Molecular Cloning and Functional Analysis of UDP N-acetylglucosamine Pyrophosphorylases Gene in Frankliniella occidentalis
-
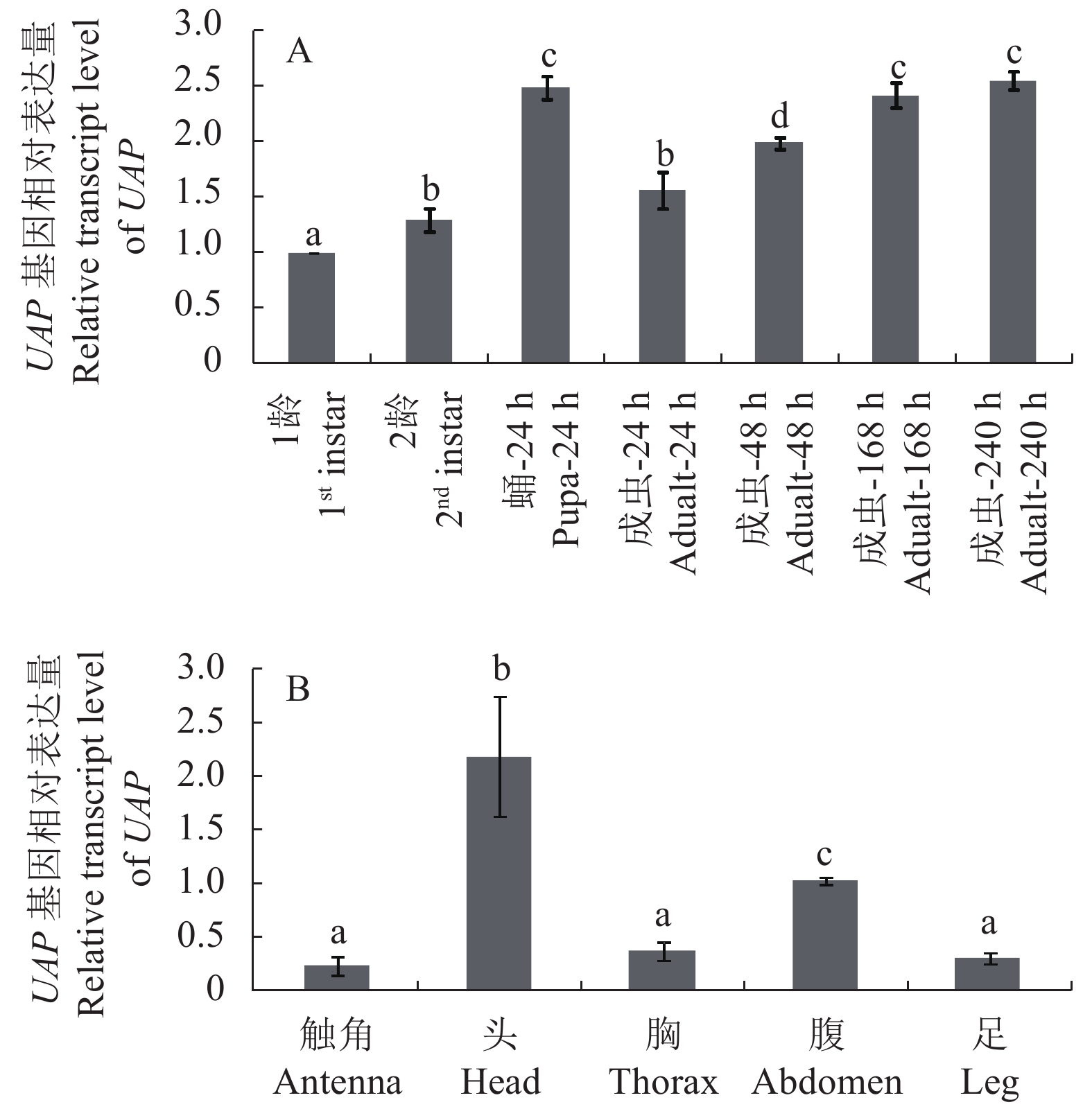
摘要:目的 阐明几丁质合成通路中的关键基因UDP-N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖焦磷酸化酶(UDP N-acetylglucosamine pyrophosphorylases, UAP)对西花蓟马Frankliniella occidentalis生长发育的影响。方法 基于西花蓟马转录组数据,克隆验证了UAP基因的开放阅读框(Open Reading Frame, ORF)全长序列,命名为FoccUAP。利用RT-qPCR方法分析FoccUAP在各个组织和不同龄期的表达情况。最后通过向西花蓟马蜕皮24 h的2龄若虫显微注射dsUAP,检测沉默效率,观察其对西花蓟马生长发育的影响。结果 FoccUAP基因开放阅读框全长1 545 bp,编码514个氨基酸,预测蛋白分子量为56.738 kDa,具有Glyco - tranf - GTA - type Super family家族的保守结构域,与等翅目、蜚蠊目、直翅目和半翅目昆虫的UAP基因亲缘关系较近。FoccUAP基因在西花蓟马各个组织都有表达,在头部和腹部相对表达量最高,触角、胸部和足相对表达量较低。该基因在虫体生长发育的各个阶段均有表达,其中2龄幼虫、蛹以及羽化后24、48、168、240 h的成虫表达量分别是1龄幼虫的1.30、2.50、1.56、2.0、2.43和2.56倍。RNAi结果表明,注射dsUAP的西花蓟马羽化率(36.3%)和注射后120 h的存活率(5.0%)均显著低于dsGFP对照组,且注射dsUAP的西花蓟马成虫出现翅膀发育不完整、胸腹部皱缩不规则等畸形现象。结论 FoccUAP基因对西花蓟马生长发育具有重要的作用。
-
关键词:
- 西花蓟马 /
- UDP-N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖焦磷酸化酶 /
- 几丁质合成 /
- RNAi
Abstract:Objective Effects of UDP N-acetylglucosamine pyrophosphorylases (UAP) on the growth and development of Frankliniella occidentalis were studied.Method Based on a transcriptome dataset, an open reading frame (ORF) of UAP gene of F. occidentalis (FoccUAP) was cloned. Expressions of the FoccUAP in different body tissues and growth stages of the insect were detected by RT-qPCR. Effects of UAP gene on the growth and development were examined by microinjecting dsRAN in the 2nd instars (eclosion about 24 h) of F. occidentalis.Result The full-length of FoccUAP ORF was 1 545 bp and encoded 514 amino acids with a predicted molecular mass of 56.738 kDa. FoccUAP contained the conserved domain of glyco-tranf-GTA-type super family, which had a close evolutionary relationship with the orthologues in Isoptera, Blattaria, Orthoptera, and Hemiptera. The RT-qPCR results showed that FoccUAP was highly expressed in the head and abdomen, detected in the antenna, thorax and leg, and found in all developmental stages of the insect. The relative transcript levels of FoccUAP in the 2nd instar, pupa, adult-24 h, adult-48 h, adult-168 h, and adult-240 h were 1.30-, 2.50-, 1.56-, 2.0-, 2.43-, and 2.56-fold, respectively, of those in the 1st instar. Further examination on the RNAi showed that the injection of dsUAP into the 2nd instar F. occidentalis significantly decreased the eclosion rate (36.3%) and the survival rate (5.0% in 120 h after microinjection) as compared to dsGFP controls. Moreover, the dsUAP treatment also induced abnormal phenotypes on wings and abdomen–thorax of the thrips.Conclusion UAP played a significant role in the growth and development of F. occidentalis. -
菜用大豆俗称毛豆,是指在大豆臌粒期后,籽粒饱满而荚色和籽粒均呈翠绿时采青食用的大豆鲜荚,是我国南方城乡人民喜食的豆科作物,是我国主要蔬菜品种之一[1-2]。由于菜用大豆食味鲜美、营养丰富、品质酥软、甜香、煮食方便,深受城乡居民的喜爱。随着高效农业的不断发展和种植业结构的深入调整,菜用大豆种植面积不断扩大,种植效益明显。目前我国已成为世界最大的菜用大豆生产国和出口国[2]。近年来,菜用大豆在福建省生产发展迅速,是福建省区域特色明显的优势农作物,已成为福建省出口创汇的蔬菜品种之一,出口数量逐年增加[3]。但在生产上,福建省应用的品种长期以来仍主要从台湾引进,这些品种存在适应范围小、种子成本高、种性容易退化等问题,不利于福建省菜用大豆生产发展。因此急需选育出适合福建省栽培生产的菜用大豆优良新品种以解决菜用大豆生产需求[3-4]。
菜用大豆育种中选择的多数农艺性状都是数量性状,它们不仅受遗传因子控制,而且很大程度上也受环境因素的支配,增加了选择的难度。因此,研究和探讨农艺性状间的遗传关系已成为许多数量遗传学家和育种工作者十分关注的问题[2]。目前,大豆育种工作者在大豆农艺性状上进行主成分分析和聚类分析研究较为广泛。如张玉革等[5]采用主成分分析和聚类分析方法研究了10个大豆品种在沈阳地区种植的适应性。李向华等[6]对89份中国春大豆根据遗传距离进行聚类分析,在分类的基础上选取11个生物学性状进行主成分分析,并对品种进行了综合评价。石惠等[7]对国家黄淮海区试A组11个大豆品种12个主要农艺性状进行变异分析、相关性分析和主成分分析,也指出在性状选择上首选变异大,品种选择上应注意产量与单株粒重、荚数、粒数较高的品种。周述明等[8]对四川74份地方大豆资源进行遗传距离测定,按距离聚类分为8类,考查了类群间的遗传差异和品种地理差异。以上研究主要是针对大豆的生物学性状进行了相关性分析、聚类分析和主成分分析,找出各品种遗传距离间的差异,为大豆育种、亲本选择及推广应用等提供科学依据。但在菜用大豆生物学性状上进行主成分分析和聚类分析的报道较之少见。王学军[2]等对江苏省鲜食夏大豆区试10个品种10个农艺性状进行遗传变异分析、相关性分析和主成分分析,指出在性状选择上首选变异大,品种选择上应注意鲜粒产量与鲜百粒重均较高的品种。
本文借鉴以往研究方法[9-18],根据刘来福[19]提出的“遗传距离”作为度量作物数量性状遗传差异的数量指标,对课题组收集的34份菜用大豆种质资源进行主要农艺性状的相关性分析、主成分分析及聚类分析,从理论上找出这些种质资源的遗传差异,探讨育种利用价值,为今后菜用大豆品种育种中性状选择及高产栽培提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
选用本课题组引进并试验鉴定多年的34份菜用大豆种质资源(表 1)。
表 1 参试的34份菜用大豆Table 1. volunteer′ vegetable soybean编号 品种 编号 品种 编号 品种 1 毛豆3号 13 H0427-82 25 K丰72-2 2 毛豆389 14 衢鲜3号 26 泉茶豆1号 3 毛豆75 15 浙5602 27 茶豆 4 浙鲜豆3号 16 浙5702-31 28 浙农6号 5 浙鲜豆4号 17 浙H0346 29 浙98015 6 浙鲜豆5号 18 沪选25-19 30 苏13-8 7 浙鲜豆10号 19 高雄5号 31 辽06M19 8 浙88005-7 20 绿领1号 32 K丰77-2 9 浙2818 21 云豆9号 33 K丰77-1 10 闽豆1711 22 矮脚白毛 34 闽豆6号 11 闽豆1号 23 太湖春早 12 青酥6号 24 Y2007-1 1.2 试验设计
试验于2016年春季在福建莆田市农业科学研究所试验田进行,试验地为红黄壤土,肥力中等,排灌方便。试验采用3重复随机区组设计,两行并排穴播,带沟畦宽1.0 m,穴距0.176 cm,每穴定苗2株,每667 m2 7 600穴,小区面积3.34 m2。采取常规栽培管理。
1.3 数据收集
收获时,每小区随机选取10株进行室内考种,统计株高X1、茎粗X2、主茎节数X3、有效分枝数X4、底荚高度X5、单株有效荚数X6、单株标准荚数X7、每㎏标准荚数X8、标准荚长X9、标准荚宽X10、单株粒数X11、鲜百粒重X12、单株荚重X13、出仁率X14、小区鲜荚产量X15、采收日数X16等16个主要农艺性状。
1.4 统计方法
研究方法采用遗传变异、相关分析、主成分分析及聚类分析等,数据采用DPS数据处理软件[20]进行分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 主要农艺性状表现及变异情况
34份菜用大豆品种的16个主要农艺性状考种结果及变异系数见表 2。由表 2可以看出,16个主要农艺性状存在丰富的变异。其中,变异系数最大的性状为底荚高度,达31.68%;其次为株高,达27.79%;再次为单株标准荚数,达22.03%;变异系数最小的为采收日数,达4.97%。底荚高度、株高、单株标准荚数、单株有效荚数及单株粒数的变异系数较大,说明以上性状可以通过品种改良和栽培措施而获得较大程度的提高;而主茎节数、有效分枝数、每公斤标准荚数、鲜百粒重、小区鲜荚产量及单株荚重等性状的变异系数处于中等水平,表明这些性状也有一定的改进空间;茎粗、标准荚长、出仁率、标准荚宽及采收日数的变异系数很小,表明通过品种改良和栽培措施获得改进的难度较大。34份菜用大豆种质资源各具特点,差距明显,类群不一。
表 2 34份菜用大豆的主要农艺性状表现及变异情况Table 2. Major agronomic traits and variations of 34 vegetable soybean品种 X1
/cmX2
/cmX3
/个X4
/个X5
/cmX6
/荚X7
/荚X8
/荚X9
/cmX10
/cmX11
/粒X12
/gX13
/gX14
/%X15
/kgX16
/d1 27.1 0.492 6.8 3 6.6 16.4 9.6 267.2 6.132 1.425 27.7 90.84 49.61 50.71 7.10 99 2 25 0.45 6.1 2.7 6.3 14 8.4 264.1 6.172 1.403 23.7 95.88 43.26 50.35 6.98 98 3 27.6 0.448 5.9 2.5 7.8 13.4 7.9 255.5 6.297 1.406 23 99.17 44.29 51.16 6.86 99 4 28.1 0.518 6 2.9 8 15 10.2 282.8 5.839 1.471 30.5 97.27 44.57 56.77 7.08 99 5 30.8 0.437 6.9 2.5 12.2 19.9 12.9 338.7 5.23 1.417 36.1 77.1 49.69 52.82 7.73 90 6 29.6 0.558 6.7 3.3 10.5 21.6 13.4 348.1 5.248 1.377 37.6 73.38 49.66 54.11 7.83 91 7 25.6 0.546 5.1 2.9 9.8 14.6 11.1 245.2 5.922 1.48 28.9 86.83 53.16 44.44 8.47 96 8 27.9 0.513 5.9 2.8 7.6 14.4 10.4 301.9 6.766 1.568 26.3 84.65 42.71 54.62 6.72 91 9 30.3 0.514 6.6 2.5 11.4 23.2 13.3 374.9 5.099 1.372 39.4 74.92 43.4 55.9 6.55 91 10 35.7 0.576 7.9 3.7 14.6 25.5 17.5 440.3 5.073 1.295 45.3 66.6 49.89 56.62 7.33 92 11 30.3 0.46 7.9 3.6 11.2 15.3 8.9 368.1 5.183 1.417 25.8 63.03 36.13 46.93 5.52 87 12 42.4 0.555 8.5 3.5 13.2 25.3 19.2 408.2 4.643 1.299 45.5 75.28 52.74 61.46 8.16 106 13 28.9 0.427 6.2 2.5 9.3 14.8 9.7 330.1 5.927 1.528 26.4 83.74 40.68 49.87 6.17 97 14 58 0.55 10.4 3.2 20.7 16.5 12.4 304.9 5.113 1.347 34.7 81.85 48.42 57.53 7.76 101 15 29.4 0.44 6.2 2.6 7.9 16.1 11.3 337.6 5.268 1.348 29.3 77.16 39.75 55.62 6.41 92 16 29.3 0.487 6.5 3.1 7.8 18.2 11.7 340.8 5.09 1.311 31.8 80.52 43.78 58.13 6.40 92 17 43.1 0.52 8.1 3.5 16.9 15.7 12.4 308.4 5.817 1.357 31.5 83.73 47.45 52 6.77 91 18 24.5 0.437 5.7 2.9 8 19.5 10.1 306.8 5.617 1.412 31.5 98.09 51.17 56.44 7.46 91 19 29.8 0.508 6.7 3.1 11.3 21.5 14.3 379.1 5.322 1.368 38.3 73.51 47.53 56.6 6.63 92 20 16.7 0.436 4.9 2.5 6.8 13.8 9.9 322.2 5.147 1.348 26.9 85.8 38.63 56.97 5.93 94 21 35.5 0.406 6.9 3.4 11.9 17.4 14.9 412.7 4.942 1.192 42.1 58.66 38.26 61.6 6.01 99 22 32.9 0.47 8.1 4.2 10.4 21.4 13.8 421.4 5.176 1.393 39.2 56.8 42.12 54.2 5.99 86 23 33.5 0.449 7.8 2.5 9.5 20.3 14.9 370.3 4.979 1.401 38.8 60.17 46.6 55.1 7.20 85 24 24 0.475 6.1 2.6 8.3 13.9 10.5 297.2 5.274 1.294 28.4 91.92 41.48 61.21 6.06 90 25 32.7 0.489 6.8 2.8 9.8 17.4 12.6 386.7 5.101 1.339 34.3 66.93 40.08 53.44 6.16 93 26 43.1 0.583 9.3 4.1 6.7 21.8 15.6 389.3 5.767 1.276 40.4 65.88 45.24 51.21 7.18 99 27 22.8 0.464 6 3 8.5 17.8 11 347.7 5.031 1.419 31 74.53 41.89 54.1 6.60 90 28 23.7 0.49 6.4 2.9 7.3 14 11.3 284.8 6.286 1.398 27.5 76.9 50.08 49.12 7.37 98 29 22 0.448 6.3 2.8 8.5 15.7 12.9 318.3 5.471 1.41 32.8 84.5 45.64 55.77 6.92 93 30 21.6 0.414 5.3 2.2 10 14.7 10.1 332.3 4.725 1.381 27.4 80.75 36.68 57.37 5.83 91 31 24.3 0.48 7.6 3.5 9.2 21.2 14.7 339.9 5.1 1.378 40.6 80.43 52.24 58.16 8.29 92 32 31 0.558 7.3 4.3 9.4 21.7 14.7 300.2 5.954 1.448 38.6 75.45 59.5 46.01 8.87 95 33 24.2 0.478 6.1 3 9 16.6 10.3 320.9 5.356 1.353 28.4 90.71 42.73 58.68 7.00 93 34 51 0.476 9.3 4.1 16.3 25.9 17.4 379.6 5.55 1.368 45.9 72.07 59.19 50.42 8.75 88 变异幅度 16.7~51.0 0.406~0.583 4.9~10.4 2.2~4.3 6.3~20.7 13.4~25.9 7.9~17.5 245.2~440.3 4.643~6.766 1.192~1.568 23.0~45.9 56.8~103.7 36.13~59.50 44.44~61.46 5.52~8.75 85~106 平均值 30.7 0.487 6.9 3.1 10.1 18.1 12.3 336.1 5.459 1.382 33.4 79.0 45.83 54.28 7.00 93.6 标准差 8.53 0.048 1.25 0.55 3.20 3.72 2.71 49.20 0.500 0.072 6.55 11.33 5.78 4.245 0.86 4.65 变异系数/% 27.79 9.86 18.12 17.74 31.68 20.55 22.03 14.64 9.16 5.21 19.61 14.34 12.61 7.82 12.29 4.97 2.2 主要农艺性状的相关性分析
主要农艺性状间的相关分析结果见表 3。由表 3结果可以看出:单株荚重与茎粗、有效分枝数、单株粒数相关系数分别达0.519 2、0.466 5、0.487 2,呈极显著正相关,表明选育优质高产的菜用大豆品种应将茎粗、有效分枝、单株粒数作为首选目标。鲜百粒重与主茎节数、有效分枝数呈极显著负相关,与主茎高呈显著负相关;单株有效荚数、单株粒数分别与主茎高、主茎节数、有效分枝数呈极显著正相关,单株粒数与标准荚长、标准荚宽呈显著负相关。以上表明了菜用大豆的各个性状间存在相互影响、相互制约的关系,特别是产量性状与生物性状间均存在一定的相关性。因此,要选育高产菜用大豆品种,须注意各性状指标间的相互协调,特别是产量性状与生物性状间的协调。
表 3 菜用大豆主要农艺性状间相关系数Table 3. Correlated coefficient of major agrinomic trait of vegetable soybean品种 X1 X2 X3 X4 X5 X6 X7 X8 X9 X10 X11 X12 X13 X14 X15 X16 株高X1 1.0000 茎粗X2 0.4524 1.0000 主茎节数X3 0.8957 0.4535 1.0000 有效分枝数数X4 0.5328 0.5267 0.6784 1.0000 底荚高度X5 0.7923 0.2970 0.6807 0.3440 1.0000 单株有效荚数X6 0.4728 0.4404 0.5696 0.5924 0.3988 1.0000 单株标准荚数X7 0.5713 0.4621 0.6375 0.5988 0.4886 0.8683 1.0000 每㎏标准荚数X8 0.3717 0.0958 0.4764 0.4328 0.3504 0.7088 0.7199 1.0000 标准荚长X9 -0.1395 0.1219 -0.2234 -0.0337 -0.3566 -0.4188 -0.4393 -0.6653 1.0000 标准荚宽X10 -0.3189 -0.0572 -0.3492 -0.2522 -0.2605 -0.3247 -0.4635 -0.5337 0.6056 1.0000 单株粒数X11 0.5639 0.4062 0.6352 0.6076 0.5030 0.9155 0.9624 0.7545 -0.4970 -0.4800 1.0000 鲜百粒重X12 -0.3729 -0.1129 -0.5081 -0.4791 -0.3096 -0.5320 -0.6259 -0.8303 0.4977 0.3730 -0.6345 1.0000 单株荚重X13 0.3495 0.5192 0.3641 0.4665 0.2982 0.5495 0.5166 -0.1125 0.2114 0.1198 0.4872 0.0720 1.0000 出仁率X14 0.0059 -0.1514 -0.0004 -0.1889 0.1151 0.1498 0.2421 0.3670 -0.5884 -0.5491 0.2788 0.0007 -0.2824 1.0000 小区鲜荚产量X15 0.3387 0.5191 0.3344 0.3868 0.2659 0.4775 0.4720 -0.1742 0.1887 0.1423 0.4391 0.1160 0.9427 -0.2614 1.0000 采收日数X16 0.1874 0.2838 0.0667 -0.0049 -0.0249 -0.1531 0.0127 -0.2682 0.2386 -0.1372 -0.0590 0.3353 0.1420 0.0484 0.2354 1.0000 注:相关系数临界值, a=0.05时, r=0.3388;a=0.01时, r=0.4357。 2.3 主要农艺性状的主成分分析
对菜用大豆16个主要农艺性状数据采用DPS数据处理软件进行主成分分析,计算得特征根λ i特征根累计百分率和主成分特征向量。各特征根大小代表各综合指标遗传方差大小,各特征根累计百分率代表各有关综合指标对总遗传方差贡献的百分率。为提高分析精度,只选用对总遗传方差贡献百分率达81.58%的前4个特征根来评价与判断34份菜用大豆的优异性(表 4)。
表 4 入选主成分的特征根和特征向量Table 4. Eigenvalue and eigenvecter of selected principal componentλ 1 λ2 λ3 λ 4 分量来源 特征根值 6.8897 3.3383 1.5093 1.3062 贡献率/% 43.0608 20.8644 9.4333 8.1637 累计贡献率/% 43.0608 63.9253 73.3586 81.5223 主成分特征向量 0.2853 0.1104 0.1896 -0.4480 株高X1 0.1968 0.2877 0.0998 -0.0126 茎粗X2 0.3120 0.0779 0.0587 -0.3838 主茎节数X3 0.2744 0.1469 -0.1801 -0.1370 有效分枝数数X4 0.2507 0.0258 0.1624 -0.3575 底荚高度X5 0.3332 0.0136 -0.1469 0.2953 单株有效荚数X6 0.3553 -0.0056 -0.0045 0.2160 单株标准荚数X7 0.2807 -0.3141 -0.1648 0.0136 每㎏标准荚数X8 -0.1799 0.3871 -0.0987 -0.1538 标准荚长X9 -0.1927 0.2769 -0.3625 -0.0260 标准荚宽X10 0.3591 -0.0380 -0.0302 0.2276 单株粒数X11 -0.2528 0.2266 0.3595 0.1674 鲜百粒重X12 0.1841 0.4122 -0.0275 0.3015 单株荚重X13 0.0685 -0.3374 0.4510 0.2823 出仁率X14 0.1654 0.4193 0.0438 0.3086 小区鲜荚产量X15 -0.0090 0.1975 0.6048 -0.0360 采收日数X16 主成分名称 荚数因子 荚大小因子 出仁率因子 株型因子 从表 4可以看出,λ1=6.889 7,对总变异的贡献率达到43.060 8%,构成变异主要来源。其相对应的特征向量中,载荷值单株粒数最大,其次为单株标准荚数、单株有效荚数,均为正值,此类性状均与总结荚数有关,故称第一主成分为荚数因子。另外,在此主成分中,鲜百粒重的负值最大,次之为标准荚长、标准荚宽,说明了单株有效荚数、单株标准荚数与鲜百粒重及标准荚长、标准荚宽呈负相关,这与相关分析结果一致。因此,育种过程中应选择有效荚数相对适中的品种,协调各性状指标,提高标准荚产量。
λ2=3.338 3,对总变异的贡献率达20.864 4%,其相对应的特征向量中,载荷较高且符号为正且较大的有小区鲜荚产量、单株荚重、标准荚长、标准荚宽等,说明标准荚的长与宽,即标准荚的大小影响单株荚重和小区鲜荚产量,故称第二主成分为荚大小因子。在此主成分中,出仁率的负值最大,其次为每千克标准荚数,说明了荚的大小与出仁率、每㎏标准荚数呈负相关。因此,育种过程中不应一味追求大荚。
λ3=1.509 3,对总变异的贡献率达9.433 3%,其相对应的特征向量中,载荷较高且符号为正的有采收日数、出仁率、鲜百粒重,说明采收日数越长,出仁率与鲜百粒重越高,故称第三主成分为出仁率因子。其中,采收日数载荷量最大,说明采收日数越长,出仁率、鲜百粒重越高,籽粒越饱满。载荷较高且符号为负的有标准荚宽、单株标准荚数、每千克标准荚数等,说明鲜荚越大,出仁率相应下降,有效产量下降。因此,育种过程中还应当考虑出仁率与单株标准荚数间的协调。
λ4=1.306 2,对总变异的贡献率达到8.163 7%,其相对应的特征向量中,株高最大,其次为主茎节数、底荚高度,均为负值,说明株高越高,主茎节数越多、底荚高度越高,由于此类性状与植株的株型有关,故称第四主成分为株型因子。但载荷较高且符号为正且较大的有小区产量、单株荚重、鲜百粒重等。因此,育种过程中应适当改进株型,以免影响育成品种的鲜荚产量与籽粒大小。
2.4 不同品种主成分值及综合评价
根据34份品种的主成分分析表明,对于菜用品种的选育,希望荚数越多越好,荚越大越好,出仁率越高越好,株高越高、主茎节数越多越好,即第1、2、3和4主成分越高越好。按照λ 1、λ 2、λ 3、λ 4和相应的特征向量及品种各性状标准化基因型值,计算出34份种质资源的第一至第四主成分λ (i, 1)、λ (i, 2)、λ (i, 3)、λ(i, 4)值(表 5)。
表 5 34份菜用大豆品种的主成分得分Table 5. Score of principal component of 34 vegetable soybeans序号 品种 各主成分得分 综合得分 排序 λ(i, 1) λ(i, 2) λ(i, 3) λ(i, 4) 1 毛豆3号 -2.2300 2.1897 0.4553 -0.0410 -0.4638 20 2 毛豆389 -3.7494 1.3296 0.6191 -0.3475 -1.3071 30 3 毛豆75 -4.0195 1.5253 1.1390 -0.5913 -1.3534 31 4 浙鲜豆3号 -2.2639 1.3872 1.2947 0.3598 -0.5339 22 5 浙鲜豆4号 0.3632 0.0543 -0.6963 0.6282 0.1533 15 6 浙鲜豆5号 1.6289 0.6673 -0.5811 1.0128 0.8685 8 7 浙鲜豆10号 -2.0065 3.7962 -0.5982 0.5029 -0.0873 16 8 浙88005-7 -3.0181 1.5842 -1.1234 -0.5275 -1.1181 27 9 浙2818 1.1080 -1.3218 -0.2513 0.7053 0.2352 13 10 闽豆1711 4.9974 -0.5494 -0.1691 0.6613 2.0753 3 11 闽豆1号 -0.8051 -1.6499 -2.4135 -2.9720 -1.1612 29 12 青酥6号 5.3658 0.2706 2.8201 1.3840 2.7460 1 13 H0427-82 -2.9969 0.2347 -0.5852 -1.1940 -1.3942 32 14 衢鲜3号 3.1711 1.5415 3.2903 -3.1485 1.7405 4 15 浙5602 -1.4478 -1.7150 0.0764 -0.1133 -0.9833 26 16 浙5702-31 -0.2726 -1.4378 0.4932 0.4603 -0.3333 18 17 浙H0346 0.9545 1.1465 0.4253 -2.3521 0.4983 9 18 沪选25-19 -1.6862 0.6430 0.0316 1.6955 -0.4505 19 19 高雄5号 1.4496 -0.7692 -0.2957 0.6663 0.4902 10 20 绿领1号 -3.2448 -2.1772 0.5474 0.7411 -1.7394 33 21 云豆9号 2.1863 -3.8427 1.5698 -0.4287 0.2528 12 22 矮脚白毛 2.4938 -1.9873 -2.4907 -0.9561 0.3462 11 23 太湖春早 1.5171 -1.5152 -1.6856 0.4710 0.2166 14 24 Y2007-1 -2.1754 -1.8088 1.3394 0.4627 -1.1500 28 25 K丰72-2 0.3678 -1.8666 -0.2982 -0.6818 -0.3149 17 26 泉茶豆1号 3.5832 0.8555 0.1794 -0.9592 1.6601 6 27 茶豆 -1.0672 -1.2986 -1.0748 0.4047 -0.7988 25 28 浙农6号 -1.9743 1.9454 -0.1738 -0.0698 -0.4663 21 29 浙98015 -1.3506 -0.3362 -0.0189 0.8684 -0.5826 23 30 苏13-8 -2.6636 -2.9985 0.2252 0.1383 -1.7401 34 31 辽06M19 1.7371 0.4177 -0.0959 2.0295 0.9918 7 32 K丰77-2 2.0909 4.2175 -1.5371 0.8640 1.7058 5 33 K丰77-1 -1.5289 -0.6559 0.8718 0.6273 -0.6618 24 34 闽豆6号 5.4859 2.1237 -1.2893 -0.3007 2.6592 2 根据各个种质资源的前4个主成分值与其对应特征根值的贡献率建立的线性方程,如式(1),通过式(1)可计算出34个菜用大豆品种的主成分综合得分,并按综合得分进行排序[17],结果如表 5。由表 5可以看出,综合得分排在前6位(大于1)的品种为青酥6号、闽豆6号、闽豆1711、衢鲜3号、K丰77-2、泉茶豆1号,这些品种多表现为植株较高、分枝性较强、单株有效荚数、标准荚数较多、产量较高;综合得分排在后8位(小于-1)的品种为苏13-8、绿领1号、H0427-82、毛豆75、毛豆389、闽豆1号、Y2007-1、浙88005-7,这些品种一致表现为植株偏矮、主茎偏细、分枝性较差、荚较宽长,以及有效荚数、标准荚数和单株粒数较少、产量低等特点。
Yi=0.430608λ(i,1)+0.208644λ(i,2)+0.094333λ(i,3)+0.081637λ(i,4) (1) 2.5 遗传距离测定与聚类分析
由供试品种的前4个主成分值计算各品种间的遗传距离,用欧氏距离、类平均法进行聚类并获得聚类图(图 1),并按照D2=3.84的聚类水平将34份菜用大豆品种分为7大类群(表 6)。第一类群包括8个品种,此类品种植株中偏低,单株有效荚数、标准荚数及籽粒数少,但荚大籽粒大,单株产量中等。第二类群包括17个品种,此类遗传关系比较复杂,可分为4个亚类群:第一亚类包括6个品种,此亚类品种单株有效荚数、标准荚数及籽粒较多,但荚小,产量较高;第二亚类包括1个品种,此亚类品种植株中等,单株有效荚数、标准荚数及籽粒较多,但荚小籽粒小,产量低;第三亚类包括7个品种,此亚类品种单株有效荚数、标准荚数中等,籽粒较少,荚小籽粒大,产量低;第四亚类群包括3个品种,此亚类品种有植株矮小,单株有效荚数、标准荚数及籽粒少,籽粒大,出仁率高,产量低。第三类群包括1个品种,此类品种除了株高中等,分枝性较好外,其他性状表现的都较差。第四类群包括1个品种,此类品种株高适中,分枝性较强,出仁率高,单株有效荚数、标准荚数多,但荚小籽粒小,产量低。第五类群包括有4个品种,此类品种株高较高,分枝性强,单株有效荚数、标准荚数及籽粒多,产量高,但荚小。第六类群包括2个品种,此类品种株高较高,分枝性中等,单株有效荚数、标准荚数中等,单株籽粒少,荚小籽粒大,产量中上。第七类群包括1个品种,此类品种株高适中,分枝性强,单株有效荚数、标准荚数较多,荚大籽粒大,产量高。
表 6 34份菜用大豆的类群组成Table 6. Groups component of 34 vegetable soybeans类群 数目 编号 品种 Ⅰ 8 1、28、4、2、3、8、13、7 毛豆3号、浙农6号、浙鲜豆3号、毛豆389、毛豆75、浙88005-7、H0427-82、浙鲜豆10号 Ⅱ 17 5、9、19、23、6、31、22、15、27、16、25、18、29、33、20、30、24 浙鲜豆4号、浙2818、高雄5号、太湖春早、浙鲜豆5号、辽06M19、矮脚白毛、浙5602、茶豆、浙5702-31、K丰72-2、沪选25-19、浙98015、K丰77-1、绿领1号、苏13-8、Y2007-1 Ⅲ 1 11 闽豆1号 Ⅳ 1 21 云豆9号 Ⅴ 4 10、26、34、12 闽豆1711、泉茶豆1号、闽豆6号、青酥6号 Ⅵ 2 14、17 衢鲜3号、浙H0346 Ⅶ 1 32 K丰77-2 3. 讨论与结论
(1) 本试验研究的16个主要农艺性状中,底荚高度、株高、单株标准荚数、单株有效荚数、单株粒数、主茎节数、有效分枝数等变异系数较大。因此,在菜用大豆品种选育中,采用本研究的34份菜用大豆育种材料作亲本的,应首先考虑选择以上这些性状。
相关性分析表明单株荚重与茎粗、有效分枝数、单株粒数呈极显著正相关,因此选育菜用大豆时,应将茎粗、单株有效荚数、单株粒数作为主要选择目标;同时,由于各农艺性状间同时也存在一定程度的正相关和负相关,如随着株高增高、主茎节数、有效分枝数增加,单株有效荚数、单株粒数也增加,但商品性降低。因此,选育高产菜用大豆时, 不能一味追求植株高度、主茎节数、有效分枝数、单株有效荚数,还应综合考虑鲜百粒重、出仁率较大的品种。
(2) 主成分分析是指在尽可能保留原有的信息前提下,用较少且彼此独立不相关的指标代替原有较多且彼此相关的指标,从而简化多指标分析[18、20],提供了数量性状的综合信息,可以对亲本品种做出评价,根据标准要求做主成分筛选[21]。很多研究结果,主成分分析法是对作物进行综合评价的一种有效方法[22]。本研究通过主成分分析将34份菜用大豆品种的16个性状归为4个主成分,即为荚数因子、荚大小因子、出仁率因子、株型因子,其累计贡献率达到了81.522 3%,这些因子综合反映了菜用大豆的绝大部分遗传信息,为品种选择提供了有力的依据。
高产菜用大豆品种理想性状应是株高适中、主茎节数多、有效分枝数多、鲜百粒重高、出仁率高且单株粒数多(多粒荚多)及标准荚数指标适宜的单株荚产量高的品种。从主成分分析看,在第1、2主成分上,主要包含有直接影响产量的产量构成性状;在第3主成分和第4主成分上,主要包含间接影响产量的品种株型与籽粒饱满度。因此,选育高产特别是优质高产出口型品种时,应着重对第1、2主成分选择的基础上,综合均衡第3、4主成分的主要性状。
根据前4个主成分值与其对应特征根值的贡献率建立方程,计算出34份种质资源的综合得分。从综合得分可以看出,综合得分前几位的与综合得分后几位的在诸多性状表现上存在明显的相反性差异,如植株高度、分枝性、有效荚数、标准荚数、产量等性状。恰好说明了选育优质高产菜用大豆新品种时应着重考虑植株高度、分枝性、有效荚数、标准荚数等性状。因此,34份菜用大豆品种中的青酥6号、闽豆6号、闽豆1711、衢鲜3号、K丰77-2、泉茶豆1号可作为菜用大豆新品种选育过程中主要亲本。
(3) 利用多元分析法测定品种间的遗传距离,对遗传差异加以数量化、具体化,并将遗传距离大小和品种综合性状优劣综合考虑,可提高亲本选择预见性,减少组合配制盲目性,提高育种效率。从遗传距离较大的两类群中选配亲本,有利于发挥远缘杂交优势,有利于培育出优良后代[21, 23]。由34份菜用大豆品种的前4个主成分值计算各品种间的遗传距离,用类平均法进行聚类,34份品种所属类群广泛,可分为7大类群,各类群间既存在着差异也存在着一定相似。其中,第七类群品种的综合性状最为优异均衡,可作为菜用大豆选育参照目标;第二、三类群的综合性状表现出明显差异,存在着明显的性状互补,可为菜用大豆选育提供重要亲本选择。
-
图 1 FoccUAP基因的核苷酸及预测的氨基酸序列
注:下划线部分为信号肽氨基酸序列;双下划线为蛋白保守结构域氨基酸序列;*为终止密码子。
Figure 1. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequence of FoccUAP
Note: The signal peptide sequence (MEHQYENLRN) is marked with underline. The conserved amino acid sequences of Glyco-tranf-GTA-type superfamily are marked with double underline. The TAA stop codon is marked with *.
图 3 FoccUAP基因在西花蓟马不同发育时期(A)和不同组织(B)的mRNA表达分析
注:数据上不同的字母表示差异显著(Tukey HSD test, P<0.05)
Figure 3. Relative expression levels of FoccUAP mRNA in different developmental stages (A) and tissues (B) of F. occidentalis
Note: Different lowercase letters means significant difference (Tukey HSD test, P<0.05).
表 1 引物信息
Table 1 Primers used
引物名称
Primer name序列
SequenceFoccUAP-ORF-F ATGGAGCACCAGTACGAAAACCTC FoccUAP-ORF-R TTAGTGAACACCATTTGATATCCCA dsFoccUAP-F TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGTACAAATGCTACCTGCACTGAAAGTAAGCT dsFoccUAP-R TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGTGGCAACATCATCCTGGATTCTCC qFoccUAP-F TCCGTTTACTGATAGTCTTGTTGTCTGGG qFoccUAP-R GCTGTGCGTGGGCAATCCTTTT qβ-actin-F CACCACCGCTGAGCGTGAAATCG qβ-actin-R GTGATGACCTGACCGTCGGGAAGC dsGFP-F TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCGAGGAGCTGTTCACCGG dsGFP-R TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGTCCTCGATGTTGTGGCGG -
[1] BAILEY S F. The distribution of injurious thrips in the United States [J]. Journal of Economic Entomology, 1940, 33: 133−136. DOI: 10.1093/jee/33.1.133
[2] KIRK W D J, TERRY L I. The spread of the western flower thrips Frankliniella occidentalis (Pergande) [J]. Agricultural and Forest Entomology, 2003, 5(4): 301−310. DOI: 10.1046/j.1461-9563.2003.00192.x
[3] 王海鸿, 雷仲仁, 李雪, 等. 西藏发现重要外来入侵害虫—西花蓟马 [J]. 植物保护, 2013, 39(1):181−183. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.2013.01.039 WANG H H, LEI Z R, LI X, et al. An important invasive pest, Frankliniella occidentalis, inspected in Tibet [J]. Plant Protection, 2013, 39(1): 181−183.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.2013.01.039
[4] 程峻峰, 万方浩, 郭建英, 等. 外来有害入侵生物--西花蓟马 [J]. 中国生物防治, 2005, 21(2):74−79. CHENG J F, WAN F H, GUO J Y, et al. Newly invaded insect pest, Frankliniella occidentalis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) [J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2005, 21(2): 74−79.(in Chinese)
[5] MESCE K A, FAHRBACH S E. Integration of endocrine signals that regulate insect ecdysis [J]. Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology, 2002, 23(2): 179−199. DOI: 10.1006/frne.2002.0228
[6] COHEN E. Chitin synthesis and inhibition: a revisit [J]. Pest Management Science, 2001, 57(10): 946−950. DOI: 10.1002/ps.363
[7] CANDY DJ, KILBY BA. Studies on chitin synthesis in the desert locust [J]. Journal of Experimental Biological, 1962, 39: 129−140.
[8] GLASER L, BROWN D H. The synthesis of chitin in cell-free extracts of Neurosporacrassa [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1957, 228: 729−742.
[9] 张文庆, 陈晓菲, 唐斌, 等. 昆虫几丁质合成及其调控研究前沿 [J]. 应用昆虫学报, 2011, 48(3):475−479. DOI: 10.7679/j.issn.2095-1353.2011.084 ZHANG W Q, CHEN X F, TANG B, et al. Insect chitin biosynthesis and its regulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Entomology, 2011, 48(3): 475−479.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.7679/j.issn.2095-1353.2011.084
[10] 刘晓健, 孙亚文, 崔淼, 等. 飞蝗海藻糖酶基因的分子特性及功能 [J]. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(22):4375−4386. DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2016.22.010 LIU X J, SUN Y W, CUI M, et al. Molecular characteristics and functional analysis of trehalase genes in Locusta migratoria [J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(22): 4375−4386.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2016.22.010
[11] TONNING A, HELMS S, SCHWARZ H, et al. Hormonal regulation of mummy is needed for apical extracellular matrix formation and epithelial morphogenesis in drosophila [J]. Development, 2006, 133(2): 331−341.
[12] ARAKANE Y, BAGUINON MC, JASRAPURIA S, et al. Both UDP-N-acetylglucosamine pyrophosphorylases of Tribolium castaneum are critical for molting, survival and fecundity [J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2011, 4l(1): 42−50.
[13] LIU X J, LI F, LI D Q, et al. Molecular and functional analysis of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine pyrophosphorylases from the migratory locust, Locusta migratoria [J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(8): e71970. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071970
[14] 陈洁, 陈宏鑫, 姚琼, 等. 甜菜夜蛾UAP的克隆、时空表达及RNAi研究 [J]. 中国农业科学, 2014, 47(7):1351−1361. DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2014.07.012 CHEN J, CHEN H X, YAO Q, et al. Molecular cloning, expression patterns and RNAi of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine pyrophosphorylase in Spodoptera exigua [J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2014, 47(7): 1351−1361.(in Chinese) DOI: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2014.07.012
[15] MIO T, YABE T, ARISAWA M, et al. The eukaryotic UDP-N- acetylglucosamine pyrophosphorylases gene cloning, protein expression, and catalytic mechanism [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1998, 273(23): 14392−14397. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.273.23.14392
[16] WANG-GILLAM A, PASTUSZAK I, STEWART M, et al. Identification and modification of the uridine-binding site of the UDP-GalNAc (GlcNAc) pyrophosphorylase [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2000, 275(2): 1433−1438. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.275.2.1433
[17] ARAKANE Y, BAGUINON M C, JASRAPURIA S, et al. Both UDP N-acetylglucosamine pyrophosphorylases of Tribolium castaneumare critical for molting, survical and fecundity [J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2011, 41(1): 42−50. DOI: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2010.09.011
[18] ARAKANE Y, MUTHUKRISHNAN S, Kramer K J, et al. The Tribolium chitin synthase genes TcCHS1 and TcCHS2 are specialized for synthesis of epidermal cuticle and midgut peritrophic matrix [J]. Insect Molecular Biology, 2005, 14(5): 453−463. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2583.2005.00576.x
[19] SCHIMMELPFENG K, STRUNK M, STORK T, et al. Mummy encodes an UDP-N-acetylglucosamine-dipohosphorylase and is required during Drosophila dorsal closure and nervous system development [J]. Mechanisms of Development, 2006, 123(6): 487−499. DOI: 10.1016/j.mod.2006.03.004
[20] SHEU K F. FREY E A UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase stereochemical course of the reaction of glucose 1-phosphate with uridine-5’[1-Thiotriphosphate] [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1978, 253(10): 3378−3380.
[21] STROMINGER J L, SMITH M S. The preparation of uridine diphospho acetylgalactosamine [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1959, 234(7): 1828−1829.
[22] RAFAELA S G, ALEX G T, MARIA GBK. Purification, characterization and structural determination of chitinases produced by Moniliophthora perniciosa [J]. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciencias, 2012, 84(2): 469−486. DOI: 10.1590/S0001-37652012000200016
-
期刊类型引用(24)
1. 罗静红,钟文娟,罗芳耀,唐月明,陈四维,高佳. 成都平原春播菜用大豆品种鲜籽粒品质对比分析. 大豆科学. 2024(03): 285-294 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 林文磊,吕美琴,李明松,施迎迎,康蓉蓉,曾红英. 47份福建省鲜食春大豆种质资源的遗传分析及综合评价. 福建农业学报. 2024(03): 276-289 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 李清华,顾智炜,林海峰,颜墩炜,郑龙,陈子琳,柯庆明. 基于主成分分析和聚类分析的鲜食大豆审定品种综合评价研究. 中国农学通报. 2024(30): 17-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 常克勤,杜燕萍,穆兰海,杨崇庆,陈一鑫,张月荷. 宁南山区苦荞新品种主要农艺性状主成分分析及综合评价. 黑龙江农业科学. 2024(12): 21-28 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 焦灰敏,桑玉伟,何宗铃,水涌,朱金成,王睿,王志军,马盼盼,王亮. 花生产量与主要农艺性状、品质性状的灰色关联度分析. 北方农业学报. 2024(06): 22-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 隋翔鹏,周永刚,孙鹏宇,李森权,叶开烨,王栋灵,井妍,李海燕. 中国热区适应性高产大豆种质的评价与筛选. 分子植物育种. 2023(21): 7292-7299 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 李炜,毕影东,刘建新,王玲,刘淼,邸树峰,樊超,杨光,谢婷婷,来永才. 寒地野生大豆资源农艺性状的相关性和主成分分析. 土壤与作物. 2022(01): 10-17 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 张华崇,闫振华,赵树琪,黄晓莉,戴宝生,李蔚. 46份棉花杂交组合主要性状主成分和聚类分析. 种子. 2022(05): 60-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 黎松松,赖建军,张红梅,崔晓艳,刘晓庆,陈新,朱月林,陈华涛. 江苏鲜食春大豆种质资源表型鉴定及综合评价. 大豆科学. 2022(04): 385-396 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 成旭,史培瑶,王磊,王黎明,董普辉,王春平. 1个小麦自然群体穗发芽抗性与主要农艺性状的相关性分析. 江苏农业科学. 2022(23): 75-80 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 陈正杰,宛永璐,钟文娟,陈四维,周永航,石盛佳,蒋理,戢沛城,杨泽湖,毛正轩,牟方生. 基于大豆基因组重测序的InDel标记开发及应用. 植物遗传资源学报. 2021(03): 815-833 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 周长军,田中艳,李建英,吴耀坤,于吉东,马兰,李泽宇. 抗线虫大豆品种(系)主要农艺性状的多重分析. 黑龙江农业科学. 2021(07): 1-5+10 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 冯花,王飞权,陈荣冰,张渤,庄晓芸,刘梦娜,曾紫青. 不同来源地茶树种质资源表型性状遗传多样性分析. 热带作物学报. 2021(10): 2758-2768 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 王桂梅,邢宝龙. 大豆农艺性状相关性及主成分分析. 安徽农学通报. 2021(24): 46-48+87 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 郑淑琳,石玉涛,王飞权,张渤,王涵,林立,石元值,叶乃兴. 乌龙茶种质资源矿质元素含量特征分析与评价. 福建农业学报. 2020(02): 150-160 .  本站查看
本站查看
16. 万何平,郑琳,廖洋,刘帅,乐帅,何冰冰,郭瑞,陈禅友. 菜用大豆资源收集与粒型性状的多样性研究. 江汉大学学报(自然科学版). 2020(03): 5-13 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 石玉涛,郑淑琳,王飞权,陈荣冰,李远华,张渤,王涵,林立. 武夷名丛茶树种质资源矿质元素含量特征分析. 中国农业科技导报. 2020(07): 37-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 吕丹,黎瑞源,郑冉,郑俊青,朱丽伟,石桃雄,陈庆富. 213份苦荞种质资源主要农艺性状分析及高产种质筛选. 南方农业学报. 2020(10): 2429-2439 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 李方舟,张海生,王军,杨婷婷,古晓红,李广信,刘晋联. 山西省大豆多点试验品系农艺性状分析. 山西农业科学. 2019(06): 931-934+1010 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 王飞权,冯花,罗盛财,陈荣冰,杨慧珠,李少华,张见明,张渤,叶江华. 武夷名丛茶树种质资源农艺性状多样性分析. 中国农业科技导报. 2019(06): 43-54 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 张自强,王良,白晨,张惠忠,李晓东,付增娟,赵尚敏,鄂圆圆,张辉,张必周. 104份甜菜种质资源主要农艺性状分析. 作物杂志. 2019(03): 29-36 .  百度学术
百度学术
22. 王慧敏,彭振英,李新国,万书波,张智猛,丁红,高文伟. 67个花生品种主要农艺性状的变异及相关性分析. 山东农业科学. 2019(09): 91-96 .  百度学术
百度学术
23. 王飞权,李纪艳,冯花,罗盛财,林美菁,李少华,张见明,张渤,陈荣冰. 武夷名丛茶树种质资源叶片解剖结构分析. 热带作物学报. 2019(12): 2375-2389 .  百度学术
百度学术
24. 林文磊,吕美琴,李明松,康蓉蓉,曾红英,姚文,蔡锦玲. 39份春大豆种质资源的主成分分析及其聚类分析. 福建农业学报. 2018(10): 1016-1022 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(5)




 下载:
下载: