Evaluation and Prediction of Carbon Emissions on Land Uses in Shaanxi
-
摘要: 从土地利用碳排放安全的内涵出发,构建基于压力-响应模型的陕西省土地利用碳排放安全评价指标体系,分析陕西省11个地级市土地利用碳排放安全的时空分异特征,并应用改进的新陈代谢无偏GM(1,1)模型进行预测。结果表明:(1)2005-2014年,陕西省土地利用碳排放安全指数先曲折上升后波动下降,2010年达到最安全状态;(2)陕西省土地利用碳排放安全与自然地理分区呈耦合关系,陕南安全水平最高,关中次之,陕北最低,各地级市安全状况存在一定的空间集聚效应;(3)陕西省大部分地级市处于土地利用碳排放临界安全或不安全状态,压力系统恶化的同时,响应系统好转;(4)2015-2025年,陕西省土地利用碳排放安全状态持续弱化,各地级市未来土地利用碳排放安全均处于临界安全或不安全状态,安全状况不容乐观。应该在认清本区域土地利用碳排放安全情况的前提下,从相对敏感的指标入手采取针对性的碳减排措施。
-
关键词:
- 碳排放安全 /
- 土地利用 /
- 无偏GM(1, 1)模型 /
- 新陈代谢 /
- 陕西省
Abstract: For environmental security, any extended land use may cause increases in carbon emissions and raise concerns. To provide a guidance for the sustainable future regional development, the stress-response model was applied to firstly establish an indexing system for analyzing the spatial and temporal carbon emissions associated with the land uses in Shaanxi. In the end, strategies to reduce air pollution could be made available for the province. The improved unbiased metabolism-GM (1, 1) model was used to project the situation for 2015 to 2025. The results showed that (1) from 2005 to 2015, the carbon emission security index increased at first, and then decreased, with the best state appeared in 2010; (2) the index was regional dependent, i.e., the highest in the southern Shaanxi followed by the central and the northern region a spatial clustering among the prefectures was evident; (3) most prefectures in the province faced a borderline or critical level on the security index challenged by various stress factors, but the response system seemed significantly improved; and, (4) the status from 2015 to 2025 was expected to continuously deteriorate as most prefectures remain in the critical or unsafe state with respect of carbon emission. It seemed imperative that appropriate measures be adopted starting from the relatively sensitive issues to safeguard the environment from serious carbon emissions in the province.-
Keywords:
- carbon emission security /
- land use /
- unbiased GM (1, 1) model /
- metabolism /
- Shaanxi Province
-
全球气候变暖引发严重的环境问题,对经济社会可持续发展造成不容忽视的影响,引起社会各界的关注。作为世界第一大碳排放国,中国的碳排放问题已经成为世界关注的焦点,进行碳排放安全评价和预测不仅是应对气候变化、环境治理的需要,也成为国家发展战略的要求。土地利用碳排放对大气二氧化碳含量增加的影响仅次于化石燃料燃烧,其安全问题关乎区域、国家乃至世界的和谐、稳定及可持续发展。陕西省作为国家“一带一路”战略安排的重要区域和西部生态环境建设的重点区域,近年来工业化、城市化水平得到了很大的提高。但是,土地生态系统受到了人类活动的较大影响,土地利用强度不断加强,土地利用碳排放压力逐年增大,土地利用所产生的碳排放与区域人口、资源、环境、经济、社会系统协调发展的状态受到威胁。因此,对陕西省进行土地利用碳排放安全评价及预警研究,从而提出土地利用碳排放安全调控对策,对促进陕西省土地绿色、低碳、可持续利用具有必要性和紧迫性。
综合国内外学者的研究,土地利用碳排放是指在一定区域内,由于土地利用或管理方式转变,不同土地利用类型产生的碳排放[1]。而根据相关研究[2-3],土地利用碳排放安全可以理解为:土地利用碳排放在满足人类自身生产、生活等方面的必要需求的前提下,与区域人口、环境、社会、经济、资源系统保持协调可持续发展的状态。目前,关于土地利用碳排放的研究主要集中于土地利用碳排放的测算[4]、时空特征分析[5]、碳效率分析[6]、影响因素分解[7]以及脱钩效应分析[8]等方面。碳排放安全评价是在碳排放研究的基础上,基于生态安全评价理论拓展出来的新的研究领域,目前尚处于起步阶段,具体到土地利用碳排放安全评价及预测的研究则更为少见,能体现安全状况时空分异特征的研究更有待加强。
当前,对区域土地利用碳排放安全进行科学合理的评价和预测需要突破以下几个方面:首先,指标的选择是评价的基础,在分析土地利用碳排放安全影响因素的基础上选择指标,土地利用变化是影响土地利用碳排放量的主要因素[9-10],经济增长对土地利用碳排放存在着明显的正效应[9, 11-12],人口规模的扩大也会增加土地利用的碳排放量[11-12],能源效率的提高是降低土地利用碳排放的主要途径,能源结构的优化对土地利用碳减排十分有利,土地利用效率是抑制区域土地利用碳排放总量的最重要原因[1, 9]。其次,设计指标框架是关键环节,压力-响应(Stress-Response,S-R)模型[13]框架及其衍生的压力-状态-响应(Pressure-State-Response)模型[14]强调社会经济运作与环境变化的互动关系,且容易与预测模型和信息系统相连接,具有可测定性、可评价性、可预测性的特点,被成功地应用在碳排放安全评价[2]、耕地资源生态安全评价[14]、土地利用可持续性水平测度[15]、土地资源安全评价[16]等众多方面。因此,构建基于S-R模型的土地利用碳排放安全评价指标体系可以从土地低碳、绿色、可持续利用的角度出发,总体反映土地利用碳排放安全与区域人口、环境、社会、经济、资源系统之间的相互关系。再次,主观赋权法能够利用专家经验判断各个指标的贡献度但存在随意性和盲目性,客观赋权法尊重样本数据真实性但存在片面性和机械性的缺点,二者各有利弊,如何将二者合理组合对评价结果至关重要。最后,GM(1, 1)预测模型[17]能够寻找出数据规律性,计算量小且易于检验,得到广泛的应用,但其适用于对连续平滑的事件进行预测且存在固有偏差,预测精度有待进一步提高。
鉴于此,本课题组以陕西省11个地级市为研究对象,在分析土地利用碳排放安全影响因素的基础上结合区域实际,基于“压力-响应”分析模型构建土地利用碳排放安全评价指标体系,采用相对熵理论将层次分析法确定的主观权重和改进的熵权法确定的客观权重相结合并应用多指标综合评价模型对陕西省11个地级市土地利用碳排放安全的时空分异特征进行评价分析;同时运用改进后的新陈代谢无偏GM(1, 1)模型预测未来陕西省土地利用碳排放安全变化趋势,以期为土地利用碳排放安全评价及预测提供方法借鉴,同时为陕西省开展土地利用碳减排工作提供科学依据。
1. 数据与方法
1.1 指标体系构建
土地利用碳排放系统具有系统性、动态性、复杂性等特点,其安全评价指标体系是一个融合人口、资源、环境、经济、社会等方面的复合系统,因地制宜地构建科学合理的评价指标体系是对土地利用碳排放安全进行有效评价的基础。本研究从土地低碳、绿色、可持续利用的角度出发,选择压力-响应模型构建指标体系。为保证指标体系的科学性、系统性、完备性和适用性,首先,将目标层分为“压力系统”、“响应系统”2个准则层;其次,从影响土地利用碳排放安全的因素入手并参考现有的各种土地评价指标,初步选择40个相关指标构建备选指标集;再次,选择31位专家(教授6人,副教授6人,专业学者12人,行业从业者7人)发放问卷进行2轮指标筛选,确定24个具体指标构成初步的评价指标体系;最后,通过改进的熵权法对指标进行初步赋权,将权重小于0.01的对评价结果无关紧要的指标筛去,最终确定20个指标构成土地利用碳排放安全评价指标体系(表 1)。其中,压力是指土地利用碳排放安全受到威胁的原因,响应是指预防土地利用碳排放安全恶化、维护土地利用碳排放安全所采取的措施。
表 1 土地利用碳排放安全评价指标体系及权重Table 1. Evaluation indices and weight of carbon emission security by land use目标层 准则层 指标层 单位 指标性质 熵权 AHP权 组合权重 土地利用碳排放安全值A 压力系统B1 (0.548) U1人口密度 人·hm-2 - 0.021 0.036 0.029 U2城市化率 % - 0.048 0.039 0.045 U3人均GDP 元·人-1 - 0.042 0.042 0.044 U4第二产业所占比重 % - 0.035 0.047 0.042 U5城镇人均可支配收入 元·人-1 - 0.030 0.041 0.037 U6农村人均纯收入 元·人-1 - 0.030 0.041 0.036 U7单位耕地化肥施用量 kg·hm-2 - 0.035 0.059 0.047 U8单位耕地地膜使用量 kg·hm-2 - 0.027 0.059 0.041 U9单位GDP能耗 kg·万元-1 - 0.025 0.063 0.041 U10单位工业增加值能耗 kg·万元-1 - 0.035 0.047 0.042 U11人均建设用地面积 hm2·人-1 - 0.024 0.049 0.036 U12单位GDP碳排放 kg·万元-1 - 0.043 0.050 0.048 U13单位建设用地碳排放 kg·hm-2 - 0.048 0.076 0.062 响应系统B2 (0.452) U14人均生态用地面积 hm2·人-1 + 0.073 0.055 0.065 U15单位农用地碳吸收 kg·hm-2 + 0.130 0.077 0.103 U16水土协调度 % + 0.082 0.037 0.057 U17粮食单产 kg + 0.061 0.031 0.045 U18城市人均园林绿地面积 hm2·人-1 + 0.109 0.062 0.085 U19工业固体废弃物综合利用率 % + 0.034 0.043 0.040 U20林业投资占GDP比重 % + 0.067 0.045 0.057 注:“+”表示正项指标,数值越大越利于安全;“-”表示负向指标,数值越大越威胁安全。 1.2 数据来源
本研究所使用的土地利用数据来源于2005-2014年陕西省土地利用变更详查数据,社会经济数据来源于2006-2015年《陕西省统计年鉴》,环境数据来源于2005-2014年《陕西省环境状况公报》,部分数据通过原始数据计算得到。需要说明的是:第一,本研究中所用GDP数据是以2005年为基期进行平减,消除价格因素影响后的数据;第二,参考南灵等[18]的研究成果,本研究中的生态用地包括耕地、园地、林地、草地和水域5种用地类型,其中,水域面积包括湖泊水面、坑塘水面、河流水面和水库水面;第三,水域及未利用地面积在陕西省土地总面积中所占比例均不超过1.5%,本研究只计算耕地、园地、林地和草地的碳吸收,耕地碳吸收量为其上农作物光合作用所固定的碳[5],园地、林地、草地碳吸收采用碳吸收系数法测算[19];第四,农用地碳排放量包括农地利用过程中农用机械使用、化肥施用、灌溉活动、地膜使用四方面主要碳源产生的碳排放,建设用地碳排放量通过单位GDP能耗间接计算[5]。
1.3 研究方法
1.3.1 基于相对熵理论的组合权重法
本研究通过相对熵理论[20]将层次分析法和改进的熵权法相结合,得到最终的组合权重,其计算公式为:
wi=p∏j=1(uji)1pm∑i=1p∏j=1(uji)1p (1) 式中,wi为组合权重,uji为第j种单一赋权法中第i个指标的权重。
1.3.2 安全值计算及分级
本研究采用极值法来确定各指标阀值[2],再根据阈值计算各指标的安全指数,最后,根据各指标的安全指数及组合权重计算土地利用碳排放安全值。计算公式为:
E=m∑i=1wi⋅Pi (2) 碳排放安全的等级划分目前并没有统一的标准,参考相关研究并结合陕西省实际[2, 20],采用非等间距法将土地利用碳排放安全值划分为5个等级(表 2)。
表 2 土地利用碳排放安全评价等级Table 2. Evaluation ranking on carbon emission security by land use等级 区间 状态 安全特征 Ⅰ (0.85, 1] 安全 人口相对稳定,能源利用效率高,土地生态环境基本未受到破坏,碳排放与经济增长处于高度耦合协调发展状态,碳排放调控及减排效果理想,实现人口、环境、社会、经济、资源系统的协调发展。 Ⅱ (0.65, 0.85] 亚安全 人口压力较小,能源利用效率较高,土地生态环境不断改善,碳排放与经济增长处于初级协调状态,碳排放调控及减排效果较好,人口、环境、社会、经济、资源系统协调发展状况较好。 Ⅲ (0.45, 0.65] 临界安全 存在一定的人口压力,能源利用效率有所提高,土地生态环境较少受到破坏,碳排放与经济发展处于协调边缘,碳排放调控及碳减排虽不理想但有初步效果,人口、环境、社会、经济、资源系统协调发展状况一般。 Ⅳ (0.25, 0.45] 不安全 人口压力较大,能源利用效率较低,土地生态环境受到较大破坏,碳排放与经济发展比较不协调,碳排放调控及碳减排效果不理想,阻碍了人口、环境、社会、经济、资源系统协调发展。 Ⅴ [0, 0.25] 病态 人口压力巨大,能源利用效率低下,土地生态环境破坏非常严重,碳排放与经济发展严重不协调,碳排放调控及碳减排效果极不理想,人口、环境、社会、经济、资源系统无序发展。 注:本表参照文献[2]中表 2编制。 1.3.3 改进的新陈代谢无偏GM(1, 1)预测模型
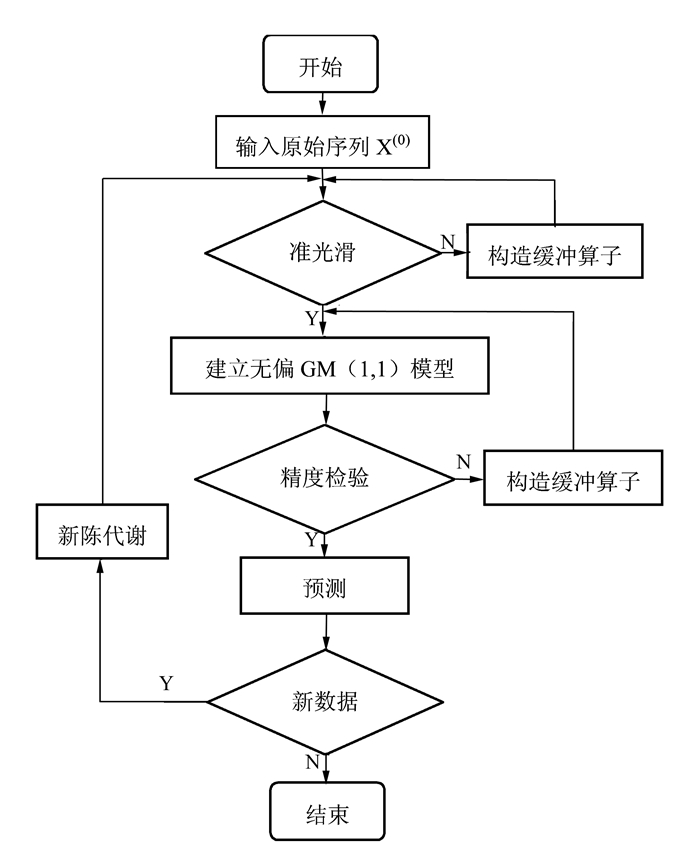
为提高模型预测精度,对传统GM(1, 1)模型做四方面改进:第一,检验原始数据序列光滑度,对级比检验未通过的原始数据序列引入平均弱化缓冲算子[21],使其达到准光滑序列要求;第二,进行无偏修正,无偏GM(1, 1)模型[14, 22]能够消除模型固有的偏差,适用范围较GM(1, 1)模型有很大扩展;第三,对未通过预测精度要求的序列引入平均弱化缓冲算子[21],从根本上改变原始数据的波动性,重新构建无偏GM(1, 1)模型;第四,将灰色新陈代谢模型[23]与无偏GM(1, 1)模型相结合构建新陈代谢无偏GM(1, 1)模型,在补充新数据的同时去掉陈旧数据,使建模序列更好地反映系统目前的特征,提高模型预测精度。建模的具体流程如图 1所示。
本研究在指标值模拟的基础上,根据后验差、小误差概率及平均相对误差判定模型的预测精度[24](表 3)。
表 3 模型精度检验等级标准Table 3. Accuracy standards for model testing预测精度等级 好 合格 勉强 不合格 α >0.95 >0.8 >0.7 ≤0.7 C <0.35 <0.5 <0.65 ≤0.65 2. 结果与分析
采用上述方法计算得到各指标组合权重(表 1),应用多指标综合评价模型计算出陕西省11个地级市2005-2014年土地利用碳排放安全值及各子系统安全值,并对其2015-2025年土地利用碳排放安全状况进行预测。
2.1 陕西省土地利用碳排放安全时序特征分析
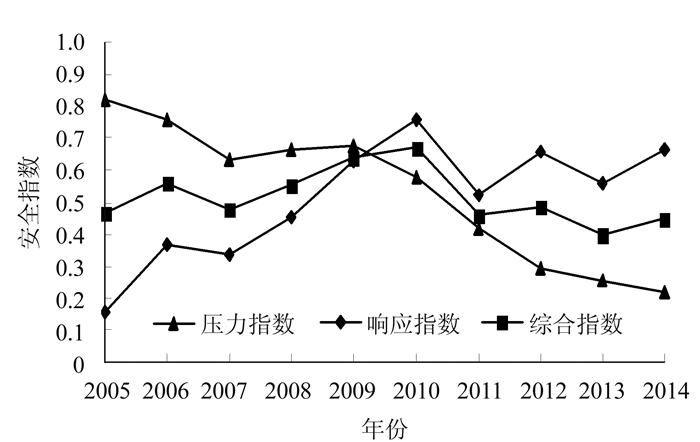
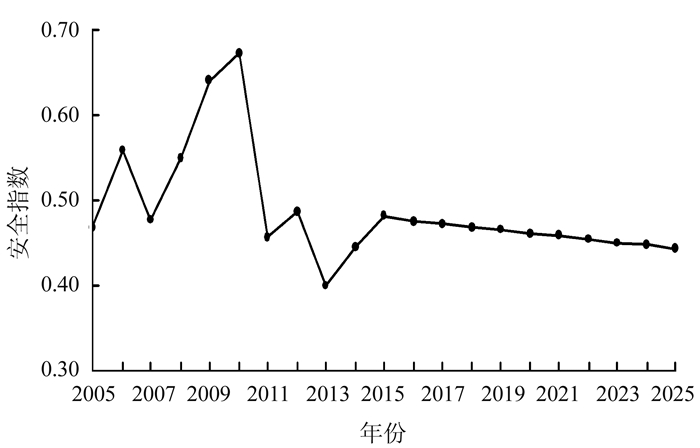
由图 2可知,压力子系统土地利用碳排放安全指数持续波动下降,由2005年的0.821下降至2014年的0.220,压力系统的指标均为负向,说明影响土地利用碳排放安全的驱动力因素在持续增强。响应子系统土地利用碳排放安全指数先曲折上升至2010年,后呈波浪式交替变化,安全值最低出现在2005年(0.155),最高出现在2010年(0.759),由于响应系统的指标性质全部为正,说明维护土地利用碳排放安全,预防安全状态恶化的措施在2010年以前成效逐年显现,后期有所波动。综合来看,2005-2014年,陕西省土地利用碳排放安全指数先曲折上升至2010年达到近十年最安全状态,后波动下降至2013年达到安全指数最低值,2014年安全状况有所回升;安全指数范围为0.399~0.672,安全等级跨越不安全、临界安全和亚安全。
通过对各指标数据的进一步分析发现:随着城市化进程的加快,陕西省的城市化率逐年提高,越来越多的农村人口向城镇转移,城市化进程带来的城市人口压力的增加以及建设用地的扩张,引起建设用地碳排放量大量增加;经济快速发展的同时环境问题日渐突出,碳排放增长速度大于GDP增长速度且绿色植被固碳能力跟不上碳排放增长的速度;单位农用地化肥施用量和地膜使用量逐年增加,2014年单位面积地膜使用量较2005年增长300%,大量农用物资欠科学地投入使用进一步加剧了土地利用碳排放安全的恶化。然而,随着低碳科技的发展和陕西省近年来对高能耗高碳排工业企业的治理,能源利用效率逐步提高,单位GDP能耗和单位工业增加值能耗逐年降低;粮食单产、单位农用地碳吸收以及人均生态用地面积在2010年达到最高值,促使2010年陕西省土地利用碳排放安全水平达到十年来最安全水平;此外,固体废弃物综合利用率稳步提高,2010年以后,林业投资所占比重也有较快提高,一系列积极的应对措施,为减缓碳排放增速,增加土地碳汇能力,提高土地利用碳排放安全水平提供了有力保障。
2.2 陕西省土地利用碳排放安全时空变化分析
2.2.1 陕西省土地利用碳排放安全总体空间分异
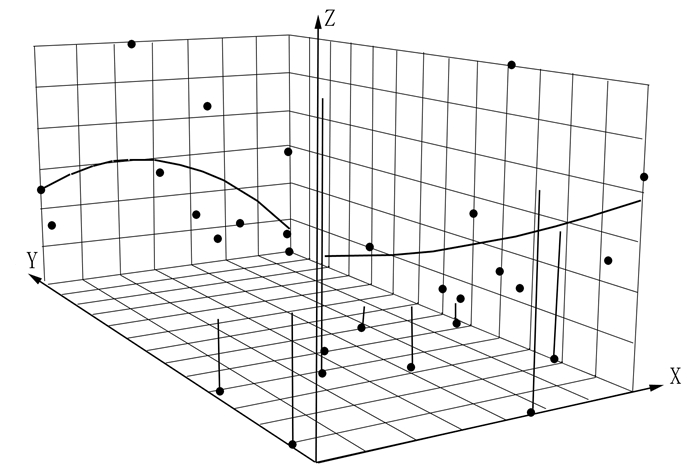
利用地统计软件中的趋势分析工具对陕西省土地利用碳排放安全进行宏观趋势分析,用X轴、Y轴代表正西、正南方向,Z轴代表陕西省各地级市土地利用碳排放安全指数平均值,生成三维宏观趋势图,以揭示陕西省土地利用碳排放安全的空间特征及趋势。由图 3可知,陕西省土地利用碳排放安全水平南北向空间分异程度大于东西向,呈现“南高北低”的趋势,空间不均衡现象较为显著。具体来看,陕西省土地利用碳排放安全与其自然地理分区呈耦合关系,陕南安全水平最高,关中次之,陕北最低。
2.2.2 陕西省土地利用碳排放安全时空演变分析
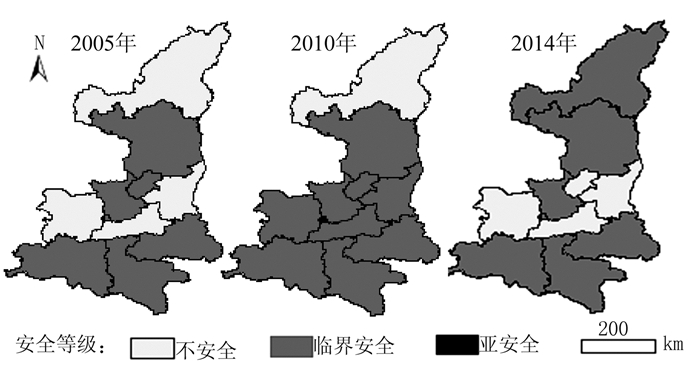
为进一步揭示陕西省土地利用碳排放安全时空演变特征,应用ArcGIS 9.3软件将安全指数计算结果与陕西省矢量数据相关联并进行可视化表达,由图 4可知,陕西省大部分地市处于土地利用碳排放临界安全或不安全状态。从等级上来看,2005年,处于临界安全状态的有陕南的安康、商洛和汉中市,关中的杨凌示范区、咸阳和铜川市以及陕北的延安市,其余各地级市均处于不安全状态;2005-2010年,陕西省土地利用碳排放安全格局发生一定的变化,榆林市处于不安全状态,杨凌示范区处于亚安全状态,其余各地级市均处于临界安全状态,安全水平总体明显提高;2010-2014年,陕西省土地利用碳排放安全水平有所下降,除关中的西安、宝鸡、渭南和铜川市处于不安全状态外,其余地级市均处于临界安全状态。由于陕西省绝大部分地区土地利用碳排放安全处于不安全和临界安全等级,但其分布原因难以通过综合指数判断,因此,以下从压力和响应系统分别进行分析。
2.2.3 各子系统碳排放安全时空差异
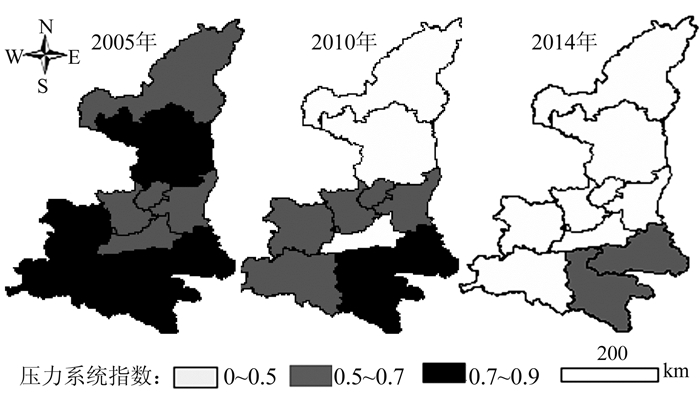
(1) 压力系统:在ArcGIS 9.3软件中采用等间距法将土地利用碳排放安全压力系统指数划分为3个等级并进行可视化表达。由图 5可知,研究期内压力系统指数明显减小,空间格局变化显著,压力系统均为负向指标,说明影响土地利用碳排放安全的驱动力因素随时间的推移逐渐增强。2005年,土地利用碳排放安全压力整体较小,汉中、安康、商洛、宝鸡、延安5个地级市处在压力最轻等级,其余各地级市均处在中间等级,无处于最严重等级的区域。2005-2010年,土地利用碳排放安全压力明显增大,榆林、延安、宝鸡、西安和汉中均发生等级恶化,其中,延安市压力连增2个等级,延安市这一阶段工业发展迅猛,人均GDP和第二产业占GDP比重快速增加,但单位GDP能耗和单位工业增加值能耗并未及时降低,碳排放压力大幅度增加。2010-2014年,土地利用碳排放安全压力继续增大,除西安、榆林和延安3个本身处在压力最严重等级的地级市外,其余各地级市均发生等级恶化,无处于压力最轻等级的区域。综合来看,2005-2014年,陕西省各地级市土地利用碳排放安全压力系统均出现不同程度的恶化。结合指标数据发现,研究期内陕西省总体经济增长较快,城市化、工业化发展迅速,农业生产物资投入量逐年增加,能源利用效率有待提高。
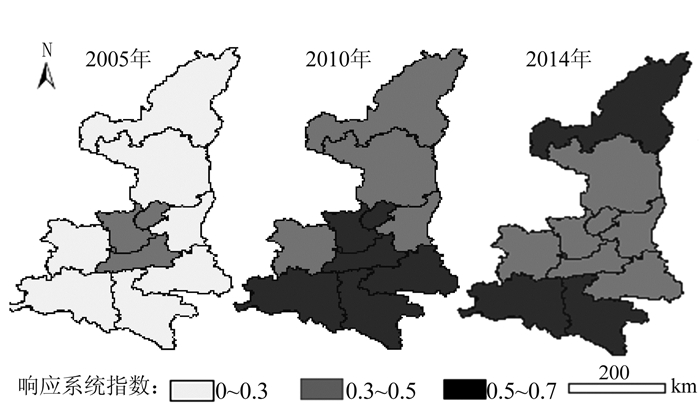
(2) 响应系统:同上,将响应系统指数划分为3个等级。由图 6可知,响应系统明显改善,说明各地级市均采取了较为有效的措施。2005年,西安、杨凌示范区、咸阳、铜川市响应程度相对较好,处在中间等级。2005-2010年,全省响应系统均发生好转,其中陕南地区的汉中、安康、商洛3市由最低等级提高到最高等级,该阶段全省人均生态用地面积和单位农用地碳吸收量增加。2010-2014年,响应系统空间格局发生显著变化,其中,榆林市响应系统好转,而西安、铜川、咸阳、商洛市响应系统恶化,其余各地级市等级未发生变化。根据指标数据,榆林市除人均生态用地面积有所减少外,各项响应指标均在2014年达到历年最好水平;而响应系统恶化的地级市均出现单位农用地碳吸收的减少。总体来看,2005-2014年,陕西省各地级市林业投资比重增加,固体废弃物综合利用率稳步提高,其他各项指标波动变化,响应系统总体好转。
2.2.4 压力-响应系统拟合分析
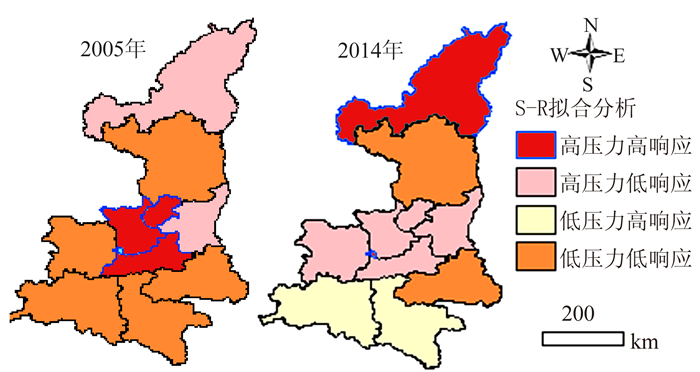
为进一步揭示各地级市在同一时间截面上土地利用碳排放安全状况在全省所处的位置,以不同时间截面上11个地级市的平均值为依据将各地级市划分为:高压力高响应、高压力低响应、低压力高响应和低压力低响应4个类别,进行压力-响应系统拟合分析,结果(图 7)表明,榆林市由高压力低响应转变为高压力高响应,说明环境改善引起了足够的重视,但土地利用碳排放安全压力仍需降低;延安市和商洛市维持低压力低响应状态,应该在保证圧力不增加的前提下尽量提高响应程度;西安、铜川、咸阳市由高压力高响应转变为高压力低响应类别,宝鸡市由低压力低响应类别变为高压力低响应,说明在压力增大的同时响应措施并未及时跟上,需要积极制定相关政策,加大改善碳排放现状的措施和力度;汉中市和安康市由初期的低压力低响应转变到低压力高响应的良好状态,需要继续维持;杨凌示范区维持在高压力高响应状态,应该采取措施降低土地利用碳排放安全压力;而维持在高压力低响应的恶劣状态的渭南市需要引起足够的重视,在发展经济的同时注重环境保护,降低碳排放压力的同时提高环境响应。此外,由图 7可知,4种压力-响应系统拟合状况下,各地区存在一定的空间集聚效应,说明相邻或相近地级市在资源禀赋、社会发展或环境政策上存在相似之处。
2.3 陕西省土地利用碳排放安全预测
2.3.1 土地利用碳排放安全总体预测
根据陕西省2005-2014年各指标数据,应用改进的新陈代谢无偏GM(1, 1)预测模型对2015-2025年各评价指标值进行预测并计算预测值的后验差C、小误差概率α和平均相对误差Q。由表 4可知,各指标预测值模拟精度均在合格级以上且Q均处在可接受的误差范围内,可用该模型进行预测。
表 4 土地利用碳排放安全各指标的模拟精度值Table 4. Accuracy of simulated carbon emission security indices on land use指标 C α Q/% 等级 U1 0.0031 1.0 0.01 好 U2 0.2316 1.0 2.92 好 U3 0.0327 1.0 0.27 好 U4 0.0849 1.0 0.17 好 U5 0.0281 1.0 0.24 好 U6 0.0281 1.0 0.24 好 U7 0.4621 0.9 1.52 合格 U8 0.2183 1.0 1.92 好 U9 0.0302 1.0 0.19 好 U10 0.0258 1.0 0.50 好 U11 0.4713 0.9 0.72 合格 U12 0.3366 1.0 1.20 好 U13 0.1285 1.0 0.50 好 U14 0.1904 1.0 0.17 好 U15 0.3919 0.9 0.29 合格 U16 0.1680 1.0 0.07 好 U17 0.4275 0.9 0.49 合格 U18 0.3970 0.8 1.77 合格 U19 0.2640 1.0 0.46 好 U20 0.1275 1.0 1.60 好 图 8为陕西省2015-2025年土地利用碳排放安全预测结果。可以看出,2015-2025年,陕西省土地利用碳排放安全指数先上升后近似直线下降,安全值范围为0.482~0.443,安全等级由临界安全下降到不安全,安全状态持续弱化。进一步分析各指标数值发现,单位GDP碳排放、单位建设用地碳排放、城市化率、第二产业所占比重、单位面积化肥施用量等指标将对未来土地利用碳排放安全的影响较大,需要采取针对性的措施预防土地利用碳排放安全恶化。
2.3.2 各地级市土地利用碳排放安全预测
根据各地级市2005-2014年数据,运用改进的新陈代谢无偏GM(1, 1)模型对2015-2025年的评价指标值进行预测,并通过精度检验,得到各地级市土地利用碳排放安全预测结果,其中2020年和2025年预测结果如表 5所示。由表 5可知,延安、汉中、榆林市未来安全水平有所提升,其他地区均出现下降,关中各地级市下降较为明显。总体来看,陕西省各地级市未来土地利用碳排放安全均处于临界安全或不安全状态,安全状况不容乐观,在未来的经济发展以及环境保护过程中,应采取积极有效的预防措施,保障人口、环境、社会、经济、资源系统协调发展。
表 5 陕西省各地级市2020年及2025年土地利用碳排放安全指数Table 5. Projected 2020 and 2025 carbon emission security indices on land uses at prefectures in Shaanxi地区 2020年 2025年 安全指数 安全等级 安全指数 安全等级 西安市 0.442 Ⅳ 0.437 Ⅳ 铜川市 0.449 Ⅳ 0.408 Ⅳ 宝鸡市 0.429 Ⅳ 0.374 Ⅳ 咸阳市 0.517 Ⅲ 0.476 Ⅲ 渭南市 0.446 Ⅳ 0.373 Ⅳ 延安市 0.507 Ⅲ 0.516 Ⅲ 汉中市 0.563 Ⅲ 0.586 Ⅲ 榆林市 0.498 Ⅲ 0.519 Ⅲ 安康市 0.541 Ⅲ 0.502 Ⅲ 商洛市 0.454 Ⅲ 0.365 Ⅳ 杨凌示范区 0.544 Ⅲ 0.483 Ⅲ 3. 讨论
本研究在分析土地利用碳排放安全影响因素的基础上选择指标,通过能反映社会经济运作与环境变化互动关系的“压力-响应”模型构建指标体系,应用相对熵理论将主观权重和客观权重相结合克服单一赋权法的缺陷,再引入平均弱化缓冲算子构建改进的新陈代谢无偏GM(1, 1)预测模型。新模型既消除了GM(1, 1)模型的固有偏差,又改进了原有模型对波动性数据预测误差较大的问题,且能实现数据的动态递补,大大提高了模型的预测精度。但是,土地利用碳排放安全评价是一项复杂而系统的工作,其指标选取、理论体系和安全阈值的计算仍需要进一步的完善,此外,评价与预测系统的有效衔接问题也有待进一步研究。
为提高土地利用碳排放安全水平,促进区域土地利用碳排放与人口、资源、环境、经济、社会系统相协调,建议从以下几个方面入手:提高决策者解决经济发展与环境保护之间矛盾的综合决策能力,增强其对环境保护和林业发展的重视程度;倡导低碳经济,发展绿色低碳产业,构建清洁、高效、低碳的现代产业体系和能源体系,减少经济增长对常规能源的过度消耗,提高能源利用效率和新型清洁能源使用率;调整产业结构,积极发展知识密集型和科技密集型的低碳产业,对以常规能源消耗为主的高碳排产业进行有选择地逐步淘汰或重组升级;支持农业高新技术的研发和推广利用项目,推广生态农业、绿色农业,引导农业生产方式的低碳化,采用秸秆还田、气化等方式综合利用秸秆资源,引导农民科学合理使用农药、农膜,进行测土配方施肥并逐步以农家肥替代化肥,减少农业生产和土地的农业三废负荷带来的碳排放;增加城市绿地、公园绿地面积,继续推进并扩大退耕还林、退牧换草工程,扩大保护面积,重视城市屋顶、路边草地、休闲旅游地的绿化,重视湿地保护和建设工作,增加土地碳汇能力,缓解城市化发展造成的建设用地碳排放量的大量增加;制定相应的减排政策,建立激励与约束机制,完善碳减排目标责任机制,促进土地低碳利用;同时,还应该加大宣传力度,提高公众对土地利用碳排放安全保护重视程度以及参与和监督的积极性。
4. 结论
本研究借鉴土地生态安全理论进行土地利用碳排放安全研究。研究结果表明:2005-2014年,陕西省土地利用碳排放安全指数先曲折上升后波动下降,2010年达到最安全状态;总体来看,陕西省土地利用碳排放安全与自然地理分区呈耦合关系,陕南安全水平最高,关中次之,陕北最低;陕西省大部分地市处于土地利用碳排放临界安全或不安全状态,压力系统恶化的同时,响应系统好转;各地级市土地利用碳排放安全空间格局差异较为显著,但存在一定的空间集聚效应;2015-2025年,陕西省土地利用碳排放安全指数近似直线下降,安全状态持续弱化;陕西省各地级市未来土地利用碳排放安全均处于临界安全或不安全状态,安全状况不容乐观。
各地级市应该在认清本地区土地利用碳排放安全情况的前提下,从单位GDP碳排放、单位建设用地碳排放、单位农用地碳吸收、单位GDP能耗、第二产业比重、人均生态用地面积、单位面积化肥施用量、林业投资比重等相对敏感的指标人手,结合区域实际采取有针对性的碳减排措施。
-
表 1 土地利用碳排放安全评价指标体系及权重
Table 1 Evaluation indices and weight of carbon emission security by land use
目标层 准则层 指标层 单位 指标性质 熵权 AHP权 组合权重 土地利用碳排放安全值A 压力系统B1 (0.548) U1人口密度 人·hm-2 - 0.021 0.036 0.029 U2城市化率 % - 0.048 0.039 0.045 U3人均GDP 元·人-1 - 0.042 0.042 0.044 U4第二产业所占比重 % - 0.035 0.047 0.042 U5城镇人均可支配收入 元·人-1 - 0.030 0.041 0.037 U6农村人均纯收入 元·人-1 - 0.030 0.041 0.036 U7单位耕地化肥施用量 kg·hm-2 - 0.035 0.059 0.047 U8单位耕地地膜使用量 kg·hm-2 - 0.027 0.059 0.041 U9单位GDP能耗 kg·万元-1 - 0.025 0.063 0.041 U10单位工业增加值能耗 kg·万元-1 - 0.035 0.047 0.042 U11人均建设用地面积 hm2·人-1 - 0.024 0.049 0.036 U12单位GDP碳排放 kg·万元-1 - 0.043 0.050 0.048 U13单位建设用地碳排放 kg·hm-2 - 0.048 0.076 0.062 响应系统B2 (0.452) U14人均生态用地面积 hm2·人-1 + 0.073 0.055 0.065 U15单位农用地碳吸收 kg·hm-2 + 0.130 0.077 0.103 U16水土协调度 % + 0.082 0.037 0.057 U17粮食单产 kg + 0.061 0.031 0.045 U18城市人均园林绿地面积 hm2·人-1 + 0.109 0.062 0.085 U19工业固体废弃物综合利用率 % + 0.034 0.043 0.040 U20林业投资占GDP比重 % + 0.067 0.045 0.057 注:“+”表示正项指标,数值越大越利于安全;“-”表示负向指标,数值越大越威胁安全。 表 2 土地利用碳排放安全评价等级
Table 2 Evaluation ranking on carbon emission security by land use
等级 区间 状态 安全特征 Ⅰ (0.85, 1] 安全 人口相对稳定,能源利用效率高,土地生态环境基本未受到破坏,碳排放与经济增长处于高度耦合协调发展状态,碳排放调控及减排效果理想,实现人口、环境、社会、经济、资源系统的协调发展。 Ⅱ (0.65, 0.85] 亚安全 人口压力较小,能源利用效率较高,土地生态环境不断改善,碳排放与经济增长处于初级协调状态,碳排放调控及减排效果较好,人口、环境、社会、经济、资源系统协调发展状况较好。 Ⅲ (0.45, 0.65] 临界安全 存在一定的人口压力,能源利用效率有所提高,土地生态环境较少受到破坏,碳排放与经济发展处于协调边缘,碳排放调控及碳减排虽不理想但有初步效果,人口、环境、社会、经济、资源系统协调发展状况一般。 Ⅳ (0.25, 0.45] 不安全 人口压力较大,能源利用效率较低,土地生态环境受到较大破坏,碳排放与经济发展比较不协调,碳排放调控及碳减排效果不理想,阻碍了人口、环境、社会、经济、资源系统协调发展。 Ⅴ [0, 0.25] 病态 人口压力巨大,能源利用效率低下,土地生态环境破坏非常严重,碳排放与经济发展严重不协调,碳排放调控及碳减排效果极不理想,人口、环境、社会、经济、资源系统无序发展。 注:本表参照文献[2]中表 2编制。 表 3 模型精度检验等级标准
Table 3 Accuracy standards for model testing
预测精度等级 好 合格 勉强 不合格 α >0.95 >0.8 >0.7 ≤0.7 C <0.35 <0.5 <0.65 ≤0.65 表 4 土地利用碳排放安全各指标的模拟精度值
Table 4 Accuracy of simulated carbon emission security indices on land use
指标 C α Q/% 等级 U1 0.0031 1.0 0.01 好 U2 0.2316 1.0 2.92 好 U3 0.0327 1.0 0.27 好 U4 0.0849 1.0 0.17 好 U5 0.0281 1.0 0.24 好 U6 0.0281 1.0 0.24 好 U7 0.4621 0.9 1.52 合格 U8 0.2183 1.0 1.92 好 U9 0.0302 1.0 0.19 好 U10 0.0258 1.0 0.50 好 U11 0.4713 0.9 0.72 合格 U12 0.3366 1.0 1.20 好 U13 0.1285 1.0 0.50 好 U14 0.1904 1.0 0.17 好 U15 0.3919 0.9 0.29 合格 U16 0.1680 1.0 0.07 好 U17 0.4275 0.9 0.49 合格 U18 0.3970 0.8 1.77 合格 U19 0.2640 1.0 0.46 好 U20 0.1275 1.0 1.60 好 表 5 陕西省各地级市2020年及2025年土地利用碳排放安全指数
Table 5 Projected 2020 and 2025 carbon emission security indices on land uses at prefectures in Shaanxi
地区 2020年 2025年 安全指数 安全等级 安全指数 安全等级 西安市 0.442 Ⅳ 0.437 Ⅳ 铜川市 0.449 Ⅳ 0.408 Ⅳ 宝鸡市 0.429 Ⅳ 0.374 Ⅳ 咸阳市 0.517 Ⅲ 0.476 Ⅲ 渭南市 0.446 Ⅳ 0.373 Ⅳ 延安市 0.507 Ⅲ 0.516 Ⅲ 汉中市 0.563 Ⅲ 0.586 Ⅲ 榆林市 0.498 Ⅲ 0.519 Ⅲ 安康市 0.541 Ⅲ 0.502 Ⅲ 商洛市 0.454 Ⅲ 0.365 Ⅳ 杨凌示范区 0.544 Ⅲ 0.483 Ⅲ -
[1] 王晓霞. 陕西省土地利用碳排放效应及影响因素研究[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2014. [2] 荣培君, 杨群涛, 秦耀辰, 等.中国省域能源消耗碳排放安全评价[J].地理科学进展, 2016, 35(4):487-495. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlkxjz201604009 [3] 李昊, 李世平, 银敏华.中国土地生态安全研究进展与展望[J].干旱区资源与环境, 2016, 30(9):50-56. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dlkxjz200605009 [4] 朱巧娴, 梅昀, 陈银蓉, 等.基于碳排放测算的湖北省土地利用结构效率的DEA模型分析与空间分异研究[J].经济地理, 2015, 35(12):176-184. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jjdl201512025 [5] 王桂波, 南灵.陕西省土地利用碳排放效应时空差异分析[J].资源与产业, 2012, 14(1):124-130. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zycy201201023 [6] 张苗, 甘臣林, 陈银蓉.基于SBM模型的土地集约利用碳排放效率分析与低碳优化[J].中国土地科学, 2016, 30(3):37-45. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zhonggtdkx201603005 [7] 冯杰, 王涛.中国土地利用碳排放演变与影响因素分析[J].软科学, 2016, 30(5):87-90. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rkx201605019 [8] 周峰. 上海市土地利用的碳排放效应及影响因素分析[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2016. [9] 张俊峰, 张安录, 董捷.武汉城市圈土地利用碳排放效应分析及因素分解研究[J].长江流域资源与环境, 2014, 23(5):595-602. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cjlyzyyhj201405001 [10] YORK R. Demographic trends and energy consumption in European Union Nations, 1960-2025[J]. Social Science research, 2007, 36(3):855-872. DOI: 10.1016/j.ssresearch.2006.06.007
[11] 冯杰, 王涛.中国土地利用碳排放演变与影响因素分析[J].软科学, 2016, 30(5):87-90. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rkx201605019 [12] 张勇, 张乐勤, 汪应宏, 等.安徽省池州市土地利用碳排放演变及其影响因素[J].中国农业大学学报, 2014, 19(2):216-223. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgnydxxb201402032 [13] RAPPORT D J, WHITFORD W G.How ecosystems respond to stress common properties of arid and aquatic systems[J].Bio Science, 1999, 49(3):193, 203.
[14] 范胜龙, 杨玉珍, 陈训争, 等.基于PSR和无偏GM(1, 1)模型的福建省耕地生态安全评价与预测[J].中国土地科学, 2016, 30(9):19-27. [15] 谢花林, 刘曲, 姚冠荣, 等.基于PSR模型的区域土地利用可持续性水平测度:以鄱阳湖生态经济区为例[J].资源科学, 2015, 37(3):449-457. [16] 陈慧, 付光辉.南京市土地资源安全SD法评价研究[J].资源科学, 2017, 39(5):846-859. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zykx201705005 [17] 刘思峰, 党耀国, 方志耕, 等.灰色系统理论及其应用[M].北京:科学出版社, 2010:146-168. [18] 陈娟, 南灵.陕西省农地非农化生态系统服务价值损失评价[J].西南农业学报, 2013, 26(1):259-263. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xnnyxb201301054 [19] 田云, 张俊飚, 李波.中国农业碳排放研究:测算、时空比较及脱钩效应[J].资源科学, 2012, 34(11):2097-2105. [20] 李春燕, 南灵.陕西省土地生态安全动态评价及障碍因子诊断[J].中国土地科学, 2015, 29(4):72-81. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zhonggtdkx201504010 [21] 程欢, 姚建, 明星, 等.等维动态递补灰色模型改进及应用研究[J].灌溉排水学报, 2016, 35(5):108-112. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ggps201605020 [22] 吉培荣, 黄巍松, 胡翔勇.无偏灰色预测模型[J].系统工程与电子技术, 2000, 22(6):6-7, 80. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xtgcydzjs200006002 [23] 曾小倩, 周新志.基于新陈代谢无偏灰色神经网络的水质预测模型[J].水电能源科学, 2012, 30(2):35-37. [24] 宋国正.修正的优化无偏GM(1, 1)模型在瓦斯事故预测中的应用[J].工矿自动化, 2013, 39(7):50-53. DOI: 10.7526/j.issn.1671-251X.2013.07.013 -
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 张茜,李登,叶志成,陈明高,张盼. 基于“水-能-碳”关联系统的城镇污水处理厂碳排放研究. 安徽化工. 2024(03): 113-116+120 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王红瑞,李晓军,张力,王力萍,姜欣. 水-能源-碳排放复杂关系研究进展及展望. 南水北调与水利科技(中英文). 2023(01): 13-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 魏心雨,王雁杰,孙梦媛,王智芳,周凯. 基于土地利用结构变化的河南省碳排放时空格局及驱动力分析. 农业现代化研究. 2023(05): 881-891 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 马肖迪,谭晓波. 基于LMDI模型的湖南省土地利用碳排放影响因素研究. 湖南工业大学学报. 2019(06): 60-66 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 赵先超,马肖迪,胡艺觉. 基于PSR模型的湖南省土地利用碳排放安全评估. 福建农业学报. 2018(08): 828-834 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(4)




 下载:
下载: