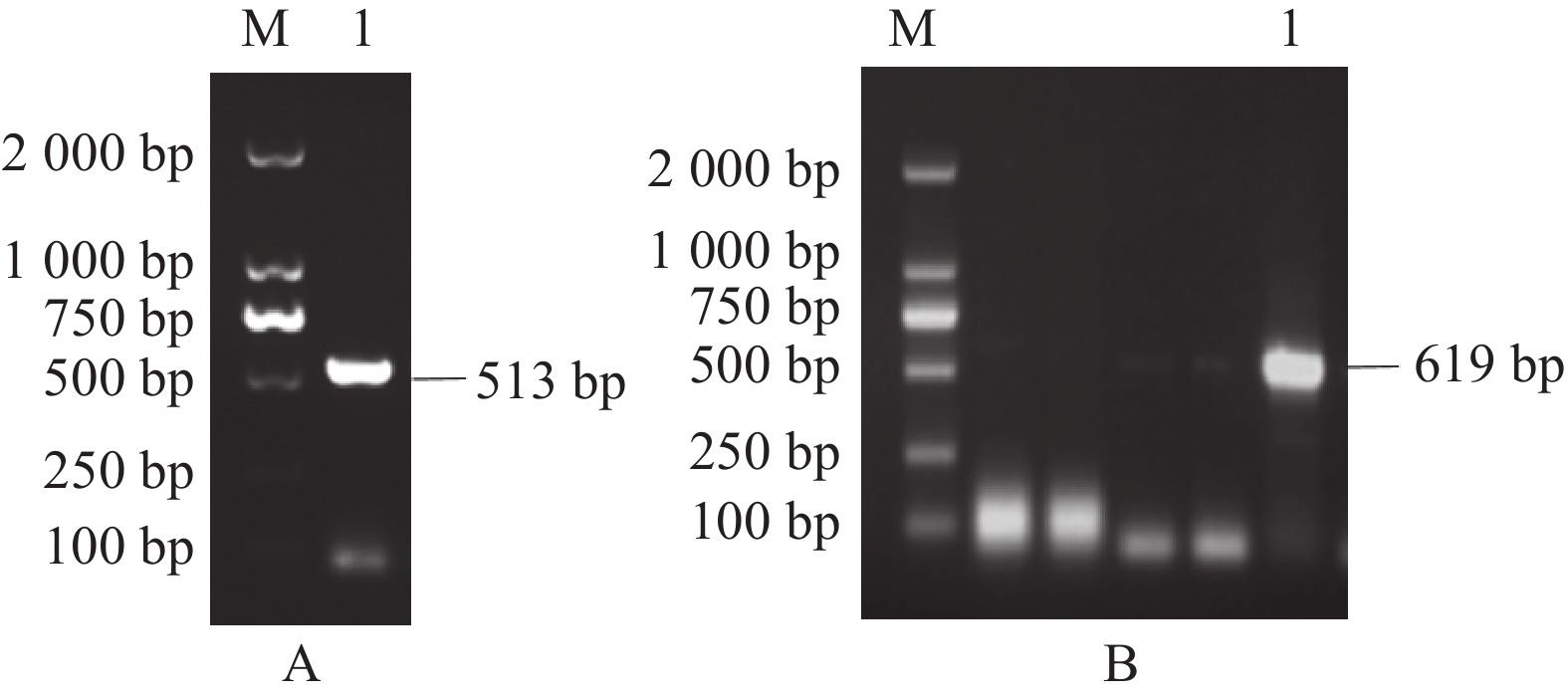
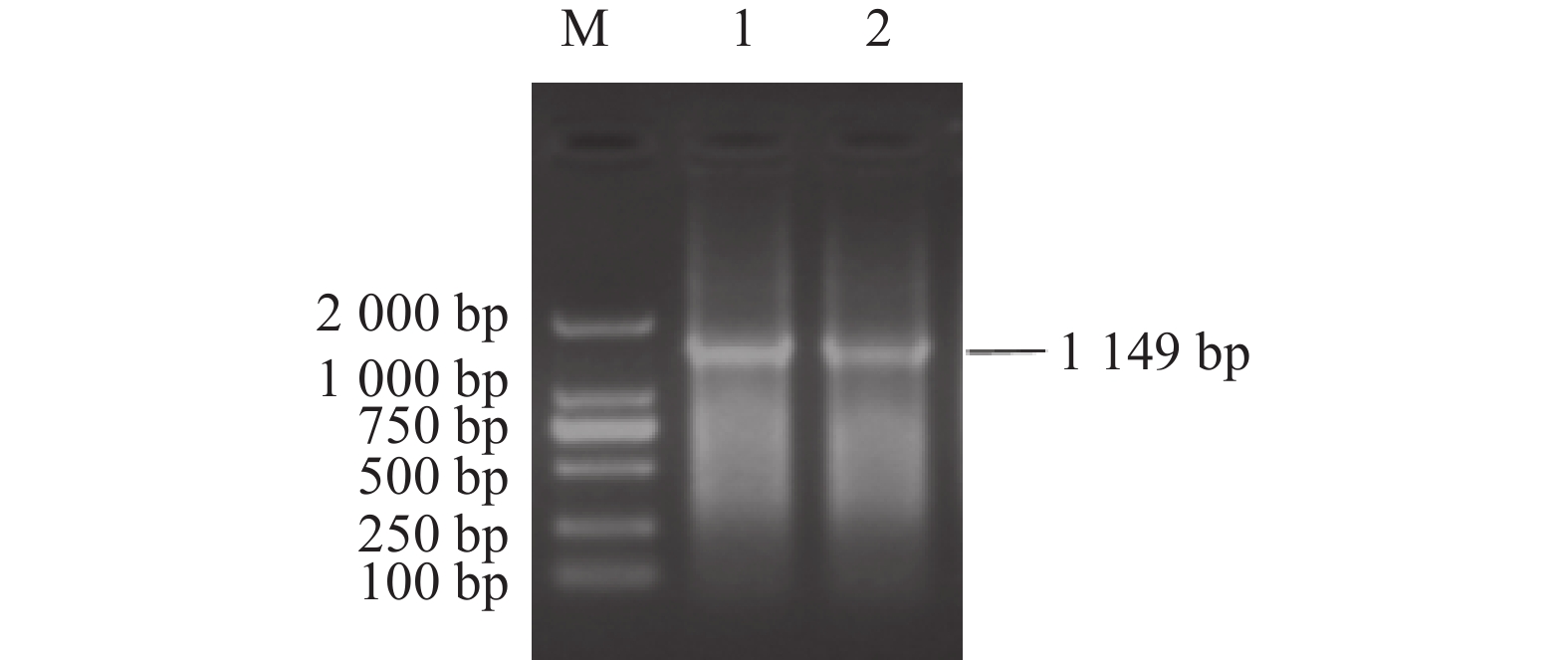
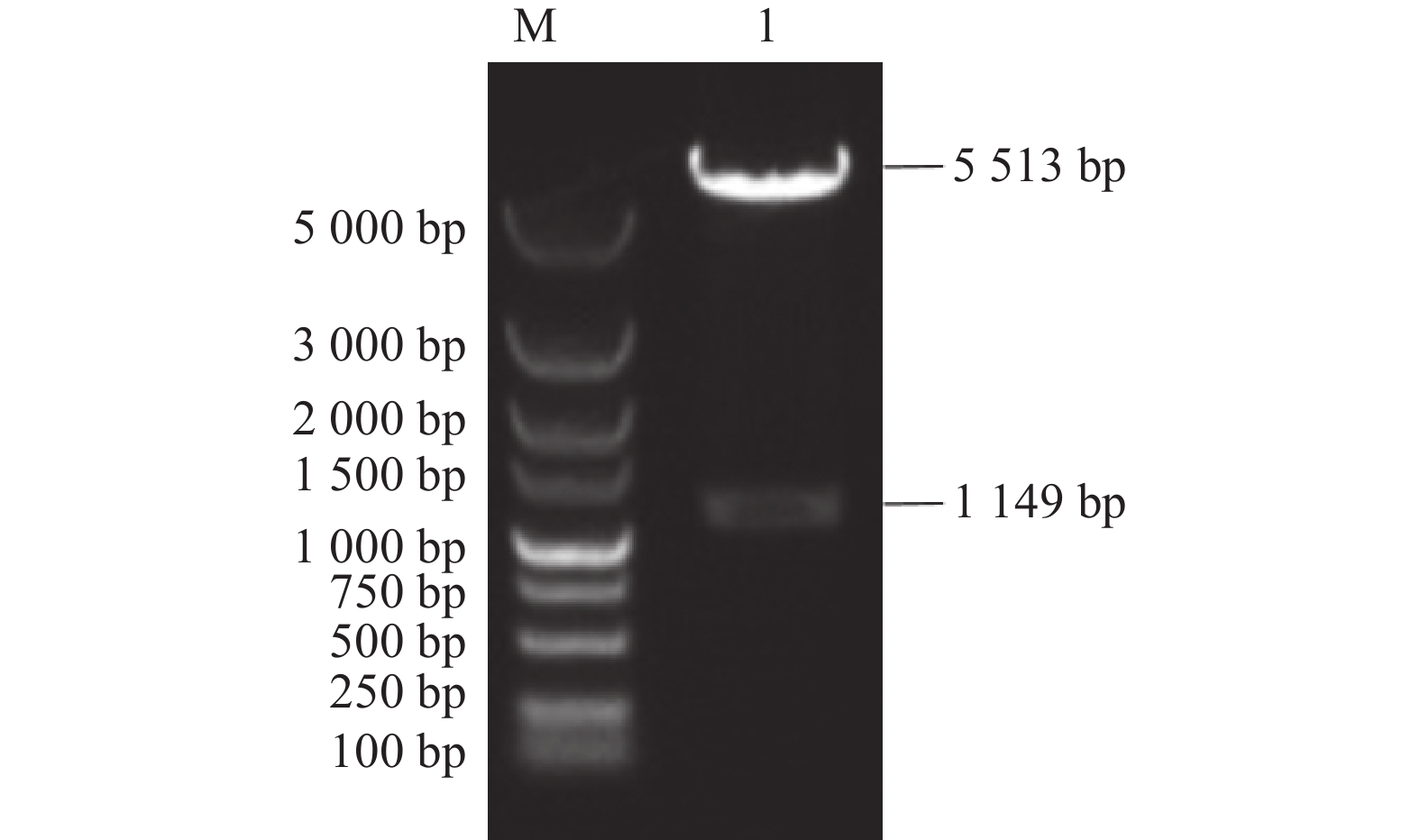
结果扩增出S基因的A位点、D位点和N基因,大小分别为498、606、
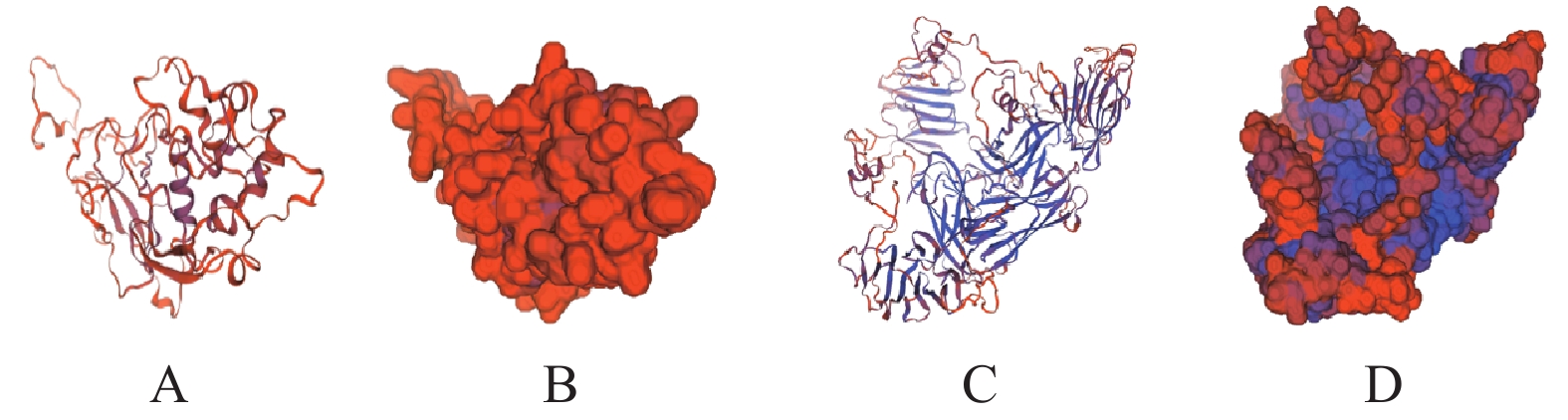
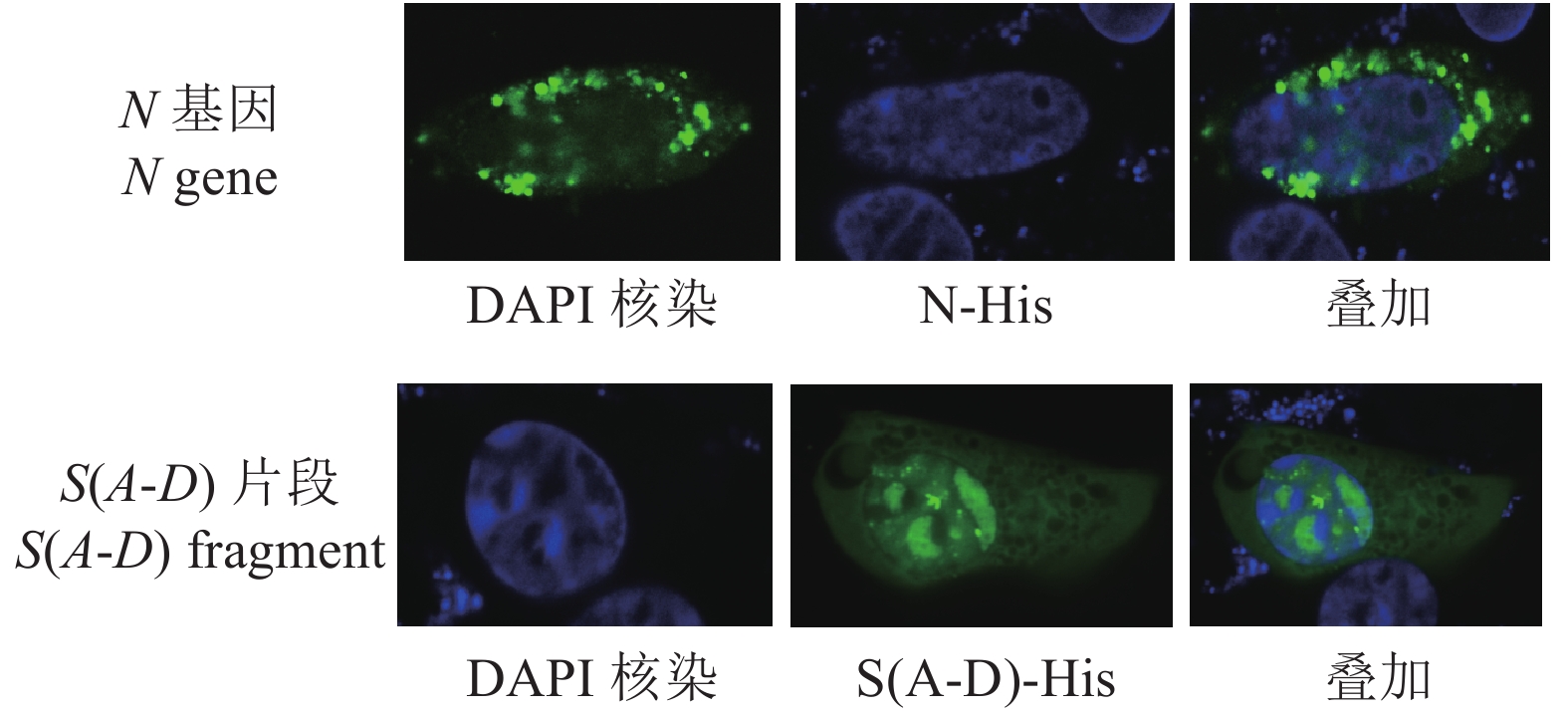
1149 bp。构建了A位点与D位点(融合)、N基因(单独)的DNA疫苗重组载体p-S(A-D)-His和p-N-His。生物信息学软件预测分析发现TGEV感染宿主细胞时N蛋白主要定位于细胞核和线粒体,S(A-D)蛋白主要定位于细胞质和线粒体,S(A-D)蛋白具有7个优势B细胞抗原表位,N蛋白具有8个优势B细胞抗原表位。重组载体p-S(A-D)-His和p-N-His均在PK-15细胞内成功表达,且S(A-D)-His和N-His在PK-15细胞核和细胞质中均有分布。重组疫苗载体免疫小鼠后,免疫效果由高至低依次为p-N-His>p-S(A-D)-His + p-N-His>p-S(A-D)-His。结论本研究构建了TGEV的 S、N基因的DNA疫苗载体,免疫小鼠后均产生了较强的特异性抗体,为TGEV的核酸疫苗的研制提供了基础材料和依据。
Abstract:ObjectiveDNA vaccine vector of S and N genes of porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV) was constructed with the vaccine immunogenicity determined to pave the way for studying, preventing, and controling TGE.
MethodA and D sites on S and N from a TGEV were amplified. The N gene alone as well as the A and D sites fusion were cloned into the vaccine vector pCDNA3.1-His-C. Bioinformatics software was used to predict and analyze the secondary structure, tertiary configuration, subcellular localization, and dominant B cell epitope of S (A-D) and N proteins. The recombinant vectors were transfected into PK-15 cells, and expression distribution of N and the A and D sites fusion detected by indirect immunofluorescence and confocal detection. Mice were immunized with the single or combined recombinant vaccine vector to detect the IgG antibody using indirect ELISA.
ResultThe A and D sites of the S were 498 bp and 606 bp, respectively, and the N,
1149 bp in length. The nucleic acid vaccine expression vectors p-S (A-D)-His and p-N-His for the A and D sites (fusion) and N were constructed. Bioinformatics software predicted that, when TGEV infected the host cells, N protein was mainly located in the nucleus and mitochondria and S (A-D) largely in the cytoplasm and mitochondria, while S (A-D) had 7 and N, 8 dominant B cell epitopes. All p-S (A-D)-His and p-N-His were successfully expressed in PK-15 cells distributed in the nucleus and cytoplasm. The immunized mice showed an effect of immunity in the order of p-N-His>p-S (A-D)-His + p-N-His>p-S (A-D)-His.ConclusionThe DNA vaccine vectors of S and N of TGEV were successfully constructed. Strong specific antibodies were generated in lab mice after the immunization.
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】植物种质资源的收集与保存是植物研究重要内容,其中超低温保存作为植物组织和细胞长期保存的理想方法,尤其适合营养繁殖作物的茎尖或分生组织的保存,具有直接再生完整小植株、减少遗传变异等优点[1]。海棠是蔷薇科(Rosaceae)苹果属(Malus)中果径较小(≤5 cm)的落叶乔木或小乔木,其中观赏海棠(Malus sp.)观赏价值高,是重要的优质绿化树种,研究海棠茎尖超低温保存在生产上具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】超低温保存后较高的存活率和再生率是主要的技术目标,已有研究显示,玻璃化超低温保存中活性氧(Reactive oxygen species, ROS)诱导的氧化应激是引起植物材料冻存后存活率下降的原因之一,因此,可以采用外源抗氧化剂来保护机体在超低温保存中免受伤害,如过氧化氢酶(Catalase, CAT)[2]、超氧化物歧化酶(Superoxide dismutase, SOD)[3]等酶类抗氧化剂以及抗坏血酸(Ascorbic acid, AsA)[4]和谷胱甘肽(Glutathione, GSH)[5]等非酶类抗氧化剂,均可以有效降低ROS生成量,减少氧化应激的发生,显著改善超低温保存效果。此外,细胞程序性死亡(Programmed cell death, PCD)作为一种基因编码主动性的死亡方式,在植物超低温保存中也扮演了重要的角色,添加细胞凋亡抑制剂D-CHO[6]、NO供体(Sodium Nitroprusside, SNP)[7]和乙烯(乙烯利Ethephon, Eth)[8] 等抑制PCD发生的物质可以提高存活率。【本研究切入点】目前除了对苹果属一些种类有少量超低温保存[9-12],特别是涉及观赏海棠的超低温保存研究极少,而极具观赏价值的北美海棠品种之一——红丽海棠(Malus Red Splendor)超低温保存鲜见报道。【拟解决的关键问题】本文以红丽海棠茎尖为试材,研究其超低温保存技术程序,探讨添加不同含量的抗氧化剂及PCD抑制剂对茎尖超低温保存冻后存活率的影响,建立红丽海棠玻璃化超低温保存技术程序,为观赏海棠种质资源保存提供一种技术思路,并为抗氧化剂和PCD抑制剂在超低温保存中的应用提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
供试材料为观赏海棠品种红丽,以健康且带有饱满腋芽的当年生枝条为外植体(采自国家植物园海棠栒子园),在1/2MS+1.5 mg·L−1 6BA+0.1 mg·L−1 IAA的培养基中诱导无菌苗,并于1/2MS+1.0 mg·L−1 6-BA+0.5 mg·L−1 IAA的培养基中进行继代培养,诱导和继代培养条件:(23±3)℃,光照强度40 μmol·m−2·s−1,光照时间14 h·d−1,取生长旺盛的组培苗用于超低温保存试验。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 茎尖玻璃化法超低温保存
根据初步预试验设置玻璃化超低温保存的基本程序,再采用“逐步单因子法”对关键环节进行优化。(1)预培养:将红丽组培苗切成5 mm左右的带顶芽茎段,分别接种在不同蔗糖浓度(0.1、0.3、0.5、0.7、0.9 mol·L−1)的MS培养基中4 ℃下培养2 d,然后继续下述程序:(2)装载(Loading):在双目解剖镜下,用镊子和手术刀切下带3~4片叶原基、大小为1.5~2.0 mm的茎尖;将切下的茎尖放入1.5 mL 装有1 mL MS溶液的离心管中,吸出离心管中的MS溶液,加入1 mL Loading溶液(2 mol·L−1丙三醇+0.4 mol·L−1蔗糖,蒸馏水配置,pH 5.8),在室温下静置处理30 min;(3)PVS2处理:吸出离心管中的Loading溶液,加入1mL PVS2溶液[30%(m/V)丙三醇+15 %(m/V)乙二醇+15%(m/V)二甲基亚砜+0.4 mol·L−1蔗糖,1/2MS盐溶液配置,pH 5.8],在0 ℃于冰浴中处理90 min;(4)液氮冻存:更换新的1 mL PVS2溶液后,封紧离心管口,立即投入液氮,冻存1 h;(5)化冻:将装有PVS2和茎尖的离心管从液氮中取出,迅速放入38 ℃水浴中化冻1 min;(6)去装载(Unloading):将离心管中的PVS2溶液吸出,加入Unloading溶液(用1/2MS盐溶液配置的1.2 mol·L−1蔗糖,pH 5.8)后在室温下震荡洗涤2次,每次10 min。然后用于存活率或恢复生长率测定。相关步骤示意图见图1。
![]() 图 1 茎尖玻璃化超低温保存及存活率检测A.红丽海棠组培苗;B.预培养;C.切取1.5~2.5 mm茎尖;D.茎尖在离心管中;E.经TTC染色变红(左)与未染色(右)的茎尖;F.冻后茎尖接种到恢复培养基中。Figure 1. Survival rate of post-cryopreservation shoot tipsA: Crabapple tissue culture; B: pre-culture; C: 1.5-2.5 mm cut of shoot tip; D: shoot tip segment in centrifugal tube; E: TTC stained red (left) and original (right) shoot tips; F: post-frozen shoot tips inoculated on recovery medium.
图 1 茎尖玻璃化超低温保存及存活率检测A.红丽海棠组培苗;B.预培养;C.切取1.5~2.5 mm茎尖;D.茎尖在离心管中;E.经TTC染色变红(左)与未染色(右)的茎尖;F.冻后茎尖接种到恢复培养基中。Figure 1. Survival rate of post-cryopreservation shoot tipsA: Crabapple tissue culture; B: pre-culture; C: 1.5-2.5 mm cut of shoot tip; D: shoot tip segment in centrifugal tube; E: TTC stained red (left) and original (right) shoot tips; F: post-frozen shoot tips inoculated on recovery medium.关键环节的优化:在获得适宜预培养蔗糖浓度基础上,分别设置不同预处理时间(1、2、3 d),不同Loading溶液处理时间(0、10、20、30、40 min)和不同PVS2溶液处理时间(0、30、60、90、120 min),每个优化环节之前的步骤采用上一步已优化的处理方法,之后的步骤采用上述基本程序,直至完成所有关键环节的优化。每处理10~15个茎尖,重复3次。
1.2.2 存活率测定
采用氯化三苯基四氮唾(TTC)法检测冻存后茎尖的存活率。将经过Unloading溶液处理的茎尖置于含0.4%(m/V)的TTC溶液的离心管中,再放入37 ℃的水浴中黑暗处理30 min,将茎尖取出后,置于体视显微镜下,观察其染色情况。顶端分生组织被染红的茎尖记为存活的茎尖,而未被染红的茎尖记为死亡的茎尖。存活率/%=(被染红的茎尖/所有经过TTC处理的茎尖)×100%。每处理10~15个茎尖,重复3次。
1.2.3 恢复生长率测定
将经过液氮保存后的茎尖接种于MS培养基中暗培养2周后,然后转入正常光照条件(与组织培养的条件相同)下培养,茎尖长叶记为恢复生长。每处理10~15个茎尖,重复3次。
1.2.4 外源抗氧化剂和PCD抑制剂的添加
在建立的玻璃化超低温保存程序的基础上,根据课题组前人研究结果[4, 7-8, 13],分别在预培养基中添加Eth(100、200、400、800 mg·L−1);在Loading溶液中添加CAT,使其终浓度分别为50、100、200、400 U·mL−1和硝普钠(SNP),使其终浓度分别为50、100、200、1000 μmol·L−1;在PVS2溶液中添加GSH,使其终浓度分别为0.04、0.08、0.16、0.32 μmol·L−1;在Unloading溶液中添加AsA,使其终浓度分别为100、200、400、600 μmol·L−1,各处理均以原溶液为对照。
1.2.5 数据处理及分析
采用SPSS 26.0和Excel软件分别对试验数据进行单因素方差分析和数据整理、图表绘制。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 红丽海棠茎尖玻璃化超低温保存程序的建立
2.1.1 预培养基蔗糖浓度对液氮冻存后茎尖存活率的影响
将红丽海棠带顶芽茎段分别在含0.1、0.3、0.5、0.7、0.9 mol·L−1蔗糖的预培养基上进行2 d的培养,之后采用后续的基本程序,测定液氮冻存后茎尖存活率。如图2所示,茎尖冻后存活率随蔗糖浓度的升高先上升再下降,0.3 、0.5 、0.7 mol·L−1蔗糖浓度培养的茎尖存活率没有显著差异,但0.7 mol·L−1蔗糖浓度的预培养基上茎尖冻后存活率最高,为76.54%,显著高于0.1 、0.9 mol·L−1蔗糖浓度。因此红丽海棠超低温保存程序中预培养基的最适蔗糖浓度为0.7 mol·L−1,浓度过低过高则会降低茎尖的存活率。
2.1.2 预处理时间对液氮冻存后茎尖存活率的影响
将带顶芽的红丽海棠茎段接种于含0.7 mol·L−1蔗糖的预培养基上,在4 ℃条件下分别培养1 、2 和3 d,继续超低温保存基本程序的后续环节,液氮冻存后红丽茎尖存活率见图3。随预处理时间的增加,茎尖存活率逐渐升高,在2 d时存活率最高达到79.24%,后又下降。表明液氮冻后茎尖存活率受预培养环节冷锻炼时间的影响,适宜时长可以提高茎尖的抗冻能力。
2.1.3 Loading溶液处理时间对液氮冻存后茎尖存活率的影响
红丽海棠茎段在含0.7 mol·L−1蔗糖浓度的预培养2 d后,将茎尖分别在Loading溶液中处理不同时间,继续超低温保存基本程序的后续环节,从液氮取出化冻后茎尖存活率的结果如图4所示。Loading处理20 min时茎尖存活率最高,为60.61%,而随着处理时间的继续延长逐渐下降,处理40 min时的茎尖存活率为0。因此,Loading溶液处理时间不宜过长,否则可能会造成茎尖过度脱水而降低存活率。红丽海棠茎尖超低温保存的适宜Loading处理时间为20 min。
2.1.4 PVS2溶液处理时间对液氮冻存后茎尖存活率的影响
红丽海棠茎段在4 ℃下,含0.7 mol·L−1蔗糖浓度的预培养基上培养2 d后,Loading溶液处理20 min,分别采用PVS2溶液处理不同时间,继续超低温保存基本程序的后续环节,结果如图5。未经PVS2溶液处理的茎尖全部死亡,说明PVS2处理对玻璃化超低温保存过程起着至关重要的作用,随处理时间的增加,茎尖冻后存活率逐渐升高,处理90 min时茎尖存活率最高,为62.88%,后随时间的延长而显著下降。红丽海棠茎尖超低温保存PVS2处理适宜时间为90 min。
2.2 外源添加剂对茎尖超低温保存效果的影响
2.2.1 预培养环节添加外源Eth对液氮冻存后茎尖存活率的影响
在红丽海棠茎尖超低温保存中预培养环节添加4个质量浓度的外源Eth,继续超低温保存优化后的后续环节,茎尖冻后存活率见图6。添加100~400 mg·L−1与对照没有显著差异,200 mg·L−1时存活率稍高,而100 、400 mg·L−1时存活率稍低,而质量浓度过高时(800 mg·L−1)存活率显著下降。说明在预培养环节导入200 mg·L−1Eth时可能起到一定保护作用,小幅度提高冻后存活率,高浓度反而会导致其存活率降低。
2.2.2 Loading环节添加外源CAT或SNP对液氮冻存后茎尖存活率的影响
采用预培养优化方案后,在Loading环节添加不同浓度的外源CAT,之后继续超低温保存优化后的后续环节,茎尖液氮冻存后存活率见图7。添加200 U·mL−1时,茎尖的存活率最高,为86.67%,显著高于其他处理;含量为50 U·mL−1稍有提高,但差异不显著,其余含量显著下降。由此可知,Loading环节添加适宜浓度的外源CAT浓度可以发挥抗氧化保护作用,显著提高茎尖冻后存活率。
采用预培养优化方案后,在Loading环节添加不同浓度的外源SNP,之后继续超低温保存优化后的后续环节,茎尖超低温保存后存活率如图8所示。各浓度处理后冻后存活率均下降,但添加100和1000 μmol·L−1SNP时与对照无明显差异,而添加50和200 μmol·L−1SNP时存活率显著下降,相比对照分别降低了23.25%和13.25%。表明对PCD有拮抗作用的SNP在这里没有显示其作用。
2.2.3 PVS2环节添加外源GSH对液氮冻存后茎尖存活率的影响
采用优化的预培养和Loading方案后,在PVS2环节添加不同浓度的外源GSH,之后继续超低温保存后优化的后续环节,茎尖液氮冻存后存活率见图9。添加各种浓度的GSH,较对照均显著提高了茎尖冻后的存活率,其中导入浓度为0.04 μmol·L−1时存活率最高,为94.19%。由此表明,在PVS2环节导入外源GSH可有效发挥抗氧化保护作用,提高存活率。
2.2.4 Unloading环节添加外源AsA对液氮冻存后茎尖存活率的影响
采用优化的保存程序后,在Unloading环节导入不同浓度的外源AsA,茎尖超低温保存后存活率如图10所示,除200 μmol·L−1存活率下降外,其余浓度均可提高冻后存活率,效果最好的浓度为400 μmol·L−1,说明外源AsA起到了一定的抗氧化保护作用,小幅度提高了存活率。
2.3 红丽海棠茎尖超低温保存后恢复培养
采用优化后的超低温保存程序,在PVS2环节添加0.04 μmol·L−1的外源GSH,之后继续超低温保存后优化的后续环节,并进行恢复培养。没有添加GSH的对照组恢复生长率为16.67%,添加0.04 μmol·L−1外源GSH的恢复生长率为41.39%,提高了24.73%。
3. 讨论
冷锻炼能够提高植物茎尖的抗冻能力[14],通过在含有一定浓度的高糖、山梨醇或DMSO的培养基中培养植物茎尖,可以显著提高冻存后茎尖的存活率[15]。在大部分苹果属玻璃化超低温保存中,都至少需要3~4周的4 ℃或5 ℃的冷锻炼[16-19]。本试验通过4 ℃预培养,起到冷锻炼作用,预培养2 d,超低温保存后的茎尖存活率可到79.24%。在苹果属其他茎尖超低温保存的研究中,有不使用Loading处理直接脱水处理[20-22],本试验不经Loading溶液处理也可达到36.11%的存活率,但经Loading溶液处理20 min的茎尖冻后存活率更高,因为装载阶段是实现玻璃化而脱水处理的过渡阶段,能够避免高浓度玻璃化溶液引起的剧烈渗透变化导致的材料损伤。另外在本试验中0 ℃条件下PVS2处理90 min后茎尖冻后存活率最高,也有研究在室温下进行脱水处理,如将苹果品种嘎啦、望山红在室温下用PVS2处理30 min[10]或40 min[11]后再生率分别为55.6%和17.9%,但Uragami等[23]认为低温能降低玻璃化溶液的高渗作用导致的植物损伤,因此在大多数植物的超低温研究中,玻璃化步骤均在0 ℃下进行[24, 25]。
ROS是需氧生物中细胞有氧代谢的副产物,在正常状态下,机体可以在ROS的产生和清除之间保持动态平衡,但当ROS在逆境胁迫下产生过量时,自身的抗氧化系统,包括CAT、SOD和POD等酶类,以及AsA和GSH等非酶类系统会协同作用清除抵抗ROS可能带来的伤害,但当抗氧化能力不足以清除过量的ROS时,机体就会出现氧化应激。这启发研究人员们通过导入外源抗氧化剂来抵御氧化损伤,研究证明外源CAT[4, 13, 26]、AsA[4, 27]和GSH[6]均有抑制氧化应激的作用。本研究结果也显示,外源抗氧化剂CAT、AsA和GSH可以提高红丽海棠茎尖冻后存活率,说明外源抗氧化剂可能抑制了ROS造成的氧化损伤。3种外源抗氧化剂在不同环节中使用,分别提高了红丽海棠茎尖冻后存活率20.28%、6.75%、27.61%。
PCD作为一种自发性、有序的细胞死亡方式,受基因调控,是生物生活的基本过程。多项研究表明植物PCD存在于植物的各个生长发育过程及植物对非生物胁迫的响应中[28]。有研究显示超低温保存中预培养是PCD的一个信号起始环节,PCD相关调控基因显著上调[7],由于细胞凋亡存在一定的延迟性,预培养后的Loading环节也成为超低温保存中PCD研究的另一重要环节。本试验在预培养和Loading环节添加了PCD抑制剂,结果显示预培养环节添加外源Eth只是小幅度提高了红丽海棠茎尖冻后存活率,而在Loading环节添加外源SNP冻后存活率反而下降了,SNP通过抑制PCD信号分子NO而其作用,而NO调控PCD具有双重作用,可以促进PCD的发生[29, 30],也可以抑制PCD的发生[31, 32],而添加环节对NO在PCD发生的作用也十分关键,如在春石斛类原球茎中预培养环节导入NO供体(SNP)促进了PCD的发生,降低了存活率,而在Loading环节添加则抑制了PCD的发生[7],故推测外源SNP对不同的植物和不同添加环节可能有不同的影响效果。
4. 结论
红丽海棠茎尖采用以下程序可以实现超低温保存:取组培苗4~5 mm带顶芽茎段,接种在含0.7 mol·L−1蔗糖的预培养基,4 ℃冰箱培养2 d;切取1.5~2.0 mm的茎尖,Loading溶液室温下处理20 min;PVS2溶液0 ℃下处理90 min,可存入液氮保存;需用时将其取出放入38 ℃水浴快速化冻1 min;在室温下Unloading溶液震荡洗涤2次,每次10 min;进行恢复培养,存活率为66.58%,恢复生长率为16.67%。在Loading、PVS2和Unloading环节导入适宜浓度的抗氧化物质CAT、GSH、AsA可明显提高冻后存活率,最佳添加量分别为200 U·ml−1、0.04 μmol·L−1和400 μmol·L−1,较对照存活率分别提高了20.28%、27.61%和6.75%,而添加PCD抑制剂没有显示明显作用
-
图 2 TGEV S基因A、D位点扩增结果
A:A位点扩增结果;M为DNA分子质量标准DL2000,1为扩增的A位点。B:D位点扩增结果;M为DNA分子质量标准DL2000,1为扩增的D位点。
Figure 2. Amplified A and D sites of TGEV S gene
A: amplification results of A site; M was DNA Marker DL2000, 1 was the PCR-amplified A site. B: amplification results of D site; M was DNA Marker DL2000, 1 was the PCR-amplified D site.
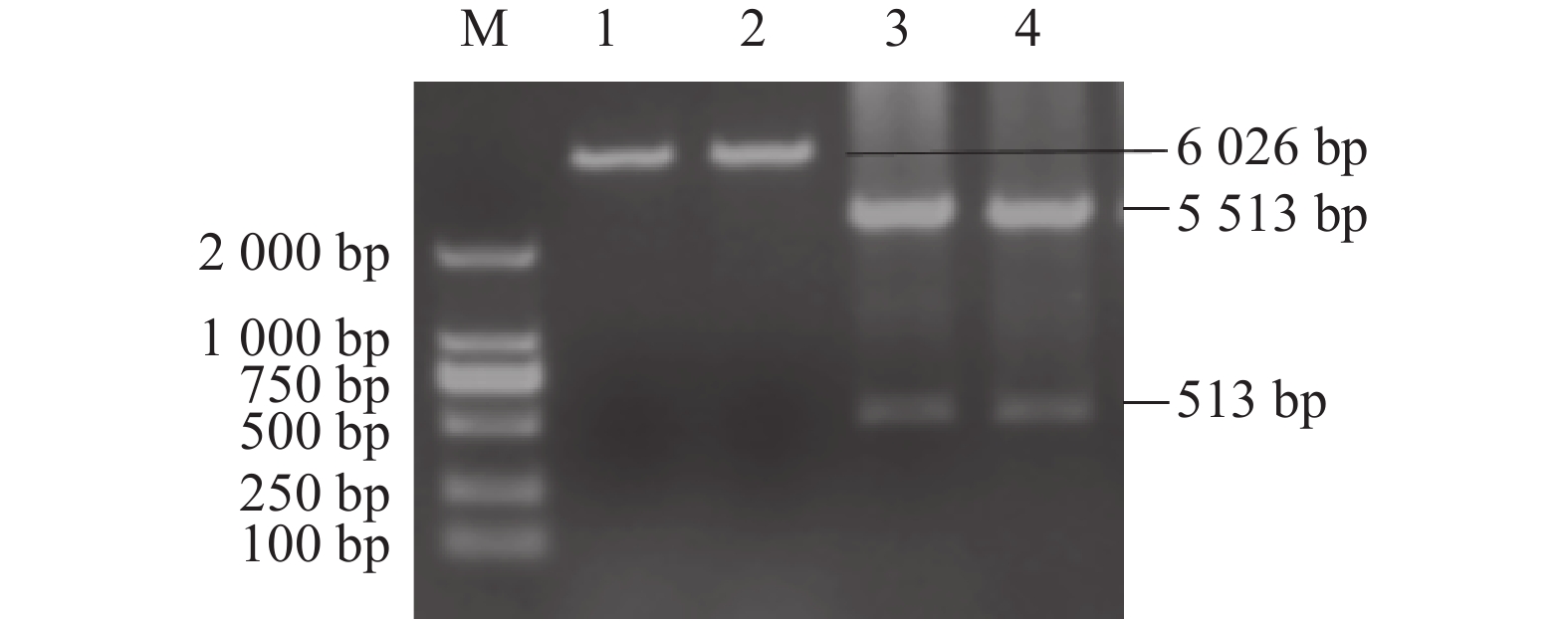
图 4 S基因A位点重组载体p-S(A)-His的构建与鉴定
M:DNA分子质量标准DL2000;1、2:重组载体p-S(A)-His的单酶切;3、4:重组载体p-S(A)-His的双酶切。
Figure 4. Construction and identification of p-S (A)-His and p-S (D)-His at A and D sites of S gene
M: DNA marker DL2000; M2: DNA marker DL10000; 1: single enzyme digestion of recombinant vector p-S (A)-His; 2: single enzyme digestion of recombinant vector p-S (D)-His; 3 and 4: double digestion of recombinant vector p-S (A)-His.
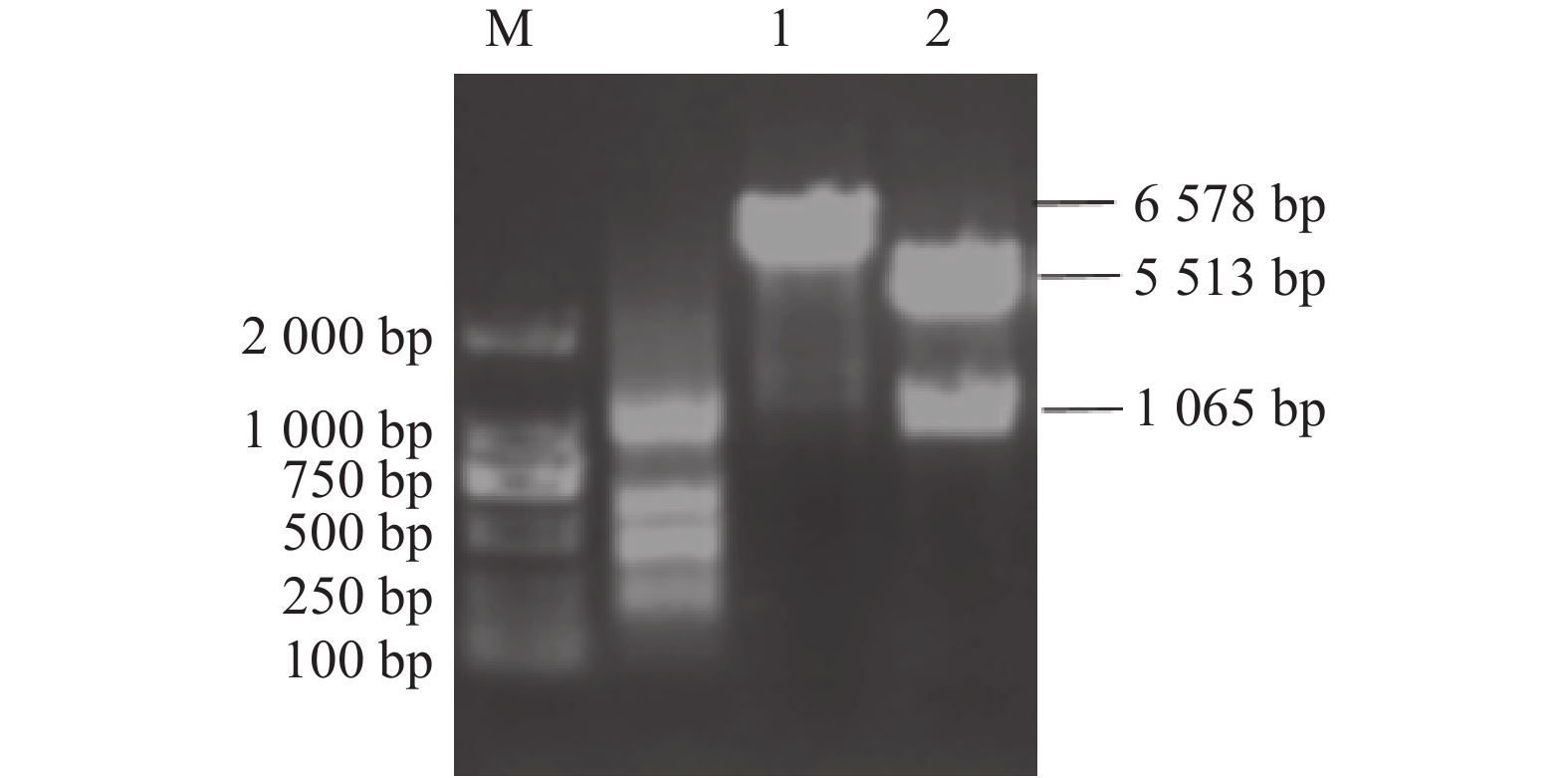
图 5 重组载体p-S(A-D)-His的构建与鉴定
M:DNA分子质量标准DL2000; 1:重组载体p-S(A-D)-His的单酶切;2:重组载体p-S(A-D)-His的双酶切。
Figure 5. Construction and identification of recombinant vectors p-S (A-D)-His
M: DNA marker DL2000; 1: single enzyme digestion of recombinant vector p-S(A-D)-His; 2: double digestion of recombinant vector p-S (A-D)-His.
表 1 S基因A位点、D位点和N基因扩增引物序列
Table 1 Sequences of primers for amplifications of A and D sites in S gene and N gene
基因
Gene引物
Primers序列(5′−3′)
Sequence(5′−3′)酶切位点
Restriction enzyme cutting siteS基因A位点
A-site in S geneP1 CGCGGATCCATGTTAGTTACCAAACAGCCGT Bam H I P2 CCGGAATTCTATTGTCCAGAAAACGTCAC Eco R I S基因D位点
D-site in S geneP3 CCGGAATTCAAGTTGAAAACACAGCTATT Eco R I P4 TGCTCTAGA ACTATTATCAGACGGTACACC Xba I N基因
N GeneP5 CGCGGATCCATGGCCAACCAGGGAC Bam H I P6 CCGGAATTCGTTCGTTACCTCATCAATT Eco R I 表中加下划线的碱基序列为酶切位点序列。
Cleavage sites are underlined.表 2 小鼠分组及免疫程序
Table 2 Groups and procedures of mice immunization
组别
Group疫苗载体种类
Vaccine carrier type免疫剂量
Immunizing dose/μg小鼠数量
Number of mice免疫时间
Immune frequency免疫位置
Immune site1 p-S(A-D)-His 240 6 第1、7、21天 脚底板 2 p-N-His 240 6 第1、7、21天 脚底板 3 p-S(A-D)-His + p-N-His 120+120 6 第1、7、21天 脚底板 4 pCDNA3.1-His-C 240 6 第1、7、21天 脚底板 表 3 S(A-D)蛋白和N蛋白亚细胞定位预测
Table 3 Predicted subcellular localization of S (A-D) and N proteins
组别
Group亚细胞定位
Subcellular localization可能性
Possibility/%S(A-D)蛋白
S(A-D) protein细胞质 Cytoplasm 34.8 线粒体 Mitochondria 17.4 细胞核 Cell nucleus 13.0 质膜 Plasmalemma 13.0 内质网 Endoplasmic reticulum 8.7 N蛋白
N protein细胞核 Cell nucleus 65.2 线粒体 Mitochondria 17.4 细胞质 Cytoplasm 13.0 溶酶体 Lysosome 4.3 表 4 S(A-D)蛋白和N蛋白的B细胞抗原表位预测
Table 4 Predicted B cell epitope of S (A-D) and N proteins
蛋白
Protein序号
Number起始位点
Start site结束位点
End site序列
Amino acid sequenceS(A-D)蛋白
S(A-D)protein1 33 43 FDQCNGAVLNN 2 55 62 TTNVQSGK 3 86 101 DSSFFSYGEIPFGVTD 4 195 211 NLNNGFYPVSSSEVGLV 5 233 250 LGMKRSGYGQPIASTLSN 6 281 295 ALWDNIFKRNCTDVL 7 306 318 CPFSFDKLNNYLT N蛋白
N protein1 4 32 QGQRVSWGDESTKTRGRSNSRGRKSNNIP 2 43 87 QGSKFWNLCPRDFVPNGIGNRDQQIGYWNRQTRYRMVKGQRKELP 3 101 108 ADAKFKDK 4 118 146 DGAMNKPTTLGSRGANNESKALKFDGKVP 5 150 189 QLEVNQSRDNSRSRSQSRSRSRNRSQSRGRQQSNNKKDDS 6 201 244 LGVDTEKQQQRSRSKSKERSNSKTRDTTPKNENKHTWKRTAGKG 7 251 271 GARSSSANFGDSDLVANGSSA 8 316 378 DPKTEQFLQQINAYARPSEVAKEQRKRKSRSKSAERSEQEVVPDALIENYTDVFDDTQVEIID 表 5 免疫小鼠抗TGEV血清IgG间接ELISA检测
Table 5 Anti-TGEV serum IgG in immunized mice detected by indirect ELISA
组别
Group疫苗载体种类
Vaccine carrier type免疫后不同时间抗TGEV血清IgG水平(OD450 nm)
Anti-TGEV serum IgG levels at different time after immunization (OD450 nm)0天
0 days14天
14 days28天
28 days42天
42 days1 p-S(A-D)-His 0.133±0.011 a 0.218± 0.0075 b0.243± 0.0060 c0.401± 0.0100 c2 p-N-His 0.138±0.016 a 0.244± 0.0025 a0.344± 0.0070 a0.504± 0.0141 a3 p-S(A-D)-His + p-N-His 0.142± 0.0050 a0.225± 0.0021 b0.300± 0.0050 b0.471± 0.0075 b4 pCDNA3.1-His-C 0.134± 0.0089 a0.144± 0.0076 c0.141± 0.0069 c0.139± 0.0020 d同列数据小写字母完全不同表示差异显著(P<0.05),含相同小写字母表示差异不显著(P>0.05)。
Data with different lowercase letters on same column indicate significant differences at P<0.05; those with same lowercase letters indicate no significant differences at P>0.05. -
[1] 张羽欣, 王树茂, 段宏勇, 等. 猪传染性胃肠炎病毒TaqMan实时荧光定量PCR检测方法的建立与应用 [J]. 中国兽医科学, 2024, 54(4):479−484. ZHANG Y X, WANG S M, DUAN H Y, et al. Establishment and application of TaqMan real-time quantitative PCR for detection of porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus [J]. Chinese Veterinary Science, 2024, 54(4): 479−484. (in Chinese)
[2] JI Z Y, DONG H, JIAO R X, et al. The TGEV membrane protein interacts with HSC70 to direct virus internalization through clathrin-mediated endocytosis [J]. Journal of Virology, 2023, 97(4): e0012823. DOI: 10.1128/jvi.00128-23
[3] PU J N, CHEN D W, TIAN G, et al. All-trans retinoic acid attenuates transmissible gastroenteritis virus-induced inflammation in IPEC-J2 cells via suppressing the RLRs/NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 2022, 13: 734171. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.734171
[4] NIU Z, XU S S, ZHANG Y L, et al. Transmissible gastroenteritis virus nucleocapsid protein interacts with Na+/H+ exchanger 3 to reduce Na+/H+ exchanger activity and promote piglet diarrhea [J]. Journal of Virology, 2022, 96(22): e0147322. DOI: 10.1128/jvi.01473-22
[5] QIAN J T, LI M J, FENG Y F, et al. Genetic epidemiology of porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus based on whole genome and S gene sequences[C]//2021 IEEE 9th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (ICBCB). May 25-27, 2021, Taiyuan, China. IEEE, 2021: 148-151.
[6] 郝振业. 猪传染性胃肠炎病毒反向遗传操作系统的构建及附属蛋白3(ORF3)的定位及功能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2023. HAO Z Y. Construction of reverse genetic operating system of porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus and study on location and function of accessory protein 3(ORF3)[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2023. (in Chinese)
[7] 王艳春. 猪传染性胃肠炎病毒S基因A位点杆状病毒表达及初步应用[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2020. WANG Y C. Expression of baculovirus at site A of S gene of porcine infectious gastroenteritis virus and its preliminary application[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2020. (in Chinese)
[8] 张海燕. PEDV和TGEV的S蛋白融合抗原表位核酸疫苗的研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2019. ZHANG H Y. Study on S protein fusion epitope nucleic acid vaccine of PEDV and TGEV[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2019. (in Chinese)
[9] LI X L, LI P C, CAO L Y, et al. Porcine IL-12 plasmid as an adjuvant improves the cellular and humoral immune responses of DNA vaccine targeting transmissible gastroenteritis virus spike gene in a mouse model [J]. Journal of Veterinary Medical Science, 2019, 81(10): 1438−1444. DOI: 10.1292/jvms.18-0682
[10] 师一鸣. TGEV单克隆抗体的制备及检测方法的建立[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2019. SHI Y M. Preparation of TGEV monoclonal antibody and establishment of detection method[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2019. (in Chinese)
[11] 李雅静, 宫强. 铜绿假单胞菌oprH基因DNA疫苗的构建与检测 [J]. 现代畜牧兽医, 2022(11):19−23. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9692.2022.11.lnxmsy202211006 LI Y J, GONG Q. Construction and detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa oprH gene DNA vaccine [J]. Modern Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2022(11): 19−23. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9692.2022.11.lnxmsy202211006
[12] 杨鹏, 吴燕, 岳筠, 等. 绵羊肺炎支原体P113蛋白C末端基因真核表达载体的构建及其小鼠免疫应答 [J]. 中国兽医学报, 2022, 42(3):496−501, 521. YANG P, WU Y, YUE J, et al. Construction of eukaryotic expression vector for C terminal gene of Mycoplasma ovipneumoniae P113 protein and its immune response in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2022, 42(3): 496−501, 521. (in Chinese)
[13] 姚思, 杨洁琼, 杨雨欣, 等. 结核分枝杆菌ESAT6-Fc DNA疫苗的免疫效应评价 [J]. 中国生物制品学杂志, 2023, 36(8):897−901. YAO S, YANG J Q, YANG Y X, et al. Evaluation of immune effect of ESAT6-Fc DNA vaccine against Mycobacterium tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Biologicals, 2023, 36(8): 897−901. (in Chinese)
[14] 黄小波, 杨恒, 曹三杰, 等. 猪传染性胃肠炎病毒S-N融合双基因疫苗的构建及其免疫原性分析 [J]. 中国兽医科学, 2012, 42(8):848−853. HUANG X B, YANG H, CAO S J, et al. Construction and immunogenicity analysis of the S-N fusion gene vaccine against porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus [J]. Chinese Veterinary Science, 2012, 42(8): 848−853. (in Chinese)
[15] WANG G, LIANG R, LIU Z W, et al. The N-terminal domain of spike protein is not the enteric tropism determinant for transmissible gastroenteritis virus in piglets [J]. Viruses, 2019, 11(4): 313. DOI: 10.3390/v11040313
[16] 韩郁茹, 石达, 张记宇, 等. 猪急性腹泻综合征冠状病毒RT-LAMP快速检测方法的建立与应用 [J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2021, 43(1):35−39. HAN Y R, SHI D, ZHANG J Y, et al. Development and application of RT-LAMP method for rapid detection of SADS-CoV [J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 2021, 43(1): 35−39. (in Chinese)
[17] 樊杰. 猪传染性胃肠炎病毒N蛋白纳米抗体的制备和基于纳米抗体竞争ELISA的建立[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2021. FAN J. Preparation of nano-antibody against N protein of transmissible gastroenteritis virus and establishment of competitive ELISA based on nano-antibody[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2021. (in Chinese)
[18] ZHANG Y D, ZHANG X H, LIAO X D, et al. Construction of a bivalent DNA vaccine co-expressing S genes of transmissible gastroenteritis virus and porcine epidemic diarrhea virus delivered by attenuated Salmonella typhimurium [J]. Virus Genes, 2016, 52(3): 354−364. DOI: 10.1007/s11262-016-1316-z
[19] 何雷, 董玲娟, 张彦明, 等. 猪传染性胃肠炎病毒ORF7蛋白在ST细胞中定位及其对病毒复制影响的研究 [J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2020, 42(6):543−548. HE L, DONG L J, ZHANG Y M, et al. The subcellular location of transmissible gastroenteritis virus protein ORF7 and its effect on viral replication [J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 2020, 42(6): 543−548. (in Chinese)
[20] 何雷, 贾艳艳, 郁川, 等. 稳定表达猪传染性胃肠炎病毒N蛋白的ST细胞株的构建及其亚细胞定位 [J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2016, 38(2):101−104. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0589.2016.02.04 HE L, JIA Y Y, YU C, et al. Establishment of stably-expressed transmissible gastroenteritis virus N protein cell line and its subcellular location [J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 2016, 38(2): 101−104. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0589.2016.02.04
[21] 韩涛涛, 黎露, 唐青海, 等. 不同佐剂对猪传染性胃肠炎病毒S蛋白和猪流行性腹泻病毒S蛋白免疫原性的影响 [J]. 中国农学通报, 2020, 36(30):143−150. DOI: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb20191000740 HAN T T, LI L, TANG Q H, et al. Different adjuvants: Effects on S protein immunogenicity of porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus and porcine epidemic diarrhea virus [J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2020, 36(30): 143−150. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb20191000740
[22] 伊立超. PEDV和TGEV受体结合区基因在昆虫杆状病毒系统的表达与免疫原性分析[D]. 延吉: 延边大学, 2022. YI L C. Expression and immunogenicity analysis of PEDV and TGEV receptor binding region genes in insect baculovirus system[D]. Yanji: Yanbian University, 2022. (in Chinese)
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 戴惠新,吴金洋,张梦樵,张湘菊,吴丽娜. 喷涂机器人用改性聚天门冬氨酸酯腻子制备及性能测试. 粘接. 2024(12): 42-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载: