Physiological and Biochemical Properties of Agaricus bisporus in Shaking Flask Culture
-
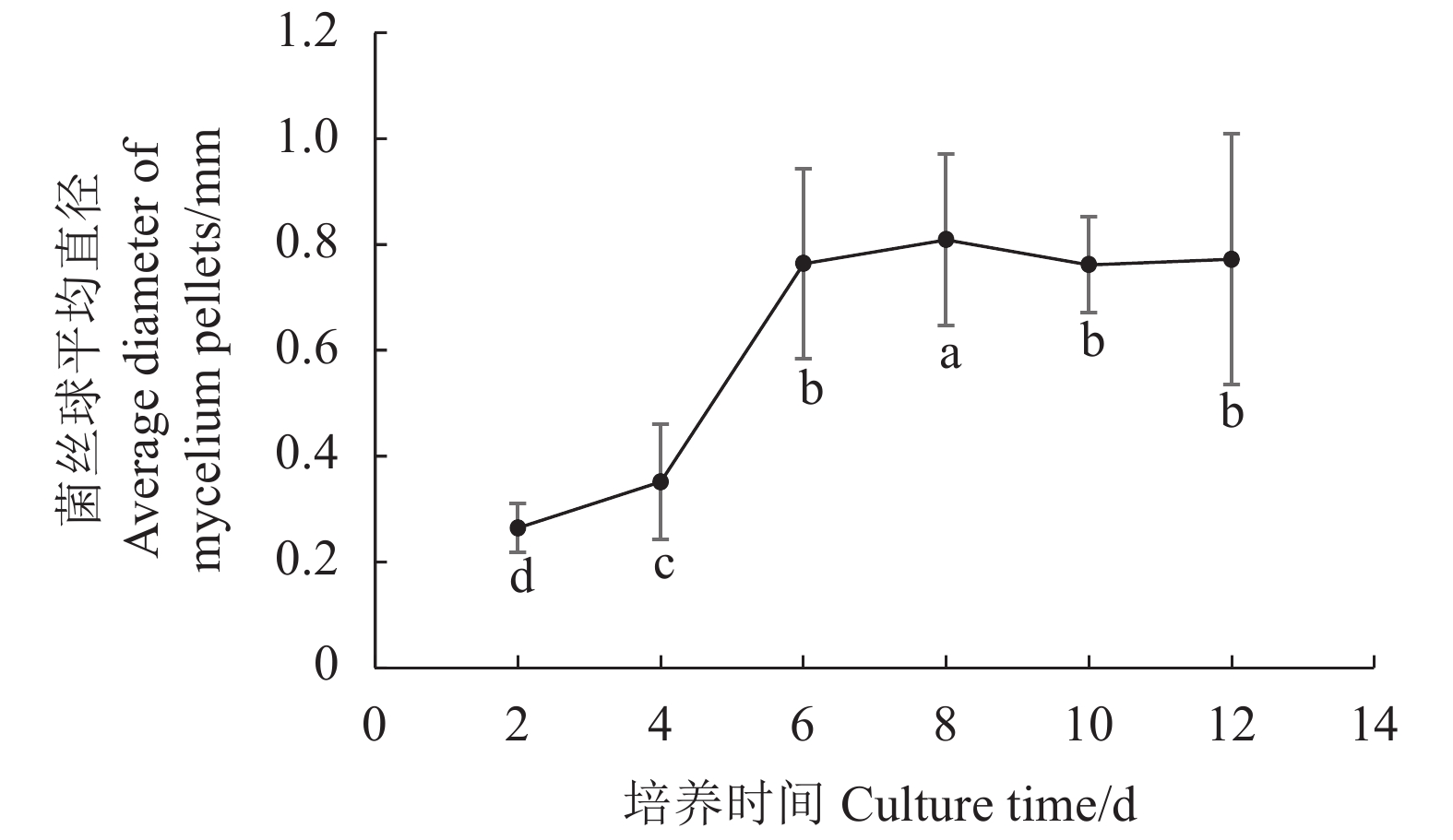
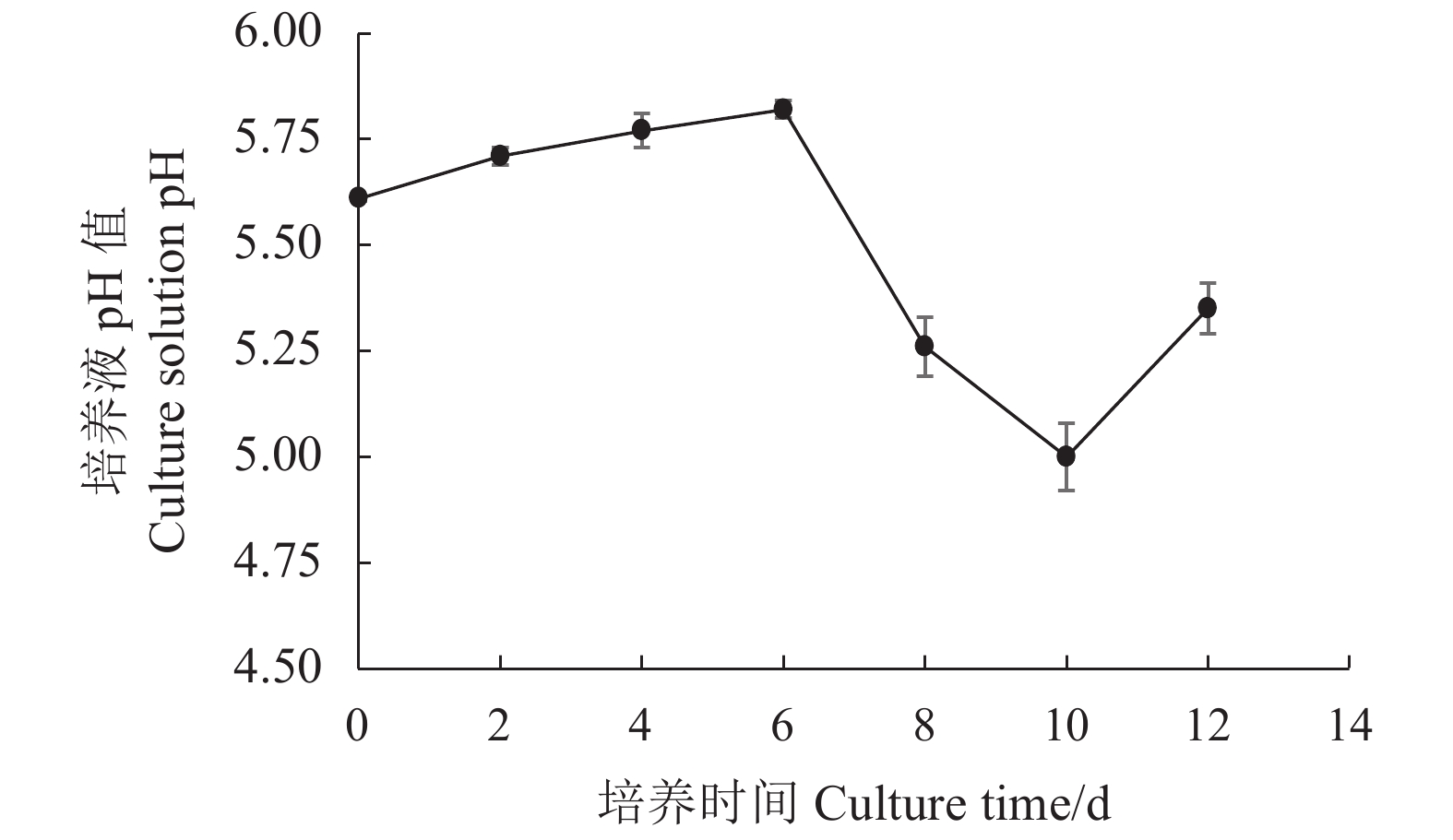
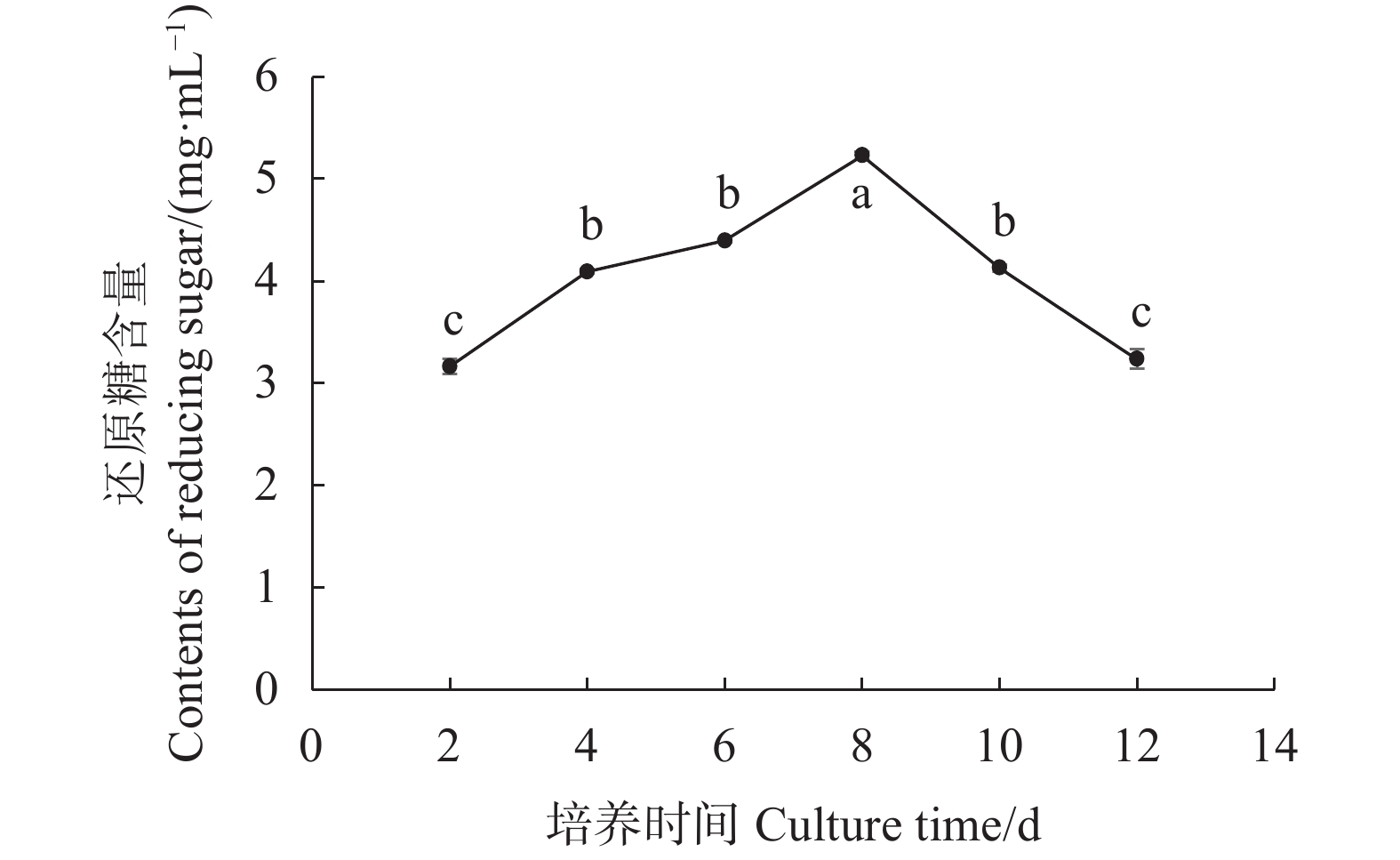
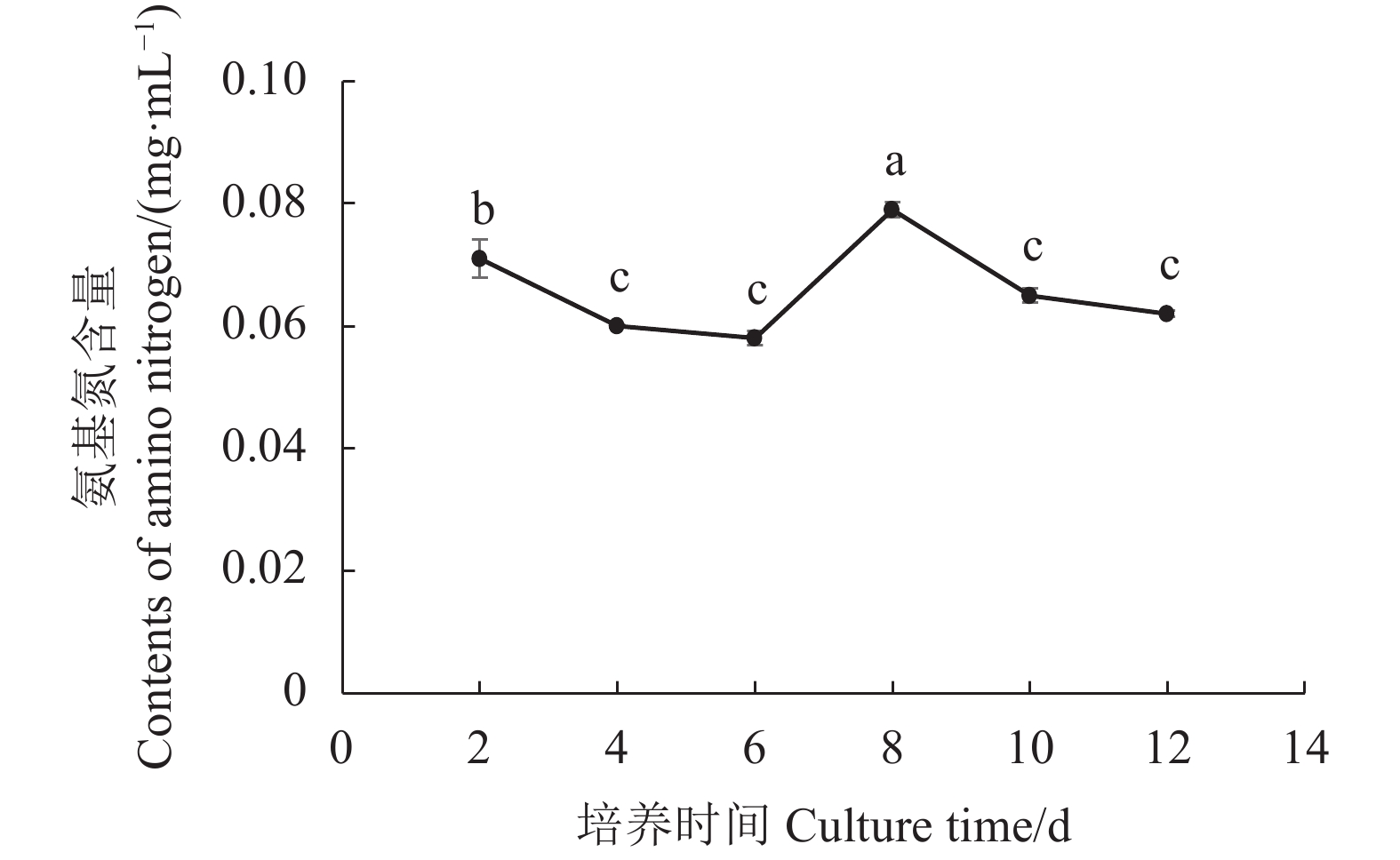
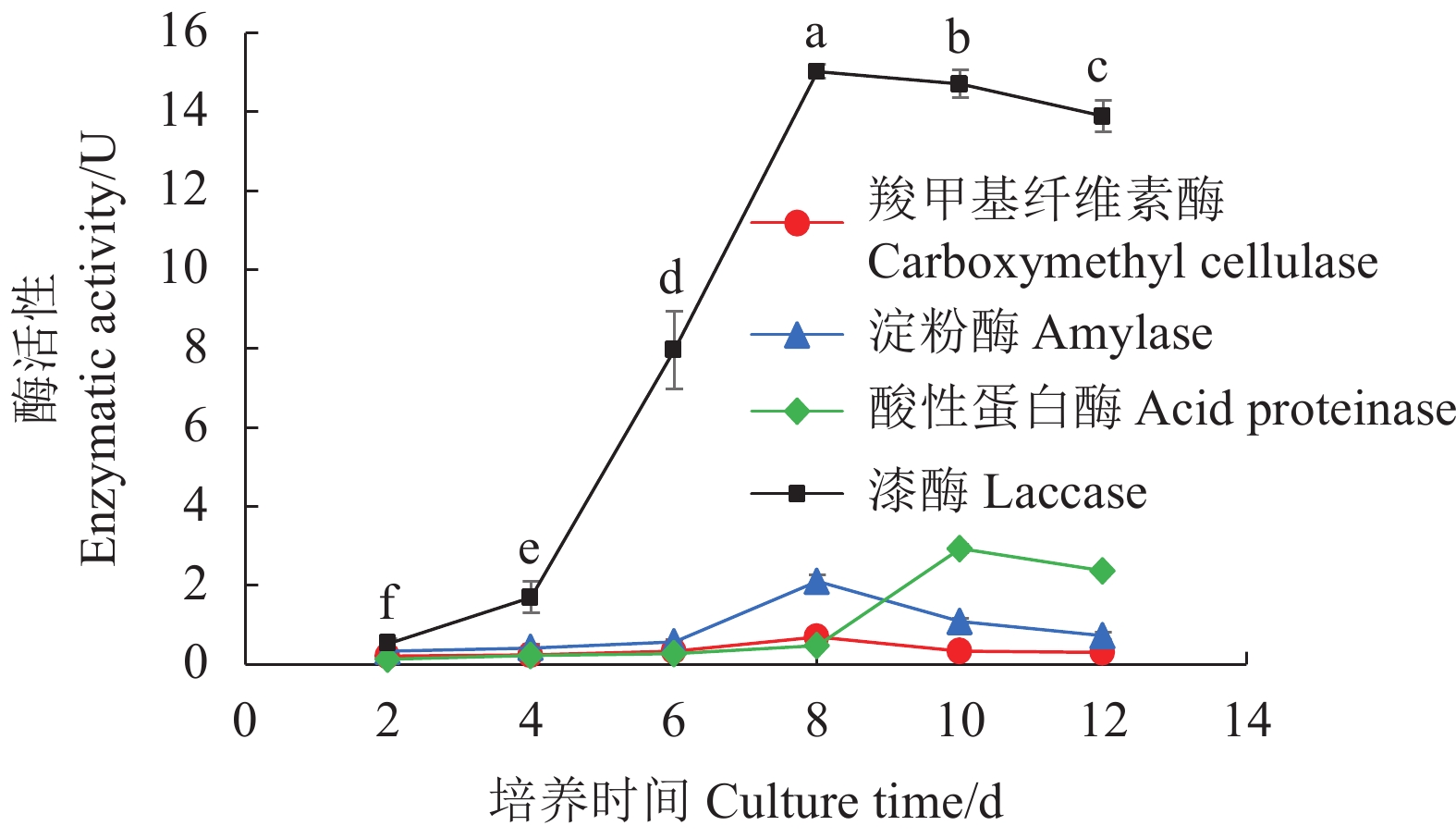
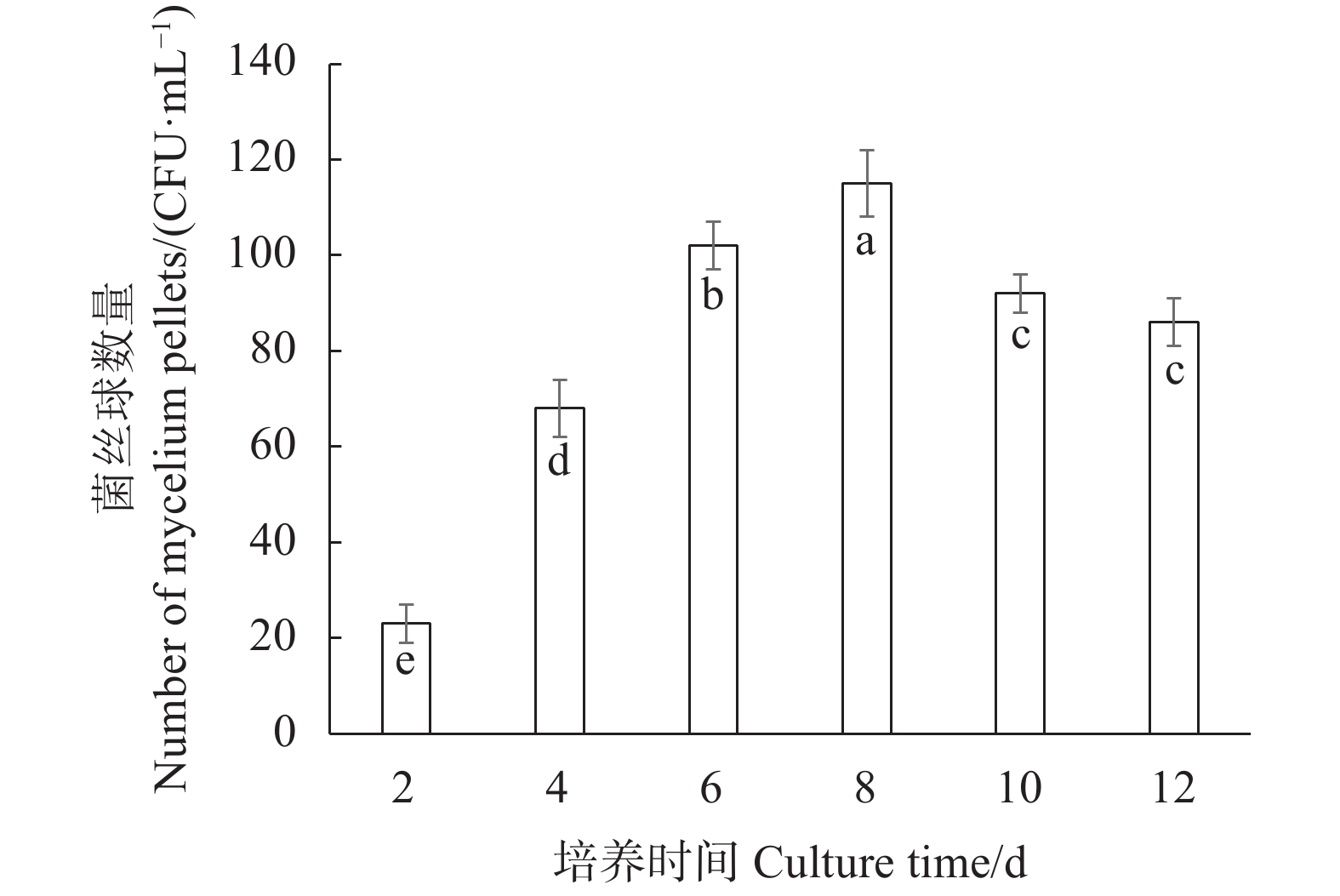
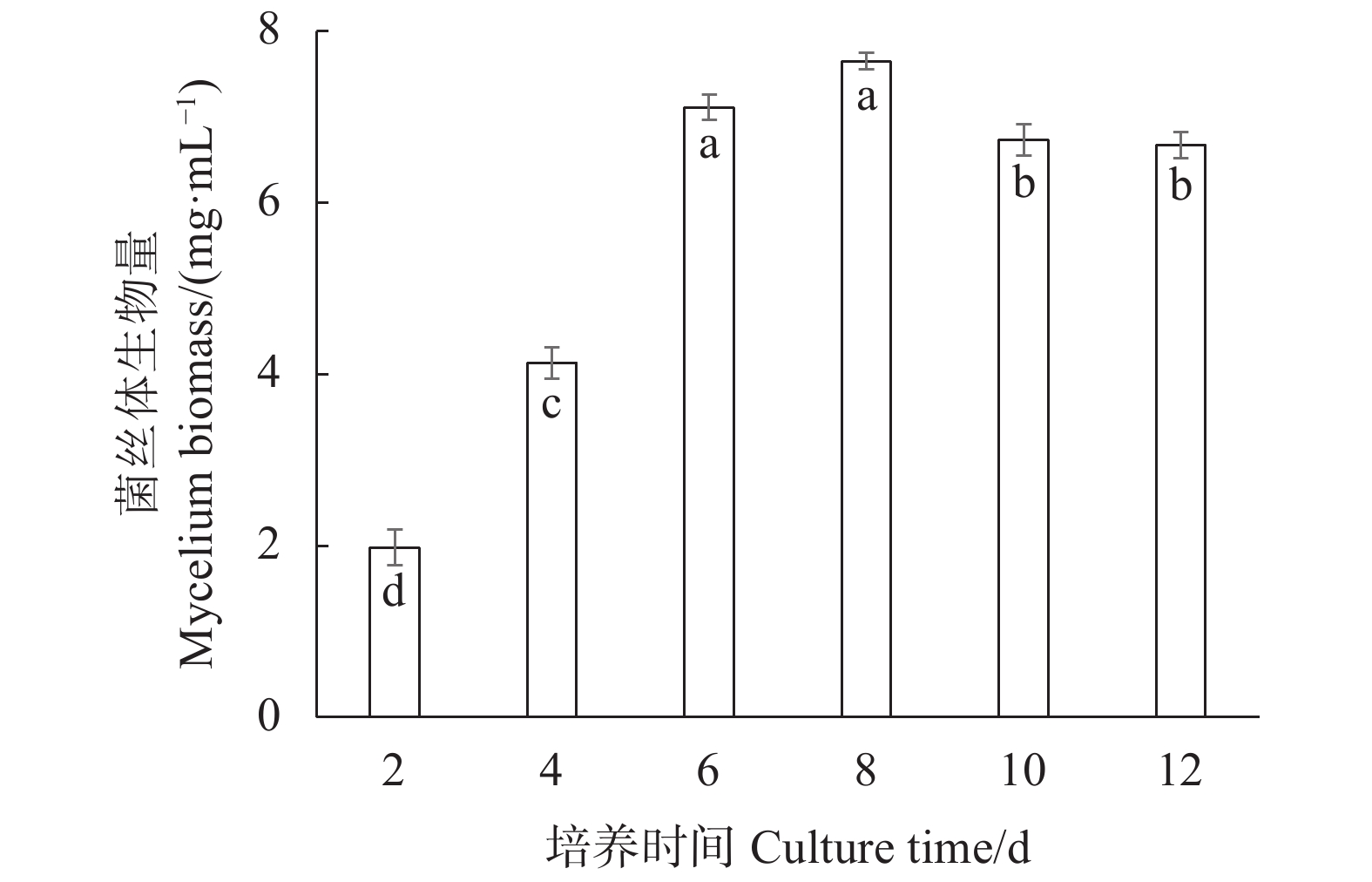
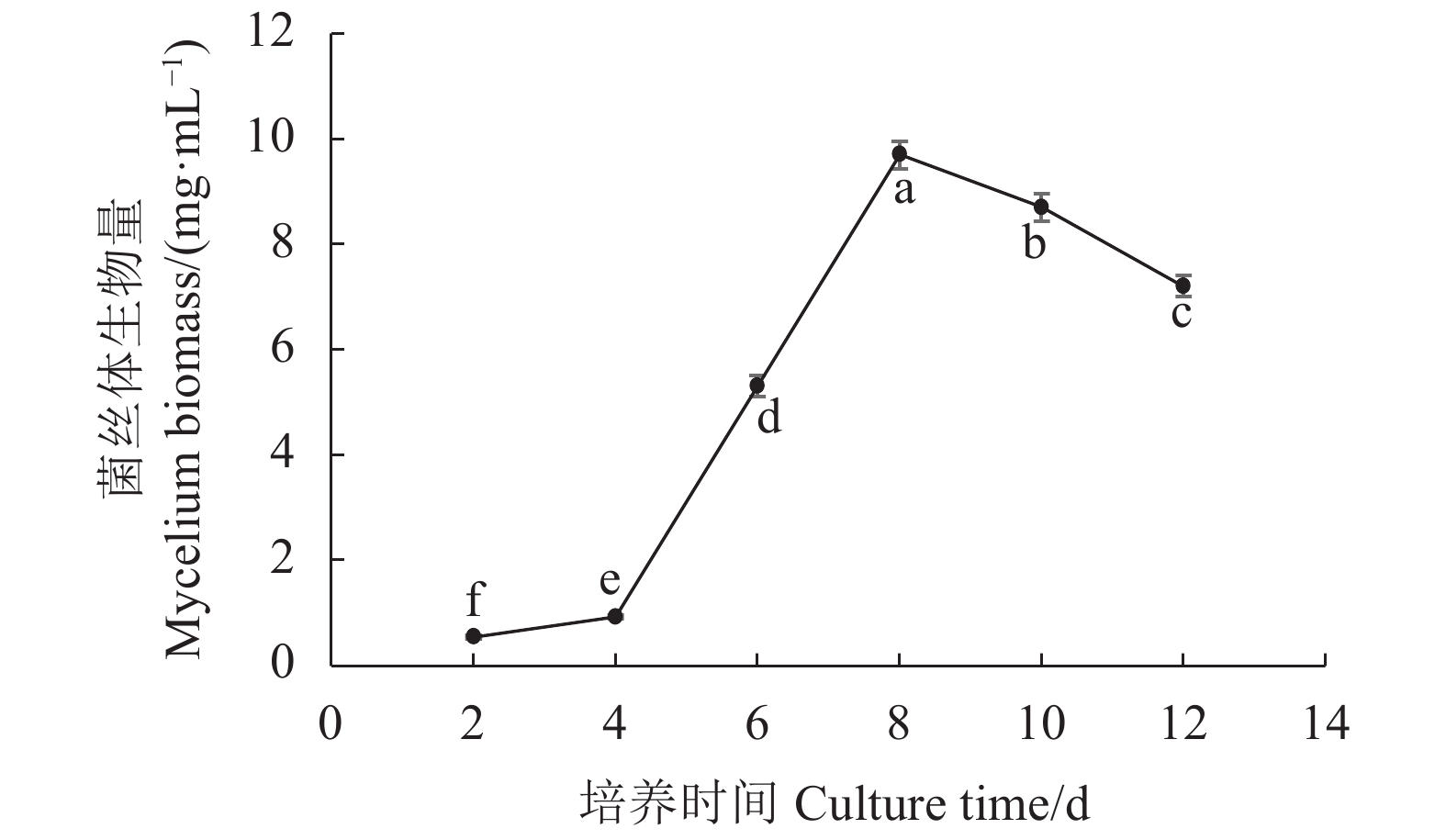
摘要:目的 研究双孢蘑菇W192液体菌种摇瓶培养菌丝体生长规律,为液体种子活力判断提供参考。方法 采用液体摇瓶培养,分别测定了液体培养过程中双孢蘑菇菌丝体生物量、菌丝球数量和直径、发酵液pH值、还原糖和氨基氮含量、羧甲基纤维素酶、淀粉酶、酸性蛋白酶、漆酶胞外酶活性生理生化指标。结果 摇瓶培养第8 d时,双孢蘑菇菌丝体生物量最大,为9.7 mg·mL−1;菌丝球数量最多,为880个·mL−1;菌丝体平均直径最大,为0.809 mm;培养液中还原糖、氨基氮含量最高,分别为5.228、0.079 mg·mL−1;羧甲基纤维素酶、淀粉酶、漆酶酶活性最高,分别为0.69 、2.11 、15.02 U。摇瓶培养第10 d时,酸性蛋白酶活性最高,酶活性为2.93 U。将摇瓶培养8 d的液体种子转接液体培养基中进行模拟发酵罐液体菌种培养,获得的菌丝球数量最多,达115个·mL−1,菌丝体生物量最大,达7.56 mg·mL−1。结论 双孢蘑菇液体菌种活性与上述指标具有一定的相关性,结合液体种子活力验证,判断第8 d的液体菌种活力最高,可作为液体种子用于发酵罐扩繁培养。Abstract:Objective Mycelial growth of Agaricus bisporus W192 in a shaking flask was monitored to determine viability of the culture method for scale-up application.Method Physiological and biochemical properties of A. bisporus mycelia biomass in the liquid culture including the number and diameter of mycelium pellets, pH of fermentation broth, content of reducing sugar and amino nitrogen as well as the activity of extracellular carboxymethyl cellulase, amylase, acid protease, and laccase were monitored for the analysis.Result On the 8th day of culture, the fungal biomass reached a maximum at 9.7 mg·ml−1, the greatest number of mycelium pellets of 880 CFU·mL−1, the largest average diameter of mycelium at 0.809 mm, the peak reducing sugar and amino nitrogen contents at 5.228 and 0.079 mg·ml−1, respectively, and the highest activities of carboxymethyl cellulase, amylase, and laccase of 0.69 , 2.11 , and 15.02 U, respectively. The acid protease activity of 2.93U maxed on the 10th day. By transferring the mycelia in a simulated liquid fermentation tank after 8d of culture, 115 CFU·mL−1 of mycelium pellets and 7.56mg·mL−1 in biomass were obtained.Conclusion The mycelial growth of A. bisporus in the liquid shaking flask culture correlated with some of selected physiological and biochemical indices. The established method was deemed applicable for tank fermentation in propagating A. bisporus for large scale production of the mushroom.
-
-
-
[1] 王贺祥. 食用菌栽培学[M]. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2008: 300-304. [2] 王泽生, 廖剑华, 陈美元, 等. 我国双孢蘑菇育种研究与产业发展 [J]. 食用菌学报, 2010(SI):19−20. WANG Z S, LIAO J H, CHEN M Y, et al. Research of Agaricusbisporus breeding and industrial development in China [J]. Acta Edulis Fungi, 2010(SI): 19−20.(in Chinese)
[3] 张鹏, 许占伍, 倪小军, 等. 金针菇工厂化生产液体菌种培养基的配方研究 [J]. 食药用菌, 2012, 20(5):296−297. ZHANG P, XU Z W, NI X J, et al. Study on the formula of liquid culture medium for the industrial production of Flammulina velutipes [J]. Edible and Medicinal Mushrooms, 2012, 20(5): 296−297.(in Chinese)
[4] 沈敏, 李文生, 周雷. 杏鲍菇液体菌种研制与工厂化栽培应用 [J]. 中国农技推广, 2011, 27(6):14−15. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-381X.2011.06.006 SHEN M, LI W S, ZHOU L. Development and application of liquid spawn of Pleurotus edodes [J]. China Agricultural Technology Extension, 2011, 27(6): 14−15.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-381X.2011.06.006
[5] 李武辉. 海鲜菇工厂化生产工艺优化[D]. 太原: 山西农业大学, 2017. LI W H. Optimization of the industrial production process of Hypsizygusmarmoreus[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi Agriculture University, 2017. (in Chinese)
[6] 戴建清, 曾志恒. 食用菌液体菌种研究现状及发展趋势 [J]. 中国食用菌, 2012, 31(5):1−3. DAI J Q, ZENG Z H. Research status and development trends of liquid spawn of edible mushroom [J]. Edible Fungi of China, 2012, 31(5): 1−3.(in Chinese)
[7] HUMFELD H. The production of mushroom mycelium (Agaricus campestris) in submerged culture [J]. Science, 1948, 107(2780): 373. DOI: 10.1126/science.107.2780.373
[8] DIJKSTRA F I, SCHEFFERS W A, WIKÉN T O. Submerged growth of the cultivated mushroom, Agaricus bisporus [J]. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 1972, 38(1): 329−340. DOI: 10.1007/BF02328102
[9] 胡贵权. 双孢蘑菇液体菌种培养基配方试验 [J]. 食用菌, 1999, 21(6):13. HU G Q. Experiment on the medium formula of liquid spawn of Agaricus bisporus [J]. Edible Fungi, 1999, 21(6): 13.(in Chinese)
[10] 罗帷. 双孢蘑菇2796菌株液体菌种的工艺研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2006. LUO W. Studies on the technics of liquid spawn of Agaricus bisporus strain 2796[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2006. (in Chinese)
[11] 黄爱荣, 缪礼鸿, 边银丙. 双孢蘑菇液体菌种发酵工艺研究 [J]. 食用菌, 2009, 31(5):12−13. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8357.2009.05.006 HUANG A R, MIAO L H, BIAN Y B. Bian Y B Study on fermentation technology of liquid spawn of Agaricus bisporus [J]. Edible Fungi, 2009, 31(5): 12−13.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8357.2009.05.006
[12] 马忠友, 周盘龙, 祝嫦巍, 等. 双孢蘑菇液体菌种培养基的优化 [J]. 安徽科技学院学报, 2012, 26(2):23−27. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8772.2012.02.007 MA Z Y, ZHOU P L, ZHU C W, et al. Optimization of media for Agaricus bisporus in liquid culture [J]. Journal of Anhui Science and Technology University, 2012, 26(2): 23−27.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8772.2012.02.007
[13] 曾志恒, 程翊, 曾辉, 等. 双孢蘑菇W192菌株液体发酵培养的研究 [J]. 福建农业学报, 2013, 28(8):763−769. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2013.08.008 ZENG Z H, CHENG Y, ZENG H, et al. Study on fermentation of Agaricus bisporus strain W192 [J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 28(8): 763−769.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2013.08.008
[14] 曾志恒, 曾辉, 程翊, 等. 双孢蘑菇发酵液还原糖和总糖的含量测定 [J]. 中国食用菌, 2018, 37(6):40−43, 49. ZENG Z H, ZENG H, CHENG Y, et al. Determination of reducing sugar and total sugar content in fermentation liquid of Agaricus bisporus [J]. Edible Fungi of China, 2018, 37(6): 40−43, 49.(in Chinese)
[15] 曾志恒, 曾辉, 程翊, 等. 双孢蘑菇发酵液氨基氮含量测定方法的研究 [J]. 食用菌, 2019, 41(5):77−80. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8357.2019.05.026 ZENG Z H, ZENG H, CHENG Y, et al. Study on determination of amino nitrogen content in in fermentation liquid of Agaricus bisporus [J]. Edible Fungi, 2019, 41(5): 77−80.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8357.2019.05.026
[16] 王玉万, 王云. 构菌栽培过程中对木质纤维素的降解和几种多糖分解酶活性的变化 [J]. 微生物学通报, 1989, 16(3):137−140, 187. WANG Y W, WANG Y. Degradation of lignocellulose and changes in the activities of several polysaccharide decomposing enzymes of Flammulina velutipes during the cultivation process [J]. Microbiology, 1989, 16(3): 137−140, 187.(in Chinese)
[17] 韩增华, 张丕奇, 孔祥辉, 等. 黑木耳胞外酶活变化与栽培性状比较的研究 [J]. 食用菌学报, 2007, 14(4):41−46. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9873.2007.04.007 HAN Z H, ZHANG P Q, KONG X H, et al. Extracellular enzyme activities, mycelial growth rates and fruit body yields of ten Auricularia auricula strains [J]. Acta Edulis Fungi, 2007, 14(4): 41−46.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9873.2007.04.007
[18] 宋爱荣, 韩立忠, 刘作亭, 等. 七个白色金针菇菌株发酵液中四种胞外酶活性的测定与分析 [J]. 中国食用菌, 1998, 18(4):31−34. SONG A R, HAN L Z, Liu Z T, et al. Test and analysis of four kinds of extracellular enzyme activation in fermented liquid of seven white Flammulina velutiper strains [J]. Edible Fungi of China, 1998, 18(4): 31−34.(in Chinese)
[19] 秦俊哲, 魏颖杰, 陈合, 等. 金针菇液体菌种培养过程检测指标的研究 [J]. 食用菌学报, 2003, 10(1):12−16. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9873.2003.01.003 QIN J Z, WEI Y J, CHEN H, et al. A study on the detection indexes of Flammulina velutipes liquid strains during the culture process [J]. Acta Edulis Fungi, 2003, 10(1): 12−16.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9873.2003.01.003
[20] 孙建华, 宇克莉, 路福平, 等. 丝状真菌Sr18发酵过程中的形态学研究 [J]. 天津科技大学学报, 2005, 20(4):1−5. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6510.2005.04.001 SUN J H, YU K L, LU F P, et al. Study on the morphology of filamentous fungus Sr18 in submerged fermentation [J]. Journal of Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2005, 20(4): 1−5.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6510.2005.04.001




 下载:
下载: