Expression and Distribution of Melatonin Receptor Mel 1a in Tissues of Wanxi White Geese
-
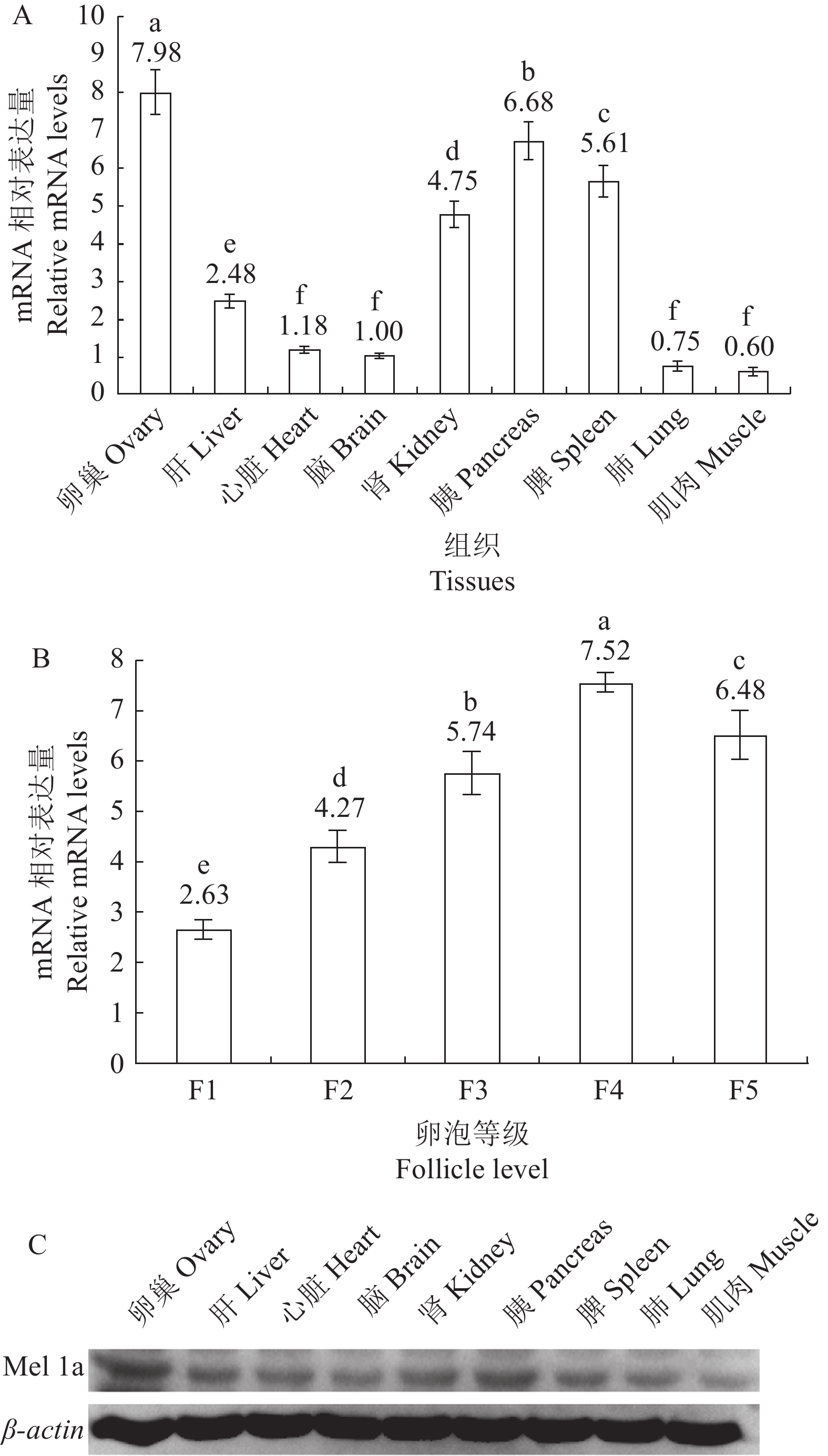
摘要:目的 探究褪黑素受体Mel 1a在皖西白鹅各组织中的分布特点和表达水平,为褪黑素在皖西白鹅的功能调控奠定理论基础。方法 以皖西白鹅作为研究对象,提取各组织器官的总RNA,采用Real- time PCR 和Western blot检测褪黑素受体Mel 1a mRNA和蛋白在鹅组织中的分布和差异性表达,免疫组化检测褪黑素受体Mel 1a蛋白在鹅的组织中的表达。结果 在心脏、肝脏、脾脏、肺脏、肾脏、胰脏、大脑、小脑、肌肉、卵巢各组织中均存在Mel 1a mRNA表达; Mel 1a蛋白广泛分布于大脑、心脏、肾脏、肝脏、肺脏、脾脏、胰脏和肌肉组织细胞中,利用Image-pro plus 6软件分析免疫组化阳性信号的IOD值显示,脾脏阳性信号最强,其次是胰腺。脾脏显著强于大脑,肺脏中的信号显著强于心脏和肌肉组织。采用Real time PCR和Western blot技术检测各组织中Mel 1a mRNA和蛋白表达水平,结果表明,卵巢中表达水平最高,其次是胰腺、脾脏、肾脏、肝脏、心脏和脑组织中,肺脏和肌肉中的表达水平最低,另外在各级卵泡中Mel 1a mRNA的表达水平随卵泡发育逐渐增加,直到卵泡发育到直径超过3 cm后,其表达量下降。结论 皖西白鹅各组织中均存在褪黑素受体,其中在卵巢中表达最高,褪黑素可通过受体介导调控皖西白鹅多种生物功能,尤其是对皖西白鹅卵泡发育的调控。Abstract:Objective Expression and distribution of Mel 1a in various organs of Wanxi White Geese were studied to reveal the regulatory mechanism of melatonin in the animal.Method Mel 1a mRNA and proteins from various tissues and organs of Wanxi White Goose were extracted for real-time PCR and western blot to determine the distribution and differential expressions.Result Mel 1a protein was widely distributed in the brain, heart, kidney, liver, lung, spleen, pancreas, and muscle cells of the geese. The IOD analysis of immunohistochemically positive signals using Image-pro plus 6 showed that the spleen had the strongest signal, followed by the pancreas. The signal from the spleen was significantly stronger than the brain, and the signal from the lungs was significantly stronger than the heart and muscles.The expression levels of Mel 1 a mRNA and protein in various organs ranked in the order of ovary, pancreas, spleen, kidney, dry, heart, brain, lungs, and muscles. And they increased gradually along with the development of follicles and decreased after the follicle diameter exceeded 3 cm.Conclusion Melatonin receptors exist in all tissues of western Anhui white geese, with the highest expression in the ovary. Melatonin can mediate the regulation of various biological functions through the receptor, especially the regulation of follicular development in western Anhui white geese.
-
Keywords:
- Melatonin receptor /
- Mel 1a /
- Wanxi white goose /
- expression /
- distribution
-
-
图 3 Mel 1a mRNA和蛋白在鹅各组织中的定量表达
A:各组织Real-time PCR分析结果;B:各级卵泡Real-time PCR分析结果;C:Western blot分析结果。
Figure 3. Quantitative expressions of Mel 1a mRNA and protein in goose tissues
A: Real-time PCR analysis results on each tissue; B: Real-time PCR analysis results on follicles ; C: Western blot analysis result.
表 1 试验引物
Table 1 Primers applied
基因
Genes序列
Sequence引物长度
Product
size/
bp退火温度
Annealing
temperature/
℃Mel 1a 5′AATTGCAGACTTGGTCGTAGC3′ 114 63 5′CCCATCAAGAATCCACTAATCTGAC3′ GAPDH 5′GTGGTGCAAGAGGCATTGCTGAC3′ 86 60 5′GCTGATGCTCCCATGTTCGTGAT3′ 表 2 荧光定量PCR反应程序
Table 2 Reaction program of real-time PCR
反应步骤
Program温度
Temperature/℃时间
Time/s循环次数
Cycles荧光信号
Fluorescence Measure预孵育 Pre-incubation 95 30 1 无 No 95 5 扩增 Amplify 63 20 45 在延伸阶段结束时 At the end of the extension phase 72 20 熔解曲线 Melting Curve 60 25 1 在温度缓慢升高过程中 During a slow rise in temperature 冷却 Cooling 40 10 1 无 No -
[1] REITER R J, SHARMA R. Central and peripheral actions of melatonin on reproduction in seasonal and continuous breeding mammals [J]. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2021, 300: 113620. DOI: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2020.113620
[2] NILES L P, WANG J X, SHEN L, et al. Melatonin receptor mRNA expression in human granulosa cells [J]. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 1999, 156(1/2): 107−110.
[3] AN P, WAN S T, LUO Y T, et al. Micronutrient supplementation to reduce cardiovascular risk [J]. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 2022, 80(24): 2269−2285. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2022.09.048
[4] WANG S J, LIU W J, WU C J, et al. Melatonin suppresses apoptosis and stimulates progesterone production by bovine granulosa cells via its receptors (MT1 and MT2) [J]. Theriogenology, 2012, 78(7): 1517−1526. DOI: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2012.06.019
[5] LEE C J, DO B R, LEE Y H, et al. Ovarian expression of melatonin Mel(1a) receptor mRNA during mouse development [J]. Molecular Reproduction and Development, 2001, 59(2): 126−132. DOI: 10.1002/mrd.1015
[6] LU J N, LUO Y J, MEI S H, et al. The effect of melatonin modulation of non-coding RNAs on central nervous system disorders: An updated review [J]. Current Neuropharmacology, 2021, 19(1): 3−23.
[7] AYRE E A, WANG Z P, BROWN G M, et al. Localization and characterization of[125I]iodomelatonin binding sites in duck gonads [J]. Journal of Pineal Research, 1994, 17(1): 39−47. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.1994.tb00112.x
[8] POON A M, CHOW P H, MAK A S, et al. Autoradiographic localization of 2[125I]iodomelatonin binding sites in the gastrointestinal tract of mammals including humans and birds [J]. Journal of Pineal Research, 1997, 23(1): 5−14. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.1997.tb00328.x
[9] POZO D, DELGADO M, FERNANDEZ-SANTOS J M, et al. Expression of the Mel1a-melatonin receptor mRNA in T and B subsets of lymphocytes from rat thymus and spleen [J]. FASEB Journal, 1997, 11(6): 466−473. DOI: 10.1096/fasebj.11.6.9194527
[10] SONG Y, PANG C S, AYRE E A, et al. Melatonin receptors in the chicken kidney are up-regulated by pinealectomy and linked to adenylate cyclase [J]. European Journal of Endocrinology, 1996, 135(1): 128−133. DOI: 10.1530/eje.0.1350128
[11] 王淑娟, 刘文举, 闻爱友, 等. 鹅褪黑素受体Mel1c基因的组织表达特征 [J]. 浙江农业学报, 2018, 30(9):1454−1459. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2018.09.02 WANG S J, LIU W J, WEN A Y, et al. Expression of Mel1c mRNA in various tissues of goose [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2018, 30(9): 1454−1459.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2018.09.02
[12] 王淑娟, 刘文举, 刘晓丽, 等. 褪黑素受体Mel1a在鸭不同组织中的表达研究 [J]. 浙江农业学报, 2016, 28(6):928−934. WANG S J, LIU W J, LIU X L, et al. Study on expression of melatonin receptor Mel1a in several duck tissues [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2016, 28(6): 928−934.(in Chinese)
[13] 刘文举, 王淑娟, 刘晓丽, 等. 褪黑素受体 Mel 1 b 基因mRNA和蛋白在鸭不同组织中的表达与分布 [J]. 浙江农业学报, 2018, 30(5):711−716. LIU W J, WANG S J, LIU X L, et al. Expression and distribution of Mel 1b mRNA and protein in various tissues of duck [J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2018, 30(5): 711−716.(in Chinese)
[14] SUNDARESAN N R, MARCUS LEO M D, SUBRAMANI J, et al. Expression analysis of melatonin receptor subtypes in the ovary of domestic chicken [J]. Veterinary Research Communications, 2009, 33(1): 49−56. DOI: 10.1007/s11259-008-9071-9
[15] HE H, JIANG D M, KANG B, et al. Gene expression profiling of melatonin receptor subtypes in the ovarian hierarchical follicles of the Sichuan white goose [J]. Animal Reproduction Science, 2014, 145(1/2): 62−68.
[16] HARDELAND R, CARDINALI D P, SRINIVASAN V, et al. Melatonin—a pleiotropic, orchestrating regulator molecule [J]. Progress in Neurobiology, 2011, 93(3): 350−384. DOI: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2010.12.004
[17] SALLINEN P, SAARELA S, ILVES M, et al. The expression of MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptor mRNA in several rat tissues [J]. Life Sciences, 2005, 76(10): 1123−1134. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2004.08.016
[18] NATESAN A K, CASSONE V M. Melatonin receptor mRNA localization and rhythmicity in the retina of the domestic chick, Gallus domesticus [J]. Visual Neuroscience, 2002, 19(3): 265−274. DOI: 10.1017/S0952523802192042
[19] EBISAWA T, KARNE S, LERNER M R, et al. Expression cloning of a high-affinity melatonin receptor from Xenopus dermal melanophores [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1994, 91(13): 6133−6137. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.6133
[20] WIECHMANN A F, SMITH A R. Melatonin receptor RNA is expressed in photoreceptors and displays a diurnal rhythm in Xenopus retina [J]. Molecular Brain Research, 2001, 91(1/2): 104−111.
[21] SAUZET S, BESSEAU L, HERRERA PEREZ P, et al. Cloning and retinal expression of melatonin receptors in the European Sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax [J]. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2008, 157(2): 186−195. DOI: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2008.04.008
[22] IKEGAMI T, MOTOHASHI E, DOI H, et al. Synchronized diurnal and circadian expressions of four subtypes of melatonin receptor genes in the diencephalon of a puffer fish with lunar-related spawning cycles [J]. Neuroscience Letters, 2009, 462(1): 58−63. DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.06.076
[23] CONFENTE F, RENDÓN M C, BESSEAU L, et al. Melatonin receptors in a pleuronectiform species, Solea senegalensis: Cloning, tissue expression, day-night and seasonal variations [J]. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2010, 167(2): 202−214. DOI: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2010.03.006
[24] FALCÓN J, BESSEAU L, SAUZET S, et al. Mélatonine et régulations neuroendocrines chez le Poisson [J]. Journal De La Société De Biologie, 2007, 201(1): 21−29.
[25] KULCZYKOWSKA E, KALAMARZ H, WARNE J M, et al. Day-night specific binding of 2-[125I]iodomelatonin and melatonin content in gill, small intestine and kidney of three fish species [J]. Journal of Comparative Physiology B, Biochemical, Systemic, and Environmental Physiology, 2006, 176(4): 277−285. DOI: 10.1007/s00360-005-0049-4
[26] ZHAO X M, WANG N, HAO H S, et al. Melatonin improves the fertilization capacity and developmental ability of bovine oocytes by regulating cytoplasmic maturation events [J]. Journal of Pineal Research, 2018, 64(1): 10.
[27] AN Q L, PENG W, CHENG Y Y, et al. Melatonin supplementation during in vitro maturation of oocyte enhances subsequent development of bovine cloned embryos [J]. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 2019, 234(10): 17370−17381. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.28357
[28] MASANA M I, SOARES J M Jr, DUBOCOVICH M L. 17Beta-estradiol modulates hMT1 melatonin receptor function [J]. Neuroendocrinology, 2005, 81(2): 87−95. DOI: 10.1159/000084897
[29] ZHANG W L, ZHANG Z L, PENG J, et al. Effects of melatonin on the production of GnRH and LH in luteal cells of pregnant sows [J]. Journal of Molecular Endocrinology, 2022, 68(2): 111−123. DOI: 10.1530/JME-21-0155




 下载:
下载: