Alkaloids in Tobaccos of Different Aromatic Characteristics
-
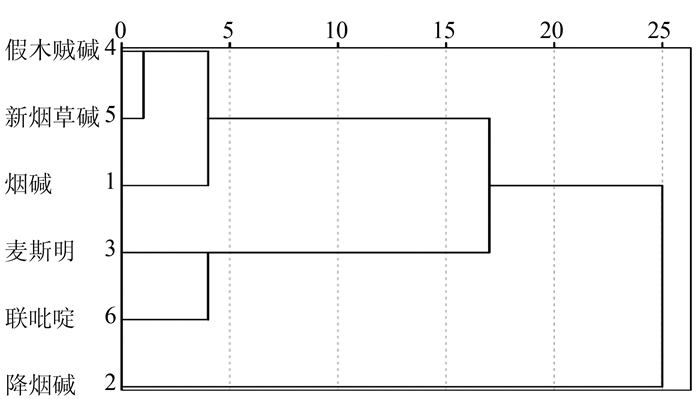
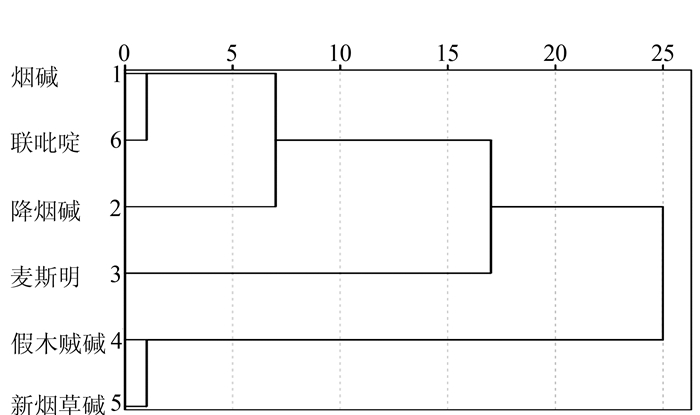
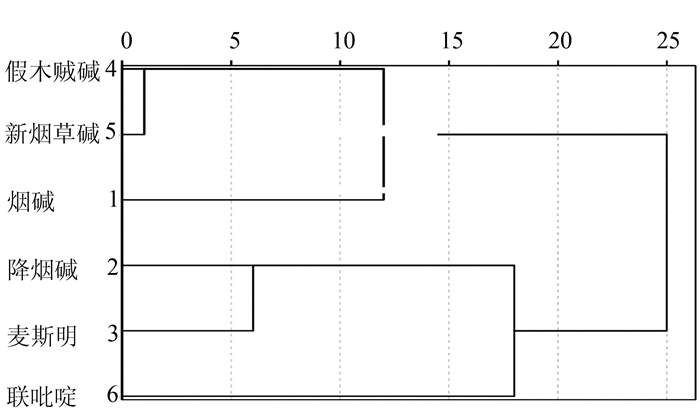
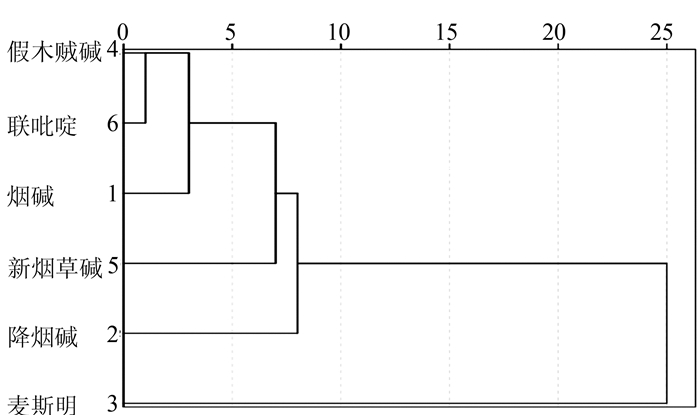
摘要: 为研究不同香型烟叶中生物碱的差异规律,运用经典的抽样方法,从国内15个省份中的71个市和县收集2011-2013年间3类香型烤烟烟叶共543个样本。根据现行相关的行业标准文献方法进行定量检测,并采用F-假设检验、Q-型聚类分析和判别分析等数理统计手段研究了不同香型烟叶中生物碱含量的差异规律。结果表明:2011年和2012年度3种香型烟叶中新烟草碱和2,3'-联吡啶含量差异水平较为相似,可以用来区分不同香型烟叶;烟叶中假木贼碱是2013年度不同香型的特征物质,可以用来区分清香和浓香型烟叶。不同年度3种香型中6种生物碱物质的含量均可以聚成3类;采用烟碱、降烟碱、麦斯明、假木贼碱、新烟草碱和2,3'-联吡啶等较少数的成分指标的含量来对3类香型烟叶样本进行模式识别和判定,回判及预测正确率分别为55.7%~71.6%、50.0%~69.8%。Abstract: Alkaloids in tobaccos of different aromatic classifications were compared. Standard sampling method was employed to collect 543 flue-cured tobacco leaf specimens from 71 cities/counties in 15 provinces in China during 2011 and 2013. The samples were analyzed using the current industry methods, F-hypothesis testing, Q-clustering and discriminant analyses, as well as statistic methodology. The results showed that, between 2011 and 2012, the differences on the contents of and 2, 3'-bipyridyl in the 3 categories of tobaccos were similar, and could be used for differentiating the varieties; while anabaseine found in 2013 was a characteristic substance that could be used to distinguish between the lightly and the strongly aromatic types of tobaccos. In those years, the 6 alkaloid compounds tested in the 3 categories of tobaccos could be clustered into 3 groups. By using the contents of nicotine, reduced nicotine, Mai Siming, anabaseine, , and 2, 3'-bipyridine as indicators, the 3 aromatically different classifications of tobaccos could be identified with a discrimination rate of 55.7-71.6% and an accuracy of 50.0-69.8%.
-
Keywords:
- cigarettes /
- alkaloids /
- pattern of differences /
- discriminant analysis /
- Q-clustering analysis
-
0. 引言
【研究意义】稻瘟病是水稻最主要病害之一,每年可造成水稻10%~30%减产,严重年份部分稻区甚至出现绝收[1-2]。因此,稻瘟病防治一直是水稻生产和育种的重中之重。长期实践证明,培育和种植抗病水稻品种是防治稻瘟病最经济、安全和有效的措施,而发掘和鉴定稻瘟病抗性基因对于开展水稻抗病育种具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】截至目前,全世界已鉴定了100多个稻瘟病抗性基因,至少24个基因被克隆,包括Pib、Pi-ta、Pi9、Pi2、Piz-t、Pigm、Pid2、Pi37、Pi36、Pik-m、Pi5、Pit、Pid3、Pid3-A4、Pi54、Pish、Pik-p、Pia、Pik、Pi-CO39、Pi25、Pi1、pi21和Pb1等[3-4],促进了水稻抗稻瘟病分子育种的发展。然而,一方面抗性基因表现出对稻瘟菌生理小种高度专化性,另一方面由于稻瘟菌生理小种存在易变性,抗性基因在利用数年后抗性容易丧失,因此寻找和鉴定更多新的抗性基因一直被植物病理工作者和水稻育种家重视。近年来,兴起一种快速简单的性状定位的方法——混合群体分离分析法(Bulked Segregant Analysis,BSA),其基于临时(如F1、F2分离群体)或永久群体(如重组自交系、近等基因系)表现出明显差异的个体,通过构建DNA混池进行基因定位。BSA已被应用于水稻质量性状基因[5]和数量性状基因(QTL)[6-7]的定位。【本研究切入点】谷丰B是福建省农业科学院水稻研究所选育的具有广谱、持久抗稻瘟病的优良品种,种植20多年仍表现出稳定抗性[8]。该材料为挖掘广谱持久抗性基因及研究抗性分子机制带来了契机。【拟解决的关键问题】本研究以谷丰B和日本晴分别作为稻瘟病抗病和感病亲本,配制F2代遗传群体,接种稻瘟菌并鉴定表型。依据水稻稻瘟病抗性评价分级标准,选出极端材料构建感、抗池。通过BSA测序分析,初步确定谷丰B抗性基因连锁区间。本研究旨在为谷丰B抗性基因精细定位及基因克隆奠定基础,并为分子标记辅助选择提供标记资源。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
水稻材料谷丰B、福恢838、甬优1号、圭630、福恢718、IR0462和日本晴均由福建省农业科学院生物技术研究所提供。以抗病品种谷丰B为母本和感病品种日本晴为父本,杂交获得F1和F2遗传群体。
稻瘟菌株501-3、KJ201、IR16-1、RB22、RB6、2Y838-1和CHNOS由福建省农业科学院生物技术研究所保存。
1.2 稻瘟病接种鉴定
稻瘟菌接种在燕麦(或米糠)培养基中,25 ℃暗培养5~7 d,随后刮掉表面菌丝并转移至25 ℃光照条件下培养3 d诱导孢子产生,供接种用。
接种试验在福建省农业科学院生物技术研究所寿山实验基地进行,接种方法参考Tian等[3]的方法。水稻幼苗生长至3~4叶龄时,进行人工喷雾接种。接种后接种池覆盖遮光膜密闭24 h,揭开遮光膜后保证棚内相对湿度90%以上,温度24~28 ℃,5~7 d后调查发病情况。
按照国际水稻研究所发布的稻瘟病分级标准进行病级统计[9],即:高抗——无病斑;抗——有针尖大小棕色斑点;中抗——有圆形至椭圆形灰色斑,褐色边缘,直径约1~2 mm;中感——有典型纺锤状病斑,病斑面积小于叶面积的10%;感病——有典型纺锤状病斑,病斑面积占叶面积的10.1%~50%;高感——有典型纺锤状病斑,病斑面积大于叶面积的50%,甚至全叶枯死。
1.3 谷丰B抗病性遗传分析
谷丰B和日本晴的F1和F2群体接种501-3和IR16-1菌株,并统计F2群体抗病和感病植株分离比,采用χ2测验进行分离比适合度检测。
1.4 极端分离混合池重测序
谷丰B与日本晴F2群体接种501-3菌株后,挑选极端抗病单株和极端感病单株各20株,同时取亲本谷丰B和日本晴各10株,采用CTAB方法提取基因组DNA。分别将各自单株DNA等量混合,利用二代测序技术对2个混合池和两亲本进行20×和10×覆盖度的全基因组测序,测序和数据处理由诺禾致源公司(中国)完成。
参考Liang等[10]的方法计算2个分离池的SNP频率(SNP-index),随后对2个子代SNP-index作差(△SNP-index)。对△SNP-index在各个染色体上的分布进行作图,选取95%置信水平作为筛选的阈值,确定连锁区间。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 谷丰B抗病性鉴定
利用7个稻瘟菌株501-3、KJ201、IR16-1、RB22、RB6、2Y838-1和CHNOS对谷丰B、福恢838、甬优1号、圭630、福恢718、IR0462及日本晴等材料进行人工接种。图1和表1结果显示,谷丰B对7个供试菌株均表现高抗性,福恢838、甬优1号、圭630、福恢718和IR0462水稻材料对501-3、IR16-1、RB6和2Y838-1菌株表现出不同程度的感病。上述结果初步表明,谷丰B基因组中可能携带了广谱高抗稻瘟病基因。
表 1 水稻品种稻瘟病抗性鉴定Table 1. Blast resistance of rice cultivars品种 Varieties 菌株 Strains 501-3 KJ201 IR16-1 RB22 CHNOS RB6 2Y838-1 IR0462 S MR S R MR MS S 福恢838 Fuhui838 S MR S MS R S HS 甬优1号 Yongyou1 S MR S MS R S S 圭630 Gui630 HS S HS S R HS MS 福恢718 Fuhui718 MS R MS R R S S 谷丰B Gufeng B HR HR HR HR HR HR HR 日本晴Nipponbare HS HS HS HS S S HS 注: HR: 高抗; R: 抗病; MR: 中抗; MS: 中感; S: 感病; HS: 高感
Note: HR: Highly resistant; R: Resistant; MS: Moderately resistant; MS: Moderately susceptible; S: Susceptible; HS: Highly susceptible.2.2 谷丰B对稻瘟菌501-3和IR16-1的遗传分析
利用501-3和IR16-1菌株对谷丰B和日本晴的F1和F2群体进行接种,分析谷丰B的抗性遗传模式。结果显示,F1群体对501-3和IR16-1菌株均表现高抗,F2植株出现不同程度抗病和感病。将抗病(包括中抗、抗和高抗)和感病(包括中感、感病和高感)植株的分离比按3:1理论比例进行卡方测验,其对应501-3和IR16-1的χ2值分别为33.09和27.98,均显著大于χ(0.05)2=3.84(表2),推测谷丰B基因组存在多个位点影响稻瘟病抗性。
表 2 谷丰B稻瘟病抗性遗传分析Table 2. Genetic analysis on blast resistance of Gufeng B群体
Population菌株
Strains总株数
Total number抗病株数
Number of resistant plants感病株数
Number of susceptible plants期望比
Expected rationχ2 F1(NPB×谷丰B) 501-3 30 30 0 — — IR16-1 30 30 0 — — F2(NPB×谷丰B) 501-3 407 255 152 3:1 33.09 IR16-1 430 275 155 3:1 27.98 注: NPB: 日本晴; χ2(0.05)=3.84
Note: NPB: Nipponbare; χ2 (0.05)=3.84.2.3 BSA测序和数据分析
基于上述结果,采用BSA方法对20个高感单株和20个高抗单株构建的DNA混合池以及亲本进行全基因组测序,共产生 32.66 G原始数据(Raw data)。过滤后获得32.475 G 有效数据(Clean data),各样本的Clean data在9.880~12.177 G,所有样品Q30≥91.52%,GC含量在44.3%~47.59%;通过与日本晴参考基因组比对,各样品比对率均在95.36%以上,4×覆盖度(至少有4个碱基的覆盖)在87.48%~97.69%(表3)。由此可知,各样本数据量足够,测序质量高,测序数据比对结果正常,可用于后续的变异检测及相关分析。
表 3 过滤后的数据统计表Table 3. Statistics on data after screening样本
Sample有效数据量
Clean Base/G准确度
Q30/%GC含量
GC content/%与参考基因组相同片段
Mapped reads匹配率
Mapped ratio/%覆盖度
Coverage/%谷丰 B 9.88 92.44 44.3 62,811,386 95.36 87.48 NPB ND ND ND 74,123,818 98.18 97.59 抗病池 R pool 12.177 92.44 47.26 77,601,474 95.59 97.69 感病池 S pool 10.417 91.52 47.59 66,943,380 96.39 96.94 将亲本谷丰B和日本晴测序结果比较,共筛选1 756 964个SNPs和409 345个InDels位点,数量足以覆盖到整个基因组;各染色体SNP和InDel分布密度分别在4.037~5.902 个·kb−1和0.967~1.300 个·kb−1(表4)。这些多态性位点可被进一步用于基因的定位及关联分析。
表 4 SNPs和InDels在水稻12条染色体的分布Table 4. Distribution of identified SNPs and InDelsk in 12 chromosomes of rice染色体
Chromosome染色体
长度
Chr. LengthSNPs InDels 数量
Number密度
Density /
(个·kb−1)数量
Number密度
Density/
(个·kb−1)Chr.1 43270923 190273 4.397 46279 1.070 Chr.2 35937250 184278 5.128 42618 1.186 Chr.3 36413819 172550 4.739 42505 1.167 Chr.4 35502694 161349 4.545 31762 0.895 Chr.5 29958434 127664 4.261 30080 1.004 Chr.6 31248787 137688 4.406 35460 1.135 Chr.7 29697621 151268 5.094 34762 1.171 Chr.8 28443022 123316 4.336 28761 1.011 Chr.9 23012720 92893 4.037 22257 0.967 Chr.10 23207287 136960 5.902 30171 1.300 Chr.11 29021106 153785 5.299 33329 1.148 Chr.12 27531856 124940 4.538 31361 1.139 总计Total 373245519 1756964 4.707 409345 1.097 2.4 BSA-Seq鉴定谷丰B抗性基因连锁区间
利用SNP位点分析2个混合池△SNP-index,以95%置信水平作为筛选的阈值进行全基因组扫描。结果(图2)发现,位于第6号和第11号染色体的2个区域出现了超过临界值水平的峰,推测这2个区域为稻瘟病抗性关联区域。其对应日本晴基因组上的位置为Chr.6: 10 082-111 397 kb和Chr.11: 120-266 kb,其中6号染色体的关联区域包含Pi2/9抗病位点,而11号染色体关联区域为新的稻瘟病抗性遗传位点。
为了精细定位谷丰B抗稻瘟病基因,从6号染色体的关联区间筛选出了4 006个SNPs和623个InDels标记,从11号染色体的关联区间筛选出了752个SNPs和195个InDels标记。
3. 讨论与结论
抗谱宽、抗性强且持久的抗源是挖掘抗病基因资源,研究稻瘟病抗性分子遗传机制的理想材料,如谷梅4和子预44。Deng等[11]从谷梅4中鉴定了1个广谱持久抗瘟性新位点Pigm,并系统解析了Pigm持久抗病机制;子预44是一个云南地方粳稻品种,截至目前已从该品种挖掘出抗不同稻瘟病菌株的主效基因Pi-zy(t)、Pi-zy3(t)、Pizy6(t)、Pi-zy4(t)和微效基因[12]。本研究人工接种鉴定结果表明,谷丰B基因组中可能携带了广谱高抗稻瘟病基因。通过抗性遗传分析以及利用BSA-seq方法,鉴定到2个稻瘟病抗性关联位点(分别为Chr.6: 10 082-11 397 kb和Chr.11: 120-266 kb)决定了谷丰B对501-3菌株的抗性。其中,6号染色体关联区域可能和Pi2/9基因座有关,而11号染色体关联区域可能是新的稻瘟病抗性遗传位点。
Pi2/9是公认对稻瘟病抗性育种有重要应用价值的位点,位于水稻第6染色体短臂端。截至目前,已报道该基因座上至少有9个稻瘟病抗性基因(Pi2、Piz、Piz-t、Pi9、Pi40、Pi50、Pi26、Pigm、Pi2-2),其中Pi2、Pi9、Pi50以及Pigm已被成功克隆[11,13-14]。张柱坚等[15]利用抗性基因标记鉴定谷丰B可能存在Pigm、Pi-d2和Pi-d3。结合本研究结果,表明谷丰B对501-3菌株的抗性是由Pigm决定的。但有意思的是,研究发现单独突变Pi-d2或Pigm均能够导致谷丰B丧失对501-3菌株抗性[15],说明谷丰B的稻瘟病抗性可能受多个位点共同影响。本研究发现一个新的关联区域(Chr.11: 120-266 kb区域)也可能对谷丰B抵抗501-3菌株侵染起关键作用,该区域包含25个水稻基因(数据来源于NCBI数据库https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/)。深入研究将有助于明确广谱高抗稻瘟病遗传构成及其分子机制。
广谱持久高抗的抗源常作为优良供体材料,应用于抗病分子育种。然而研究人员时常发现在选育过程中培育的新材料相比于原始供体亲本,其抗谱变窄。这种现象的根本原因在于,我们对亲本广谱高抗稻瘟病遗传构成及其内在机制缺乏了解,限制了分子标记辅助选择准确、有效的应用。本研究结果可为后续合理利用谷丰B抗病亲本培育抗病品种提供有效信息。
-
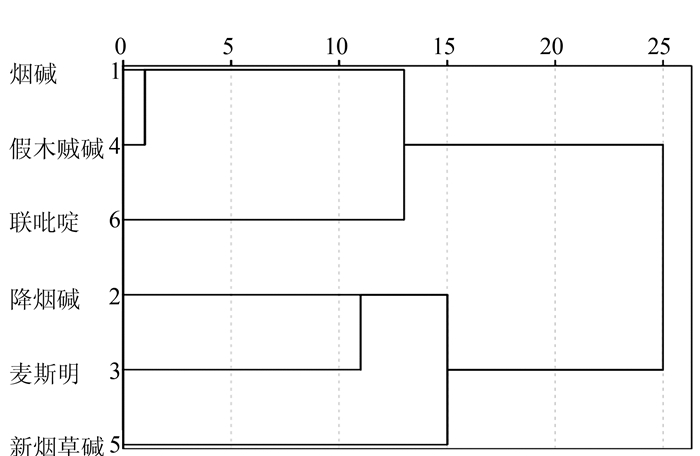
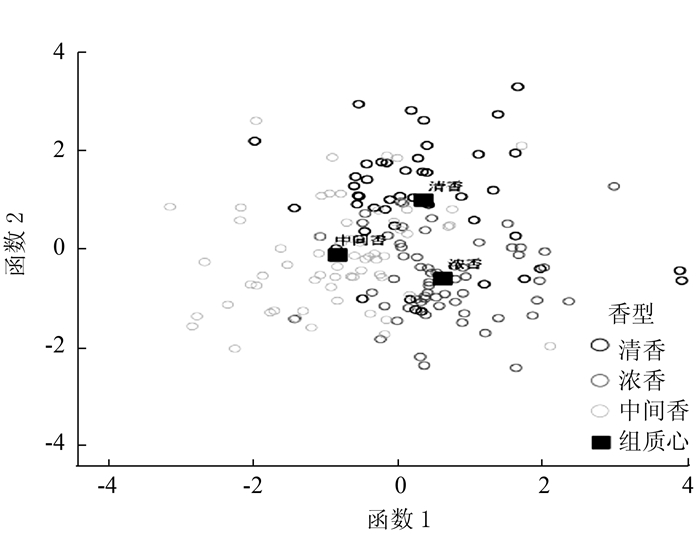
图 10 典型判别函数的双坐标投影
Figure 10. Two-coordinate projection of a typical discriminant function for Table 5
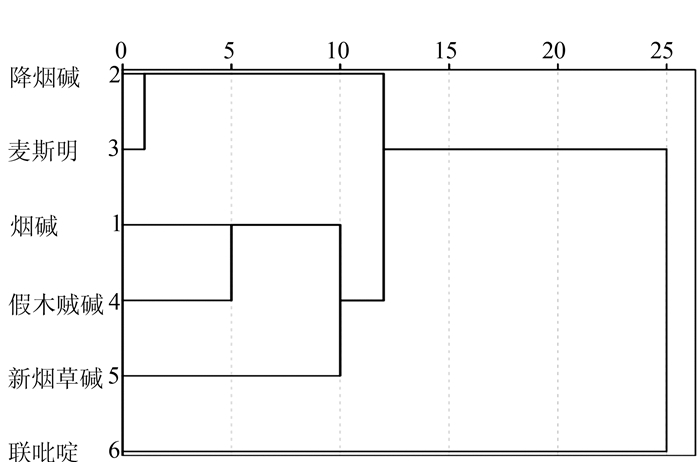
图 11 典型判别函数的双坐标投影
Figure 11. Two-coordinate projection of a typical discriminant function for Table 6
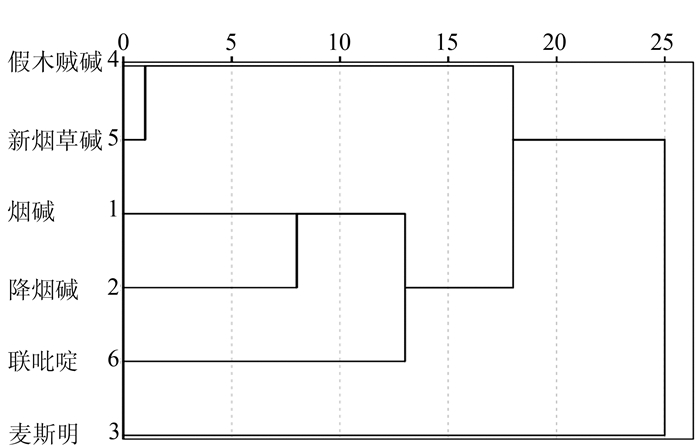
图 12 典型判别函数的双坐标投影
Figure 12. Two-coordinate projection of a typical discriminant function for Table 7
表 1 2011-2013年烤烟烟叶样品的地区数量描述
Table 1 Number of flue-cured tobacco leaf samples, 2011-2013
烟叶香型 样品数量/个 采集的省份 采样的市(县) 清香型 177 云南、福建、贵州、四川 楚雄禄丰、毕节威宁、玉溪江川、玉溪华宁、文山砚山三明宁化、、三明泰宁、曲靖陆良、黔西南兴仁、曲靖师宗、黔东南天柱、普洱宁洱、普洱墨江、攀枝花米易、龙岩永定、南平建阳、龙岩长汀、六盘水盘县、凉山会理、临沧临翔、昆明宜良、红河泸西、红河建水、大理南涧、大理祥云 中间香型 177 贵州、湖北、湖南、辽宁、陕西、重庆、山东、黑龙江 张家界桑植、遵义、湘西凤凰、武隆、宜昌兴山、巫山、潍坊临朐铜仁德江、黔东南凯里、黔南贵定、牡丹江宁安、临沂蒙阴、彭水、汉中南郑、临沂费县、怀化靖州、恩施利川、恩施咸丰、贵阳开阳、丹东宽甸、安康旬阳、毕节黔西、安顺西秀、 浓香型 189 河南、广东、安徽、湖南、江西、山东、陕西 宝鸡陇县、郴州桂阳、赣州信丰、漯河临颍、南阳内乡、平顶山宝丰、南阳方城、平顶山郏县、三门峡灵宝、商洛洛南、韶关南雄、皖南泾县、皖南旌德、皖南宣州、潍坊昌乐、潍坊高密、潍坊诸城、许昌襄县、延安富县、永州江华、驻马店确山、驻马店泌阳、长沙浏阳 表 2 2011年3种香型烤烟烟叶样品6种生物碱物质的F检验①
Table 2 F-test on 6 alkaloids in 3 categories of tobaccos in 2011 ①
序号 检测成分 对比香型 df1 df2 F值 f单尾临界值 P(F≤f)单尾 显著性程度 1 烟碱 清-浓 66 65 0.077 3.912 0.782 - 浓-中 65 49 3.916 3.923 0.050 - 中-清 49 66 2.569 3.925 0.112 - 2 降烟碱 清-浓 66 65 6.133 3.915 0.015 * 浓-中 65 49 1.424 3.926 0.235 - 中-清 49 66 1.243 3.925 0.267 - 3 麦斯明 清-浓 66 65 6.260 3.915 0.014 * 浓-中 65 49 2.152 3.926 0.145 - 中-清 49 66 0.386 3.925 0.536 - 4 假木贼碱 清-浓 66 65 3.465 3.915 0.065 - 浓-中 65 49 8.912 3.926 0.003 ** 中-清 49 66 0.690 3.925 0.408 - 5 新烟草碱 清-浓 66 65 0.051 3.915 0.821 - 浓-中 65 49 13.095 3.926 <0.0001 ** 中-清 49 66 12.185 3.925 <0.0001 ** 6 2, 3′-联吡啶 清-浓 66 65 13.261 3.915 <0.0001 ** 浓-中 65 49 41.096 3.926 3.5511E-09 ** 中-清 49 66 5.422 3.925 0.022 * 注:①显著性程度:当P>0.025时,表示为-,没有显著性差异;当0.01<P≤0.025时,表示为*,存在显著性差异;当P≤0.01时,表示为**,存在极显著性差异。表 3~4同。 表 3 2012年3种香型烤烟烟叶样品6种生物碱物质的F检验
Table 3 F-test on 6 alkaloids in 3 categories of tobaccos in 2012
序号 检测成分 对比香型 df1 df2 F值 f单尾临界值 P(F≤f)单尾 显著性程度 1 烟碱 清-浓 46 60 1.888 3.932 0.172 - 浓-中 60 63 0.203 3.919 0.653 - 中-清 63 46 0.797 3.930 0.374 - 2 降烟碱 清-浓 46 60 1.726 3.932 0.192 - 浓-中 60 63 0.030 3.919 0.864 - 中-清 63 46 1.558 3.930 0.215 - 3 麦斯明 清-浓 46 60 0.546 3.932 0.461 - 浓-中 60 63 0.593 3.919 0.443 - 中-清 63 46 0.004 3.930 0.948 - 4 假木贼碱 清-浓 46 60 0.933 3.932 0.336 - 浓-中 60 63.000 3.082 3.919 0.082 - 中-清 63 46.000 0.411 3.930 0.523 - 5 新烟草碱 清-浓 46 60.000 19.838 3.932 <0.0001 ** 浓-中 60 63.000 4.386 3.919 0.038 - 中-清 63 46.000 5.827 3.930 0.017 ** 6 2, 3′-联吡啶 清-浓 46 60.000 0.279 3.932 0.598 - 浓-中 60 63.000 9.999 3.919 0.002 ** 中-清 63 46.000 5.205 3.930 0.025 ** 表 4 2013年3种香型烤烟烟叶样品6种生物碱物质的F检验
Table 4 F-test on 6 alkaloids in 3 categories of tobaccos in 2013
序号 检测成分 对比香型 df1 df2 F值 f单尾临界值 P(F≤f)单尾 显著性程度 1 烟碱 清-浓 65 64 0.411 3.916 0.523 - 浓-中 64 65 0.483 3.916 0.488 - 中-清 65 65 0.011 3.915 0.918 - 2 降烟碱 清-浓 65 64 1.175 3.916 0.280 - 浓-中 64 65 0.284 3.916 0.595 - 中-清 65 65 0.223 3.915 0.638 - 3 麦斯明 清-浓 65 64 0.811 3.916 0.369 - 浓-中 64 65 0.785 3.916 0.377 - 中-清 65 65 0.001 3.915 0.977 - 4 假木贼碱 清-浓 65 64 0.355 3.916 0.552 - 浓-中 64 65 0.039 3.916 0.844 - 中-清 65 65 0.612 3.915 0.435 - 5 新烟草碱 清-浓 65 64 5.300 3.916 0.023 * 浓-中 64 65 2.801 3.916 0.097 - 中-清 65 65 0.257 3.915 0.613 - 6 2, 3′-联吡啶 清-浓 65 64 1.186 3.916 0.278 - 浓-中 64 65 3.540 3.916 0.062 - 中-清 65 65 1.044 3.916 0.309 - 表 5 2011年不同烟叶样本判别分类结果
Table 5 Classification of tobacco samples in 2011
项目 香型 预测组成员 合计 清 浓 中 初始 计数 清 44 16 6 66 浓 16 37 12 65 中 8 4 37 49 % 清 66.7 24.2 9.1 100.0 浓 24.6 56.9 18.5 100.0 中 16.3 8.2 75.5 100.0 交叉验证① 计数 清 43 16 7 66 浓 20 32 13 65 中 9 6 34 49 % 清 65.2 24.2 10.6 100.0 浓 30.8 49.2 20.0 100.0 中 18.4 12.2 69.4 100.0 注:①仅对案例样本进行交叉验证;②已对交叉验证分组案例中的60.6%个进行了正确分类;③已对初始分组案例中的65.6%个进行了正确分类。 表 6 2012年不同烟叶样本判别分类结果
Table 6 Classification of tobacco samples in 2012
项目 香型 预测组成员 合计 清 浓 中 初始 计数 清 32 9 5 46 浓 7 46 7 60 中 15 5 43 63 % 清 69.6 19.6 10.9 100.0 浓 11.7 76.7 11.7 100.0 中 23.8 7.9 68.3 100.0 交叉验证① 计数 清 32 9 5 46 浓 7 45 8 60 中 17 5 41 63 % 清 69.6 19.6 10.9 100.0 浓 11.7 75.0 13.3 100.0 中 27.0 7.9 65.1 100.0 注:①仅对案例样本进行交叉验证;②已对交叉验证分组案例中的69.8%个进行了正确分类;③已对初始分组案例中的71.6%个进行了正确分类。 表 7 2013年不同烟叶样本判别分类结果
Table 7 Classification of tobacco samples in 2013
项目 香型 预测组成员 合计 清 浓 中 初始 计数 清 34 18 13 65 浓 11 41 12 64 中 19 13 33 65 % 清 52.3 27.7 20.0 100.0 浓 17.2 64.1 18.8 100.0 中 29.2 20.0 50.8 100.0 交叉验证a 计数 清 32 18 15 65 浓 13 38 13 64 中 22 16 27 65 % 清 49.2 27.7 23.1 100.0 浓 20.3 59.4 20.3 100.0 中 33.8 24.6 41.5 100.0 注:①仅对案例样本进行交叉验证;②已对交叉验证分组案例中的50.0%个进行了正确分类;③已对初始分组案例中的55.7%个进行了正确分类。 -
[1] 丁瑞康, 王承瀚, 朱尊权, 等.卷烟工艺学[M].北京:食品工业出版社, 1958:49-71. [2] 张槐苓, 葛翠英, 穆怀静, 等.烟草分析与检验[M].郑州:河南科学技术出版社, 1994:103-111. [3] 谢剑平.烟草香原料[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2009:70-447. [4] 谢剑平.烟草与烟气化学成分[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2010:73-903. [5] 陆龙建, 陈磊, 余苓, 等.多元因子分析在卷烟风格特征剖析中的应用[J].烟草科技, 2012, 45(10):36-40. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0861.2012.10.009 [6] 常爱霞, 张建平, 杜咏梅, 等.烤烟香型相关化学成分主导的不同产区烟叶聚类分析[J].中国烟草学报, 2010, 16(2):14-19. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgycxb201002004 [7] 谢剑平, 赵明月, 吴鸣, 等.白肋烟重要香味物质组成分析的研究[J].烟草科技, 2002, 35(10):3-16. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0861.2002.10.001 [8] 刘百战, 宗若雯, 岳勇, 等.国内外部分白肋烟香味成分的对比分析[J].中国烟草学报, 2000, 6(2):1-5. [9] 邵岩, 宋春满, 邓建华, 等.云南与津巴布韦烤烟致香物质的相似性分析[J].中国烟草学报, 2007, 14(4):19-25. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgycxb200704004 [10] 冼可法, 沈朝智, 戚万敏, 等.云南烤烟中性香味物质分析研究[J].中国烟草学报, 1992, 1(2):1-91. [11] 常爱霞, 贾兴华, 郝廷亮, 等.特香型烤烟挥发性致香物质的测定与分析[J].中国烟草科学, 2002, (1):1-5. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgyckx200201011 [12] 李伟, 陈江华, 詹军, 等.烤烟香型间致香物质组成比例及其差异分析[J].中国烟草学报, 2013, 19(2):1-6. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgycxb201302003 [13] 杜咏梅, 张建平, 王树声, 等.主导烤烟香型风格及感官质量差异的主要化学指标分析[J].中国烟草科学, 2010, 31(5):7-12. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgyckx201005002 [14] 朱忠, 冼可法, 尚希勇, 等.中上部不同成熟度烤烟烟叶与主要化学成分和香味物质组成关系的研究[J].中国烟草学报, 2008, 14(1):6-12. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgycxb200801002 [15] 詹军, 周芳芳, 邓国宾, 等.基于化学成分和致香物质的烤烟上部烟叶香型判别分析[J].湖南农业大学学报:自然科学版, 2013, 39(3):232-241. [16] 李雪君, 郭芳阳, 李耀宇, 等.浓香型风格烤烟品种的筛选研究[J].河南农业科学, 2010, 39(11):45-49. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3268.2010.11.012 [17] 李宏光, 周玲红, 罗经仁.湖南浓香型特色烟叶品种筛选研究[J].作物研究, 2013, 27(6):568-571. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zuowuyj201306010 [18] 胡亚杰, 石保峰, 首安发, 等.不同品种对贺州浓香型特色优质烟叶形成的影响[J].广东农业科学, 2013, 40(5):18-21. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gdnykx201305007 [19] 唐远驹.关于烤烟香型问题的探讨[J].中国烟草科学, 2011, 32(3):1-7. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgyckx201103001 [20] 王文胜, 马戎.浓香型产区烟叶主要化学成分与风格品质特色及其关系研究[J].中国烟草科学, 2013, 34(5):28-32. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgyckx201305006 [21] 杨天沛, 钟蕾, 付继刚, 等.黔东南烟区烟叶致香物质的定量分析[J].中国烟草科学, 2013, 34(1):22-28. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgyckx201301007 [22] Richard A, Johnson, Dean W, Wichern. 实用多元统计分析[M]. 陆璇译, 译. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2001: 17-103. [23] 朱万森等.应用因子分析法对地面水质污染状况的研究[J].复旦学报, 2003, 33(3):141-146. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fdxb200303058 [24] 袁志发, 周净芋.多元统计分析[M].北京:北京科学出版社, 2002:139-141. -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 穆子涵,吴晓花,李艳伟,鲁忠富,王尖,吴新义,汪宝根,王华森,李国景,汪颖. 基于BSA方法的瓠瓜果形相关性状主效QTL分析. 分子植物育种. 2024(13): 4291-4296 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 唐亮,蒋满贵,唐名艳,黄深惠,陈小青,董桂清,王平阳,潘志新. 基于BSA-Seq的家蚕NC99R抗BmNPV分子标记鉴定. 南方农业学报. 2023(08): 2406-2414 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 田大刚. 水稻稻瘟病抗性基因座Piz和Pik的探秘之旅. 福建农业科技. 2022(05): 1-11 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)





 下载:
下载: